Genome-Wide Association Study of Egg Production Traits in Shuanglian Chickens Using Whole Genome Sequencing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Population and Phenotyping Measurement
2.3. Whole Genome Sequencing and Quality Control
2.4. Estimation of Genetic Parameters
2.5. Genome-Wide Association Study
2.6. Variance Explained by the Most Significant SNPs
2.7. Linkage Disequilibrium Analysis and Identification of Candidate Genes
3. Results
3.1. Phenotype Data, Whole Genome Sequencing Data, and Population Structure
3.2. Estimation of Phenotypic and Genetic Parameters
3.3. Genome-Wide Association Analysis
3.4. Linkage Disequilibrium Analysis
3.5. Enrichment Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- The Development Status and Trends of China’s Laying Hen Industry. Available online: https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/628010784?utm_id=0 (accessed on 9 May 2023). (In Chinese).
- Liu, Z.; Yang, N.; Yan, Y.; Li, G.; Liu, A.; Wu, G.; Sun, C. Genome-wide association analysis of egg production performance in chickens across the whole laying period. BMC Genet. 2019, 20, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Nie, C.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Zhu, T.; Guan, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Lv, X.Z.; Yang, W.; et al. Identification of candidate genomic regions for chicken egg number traits based on genome-wide association study. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, P.; Yuan, J.; Sun, C.; Dou, T.; Yi, G.; Qu, L.; Qu, L.; Wang, K.; Yang, N. Identification of Promising Mutants Associated with Egg Production Traits Revealed by Genome-Wide Association Study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140615. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Q.C.; Wu, P.F.; Dai, G.J.; Zhang, G.X.; Zhang, T.; Xue, Q.; Shi, H.Q.; Wang, J.Y. Identification of 19 loci for reproductive traits in a local Chinese chicken by genome-wide study. Genet. Mol. Res. 2017, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Sun, C.; Yan, Y.; Li, G.; Wu, G.; Liu, A.; Yang, N. Genome-Wide Association Analysis of Age-Dependent Egg Weights in Chickens. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pértille, F.; Moreira, G.C.M.; Zanella, R.; Nunes, J.d.R.d.S.; Boschiero, C.; Rovadoscki, G.A.; Mourão, G.B.; Ledur, M.C.; Coutinho, L.L. Genome-wide association study for performance traits in chickens using genotype by sequencing approach. