The Complete Chloroplast Genome of Camellia tianeensis (Camellia L.) and Phylogenetic Relationships with Other Plants of the Genus Camellia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material Collection, DNA Extraction, and Sequencing
2.2. Assembly and Annotation of the Chloroplast Genome
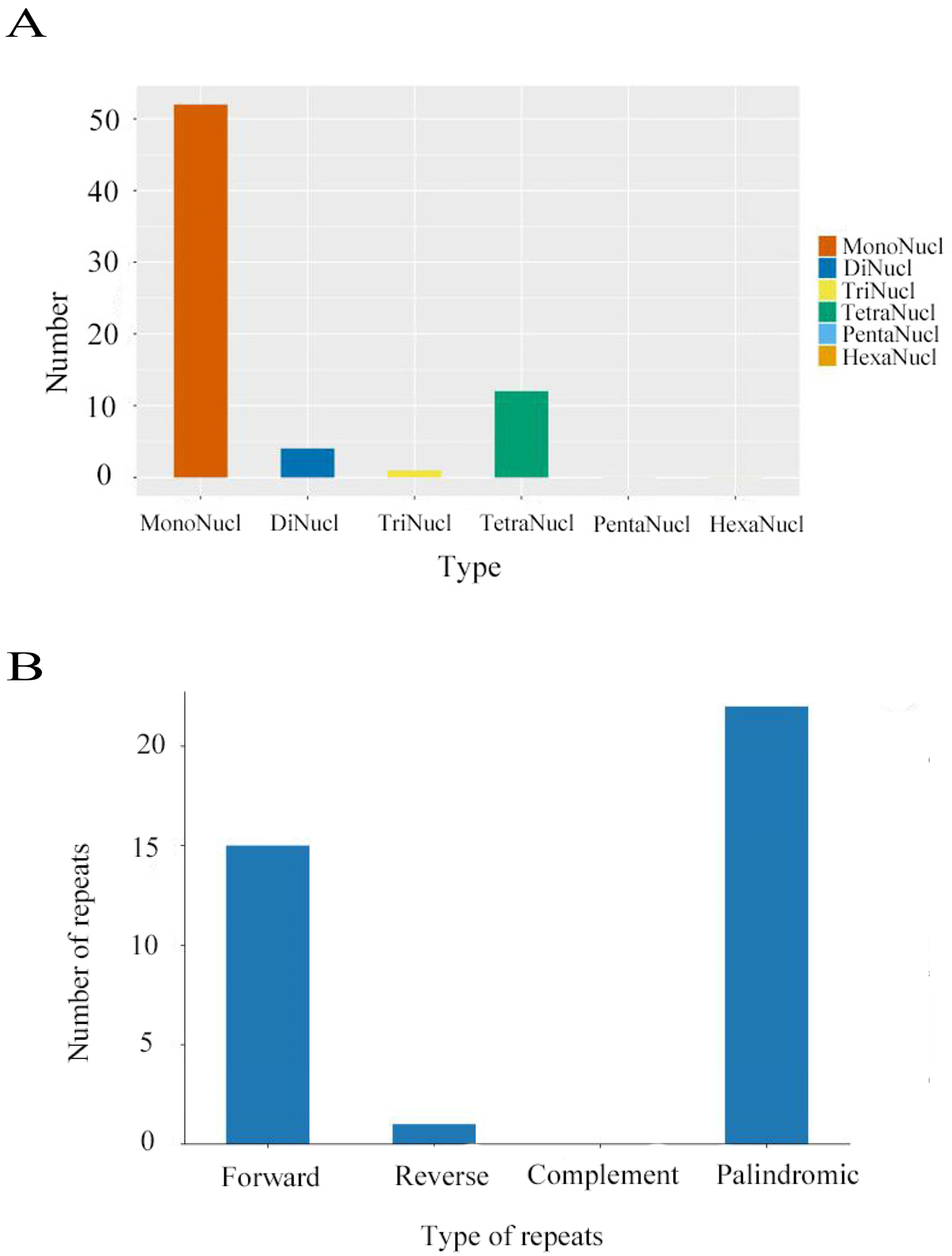
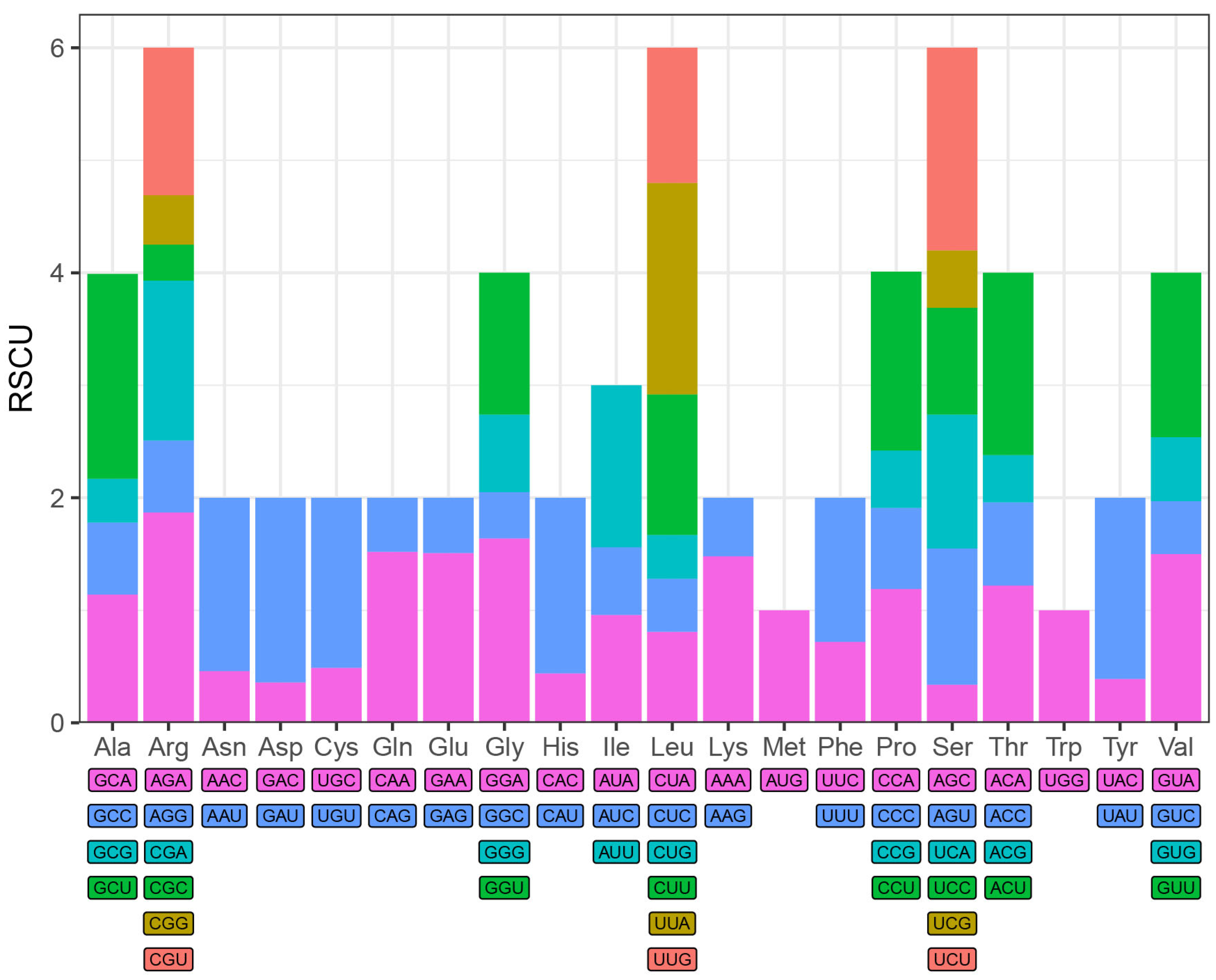
2.3. Repeat Sequence Analysis and Codon Preference
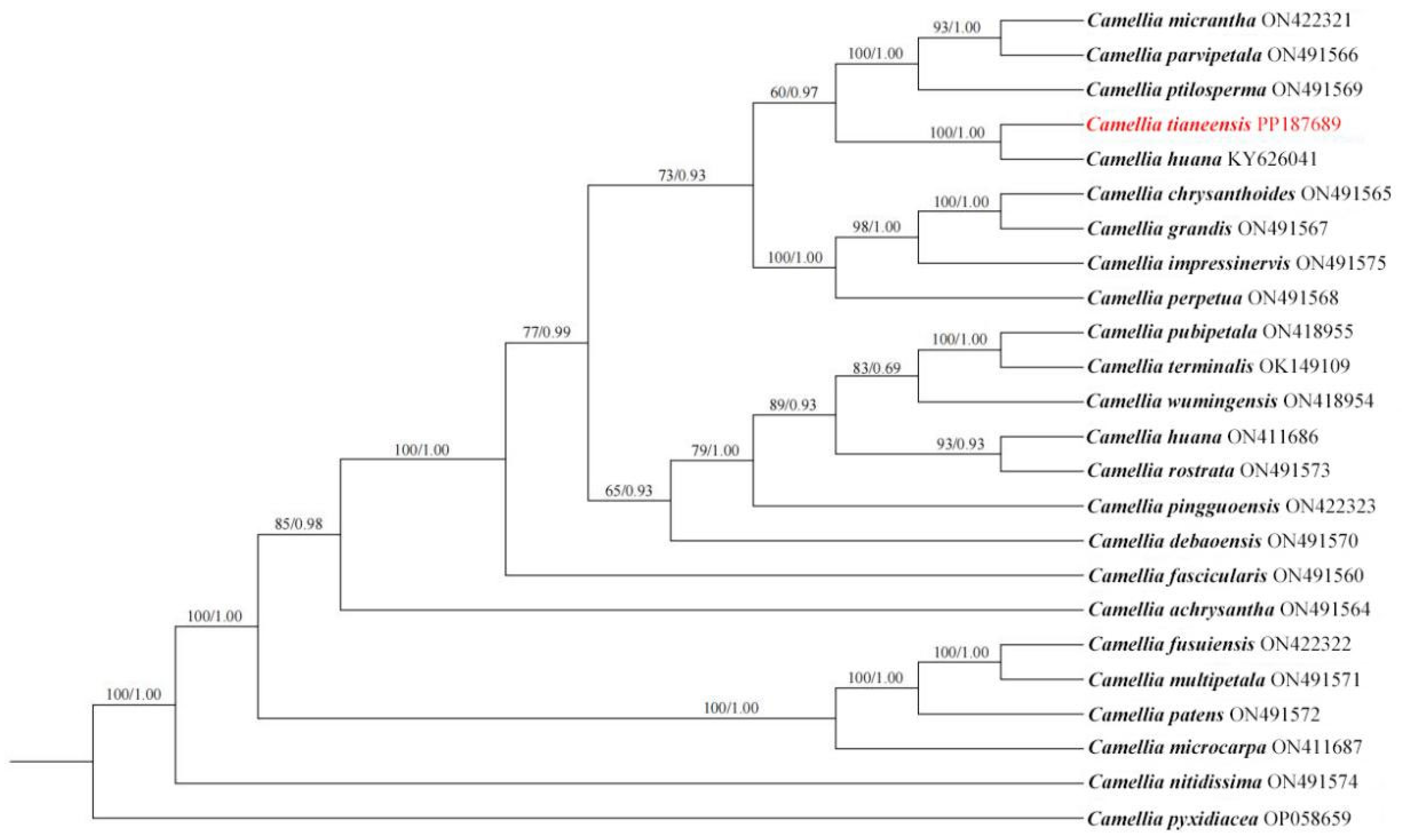
3. Phylogenetic Analysis
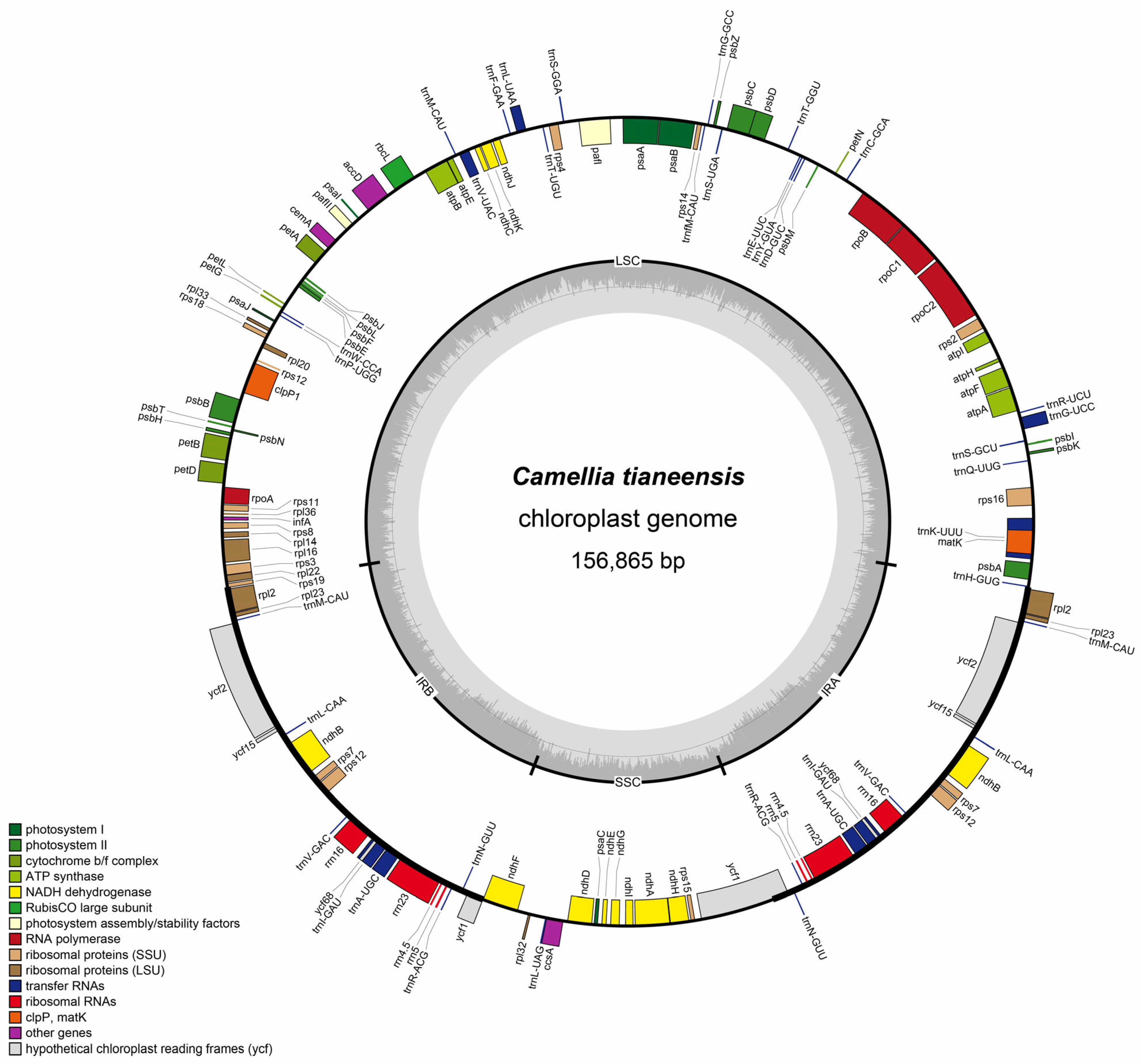
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LSC | large single-copy region |
| SSC | small single-copy region |
| IR | inverted-repeat regions |
| SSR | simple sequence repeat |
| RSCU | relative synonymous codon usage |
| F | Forward |
| R | Reverse |
| C | Complement |
| P | Palindromic |
References
- Zhang, H.D.; Ren, S.X. Flora of China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1998; pp. 101–112. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, S.Y. The World List of Camellia. Guangxi For. Sci. 2007, 4, 221–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Jiang, Y.S.; Wei, J.Q.; Chen, Z.Y.; Wang, M.L.; Zhao, R.F. Investigation on the geographical distribution and habitat of Camellia nitidissma. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2007, 895–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y. Study on the Evolution of Chloroplast Genome of Sect. Chrysantha Chang. Master’s Thesis, ShanXi University, Taiyuan, China, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.C. Overview of the development and utilization of Camellia nitidissima and Its Future Prospects. Chin. J. Inf. Tradit. Chin. Med. 1994, 6, 10–11. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, X.; Huang, J.X.; Wang, Z.P.; Wang, Q.; Pan, L.G. Studies on the hypoglycemic effect and acute toxicity of Camellia nitidssima leaves. Lishizhen Med. Mater. Medica Res. 2013, 24, 1281–1282. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.L.; Chen, Y.Y.; Wen, Y.X.; Li, D.P.; Liang, R.G.; Wei, X. Effects of the Extracts from Camellia nitidssima Leaves on Blood Lipids. Lishizhen Med. Mater. Medica Res. 2009, 20, 776–777. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.L.; Guo, Y.J.; Zhu, Y.Y.; Chen, L.; Wu, T.; Liu, D.H.; Huang, B.S.; Du, H.Z. Active fractions of Camellia nitidissima inhibit non-small cell lung cancer via suppressing epidermal growth factor receptor. China J. Chin. Mater. Medica 2021, 46, 5362–5371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.Y.; Luo, Y.T. A new species of Camellia sinensis from China. Guangxi For. Sci. 1995, 24, 83–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, T.; Bruce, B. Flora of China; Science Press and Missouri Botanical Garden Press: Beijing, China, 2007; pp. 367–372. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, G.B.; Li, H.; Yang, Y.B.; Xu, C.R.; Guo, Z.X.; Deng, L.X. Taxonomic Notes on Camellia huana (Theaceae). Bull. Bot. Res. 2024, 44, 901–913. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, D.Z.; Qin, L.X.; Qin, G.L.; Wei, L.; Fu, Y.J.; Ya, Z.G. The Community Characteristics of Accompanying Plants of Camellia tianeensis in Guangxi. Guizhou Agric. Sci. 2013, 41, 40–43. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, D.Z.; Ya, Z.G.; Han, J.Y.; Wei, Y.; Wei, L. Study of Distribution and Protection Stategies of Camellia tianeensis. J. Green Sci. Technol. 2014, 4, 89–91. [Google Scholar]
