The Biochemical Activities of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae Pif1 Helicase Are Regulated by Its N-Terminal Domain
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Yeast Strains, Media, and Other Reagents
2.2. Recombinant Proteins
2.3. Telomerase Assays
2.4. Southern Blotting
2.5. Helicase Assays
2.6. Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assays
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
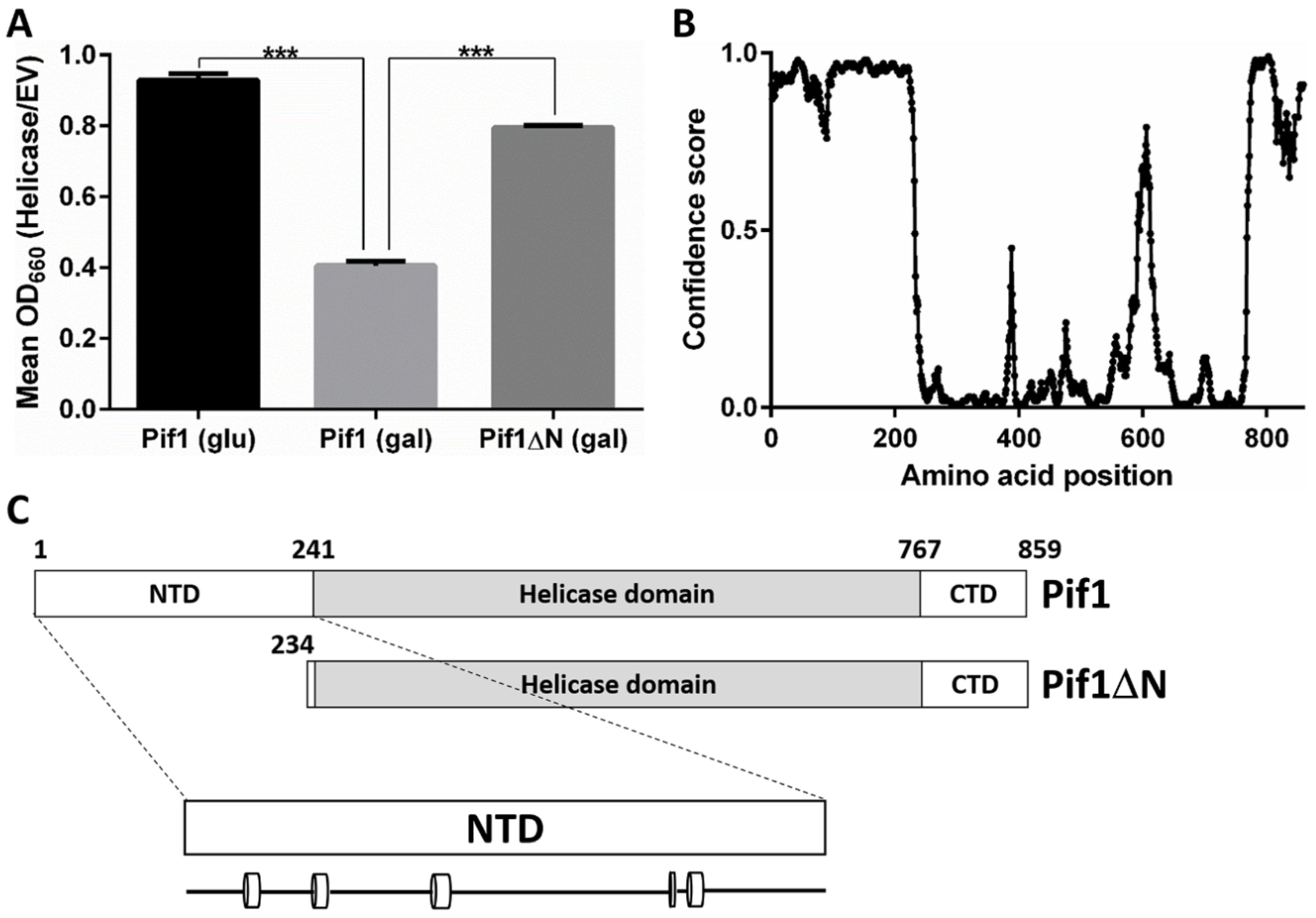
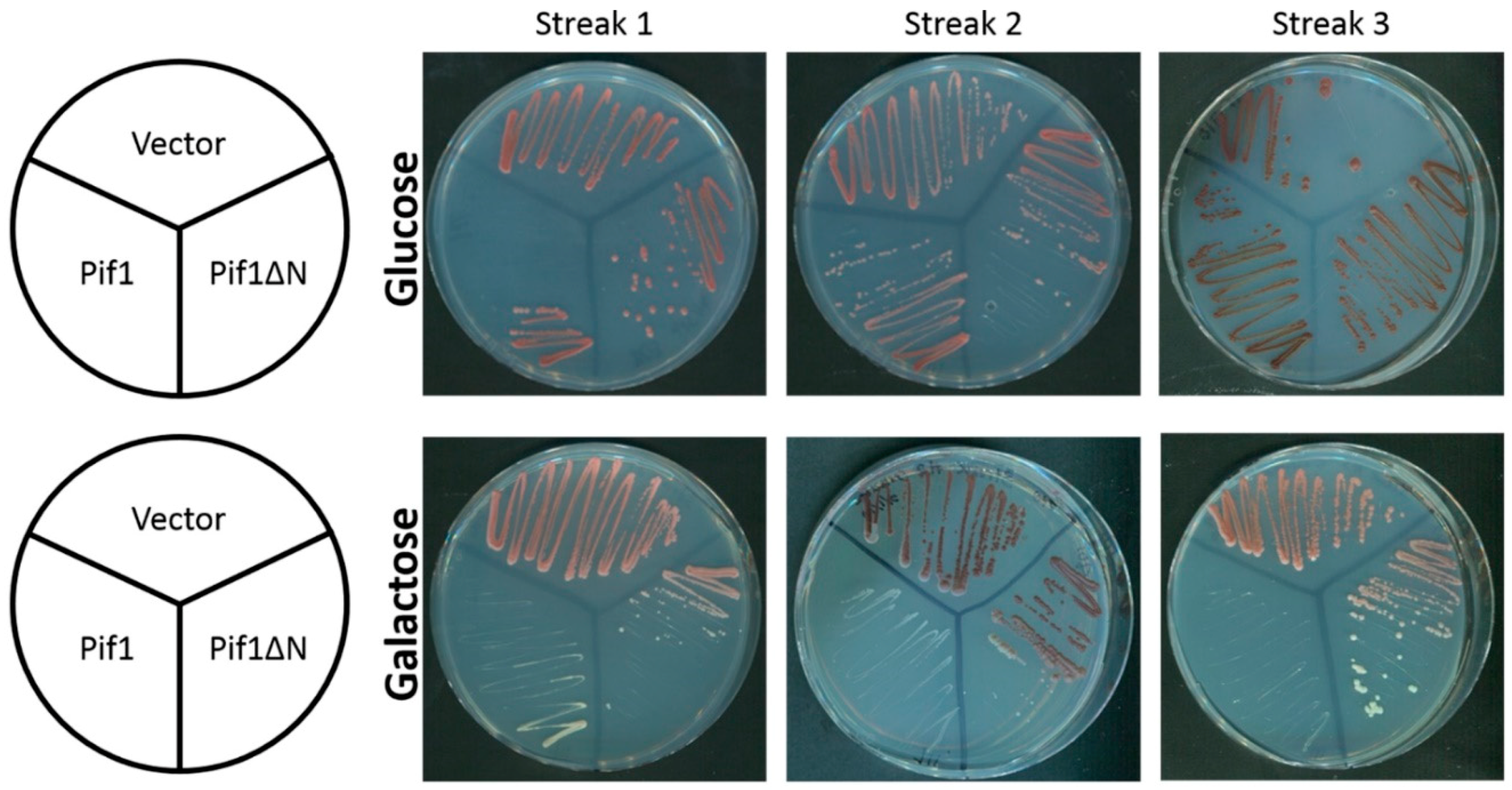
3.1. Removal of the Pif1 NTD Relieves the Toxicity of Pif1 Overexpression
