The CaAP2/ERF064 Regulates Dual Functions in Pepper: Plant Cell Death and Resistance to Phytophthora capsici
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Phytohormones Treatments
2.2. Pathogen Preparation and Inoculation
2.3. Transient Expression Assay in Tobacco
2.4. Transcriptional Activation and Yeast One-Hybrid Assay
2.5. Virus-Induced Gene Silencing in Pepper
2.6. Tobacco Transformation
2.7. Histochemical Staining
2.8. qRT-PCR Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
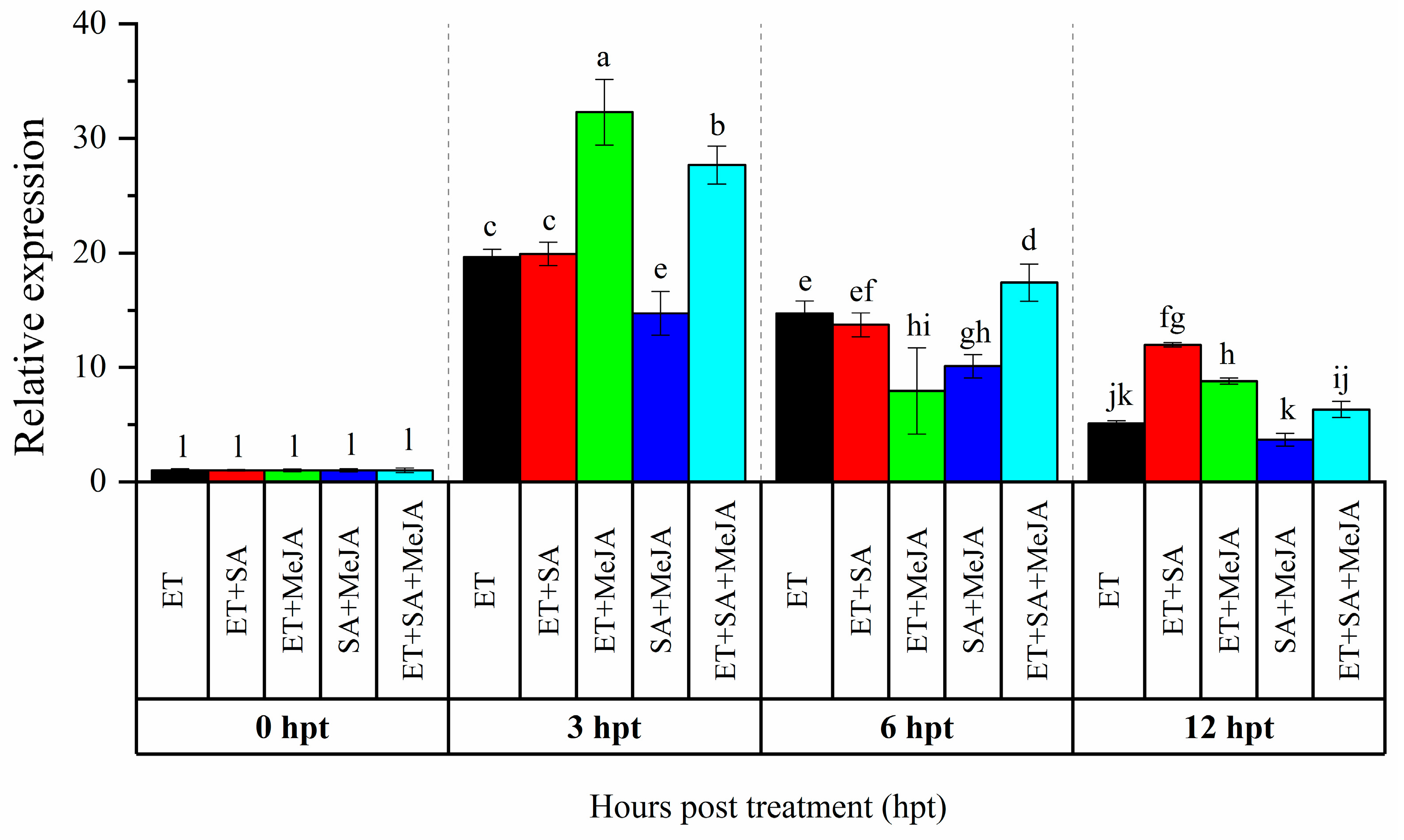
3.1. Expression Analysis of CaAP2/ERF064 in Response to Combinations of Phytohormones
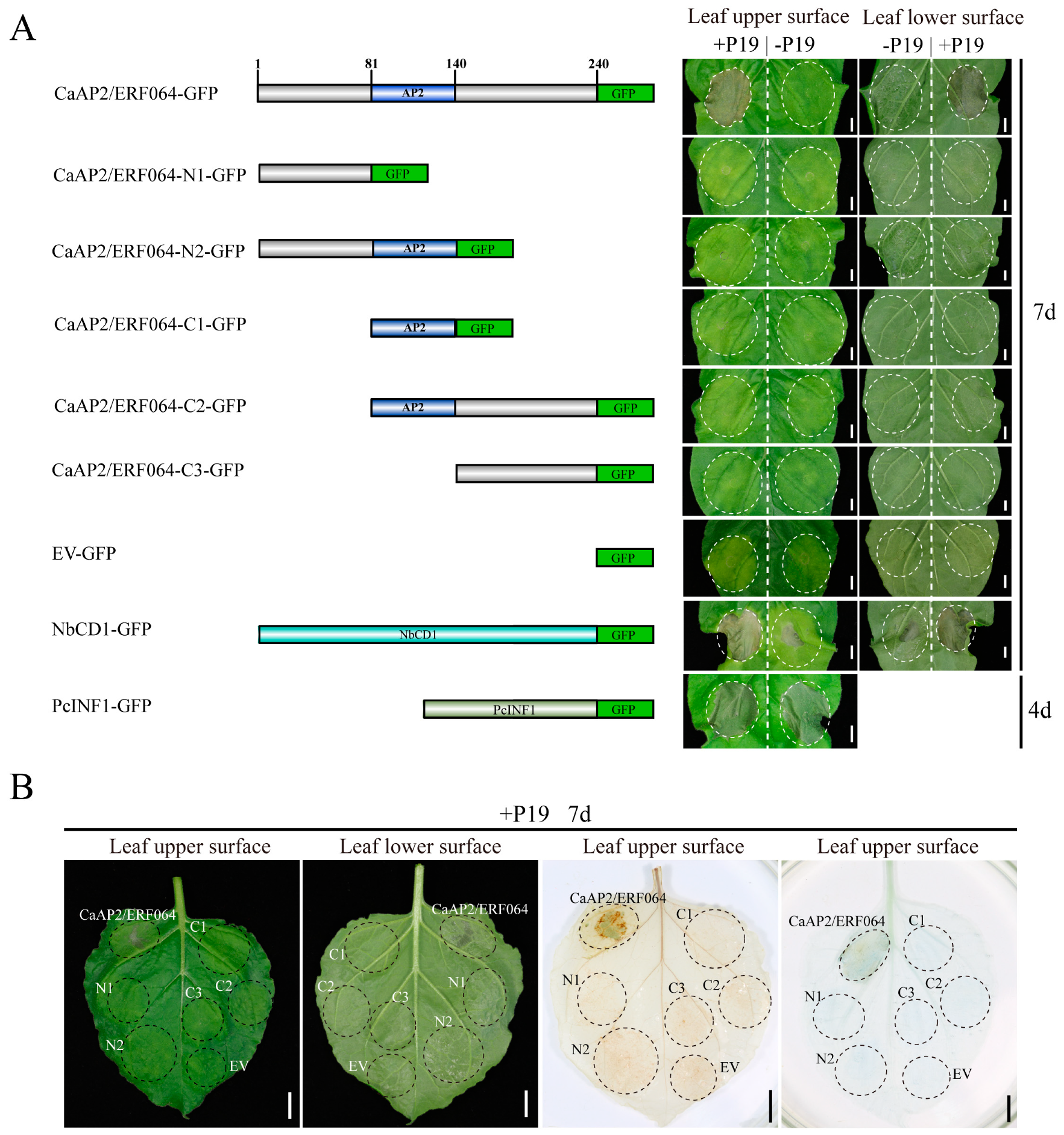
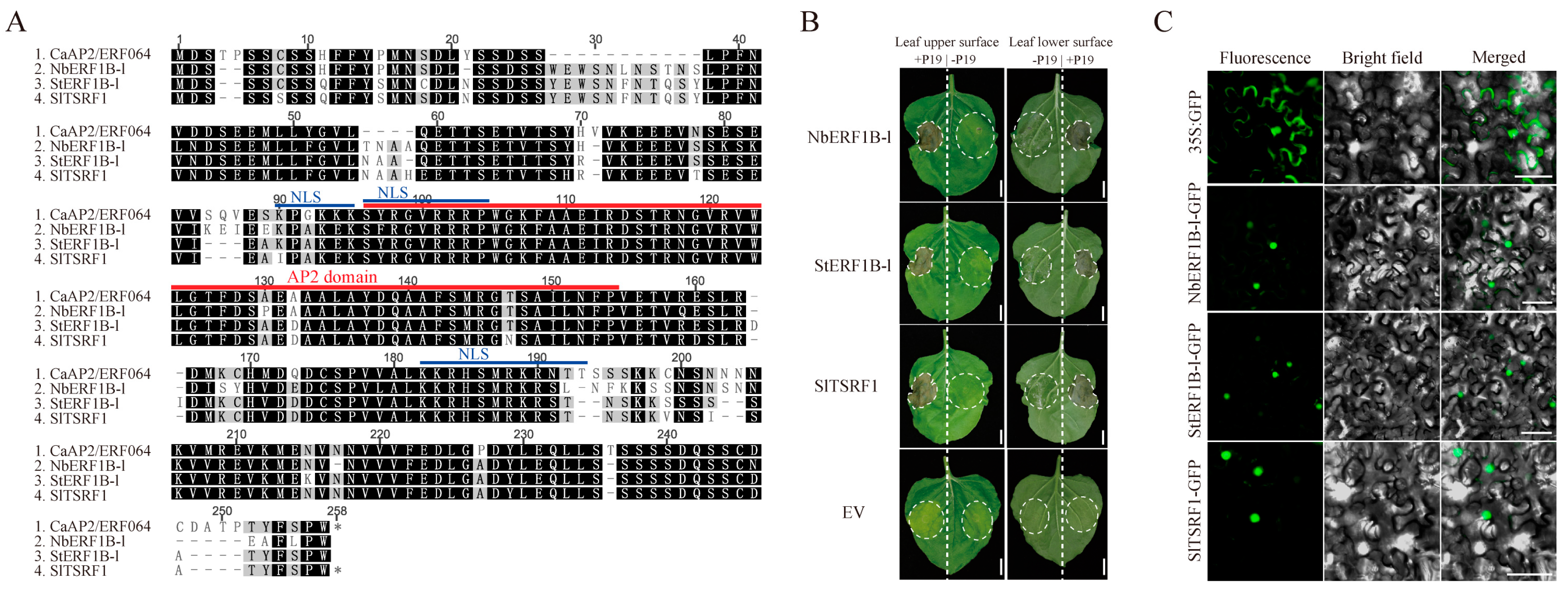
3.2. Transient Over-Expression of CaAP2/ERF064 Induces Cell Death in N. benthamiana
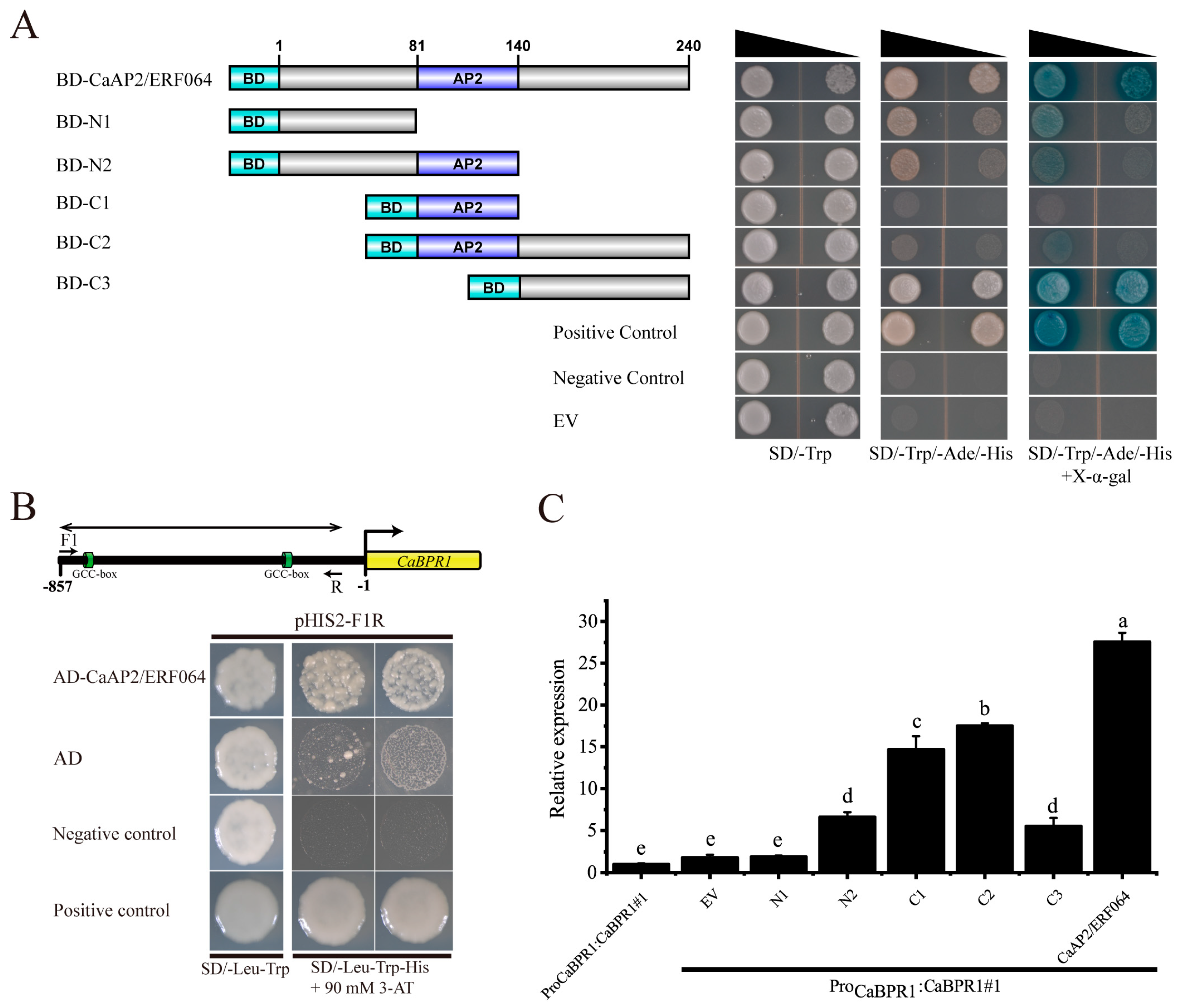
3.3. CaAP2/ERF064 Regulates the Expression of CaBPR1
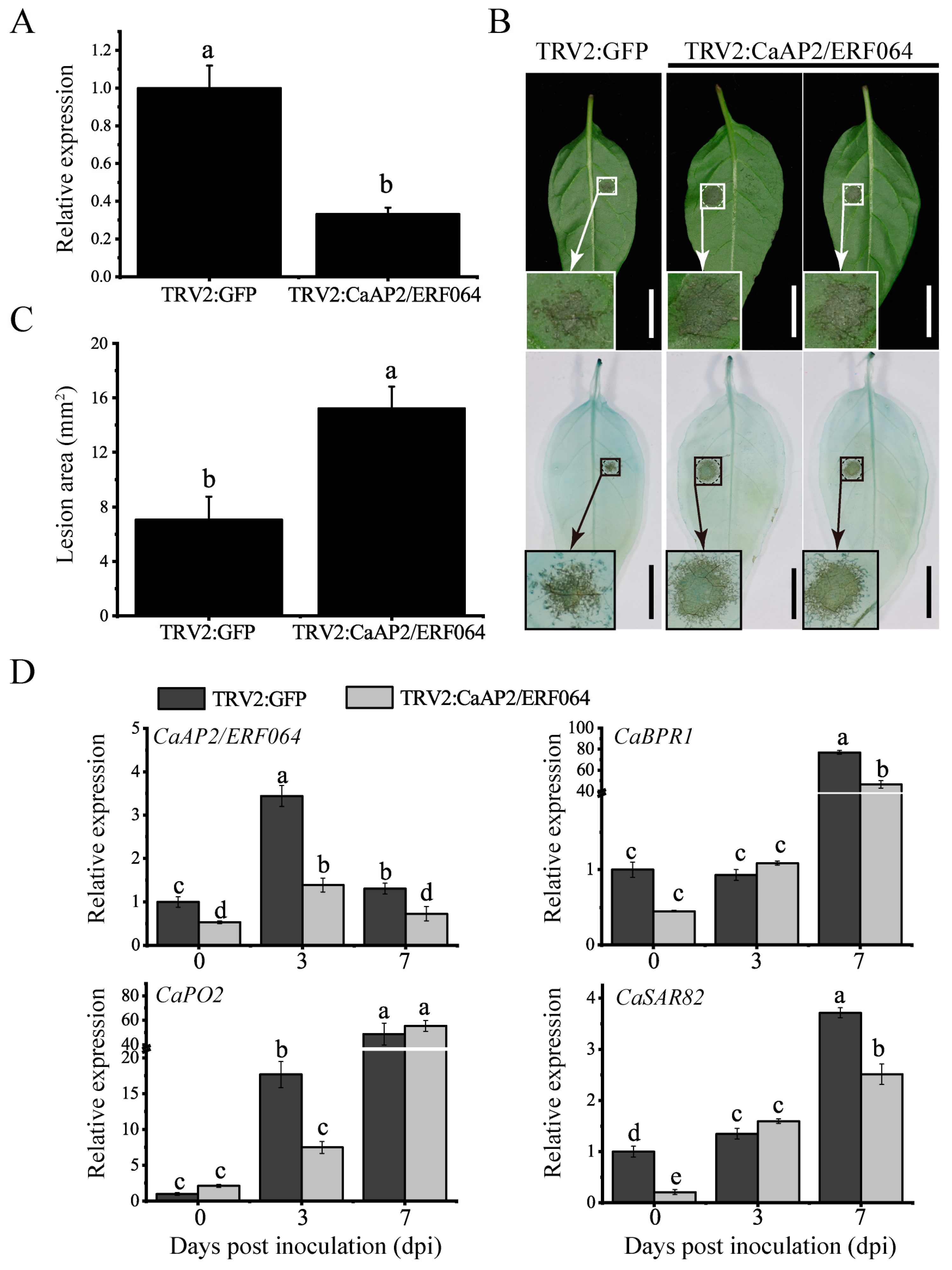
3.4. Silencing of CaAP2/ERF064 in Pepper Enhances the Susceptibility to P. capsici
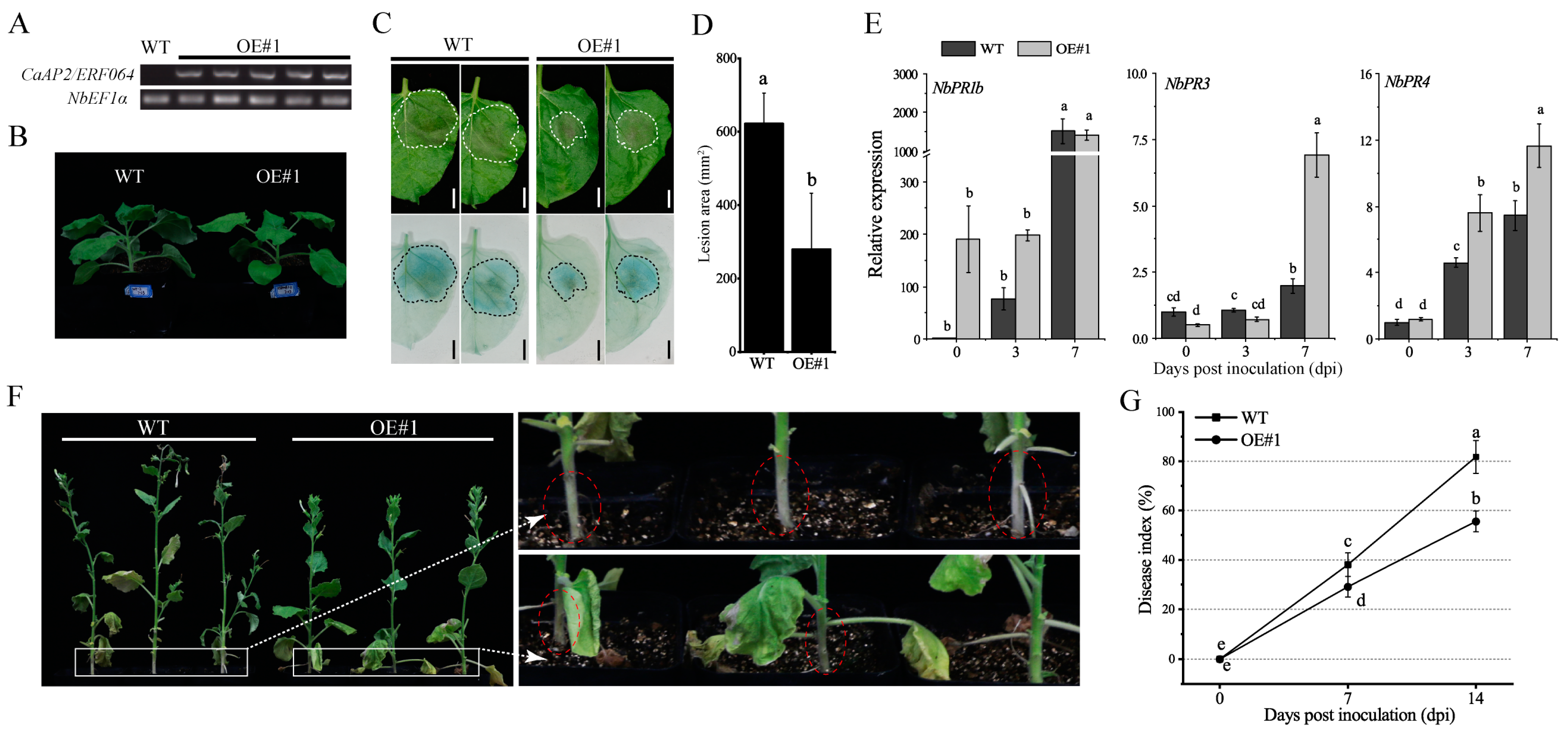
3.5. Ectopic Expression of CaAP2/ERF064 Enhances Tobacco Resistance to P. capsici
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peng, Y.; Van Wersch, R.; Zhang, Y. Convergent and Divergent Signaling in PAMP-Triggered Immunity and Effector-Triggered Immunity. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2018, 31, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chisholm, S.T.; Coaker, G.; Day, B.; Staskawicz, B.J. Host-Microbe Interactions: Shaping the Evolution of the Plant Immune Response. Cell 2006, 124, 803–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, P.Y.; Catinot, J.; Zimmerli, L. Ethylene response factors in Arabidopsis immunity. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 1231–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, M.; Munné-Bosch, S. Ethylene Response Factors: A Key Regulatory Hub in Hormone and Stress Signaling1. Plant Physiol. 2015, 169, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohme-Takagi, M.; Shinshi, H. Ethylene-inducible DNA binding proteins that interact with an ethylene-responsive element. Plant Cell 1995, 7, 173–182. [Google Scholar]
