A Case of Infantile Epileptic Spasms Syndrome with the SPTBN1 Mutation and Review of βII-Spectrin Variants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
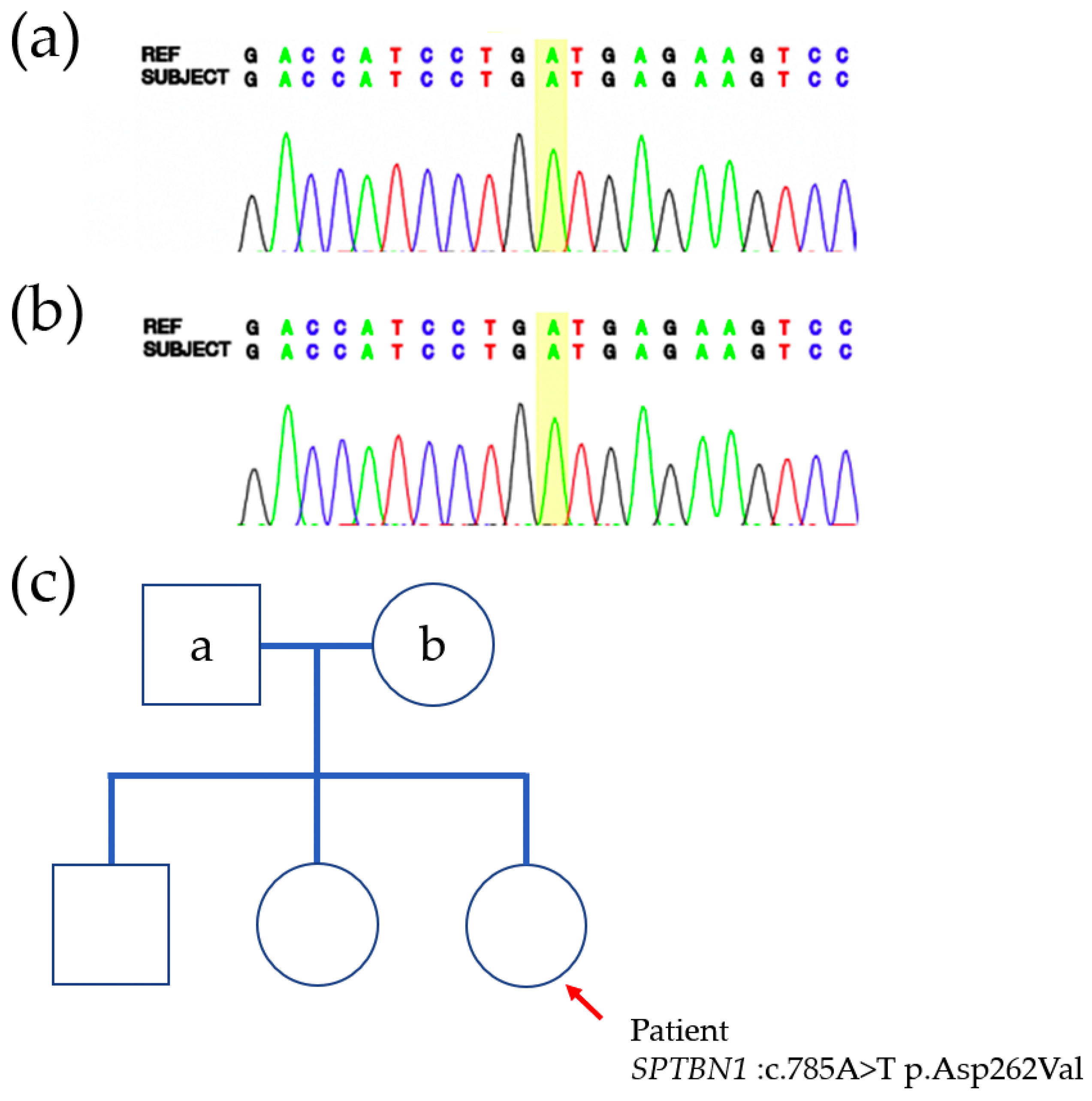
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADHD | Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder |
| ASD | Autism spectrum disorder |
| CH | Calponin homology |
| CMA | Chromosomal Microarray Analysis |
| DD | Delayed development |
| DQ | Developmental quotient |
| EEG | Electroencephalography |
| EIEE | Early infantile epileptic encephalopathy |
| HC | Head circumference |
| ID | Intellectual disability |
| IESS | Infantile epilepsy spasm syndrome |
| PH | Pleckstrin homology domain |
| SR | Spectrin repeat |
References
- Liem, R.K. Cytoskeletal Integrators: The Spectrin Superfamily. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2016, 8, a018259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo, D.N.; Edwards, R.J.; Slavutsky, A.L. Spectrins: Molecular organizers and targets of neurological disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2023, 24, 195–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cousin, M.A.; Creighton, B.A.; Breau, K.A.; Spillmann, R.C.; Torti, E.; Dontu, S.; Tripathi, S.; Ajit, D.; Edwards, R.J.; Afriyie, S.; et al. Pathogenic SPTBN1 variants cause an autosomal dominant neurodevelopmental syndrome. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 1006–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iossifov, I.; O’Roak, B.J.; Sanders, S.J.; Ronemus, M.; Krumm, N.; Levy, D.; Stessman, H.A.; Witherspoon, K.T.; Vives, L.; Patterson, K.E.; et al. The contribution of de novo coding mutations to autism spectrum disorder. Nature 2014, 515, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snyder, H.E.; Jain, P.; RamachandranNair, R.; Jones, K.C.; Whitney, R. Genetic Advancements in Infantile Epileptic Spasms Syndrome and Opportunities for Precision Medicine. Genes 2024, 15, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohyama, J.; Nakashima, M.; Nabatame, S.; Gaik-Siew, C.n.; Miyata, R.; Rener-Primec, Z.; Kato, M.; Matsumoto, N.; Saitsu, H. SPTAN1 encephalopathy: Distinct phenotypes and genotypes. J. Hum. Genet. 2015, 60, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.C.; Ortiz-González, X.R.; Yum, S.W.; Gill, S.M.; White, A.; Kelter, E.; Seaver, L.H.; Lee, S.; Wiley, G.; Gaffney, P.M.; et al. βIV Spectrinopathies Cause Profound Intellectual Disability, Congenital Hypotonia, and Motor Axonal Neuropathy. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2018, 102, 1158–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, Y.; Dick, K.A.; Weatherspoon, M.R.; Gincel, D.; Armbrust, K.R.; Dalton, J.C.; Stevanin, G.; Dürr, A.; Zühlke, C.; Bürk, K.; et al. Spectrin mutations cause spinocerebellar ataxia type 5. