Abstract
While the typical Arabian camel is characterized by a single colored coat, there are rare populations with white spotting patterns. White spotting coat patterns are found in virtually all domesticated species, but are rare in wild species. Theories suggest that white spotting is linked to the domestication process, and is occasionally associated with health disorders. Though mutations have been found in a diverse array of species, fewer than 30 genes have been associated with spotting patterns, thus providing a key set of candidate genes for the Arabian camel. We obtained 26 spotted camels and 24 solid controls for candidate gene analysis. One spotted and eight solid camels were whole genome sequenced as part of a separate project. The spotted camel was heterozygous for a frameshift deletion in KIT (c.1842delG, named KITW1 for White spotting 1), whereas all other camels were wild-type (KIT+/KIT+). No additional mutations unique to the spotted camel were detected in the EDNRB, EDN3, SOX10, KITLG, PDGFRA, MITF, and PAX3 candidate white spotting genes. Sanger sequencing of the study population identified an additional five KITW1/KIT+ spotted camels. The frameshift results in a premature stop codon five amino acids downstream, thus terminating KIT at the tyrosine kinase domain. An additional 13 spotted camels tested KIT+/KIT+, but due to phenotypic differences when compared to the KITW1/KIT+ camels, they likely represent an independent mutation. Our study suggests that there are at least two causes of white spotting in the Arabian camel, the newly described KITW1 allele and an uncharacterized mutation.
1. Introduction
Coat color variation was valued throughout animal domestication [1]. Human selection favors unique morphological characteristics, resulting in the diverse array of coat pigmentation present in many species. Many genes are associated with white spotting patterns in domestic animals [2]. However, color variation is often associated with other behavioral or health traits, due to the phenomenon of genetic pleiotropy [3]. White spotting in particular is linked with conditions such as anemia, deafness, gastrointestinal abnormalities, skin cancers, and sterility [4]. However, while white spotting phenotypes are common among domesticated species, not all have known pleiotropy.
The Arabian camel is an important domestic species selected for draught, meat, milk, racing, and riding. Though usually with a uniform coat of varying shades of brown or black, there are rare spotted or fully white populations [5,6,7,8]. To our knowledge, there have been no published studies on the genetics of camel coat color patterns. In this work, we report on a candidate gene approach using whole genome sequencing to characterize the genetics of white spotting.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
Sample collection for this study was approved by the University of Florida Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) under protocol #201408506. All animals were voluntarily enrolled by private owners. Blood or hair samples were collected from 50 Arabian camels. Photographs were obtained for all but three animals, which were used to assess phenotype (Table 1). For the three animals without photos, phenotype was recorded as a written description at the time of sample collection. Individuals were identified as spotted if they exhibited a region of white fur with pink skin underneath on a background of normal pigmentation. Pedigree information was only available for five dam-offspring pairs (Table 1). Additionally, camels US12 and US15 as well as US14 and US17 were identified as possible half siblings, though the owner was not certain. DNA was extracted using either the Gentra Puregene buffy coat protocol (Qiagen, Valencia, CA, USA) or a modified Puregene protocol for hair [9].

Table 1.
Origin and coat color information for the camels in this study.
2.2. Next-Generation Sequencing
Whole genome sequencing was performed on eight camels (QA1-5, US1, US3-4, US6). Each sample was sequenced on a single lane of an Illumina HiSeq 2500 with 2 × 100 bp reads. We obtained an average of 184 million read pairs per lane. Raw sequencing reads were submitted to the ENA under accession number PRJEB15365. A custom reference sequence file was prepared, comprised of Arabian camel scaffolds matching known white spotting genes EDNRB, EDN3, SOX10, KIT, KITLG, PDGFRA, MITF, and PAX3 [10,11] (Supplementary Table S1). Sequencing reads were aligned with BWA 0.7.12-r1039 using default parameters, and were converted to BAM format using SAMtools 0.1.19-44428cd [12,13].