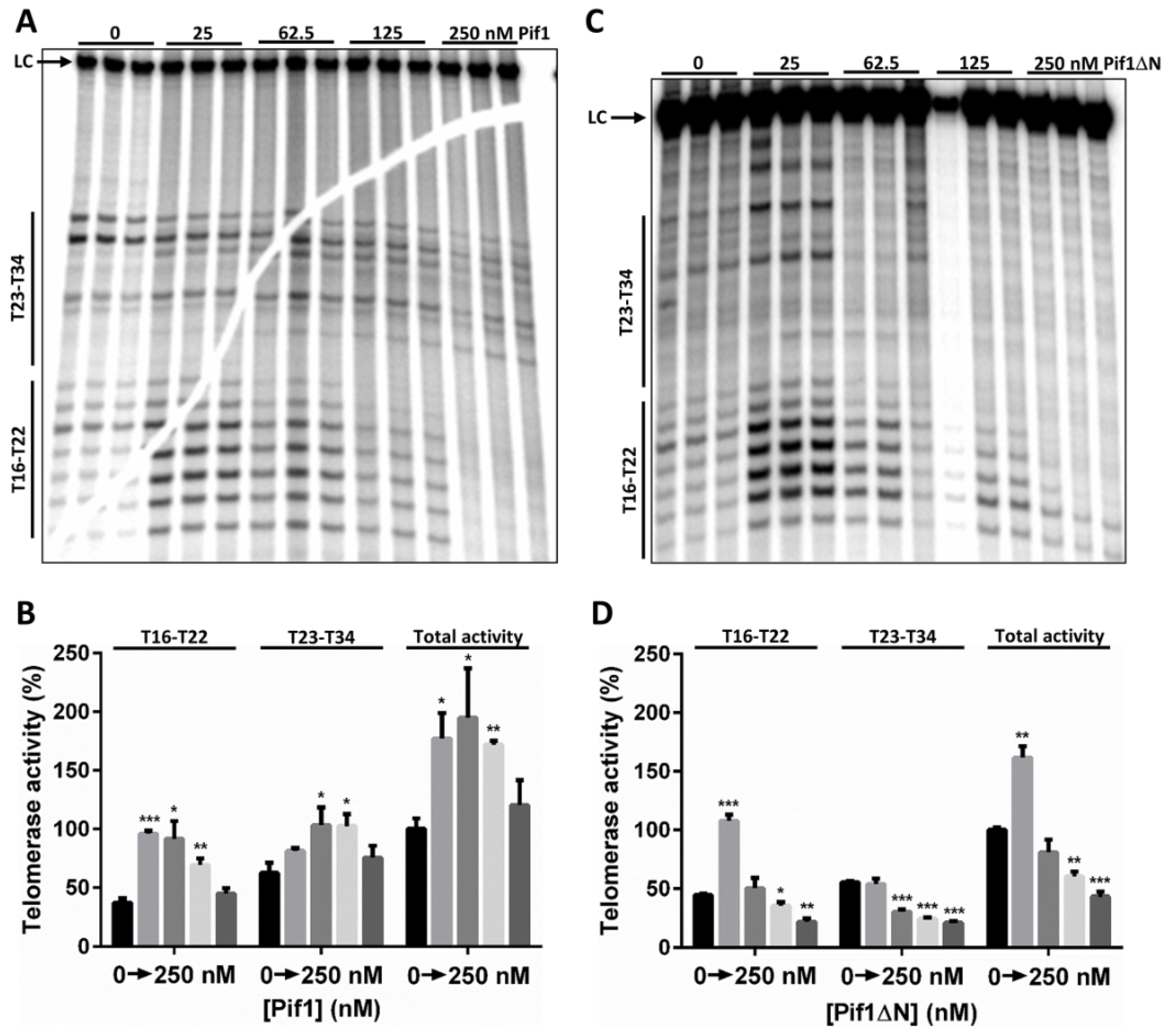
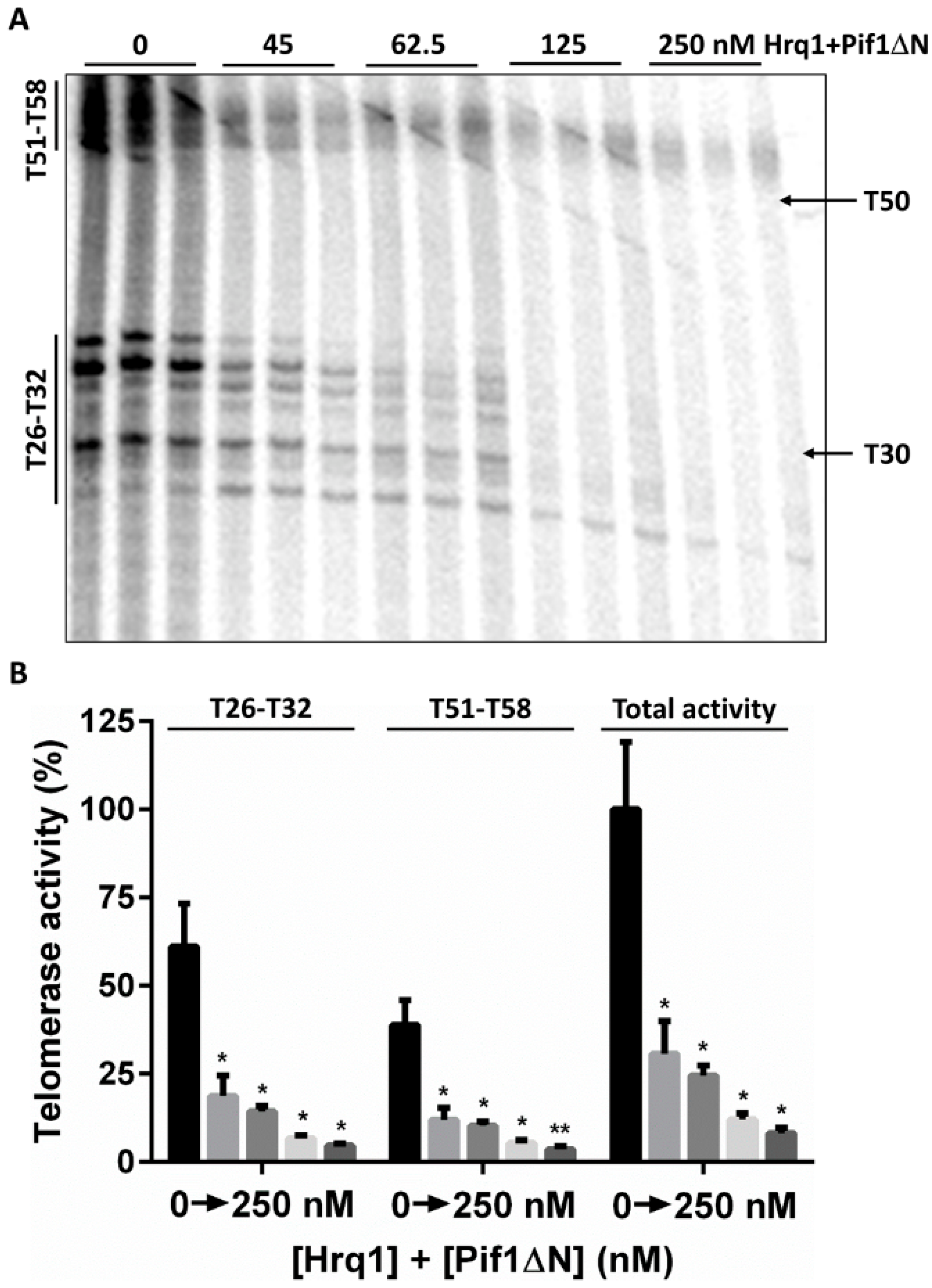
3.2. In Vitro Pif1ΔN Is a More Potent Telomerase Inhibitor Than Full-Length Pif1
