GONNMDA: A Ordered Message Passing GNN Approach for miRNA–Disease Association Prediction
Abstract
1. Introduction
- The ordered message-passing mechanism of the ordered GNN model, guided by the root–tree hierarchy, prevents the confusion of node features during the combination stage. By modeling information in different sequences, it effectively mitigates the over-smoothing problem, where nodes become indistinguishable as the number of layers increases, thus optimizing the model’s prediction performance.
- A comprehensive biological molecular heterograph is introduced, where different types of nodes interact through various edge types. By integrating multi-level information into the heterograph, the information flow becomes more enriched.
- Multiple similarity measures are integrated, and singular value decomposition (SVD) is employed to effectively remove noise while capturing commonalities and underlying structures across different similarity types, thereby extracting more critical latent features.
- Compared to the current state-of-the-art methods, GONNMDA demonstrates outstanding performance. Case studies and survival analysis further highlight the model’s effectiveness and superiority in miRNA–disease association prediction.
2. Results
2.1. Cross Validation and Evaluation Metrics
2.2. Comparative Analysis with State-of-the-Art Methods
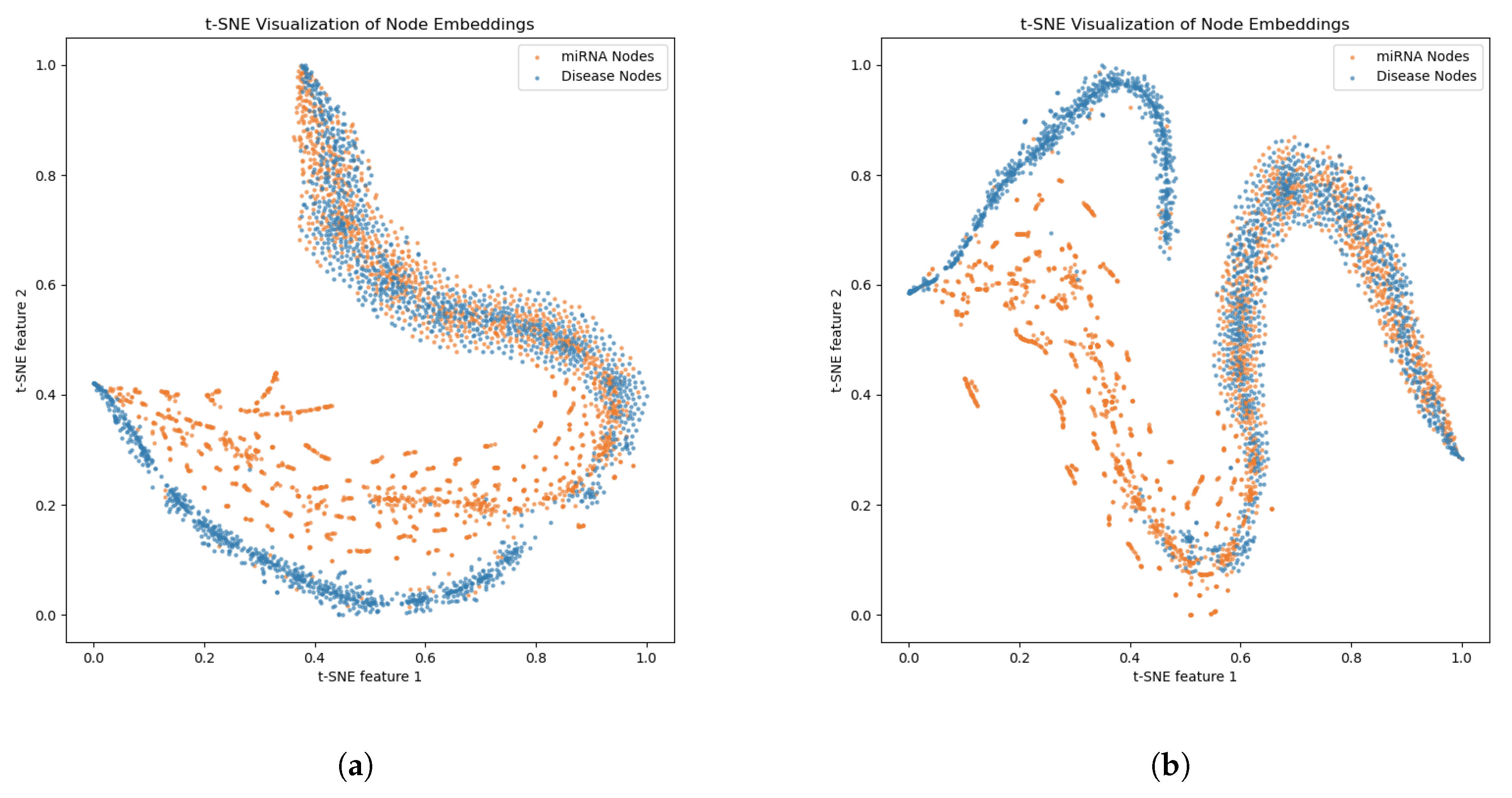
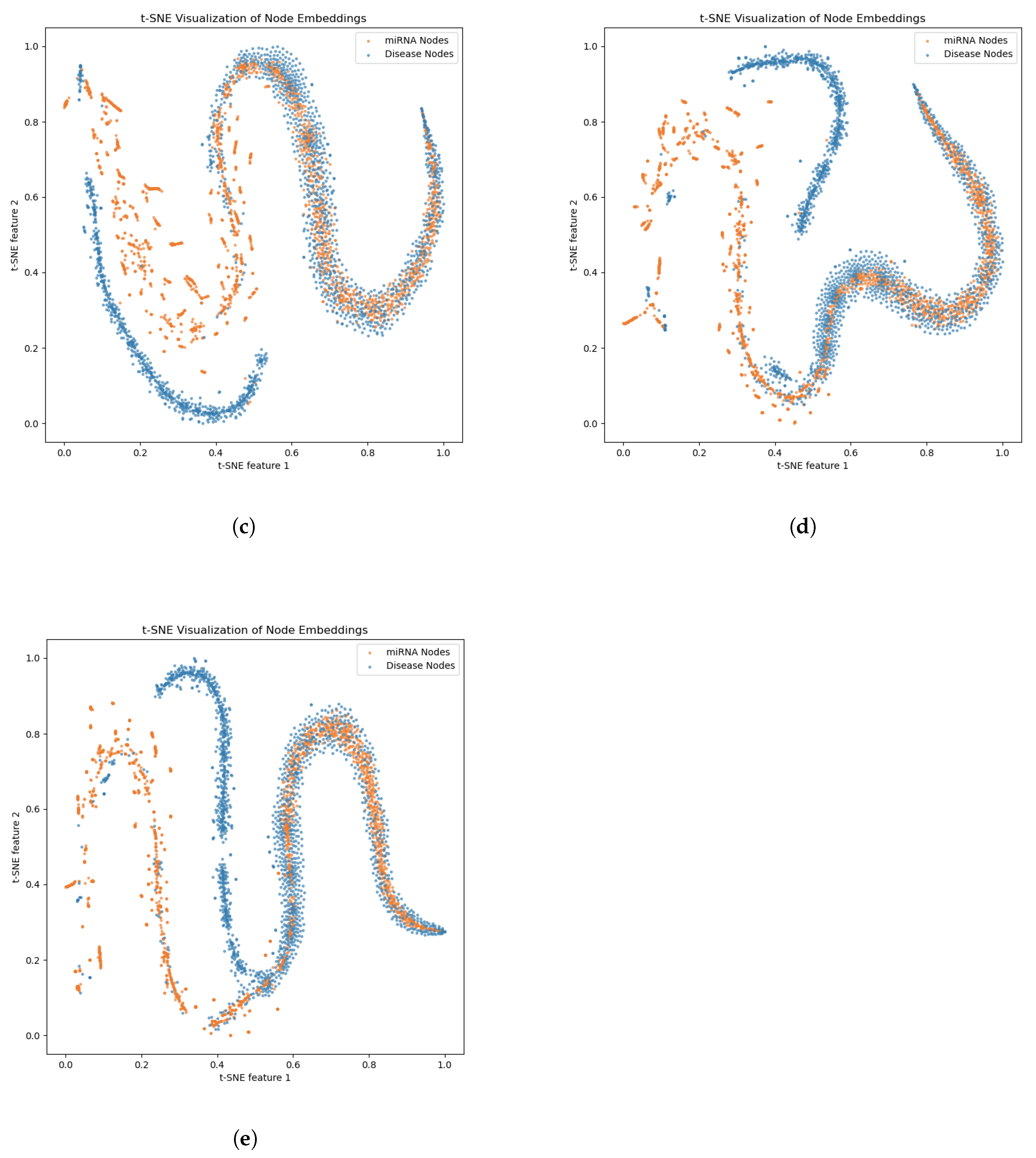
2.3. Ablation Experiments
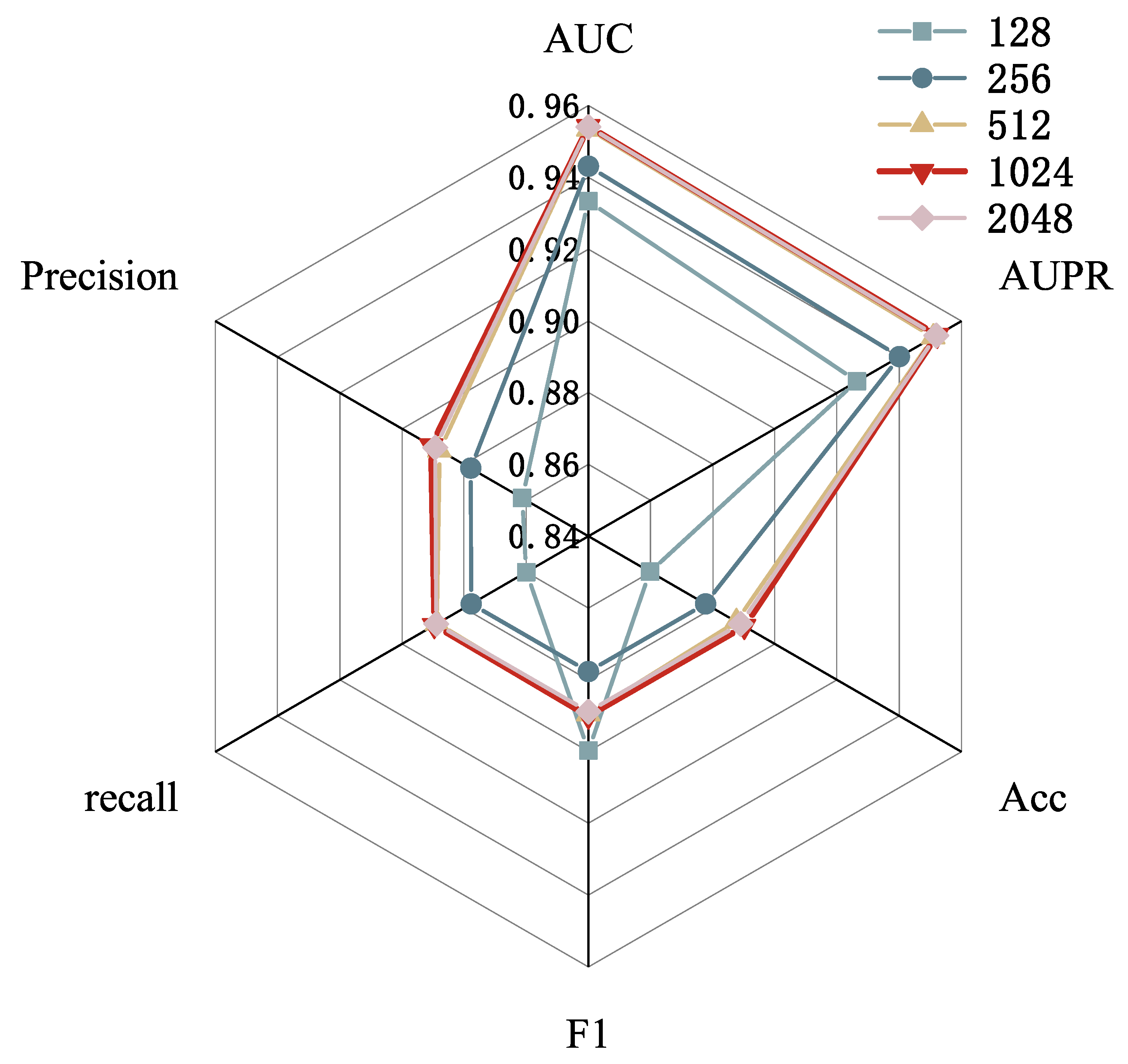
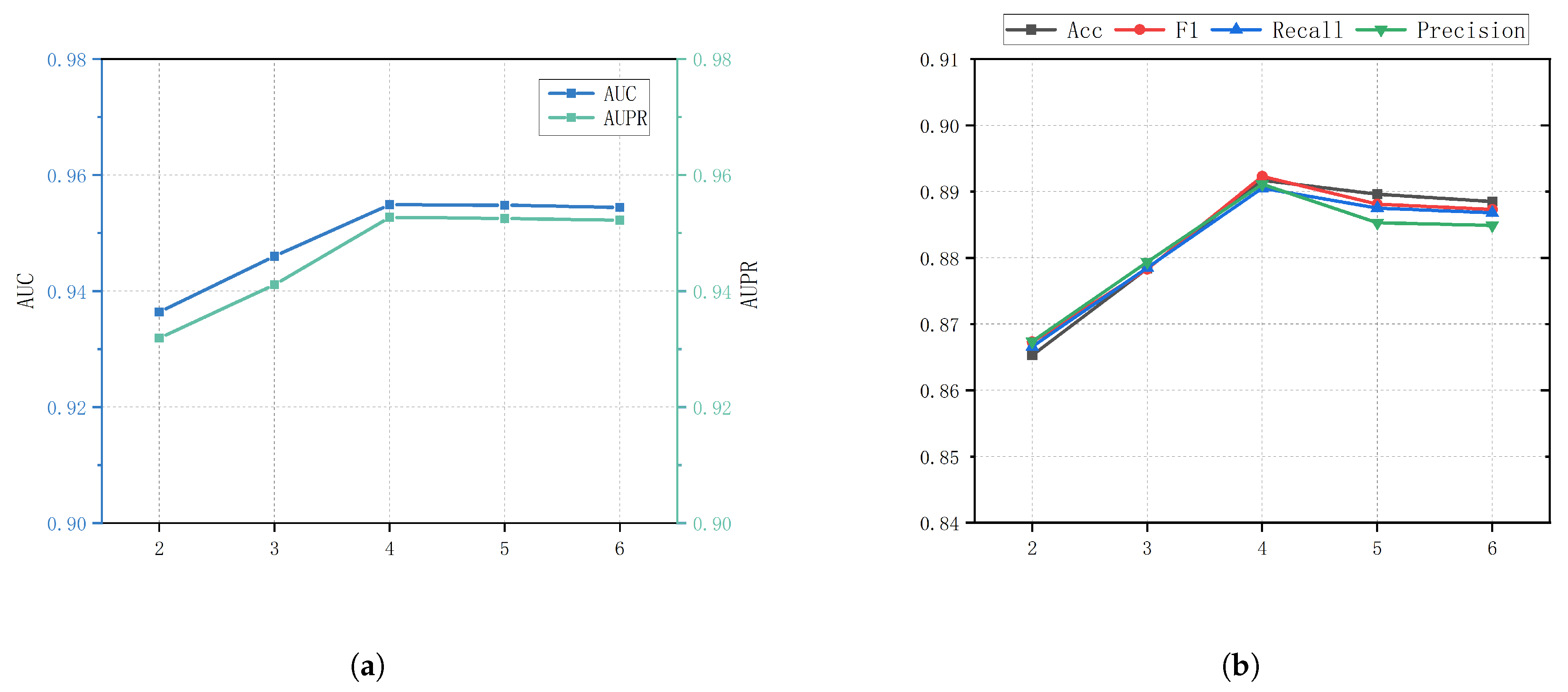
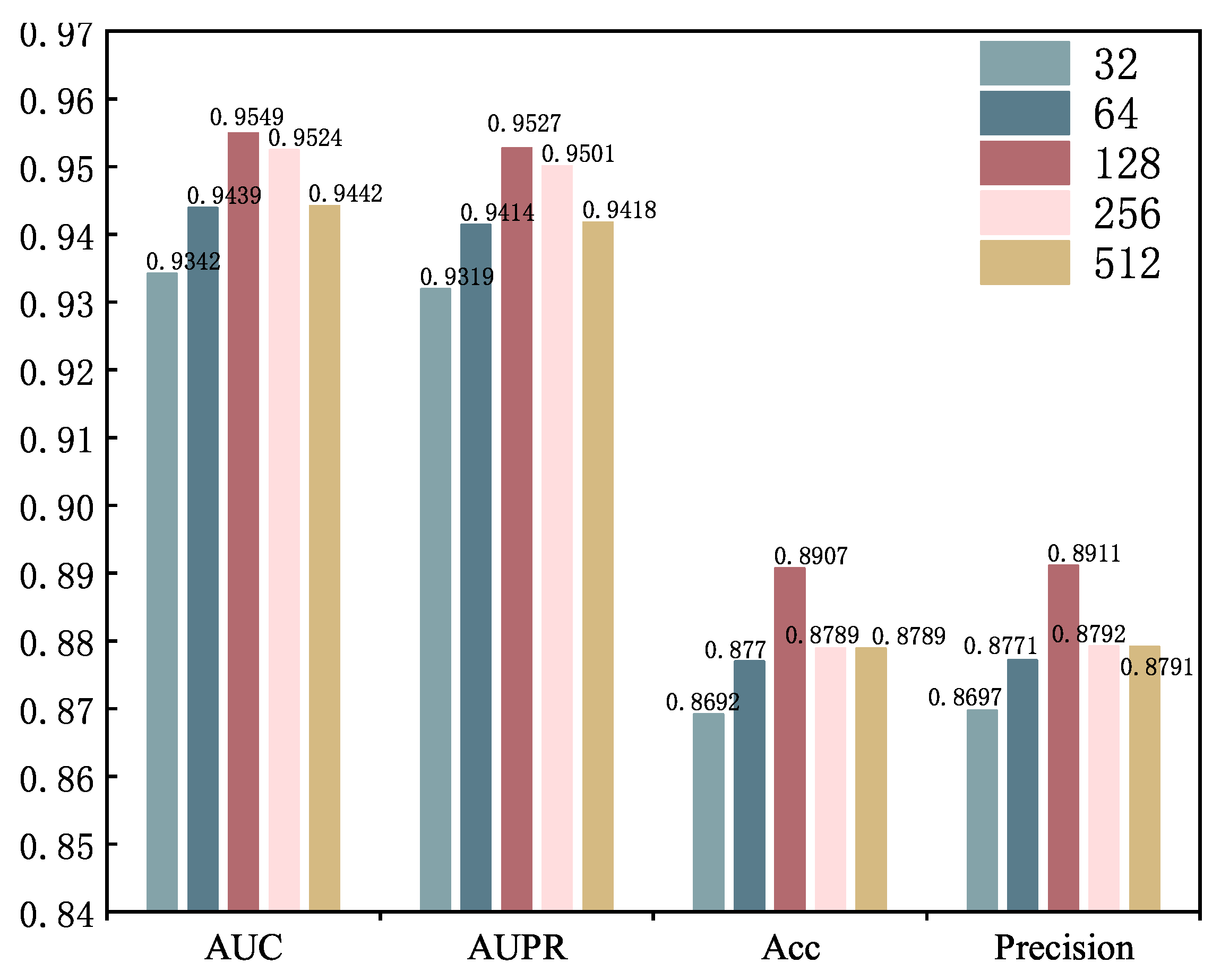
2.4. Parameter Analysis
2.5. Case Studies
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Dataset
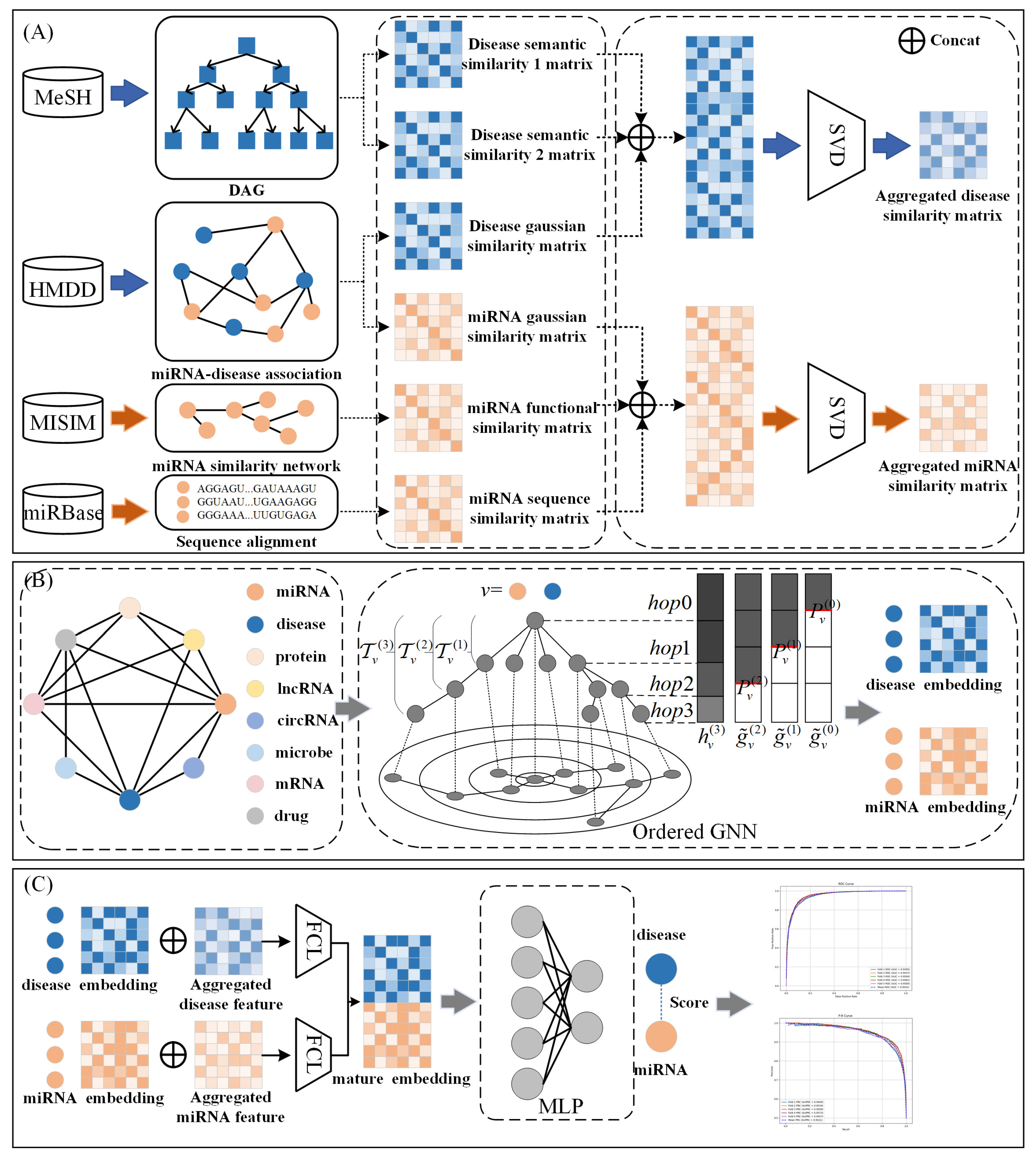
3.2. GONNMDA
3.2.1. Disease Semantic Similarity
3.2.2. MiRNA Similarity
3.2.3. Reconstructed Comprehensive Similarity Features
3.2.4. Heterogeneous Biological Molecular Graph
3.2.5. Ordered GNN
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mattie, M.D.; Benz, C.C.; Bowers, J.; Sensinger, K.; Wong, L.; Scott, G.K.; Fedele, V.; Ginzinger, D.; Getts, R.; Haqq, C. Optimized high throughput microRNA expression profiling provides novel biomarker assessment of clinical prostate and breast cancer biopsies. Mol. Cancer 2006, 5, 24. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.-S.; Su, J.-L.; Cha, S.-T.; Tarn, W.-Y.; Wang, M.-Y.; Hsu, H.-C.; Lin, M.-T.; Chu, C.-Y.; Hua, K.-T.; Chen, C.-N. Erratum: MiR-107 promotes tumor progression by targeting the let-7 microRNA in mice and humans. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 3442–3455. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Li, P.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Y. The diagnostic role of miR-122 in drug-induced liver injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2018, 97, e13478. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Raponi, M.; Dossey, L.; Jatkoe, T.; Wu, X.; Chen, G.; Fan, H.; Beer, D.G. MicroRNA classifiers for predicting prognosis of squamous cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 5776–5783. [Google Scholar]