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.X.; Fan, Q.C.; Wang, J.Y.; Zhang, T.; Xue, Q.; Shi, H.Q. Genome-wide association study on reproductive traits in Jinghai Yellow Chicken. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2015, 163, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Liu, L.; He, Y.; Dou, T.; Jia, J.; Ge, C. Endocrine and genetic factors affecting egg laying performance in chickens: A review. Br. Poultry Sci. 2020, 61, 538–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.D.; Huang, Q.K.; Zhu, Q.; Lan, D.; Feng, Z.Q.; Zhang, L.; Lan, X.; Ye, L.; Liu, Y.P.; He, M.; et al. Identification and association of single-nucleotide polymorphisms in gonadotropin-inhibitory hormone (GnIH) gene with egg production traits in Erlang mountainous chickens. Genet. Mol. Res. 2015, 14, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christoffels, A.; Liu, W.; Li, D.; Liu, J.; Chen, S.; Qu, L.; Zheng, J.; Xu, G.; Yang, N. A Genome-Wide SNP Scan Reveals Novel Loci for Egg Production and Quality Traits in White Leghorn and Brown-Egg Dwarf Layers. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28600. [Google Scholar]
- Goto, T.; Ishikawa, A.; Onitsuka, S.; Goto, N.; Fujikawa, Y.; Umino, T.; Nishibori, M.; Tsudzuki, M. Mapping quantitative trait loci for egg production traits in an F2 intercross of Oh-Shamo and White Leghorn chickens. Anim. Genet. 2011, 42, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolc, A.; Arango, J.; Jankowski, T.; Dunn, I.; Settar, P.; Fulton, J.E.; O’Sullivan, N.P.; Preisinger, R.; Fernando, R.L.; Garrick, D.J.; et al. Genome-wide association study for egg production and quality in layer chickens. J. Anim. Breed. Genet. 2014, 131, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Chen, S.; Shi, F.; Wu, G.; Liu, A.; Yang, N.; Sun, C. Genome-wide association study reveals putative role of gga-miR-15a in controlling feed conversion ratio in layer chickens. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, J.; Sun, H.; Ning, Z.; Xu, G.; Yang, N.; Qu, L. Genome-wide association study revealed genomic regions related to white/red earlobe color trait in the Rhode Island Red chickens. BMC Genet. 