- Catinot, J.; Huang, J.-B.; Huang, P.-Y.; Tseng, M.-Y.; Chen, Y.-L.; Gu, S.-Y.; Lo, W.-S.; Wang, L.-C.; Chen, Y.-R.; Zimmerli, L. ETHYLENE RESPONSE FACTOR 96 positively regulates Arabidopsis resistance to necrotrophic pathogens by direct binding to GCC elements of jasmonate- and ethylene-responsive defence genes. Plant Cell Environ. 2015, 38, 2721–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Wei, T.; Yin, K.-Q.; Chen, Z.; Gu, H.; Qu, L.-J.; Qin, G. Arabidopsis RAP2.2 plays an important role in plant resistance to Botrytis cinerea and ethylene responses. New Phytol. 2012, 195, 450–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, G.H.; Wan, J.; Kim, H.J.; Nguyen, X.C.; Chung, W.S.; Hong, J.C.; Stacey, G. Ethylene-Responsive Element-Binding Factor 5, ERF5, Is Involved in Chitin-Induced Innate Immunity Response. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2012, 25, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McGrath, K.C.; Dombrecht, B.; Manners, J.M.; Schenk, P.M.; Edgar, C.I.; MacLean, D.J.; Scheible, W.-R.; Udvardi, M.K.; Kazan, K. Repressor-and Activator-Type Ethylene Response Factors Functioning in Jasmonate Signaling and Disease Resistance Identified via a Genome-Wide Screen of Arabidopsis Transcription Factor Gene Expression. Plant Physiol. 2005, 139, 949–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, M.; Matsui, K.; Hiratsu, K.; Shinshi, H.; Ohme-Takagi, M. Repression Domains of Class II ERF Transcriptional Repressors Share an Essential Motif for Active Repression. Plant Cell 2001, 13, 1959–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, Z.; He, Q.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shao, F.; Xie, C. The Potato ERF Transcription Factor StERF3 Negatively Regulates Resistance to Phytophthora infestans and Salt Tolerance in Potato. Plant Cell Physiol. 2015, 56, 992–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, L.D.; Cheng, Y.X.; Wu, J.J.; Cheng, Q.; Li, W.B.; Fan, S.J.; Jiang, L.Y.; Xu, Z.L.; Kong, F.J.; Zhang, D.Y.; et al. Overexpression of GmERF5, a new member of the soybean EAR motif-containing ERF transcription factor, enhances resistance to Phytophthora sojae in soybean. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 2635–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, F.Y.; DeFalco, T.A.; Moeder, W.; Li, B.; Gong, Y.; Liu, X.-M.; Taniguchi, M.; Lumba, S.; Toh, S.; Shan, L.; et al. Arabidopsis ETHYLENE RESPONSE FACTOR 8 (ERF8) has dual functions in ABA signaling and immunity. BMC Plant Boil. 2018, 18, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, F.Y.; Khan, M.; Taniguchi, M.; Mirmiran, A.; Moeder, W.; Lumba, S.; Yoshioka, K.; Desveaux, D. A host–pathogen interactome uncovers phytopathogenic strategies to manipulate plant ABA responses. Plant J. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-H.; Hong, J.-P.; Oh, S.-K.; Lee, S.; Choi, D.; Kim, W. The ethylene-responsive factor like protein 1 (CaERFLP1) of hot pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) interacts in vitro with both GCC and DRE/CRT sequences with different binding affinities: Possible biological roles of CaERFLP1 in response to pathogen infection and high salinity conditions in transgenic tobacco plants. Plant Mol. Boil. 2004, 55, 61–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, S.Y.; Kim, J.-H.; Joung, Y.-H.; Lee, S.; Kim, W.-T.; Yu, S.H.; Choi, D. The Pepper Transcription Factor CaPF1 Confers Pathogen and Freezing Tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2004, 136, 2862–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.H.; Zhang, H.X.; Tan, J.Y.; Yan, M.J.; Li, D.W.; Khan, A.; Gong, Z.H. A New Ethylene-Responsive Factor CaPTI1 Gene of Pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) Involved in the Regulation of Defense Response to Phytophthora capsici. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 6, 1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, E.; Lim, C.W.; Han, S.-W.; Lee, S.C. Functional Analysis of the Pepper Ethylene-Responsive Transcription Factor, CaAIEF1, in Enhanced ABA Sensitivity and Drought Tolerance. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamoun, S.; Furzer, O.; Jones, J.D.; Judelson, H.S.; Ali, G.S.; Dalio, R.J.; Roy, S.G.; Schena, L.; Zambounis, A.; Panabieres, F.; et al. The Top 10 oomycete pathogens in molecular plant pathology. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2015, 16, 413–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamour, K.H.; Stam, R.; Jupe, J.; Huitema, E. The oomycete broad-host-range pathogen Phytophthora capsici. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2012, 13, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.-H.; Wang, M.; Zhang, H.-X.; Khan, A.; Wei, A.-M.; Luo, D.-X.; Gong, Z.-H. Genome-wide identification of the AP2/ERF transcription factor family in pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). Genome 2018, 61, 663–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Meng, Y.; Zhang, M.; Tong, X.; Wang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Quan, J.; Govers, F.; Shan, W. Infection of Arabidopsis thaliana by Phytophthora parasitica and identification of variation in host specificity. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2011, 12, 187–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Mpina, M.H.; Birch, P.R.J.; Bouwmeester, K.; Govers, F. Phytophthora infestans RXLR Effector AVR1 Interacts with Exocyst Component Sec5 to Manipulate Plant Immunity. Plant Physiol. 2015, 169, 1975–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.X.; Ali, M.; Feng, X.H.; Jin, J.H.; Huang, L.J.; Khan, A.; Lv, J.G.; Gao, S.Y.; Luo, D.X.; Gong, Z.H. A Novel Transcription Factor CaSBP12 Gene Negatively Regulates the Defense Response against Phytophthora capsici in Pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 20, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.-E.; Liu, K.-K.; Li, D.-W.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Zhao, Q.; He, Y.-M.; Gong, Z.-H. A Novel Peroxidase CanPOD Gene of Pepper Is Involved in Defense Responses to Phytophtora capsici Infection as well as Abiotic Stress Tolerance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 3158–3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendel, R.R.; Schiemann, J.; Simoens, C. High meiotic stability of a foreign gene introduced into tobacco by Agrobacterium-mediated transformation. Mol. Genet. Genom. 