Platinum-Quality Mitogenome Haplotypes from United States Populations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Description
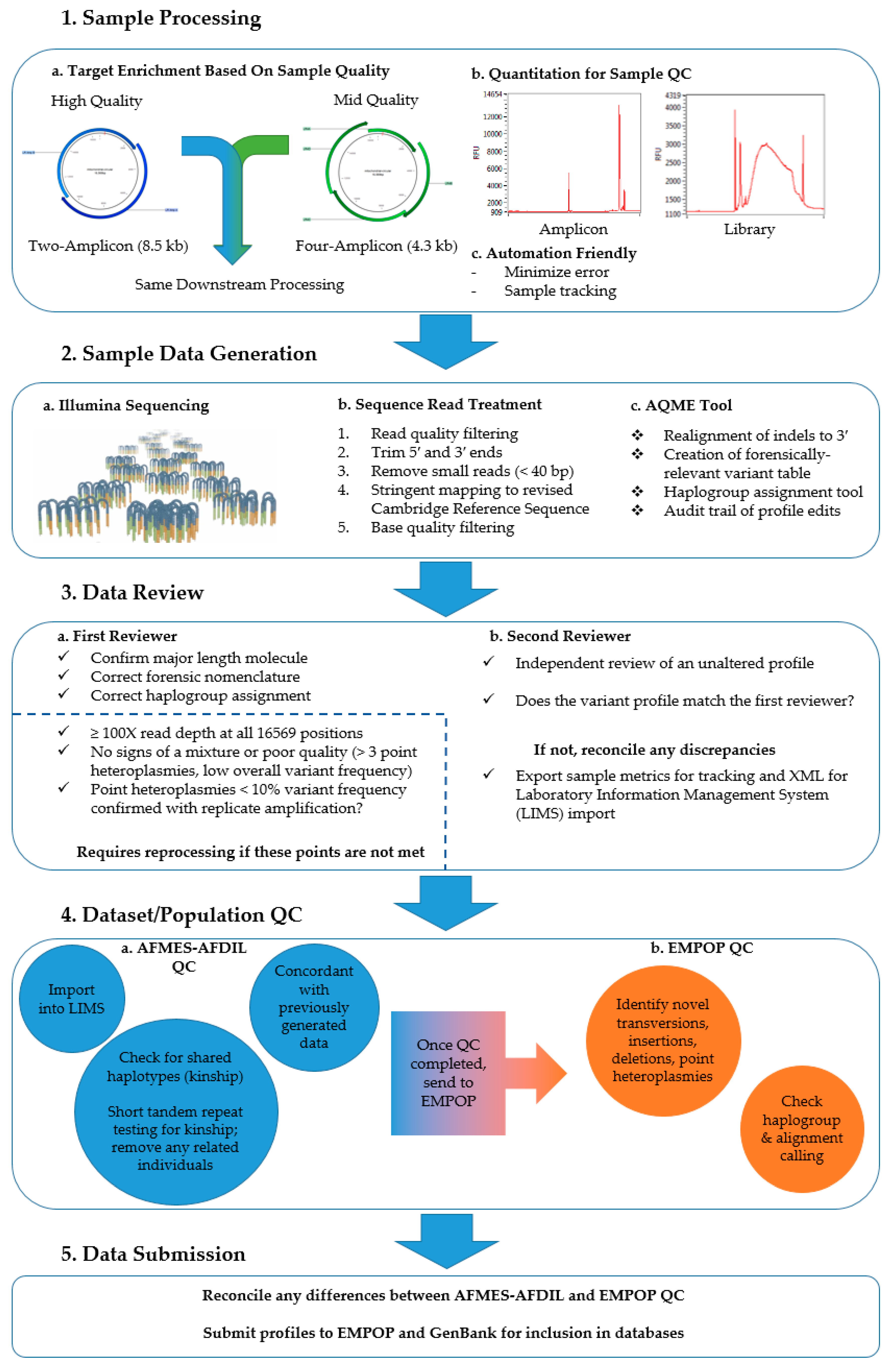
2.2. Two-Amplicon Mitogenome Enrichment, Library Preparation, and Sequencing
2.3. Data Analysis
2.4. Sample Reprocessing
2.5. Quality Control
2.6. Population-Level Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Sample Quality Metrics
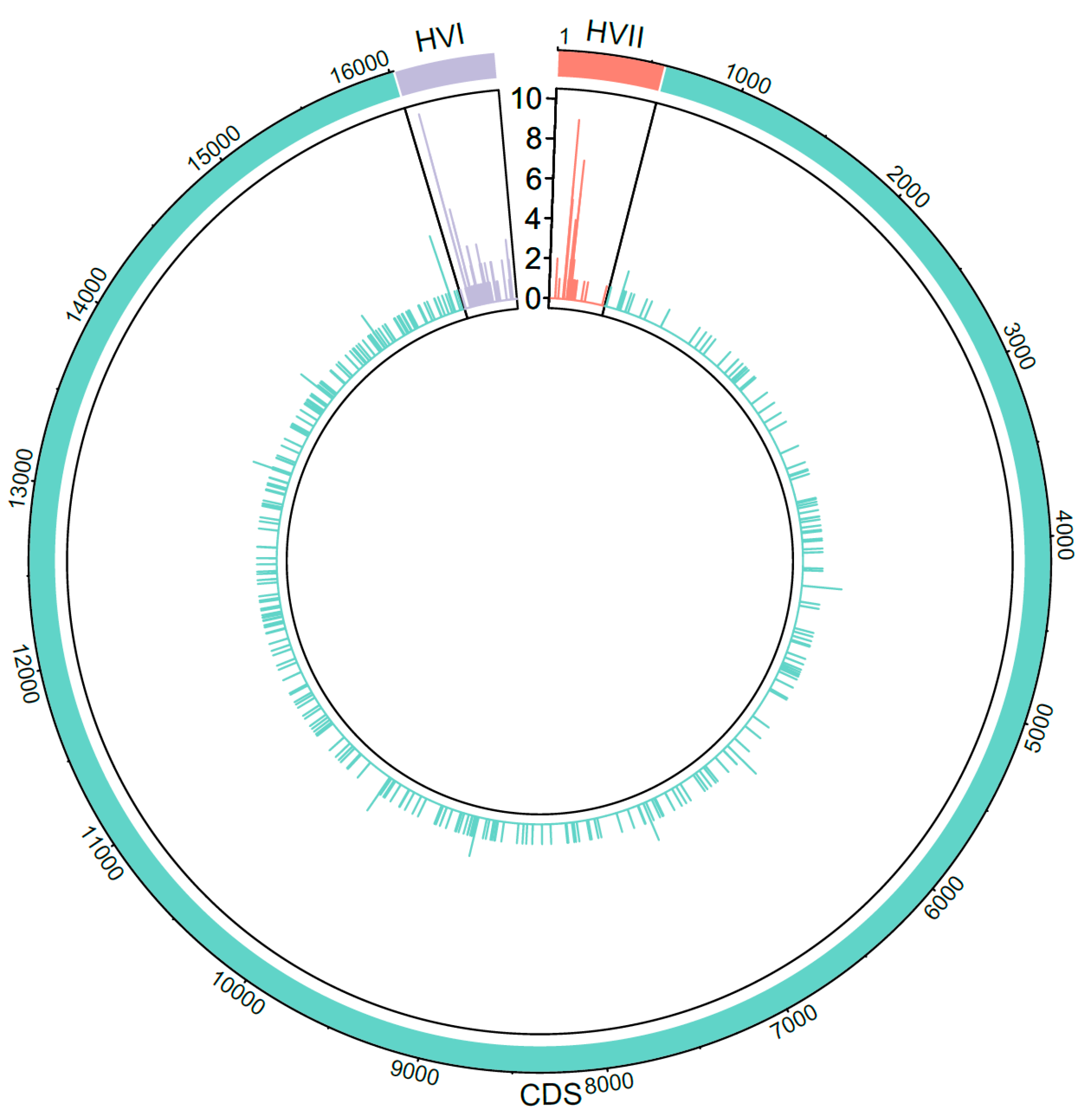
3.2. NUMT Interference in Four-Amplicon Data
3.3. STR and Kinship Analyses of Samples with Shared Haplotypes
3.4. CR Sanger Concordance
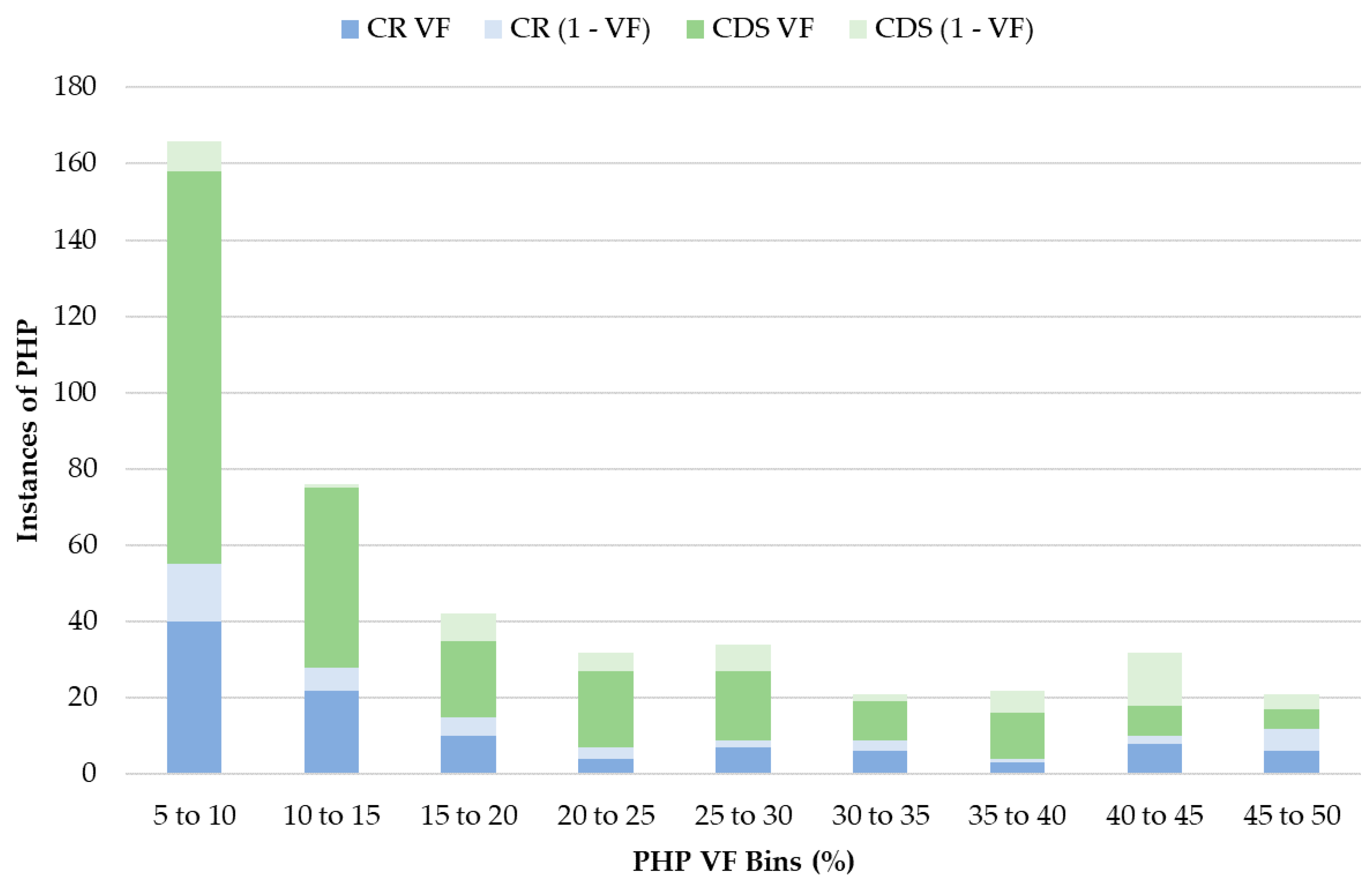
3.5. Heteroplasmy
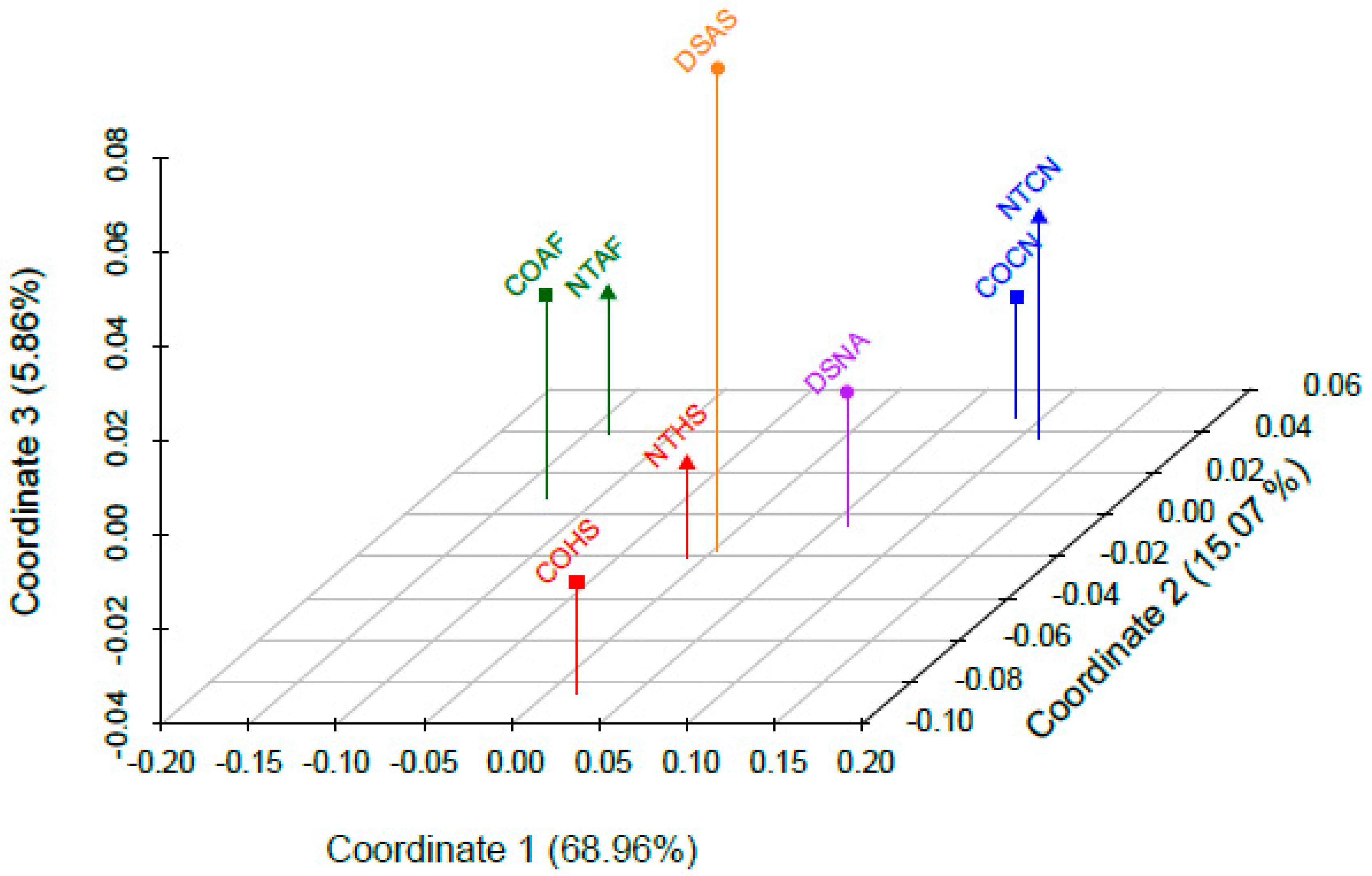
3.6. Population-Level Analyses
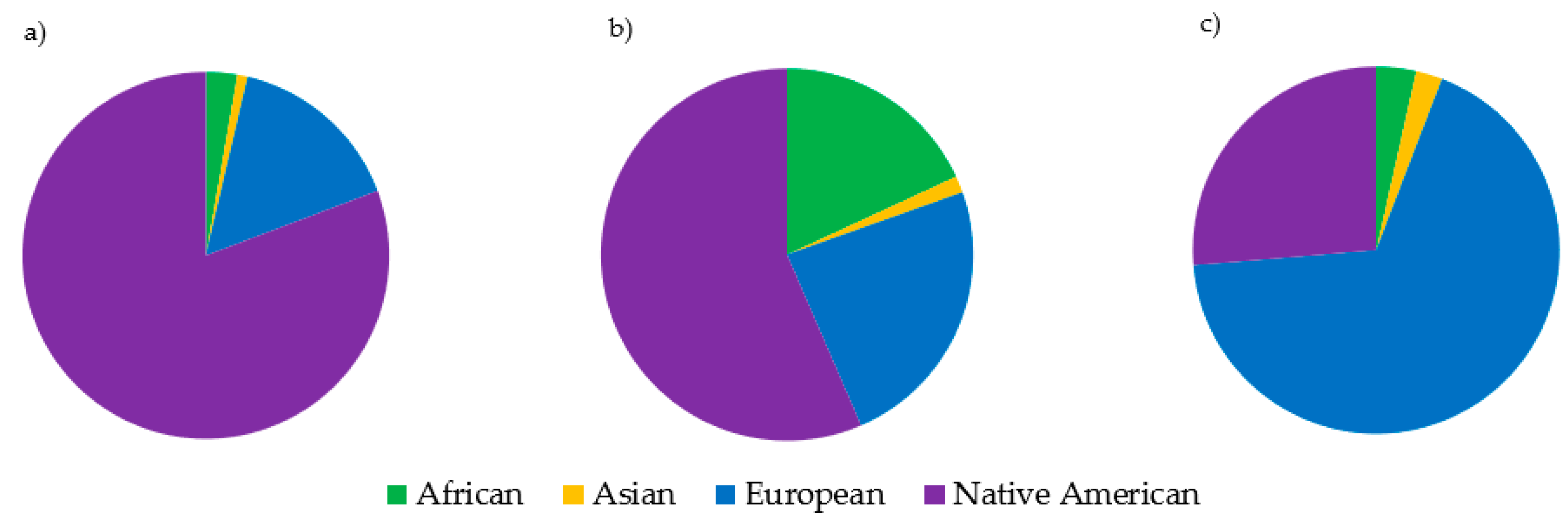
3.7. Haplogroup Distribution
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Templeton, J.E.; Brotherton, P.M.; Llamas, B.; Soubrier, J.; Haak, W.; Cooper, A.; Austin, J.J. DNA capture and next-generation sequencing can recover whole mitochondrial genomes from highly degraded samples for human identification. Investig. Genet. 2013, 4, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parson, W.; Strobl, C.; Huber, G.; Zimmermann, B.; Gomes, S.M.; Souto, L.; Fendt, L.; Delport, R.; Langit, R.; Wootton, S.; et al. Evaluation of next generation mtGenome sequencing using the Ion Torrent Personal Genome Machine (PGM). Forensic. Sci. Int. Genet. 2013, 7, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- King, J.L.; LaRue, B.L.; Novroski, N.M.; Stoljarova, M.; Seo, S.B.; Zeng, X.; Warshauer, D.H.; Davis, C.P.; Parson, W.; Sajantila, A.; et al. High-quality and high-throughput massively parallel sequencing of the human mitochondrial genome using the Illumina MiSeq. Forensic. Sci. Int. Genet. 2014, 12, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parson, W.; Huber, G.; Moreno, L.; Madel, M.B.; Brandhagen, M.D.; Nagl, S.; Xavier, C.; Eduardoff, M.; Callaghan, T.C.; Irwin, J.A. Massively parallel sequencing of complete mitochondrial genomes from hair shaft samples. Forensic. Sci. Int. Genet. 