2016, 17, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenna, A.; Hanna, M.; Banks, E.; Sivachenko, A.; Cibulskis, K.; Kernytsky, A.; Garimella, K.; Altshuler, D.; Gabriel, S.; Daly, M.; et al. The Genome Analysis Toolkit: A MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purcell, S.; Neale, B.; Todd-Brown, K.; Thomas, L.; Ferreira, M.A.R.; Bender, D.; Maller, J.; Sklar, P.; de Bakker, P.I.W.; Daly, M.J.; et al. PLINK: A tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browning, S.R.; Browning, B.L. Rapid and Accurate Haplotype Phasing and Missing-Data Inference for Whole-Genome Association Studies By Use of Localized Haplotype Clustering. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 1084–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.A.; Lee, S.H.; Goddard, M.E.; Visscher, P.M. GCTA: A Tool for Genome-wide Complex Trait Analysis. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2011, 88, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Stephens, M. Genome-wide efficient mixed-model analysis for association studies. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 821–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.-S.; He, W.-M.; Ji, J.-J.; Zhang, C.; Guo, Y.; Yang, T.-L. LDBlockShow: A fast and convenient tool for visualizing linkage disequilibrium and haplotype blocks based on variant call format files. Brief. Bioinform. 2021, 22, bbaa227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raeesi, V.; Ehsani, A.; Torshizi, R.V.; Sargolzaei, M.; Masoudi, A.A.; Dideban, R. Genome-wide association study of cell-mediated immune response in chicken. J. Anim. Breed. Genet. 2017, 134, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, P.T.; Yang, R.Q.; Yang, N. Estimation of genetic parameters for cumulative egg numbers in a broiler dam line by using a random regression model. Poultry Sci. 2007, 86, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.C.; Ning, Z.H.; Xu, G.Y.; Hou, Z.C.; Yang, N. Heritabilities and genetic and phenotypic correlations of egg quality traits in brown-egg dwarf layers. Poultry Sci. 2005, 84, 1209–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Cahaner, A.; Lou, L.; Zhang, L.; Ge, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, X. Genetics and breeding of a black-bone and blue eggshell chicken line. 2. Laying patterns and egg production in two consecutive generations. Poultry Sci. 2022, 101, 101679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, A.; Pan, P.; Parkkila, S. Expression Studies of Neogenin and Its Ligand Hemojuvelin in Mouse Tissues. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2006, 55, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooda, I.; Hensen, K.; Kaselt, B.; Kasvandik, S.; Pook, M.; Kurg, A.; Salumets, A.; Velthut-Meikas, A. Target prediction and validation of microRNAs expressed from FSHR and aromatase genes in human ovarian granulosa cells. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugihara, I.; Phan, K.D.; Croteau, L.-P.; Kam, J.W.K.; Kania, A.; Cloutier, J.-F.; Butler, S.J. Neogenin May Functionally Substitute for Dcc in Chicken. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22072. [Google Scholar]
- Imle, R.; Wang, B.-T.; Stützenberger, N.; Birkenhagen, J.; Tandon, A.; Carl, M.; Himmelreich, N.; Thiel, C.; Gröne, H.-J.; Poschet, G.; et al. ADP-dependent glucokinase regulates energy metabolism via ER-localized glucose sensing. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, R.; Lu, T.; Liu, J.; Li, W.; Weng, X.; Yue, X.; Li, F. Variants of ADPGK gene and its effect on the male reproductive organ parameters and sperm count in Hu sheep. Anim. Biotechnol. 2021, 34, 664–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidarzadehpilehrood, R.; Pirhoushiaran, M.; Abdollahzadeh, R.; Binti Osman, M.; Sakinah, M.; Nordin, N.; Abdul Hamid, H. A Review on CYP11A1, CYP17A1, and CYP19A1 Polymorphism Studies: Candidate Susceptibility Genes for Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) and Infertility. Genes 2022, 13, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, D.; Shen, L.; Zhou, J.; Cao, Z.; Luan, P.; Li, Y.; Xiao, F.; Guo, H.; Li, H.; Zhang, H. Genome-wide association studies for growth traits in broilers. BMC Genom. Data 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, C.; Hou, D.; Feng, Y.; Li, T.; Jing, Z.; Li, W.; Han, R.; Li, G.; Sun, G.; Tian, Y.; et al. Molecular characterization and a duplicated 31-bp indel within the LDB2 gene and its associations with production performance in chickens. Gene 2020, 761, 145046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, X.; Bian, C.; Tian, Y.; Sun, G.; Han, R.; Liu, X.; et al. Genome-wide association study reveals the genetic determinism of growth traits in a Gushi-Anka F2 chicken population. Heredity 2020, 126, 293–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Tao, H.; Li, P.; Li, L.; Zhong, T.; Wang, L.; Ma, J.; Chen, X.; Song, T.; Zhang, H. Whole-genome sequencing reveals selection signatures associated with important traits in six goat breeds. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, F.; Gao, G.; Yan, X.; Liu, H.