Predicted dromedary camel mRNA sequences for the candidate genes were obtained from Genbank and aligned to the custom reference using BLAT 20140318 [14] (Supplementary Table S1). Alignments were visualized in IGV 2.3.55 [15]. The coding regions and immediately surrounding introns were manually inspected for variant annotation (Supplementary Table S2). At least three reads for homozygous variants and six for heterozygous variants were required to record a genotype.
2.3. Variant Validation and Genotyping
Variants observed only in the spotted camel genome were selected for further evaluation. PCR primers were designed using the reference scaffolds and Primer3 [16] (Supplementary Table S3). Additional samples were genotyped by Sanger sequencing of PCR amplicons. Chromatograms in PDF format were visually inspected to assess genotype. Sanger sequences for camel KIT exons 12 and 13 were submitted to Genbank and are available under accession numbers KX784929 (KITW1) and KX784928 (KIT+).
3. Results and Discussion
The degree of white spotting of each animal varied greatly, ranging from white only on the lips, to white on approximately 80% of the body (Table 1, Figure 1). Camels with extensive markings had blue eyes. Samples US27 and US41 were recorded as solid white as there were no obvious colored patches of fur. “Mottled white” indicates that the border between the colored and white fur was jagged and uneven, and/or with regions where colored and white fur were intermingled (Figure 1C). “Clear white” indicates a well-defined border between colored and white fur, though with possible flecks of color within predominantly white patches (Figure 1D). Minimally spotted camels often had white restricted to the “points”—the face, legs, and tail. The US spotted camels were visibly smaller in overall body size than the solid camels, though no quantitative measures were assessed. Two of the owners mentioned that spotted camels are known for being roughly 30 cm shorter at maturity.

Figure 1.
Range of white spotting phenotypes in this study. (A) A minimally spotted camel (US30), displaying white patches on both upper lips. (B) A minimally spotted camel (US25), showing a facial marking and white spot in front of the hump. (C) An extensively spotted “mottled white” camel (US28), with pigmented regions concentrated along the topline. (D) A moderately spotted “clear white” camel (US34), showing clear definition between pigmented and white regions.
Most US owners did not have information on the colors of the parents of the spotted camels. One owner described that many of the breeders he knew of bred white spotted bulls to non-spotted cows in order to produce color. He knew of one spotted bull (~50% of the body with white spotting) that produced all minimally spotted offspring (dark eyes with white on the face, legs, and/or tail) out of solid cows. However, the mottled white phenotype is not likely to be incompletely dominant, as one of the extensively marked camels in the study (US28) produced a completely non-spotted calf (US29). We thus assumed the mottled white trait would be dominant based on similarities to white spotting patterns in the horse.
The spotted Algerian camels, known locally as Azerghaf or Zarwala, are found in the southwest regions of the country. Some tribes prefer the spotted camels as they are born deaf, and thus are easier to raise. Interviews with local farmers indicate the color is likely autosomal recessive in inheritance. A secondary type of spotted Algerian camel (characterized by a white spot on the forehead, found in the extreme south) was not available for genotyping.
Variant screening identified one mutation in KIT as a likely candidate (Supplementary Table S2). There were no variants detected in PAX3, whereas candidate genes SOX10, MITF, and KITLG only had variants in the untranslated regions (only one of which was uniquely present in spotted camel US4). Silent variants in KIT, EDN3, EDNRB, and PDGFRA were found in both US4 and non-spotted camels (QA1-5, US1, US3, US6). There was one homozygous missense variant in PDGFRA present in US4, but it was not considered further as QA4 was heterozygous for this variant as well. The only coding variant unique to US4 was a heterozygous single base deletion within exon 12 of 21 in KIT (c.1842delG). This mutation results in a frameshift, leading to a premature stop codon five amino acids downstream (p.M614IfsX5). This mutation ultimately truncates the protein at the intracellular tyrosine kinase domain. Sanger sequencing identified eight additional heterozygotes and no homozygous mutants (Figure 2, Table 2). Five heterozygotes were in the mottled white category, whereas the remaining four animals had too little white to define as clear or mottled (Table 1). Based on the appearance of the minimally spotted camels, we have termed the allele KITW1 for White spotting 1.