2015, 15, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Just, R.S.; Irwin, J.A.; Parson, W. Mitochondrial DNA heteroplasmy in the emerging field of massively parallel sequencing. Forensic. Sci. Int. Genet. 2015, 18, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McElhoe, J.A.; Holland, M.M.; Makova, K.D.; Su, M.S.W.; Paul, I.M.; Baker, C.H.; Faith, S.A.; Young, B. Development and assessment of an optimized next-generation DNA sequencing approach for the mtgenome using the Illumina MiSeq. Forensic. Sci. Int. Genet. 2014, 13, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hess, J.F.; Kohl, T.A.; Kotrová, M.; Roensch, K.; Paprotka, T.; Mohr, V.; Hutzenlaub, T.; Brüggemann, M.; Zengerle, R.; Niemann, S.; et al. Library preparation for next generation sequencing: A review of automation strategies. Biotechnol. Adv. 2020, 41, 107537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturk-Andreaggi, K.; Peck, M.A.; Boysen, C.; Dekker, P.; McMahon, T.P.; Marshall, C.K. AQME: A forensic mitochondrial DNA analysis tool for next-generation sequencing data. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2017, 31, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturk-Andreaggi, K.; Parson, W.; Allen, M.; Marshall, C. Impact of the sequencing method on the detection and interpretation of mitochondrial DNA length heteroplasmy. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2020, 44, 102205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holland, M.M.; Pack, E.D.; McElhoe, J.A. Evaluation of GeneMarker(R) HTS for improved alignment of mtDNA MPS data, haplotype determination, and heteroplasmy assessment. