Identification of Long Non-Coding RNA MIR4435-2HG as a Prognostic Biomarker in Bladder Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Source and Preprocessing
2.2. Differently Expressed Gene (DEG) Analysis
2.3. Survival Analysis
2.4. Function Enrichment
2.5. Association with Other Biomarkers
2.6. Statistics Analysis and Codes
3. Results
3.1. Identification of Differentially Expressed lncRNA MIR4435-2HG
3.2. Expressed Level of MIR4435-2HG in Diverse Clinical Groups
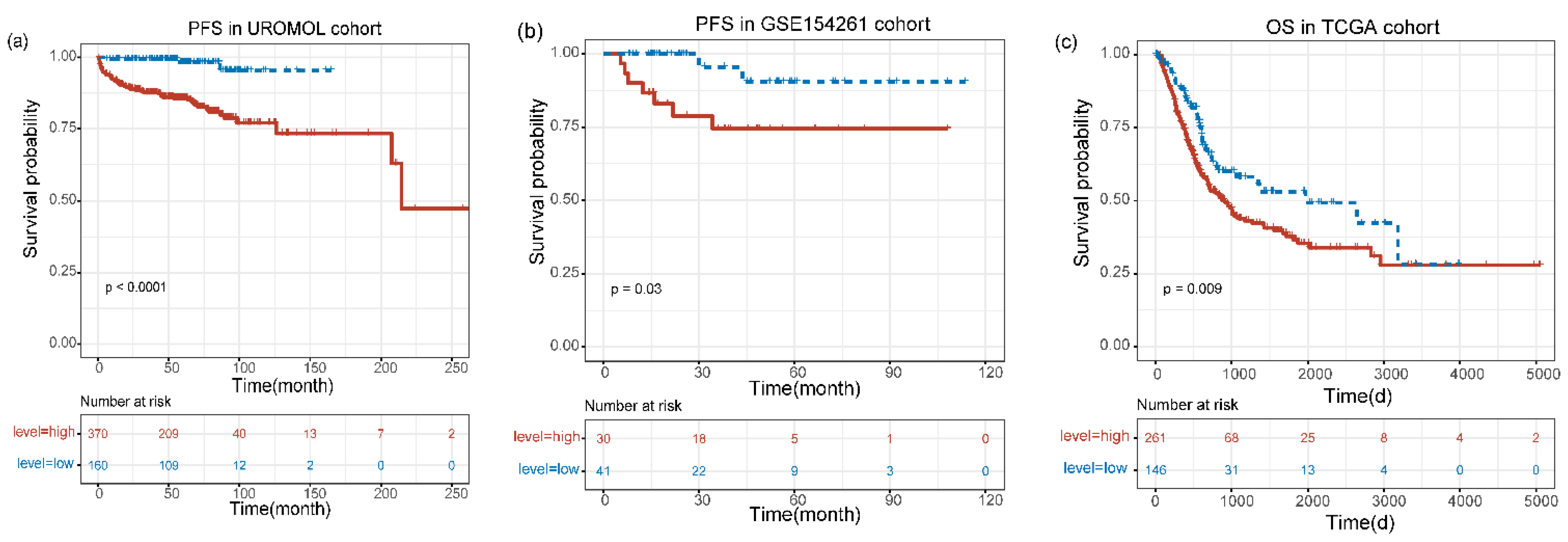
3.3. The Prognostic Value of MIR4435-2HG was Confirmed by Survival Analysis
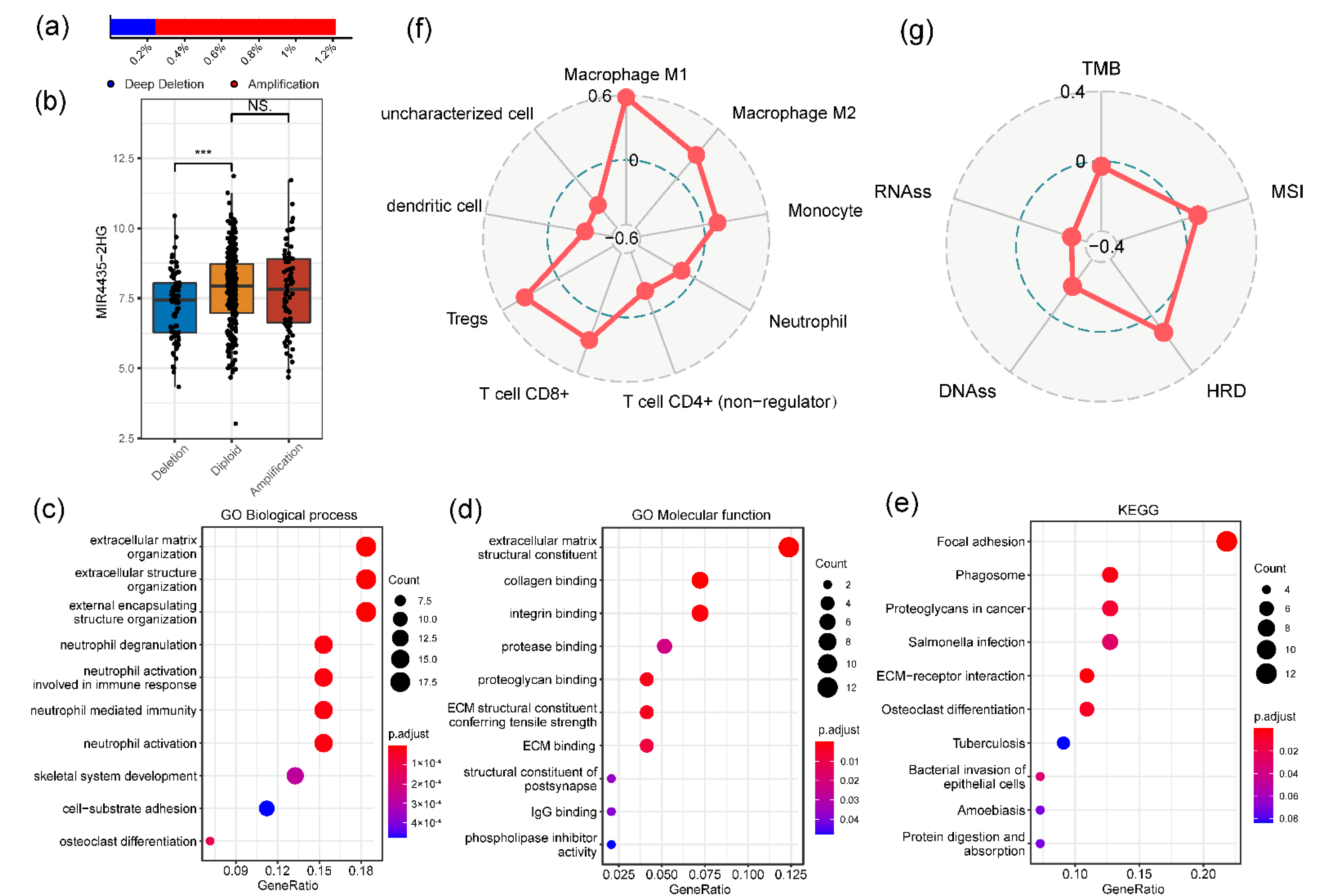
3.4. The Genetic Variations, Functional Enrichment and Association with Other Biomarkers of MIR4435-2HG
3.5. The Independent Predictors of BCa Were Identified by Univariate and Multivariate Cox Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lenis, A.T.; Lec, P.M.; Chamie, K.; Mshs, M.D. Bladder Cancer: A Review. Jama 2020, 324, 1980–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanli, O.; Dobruch, J.; Knowles, M.A.; Burger, M.; Alemozaffar, M.; Nielsen, M.E.; Lotan, Y. Bladder cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2017, 3, 17022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, H.B.; Natale, R.B.; Tangen, C.M.; Speights, V.O.; Vogelzang, N.J.; Trump, D.L.; de Vere White, R.W.; Sarosdy, M.F.; Wood, D.P., Jr.; Raghavan, D.; et al. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy plus cystectomy compared with cystectomy alone for locally advanced bladder cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 859–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cumberbatch, M.G.K.; Jubber, I.; Black, P.C.; Esperto, F.; Figueroa, J.D.; Kamat, A.M.; Kiemeney, L.; Lotan, Y.; Pang, K.; Silverman, D.T.; et al. Epidemiology of Bladder Cancer: A Systematic Review and Contemporary Update of Risk Factors in 2018. Eur. Urol. 2018, 74, 784–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sylvester, R.J.; van der Meijden, A.P.; Oosterlinck, W.; Witjes, J.A.; Bouffioux, C.; Denis, L.; Newling, D.W.; Kurth, K. Predicting recurrence and progression in individual patients with stage Ta T1 bladder cancer using EORTC risk tables: A combined analysis of 2596 patients from seven EORTC trials. Eur. Urol. 2006, 49, 466–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babjuk, M.; Burger, M.; Compérat, E.M.; Gontero, P.; Mostafid, A.H.; Palou, J.; van Rhijn, B.W.; Rouprêt, M.; Shariat, S.F.; Sylvester, R.; et al. European Association of Urology Guidelines on Non-muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer (TaT1 and Carcinoma in Situ)-2019 Update. Eur. Urol. 2019, 76, 639–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kates, M.; Matoso, A.; Choi, W.; Baras, A.S.; Daniels, M.J.; Lombardo, K.; Brant, A.; Mikkilineni, N.; McConkey, D.J.; Kamat, A.M.; et al. Adaptive Immune Resistance to Intravesical BCG in Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer: Implications for Prospective BCG-Unresponsive Trials. