The Complete Chloroplast Genome Sequences of Six Rehmannia Species
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. DNA Extraction and Sequencing
2.2. Chloroplast Genome Assembling and Annotation
2.3. Sequence Analysis and Repeat Structure
2.4. Selective Pressure Analysis
2.5. Comparative Genome Analysis
2.6. Phylogenomic Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Genome Sequencing, Assembly, and Validation
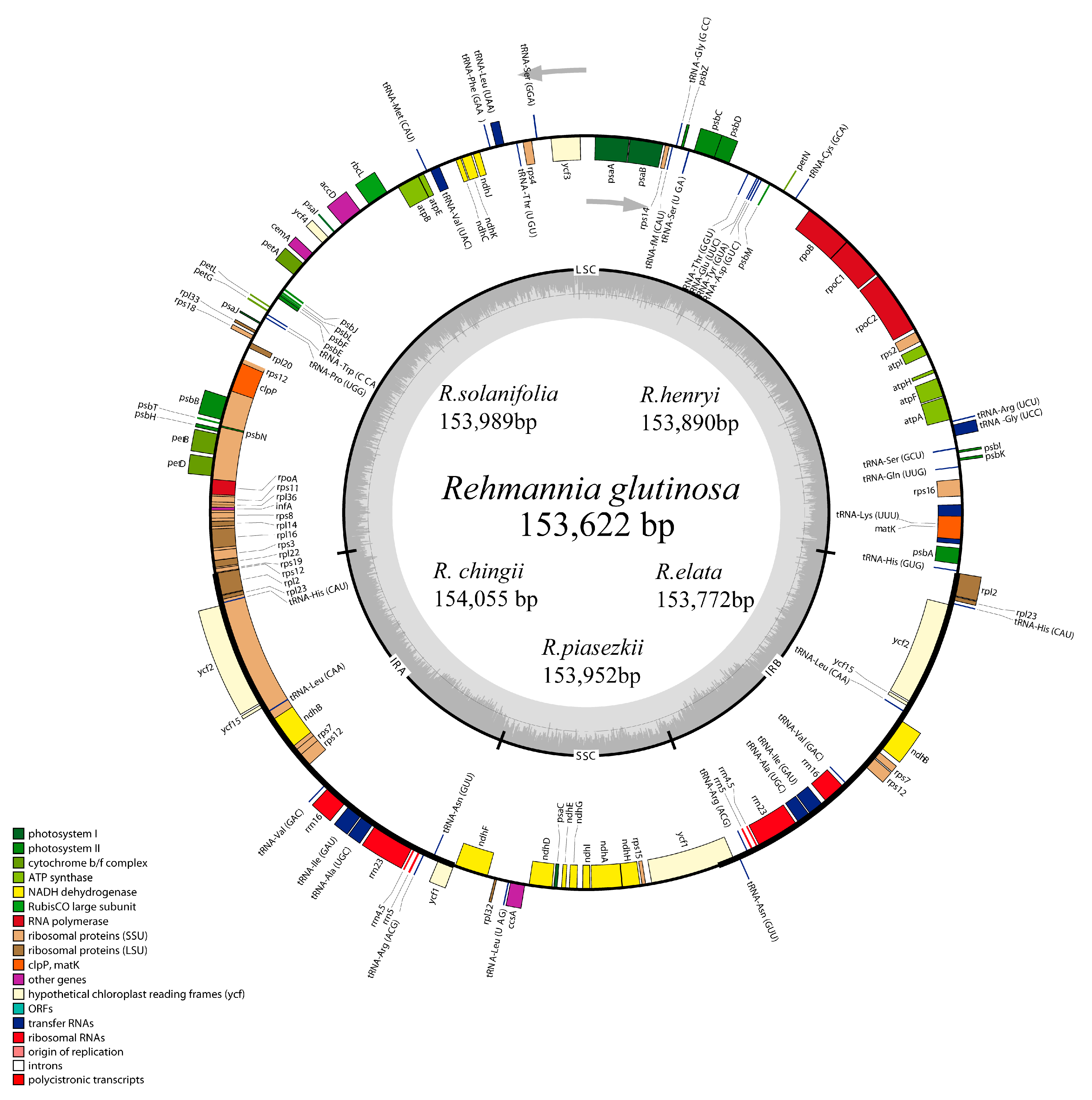
3.2. Complete Chloroplast Genomes of Rehmannia Species
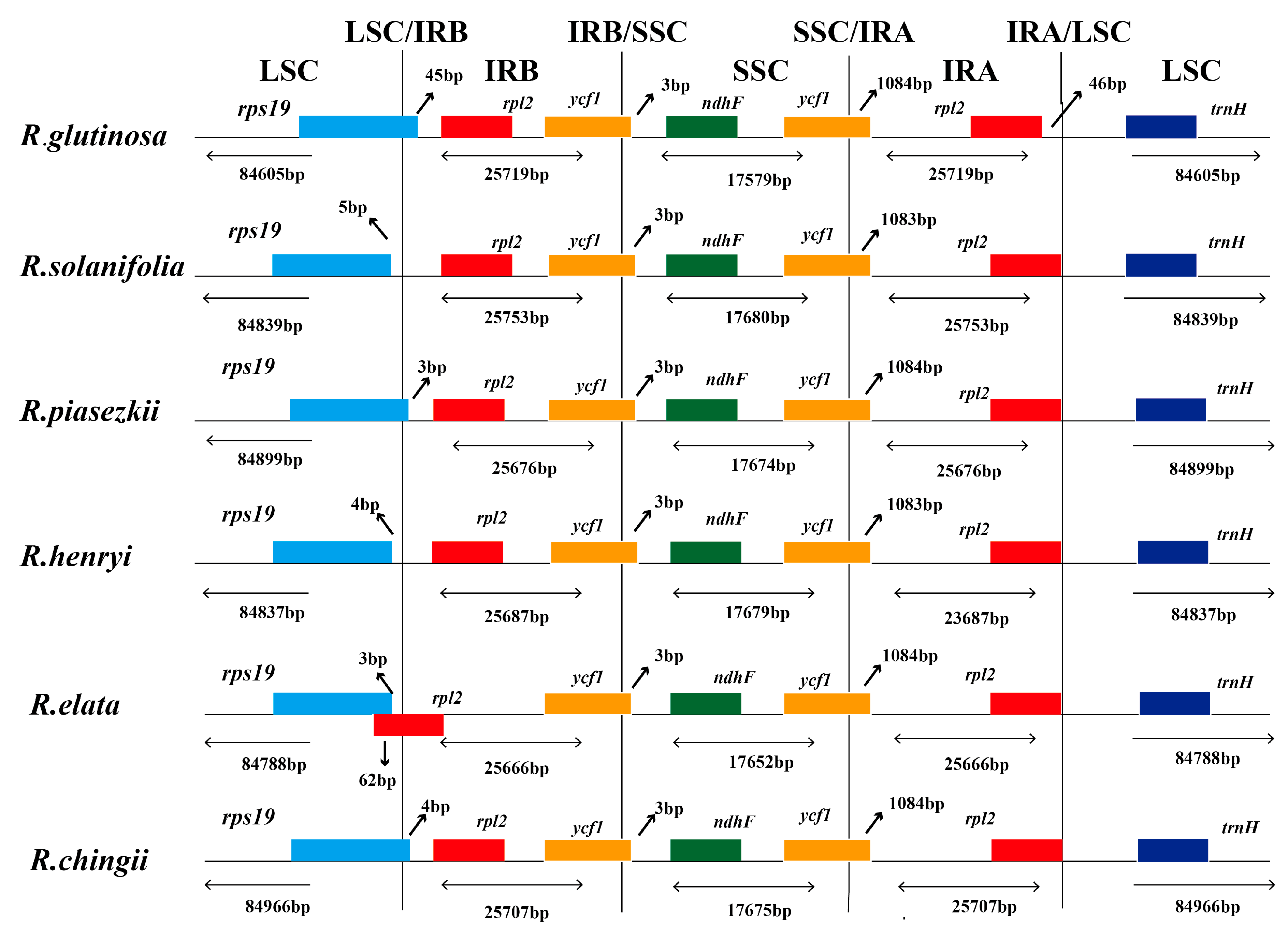
3.3. IR Boundary Changes and Gene Rearrangement
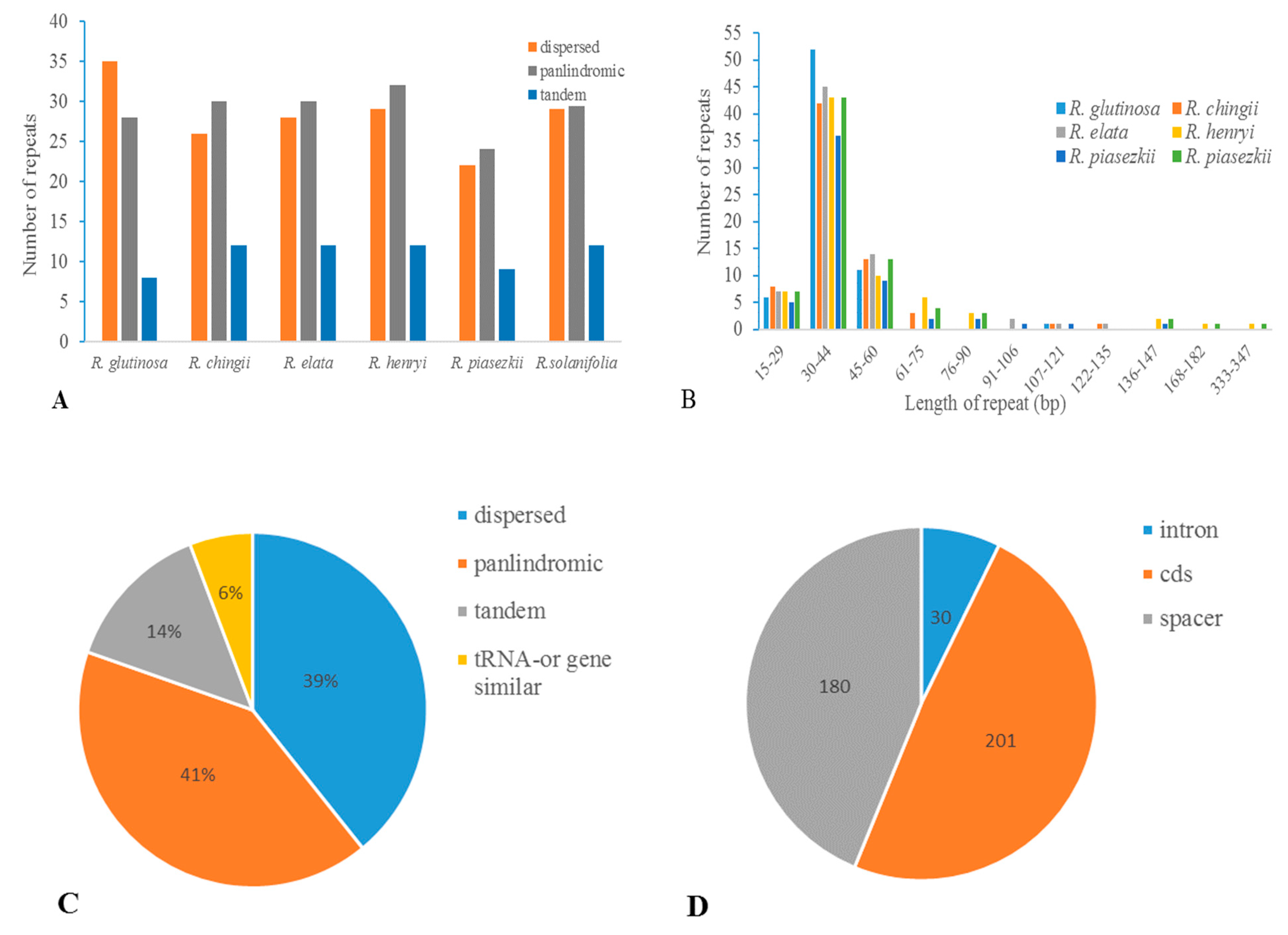
3.4. Repetitive Sequences
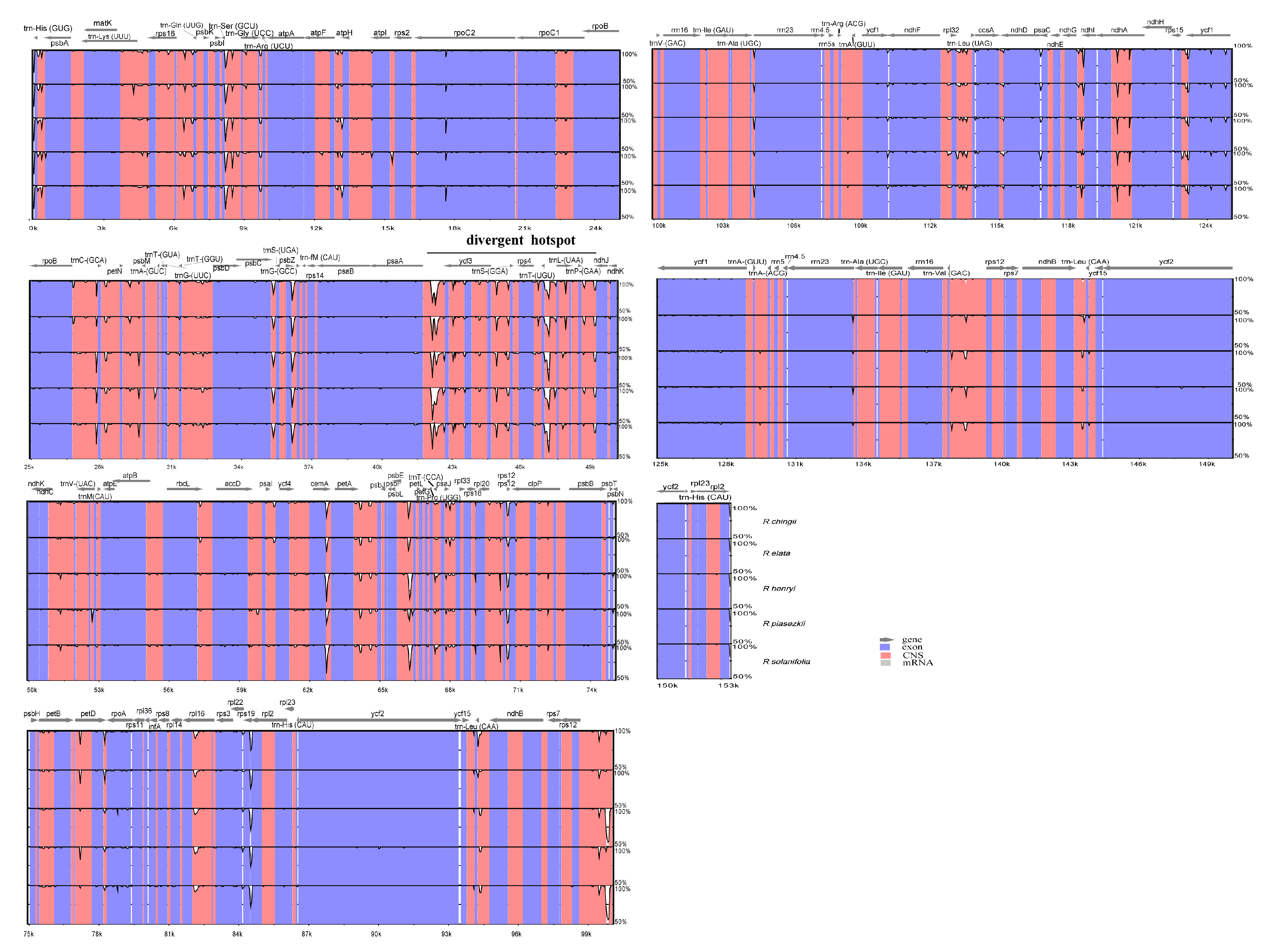
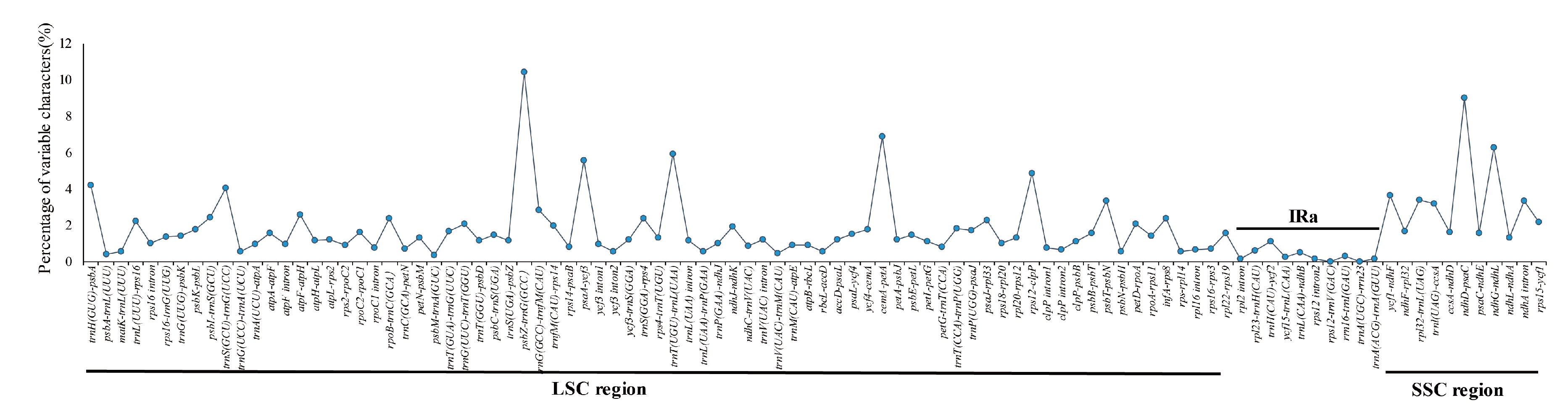
3.5. Sequence Divergence and Divergence Hotspot
3.6. Selective Pressure Analysis
3.7. Phylogenomic Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Genome Characteristics and Sequence Differences
4.2. Phylogenetic Implications
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rix, M. The genus Rehmannia. Plantsman 1987, 8, 193–195. [Google Scholar]
- Olmstead, R.G.; DePamphilis, C.W.; Wolfe, A.D.; Young, N.D.; Elisons, W.J.; Reeves, P.A. Disintegration of the Scrophulariaceae. Am. J. Bot. 2001, 88, 348–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Angiosperm Phylogeny Group. An update of the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group classification for the orders and families of flowering plants: APG II. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2003, 141, 399–436. [Google Scholar]
- The Angiosperm Phylogeny Group. An update of the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group classification for the orders and families of flowering plants: APG IV. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2016, 181, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, Z.; Wang, Y.-Z.; Smith, J.F. Familial placement and relations of Rehmannia and Triaenophora (Scrophulariaceae s.l.) inferred from five gene regions. Am. J. Bot. 2009, 96, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reveal, J.L.; Chase, M.W. APG III: Bibliographical Information and Synonymy of Magnoliidae. Phytotaxa 2011, 19, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zeng, S.-Y.; Zhao, J.-H.; Han, K.; Li, J.; Li, Z.; Liu, Z.-L. Genetic variation and phylogenetic relationships among Rehmannia (Scrophulariaceae) species as revealed by a novel set of single-copy nuclear gene markers. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2016, 66, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.