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Zhong, G.; Zhuang, X. Actin, spectrin, and associated proteins form a periodic cytoskeletal structure in axons. Science 2013, 339, 452–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo, D.N.; Badea, A.; Zhou, R.; Mohler, P.J.; Zhuang, X.; Bennett, V. βII-spectrin promotes mouse brain connectivity through stabilizing axonal plasma membranes and enabling axonal organelle transport. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 15686–15695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lek, M.; Karczewski, K.J.; Minikel, E.V.; Samocha, K.E.; Banks, E.; Fennell, T.; O’Donnell-Luria, A.H.; Ware, J.S.; Hill, A.J.; Cummings, B.B.; et al. Analysis of protein-coding genetic variation in 60,706 humans. Nature 2016, 536, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirnigliaro, M.; Chang, T.S.; Arteaga, S.A.; Pérez-Cano, L.; Ruzzo, E.K.; Gordon, A.; Bicks, L.K.; Jung, J.Y.; Lowe, J.K.; Wall, D.P.; et al. The contributions of rare inherited and polygenic risk to ASD in multiplex families. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2215632120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connell, M.; Harstad, E.; Aites, J.; Hayes, K.; Arnett, A.B.; Scotellaro, J.; Patel, S.; Brewster, S.J.; Barbaresi, W.; Doan, R.N. Diverse clinical presentation of SPTBN1 variants: Complex versus primary attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2025, 197, e63851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval-Talamantes, A.K.; Tenorio-Castaño, J.A.; Santos-Simarro, F.; Adán, C.; Fernández-Elvira, M.; García-Fernández, L.; Muñoz, Y.; Lapunzina, P.; Nevado, J. NGS Custom Panel Implementation in Patients with Non-Syndromic Autism Spectrum Disorders in the Clinical Routine of a Tertiary Hospital. Genes 2023, 14, 2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satterstrom, F.K.; Kosmicki, J.A.; Wang, J.; Breen, M.S.; De Rubeis, S.; An, J.Y.; Peng, M.; Collins, R.; Grove, J.; Klei, L.; et al. Large-Scale Exome Sequencing Study Implicates Both Developmental and Functional Changes in the Neurobiology of Autism. Cell 2020, 180, 568–584.e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, A.; Danyel, M.; Grundmann, K.; Brunet, T.; Klinkhammer, H.; Hsieh, T.C.; Engels, H.; Peters, S.; Knaus, A.; Moosa, S.; et al. Next-generation phenotyping integrated in a national framework for patients with ultrarare disorders improves genetic diagnostics and yields new molecular findings. Nat. Genet. 2024, 56, 1644–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuncay, I.O.; Parmalee, N.L.; Khalil, R.; Kaur, K.; Kumar, A.; Jimale, M.; Howe, J.L.; Goodspeed, K.; Evans, P.; Alzghoul, L.; et al. Analysis of recent shared ancestry in a familial cohort identifies coding and noncoding autism spectrum disorder variants. NPJ Genom. Med. 2022, 7, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodbury-Smith, M.; Lamoureux, S.; Begum, G.; Nassir, N.; Akter, H.; O’Rielly, D.D.; Rahman, P.; Wintle, R.F.; Scherer, S.W.; Uddin, M. Mutational Landscape of Autism Spectrum Disorder Brain Tissue. Genes 2022, 13, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Li, X.; Meng, Z.; Li, P.; He, Z.; Liang, L. Phenotypic and genetic analysis of children with unexplained neurodevelopmental delay and neurodevelopmental comorbidities in a Chinese cohort using trio-based whole-exome sequencing. