The CaAP2/ERF064 Regulates Dual Functions in Pepper: Plant Cell Death and Resistance to Phytophthora capsici
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Phytohormones Treatments
2.2. Pathogen Preparation and Inoculation
2.3. Transient Expression Assay in Tobacco
2.4. Transcriptional Activation and Yeast One-Hybrid Assay
2.5. Virus-Induced Gene Silencing in Pepper
2.6. Tobacco Transformation
2.7. Histochemical Staining
2.8. qRT-PCR Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
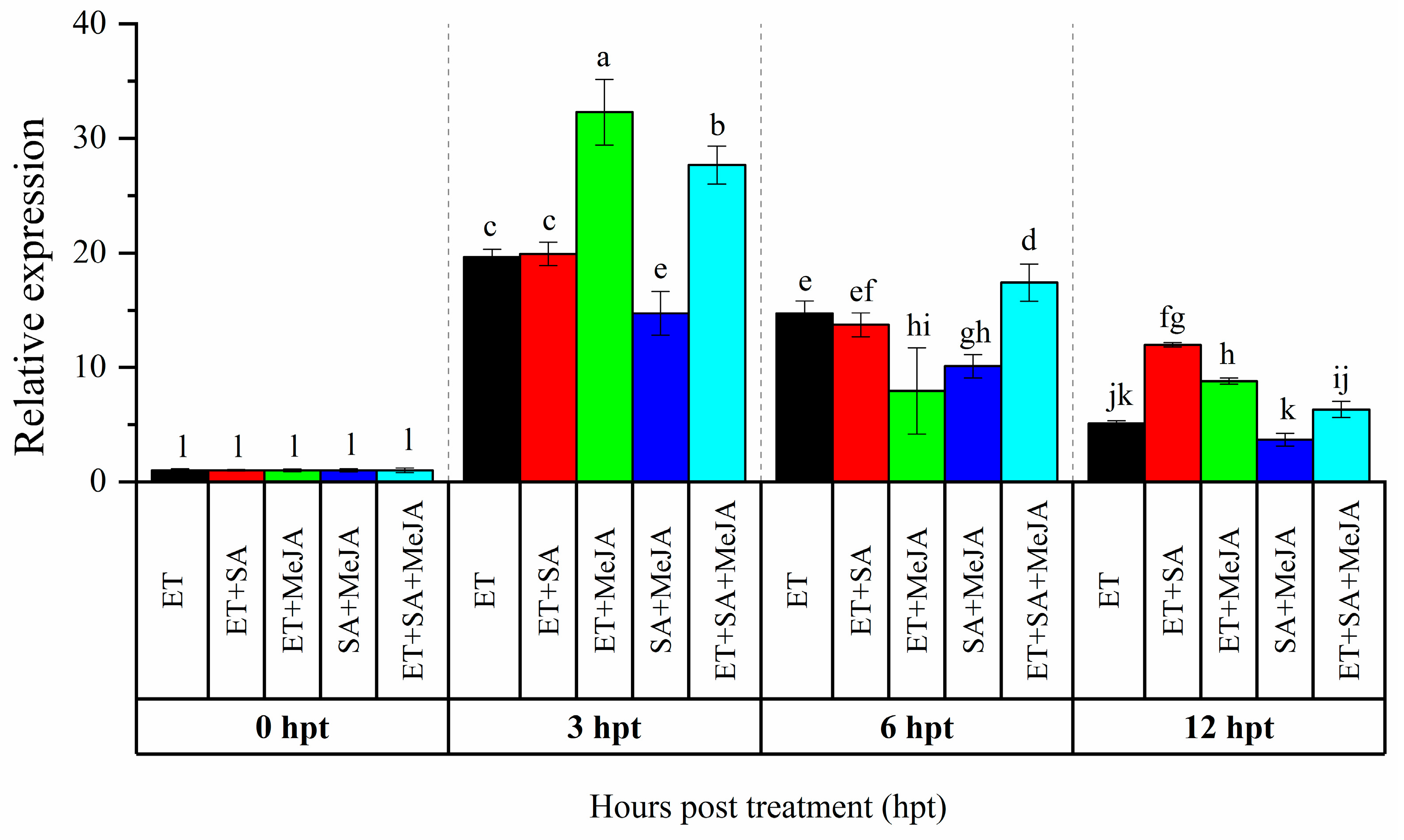
3.1. Expression Analysis of CaAP2/ERF064 in Response to Combinations of Phytohormones
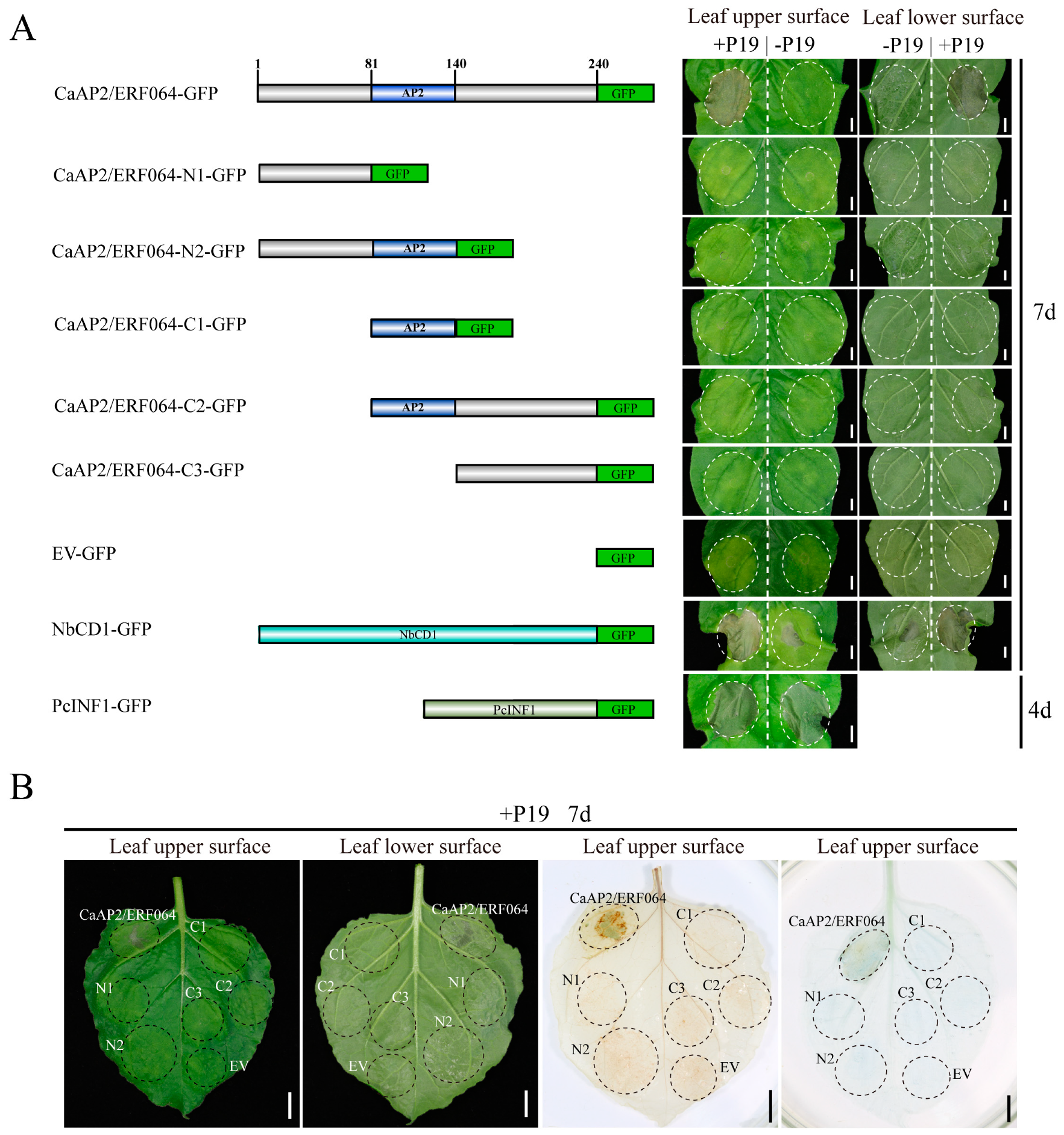
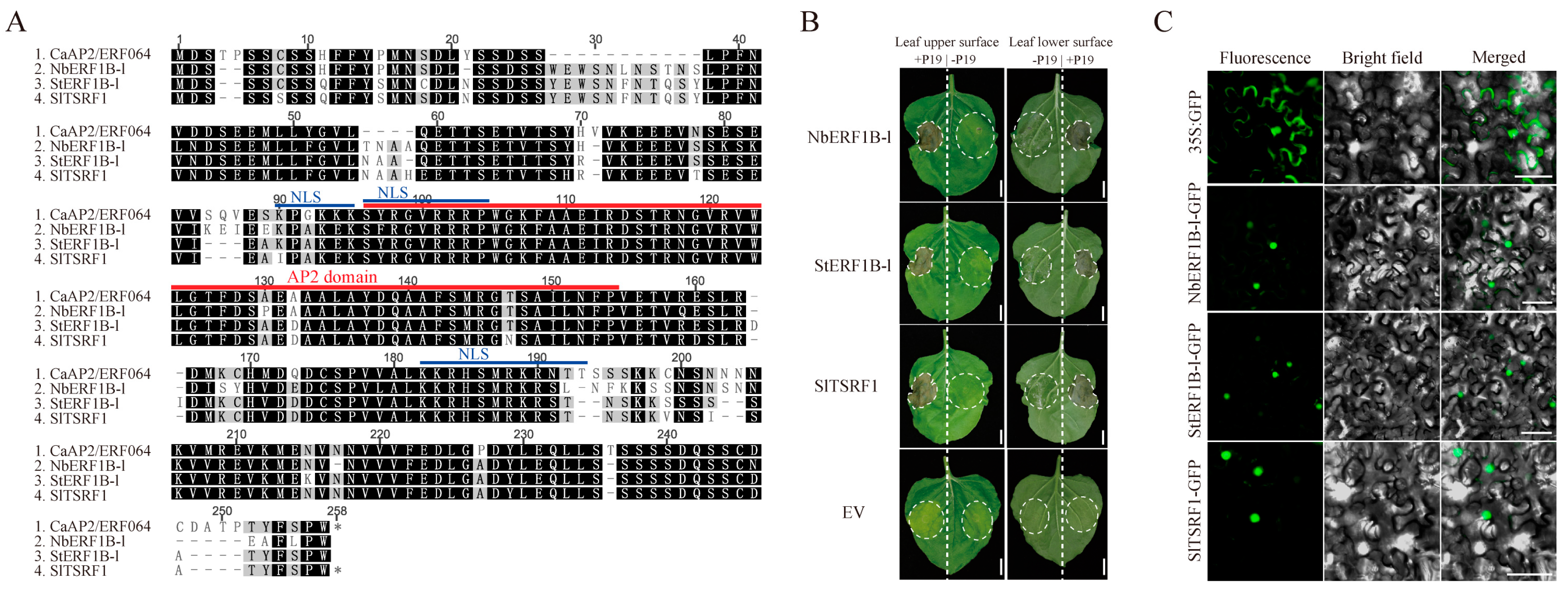
3.2. Transient Over-Expression of CaAP2/ERF064 Induces Cell Death in N. benthamiana
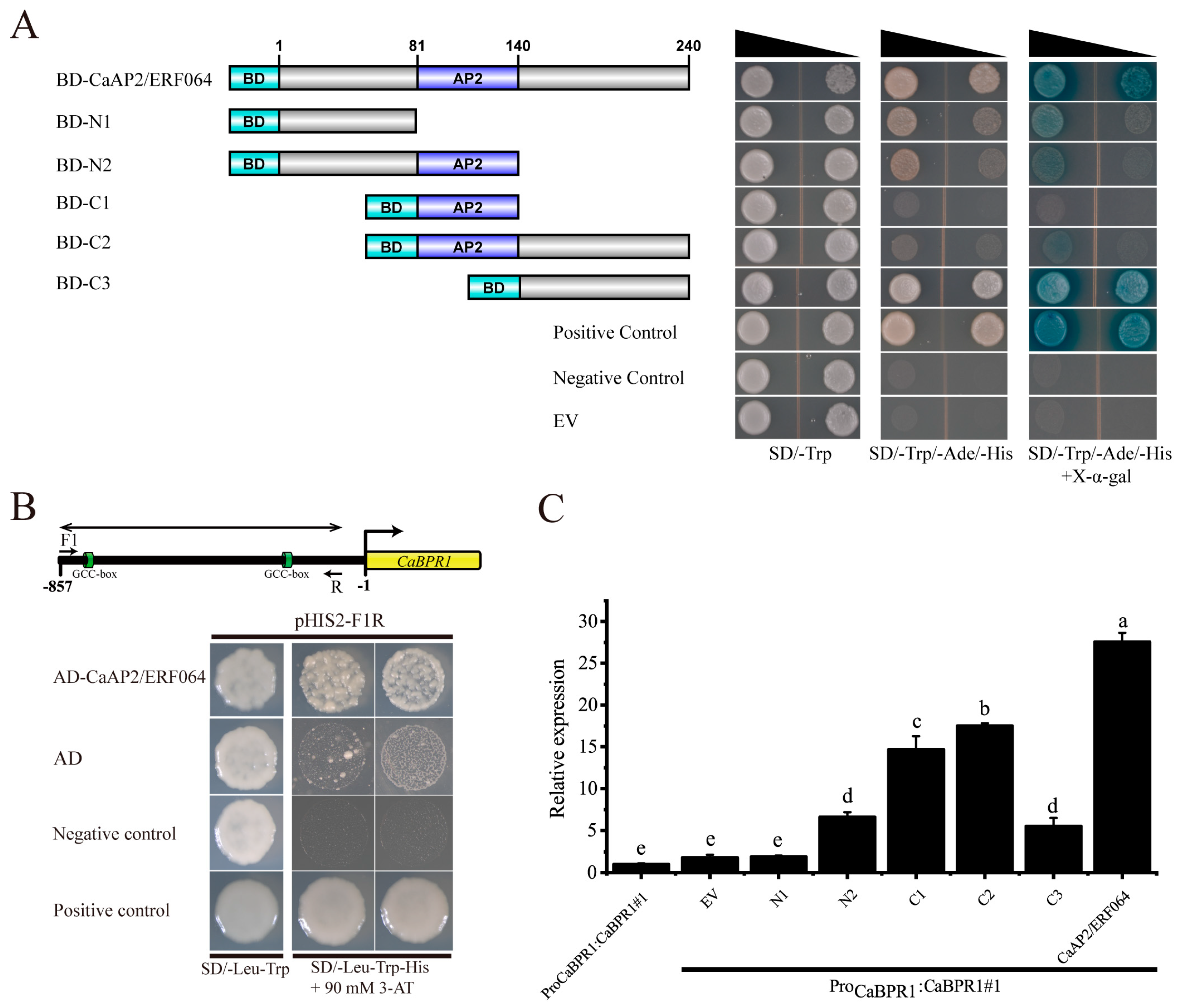
3.3. CaAP2/ERF064 Regulates the Expression of CaBPR1
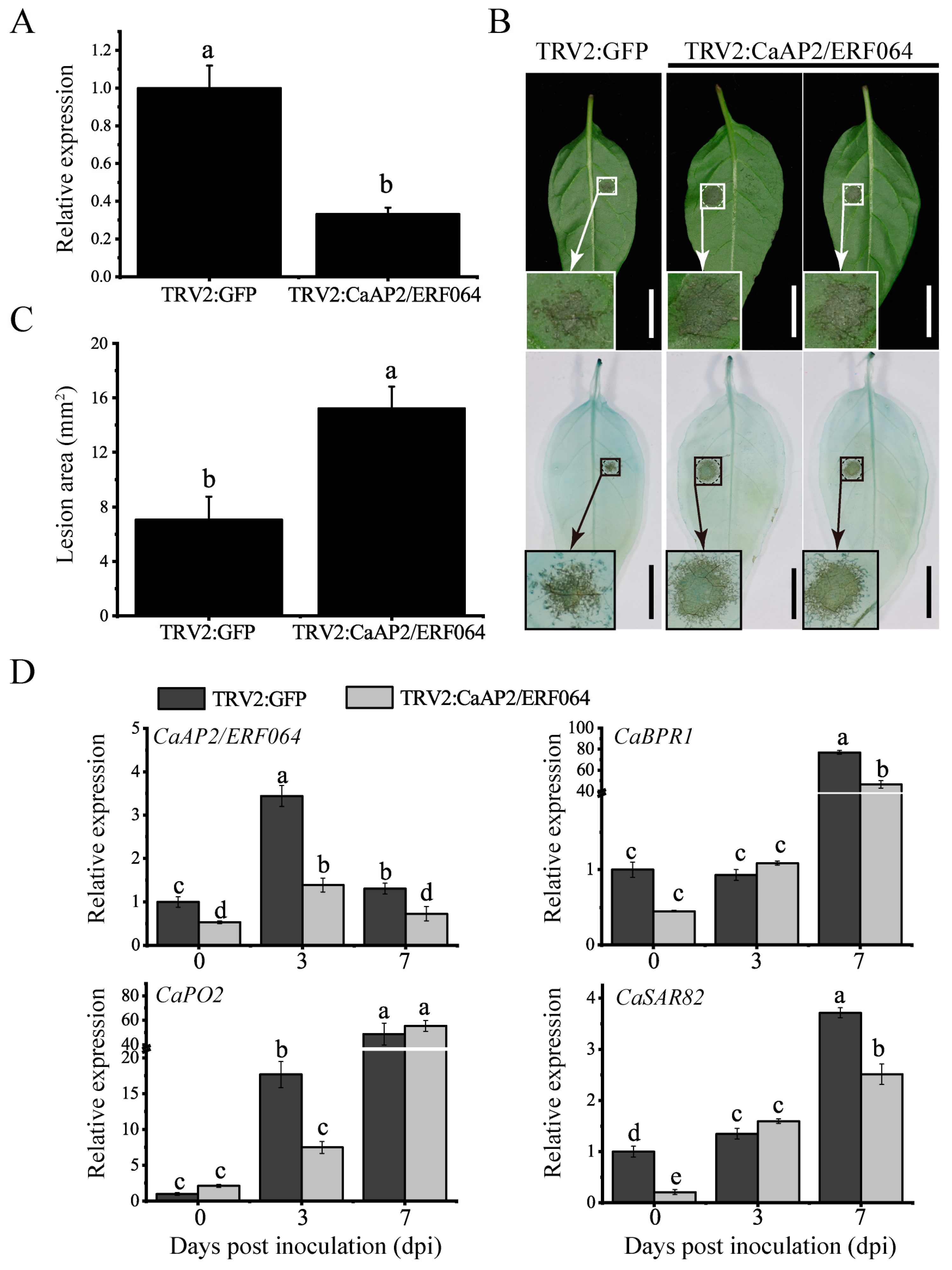
3.4. Silencing of CaAP2/ERF064 in Pepper Enhances the Susceptibility to P. capsici
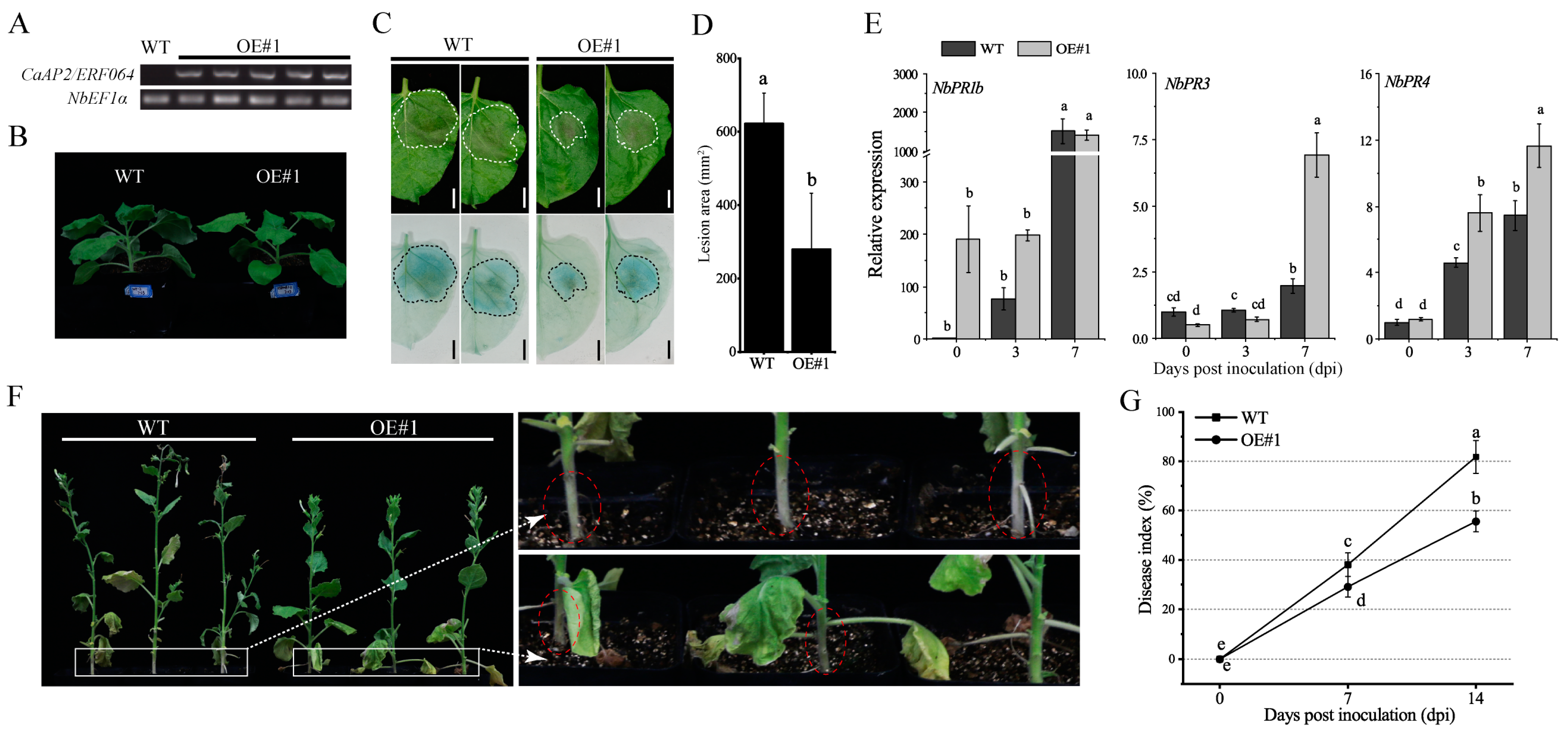
3.5. Ectopic Expression of CaAP2/ERF064 Enhances Tobacco Resistance to P. capsici
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peng, Y.; Van Wersch, R.; Zhang, Y. Convergent and Divergent Signaling in PAMP-Triggered Immunity and Effector-Triggered Immunity. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2018, 31, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chisholm, S.T.; Coaker, G.; Day, B.; Staskawicz, B.J. Host-Microbe Interactions: Shaping the Evolution of the Plant Immune Response. Cell 2006, 124, 803–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.Y.; Catinot, J.; Zimmerli, L. Ethylene response factors in Arabidopsis immunity. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 1231–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, M.; Munné-Bosch, S. Ethylene Response Factors: A Key Regulatory Hub in Hormone and Stress Signaling1. Plant Physiol. 2015, 169, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohme-Takagi, M.; Shinshi, H. Ethylene-inducible DNA binding proteins that interact with an ethylene-responsive element. Plant Cell 1995, 7, 173–182. [Google Scholar]