- Calabrese, F.; Lunardi, F.; Pezzuto, F.; Fortarezza, F.; Vuljan, S.E.; Marquette, C.; Hofman, P. Are there new biomarkers in tissue and liquid biopsies for the early detection of non-small cell lung cancer? J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Luo, J.; Xiao, Q.; Liang, C.; Ding, P. Predicting microRNA-disease associations using label propagation based on linear neighborhood similarity. J. Biomed. Inform. 2018, 82, 169–177. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Wang, L.; Qu, J.; Guan, N.-N.; Li, J.-Q. Predicting miRNA-disease association based on inductive matrix completion. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 4256–4265. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.-T.; Wu, Q.-W.; Gao, Z.; Ni, J.-C.; Zheng, C.-H. MiRNA-disease association prediction via hypergraph learning based on high-dimensionality features. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2021, 21, 133. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Huang, L.; Xie, D.; Zhao, Q. EGBMMDA: Extreme gradient boosting machine for MiRNA-disease association prediction. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Wang, C.-C.; Yin, J.; You, Z.-H. Novel human miRNA-disease association inference based on random forest. Mol. Ther.-Nucleic Acids 2018, 13, 568–579. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, B.-Y.; You, Z.-H.; Cheng, L.; Zhou, J.-R.; Alghazzawi, D.; Li, L.-P. Predicting miRNA-disease association from heterogeneous information network with GraRep embedding model. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6658. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Lin, H.; Huang, L.; Peng, L.; Tang, T.; Zhao, Q.; Yang, L. Identification of miRNA–disease associations via deep forest ensemble learning based on autoencoder. Brief. Bioinform. 2022, 23, bbac104. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Fang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, C.; Xiao, Q.; Luo, J. Predicting miRNA-disease associations based on graph attention network with multi-source information. BMC Bioinform. 2022, 23, 244. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Li, J.; Yue, K.; Wang, L.; Ma, Y.; Li, Q. NMCMDA: Neural multicategory MiRNA–disease association prediction. Brief. Bioinform. 2021, 22, bbab074. [Google Scholar]
