Network-Based Methods for Approaching Human Pathologies from a Phenotypic Point of View
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Overview of Network Approaches for Studying Human Pathologies
3. Phenotypes and Molecular Networks
4. Disease–Gene Predictions Using Phenotypic Descriptions and Molecular Networks
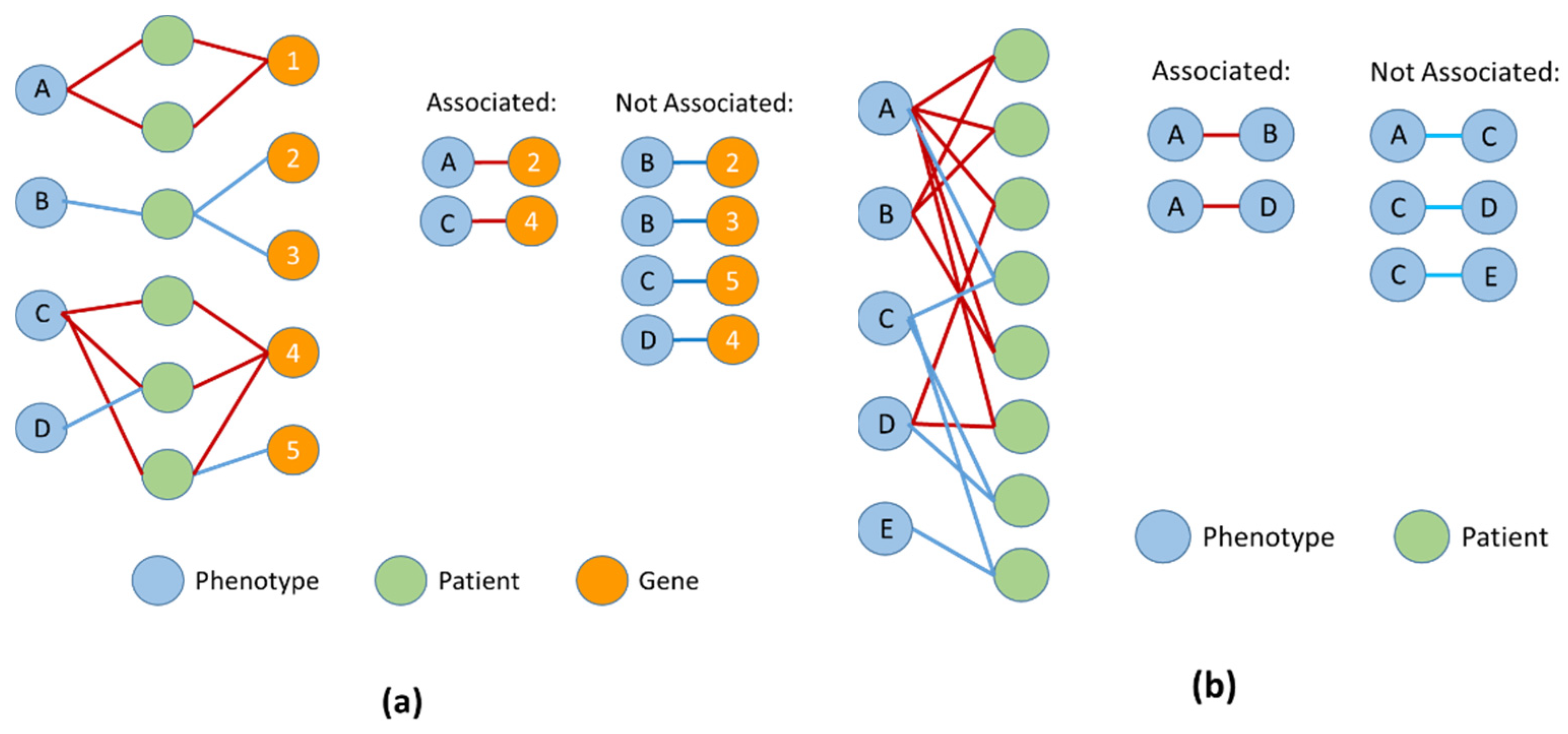
5. Phenotype–Gene Predictions
6. Phenotypes and Patient Stratification
7. Phenotypes and Co-Morbidity
8. Resources
9. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mazzocchi, F. Complexity in Biology. Exceeding the Limits of Reductionism and Determinism Using Complexity Theory. EMBO Rep. 2008, 9, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oltvai, Z.N.; Barabási, A.-L. Life’s Complexity Pyramid. Science 2002, 298, 763–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Regenmortel, M.H. Reductionism and Complexity in Molecular Biology. Scientists Now Have the Tools to Unravel Biological and Overcome the Limitations of Reductionism. EMBO Rep. 2004, 5, 1016–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Avi Ma’ayan Complex Systems Biology. J. R. Soc. Interface 2017, 14, 20170391. [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nurse, P. Systems Biology: Understanding Cells. Nature 2003, 424, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitano, H. Systems Biology: A Brief Overview. Science 2002, 295, 1662–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barabasi, A.L.; Oltvai, Z.N. Network Biology: Understanding the Cell’s Functional Organization. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2004, 5, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGillivray, P.; Clarke, D.; Meyerson, W.; Zhang, J.; Lee, D.; Gu, M.; Kumar, S.; Zhou, H.; Gerstein, M.B. Network Analysis as a Grand Unifier in Biomedical Data Science. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Data Sci. 2018, 1, 153–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barabási, A.-L.; Gulbahce, N.; Loscalzo, J. Network Medicine: A Network-Based Approach to Human Disease. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011, 12, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Furlong, L.I. Human Diseases through the Lens of Network Biology. Trends Genet. 2013, 29, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chagoyen, M.; Ranea, J.A.; Pazos, F. Applications of Molecular Networks in Biomedicine. Biol. Methods Protoc. 2019, 4, bpz012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanzoni, A.; Soler-Lopez, M.; Aloy, P. A Network Medicine Approach to Human Disease. FEBS Lett. 2009, 583, 1759–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mitra, K.; Carvunis, A.-R.; Ramesh, S.K.; Ideker, T. Integrative Approaches for Finding Modular Structure in Biological Networks. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2013, 14, 719–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavin, A.C.; Aloy, P.; Grandi, P.; Krause, R.; Boesche, M.; Marzioch, M.; Rau, C.; Jensen, L.J.; Bastuck, S.; Dumpelfeld, B.; et al. Proteome Survey Reveals Modularity of the Yeast Cell Machinery. Nature 2006, 440, 631–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-Y.; Lee, T.-L.; Chiu, Y.-Y.; Lin, Y.-W.; Lo, Y.-S.; Lin, C.-T.; Yang, J.-M. Module Organization and Variance in Protein-Protein Interaction Networks. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsia, C.-W.; Ho, M.-Y.; Shui, H.-A.; Tsai, C.-B.; Tseng, M.-J. Analysis of Dermal Papilla Cell Interactome Using STRING Database to Profile the Ex Vivo Hair Growth Inhibition Effect of a Vinca Alkaloid Drug, Colchicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 3579–3598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ravasz, E.; Somera, L.; Mongru, D.A.; Oltvai, Z.N.; Barabási, A.L. Hierarchical Organization of Modularity in Metabolic Networks. Science 2002, 297, 1551–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freyre-González, J.A.; Alonso-Pavón, J.A.; Treviño-Quintanilla, L.G.; Collado-Vides, J. Functional Architecture of Escherichia Coli: New Insights Provided by a Natural Decomposition Approach. Genome Biol. 2008, 9, R154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiassian, S.D.; Menche, J.; Barabási, A.