- Catinot, J.; Huang, J.-B.; Huang, P.-Y.; Tseng, M.-Y.; Chen, Y.-L.; Gu, S.-Y.; Lo, W.-S.; Wang, L.-C.; Chen, Y.-R.; Zimmerli, L. ETHYLENE RESPONSE FACTOR 96 positively regulates Arabidopsis resistance to necrotrophic pathogens by direct binding to GCC elements of jasmonate- and ethylene-responsive defence genes. Plant Cell Environ. 2015, 38, 2721–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Wei, T.; Yin, K.-Q.; Chen, Z.; Gu, H.; Qu, L.-J.; Qin, G. Arabidopsis RAP2.2 plays an important role in plant resistance to Botrytis cinerea and ethylene responses. New Phytol. 2012, 195, 450–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, G.H.; Wan, J.; Kim, H.J.; Nguyen, X.C.; Chung, W.S.; Hong, J.C.; Stacey, G. Ethylene-Responsive Element-Binding Factor 5, ERF5, Is Involved in Chitin-Induced Innate Immunity Response. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2012, 25, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrath, K.C.; Dombrecht, B.; Manners, J.M.; Schenk, P.M.; Edgar, C.I.; MacLean, D.J.; Scheible, W.-R.; Udvardi, M.K.; Kazan, K. Repressor-and Activator-Type Ethylene Response Factors Functioning in Jasmonate Signaling and Disease Resistance Identified via a Genome-Wide Screen of Arabidopsis Transcription Factor Gene Expression. Plant Physiol. 2005, 139, 949–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, M.; Matsui, K.; Hiratsu, K.; Shinshi, H.; Ohme-Takagi, M. Repression Domains of Class II ERF Transcriptional Repressors Share an Essential Motif for Active Repression. Plant Cell 2001, 13, 1959–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; He, Q.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shao, F.; Xie, C. The Potato ERF Transcription Factor StERF3 Negatively Regulates Resistance to Phytophthora infestans and Salt Tolerance in Potato. Plant Cell Physiol. 2015, 56, 992–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, L.D.; Cheng, Y.X.; Wu, J.J.; Cheng, Q.; Li, W.B.; Fan, S.J.; Jiang, L.Y.; Xu, Z.L.; Kong, F.J.; Zhang, D.Y.; et al. Overexpression of GmERF5, a new member of the soybean EAR motif-containing ERF transcription factor, enhances resistance to Phytophthora sojae in soybean. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 2635–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, F.Y.; DeFalco, T.A.; Moeder, W.; Li, B.; Gong, Y.; Liu, X.-M.; Taniguchi, M.; Lumba, S.; Toh, S.; Shan, L.; et al. Arabidopsis ETHYLENE RESPONSE FACTOR 8 (ERF8) has dual functions in ABA signaling and immunity. BMC Plant Boil. 2018, 18, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, F.Y.; Khan, M.; Taniguchi, M.; Mirmiran, A.; Moeder, W.; Lumba, S.; Yoshioka, K.; Desveaux, D. A host–pathogen interactome uncovers phytopathogenic strategies to manipulate plant ABA responses. Plant J. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-H.; Hong, J.-P.; Oh, S.-K.; Lee, S.; Choi, D.; Kim, W. The ethylene-responsive factor like protein 1 (CaERFLP1) of hot pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) interacts in vitro with both GCC and DRE/CRT sequences with different binding affinities: Possible biological roles of CaERFLP1 in response to pathogen infection and high salinity conditions in transgenic tobacco plants. Plant Mol. Boil. 2004, 55, 61–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, S.Y.; Kim, J.-H.; Joung, Y.-H.; Lee, S.; Kim, W.-T.; Yu, S.H.; Choi, D. The Pepper Transcription Factor CaPF1 Confers Pathogen and Freezing Tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2004, 136, 2862–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.H.; Zhang, H.X.; Tan, J.Y.; Yan, M.J.; Li, D.W.; Khan, A.; Gong, Z.H. A New Ethylene-Responsive Factor CaPTI1 Gene of Pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) Involved in the Regulation of Defense Response to Phytophthora capsici. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 6, 1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, E.; Lim, C.W.; Han, S.-W.; Lee, S.C. Functional Analysis of the Pepper Ethylene-Responsive Transcription Factor, CaAIEF1, in Enhanced ABA Sensitivity and Drought Tolerance. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamoun, S.; Furzer, O.; Jones, J.D.; Judelson, H.S.; Ali, G.S.; Dalio, R.J.; Roy, S.G.; Schena, L.; Zambounis, A.; Panabieres, F.; et al. The Top 10 oomycete pathogens in molecular plant pathology. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2015, 16, 413–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamour, K.H.; Stam, R.; Jupe, J.; Huitema, E. The oomycete broad-host-range pathogen Phytophthora capsici. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2012, 13, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.-H.; Wang, M.; Zhang, H.-X.; Khan, A.; Wei, A.-M.; Luo, D.-X.; Gong, Z.-H. Genome-wide identification of the AP2/ERF transcription factor family in pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). Genome 2018, 61, 663–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Meng, Y.; Zhang, M.; Tong, X.; Wang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Quan, J.; Govers, F.; Shan, W. Infection of Arabidopsis thaliana by Phytophthora parasitica and identification of variation in host specificity. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2011, 12, 187–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Mpina, M.H.; Birch, P.R.J.; Bouwmeester, K.; Govers, F. Phytophthora infestans RXLR Effector AVR1 Interacts with Exocyst Component Sec5 to Manipulate Plant Immunity. Plant Physiol. 2015, 169, 1975–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.X.; Ali, M.; Feng, X.H.; Jin, J.H.; Huang, L.J.; Khan, A.; Lv, J.G.; Gao, S.Y.; Luo, D.X.; Gong, Z.H. A Novel Transcription Factor CaSBP12 Gene Negatively Regulates the Defense Response against Phytophthora capsici in Pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 20, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.-E.; Liu, K.-K.; Li, D.-W.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Zhao, Q.; He, Y.-M.; Gong, Z.-H. A Novel Peroxidase CanPOD Gene of Pepper Is Involved in Defense Responses to Phytophtora capsici Infection as well as Abiotic Stress Tolerance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 3158–3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendel, R.R.; Schiemann, J.; Simoens, C. High meiotic stability of a foreign gene introduced into tobacco by Agrobacterium-mediated transformation. Mol. Genet. Genom. 