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2017, 28, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ring, J.D.; Sturk-Andreaggi, K.; Peck, M.A.; Marshall, C. Bioinformatic removal of NUMT-associated variants in mitotiling next-generation sequencing data from whole blood samples. Electrophoresis 2018, 39, 2785–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woerner, A.E.; Cihlar, J.C.; Smart, U.; Budowle, B. Numt identification and removal with RtN! Bioinformatics 2020, btaa642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parson, W.; Dur, A. EMPOP—A forensic mtDNA database. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2007, 1, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parson, W.; Gusmao, L.; Hares, D.R.; Irwin, J.A.; Mayr, W.R.; Morling, N.; Pokorak, E.; Prinz, M.; Salas, A.; Schneider, P.M.; et al. DNA Commission of the International Society for Forensic Genetics: Revised and extended guidelines for mitochondrial DNA typing. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2014, 13, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, J.A.; Saunier, J.L.; Strouss, K.M.; Sturk, K.A.; Diegoli, T.M.; Just, R.S.; Coble, M.D.; Parson, W.; Parsons, T.J. Development and expansion of high-quality control region databases to improve forensic mtDNA evidence interpretation. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2007, 1, 154–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunier, J.L.; Irwin, J.A.; Just, R.S.; O’Callaghan, J.; Parsons, T.J. Mitochondrial control region sequences from a U.S. “Hispanic” population sample. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2008, 2, e19–e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diegoli, T.M.; Irwin, J.A.; Just, R.S.; Saunier, J.L.; O’Callaghan, J.E.; Parsons, T.J. Mitochondrial control region sequences from an African American population sample. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2009, 4, e45–e52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheible, M.; Just, R.; Sturk-Andreaggi, K.; Saunier, J.; Parson, W.; Parsons, T.; Coble, M.; Irwin, J. The mitochondrial landscape of African Americans: An examination of more than 2500 control region haplotypes from 22 U.S. locations. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2016, 22, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ring, J.D.; Sturk-Andreaggi, K.; Peck, M.A.; Marshall, C.K. A Performance Evaluation of Nextera XT and KAPA HyperPlus for Rapid Illumina Library Preparation of Long-Range Mitogenome Amplicons. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2017, 29, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peck, M.A.; Sturk-Andreaggi, K.; Thomas, J.T.; Oliver, R.S.; Barritt-Ross, S.M.; Marshall, C.K. Developmental Validation of a Nextera XT Mitogenome Illumina MiSeq Sequencing Method for High Quality Samples. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2018, 34, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bintz, B.J.; Dixon, G.B.; Wilson, M.R. Simultaneous detection of human mitochondrial DNA and nuclear-inserted mitochondrial-origin sequences (NumtS) using forensic mtDNA amplification strategies and pyrosequencing technology. J. Forensic Sci. 2014, 59, 1064–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Just, R.S.; Irwin, J.A.; Parson, W. Questioning the prevalence and reliability of human mitochondrial DNA heteroplasmy from massively parallel sequencing data. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E4546–E4547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wei, W.; Pagnamenta, A.T.; Gleadall, N.; Sanchis-Juan, A.; Stephens, J.; Broxholme, J.; Tuna, S.; Odhams, C.A.; Fratter, C.; Turro, E.; et al. Nuclear-mitochondrial DNA segments resemble paternally inherited mitochondrial DNA in humans. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Loman, N.J.; Misra, R.V.; Dallman, T.J.; Constantinidou, C.; Gharbia, S.E.; Wain, J.; Pallen, M.J. Performance comparison of benchtop high-throughput sequencing platforms. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 434–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lao, O.; Vallone, P.M.; Coble, M.D.; Diegoli, T.M.; Van Oven, M.; Van Der Gaag, K.J.; Pijpe, J.; De Knijff, P.; Kayser, M. Evaluating self-declared ancestry of U.S. Americans with autosomal, Y-chromosomal and mitochondrial DNA. Hum.Mutat. 