- He, Q.; Qiao, W.; Fang, H.; Bao, Y. Improving the identification of miRNA–disease associations with multi-task learning on gene–disease networks. Brief. Bioinform. 2023, 24, bbad203. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Chen, H. Predicting miRNA-disease associations based on lncRNA–miRNA interactions and graph convolution networks. Brief. Bioinform. 2023, 24, bbac495. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, Q.; Chen, X.; Ning, B.; Zhang, X.; Nie, H.; Zeng, L.; Chen, H.; Fu, X. Prediction of miRNA-disease associations by neural network-based deep matrix factorization. Methods 2023, 212, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, H.; Ji, B.; Zhang, M.; Liu, F.; Xie, X.; Peng, S. MHGTMDA: Molecular heterogeneous graph transformer based on biological entity graph for miRNA-disease associations prediction. Mol. Ther.-Nucleic Acids 2024, 35, 102139. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Wang, Y.-T.; Ji, C.-M.; Zheng, C.-H.; Ni, J.-C.; Su, Y.-S. GCAEMDA: Predicting miRNA-disease associations via graph convolutional autoencoder. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2021, 17, e1009655. [Google Scholar]
- Lou, Z.; Cheng, Z.; Li, H.; Teng, Z.; Liu, Y.; Tian, Z. Predicting miRNA–disease associations via learning multimodal networks and fusing mixed neighborhood information. Brief. Bioinform. 2022, 23, bbac159. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.-A.; Chan, K.C.; You, Z.-H.; Hu, P.; Wang, L.; Huang, Z.-A. Predicting microRNA–disease associations from lncRNA–microRNA interactions via multiview multitask learning. Brief. Bioinform. 2021, 22, bbaa133. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ning, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, J.; Chen, C.; Li, X.; Li, T.; Yin, M. AMHMDA: Attention aware multi-view similarity networks and hypergraph learning for miRNA–disease associations identification. Brief. Bioinform. 2023, 24, bbad094. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dong, B.; Sun, W.; Xu, D.; Wang, G.; Zhang, T. MDformer: A transformer-based method for predicting miRNA-Disease associations using multi-source feature fusion and maximal meta-path instances encoding. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 167, 107585. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lu, D.; Li, J.; Zheng, C.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Q. HGTMDA: A Hypergraph Learning Approach with Improved GCN-Transformer for miRNA–Disease Association Prediction. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Wang, Y.; Ling, Y.; Zhou, C.; Wang, H.; Teschendorff, A.E.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, H.; He, Y.; Zhang, G.; et al. dbDEMC 3.0: Functional exploration of differentially expressed miRNAs in cancers of human and model organisms. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2022, 20, 446–454. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Hao, Y.; Juan, L.; Teng, M.; Zhang, X.; Li, M.; Wang, G.; Liu, Y. miR2Disease: A manually curated database for microRNA deregulation in human disease. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, D98–D104. [Google Scholar]
- Berger, A.C.; Korkut, A.; Kanchi, R.S.; Hegde, A.M.; Lenoir, W.; Liu, W.; Liu, Y.; Fan, H.; Shen, H.; Ravikumar, V.; et al. A comprehensive pan-cancer molecular study of gynecologic and breast cancers. Cancer Cell 2018, 33, 690–705.e9. [Google Scholar]
- Győrffy, B. Integrated analysis of public datasets for the discovery and validation of survival-associated genes in solid tumors. Innovation 2024, 5, 100625. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson, L.; Gathani, T. Understanding breast cancer as a global health concern. Br. J. Radiol. 2022, 95, 20211033. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.-F.; Wu, Z.-P.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, Q.-S.; Hamidi, S.; Navab, R. MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) regulates cellular proliferation, invasion, migration, and apoptosis by targeting PTEN, RECK and Bcl-2 in lung squamous carcinoma, Gejiu City, China. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103698. [Google Scholar]
- Indraswary, R.; Haryana, S.M.; Surono, A. Expression of HSA-MIR-155-5P and mRNA Suppressor of Cytokine Signalling 1 (SOCS1) on Plasma at Early-stage and Late-stage of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma; SciTePress—Science and Technology Publications, Ltd.: Setúbal, Portugal, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Aguilar, J.; Patil, S.; Gollub, M.J.; Kim, J.K.; Yuval, J.B.; Thompson, H.M.; Verheij, F.S.; Omer, D.M.; Lee, M.; Dunne, R.F.; et al. Organ preservation in patients with rectal adenocarcinoma treated with total neoadjuvant therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 2546–2556. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sriharikrishnaa, S.; Shukla, V.; Khan, G.N.; Eswaran, S.; Adiga, D.; Kabekkodu, S.P. Integrated bioinformatic analysis of miR-15a/16-1 cluster network in cervical cancer. Reprod. Biol. 2021, 21, 100482. [Google Scholar]