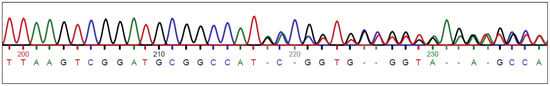
Figure 2.
Sanger sequencing confirms the presence of a heterozygous deletion. The KIT:c.1842delG variant results in a frameshift five bases downstream, truncating the protein at the intracellular tyrosine kinase domain.

Table 2.
Genotyping results for the KIT:c.1842delG mutation (KITW1).
KIT, v-kit Hardy-Zuckerman 4 feline sarcoma viral oncogene homolog, is one of the most commonly implicated genes for white spotting phenotypes in animals [17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24]. There are four reported frameshift mutations in the domestic horse, all of which were associated with extensive white spotting [17,25,26]. KIT encodes a tyrosine kinase receptor involved in the development of erthyrocytes, melanocytes, germ cells, mast cells, and interstitial cells of Cajal [27]. As a result, loss-of-function mutations have been associated with a variety of negative pleiotropic effects, and in some cases are hypothesized to be homozygous lethal [20,28,29]. However, not all KIT variants have reported pleiotropy, and specific variants in cats and horses were shown to have normal hematological parameters [18,30]. All nine camels with the KIT:c.1842delG variant were mature without obvious health issues, although detailed histories were not available. Additionally, one of the animals had two previous successful pregnancies, and thus was fertile. The KITW1 allele does not appear to be detrimental in heterozygotes, although homozygous embryos are likely not viable, similar to dogs with a frameshift mutation in KIT [20].
The appearance of the nine KITW1/KITW+ camels was highly variable. Minimally spotted animals (white on face, legs, or tail only) had dark eyes, whereas the more extensively marked camels had blue eyes (Table 1). Blue eyes are commonly associated with white markings in a variety of species. Several of the equine KIT variants also show considerable variation in the degree of spotting, including horses with white found only on the head and legs [25,31,32]. Intense selection for the degree of white spotting in the mouse has demonstrated that a large number of additive and modifying loci cumulatively contribute to overall color, in addition to non-genetic factors [33]. Heterozygous KIT mice display the full range of color, from completely solid to completely white. It is thus likely that the more extensively marked mottled white camels possessed additional genetic variants that we did not detect.
As the remaining spotted camels were wild-type for KIT:c.1842delG, they likely have a different mutation responsible for white spotting. The overall appearance of the moderately marked animals was quite distinct between the “mottled white” and “clear white” patterns, with the “clear white” animals appearing similar to the “splashed white” coat color of the horse [34]. Interestingly, both the Algerian spotted camels and some splashed white horses have a congenital deafness. Splashed white is associated with mutations in MITF and PAX3, both of which are genes implicated in the human Waardenburg Syndrome (characterized by white patches of skin, blue eyes, and some degree of deafness). Thus, MITF and PAX3 are attractive candidates for the “clear white” Arabian camel phenotype.
4. Conclusions
In conclusion, the c.1842delG mutation in KIT is likely responsible for one form of white spotting in the dromedary camel. We propose to name this allele KITW1 for White spotting 1. However, due to the wide variation in KITW1/KIT+ animals, and the presence of KIT+/KIT+ spotted camels, there are likely other mutations that we did not characterize. Further research should elucidate the genes responsible for other white phenotypes.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at www.mdpi.com/2073-4425/8/3/102/s1, Table S1: NCBI accession numbers for the scaffolds and proteins used as reference sequences, Table S2: Detected variants in candidate white spotting genes, Table S3: PCR primers used for Sanger sequencing validation.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the owners for providing samples, as well as Dr. Fahad Alshanbari for his assistance in blood collection. This study was made possible by National Priorities Research Program (NPRP) grant 6-1303-4-023 from the Qatar National Research Fund (a member of Qatar Foundation). The statements made herein are solely the responsibility of the authors.