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Z.; He, L.; Lv, Q.; Wang, Z.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study of Body Weight Traits in Inner Mongolia Cashmere Goats. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 752746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Ouyang, J.; Liu, S.; Tang, H.; Xiong, Y.; Yan, X.; Chen, H. Genomic signatures reveal selection in Lingxian white goose. Poultry Sci. 2023, 102, 102269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, S.W.; Soder, S.; Duvoisin, R.M.; Huizenga, J.J.; Tsui, L.C. The human metabotropic glutamate receptor 8 (GRM8) gene: A disproportionately large gene located at 7q31.3-q32.1. Genomics 1997, 44, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessi, M.; Duan, H.; Xiong, J.; Chen, B.; He, F.; Yang, L.; Ma, Y.; Bamgbade, O.A.; Peng, J.; Yin, F. Attention-deficit/hyperactive disorder updates. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 925049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ncho, C.-M.; Goel, A.; Jeong, C.-M.; Youssouf, M.; Choi, Y.-H. In Ovo Injection of GABA Can Help Body Weight Gain at Hatch, Increase Chick Weight to Egg Weight Ratio, and Improve Broiler Heat Resistance. Animals 2021, 11, 1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jozefczuk, E.; Guzik, T.J.; Siedlinski, M. Significance of sphingosine-1-phosphate in cardiovascular physiology and pathology. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 156, 104793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.; Miao, S.; Zhou, W.; Elnesr, S.S.; Dong, X.; Zou, X. MAPK, AKT/FoxO3a and mTOR pathways are involved in cadmium regulating the cell cycle, proliferation and apoptosis of chicken follicular granulosa cells. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safe 2021, 214, 112091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
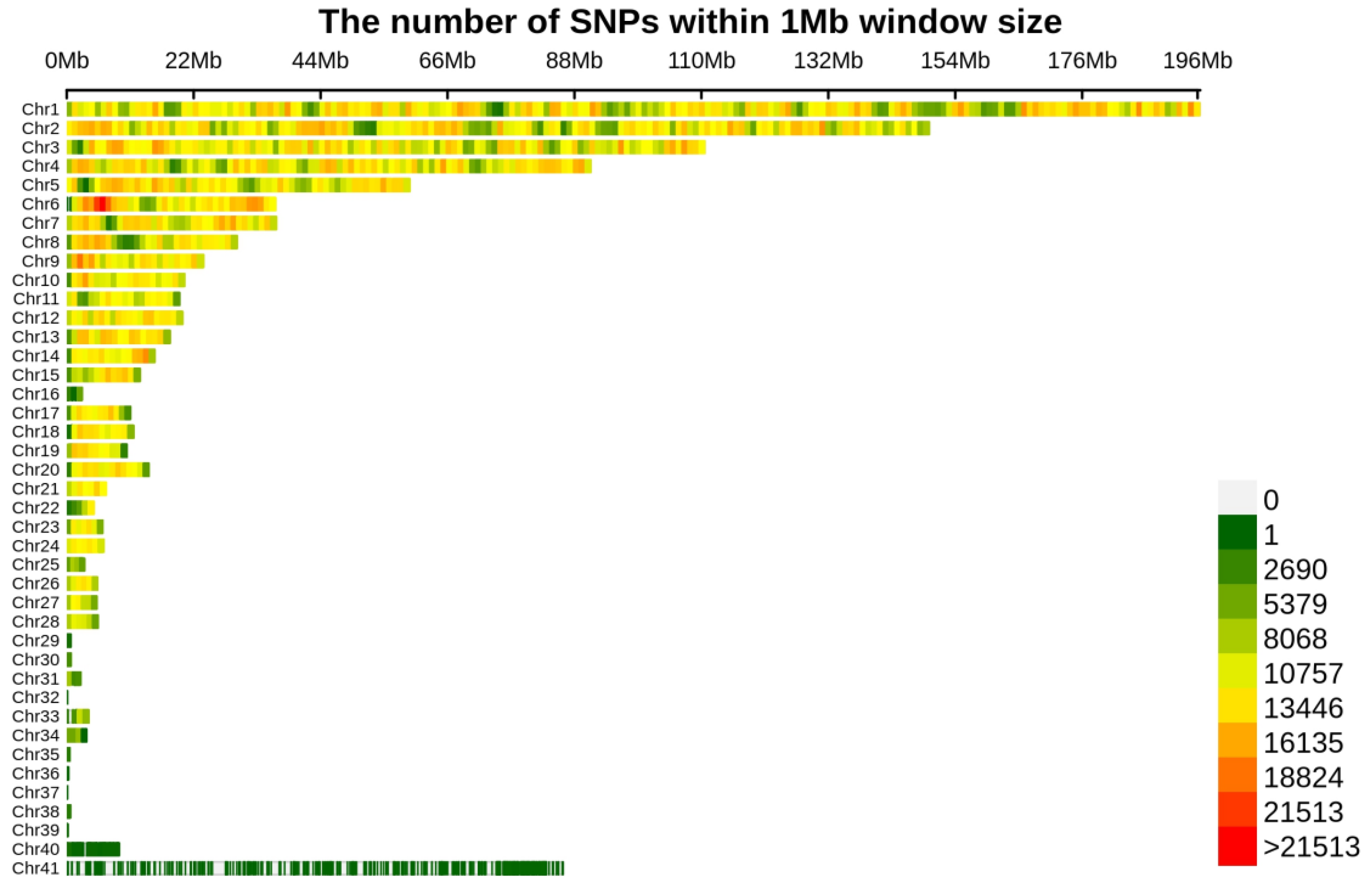
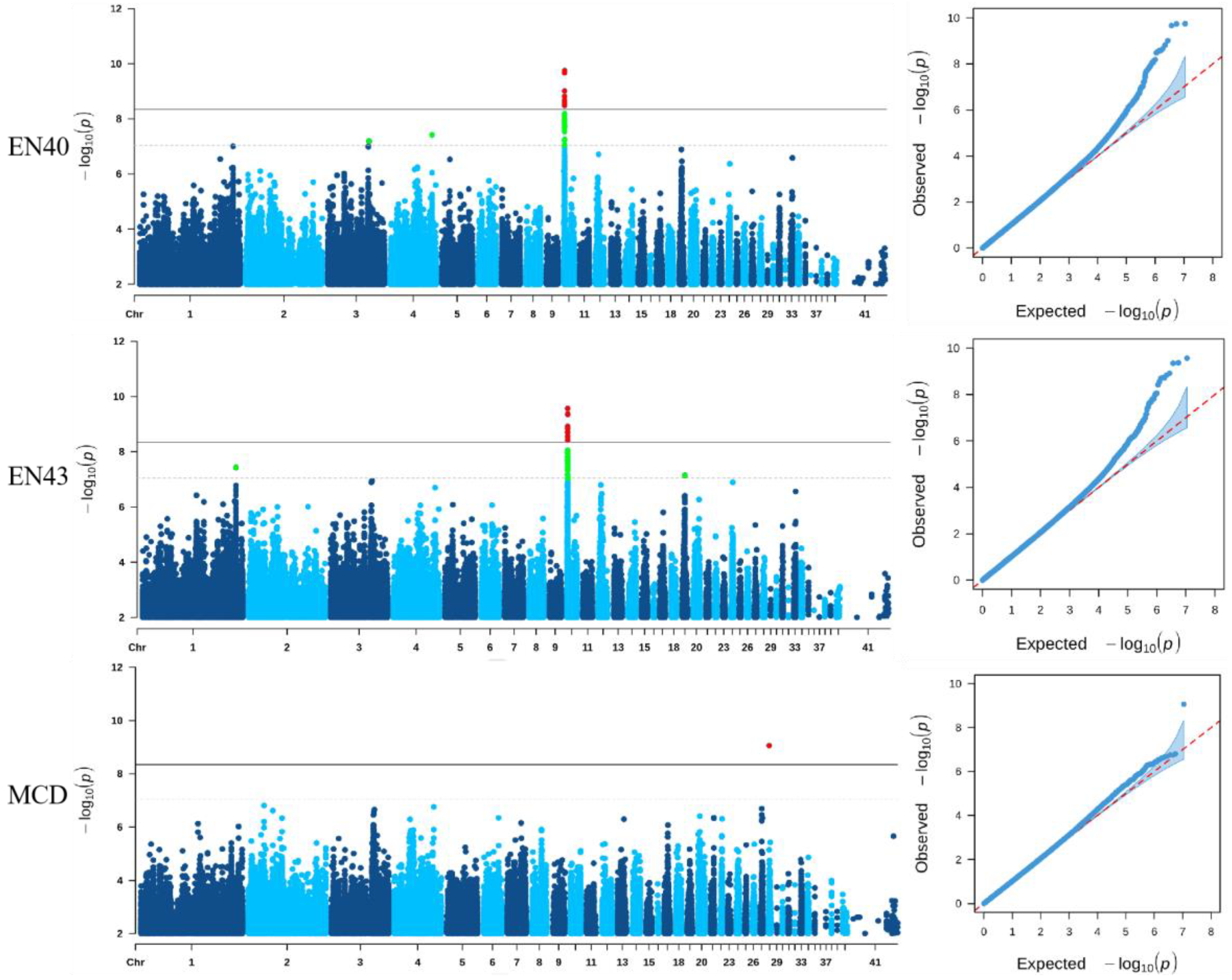
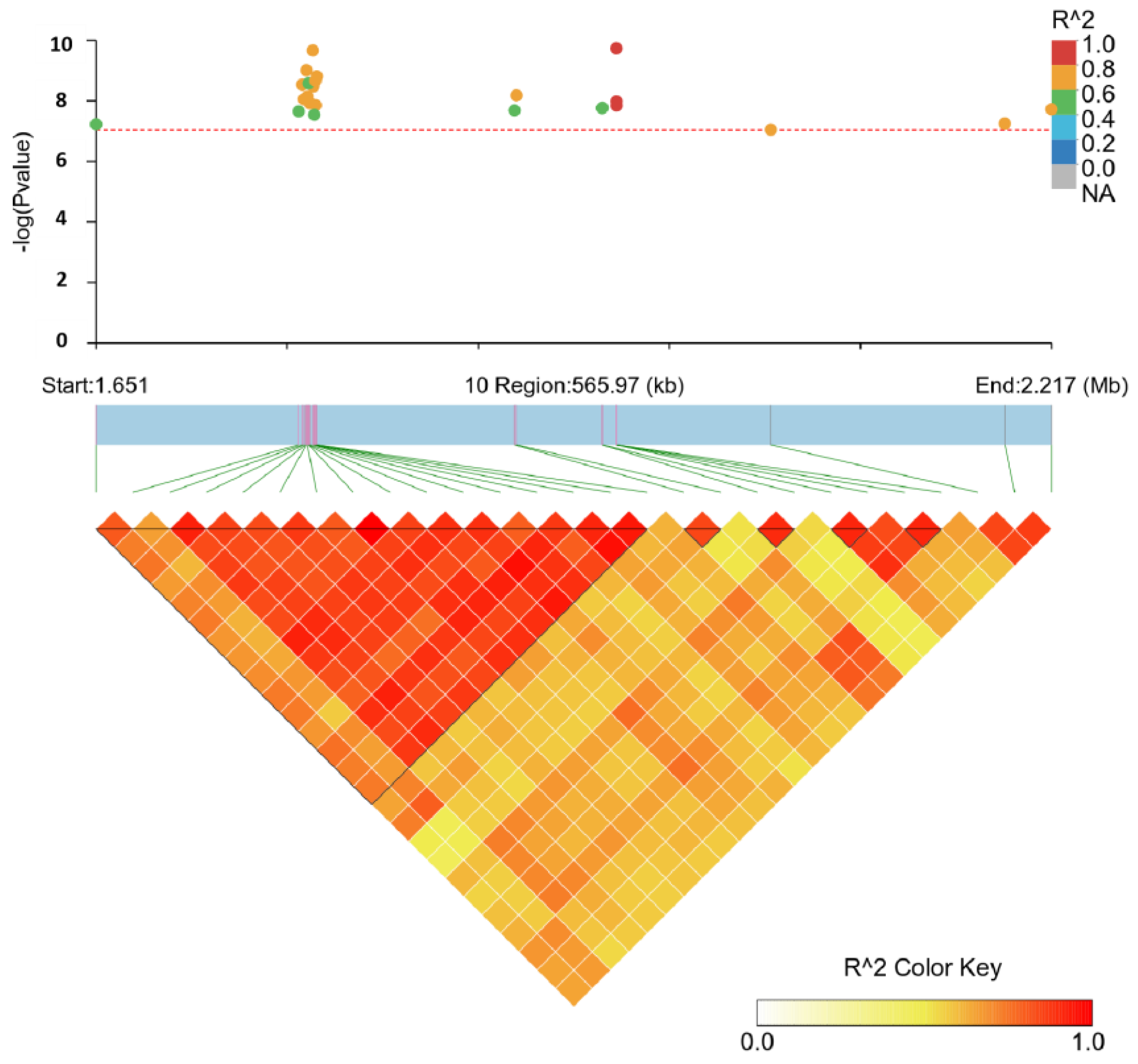

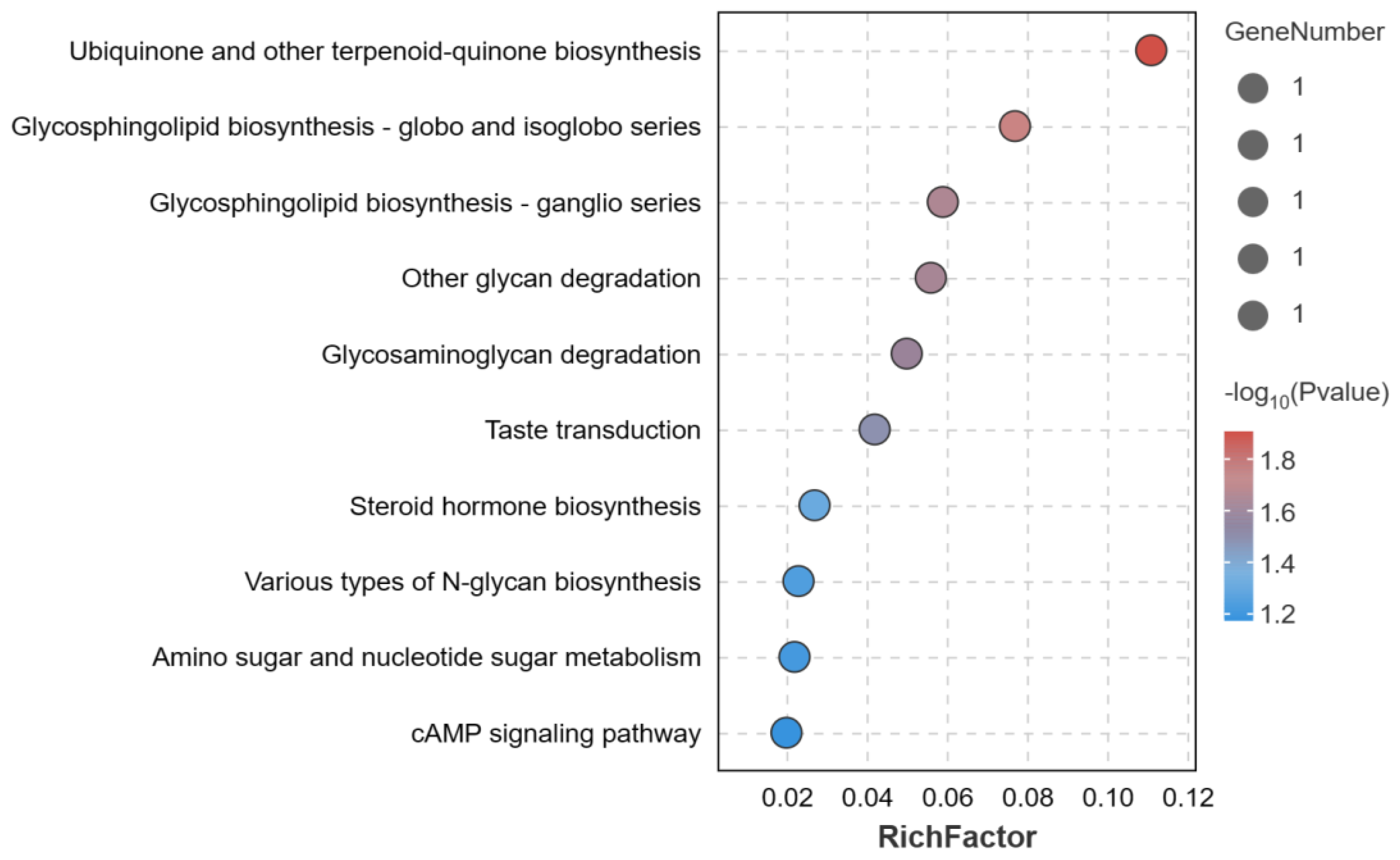
| Traits | N | Mean ± SD | Minimum | Maximum | CV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AFE (d) | 163 | 131.7 ± 14.8 | 106 | 169 | 11.2 |
| WFE (g) | 163 | 1491.8 ± 195.1 | 1060 | 2020 | 13.1 |
| EW (g) | 163 | 48.4 ± 4.0 | 38.0 | 64.6 | 8.2 |
| EN40 | 163 | 111.3 ± 25.5 | 29 | 182 | 22.9 |
| EN43 | 163 | 125.6 ± 28.0 | 29 | 165 | 22.3 |
| MCD (d) | 163 | 14.6 ± 7.9 | 3 | 49 | 54.3 |