- Marini, F.; Brandi, M.L. Role of miR-24 in multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1: A potential target for molecular therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thandra, K.C.; Barsouk, A.; Saginala, K.; Aluru, J.S.; Barsouk, A. Epidemiology of lung cancer. Contemp. Oncol. Onkol. 2021, 25, 45–52. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, X.; Guan, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, H. Microarray data analysis on gene and miRNA expression to identify biomarkers in non-small cell lung cancer. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 329. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Shi, J.; Gao, Y.; Cui, C.; Zhang, S.; Li, J.; Zhou, Y.; Cui, Q. HMDD v3.0: A database for experimentally supported human microRNA–disease associations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D1013–D1017. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, C.; Lei, X.; Tie, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, F.-X.; Pan, Y. CircR2Disease v2.0: An updated web server for experimentally validated circRNA–disease associations and its application. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2022, 20, 435–445. [Google Scholar]
- Dudekula, D.B.; Panda, A.C.; Grammatikakis, I.; De, S.; Abdelmohsen, K.; Gorospe, M.; Gorospe, M. CircInteractome: A web tool for exploring circular RNAs and their interacting proteins and microRNAs. RNA Biol. 2016, 13, 34–42. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Chen, M. Circular RNA Databases. In Plant Circular RNAs: Methods and Protocols; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 109–118. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Lin, J.; Hu, Y.; Ye, M.; Yao, L.; Wu, L.; Zhang, W.; Wang, M.; Deng, T.; Guo, F. RNADisease v4.0: An updated resource of RNA-associated diseases, providing RNA-disease analysis, enrichment and prediction. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D1397–D1404. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ma, W.; Zhang, L.; Zeng, P.; Huang, C.; Li, J.; Geng, B.; Yang, J.; Kong, W.; Zhou, X.; Cui, Q. An analysis of human microbe–disease associations. Brief. Bioinform. 2017, 18, 85–89. [Google Scholar]
- Knox, C.; Wilson, M.; Klinger, C.M.; Franklin, M.; Oler, E.; Wilson, A.; Pon, A.; Cox, J.; Chin, N.E.; Strawbridge, S.A. DrugBank 6.0: The DrugBank knowledgebase for 2024. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, D1265–D1275. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Ouyang, J.; Gao, Z.; Qin, H.; Jun, W.; Shi, T. MagMD: Database summarizing the metabolic action of gut microbiota to drugs. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2022, 20, 6427–6430. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Whirl-Carrillo, M.; Huddart, R.; Gong, L.; Sangkuhl, K.; Thorn, C.F.; Whaley, R.; Klein, T.E. An evidence-based framework for evaluating pharmacogenomics knowledge for personalized medicine. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 110, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Cui, Q.; Tang, Y.