-L.; Li, J.-F. Molecular phylogeny analysis of Rehmannia. Acta Bot. Bor. Occid. Sin. 2014, 34, 77–82. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Li, J. Morphology characters of leaf epidermis of the genera Rehmannia and Triaenophora. J. Plant Sci. 2006, 24, 559–564. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, K.; Zhao, N.; Li, H.Q. Systematic relationships among Rehmannia (Scrophulariaceae) species. Acta Bot. Boreal. Occident Sin. 2007, 27, 1112–1120. [Google Scholar]
- Sugiura, M. The chloroplast genome. Plant Mol. Biol. 1992, 19, 149–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bewick, A.J.; Chain, F.J.J.; Heled, J.; Evans, B.J. The Pipid Root. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 913–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbonell-Caballero, J.; Alonso, R.; Ibañez, V.; Terol, J.; Talon, M.; Dopazo, J. A Phylogenetic Analysis of 34 Chloroplast Genomes Elucidates the Relationships between Wild and Domestic Species within the Genus Citrus. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 2015–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, R.K.; Cai, Z.; Raubeson, L.A.; Daniell, H.; dePamphilis, C.W.; Leebens-Mack, J.; Müller, K.F.; Guisinger-Bellian, M.; Haberle, R.C.; Hansen, A.K.; et al. Analysis of 81 genes from 64 plastid genomes resolves relationships in angiosperms and identifies genome-scale evolutionary patterns. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 19369–19374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uribe-Convers, S.; Duke, J.R.; Moore, M.J.; Tank, D.C. A Long PCR–Based Approach for DNA Enrichment Prior to Next-Generation Sequencing for Systematic Studies. Appl. Plant Sci. 2014, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, J.; Cai, M.; Yan, G.; Wang, N.; Li, F.; Chen, B.; Gao, G.; Xu, K.; Li, J.; Wu, X. High-throughput multiplex cpDNA resequencing clarifies the genetic diversity and genetic relationships among Brassica napus, Brassica rapa and Brassica oleracea. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2016, 14, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruhsam, M.; Rai, H.S.; Mathews, S.; Ross, T.G.; Graham, S.W.; Raubeson, L.A.; Mei, W.; Thomas, P.I.; Gardner, M.F.; Ennos, R.A.; et al. Does complete plastid genome sequencing improve species discrimination and phylogenetic resolution in Araucaria? Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2015, 15, 1067–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandbrink, J.M.; Vellekoop, P.; Van Ham, R.; Van Brederode, J. A method for evolutionary studies on RFLP of chloroplast DNA, applicable to a range of plant species. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 1989, 17, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, J.J. A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochem. Bull. 1987, 19, 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Zerbino, D.R.; Birney, E. Velvet: Algorithms for de novo short read assembly using de Bruijn graphs. Genome Res. 2008, 18, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A New Genome Assembly Algorithm and Its Applications to Single-Cell Sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boetzer, M.; Henkel, C.V.; Jansen, H.J.; Butler, D.; Pirovano, W. Scaffolding pre-assembled contigs using SSPACE. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 578–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, C.; Bachmann, L.; Chevreux, B. Reconstructing mitochondrial genomes directly from genomic next-generation sequencing reads—A baiting and iterative mapping approach. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, e129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohse, M.; Drechsel, O.; Kahlau, S.; Bock, R. OrganellarGenomeDRAW—A suite of tools for generating physical maps of plastid and mitochondrial genomes and visualizing expression data sets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, W575–W581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT Multiple Sequence Alignment Software Version 7: Improvements in Performance and Usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frazer, K.A.; Pachter, L.; Poliakov, A.; Rubin, E.M.; Dubchak, I. VISTA: Computational tools for comparative genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32 (Suppl. 2), W273–W279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.-J.; Ma, P.-F.; Li, D.-Z. High-Throughput Sequencing of Six Bamboo Chloroplast Genomes: Phylogenetic Implications for Temperate Woody Bamboos (Poaceae: Bambusoideae). PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurtz, S.; Choudhuri, J.V.; Ohlebusch, E.; Schleiermacher, C.; Stoye, J.; Giegerich, R. REPuter: The manifold applications of repeat analysis on a genomic scale. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 4633–4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benson, G. Tandem repeats finder: A program to analyze DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z. PAML 4: Phylogenetic Analysis by Maximum Likelihood. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2007, 24, 1586–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darling, A.E.; Mau, B.; Perna, N.T. progressiveMauve: Multiple Genome Alignment with Gene Gain, Loss and Rearrangement. PLOS ONE 2010, 5, e11147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML-VI-HPC: Maximum likelihood-based phylogenetic analyses with thousands of taxa and mixed models. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 2688–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronquist, F.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 1572–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posada, D.; Buckley, T.R. Model Selection and Model Averaging in Phylogenetics: Advantages of Akaike Information Criterion and Bayesian Approaches over Likelihood Ratio Tests. Syst. Biol. 2004, 53, 793–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posada, D.; Crandall, K.A. Modeltest: Testing the model of DNA substitution. Bioinformatics 1998, 14, 817–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timme, R.E.; Kuehl, J.V.; Boore, J.L.; Jansen, R.K. A comparative analysis of the Lactuca and Helianthus (Asteraceae) plastid genomes: Identification of divergent regions and categorization of shared repeats. Am. J. Bot. 2007, 94, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schäferhoff, B.; Fleischmann, A.; Fischer, E.; Albach, D.C.; Borsch, T.; Heubl, G.; Müller, K.F. Towards resolving Lamiales relationships: Insights from rapidly evolving chloroplast sequences. BMC Evol. Biol. 2010, 10, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, D.R.; Dastidar, S.G.; Cai, Z.; Penaflor, C.; Kuehl, J.V.; Boore, J.L.; Jansen, R.K. Phylogenetic and evolutionary implications of complete chloroplast genome sequences of four early-diverging angiosperms: Buxus (Buxaceae), Chloranthus (Chloranthaceae), Dioscorea (Dioscoreaceae), and Illicium (Schisandraceae). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2007, 45, 547–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Shi, C.; Liu, Y.; Mao, S.-Y.; Gao, L.-Z. Thirteen Camelliachloroplast genome sequences determined by high-throughput sequencing: Genome structure and phylogenetic relationships. BMC Evol. Biol. 2014, 14, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.J.; Lee, H.L. Complete chloroplast genome sequences from Korean ginseng (Panax schinseng Nees) and comparative analysis of sequence evolution among 17 vascular plants. DNA Res. 2004, 11, 247–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bortiri, E.; Coleman-Derr, D.; Lazo, G.R.; Anderson, O.D.; Gu, Y.Q. The complete chloroplast genome sequence of Brachypodium distachyon: Sequence