| Traits | AFE | WFE | EW | EN43 | EN40 | MCD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AFE | 0.193 | −0.006 | 0.283 *** | −0.474 *** | −0.512 *** | −0.234 ** |
| WFE | −0.01 | 0.379 | 0.208 ** | −0.311 *** | −0.304 *** | −0.269 *** |
| EW | 0.678 | 0.338 | 0.897 | −0.257 *** | −0.261 *** | −0.164 * |
| EN43 | −0.764 | −0.695 | −0.283 | 0.246 | 0.991 *** | 0.702 *** |
| EN40 | −0.789 | −0.704 | −0.277 | 1 | 0.242 | 0.694 *** |
| MCD | −0.442 | −0.429 | −0.15 | 1 | 1 | 0.632 |
| Trait | Chr | SNP | Pos (bp) 1 | MAF 2 | Consequence | p-Value | Candidate Gene |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EN40 | 10 | rs794599852 | 1,959,133 | 0.135 | intron variant | 1.79 × 10−10 | NEO1 |
| 10 | rs794410298 | 1,959,103 | 0.138 | intron variant | 1.84 × 10−10 | NEO1 | |
| 10 | rs737101872 | 1,779,403 | 0.153 | intron variant | 2.16 × 10−10 | ENSGALG00010025119 | |
| 10 | rs733757787 | 1,775,498 | 0.150 | intron variant | 9.77 × 10−10 | ENSGALG00010025119 | |
| 10 | rs733219775 | 1,781,689 | 0.147 | intron variant | 1.54 × 10−9 | ENSGALG00010025119 | |
| 10 | rs732611081 | 1,780,940 | 0.150 | intron variant | 2.19 × 10−9 | ENSGALG00010025119 | |
| 10 | rs737141396 | 1,776,849 | 0.141 | intron variant | 2.63 × 10−9 | ENSGALG00010025119 | |
| 10 | rs732388748 | 1,776,854 | 0.141 | intron variant | 2.63 × 10−9 | ENSGALG00010025119 | |
| 10 | rs738796503 | 1,773,085 | 0.156 | intron variant | 2.91 × 10−9 | ENSGALG00010025119 | |
| 10 | rs732783139 | 1,779,757 | 0.137 | intron variant | 3.31 × 10−9 | ENSGALG00010025119 | |
| EN43 | 10 | rs737101872 | 1,779,403 | 0.153 | intron variant | 2.72 × 10−10 | ENSGALG00010025119 |
| 10 | rs794410298 | 1,959,103 | 0.138 | intron variant | 4.30 × 10−10 | NEO1 | |
| 10 | rs794599852 | 1,959,133 | 0.135 | intron variant | 4.52 × 10−10 | NEO1 | |
| 10 | rs733757787 | 1,775,498 | 0.15 | intron variant | 1.21 × 10−9 | ENSGALG00010025119 | |
| 10 | rs733219775 | 1,781,689 | 0.147 | intron variant | 1.45 × 10−9 | ENSGALG00010025119 | |
| 10 | rs737141396 | 1,776,849 | 0.141 | intron variant | 1.93 × 10−9 | ENSGALG00010025119 | |
| 10 | rs732388748 | 1,776,854 | 0.141 | intron variant | 1.93 × 10−9 | ENSGALG00010025119 | |
| 10 | rs732611081 | 1,780,940 | 0.15 | intron variant | 2.03 × 10−9 | ENSGALG00010025119 | |
| 10 | rs738796503 | 1,773,085 | 0.156 | intron variant | 2.86 × 10−9 | ENSGALG00010025119 | |
| 10 | rs732783139 | 1,779,757 | 0.137 | intron variant | 3.78 × 10−9 | ENSGALG00010025119 | |