1987, 207, 171–175. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, D.S.; Hwang, I.S.; Hwang, B.K. Requirement of the Cytosolic Interaction between PATHOGENESIS-RELATED PROTEIN10 and LEUCINE-RICH REPEAT PROTEIN1 for Cell Death and Defense Signaling in Pepper. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 1675–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(T)(-Delta Delta C) method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholthof, H.B. The Tombusvirus-encoded P19: From irrelevance to elegance. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2006, 4, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silhavy, D.; Burgyán, J. Effects and side-effects of viral RNA silencing suppressors on short RNAs. Trends Plant Sci. 2004, 9, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.K.; Lee, S.C.; Hwang, B.K. Activation of pepper basic PR-1 gene promoter during defense signaling to pathogen, abiotic and environmental stresses. Gene 2005, 356, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.J.; Hwang, B.K. Pepper gene encoding a basic pathogenesis-related 1 protein is pathogen and ethylene inducible. Physiol. Plant. 2000, 108, 51–60. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, H.W.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, S.C.; Hong, J.K.; Hwang, B.K. Hydrogen Peroxide Generation by the Pepper Extracellular Peroxidase CaPO2 Activates Local and Systemic Cell Death and Defense Response to Bacterial Pathogens. Plant Physiol. 2007, 145, 890–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.C.; Hwang, B.K. Identification of the pepper SAR8.2 gene as a molecular marker for pathogen infection, abiotic elicitors and environmental stresses in Capsicum annuum. Planta 2003, 216, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broekaert, W.F.; Delauré, S.L.; De Bolle, M.F.; Cammue, B.P. The Role of Ethylene in Host-Pathogen Interactions. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2006, 44, 393–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieterse, C.M.; Van Der Does, D.; Zamioudis, C.; Leon-Reyes, A.; Van Wees, S.C. Hormonal Modulation of Plant Immunity. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Boil. 2012, 28, 489–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kunkel, B.N.; Brooks, D.M. Cross talk between signaling pathways in pathogen defense. Curr. Opin. Plant Boil. 2002, 5, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo, O.; Piqueras, R.; Sánchez-Serrano, J.J.; Solano, R. ETHYLENE RESPONSE FACTOR1 integrates signals from ethylene and jasmonate pathways in plant defense. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin Nasir, K.H.; Takahashi, Y.; Ito, A.; Saitoh, H.; Matsumura, H.; Kanzaki, H.; Shimizu, T.; Ito, M.; Fujisawa, S.; Sharma, P.C.; et al. High-throughput in planta expression screening identifies a class II ethylene-responsive element binding factor-like protein that regulates plant cell death and non-host resistance. Plant J. 2005, 43, 491–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata, T.; Kida, Y.; Arai, T.; Kishi, Y.; Manago, Y.; Murai, M.; Matsushita, Y. Overexpression of tobacco ethylene response factor NtERF3 gene and its homologues from tobacco and rice induces hypersensitive response-like cell death in tobacco. J. Gen. Plant Pathol. 2012, 78, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata, T.; Kida, Y.; Tochigi, M.; Matsushita, Y. Analysis of the cell death-inducing ability of the ethylene response factors in group VIII of the AP2/ERF family. Plant Sci. 2013, 209, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsushita, T.; Mochizuki, N.; Nagatani, A. Dimers of the N-terminal domain of phytochrome B are functional in the nucleus. Nature 2003, 424, 571–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.Y.; Shi, Y.; Lei, Y.; Li, Y.; Fan, J.; Xu, Y.J.; Ma, X.F.; Zhao, J.Q.; Xiao, S.Y.; Wang, W.M. Functional identification of multiple nucleocytoplasmic trafficking signals in the broad-spectrum resistance protein RPW8.2. Planta 2014, 239, 455–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.Y.; Zhang, L.L.; Ma, X.F.; Zhao, Z.X.; Zhao, J.H.; Zhao, J.Q.; Fan, J.; Li, Y.; He, P.; Xiao, S.; et al. Multiple intramolecular trafficking signals in RESISTANCE TO POWDERY MILDEW 8.2 are engaged in activation of cell death and defense. Plant J. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Li, W.; Chen, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.C.; Huang, R. Transcriptional activator TSRF1 reversely regulates pathogen resistance and osmotic stress tolerance in tobacco. Plant Mol. Biol. 2007, 63, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Licausi, F.; Perata, P.; Ohme-Takagi, M.; Ohme-Takagi, M. APETALA2/Ethylene Responsive Factor (AP2/ERF) transcription factors: Mediators of stress responses and developmental programs. New Phytol. 2013, 199, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, A.; Li, X.; Weng, Y.; Liu, Z.; Ashraf, M.F.; Noman, A.; Yang, S.; Ifnan, M.; Qiu, S.; Yang, Y.; et al. CaWRKY22 Acts as a Positive Regulator in Pepper Response to Ralstonia Solanacearum by Constituting Networks with CaWRKY6, CaWRKY27, CaWRKY40, and CaWRKY58. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarowar, S.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, E.N.; Kim, K.D.; Hwang, B.K.; Islam, R.; Shin, J.S. Overexpression of a pepper basic pathogenesis-related protein 1 gene in tobacco plants enhances resistance to heavy metal and pathogen stresses. Plant Cell Rep. 2005, 24, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, F.F.; Wang, Y.N.; Yu, L.; Eulgem, T.; Lai, Y.; Liu, Z.Q.; Wang, X.; Qiu, A.L.; Zhang, T.X.; Lin, J.; et al. CaWRKY40, a WRKY protein of pepper, plays an important role in the regulation of tolerance to heat stress and resistance to Ralstonia solanacearum infection. Plant Cell Environ. 2013, 36, 757–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Cui, J.; Liu, Z.; Luan, Y. SpWRKY6 acts as a positive regulator during tomato resistance to Phytophthora infestans infection. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 506, 787–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Tian, Y.; Xu, J.; Fu, X.; Gao, J.; Wang, B.; Han, H.; Wang, L.; Peng, R.; Yao, Q. A tomato ERF transcription factor, SlERF84, confers enhanced tolerance to drought and salt stress but negatively regulates immunity against Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000. Plant Physiol. Biochem. PPB 2018, 132, 683–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.Y.