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 882–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oddens, J.; Brausi, M.; Sylvester, R.; Bono, A.; van de Beek, C.; van Andel, G.; Gontero, P.; Hoeltl, W.; Turkeri, L.; Marreaud, S.; et al. Final results of an EORTC-GU cancers group randomized study of maintenance bacillus Calmette-Guérin in intermediate- and high-risk Ta, T1 papillary carcinoma of the urinary bladder: One-third dose versus full dose and 1 year versus 3 years of maintenance. Eur. Urol. 2013, 63, 462–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Gomez, J.; Madero, R.; Solsona, E.; Unda, M.; Martinez-Piñeiro, L.; Ojea, A.; Portillo, J.; Montesinos, M.; Gonzalez, M.; Pertusa, C.; et al. The EORTC tables overestimate the risk of recurrence and progression in patients with non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer treated with bacillus Calmette-Guérin: External validation of the EORTC risk tables. Eur. Urol. 2011, 60, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lobo, N.; Hensley, P.J.; Bree, K.K.; Nogueras-Gonzalez, G.M.; Navai, N.; Dinney, C.P.; Sylvester, R.J.; Kamat, A.M. Updated European Association of Urology (EAU) Prognostic Factor Risk Groups Overestimate the Risk of Progression in Patients with Non-muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer Treated with Bacillus Calmette-Guérin. Eur. Urol. Oncol. 2022, 5, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acevedo, O.A.; Berrios, R.V.; Rodríguez-Guilarte, L.; Lillo-Dapremont, B.; Kalergis, A.M. Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms Modulating Trained Immunity by Various Cell Types in Response to Pathogen Encounter. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 745332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanucchi, S.; Mhlanga, M.M. Lnc-ing Trained Immunity to Chromatin Architecture. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteller, M. Non-coding RNAs in human disease. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011, 12, 861–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodall, G.J.; Wickramasinghe, V.O. RNA in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2021, 21, 22–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cech, T.R.; Steitz, J.A. The noncoding RNA revolution-trashing old rules to forge new ones. Cell 2014, 157, 77–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasiadou, E.; Jacob, L.S.; Slack, F.J. Non-coding RNA networks in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsui, M.; Corey, D.R. Non-coding RNAs as drug targets. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, M.J.; Craft, B.; Hastie, M.; Repečka, K.; McDade, F.; Kamath, A.; Banerjee, A.; Luo, Y.; Rogers, D.; Brooks, A.N.; et al. Visualizing and interpreting cancer genomics data via the Xena platform. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 675–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, M.E.; Phipson, B.; Wu, D.; Hu, Y.; Law, C.W.; Shi, W.; Smyth, G.K. Limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindskrog, S.V.; Prip, F.; Lamy, P.; Taber, A.; Groeneveld, C.S.; Birkenkamp-Demtröder, K.; Jensen, J.B.; Strandgaard, T.; Nordentoft, I.; Christensen, E.; et al. An integrated multi-omics analysis identifies prognostic molecular subtypes of non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, J.A.; Frasier, C.; Matulay, J.T.; Steuerwald, N.M.; Zhu, J.; Grigg, C.M.; Kearns, J.T.; Riggs, S.B.; Gaston, K.E.; Brouwer, C.R.; et al. Genomic analysis of response to bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) treatment in high-grade stage 1 bladder cancer patients. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2021, 10, 2998–3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Aksoy, B.A.; Dogrusoz, U.; Dresdner, G.; Gross, B.; Sumer, S.O.; Sun, Y.; Jacobsen, A.; Sinha, R.; Larsson, E.; et al. Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical profiles using the cBioPortal. Sci. Signal. 2013, 6, pl1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Hu, E.; Xu, S.; Chen, M.; Guo, P.; Dai, Z.; Feng, T.; Zhou, L.; Tang, W.; Zhan, L.; et al. clusterProfiler 4.0: A universal enrichment tool for interpreting omics data. Innovation 2021, 2, 100141. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Fu, J.; Zeng, Z.; Cohen, D.; Li, J.; Chen, Q.; Li, B.; Liu, X.S. TIMER2.0 for analysis of tumor-infiltrating immune cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, W509–W514. [Google Scholar]
- Finotello, F.; Mayer, C.; Plattner, C.; Laschober, G.; Rieder, D.; Hackl, H.; Krogsdam, A.; Loncova, Z.; Posch, W.; Wilflingseder, D.; et al. Molecular and pharmacological modulators of the tumor immune contexture revealed by deconvolution of RNA-seq data. Genome Med. 2019, 11, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayakonda, A.; Lin, D.C.; Assenov, Y.; Plass, C.; Koeffler, H.P. Maftools: Efficient and comprehensive analysis of somatic variants in cancer. Genome Res. 2018, 28, 1747–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonneville, R.; Krook, M.A.; Kautto, E.A.; Miya, J.; Wing, M.R.; Chen, H.Z.; Reeser, J.W.; Yu, L.; Roychowdhury, S. Landscape of Microsatellite Instability Across 39 Cancer Types. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2017, 2017, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettenati, C.; Ingersoll, M.A. Mechanisms of BCG immunotherapy and its outlook for bladder cancer. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2018, 15, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, G.; Guo, X.; Yao, H.; Wang, G.; Li, C. Non-coding RNA in bladder cancer. Cancer Lett. 2020, 485, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, E.S.; Joensen, U.N.; Poulsen, A.M.; Goletti, D.; Johansen, I.S. Bacillus Calmette-Guérin immunotherapy for bladder cancer: A review of immunological aspects, clinical effects and BCG infections. APMIS 2020, 128, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Gu, X.; Li, Y.; Wu, Q. Mechanisms of BCG in the treatment of bladder cancer-current understanding and the prospect. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 129, 110393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, J.; Pan, X.; Zhao, L.; Li, Z.; Dai, K.; Yan, F.; Liu, S.; Ma, H.; Lai, Y. LncRNA as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in bladder cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. OncoTargets Ther. 2018, 11, 6415–6424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avgeris, M.; Tsilimantou, A.; Levis, P.K.; Tokas, T.; Sideris, D.C.; Stravodimos, K.; Ardavanis, A.; Scorilas, A. Loss of GAS5 tumour suppressor lncRNA: An independent molecular cancer biomarker for short-term relapse and progression in bladder cancer patients. Br. J. Cancer 2018, 119, 1477–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, Y.; Du, L.; Wang, L.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, S.; Li, J.; Yan, K.; Duan, W.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, L.; et al. Expression signatures of exosomal long non-coding RNAs in urine serve as novel non-invasive biomarkers for diagnosis and recurrence prediction of bladder cancer. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Du, L.; Wang, L.; Jiang, X.; Zhan, Y.; Li, J.; Yan, K.; Duan, W.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, L.; et al. Evaluation of serum exosomal LncRNA-based biomarker panel for diagnosis and recurrence prediction of bladder cancer. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 1396–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wu, M.; Lu, Y.; He, K.; Cai, X.; Yu, X.; Lu, J.; Teng, L. LncRNA MIR4435-2HG targets desmoplakin and promotes growth and metastasis of gastric cancer by activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Aging 2019, 11, 6657–6673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Li, B.; Xu, G.; Han, C.; Xing, G. lncRNA MIR4435-2HG promotes the progression of liver cancer by upregulating B3GNT5 expression. Mol. Med. Rep. 2022, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ren, Y.; Zuo, T. Long noncoding RNA LINC00978 promotes cell proliferation and invasion in non-small cell lung cancer by inhibiting miR-6754-5p. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 18, 4725–4732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, P.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ma, C.; Lu, J. Knockdown of lncRNA MIR4435-2HG and ST8SIA1 expression inhibits the proliferation, invasion and migration of prostate cancer cells in vitro and in vivo by blocking the activation of the FAK/AKT/β-catenin signaling pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2021, 47, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Tang, P.; Wang, Y.; Wan, F.; Long, J.; Zhou, J.; Zhuang, M.; Chen, X. Downregulation of long non-coding RNA MR4435-2HG suppresses breast cancer progression via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Oncol. Lett. 2021, 21, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Xu, Z.; Wang, J.; Chen, R. LINC00978 promotes bladder cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion by sponging miR-4288. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 20, 1866–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Variable | Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | p-Value | HR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| MIR4435-2HG level (Ref: Low) | 9.08 (2.85–28.97) | 0.0002 | 9.14 (2.21–37.76) | 0.0022 |
| Age (Ref: ≤50 yr) | 3.11 (0.74–13.08) | 0.1217 | ||
| Gender (Ref: Female) | 1.4 (0.74–2.62) | 0.2984 | ||
| Tumor stage T1 (Ref: Ta-CIS) | 4.59 (2.8–7.53) | <0.0001 | 2.9 (1.46–5.77) | 0.0024 |
| Tumor grade (Ref: Low) | 3.36 (2.01–5.63) | <0.0001 | ||
| Tumor Size (Ref: <3 cm) | 1.46 (0.79–2.69) | 0.2242 | ||
| EORTC risk High (Ref: Low) | 4.42 (2.59–7.55) | <0.0001 | 7.82 (1.01–60.45) | 0.0488 |
| EAU risk | ||||
| Intermediate (Ref: Low) | 2.74 (0.62–12.22) | 0.1852 | ||
| High (Ref: Low) | 6.74 (1.64–27.78) | 0.0082 | ||
| Variable | Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | p-Value | HR (95%CI) | p-Value | ||
| MIR4435-2HG level (Ref: Low) | 1.56 (1.11–2.18) | 0.0096 | 1.52 (1.08–2.14) | 0.0171 | |
| Age (Ref: ≤50 yr) | 2.67 (1.1–6.49) | 0.0307 | 2.57 (1.05–6.31) | 0.0389 | |
| Gender (Ref: Female) | 0.87 (0.63–1.21) | 0.4174 | |||
| Stage M | M1 (Ref: M0) | 3.2 (1.54–6.65) | 0.0019 | ||
| Mx (Ref: M0) | 1.44 (1.06–1.95) | 0.0184 | |||
| Stage N | N1 (Ref: N0) | 2.29 (1.67–3.14) | <0.0001 | 2.02 (1.46–2.8) | <0.0001 |
| NX (Ref: N0) | 1.71 (1.05–2.78) | 0.0302 | 1.77 (1.08–2.89) | 0.0224 | |
| Stage T | T3 (Ref: T2) | 1.2 (0.83–1.74) | 0.3417 | ||
| T4 (Ref: T2) | 1.05 (0.65–1.68) | 0.8423 | |||
| Pathologic grade (Ref: Low) | 2.9 (0.72–11.72) | 0.1353 | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, Z.; Ma, S.; Sun, Y.; Long, G.; Chen, K. Identification of Long Non-Coding RNA MIR4435-2HG as a Prognostic Biomarker in Bladder Cancer. Genes 2022, 13, 1462. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13081462
Hu Z, Ma S, Sun Y, Long G, Chen K. Identification of Long Non-Coding RNA MIR4435-2HG as a Prognostic Biomarker in Bladder Cancer. Genes. 2022; 13(8):1462. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13081462
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Zhiquan, Siquan Ma, Yi Sun, Gongwei Long, and Ke Chen. 2022. "Identification of Long Non-Coding RNA MIR4435-2HG as a Prognostic Biomarker in Bladder Cancer" Genes 13, no. 8: 1462. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13081462
APA StyleHu, Z., Ma, S., Sun, Y., Long, G., & Chen, K. (2022). Identification of Long Non-Coding RNA MIR4435-2HG as a Prognostic Biomarker in Bladder Cancer. Genes, 13(8), 1462. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13081462