2010, 31, E1875–E1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miller, S.A.; Dykes, D.D.; Polesky, H.F. A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988, 16, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kline, M.C.; Duewer, D.L. Evaluating digital PCR for the quantification of human nuclear DNA: Determining target strandedness. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 4749–4760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozarewa, I.; Ning, Z.; Quail, M.A.; Sanders, M.J.; Berriman, M.; Turner, D.J. Amplification-free Illumina sequencing-library preparation facilitates improved mapping and assembly of (G+C)-biased genomes. Nat. Methods 2009, 6, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anderson, S.; Bankier, A.T.; Barrell, B.G.; de Bruijn, M.H.; Coulson, A.R.; Drouin, J.; Eperon, I.C.; Nierlich, D.P.; Roe, B.A.; Sanger, F.; et al. Sequence and organization of the human mitochondrial genome. Nature 1981, 290, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, R.M.; Kubacka, I.; Chinnery, P.F.; Lightowlers, R.N.; Turnbull, D.M.; Howell, N. Reanalysis and revision of the Cambridge reference sequence for human mitochondrial DNA. Nat. Genet. 1999, 23, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Oven, M.; Kayser, M. Updated comprehensive phylogenetic tree of global human mitochondrial DNA variation. Hum. Mutat. 2009, 30, E386–E394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Oven, M. PhyloTree Build 17: Growing the human mitochondrial DNA tree. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. Suppl. Ser. 2015, 5, e392–e394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scientific Working Group on DNA Analysis Methods (SWGDAM). Interpretation Guidelines for Mitochondrial DNA Analysis by Forensic DNA Testing Laboratories. Available online: https://www.swgdam.org/publications (accessed on 28 October 2020).