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, B.; Chan, C.; Yu, J.H.; Lu, Y.P.; Chung, K.; Zimmerli, L. NINJA-associated ERF19 negatively regulates Arabidopsis pattern-triggered immunity. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 1033–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onate-Sanchez, L.; Anderson, J.P.; Young, J.; Singh, K.B. AtERF14, a member of the ERF family of transcription factors, plays a nonredundant role in plant defense. Plant Physiol. 2007, 143, 400–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huot, B.; Yao, J.; Montgomery, B.L.; He, S.Y. Growth–Defense Tradeoffs in Plants: A Balancing Act to Optimize Fitness. Mol. Plant 2014, 7, 1267–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, G.-L. Balancing Immunity and Yield in Crop Plants. Trends Plant Sci. 2017, 22, 1069–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, J.-H.; Zhang, H.-X.; Ali, M.; Wei, A.-M.; Luo, D.-X.; Gong, Z.-H. The CaAP2/ERF064 Regulates Dual Functions in Pepper: Plant Cell Death and Resistance to Phytophthora capsici. Genes 2019, 10, 541. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10070541
Jin J-H, Zhang H-X, Ali M, Wei A-M, Luo D-X, Gong Z-H. The CaAP2/ERF064 Regulates Dual Functions in Pepper: Plant Cell Death and Resistance to Phytophthora capsici. Genes. 2019; 10(7):541. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10070541
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Jing-Hao, Huai-Xia Zhang, Muhammad Ali, Ai-Min Wei, De-Xu Luo, and Zhen-Hui Gong. 2019. "The CaAP2/ERF064 Regulates Dual Functions in Pepper: Plant Cell Death and Resistance to Phytophthora capsici" Genes 10, no. 7: 541. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10070541
APA StyleJin, J.-H., Zhang, H.-X., Ali, M., Wei, A.-M., Luo, D.-X., & Gong, Z.-H. (2019). The CaAP2/ERF064 Regulates Dual Functions in Pepper: Plant Cell Death and Resistance to Phytophthora capsici. Genes, 10(7), 541. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10070541