-L. A DIseAse MOdule Detection (DIAMOnD) Algorithm Derived from a Systematic Analysis of Connectivity Patterns of Disease Proteins in the Human Interactome. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2015, 11, e1004120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.; Lee, J.; Gong, J.-R.; Cho, K.-H. Percolation Transition of Cooperative Mutational Effects in Colorectal Tumorigenesis. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oti, M.; Brunner, H.G. The Modular Nature of Genetic Diseases. Clin. Genet. 2007, 71, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossin, E.J.; Lage, K.; Raychaudhuri, S.; Xavier, R.J.; Tatar, D.; Benita, Y.; Cotsapas, C.; Daly, M.J. Proteins Encoded in Genomic Regions Associated with Immune-Mediated Disease Physically Interact and Suggest Underlying Biology. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1001273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Menche, J.; Sharma, A.; Kitsak, M.; Ghiassian, S.D.; Vidal, M.; Loscalzo, J.; Barabási, A.-L. Uncovering Disease-Disease Relationships through the Incomplete Interactome. Science 2015, 347, 1257601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krishnan, A.; Zhang, R.; Yao, V.; Theesfeld, C.L.; Wong, A.K.; Tadych, A.; Volfovsky, N.; Packer, A.; Lash, A.; Troyanskaya, O.G. Genome-Wide Prediction and Functional Characterization of the Genetic Basis of Autism Spectrum Disorder. Nat. Neurosci. 2016, 19, 1454. Available online: https://www.nature.com/articles/nn.4353#supplementary-information (accessed on 1 January 2022). [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, D.Y.; Kim, Y.A.; Przytycka, T.M. Chapter 5: Network Biology Approach to Complex Diseases. PLoS Comp. Biol. 2012, 8, e1002820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cowen, L.; Ideker, T.; Raphael, B.J.; Sharan, R. Network Propagation: A Universal Amplifier of Genetic Associations. Nature Rev. Genet. 2017, 18, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanunu, O.; Magger, O.; Ruppin, E.; Shlomi, T.; Sharan, R. Associating Genes and Protein Complexes with Disease via Network Propagation. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2010, 6, e1000641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.A.; Przytycka, T.M. Bridging the Gap between Genotype and Phenotype via Network Approaches. Front. Genet. 2012, 3, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moreau, Y.; Tranchevent, L.C. Computational Tools for Prioritizing Candidate Genes: Boosting Disease Gene Discovery. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 523–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolotareva, O.; Kleine, M. A Survey of Gene Prioritization Tools for Mendelian and Complex Human Diseases. J. Integr. Bioinform. 2019, 16, 20180069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.J.; Ye, A.S.; Gardino, A.K.; Heijink, A.M.; Sorger, P.K.; MacBeath, G.; Yaffe, M.B. Sequential Application of Anticancer Drugs Enhances Cell Death by Rewiring Apoptotic Signaling Networks. Cell 2012, 149, 780–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shahreza, M.L.; Ghadiri, N.; Mousavi, S.R.; Varshosaz, J.; Green, J.R. A Review of Network-Based Approaches to Drug Repositioning. Brief. Bioinform. 2017, 19, 878–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köhler, S.; Carmody, L.; Vasilevsky, N.; Jacobsen, J.O.B.; Danis, D.; Gourdine, J.-P.; Gargano, M.; Harris, N.L.; Matentzoglu, N.; McMurry, J.A.; et al. Expansion of the Human Phenotype Ontology (HPO) Knowledge Base and Resources. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D1018–D1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunner, H.G.; van Driel, M.A. From Syndrome Families to Functional Genomics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2004, 5, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goh, K.