Author Contributions
Heather Holl and Samantha Brooks designed the study; Heather Holl, Samantha Brooks, Ramiro Isaza, Faisal Almathen, Cherifi Youcef, and Semir Gaouar collected samples; Yasmin Mohamoud and Ayeda Ahmed performed the next-generation sequencing; Heather Holl performed Sanger sequencing and data analysis; Heather Holl, Samantha Brooks, Semir Gaouar and Douglas F. Antczak drafted the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Ludwig, A.; Pruvost, M.; Reissmann, M.; Benecke, N.; Brockmann, G.A.; Castaños, P.; Cieslak, M.; Lippold, S.; Llorente, L.; Malaspinas, A.S.; et al. Coat color variation at the beginning of horse domestication. Science 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reissmann, M.; Ludwig, A. Pleiotropic effects of coat colour-associated mutations in humans, mice, and other mammals. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellone, R.R. Pleiotropic effects of pigmentation genes in horses. Anim. Genet. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, I. Molecular and developmental genetics of mouse coat color. Annu. Rev. Genet. 1994, 28, 189–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bornstein, S. The ship of the desert. The dromedary camel (Camelus dromedarius), a domesticated animal species well adapted to extreme conditions of aridness and heat. Rangifer 1990, 10, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishag, I.A.; Eisa, M.O.; Ahmed, M.K.A. Phenotypic characteristics of Sudanese camels (Camelus dromedarius). Livestock Res. Rural Dev. 2011, 23. Article #99. [Google Scholar]
- Abdussamad, A.M.; Charruau, P.; Kalla, D.J.U.; Burger, P.A. Validating local knowledge on camels: Colour phenotypes and genetic variation of dromedaries in the Nigeria-Niger corridor. Livest. Sci. 2015, 181, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherifi, Y.A.; Gaouar, S.B.S.; Moussi, N.; Tabet, A.N.; Saïdi-Mehtar, N. Study of Camelina Biodiversity in Southwestern of Algeria. J. Life Sci. 2013, 7, 416–427. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, D.; Gallagher, P.C.; Bailey, E. Genetics of swayback in American Saddlebred horses. Animal Genet 2010, 41 (Suppl 2), 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Guang, X.; Al-Fageeh, M.B.; Cao, J.; Pan, S.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, L.; Abutarboush, M.H.; Xing, Y.; Xie, Z.; et al. Camelid genomes reveal evolution and adaptation to desert environments. Nat. Commun. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephenson, D.A; Mercola, M.; Anderson, E.; Wang, C.Y.; Stiles, C.D.; Bowen-Pope, D.F.; Chapman, V.M. Platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha-subunit gene (Pdgfra) is deleted in the mouse patch (Ph) mutation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1991, 88, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R. 1000 Genome Project Data Processing Subgroup. The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kent, W.J. BLAT—The BLAST-like alignment tool. Genome Res. 2002, 12, 656–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, J.T.; Thorvaldsdóttir, H.; Winckler, W.; Guttman, M.; Lander, E.S.; Getz, G.; Mesirov, J.P. Integrative Genomics Viewer. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 24–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozen, S.; Skaletsky, H. Primer3 on the WWW for general users and for biologist programmers. Methods Mol. Biol. 2000, 132, 365–386. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Haase, B.; Jagannathan, V.; Rieder, S.; Leeb, T. A novel KIT variant in an Icelandic horse with white-spotted coat color. Anim. Genet. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, V.A.; Menotti-Raymond, M.; Wallace, A.C.; Roelke, M.; Kehler, J.; Leighty, R.; Eizirik, E.; Hannah, S.S.; Nelson, G.; Schäffer, A.A.; et al. Endogenous retrovirus insertion in the KIT oncogene determines white and white spotting in domestic cats. G3 (Bethesda) 2014, 4, 1881–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontanesi, L.; Vargiolu, M.; Scotti, E.; Latorre, R.; Faussone Pellegrini, M.S.; Mazzoni, M.; Asti, M.; Chiocchetti, R.; Romeo, G.; Clavenzani, P.; et al. The KIT gene is associated with the English spotting coat color locus and congenital megacolon in Checkered Giant rabbits (Oryctolagus cuniculus). PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, A.K.; Ruhe, A.L.; Robertson, K.R.; Loew, E.R.; Williams, D.C.; Neff, M.W. A de novo mutation in KIT causes white spotting in a subpopulation of German Shepherd dogs. Anim. Genet. 