- Lyons, E.A.; Scheible, M.K.; Sturk-Andreaggi, K.; Irwin, J.A.; Just, R.S. A high-throughput Sanger strategy for human mitochondrial genome sequencing. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Z.; Gu, L.; Eils, R.; Schlesner, M.; Brors, B. circlize Implements and enhances circular visualization in R. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2811–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bodner, M.; Irwin, J.A.; Coble, M.D.; Parson, W. Inspecting close maternal relatedness: Towards better mtDNA population samples in forensic databases. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2011, 5, 138–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Egeland, T.; Kling, D.; Mostad, P. Relationship Inference with Familias and R: Statistical Methods in Forensic Genetics; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kling, D.; Tillmar, A.O.; Egeland, T. Familias 3—Extensions and new functionality. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2014, 13, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Churchill, J.D.; Novroski, N.M.M.; King, J.L.; Seah, L.H.; Budowle, B. Population and performance analyses of four major populations with Illumina’s FGx Forensic Genomics System. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2017, 30, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wendt, F.R.; Churchill, J.D.; Novroski, N.M.; King, J.L.; Ng, J.; Oldt, R.F.; McCulloh, K.L.; Weise, J.A.; Smith, D.G.; Kanthaswamy, S.; et al. Genetic analysis of the Yavapai Native Americans from West-Central Arizona using the Illumina MiSeq FGx forensic genomics system. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2016, 24, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, B.; Rock, A.; Huber, G.; Kramer, T.; Schneider, P.M.; Parson, W. Application of a west Eurasian-specific filter for quasi-median network analysis: Sharpening the blade for mtDNA error detection. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2011, 5, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huber, N.; Parson, W.; Dur, A. Next generation database search algorithm for forensic mitogenome analyses. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2018, 37, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benson, D.A.; Karsch-Mizrachi, I.; Lipman, D.J.; Ostell, J.; Rapp, B.A.; Wheeler, D.L. GenBank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D41–D47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kivisild, T. Maternal ancestry and population history from whole mitochondrial genomes. Investig.Genet. 2015, 6, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Excoffier, L.; Lischer, H.E. Arlequin suite ver 3.5: A new series of programs to perform population genetics analyses under Linux and Windows. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2010, 10, 564–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meirmans, P.G. genodive version 3.0: Easy-to-use software for the analysis of genetic data of diploids and polyploids. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2020, 20, 1126–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ligges, U.; Maechler, M. scatterplot3d—An R Package for Visualizing Multivariate Data. J. Stat. Softw. 2003, 1, 1–36. [Google Scholar]
- Wachsmuth, M.; Hubner, A.; Li, M.; Madea, B.; Stoneking, M. Age-Related and Heteroplasmy-Related Variation in Human mtDNA Copy Number. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12, e1005939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woerner, A.E.; Ambers, A.; Wendt, F.R.; King, J.L.; Moura-Neto, R.S.; Silva, R.; Budowle, B. Evaluation of the precision ID mtDNA whole genome panel on two massively parallel sequencing systems. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2018, 36, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Li, H.; Peng, D.; Hao, B.; Wang, Z.; Huang, E.; Wu, R.; Sun, H. Improved pairwise kinship analysis using massively parallel sequencing. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2019, 38, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Du, Q.; Ma, G.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Q.; Fu, L.; Cong, B.; Li, S. Utility of ForenSeq™ DNA Signature Prep Kit in the research of pairwise 2nd-degree kinship identification. Int. J. Legal Med. 2019, 133, 1641–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, C.; Amigo, J.; Tillmar, A.O.; Peck, M.A.; de la Puente, M.; Ruiz-Ramírez, J.; Bittner, F.; Idrizbegović, Š; Wang, Y.; Parsons, T.J.; et al. A compilation of tri-allelic SNPs from 1000 Genomes and use of the most polymorphic loci for a large-scale human identification panel. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2020, 46, 102232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bandelt, H.J.; Quintana-Murci, L.; Salas, A.; Macaulay, V. The fingerprint of phantom mutations in mitochondrial DNA data. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2002, 71, 1150–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- YYao, G.; Salas, A.; Logan, I.; Bandelt, H.J. mtDNA data mining in GenBank needs surveying. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2009, 85, 929–933; author reply 933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Irwin, J.A.; Parson, W.; Coble, M.D.; Just, R.S. mtGenome reference population databases and the future of forensic mtDNA analysis. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2011, 5, 222–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Just, R.S.; Scheible, M.K.; Fast, S.A.; Sturk-Andreaggi, K.; Röck, A.W.; Bush, J.M.; Higginbotham, J.L.; Peck, M.A.; Ring, J.D.; Huber, G.E.; et al. Full mtGenome reference data: Development and characterization of 588 forensic-quality haplotypes representing three U.S. populations. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2015, 14, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramos, A.; Santos, C.; Mateiu, L.; del Mar Gonzalez, M.; Alvarez, L.; Azevedo, L.; Amorim, A.; Aluja, M.P. Frequency and pattern of heteroplasmy in the complete human mitochondrial genome. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Irwin, J.A.; Saunier, J.L.; Niederstätter, H.; Strouss, K.M.; Sturk, K.A.; Diegoli, T.M.; Brandstätter, A.; Parson, W.; Parsons, T.J. Investigation of heteroplasmy in the human mitochondrial DNA control region: A synthesis of observations from more than 5000 global population samples. J. Mol. Evol. 2009, 68, 516–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, P.; Ermini, L.; Thomson, N.; Mormina, M.; Rito, T.; Röhl, A.; Salas, A.; Oppenheimer, S.; Macaulay, V.; Richards, M.B. Correcting for purifying selection: An improved human mitochondrial molecular clock. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2009, 84, 740–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ennis, S.R.; Ríos-Vargas, M.; Albert, N.G. The Hispanic Population: 2010. Available online: https://www.census.gov/prod/cen2010/briefs/c2010br-04.pdf (accessed on 28 October 2020).
- Moreno-Estrada, A.; Gravel, S.; Zakharia, F.; McCauley, J.L.; Byrnes, J.K.; Gignoux, C.R.; Ortiz-Tello, P.A.; Martínez, R.J.; Hedges, D.J.; Morris, R.W.; et al. Reconstructing the population genetic history of the Caribbean. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achilli, A.; Perego, U.A.; Lancioni, H.; Olivieri, A.; Gandini, F.; Kashani, B.H.; Battaglia, V.; Grugni, V.; Angerhofer, N.; Rogers, M.P.; et al. Reconciling migration models to the Americas with the variation of North American native mitogenomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 14308–14313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kemp, B.M.; González-Oliver, A.; Malhi, R.S.; Monroe, C.; Schroeder, K.B.; McDonough, J.; Rhett, G.; Resendéz, A.; Peñaloza-Espinosa, R.I.; Buentello-Malo, L.; et al. Evaluating the Farming/Language Dispersal Hypothesis with genetic variation exhibited by populations in the Southwest and Mesoamerica. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 6759–6764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tackney, J.C.; Potter, B.A.; Raff, J.; Powers, M.; Watkins, W.S.; Warner, D.; Reuther, J.D.; Irish, J.D.; O’Rourke, D.H. Two contemporaneous mitogenomes from terminal Pleistocene burials in eastern Beringia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 13833–13838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Sample Set | Source | U.S. Geographic Origin | Metapopulation | Sample Type | Count |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COAF | Analytical Genetic Testing Center (Denver, CO) | Colorado * | African American | Whole blood, buccal swabs | 123 |
| COCN | Analytical Genetic Testing Center (Denver, CO) | Colorado * | Caucasian | Whole blood, buccal swabs | 118 |
| COHS | Analytical Genetic Testing Center (Denver, CO) | Colorado * | Hispanic | Whole blood, buccal swabs | 113 |
| NTAF | National Institute of Standards and Technology (Gaithersburg, MD) | Multiple States | African American | Whole blood | 258 |
| NTCN | National Institute of Standards and Technology (Gaithersburg, MD) | Multiple States | Caucasian | Whole blood | 262 |
| NTHS | National Institute of Standards and Technology (Gaithersburg, MD) | Multiple States | Hispanic | Whole blood | 139 |
| DSAS | Department of Defense Serum Repository (Silver Spring, CO) | Multiple States/Territories | Asian American | Serum | 175 |
| DSNA | Department of Defense Serum Repository (Silver Spring, CO) | Multiple States | Native American | Serum | 175 |