comparison and phylogenetic analysis of eight grass plastomes. BMC Res. Notes 2008, 1, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cahoon, A.B.; Sharpe, R.M.; Mysayphonh, C.; Thompson, E.J.; Ward, A.D.; Lin, A. The complete chloroplast genome of tall fescue (Lolium arundinaceum; Poaceae) and comparison of whole plastomes from the family Poaceae. Am. J. Bot. 2010, 97, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asano, T.; Tsudzuki, T.; Takahashi, S.; Shimada, H.; Kadowaki, K. Complete nucleotide sequence of the sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum) chloroplast genome: A comparative analysis of four monocot chloroplast genomes. DNA Res. 2004, 11, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalier-Smith, T. Chloroplast evolution: Secondary symbiogenesis and multiple losses. Curr. Biol. 2002, 12, R62–R64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwickl, D.J.; Hillis, D.M. Increased taxon sampling greatly reduces phylogenetic error. Syst. Biol. 2002, 51, 588–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diekmann, K.; Hodkinson, T.R.; Wolfe, K.H.; van den Bekerom, R.; Dix, P.J.; Barth, S. Complete Chloroplast Genome Sequence of a Major Allogamous Forage Species, Perennial Ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.). DNA Res. 2009, 16, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier, R.M.; Neckermann, K.; Igloi, G.L.; Kössel, H. Complete Sequence of the Maize Chloroplast Genome: Gene Content, Hotspots of Divergence and Fine Tuning of Genetic Information by Transcript Editing. J. Mol. Biol. 1995, 251, 614–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, X.; Lv, S.; Zhang, Y.; Du, X.; Wang, L.; Biradar, S.S.; Tan, X.; Wan, F.; Weining, S. Complete Chloroplast Genome Sequence of a Major Invasive Species, Crofton Weed (Ageratina adenophora). PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.-H.; Chan, M.-T.; Liao, D.-C.; Hsu, C.-T.; Lee, Y.-W.; Daniell, H.; Duvall, M.; Lin, C.-S. Complete chloroplast genome of Oncidium Gower Ramsey and evaluation of molecular markers for identification and breeding in Oncidiinae. BMC Plant Biol. 2010, 10, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blazier, J.C.; Ruhlman, T.A.; Weng, M.-L.; Rehman, S.K.; Sabir, J.S. M.; Jansen, R.K. Divergence of RNA polymerase α subunits in angiosperm plastid genomes is mediated by genomic rearrangement. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakkaew, A.; Chotigeat, W.; Eksomtramage, T.; Phongdara, A. Cloning and expression of a plastid-encoded subunit, beta-carboxyltransferase gene (accD) and a nuclear-encoded subunit, biotin carboxylase of acetyl-CoA carboxylase from oil palm (Elaeis guineensis Jacq.). Plant Sci. 2008, 175, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajdukiewicz, P.T.J.; Allison, L.A.; Maliga, P. The two RNA polymerases encoded by the nuclear and the plastid compartments transcribe distinct groups of genes in tobacco plastids. EMBO J 1997, 16, 4041–4048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leebens-Mack, J.; Raubeson, L.A.; Cui, L.Y.; Kuehl, J.V.; Fourcade, M.H.; Chumley, T.W.; Boore, J.L.; Jansen, R.K.; dePamphilis, C.W. Identifying the basal angiosperm node in chloroplast genome phylogenies: Sampling one's way out of the Felsenstein zone. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2005, 22, 1948–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, M.J.; Bell, C.D.; Soltis, P.S.; Soltis, D.E. Using plastid genome-scale data to resolve enigmatic relationships among basal angiosperms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 19363–19368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parks, M.; Cronn, R.; Liston, A. Increasing phylogenetic resolution at low taxonomic levels using massively parallel sequencing of chloroplast genomes. BMC Biol. 2009, 7, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, Y.; Glazko, G.V.; Nei, M. Overcredibility of molecular phylogenies obtained by Bayesian phylogenetics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 16138–16143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wortley, A.H.; Rudall, P.J.; Harris, D.J.; Scotland, R.W. How much data are needed to resolve a difficult phylogeny? Case study in Lamiales. Syst. Biol. 2005, 54, 697–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Species | Location | Longitude | Latitude | Clean reads | Mean coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R. glutinosa | Yulin, Shaanxi, China | 110.57 | 37.77 | 3,721,846 | 1583.5× |
| R. henryi | Yichang, Hubei, China | 10.68 | 31.31 | 31,171,142 | 119.6× |
| R. elata | Amsterdam, Holland | 4.88 | 52.36 | 26,976,944 | 137.1× |
| R. piasezkii | Shiquan, Shaanxi, China | 108.63 | 32.04 | 26,815,865 | 125.3× |
| R. chingii | Lishui, Zhejiang, China | 120.15 | 28.64 | 25,724,095 | 131.5× |
| R. solanifolia | Chengkou, Chongqing, China | 108.62 | 1.54 | 29,076,484 | 141.8× |
| Taxon | Species | GenBank | Length | LSC | SSC | IR | Gene | PCG | tRNA | rRNA | GC (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Orobanchaceae | Rehmannia glutinosa (Gaetn.) Libosch. ex Fisch. et Mey. | KX636157 | 153622 | 84605 | 17579 | 25719 | 133 | 88 | 37 (7) | 8 (4) | 38 |