2013, 44, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haase, B.; Rieder, S.; Leeb, T. Two variants in the KIT gene as candidate causative mutations for a dominant white and a white spotting phenotype in the donkey. Anim. Genet. 2015, 46, 321–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, J.L.; Kozysa, A.; Kharlamova, A.V.; Gulevich, R.G.; Perelman, P.L.; Fong, H.W.; Vladimirova, A.V.; Oskina, I.N.; Trut, L.N.; Kukekova, A.V. Platinum coat color in red fox (Vulpes vulpes) is caused by a mutation in an autosomal copy of KIT. Anim. Genet. 2015, 46, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, S.Q.; Hou, J.N.; Bai, C.Y.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, X.J.; Ren, H.L.; Sun, B.X.; Zhao, Z.H.; Sun, J.H. A base substitution in the donor site of intron 12 of KIT gene is responsible for the dominant white coat colour of blue fox (Alopex lagopus). Anim. Genet. 2014, 45, 293–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durkin, K.; Coppieters, W.; Drögemüller, C.; Ahariz, N.; Cambisano, N.; Druet, T.; Fasquelle, C.; Haile, A.; Horin, P.; Huang, L.; et al. Serial translocation by means of circular intermediates underlies colour sidedness in cattle. Nature 2012, 482, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haase, B.; Brooks, S.A.; Tozaki, T.; Burger, D.; Poncet, P.A.; Rieder, S.; Hasegawa, T.; Penedo, C.; Leeb, T. Seven novel KIT mutations in horses with white coat colour phenotypes. Anim. Genet. 2009, 40, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holl, H.; Brooks, S.A.; Bailey, E. De novo mutation of KIT discovered as a result of a non-hereditary white coat colour pattern. Anim. Genet. 2010, 41 (Suppl 2), 196–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, Y.; Hirotab, S. Kit as a human oncogenic tyrosine kinase. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2004, 61, 2924–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bult, C.; Eppig, J.; Kadin, J.; Richardson, J.E.; Blake, J.A. Mouse Genome Database Group. The Mouse Genome Database (MGD): Mouse biology and model systems. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, D724–D728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackling, F.C.; Johnson, W.E.; Appleton, B.R. The genetic inheritance of the blue-eyed white phenotype in alpacas (Vicugna pacos). J. Hered. 2014, 105, 847–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haase, B.; Obexer-Ruff, G.; Dolf, G.; Rieder, S.; Burger, D.; Poncet, P.A.; Gerber, V.; Howard, J.; Leeb, T. Haematological parameters are normal in dominant white Franches-Montagnes horses carrying a KIT mutation. Vet. J. 2010, 184, 315–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauswirth, R.; Jude, R.; Haase, B.; Bellone, R.R.; Archer, S.; Holl, H.; Brooks, S.A.; Tozaki, T.; Penedo, M.C.; Rieder, S.; et al. Novel variants in the KIT and PAX3 genes in horses with white-spotted coat colour phenotypes. Anim. Genet. 2013, 44, 763–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dürig, N.; Jude, R.; Holl, H.; Brooks, S.A.; Lafayette, C; Jagannathan, V.; Leeb, T. Whole genome sequencing reveals a novel deletion variant in the KIT gene in horses with white spotted coat colour phenotypes. Anim. Genet. 2017, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Dunn, L.C. Studies on Spotting Patterns II. Genetic Analysis of Variegated Spotting in the House Mouse. Genetics 1937, 22, 43–64. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hauswirth, R.; Haase, B.; Blatter, M.; Brooks, S.A.; Burger, D.; Drögemüller, C.; Gerber, V.; Henke, D.; Janda, J.; Jude, R.; et al. Mutations in MITF and PAX3 cause "splashed white" and other white spotting phenotypes in horses. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).