| Sample Source | Processing Laboratory | Amplification Input (µL) | Amplicon Purification | Library Preparation | Sequencing | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input (ng) | Reaction | Method | Input (pM) | Reagent Kit | Read Type | ||||
| AGTC-CO | AFMES-AFDIL | 3 | Yes | 150 | Half-reaction | Manual | 12 | 150 cycle v3 | Single end |
| NIST | NIST | 2 | No | 350 | Full-reaction | Manual | 20 | 600 cycle v3 | Paired end |
| DoDSR | AFMES-AFDIL | 5 | Yes | 50 | Half-reaction | Automated | 12 | 600 cycle v3 | Paired end |
| Dataset | Samples Attempted | Finalized Samples | Passing | Excluded | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Two Amplicon | Four Amplicon | Failed | Mixed | Duplicate | Related | |||
| COAF | 123 | 112 | 112 | 0 | 6 | 3 | 2 | 0 |
| COCN | 118 | 112 | 112 | 0 | 5 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| COHS | 113 | 109 | 109 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| NTAF | 258 | 256 | 251 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| NTCN | 262 | 260 | 258 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| NTHS | 139 | 138 | 138 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| DSAS | 175 | 169 | 165 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| DSNA | 175 | 171 | 158 | 13 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| Total | 1363 | 1327 | 1303 | 24 | 18 | 14 | 2 | 2 |
| Data Source | Total Reads | Reads After Trim | Reads Mapped | Trimmed Reads Mapped (%) | Average Read Depth | Average Major Base Frequency (%) | Average Major Base Frequency Excluding Heteroplasmy (%) | Average Variant Position Read Depth |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AGTC-CO | 352,136 | 313,022 | 293,667 | 94 | 1658.8 | 98.6 | 99.5 | 1499.6 |
| NIST | 383,834 | 272,090 | 256,309 | 95 | 1558.4 | 98.0 | 99.1 | 1466.0 |
| DoDSR | 688,530 | 566,775 | 504,600 | 90 | 2385.4 | 97.5 | 99.2 | 2198.7 |
| Dataset | Total Individuals | Total PHPs | Individuals with PHPs | Individuals with 1 PHP | Individuals with 2 PHPs | Individuals with 3 PHPs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COAF | 112 | 37 | 31 (28%) | 26 | 4 | 1 |
| COCN | 112 | 41 | 30 (27%) | 20 | 9 | 1 |
| COHS | 109 | 36 | 27 (25%) | 20 | 5 | 2 |
| NTAF | 256 | 77 | 60 (23%) | 43 | 17 | 0 |
| NTCN | 260 | 92 | 77 (30%) | 65 | 10 | 2 |
| NTHS | 138 | 53 | 43 (31%) | 34 | 8 | 1 |
| DSAS | 169 | 62 | 54 (32%) | 49 | 2 | 3 |
| DSNA | 171 | 48 | 43 (25%) | 38 | 5 | 0 |
| All | 1327 | 446 | 365 (28%) | 295 | 60 | 10 |
| Dataset | Sample Size | Including PHP | Excluding PHP | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Haplotypes | Unique Haplotypes | Observed RMP (%) | Empirical RMP (%) | Haplotype Diversity | Total Haplotypes | Unique Haplotypes | Observed RMP (%) | Empirical RMP (%) | Haplotype Diversity | ||
| COAF | 112 | 112 | 112 | 0.89 | 0.00 | 1 | 110 | 108 | 0.92 | 0.03 | 0.9997 |
| COCN | 112 | 112 | 112 | 0.89 | 0.00 | 1 | 112 | 112 | 0.89 | 0.00 | 1 |
| COHS | 109 | 102 | 97 | 1.09 | 0.17 | 0.9983 | 94 | 83 | 1.34 | 0.42 | 0.9958 |
| NTAF | 256 | 251 | 247 | 0.41 | 0.02 | 0.9998 | 246 | 237 | 0.42 | 0.03 | 0.9997 |
| NTCN | 260 | 254 | 250 | 0.41 | 0.02 | 0.9998 | 250 | 244 | 0.43 | 0.05 | 0.9995 |
| NTHS | 138 | 131 | 127 | 0.86 | 0.14 | 0.9986 | 125 | 116 | 0.97 | 0.24 | 0.9976 |
| DSAS | 169 | 167 | 165 | 0.61 | 0.01 | 0.9999 | 165 | 161 | 0.62 | 0.03 | 0.9997 |
| DSNA | 171 | 167 | 163 | 0.61 | 0.03 | 0.9997 | 164 | 159 | 0.65 | 0.07 | 0.9993 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Taylor, C.R.; Kiesler, K.M.; Sturk-Andreaggi, K.; Ring, J.D.; Parson, W.; Schanfield, M.; Vallone, P.M.; Marshall, C. Platinum-Quality Mitogenome Haplotypes from United States Populations. Genes 2020, 11, 1290. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11111290
Taylor CR, Kiesler KM, Sturk-Andreaggi K, Ring JD, Parson W, Schanfield M, Vallone PM, Marshall C. Platinum-Quality Mitogenome Haplotypes from United States Populations. Genes. 2020; 11(11):1290. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11111290
Chicago/Turabian StyleTaylor, Cassandra R., Kevin M. Kiesler, Kimberly Sturk-Andreaggi, Joseph D. Ring, Walther Parson, Moses Schanfield, Peter M. Vallone, and Charla Marshall. 2020. "Platinum-Quality Mitogenome Haplotypes from United States Populations" Genes 11, no. 11: 1290. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11111290
APA StyleTaylor, C. R., Kiesler, K. M., Sturk-Andreaggi, K., Ring, J. D., Parson, W., Schanfield, M., Vallone, P. M., & Marshall, C. (2020). Platinum-Quality Mitogenome Haplotypes from United States Populations. Genes, 11(11), 1290. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11111290