| Rehmannia chingii Li. | KX426347 | 154055 | 84966 | 17675 | 25707 | 133 | 88 | 37 (7) | 8 (4) | 38 | |
| Rehmannia henryi N.E. Brown | KX636158 | 153890 | 84837 | 17679 | 25687 | 133 | 88 | 37 (7) | 8 (4) | 37.9 | |
| Rehmannia elata N.E. Brown | KX636161 | 153772 | 84788 | 17652 | 25666 | 133 | 88 | 37 (7) | 8 (4) | 38 | |
| Rehmannia piasezkii Maxim. | KX636160 | 153952 | 84899 | 17674 | 25676 | 133 | 88 | 37 (7) | 8 (4) | 37.9 | |
| Rehmannia solanifolia Tsoong et Chin | KX636159 | 153989 | 84839 | 17680 | 25735 | 133 | 88 | 37 (7) | 8 (4) | 37.9 | |
| Cistanche phelypaea (L.) Coutinho | NC_025642 | 94380 | 32648 | 8646 | 26543 | 99 | 30 | 42 (9) | 8 (4) | 36.6 | |
| Cistanche deserticola Ma | KC_128846 | 102657 | 49130 | 8819 | 22354 | 106 | 31 | 36 (7) | 8 (4) | 36.8 | |
| Orobanche californica Cham. & Schltdl. | NC_025651 | 120840 | 62000 | 8516 | 25162 | 123 | 45 | 41 (6) | 8 (4) | 36.7 | |
| Lindenbergia philippensis (Cham.) Benth. | NC_022859 | 155103 | 85594 | 17885 | 25812 | 137 | 85 | 37 (7) | 8 (4) | 37.8 | |
| Schwalbea americana L. | HG_738866 | 160910 | 84756 | 18899 | 28627 | 128 | 82 | 37 (7) | 8 (4) | 38.1 | |
| Lamiaceae | Rosmarinus officinalis L. | KR_232566 | 152462 | 83355 | 17969 | 25569 | 134 | 86 | 37 (7) | 8 (4) | 38 |
| Salvia miltiorrhiza Bge. | NC_020098 | 153953 | 85318 | 17741 | 25447 | 134 | 86 | 37 (7) | 8 (4) | 37.9 | |
| Origanum vulgare L. | JX_880022 | 151935 | 83135 | 17727 | 25533 | 134 | 86 | 37 (7) | 8 (4) | 37.8 | |
| Tectona grandis L.F. | NC_020431 | 151328 | 82695 | 17555 | 25539 | 133 | 87 | 37 (7) | 8 (4) | 38 | |
| Premna microphyllaTurcz | NC_026291 | 155293 | 86078 | 17689 | 25763 | 133 | 87 | 37 (7) | 8 (4) | 37.9 | |
| Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi | KR_233163 | 152731 | 83946 | 17477 | 25654 | 132 | 87 | 36 (7) | 8 (4) | 38.4 | |
| Scrophulariaceae | Scrophularia takesimensis Nakai | KM_590983 | 152425 | 85531 | 17938 | 23478 | 132 | 88 | 36 (6) | 8 (4) | 38.1 |
| Gesneriaceae | Boea hygrometrica (Bunge) R. Br. | NC_016468 | 153493 | 84698 | 17903 | 25446 | 145 | 85 | 36 (7) | 8 (4) | 37.6 |
| Acanthaceae | Andrographis paniculata (Burm. f.) Nees | NC_022451 | 150249 | 82459 | 17110 | 25340 | 132 | 87 | 37 (7) | 8 (4) | 38.3 |
| Lentibulariaceae | Utricularia gibba L. | NC_021449 | 152113 | 81818 | 14187 | 27904 | 133 | 87 | 37 (6) | 8 (4) | 37.6 |
| Pedaliaceae | Sesamum indicum Linn. | JN_637766 | 153324 | 85170 | 17872 | 25141 | 134 | 87 | 37 (7) | 8 (4) | 38.2 |