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2024, 19, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Feliciano, P.; Shu, C.; Wang, T.; Astrovskaya, I.; Hall, J.B.; Obiajulu, J.U.; Wright, J.R.; Murali, S.C.; Xu, S.X.; et al. Integrating de novo and inherited variants in 42,607 autism cases identifies mutations in new moderate-risk genes. Nat. Genet. 2022, 54, 1305–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willsey, A.J.; Fernandez, T.V.; Yu, D.; King, R.A.; Dietrich, A.; Xing, J.; Sanders, S.J.; Mandell, J.D.; Huang, A.Y.; Richer, P.; et al. De Novo Coding Variants Are Strongly Associated with Tourette Disorder. Neuron 2017, 94, 486–499.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeld, J.A.; Xiao, R.; Bekheirnia, M.R.; Kanani, F.; Parker, M.J.; Koenig, M.K.; van Haeringen, A.; Ruivenkamp, C.; Rosmaninho-Salgado, J.; Almeida, P.M.; et al. Heterozygous variants in SPTBN1 cause intellectual disability and autism. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2021, 185, 2037–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitsu, H.; Tohyama, J.; Kumada, T.; Egawa, K.; Hamada, K.; Okada, I.; Mizuguchi, T.; Osaka, H.; Miyata, R.; Furukawa, T.; et al. Dominant-negative mutations in alpha-II spectrin cause West syndrome with severe cerebral hypomyelination, spastic quadriplegia, and developmental delay. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2010, 86, 881–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jang, H.N.; Ryu, J.; Kim, S.S.; Moon, J.-H. A Case of Infantile Epileptic Spasms Syndrome with the SPTBN1 Mutation and Review of βII-Spectrin Variants. Genes 2025, 16, 904. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16080904
Jang HN, Ryu J, Kim SS, Moon J-H. A Case of Infantile Epileptic Spasms Syndrome with the SPTBN1 Mutation and Review of βII-Spectrin Variants. Genes. 2025; 16(8):904. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16080904
Chicago/Turabian StyleJang, Han Na, Juyeon Ryu, Seung Soo Kim, and Jin-Hwa Moon. 2025. "A Case of Infantile Epileptic Spasms Syndrome with the SPTBN1 Mutation and Review of βII-Spectrin Variants" Genes 16, no. 8: 904. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16080904
APA StyleJang, H. N., Ryu, J., Kim, S. S., & Moon, J.-H. (2025). A Case of Infantile Epileptic Spasms Syndrome with the SPTBN1 Mutation and Review of βII-Spectrin Variants. Genes, 16(8), 904. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16080904