-I.; Cusick, M.E.; Valle, D.; Childs, B.; Vidal, M.; Barabási, A.-L. The Human Disease Network. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 8685–8690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Driel, M.A.; Bruggeman, J.; Vriend, G.; Brunner, H.G.; Leunissen, J.A.M. A Text-Mining Analysis of the Human Phenome. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2006, 14, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Menche, J.; Barabási, A.-L.; Sharma, A. Human Symptoms–Disease Network. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chagoyen, M.; Pazos, F. Characterization of Clinical Signs in the Human Interactome. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 1761–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Iratxeta, C.; Bork, P.; Andrade, M.A. Association of Genes to Genetically Inherited Diseases Using Data Mining. Nat. Genet. 2002, 31, 316–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freudenberg, J.; Propping, P. A Similarity-Based Method for Genome-Wide Prediction of Disease-Relevant Human Genes. Bioinformatics 2002, 18 (Suppl. S2), S110–S115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oti, M.; Snel, B.; Huynen, M.A.; Brunner, H.G. Predicting Disease Genes Using Protein-Protein Interactions. J. Med. Genet. 2006, 43, 691–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lage, K.; Karlberg, E.O.; Størling, Z.M.; Olason, P.I.; Pedersen, A.G.; Rigina, O.; Hinsby, A.M.; Tümer, Z.; Pociot, F.; Tommerup, N.; et al. A Human Phenome-Interactome Network of Protein Complexes Implicated in Genetic Disorders. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamosh, A.; Scott, A.F.; Amberger, J.S.; Bocchini, C.A.; McKusick, V.A. Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), a Knowledgebase of Human Genes and Genetic Disorders. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, D514–D517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodenreider, O. The Unified Medical Language System (UMLS): Integrating Biomedical Terminology. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, D267–D270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Gulbahce, N.; Yu, H. Network-Based Methods for Human Disease Gene Prediction. Brief Funct. Genom. 2011, 10, 280–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Navlakha, S.; Kingsford, C. The Power of Protein Interaction Networks for Associating Genes with Diseases. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 1057–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.K.; Carlin, D.E.; Yu, M.K.; Zhang, W.; Kreisberg, J.F.; Tamayo, P.; Ideker, T. Systematic Evaluation of Molecular Networks for Discovery of Disease Genes. Cell Syst. 2018, 6, 484–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Köhler, S.; Bauer, S.; Horn, D.; Robinson, P.N. Walking the Interactome for Prioritization of Candidate Disease Genes. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2008, 82, 949–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, X.; Jiang, R.; Zhang, M.Q.; Li, S. Network-Based Global Inference of Human Disease Genes. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2008, 4, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cáceres, J.J.; Paccanaro, A. Disease Gene Prediction for Molecularly Uncharacterized Diseases. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2019, 15, e1007078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smedley, D.; Jacobsen, J.O.; Jager, M.; Kohler, S.; Holtgrewe, M.; Schubach, M.; Siragusa, E.; Zemojtel, T.; Buske, O.J.; Washington, N.L.; et al. Next-Generation Diagnostics and Disease-Gene Discovery with the Exomiser. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 2004–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Javed, A.; Agrawal, S.; Ng, P.C. Phen-Gen: Combining Phenotype and Genotype to Analyze Rare Disorders. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 935–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, L.; Zhao, H.; Wang, P.; Zhou, W.; Luo, M.; Li, T.; Han, J.; Liu, S.; Jiang, Q. Computational Methods for Identifying Similar Diseases. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2019, 18, 590–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Patra, J.C. Genome-Wide Inferring Gene-Phenotype Relationship by Walking on the Heterogeneous Network. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 1219–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, R. Context-Sensitive Network-Based Disease Genetics Prediction and Its Implications in Drug Discovery. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 1031–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, N.; Jiang, Y.; Bergquist, T.R.; Lee, A.J.; Kacsoh, B.Z.; Crocker, A.W.; Lewis, K.A.; Georghiou, G.; Nguyen, H.N.; Hamid, M.N.; et al. The CAFA Challenge Reports Improved Protein Function Prediction and New Functional Annotations for Hundreds of Genes through Experimental Screens. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Zhou, X.; Peng, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhang, R.; Hu, J.; Yu, J.; Jia, C.; Sun, C. Network Based Integrated Analysis of Phenotype-Genotype Data for Prioritization of Candidate Symptom Genes. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahanda, I.; Funk, C.; Verspoor, K.; Ben-Hur, A. PHENOstruct: Prediction of Human Phenotype Ontology Terms Using Heterogeneous Data Sources. F1000Research 2015, 4, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petegrosso, R.; Park, S.; Hwang, T.H.; Kuang, R. Transfer Learning across Ontologies for Phenome-Genome Association Prediction. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez-Perez, S.; Pazos, F.; Chagoyen, M. Factors Affecting Interactome-Based Prediction of Human Genes Associated with Clinical Signs. BMC Bioinform. 2017, 18, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, K.; Wang, N.; Liu, G.; Wang, R.; Yu, J.; Zhang, R.; Chen, J.; Zhou, X. Heterogeneous Network Embedding for Identifying Symptom Candidate Genes. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 2018, 25, 1452–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabato, F.M.; Seoane, P.; Perkins, J.R.; Rojano, E.; García Moreno, A.; Chagoyen, M.; Pazos, F.; Ranea, J.A.G. Systematic Identification of Genetic Systems Associated with Phenotypes in Patients with Rare Genomic Copy Number Variations. Hum. Genet. 2021, 140, 457–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lötvall, J.; Akdis, C.A.; Bacharier, L.B.; Bjermer, L.; Casale, T.B.; Custovic, A.; Lemanske, R.F., Jr.; Wardlaw, A.J.; Wenzel, S.E.; Greenberger, P.A. Asthma Endotypes: A New Approach to Classification of Disease Entities within the Asthma Syndrome. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 127, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Fan, Y.; Man, T.-K.; Hung, Y.S.; Lau, C.C.; Wong, S.T.C. A Gene Signature Based Method for Identifying Subtypes and Subtype-Specific Drivers in Cancer with an Application to Medulloblastoma. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14 (Suppl. S18), S1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lundberg, A.; Lindström, L.S.; Harrell, J.C.; Falato, C.; Carlson, J.W.; Wright, P.K.; Foukakis, T.; Perou, C.M.; Czene, K.; Bergh, J.; et al. Gene Expression Signatures and Immunohistochemical Subtypes Add Prognostic Value to Each Other in Breast Cancer Cohorts. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 7512–7520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mueller, Y.M.; Schrama, T.J.; Ruijten, R.; Schreurs, M.W.J.; Grashof, D.G.B.; van de Werken, H.J.G.; Lasinio, G.J.; Álvarez-Sierra, D.; Kiernan, C.H.; Castro Eiro, M.D.; et al. Stratification of Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients into Clinical Severity Progression Groups by Immuno-Phenotyping and Machine Learning. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollert, J.; Maier, C.; Attal, N.; Bennett, D.L.H.; Bouhassira, D.; Enax-Krumova, E.K.; Finnerup, N.B.; Freynhagen, R.; Gierthmühlen, J.; Haanpää, M.; et al. Stratifying Patients with Peripheral Neuropathic Pain Based on Sensory Profiles: Algorithm and Sample Size Recommendations. Pain 2017, 158, 1446–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rojano, E.; Córdoba-Caballero, J.; Jabato, F.M.; Gallego, D.; Serrano, M.; Pérez, B.; Parés-Aguilar, Á.; Perkins, J.R.; Ranea, J.A.G.; Seoane-Zonjic, P. Evaluating, Filtering and Clustering Genetic Disease Cohorts Based on Human Phenotype Ontology Data with Cohort Analyzer. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Yarnitsky, D. Experimental and Clinical Applications of Quantitative Sensory Testing Applied to Skin, Muscles and Viscera. J. Pain 2009, 10, 556–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krumova, E.K.; Geber, C.; Westermann, A.; Maier, C. Neuropathic Pain: Is Quantitative Sensory Testing Helpful? Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2012, 12, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westbury, S.K.; Turro, E.; Greene, D.; Lentaigne, C.; Kelly, A.M.; Bariana, T.K.; Simeoni, I.; Pillois, X.; Attwood, A.; Austin, S.; et al. Human Phenotype Ontology Annotation and Cluster Analysis to Unravel Genetic Defects in 707 Cases with Unexplained Bleeding and Platelet Disorders. Genome Med. 2015, 7, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Gable, A.L.; Lyon, D.; Junge, A.; Wyder, S.; Huerta-Cepas, J.; Simonovic, M.; Doncheva, N.T.; Morris, J.H.; Bork, P.; et al. STRING V11: Protein-Protein Association Networks with Increased Coverage, Supporting Functional Discovery in Genome-Wide Experimental Datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D607–D613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Ji, H.; Aihara, K.; Chen, L. Personalized Characterization of Diseases Using Sample-Specific Networks. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, e164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuijjer, M.L.; Tung, M.G.; Yuan, G.; Quackenbush, J.; Glass, K. Estimating Sample-Specific Regulatory Networks. iScience 2019, 14, 226–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, H.; Li, L.; Zeng, T.; Chen, L. Cell-Specific Network Constructed by Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, e62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harrison, J.E.; Weber, S.; Jakob, R.; Chute, C.G. ICD-11: An International Classification of Diseases for the Twenty-First Century. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2021, 21, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo, C.A.; Blumm, N.; Barabási, A.-L.; Christakis, N.A. A Dynamic Network Approach for the Study of Human Phenotypes. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2009, 5, e1000353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Wang, L.; Ding, S.; Shen, M.; Qiu, H. Phenotypic Disease Network Analysis to Identify Comorbidity Patterns in Hospitalized Patients with Ischemic Heart Disease Using Large-Scale Administrative Data. Healthcare 2022, 10, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Wang, L.; Zeng, X.; Pan, J. Comorbidity Patterns in Depression: A Disease Network Analysis Using Regional Hospital Discharge Records. J. Affect. Disord. 2022, 296, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Uddin, S.; Srinivasan, U. Comorbidity Network for Chronic Disease: A Novel Approach to Understand Type 2 Diabetes Progression. Int. J. Med. Inform. 2018, 115, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, E.; Ko, K.; Oh, S.; Han, H.W. Network-Based Analysis of Diagnosis Progression Patterns Using Claims Data. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liebovitz, D.M.; Fahrenbach, J. COUNTERPOINT: Is ICD-10 Diagnosis Coding Important in the Era of Big Data? No. Chest 2018, 153, 1095–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Díaz-Santiago, E.; Jabato, F.M.; Rojano, E.; Seoane, P.; Pazos, F.; Perkins, J.R.; Ranea, J.A.G. Phenotype-Genotype Comorbidity Analysis of Patients with Rare Disorders Provides Insight into Their Pathological and Molecular Bases. PLoS Genet. 2020, 16, e1009054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavan, S.; Rommel, K.; Mateo Marquina, M.E.; Höhn, S.; Lanneau, V.; Rath, A. Clinical Practice Guidelines for Rare Diseases: The Orphanet Database. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Díaz-Santiago, E.; Claros, M.G.; Yahyaoui, R.; de Diego-Otero, Y.; Calvo, R.; Hoenicka, J.; Palau, F.; Ranea, J.A.G.; Perkins, J.R. Decoding Neuromuscular Disorders Using Phenotypic Clusters Obtained from Co-Occurrence Networks. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 635074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.; Hui, W.; Shang, X. Measuring Phenotype-Phenotype Similarity through the Interactome. BMC Bioinform. 2018, 19, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lowe, H.J.; Barnett, G.O. Understanding and Using the Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) Vocabulary to Perform Literature Searches. JAMA 1994, 271, 1103–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazos, F.; Chagoyen, M.; Seoane, P.; Ranea, J.A.G. CoMent: Relationships Between Biomedical Concepts Inferred From the Scientific Literature. J. Mol. Biol. 2022, 434, 167568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smoot, M.E.; Ono, K.; Ruscheinski, J.; Wang, P.-L.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape 2.8: New Features for Data Integration and Network Visualization. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 431–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guggino, W.B.; Stanton, B.A. New Insights into Cystic Fibrosis: Molecular Switches That Regulate CFTR. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 7, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, J.T.; Herzberg, M.C. Science for the next Century: Deep Phenotyping. J. Dent. Res. 2021, 100, 785–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Name | Description | URL 1 | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| CytoScape | Widely used software for interactively representing and studying biological networks. Freely available for different operative systems | https://cytoscape.org/ | [89] |
| STRING | Resource with networks of interactions and functional relationships between proteins in different organisms, inferred from different evidences | https://string-db.org/ | [72] |
| Human Phenotype Ontology (HPO) | Controlled structured vocabulary for describing different aspects of human disease phenotypes/clinical signs | https://hpo.jax.org/app/ | [33] |
| Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) | Catalogue of human genetic disorders and their related genes | https://www.omim.org/ | [43] |
| Orphanet | Resource with information on rare diseases and orphan drugs | https://www.orpha.net/ | [84] |
| Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) | Controlled vocabulary used to annotate PubMed bibliographic entries | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/ | [87] |
| CoMent | Relationships between biomedical concepts extracted from the literature | https://sysbiol.cnb.csic.es/CoMent/ | [88] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ranea, J.A.G.; Perkins, J.; Chagoyen, M.; Díaz-Santiago, E.; Pazos, F. Network-Based Methods for Approaching Human Pathologies from a Phenotypic Point of View. Genes 2022, 13, 1081. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13061081
Ranea JAG, Perkins J, Chagoyen M, Díaz-Santiago E, Pazos F. Network-Based Methods for Approaching Human Pathologies from a Phenotypic Point of View. Genes. 2022; 13(6):1081. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13061081
Chicago/Turabian StyleRanea, Juan A. G., James Perkins, Mónica Chagoyen, Elena Díaz-Santiago, and Florencio Pazos. 2022. "Network-Based Methods for Approaching Human Pathologies from a Phenotypic Point of View" Genes 13, no. 6: 1081. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13061081
APA StyleRanea, J. A. G., Perkins, J., Chagoyen, M., Díaz-Santiago, E., & Pazos, F. (2022). Network-Based Methods for Approaching Human Pathologies from a Phenotypic Point of View. Genes, 13(6), 1081. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13061081