| MCD | 28 | 28:1696604 | 1,696,604 | 0.064 | upstream_gene_variant | 8.70 × 10−10 | S1PR4 |
| Trait | Chr | SNP | Pos (bp) 1 | MAF 2 | Consequence | p-Value | Candidate Gene |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EN40 | 3 | rs733670986 | 80,457,964 | 0.064 | intron variant | 6.45 × 10−8 | FILIP1 |
| 4 | rs14498714 | 82,228,007 | 0.095 | intron variant | 3.81 × 10−8 | ZFYVE28 | |
| 10 | 10:1899911 | 1,899,911 | 0.12 | intron variant | 6.60 × 10−9 | NEO1 | |
| 10 | rs732015286 | 1,776,094 | 0.147 | intron variant | 7.15 × 10−9 | ENSGALG00010025119 | |
| 10 | rs737315097 | 1,775,174 | 0.16 | intron variant | 8.72 × 10−9 | ENSGALG00010025119 | |
| 10 | rs14000416 | 1,774,142 | 0.16 | splice donor variant | 8.77 × 10−9 | ENSGALG00010025119 | |
| 10 | rs794011707 | 1,959,182 | 0.135 | intron variant | 1.04 × 10−8 | NEO1 | |
| 10 | rs735135718 | 1,777,599 | 0.154 | intron variant | 1.19 × 10−8 | ENSGALG00010025119 | |
| 10 | rs740745767 | 1,781,067 | 0.141 | intron variant | 1.39 × 10−8 | ENSGALG00010025119 | |
| 10 | rs794188332 | 1,959,213 | 0.142 | intron variant | 1.42 × 10−8 | NEO1 | |
| 10 | rs737509451 | 1,950,938 | 0.163 | intron variant | 1.69 × 10−8 | NEO1 | |
| 10 | rs737799627 | 1,950,648 | 0.175 | intron variant | 1.73 × 10−8 | NEO1 | |
| 10 | rs740728260 | 2,216,957 | 0.104 | intron variant | 1.89 × 10−8 | NPTN | |
| 10 | 10:1898764 | 1,898,764 | 0.104 | intron variant | 2.06 × 10−8 | NEO1 | |
| 10 | rs732281842 | 1,770,938 | 0.123 | noncoding transcript exon variant | 2.22 × 10−8 | ENSGALG00010025119 | |
| 10 | rs735734105 | 1,780,269 | 0.141 | intron variant | 2.89 × 10−8 | ENSGALG00010025119 | |
| 10 | 10:2189290 | 2,189,290 | 0.104 | intergenic variant | 5.62 × 10−8 | HCN4 REC114 | |
| 10 | 10:1650989 | 1,650,989 | 0.126 | intergenic variant | 5.97 × 10−8 | CELF6 HEXA | |
| 10 | rs732724738 | 2,050,616 | 0.12 | upstream gene variant | 8.93 × 10−8 | HCN4 | |
| EN43 | 1 | rs733976198 | 182,156,165 | 0.068 | intron variant | 3.71 × 10−8 | DYNC2H1 |
| 10 | rs737315097 | 1,775,174 | 0.16 | intron variant | 8.86 × 10−9 | ENSGALG00010025119 | |
| 10 | rs14000416 | 1,774,142 | 0.16 | splice donor variant | 9.13 × 10−9 | ENSGALG00010025119 | |
| 10 | rs732015286 | 1,776,094 | 0.147 | intron variant | 1.11 × 10−8 | ENSGALG00010025119 | |
| 10 | rs794011707 | 1,959,182 | 0.135 | intron variant | 1.52 × 10−8 | NEO1 | |