-D.; Ji, X.; Cui, C. LncRNADisease v3.0: An updated database of long non-coding RNA-associated diseases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, D1365–D1369. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.-H.; Liu, S.; Zhou, H.; Qu, L.-H.; Yang, J.-H. starBase v2.0: Decoding miRNA-ceRNA, miRNA-ncRNA and protein-RNA interaction networks from large-scale CLIP-Seq data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D92–D97. [Google Scholar]
- Teng, X.; Chen, X.; Xue, H.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Kang, Q.; Hao, Y.; Chen, R.; Zhao, Y.; He, S. NPInter v4.0: An integrated database of ncRNA interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D160–D165. [Google Scholar]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Kirsch, R.; Koutrouli, M.; Nastou, K.; Mehryary, F.; Hachilif, R.; Gable, A.L.; Fang, T.; Doncheva, N.T.; Pyysalo, S. The STRING database in 2023: Protein–protein association networks and functional enrichment analyses for any sequenced genome of interest. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D638–D646. [Google Scholar]
- Holmes, J.B.; Moyer, E.; Phan, L.; Maglott, D.; Kattman, B. SPDI: Data model for variants and applications at NCBI. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 1902–1907. [Google Scholar]
- Kahn, T.J.; Ninomiya, H. Changing vocabularies: A guide to help bioethics searchers find relevant literature in National Library of Medicine databases using the Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) indexing vocabulary. Kennedy Inst. Ethics J. 2003, 13, 275–311. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Zhang, S.; Wan, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, J.; Zhou, Y.; Cui, Q. MISIM v2.0: A web server for inferring microRNA functional similarity based on microRNA-disease associations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W536–W541. [Google Scholar]
- Likic, V. The Needleman-Wunsch algorithm for sequence alignment. In Proceedings of the 7th Melbourne Bioinformatics Course, Melbourne, Australia, 24–28 November 2008; Bi021 Molecular Science and Biotechnology Institute, University of Melbourne: Melbourne, Australia, 2008; pp. 1–46. [Google Scholar]
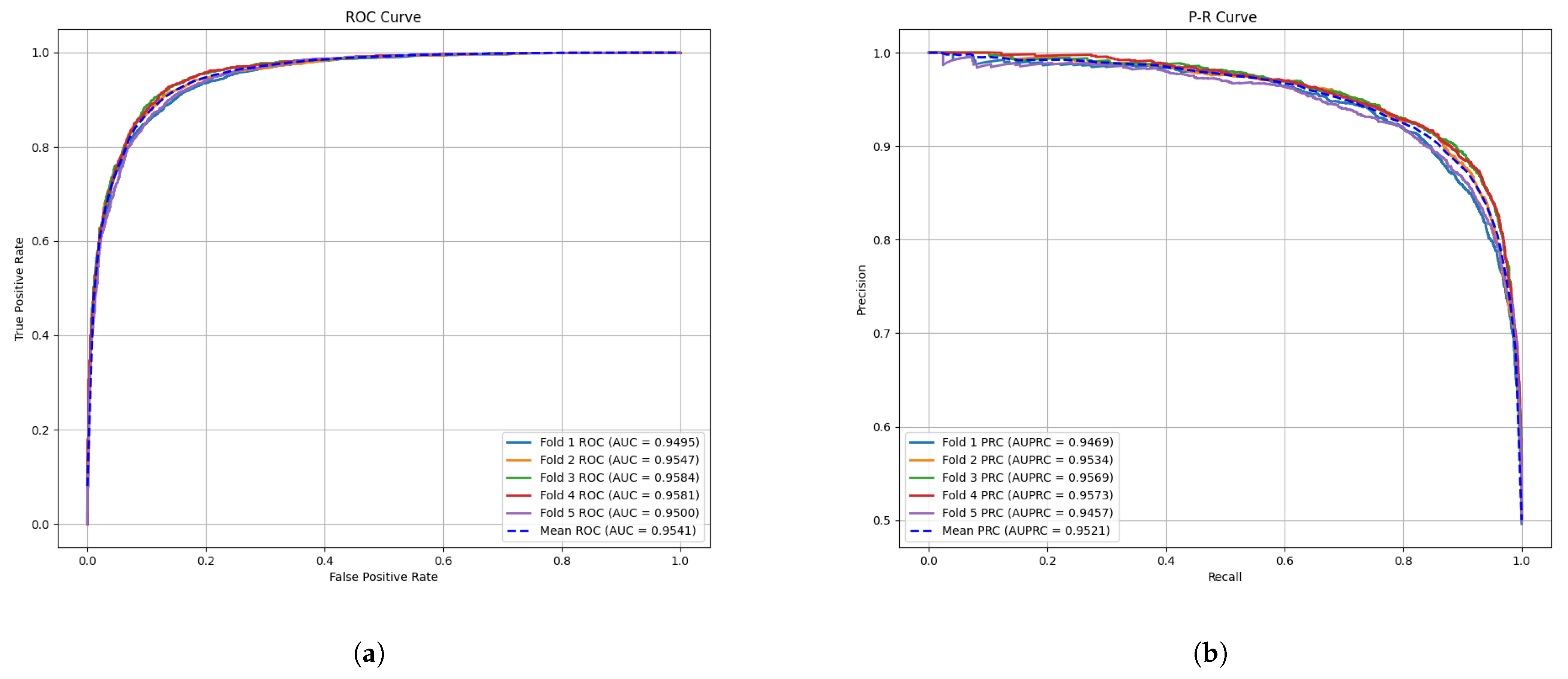
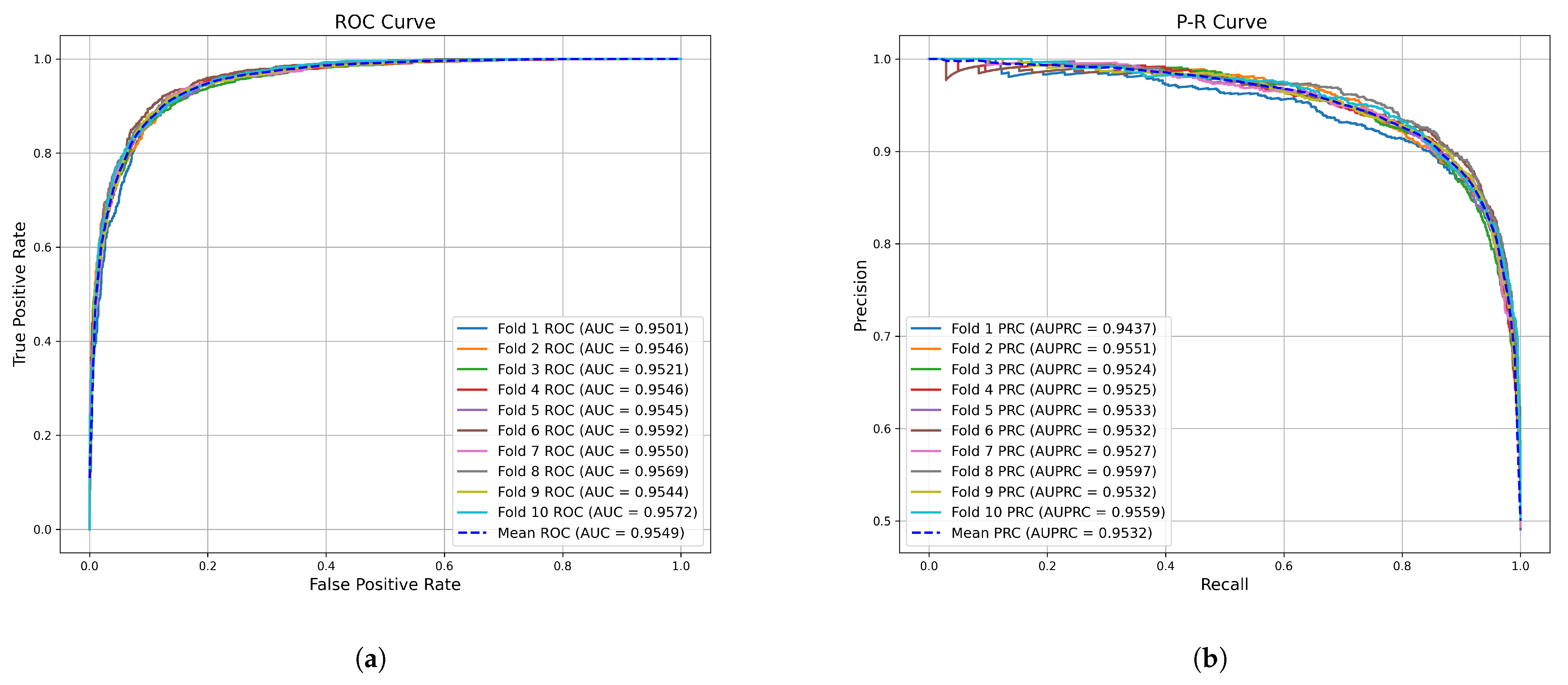
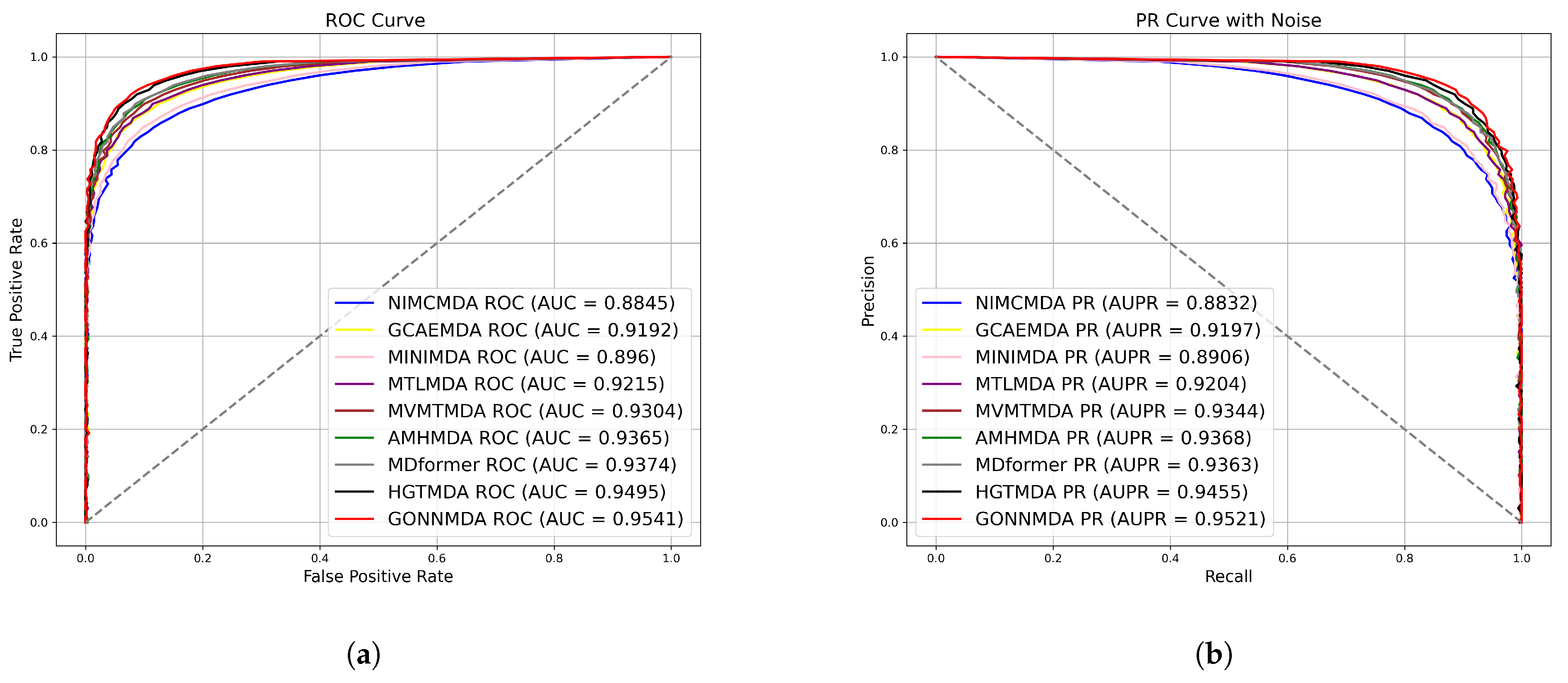




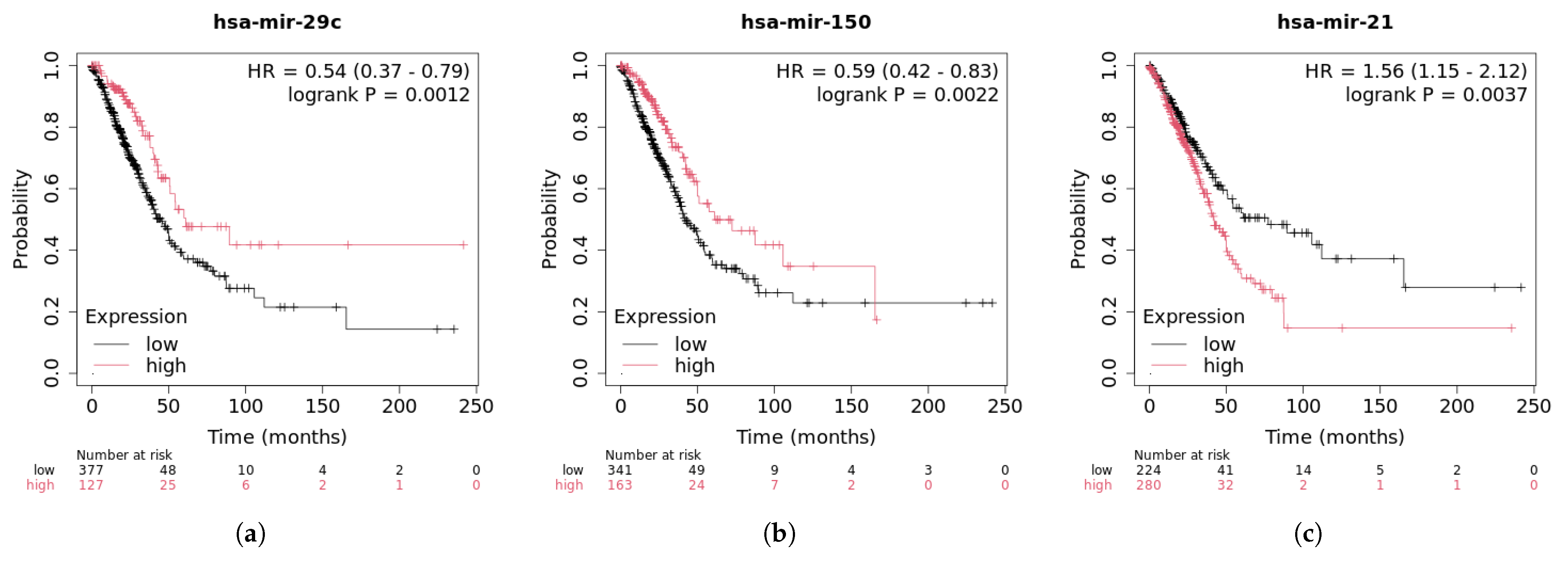
| Method | AUC (%) | AUPR (%) | Accuracy (%) | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1-Score (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5-fold | NIMCMDA | 88.45 | 88.32 | 81.28 | 80.76 | 81.22 | 81.48 |
| GCAEMDA | 91.92 | 91.97 | 84.15 | 85.18 | 88.87 | 84.85 | |
| MINIMDA | 89.60 | 89.06 | 85.54 | 85.43 | 86.73 | 85.18 | |