| Oleaceae | Olea europaea L. | GU_931818 | 155889 | 86614 | 17791 | 25742 | 133 | 87 | 37 (7) | 8 (4) | 37.8 |
| Category | Group | Name |
|---|---|---|
| Photosynthesis related genes | Rubisco | rbcL |
| Photosystem I | psaA, psaB, psaC, psaI, psaJ | |
| Assembly/stability of photosystem I | ** ycf3 | |
| Photosystem II | psbA, psbB, psbC, psbD, psbE, psbF, psbH, psbI, psbJ, psbK, psbL, psbM, psbN, psbT, psbZ | |
| ATP synthase | atpA, atpB, atpE, * atpF, atpH, atpI | |
| cytochrome b/f complex | petA, * petB, * petD, petG, petL, petN | |
| cytochrome c synthesis | ccsA | |
| NADPH dehydrogenase | * ndhA, *,a ndhB, ndhC, ndhD, ndhE, ndhF, ndhG, ndhH, ndhI, ndhJ, ndhK | |
| Transcription and translation related genes | transcription | rpoA, rpoB, *rpoC1, rpoC2 |
| ribosomal proteins | rps2, rps3, rps4, a rps7, rps8, rps11, ** rps12, rps14, rps15, *rps16, rps18, rps19, *,arpl2, rpl14, * rpl16, rpl20, rpl22, a rpl23, rpl32, rpl33, rpl36 | |
| translation initiation factor | infA | |
| RNA genes | ribosomal RNA | arrn5, a rrn4.5, a rrn16, a rrn23 |
| transfer RNA | *,a trnA-UGC, # trnA-ACG, trnL-UAG, atrnA-GUU, *,atrnI-GAU, a trnV-(GAC), a trnL-CAA, a trnH-CAU, trnP-UGG, trnT-CCA, trnM-CAU, * trnV-UAC, trnP-GAA, * trnL-UAA, trnT-UGU, trnS-GGA, trnfM-CAU, trnG-GCC, trnS-UGA, trnT-GGU, trnG-UUC, trnT-GUA, trnA-GUC, trnC-GCA, trnA-UCU, * trnG-UCC, trnS-GCU, trnG-UUG, * trnL -UUU, trnH-GUG, trnA-GUU | |
| Other genes | RNA processing | matK |
| carbon metabolism | cemA | |
| fatty acid synthesis | accD | |
| proteolysis | ** clpP | |
| Genes of unknown function | conserved reading frames | a ycf1, a ycf2, ycf4, a ycf15 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeng, S.; Zhou, T.; Han, K.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Liu, Z.-L. The Complete Chloroplast Genome Sequences of Six Rehmannia Species. Genes 2017, 8, 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes8030103
Zeng S, Zhou T, Han K, Yang Y, Zhao J, Liu Z-L. The Complete Chloroplast Genome Sequences of Six Rehmannia Species. Genes. 2017; 8(3):103. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes8030103
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeng, Shuyun, Tao Zhou, Kai Han, Yanci Yang, Jianhua Zhao, and Zhan-Lin Liu. 2017. "The Complete Chloroplast Genome Sequences of Six Rehmannia Species" Genes 8, no. 3: 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes8030103
APA StyleZeng, S., Zhou, T., Han, K., Yang, Y., Zhao, J., & Liu, Z.-L. (2017). The Complete Chloroplast Genome Sequences of Six Rehmannia Species. Genes, 8(3), 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes8030103