1987, 207, 171–175. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, D.S.; Hwang, I.S.; Hwang, B.K. Requirement of the Cytosolic Interaction between PATHOGENESIS-RELATED PROTEIN10 and LEUCINE-RICH REPEAT PROTEIN1 for Cell Death and Defense Signaling in Pepper. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 1675–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(T)(-Delta Delta C) method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholthof, H.B. The Tombusvirus-encoded P19: From irrelevance to elegance. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2006, 4, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silhavy, D.; Burgyán, J. Effects and side-effects of viral RNA silencing suppressors on short RNAs. Trends Plant Sci. 2004, 9, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.K.; Lee, S.C.; Hwang, B.K. Activation of pepper basic PR-1 gene promoter during defense signaling to pathogen, abiotic and environmental stresses. Gene 2005, 356, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.J.; Hwang, B.K. Pepper gene encoding a basic pathogenesis-related 1 protein is pathogen and ethylene inducible. Physiol. Plant. 2000, 108, 51–60. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, H.W.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, S.C.; Hong, J.K.; Hwang, B.K. Hydrogen Peroxide Generation by the Pepper Extracellular Peroxidase CaPO2 Activates Local and Systemic Cell Death and Defense Response to Bacterial Pathogens. Plant Physiol. 2007, 145, 890–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.C.; Hwang, B.K. Identification of the pepper SAR8.2 gene as a molecular marker for pathogen infection, abiotic elicitors and environmental stresses in Capsicum annuum. Planta 2003, 216, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broekaert, W.F.; Delauré, S.L.; De Bolle, M.F.; Cammue, B.P. The Role of Ethylene in Host-Pathogen Interactions. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2006, 44, 393–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieterse, C.M.; Van Der Does, D.; Zamioudis, C.; Leon-Reyes, A.; Van Wees, S.C. Hormonal Modulation of Plant Immunity. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Boil. 2012, 28, 489–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunkel, B.N.; Brooks, D.M. Cross talk between signaling pathways in pathogen defense. Curr. Opin. Plant Boil. 2002, 5, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo, O.; Piqueras, R.; Sánchez-Serrano, J.J.; Solano, R. ETHYLENE RESPONSE FACTOR1 integrates signals from ethylene and jasmonate pathways in plant defense. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin Nasir, K.H.; Takahashi, Y.; Ito, A.; Saitoh, H.; Matsumura, H.; Kanzaki, H.; Shimizu, T.; Ito, M.; Fujisawa, S.; Sharma, P.C.; et al. High-throughput in planta expression screening identifies a class II ethylene-responsive element binding factor-like protein that regulates plant cell death and non-host resistance. Plant J. 2005, 43, 491–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata, T.; Kida, Y.; Arai, T.; Kishi, Y.; Manago, Y.; Murai, M.; Matsushita, Y. Overexpression of tobacco ethylene response factor NtERF3 gene and its homologues from tobacco and rice induces hypersensitive response-like cell death in tobacco. J. Gen. Plant Pathol. 2012, 78, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata, T.; Kida, Y.; Tochigi, M.; Matsushita, Y. Analysis of the cell death-inducing ability of the ethylene response factors in group VIII of the AP2/ERF family. Plant Sci. 2013, 209, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsushita, T.; Mochizuki, N.; Nagatani, A. Dimers of the N-terminal domain of phytochrome B are functional in the nucleus. Nature 2003, 424, 571–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.Y.; Shi, Y.; Lei, Y.; Li, Y.; Fan, J.; Xu, Y.J.; Ma, X.F.; Zhao, J.Q.; Xiao, S.Y.; Wang, W.M. Functional identification of multiple nucleocytoplasmic trafficking signals in the broad-spectrum resistance protein RPW8.2. Planta 2014, 239, 455–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.Y.; Zhang, L.L.; Ma, X.F.; Zhao, Z.X.; Zhao, J.H.; Zhao, J.Q.; Fan, J.; Li, Y.; He, P.; Xiao, S.; et al. Multiple intramolecular trafficking signals in RESISTANCE TO POWDERY MILDEW 8.2 are engaged in activation of cell death and defense. Plant J. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Li, W.; Chen, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.C.; Huang, R. Transcriptional activator TSRF1 reversely regulates pathogen resistance and osmotic stress tolerance in tobacco. Plant Mol. Biol. 2007, 63, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Licausi, F.; Perata, P.; Ohme-Takagi, M.; Ohme-Takagi, M. APETALA2/Ethylene Responsive Factor (AP2/ERF) transcription factors: Mediators of stress responses and developmental programs. New Phytol. 2013, 199, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, A.; Li, X.; Weng, Y.; Liu, Z.; Ashraf, M.F.; Noman, A.; Yang, S.; Ifnan, M.; Qiu, S.; Yang, Y.; et al. CaWRKY22 Acts as a Positive Regulator in Pepper Response to Ralstonia Solanacearum by Constituting Networks with CaWRKY6, CaWRKY27, CaWRKY40, and CaWRKY58. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarowar, S.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, E.N.; Kim, K.D.; Hwang, B.K.; Islam, R.; Shin, J.S. Overexpression of a pepper basic pathogenesis-related protein 1 gene in tobacco plants enhances resistance to heavy metal and pathogen stresses. Plant Cell Rep. 2005, 24, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, F.F.; Wang, Y.N.; Yu, L.; Eulgem, T.; Lai, Y.; Liu, Z.Q.; Wang, X.; Qiu, A.L.; Zhang, T.X.; Lin, J.; et al. CaWRKY40, a WRKY protein of pepper, plays an important role in the regulation of tolerance to heat stress and resistance to Ralstonia solanacearum infection. Plant Cell Environ. 2013, 36, 757–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Cui, J.; Liu, Z.; Luan, Y. SpWRKY6 acts as a positive regulator during tomato resistance to Phytophthora infestans infection. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 506, 787–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Tian, Y.; Xu, J.; Fu, X.; Gao, J.; Wang, B.; Han, H.; Wang, L.; Peng, R.; Yao, Q. A tomato ERF transcription factor, SlERF84, confers enhanced tolerance to drought and salt stress but negatively regulates immunity against Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000. Plant Physiol. Biochem. PPB 2018, 132, 683–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.Y.