| 10 | rs735135718 | 1,777,599 | 0.154 | intron variant | 1.54 × 10−8 | ENSGALG00010025119 | |
| 10 | 10:1899911 | 1,899,911 | 0.12 | intron variant | 1.63 × 10−8 | NEO1 | |
| 10 | rs740745767 | 1,781,067 | 0.141 | intron variant | 2.02 × 10−8 | ENSGALG00010025119 | |
| 10 | rs735734105 | 1,780,269 | 0.141 | intron variant | 2.15 × 10−8 | ENSGALG00010025119 | |
| 10 | rs794188332 | 1,959,213 | 0.142 | intron variant | 2.22 × 10−8 | NEO1 | |
| 10 | rs737509451 | 1,950,938 | 0.163 | intron variant | 2.34 × 10−8 | NEO1 | |
| 10 | 10:1898764 | 1,898,764 | 0.104 | intron variant | 2.76 × 10−8 | NEO1 | |
| 10 | rs737799627 | 1,950,648 | 0.175 | intron variant | 3.54 × 10−8 | NEO1 | |
| 10 | rs732281842 | 1,770,938 | 0.123 | noncoding transcript exon variant | 4.61 × 10−8 | ENSGALG00010025119 | |
| 10 | 10:1650989 | 1,650,989 | 0.126 | intergenic variant | 6.88 × 10−8 | CELF6 HEXA | |
| 10 | rs740728260 | 2,216,957 | 0.104 | intron variant | 9.07 × 10−8 | NPTN | |
| 19 | rs15845543 | 5,400,291 | 0.27 | intron variant | 7.23 × 10−8 | VKORC1L1 | |
| WFE | 4 | rs317659920 | 75,866,861 | 0.389 | intron variant | 1.62 × 10−8 | LDB2 |
| EW | 1 | rs736022615 | 21,149,255 | 0.104 | intron variant | 5.55 × 10−8 | GRM8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, M.; Wu, Y.; Shen, J.; Pan, A.; Zhang, H.; Sun, J.; Liang, Z.; Huang, T.; Du, J.; Pi, J. Genome-Wide Association Study of Egg Production Traits in Shuanglian Chickens Using Whole Genome Sequencing. Genes 2023, 14, 2129. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14122129
Fu M, Wu Y, Shen J, Pan A, Zhang H, Sun J, Liang Z, Huang T, Du J, Pi J. Genome-Wide Association Study of Egg Production Traits in Shuanglian Chickens Using Whole Genome Sequencing. Genes. 2023; 14(12):2129. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14122129
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Ming, Yan Wu, Jie Shen, Ailuan Pan, Hao Zhang, Jing Sun, Zhenhua Liang, Tao Huang, Jinping Du, and Jinsong Pi. 2023. "Genome-Wide Association Study of Egg Production Traits in Shuanglian Chickens Using Whole Genome Sequencing" Genes 14, no. 12: 2129. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14122129
APA StyleFu, M., Wu, Y., Shen, J., Pan, A., Zhang, H., Sun, J., Liang, Z., Huang, T., Du, J., & Pi, J. (2023). Genome-Wide Association Study of Egg Production Traits in Shuanglian Chickens Using Whole Genome Sequencing. Genes, 14(12), 2129. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14122129