- Su, F.B.; Feng, L.X.; Huang, H.H.; Luo, Q.G.; Xu, R.R.; Lin, H.; Li, R.Z.; Li, S. Preliminary Study of the Selection of Superior Individuals from Late Blooming Camellia nitidssima Chi. in Tian’e. J. Hechi Univ. 2017, 37, 12–16. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Q.G.; Shu, F.B.; Feng, L.X.; Huang, H.H.; Su, B.C.; Li, S.; Mai, K.L. Study on the effect of fertilization on the growth of a high crown and the total flavonoid content of Camellia tianeensis. J. Green Sci. Technol. 2021, 23, 52–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.T.; Su, F.B.; Feng, L.X.; Yang, C.S.; Huang, Z.X.; He, H.J.; Su, B.C. High-yield Cultivation Techniques of Camellia tianeensis in Forests. J. Smart Agric. 2022, 2, 49–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.S.; Luo, Q.G.; Su, F.B.; Feng, L.X.; Mai, K.L.; Su, B.C. Selection of superior individual of early-flowering and late-flowering Camellia tianeensis. South China Agric. 2023, 17, 13–17+22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahlich, E.; Gerliz, C. A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochemistry 1980, 19, 11–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.J.; Yu, W.B.; Yang, J.B.; Song, Y.; Depamphilis, C.W.; Yi, T.S.; Li, D.Z. Getorganelle: A fast and versatile toolkit for accurate de novo assembly of organelle genomes. Genome Biol. 2020, 21, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.C.; Chen, H.; Jiang, M.; Wang, L.Q.; Wu, X.; Huang, L.F.; Liu, C. CPGAVAS2, an integrated plastome sequence annotator and analyzer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohse, M.; Drechsel, O.; Bock, R. Organellar Genome DRAW (OGDRAW): A tool for the easy generation of highquality custom graphical maps of plastid and mitochondrial genome. Curr. Genet. 2007, 52, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beier, S.; Thiel, T.; Munch, T.; Scholz, U.; Mascher, M. MISA-web: A web server for microsatellite prediction. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 2583–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, W.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Q.M.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Z.H.; Sun, Y.X. Complete Chloroplast Genome Sequence of Clivia miniata and Its Characteristics. Acta Hortic. Sin. 2020, 47, 2439–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, S.; Choudhuri, J.V.; Ohlebusch, E.; Schleiermacher, C.; Stoye, J.; Giegerich, R. REPuter: The manifold applications of repeat analysis on a genomic scale. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 4633–4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shield, D.C.; Sharp, P.M. Synonymous codon usage in Bacillus subtilis reflects both translational selection and mutational biases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987, 15, 8023–8040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT: Iterative refinement and additional methods. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1079, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trifinopoulos, J.; Nguyen, L.T.; Von, H.A.; Minh, B.Q. W-IQTREE: A fast online phylogenetic tool for maximum likelihood analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 232–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huelsenbeck, J.P.; Ronquist, F. MRBAYES: Bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics 2001, 17, 754–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL)v5: An online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 293–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.J.; Liu, K.; Gao, X.P.; Yu, C.J.; Wang, X.F.; Shi, J.J.; Chao, Y.R.; Yu, Q.; Zhou, G.K.; Ge, L. Diurnal variation of transitory starch metabolism is regulated by plastid proteins WXR1/WXR3 in Arabidopsis young seedlings. J. Exp. Bot. 2021, 72, 3074–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.L.; Yao, H.; Han, J.P.; Liu, C.; Song, J.Y.; Shi, L.C.; Zhu, Y.G.; Ma, X.Y.; Gao, T.; Pang, X.H.; et al. Validation of the ITS2 region as a novel DNA barcode for identifying medicinal plant species. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e8613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Q.Z.; Wang, B.W.; Wei, Z.Z.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Zhang, D.Q.; Li, B.L. Genetic diversity and population structure of Chinese white poplar (Populus tomentosa) revealed by SSR markers. J. Hered. 2012, 103, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.Y.; Geng, Y.P.; Song, M.L.; Zhang, P.F.; Hou, J.L.; Wang, W.Q. Genetic structure and diversity of glycyrrhiza populations based on transcriptome SSR markers. Plant Mol. Biol. Report. 2019, 37, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.Z.; Du, Z.Y.; Wang, H.T. Chloroplast genome characteristics of endangered relict plant Tetraena mongolica in the arid region of northwest China. Bull. Bot. Res. 2019, 39, 653–663. [Google Scholar]
- Kuang, D.Y.; Wu, H.; Wang, Y.L.; Gao, L.M.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Lu, L. Complete chloroplast genome sequence of Magnolia kwangsiensis (Magnoliaceae): Implication for DNA barcoding and population genetic. Genome 2011, 54, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.J. Codon Analysis and Its Application in Bioinformatics and Evolutionary Studies. Ph.D. Thesis, Fudan University, Shanghai, China, 2007; pp. 10–23. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, H.M.; Gu, Y.; Huang, Y.B. Analysis of Characteris tic of Codon Usage in waxy Gene of Zea mays. J. Maize Sci. 2008, 16, 16–21. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, S.J.; Liufu, Y.Q.; Zheng, H.W.; Chen, H.L.; Lai, Y.C.; Liu, Y.; Ye, Q.Q.; Tang, S.Q. Using phylogenomics to untangle the taxonomic incongruence of yellow-flowered Camellia species (Theaceae) in China. J. Syst. Evol. 2022, 61, 748–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.J.; Bai, Y.Y.; Gao, H.; Li, Y.Y.; Su, M.X.; Li, S.S.; Chen, J.M.; Li, T.; Yan, G.Y. Phylotranscriptomics resolved phylogenetic relationships and divergence time between 20 golden camellia species. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 6073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, J.; Li, H.; Deng, L. The Complete Chloroplast Genome of Camellia tianeensis (Camellia L.) and Phylogenetic Relationships with Other Plants of the Genus Camellia. Genes 2025, 16, 1217. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16101217
Chen J, Li H, Deng L. The Complete Chloroplast Genome of Camellia tianeensis (Camellia L.) and Phylogenetic Relationships with Other Plants of the Genus Camellia. Genes. 2025; 16(10):1217. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16101217
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Juyan, He Li, and Lunxiu Deng. 2025. "The Complete Chloroplast Genome of Camellia tianeensis (Camellia L.) and Phylogenetic Relationships with Other Plants of the Genus Camellia" Genes 16, no. 10: 1217. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16101217
APA StyleChen, J., Li, H., & Deng, L. (2025). The Complete Chloroplast Genome of Camellia tianeensis (Camellia L.) and Phylogenetic Relationships with Other Plants of the Genus Camellia. Genes, 16(10), 1217. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16101217