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, B.; Chan, C.; Yu, J.H.; Lu, Y.P.; Chung, K.; Zimmerli, L. NINJA-associated ERF19 negatively regulates Arabidopsis pattern-triggered immunity. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 1033–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onate-Sanchez, L.; Anderson, J.P.; Young, J.; Singh, K.B. AtERF14, a member of the ERF family of transcription factors, plays a nonredundant role in plant defense. Plant Physiol. 2007, 143, 400–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huot, B.; Yao, J.; Montgomery, B.L.; He, S.Y. Growth–Defense Tradeoffs in Plants: A Balancing Act to Optimize Fitness. Mol. Plant 2014, 7, 1267–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, G.-L. Balancing Immunity and Yield in Crop Plants. Trends Plant Sci. 2017, 22, 1069–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, J.-H.; Zhang, H.-X.; Ali, M.; Wei, A.-M.; Luo, D.-X.; Gong, Z.-H. The CaAP2/ERF064 Regulates Dual Functions in Pepper: Plant Cell Death and Resistance to Phytophthora capsici. Genes 2019, 10, 541. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10070541
Jin J-H, Zhang H-X, Ali M, Wei A-M, Luo D-X, Gong Z-H. The CaAP2/ERF064 Regulates Dual Functions in Pepper: Plant Cell Death and Resistance to Phytophthora capsici. Genes. 2019; 10(7):541. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10070541
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Jing-Hao, Huai-Xia Zhang, Muhammad Ali, Ai-Min Wei, De-Xu Luo, and Zhen-Hui Gong. 2019. "The CaAP2/ERF064 Regulates Dual Functions in Pepper: Plant Cell Death and Resistance to Phytophthora capsici" Genes 10, no. 7: 541. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10070541
APA StyleJin, J.-H., Zhang, H.-X., Ali, M., Wei, A.-M., Luo, D.-X., & Gong, Z.-H. (2019). The CaAP2/ERF064 Regulates Dual Functions in Pepper: Plant Cell Death and Resistance to Phytophthora capsici. Genes, 10(7), 541. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10070541