| MTLMDA | 92.15 | 92.04 | 84.99 | 83.37 | 88.89 | 85.45 | |
| MVMTMDA | 93.04 | 93.44 | 84.83 | 84.81 | 85.29 | 85.13 | |
| AMHMDA | 93.65 | 93.68 | 86.08 | 86.33 | 84.89 | 84.55 | |
| MDformer | 93.74 | 93.63 | 87.84 | 89.00 | 88.19 | 87.66 | |
| HGTMDA | 94.95 | 94.55 | 88.95 | 88.90 | 89.11 | 88.93 | |
| GONNMDA | 95.41 | 95.21 | 89.01 | 89.04 | 88.96 | 89.01 | |
| 10-fold | NIMCMDA | 88.66 | 88.59 | 81.45 | 80.93 | 81.50 | 82.01 |
| GCAEMDA | 92.54 | 92.68 | 85.43 | 86.12 | 89.42 | 86.03 | |
| MINIMDA | 90.89 | 90.75 | 87.76 | 87.77 | 88.46 | 86.88 | |
| MTLMDA | 94.03 | 93.60 | 87.16 | 88.13 | 89.56 | 87.13 | |
| MVMTMDA | 93.24 | 93.14 | 85.46 | 86.17 | 83.64 | 86.66 | |
| AMHMDA | 94.44 | 94.43 | 86.78 | 88.41 | 89.00 | 87.10 | |
| MDformer | 95.09 | 94.99 | 89.34 | 88.97 | 88.49 | 88.95 | |
| HGTMDA | 95.01 | 94.84 | 88.95 | 88.89 | 89.12 | 89.20 | |
| GONNMDA | 95.49 | 95.32 | 89.23 | 89.30 | 89.18 | 89.24 |
| Dimension | AUC | AUPR | Accuracy | F1-Score | Recall | Precision |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E = 512 | 0.9305 | 0.9252 | 0.8609 | 0.8603 | 0.8605 | 0.8640 |
| E = 600 | 0.9348 | 0.9301 | 0.8608 | 0.8607 | 0.8610 | 0.8619 |
| E = 700 | 0.9360 | 0.9314 | 0.8616 | 0.8614 | 0.8618 | 0.8636 |
| E = 800 | 0.9445 | 0.9422 | 0.8797 | 0.8797 | 0.8797 | 0.8789 |
| E = 1024 | 0.9549 | 0.9527 | 0.8907 | 0.8907 | 0.8906 | 0.8911 |
| E = 1200 | 0.9542 | 0.9519 | 0.8886 | 0.8885 | 0.8886 | 0.8896 |
| Rank | miRNA | Evidence | Rank | miRNA | Evidence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | hsa-mir-21 | dbDEMC | 16 | hsa-mir-20b | dbDEMC |
| 2 | hsa-mir-146a | dbDEMC | 17 | hsa-mir-145 | dbDEMC |
| 3 | hsa-mir-29a | dbDEMC | 18 | hsa-mir-34a | dbDEMC |
| 4 | hsa-mir-222 | dbDEMC | 19 | hsa-mir-221 | miR2Disease |
| 5 | hsa-mir-196a | dbDEMC | 20 | hsa-mir-29b | miR2Disease |
| 6 | hsa-mir-19a | dbDEMC | 21 | hsa-mir-133a | dbDEMC |
| 7 | hsa-mir-19b | dbDEMC | 22 | hsa-mir-18a | miR2Disease |
| 8 | hsa-mir-155 | dbDEMC | 23 | hsa-mir-146b | dbDEMC |
| 9 | hsa-mir-17 | dbDEMC | 24 | hsa-mir-143 | dbDEMC |
| 10 | hsa-mir-125b | dbDEMC | 25 | hsa-mir-31 | dbDEMC |
| 11 | hsa-mir-126 | dbDEMC | 26 | hsa-mir-199a | miR2Disease |
| 12 | hsa-mir-16 | miR2Disease | 27 | hsa-mir-200c | dbDEMC |
| 13 | hsa-mir-92a | miR2Disease | 28 | hsa-mir-200a | dbDEMC |
| 14 | hsa-mir-15a | dbDEMC | 29 | hsa-mir-150 | dbDEMC |
| 15 | hsa-mir-20a | dbDEMC | 30 | hsa-mir-9 | dbDEMC |
| Rank | miRNA | Evidence | Rank | miRNA | Evidence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | hsa-mir-15a | dbDEMC | 16 | hsa-mir-15b | miR2Disease |
| 2 | hsa-mir-24 | dbDEMC | 17 | hsa-mir-20b | dbDEMC |
| 3 | hsa-mir-223 | dbDEMC | 18 | hsa-mir-193b | dbDEMC |
| 4 | hsa-mir-130b | dbDEMC | 19 | hsa-mir-615 | dbDEMC |
| 5 | hsa-mir-140 | dbDEMC | 20 | hsa-mir-30c | dbDEMC |
| 6 | hsa-mir-582 | dbDEMC | 21 | hsa-mir-130b | dbDEMC |
| 7 | hsa-mir-208b | dbDEMC | 22 | hsa-mir-100 | dbDEMC |
| 8 | hsa-mir-34a | dbDEMC | 23 | hsa-mir-222 | dbDEMC |
| 9 | hsa-mir-16 | dbDEMC | 24 | hsa-mir-142 | dbDEMC |
| 10 | hsa-mir-145 | dbDEMC | 25 | hsa-mir-31 | dbDEMC |
| 11 | hsa-mir-29b | dbDEMC | 26 | hsa-mir-196a | dbDEMC |
| 12 | hsa-let-7f | miR2Disease | 27 | hsa-mir-199a | dbDEMC |
| 13 | hsa-mir-101 | dbDEMC | 28 | hsa-mir-1 | dbDEMC |
| 14 | hsa-let-7g | dbDEMC | 29 | hsa-mir-200b | dbDEMC |
| 15 | hsa-mir-221 | dbDEMC | 30 | hsa-mir-331 | dbDEMC |
| Rank | miRNA | Evidence | Rank | miRNA | Evidence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | hsa-mir-29c | dbDEMC | 16 | hsa-mir-34a | dbDEMC |
| 2 | hsa-mir-150 | dbDEMC | 17 | hsa-mir-125b | dbDEMC |
| 3 | hsa-mir-21 | dbDEMC | 18 | hsa-mir-16 | miR2Disease |
| 4 | hsa-mir-133a | dbDEMC | 19 | hsa-mir-20a | dbDEMC |
| 5 | hsa-mir-29b | dbDEMC | 20 | hsa-mir-222 | dbDEMC |
| 6 | hsa-mir-9 | dbDEMC | 21 | hsa-mir-15a | dbDEMC |
| 7 | hsa-mir-1 | dbDEMC | 22 | hsa-mir-19b | dbDEMC |
| 8 | hsa-let-7e | dbDEMC | 23 | hsa-mir-221 | dbDEMC |
| 9 | hsa-mir-199a | dbDEMC | 24 | hsa-mir-106b | dbDEMC |
| 10 | hsa-mir-146a | dbDEMC | 25 | hsa-mir-223 | dbDEMC |
| 11 | hsa-mir-29a | dbDEMC | 26 | hsa-mir-200b | dbDEMC |
| 12 | hsa-mir-17 | dbDEMC | 27 | hsa-mir-200c | dbDEMC |
| 13 | hsa-mir-21 | dbDEMC | 28 | hsa-mir-19a | dbDEMC |
| 14 | hsa-mir-155 | dbDEMC | 29 | hsa-mir-18a | dbDEMC |
| 15 | hsa-mir-145 | dbDEMC | 30 | hsa-let-7a | dbDEMC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeng, S.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Z.; Yang, C.; Yuan, S. GONNMDA: A Ordered Message Passing GNN Approach for miRNA–Disease Association Prediction. Genes 2025, 16, 425. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16040425
Zeng S, Zhang S, Wang Z, Yang C, Yuan S. GONNMDA: A Ordered Message Passing GNN Approach for miRNA–Disease Association Prediction. Genes. 2025; 16(4):425. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16040425
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeng, Sihao, Shanwen Zhang, Zhen Wang, Chen Yang, and Shenao Yuan. 2025. "GONNMDA: A Ordered Message Passing GNN Approach for miRNA–Disease Association Prediction" Genes 16, no. 4: 425. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16040425
APA StyleZeng, S., Zhang, S., Wang, Z., Yang, C., & Yuan, S. (2025). GONNMDA: A Ordered Message Passing GNN Approach for miRNA–Disease Association Prediction. Genes, 16(4), 425. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16040425