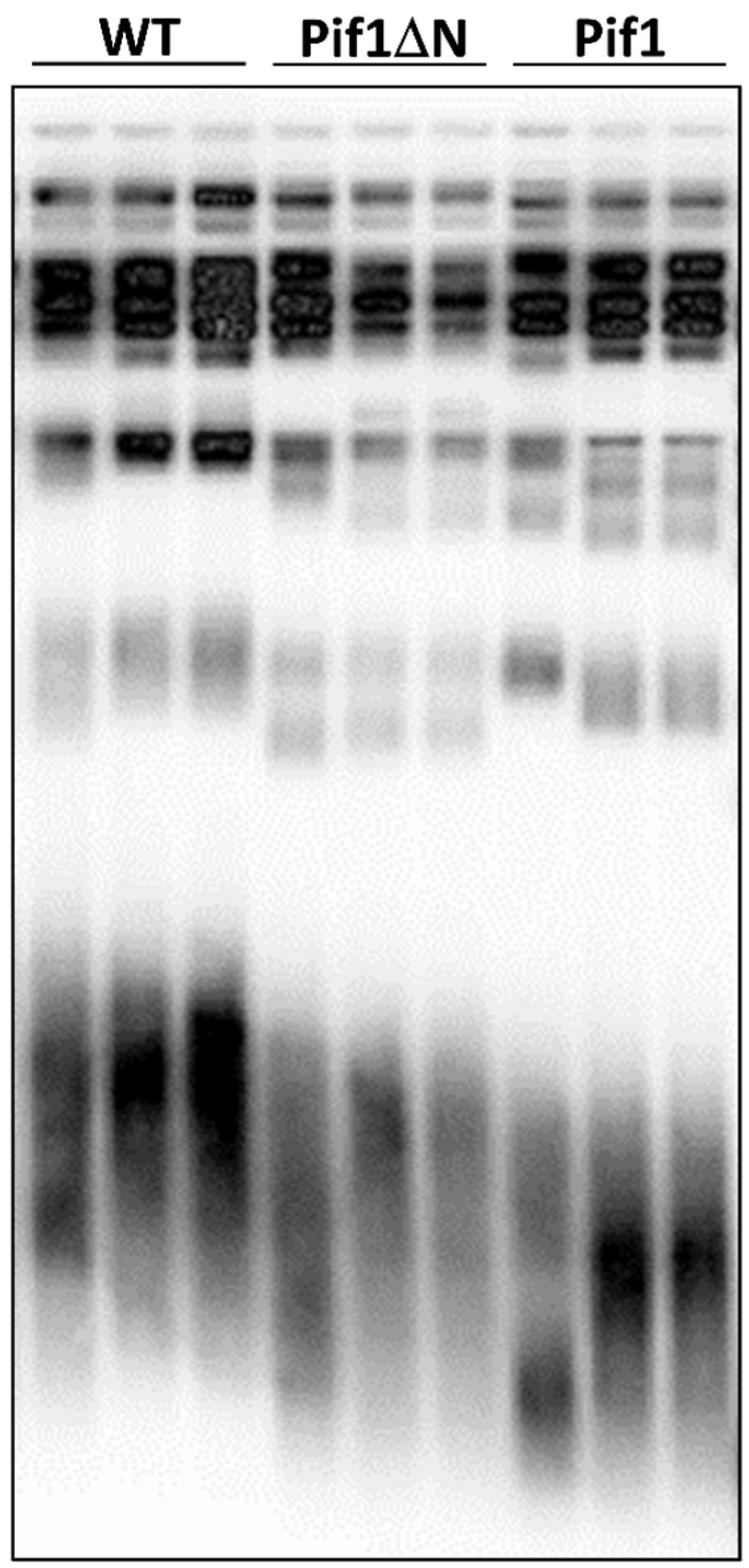
3.3. Chronic Overexpression of Pif1ΔN Does Not Lead to Telomere Length Crisis
3.4. Pif1ΔN Expression Has a Mild Effect on Bulk Telomere Length In Vivo
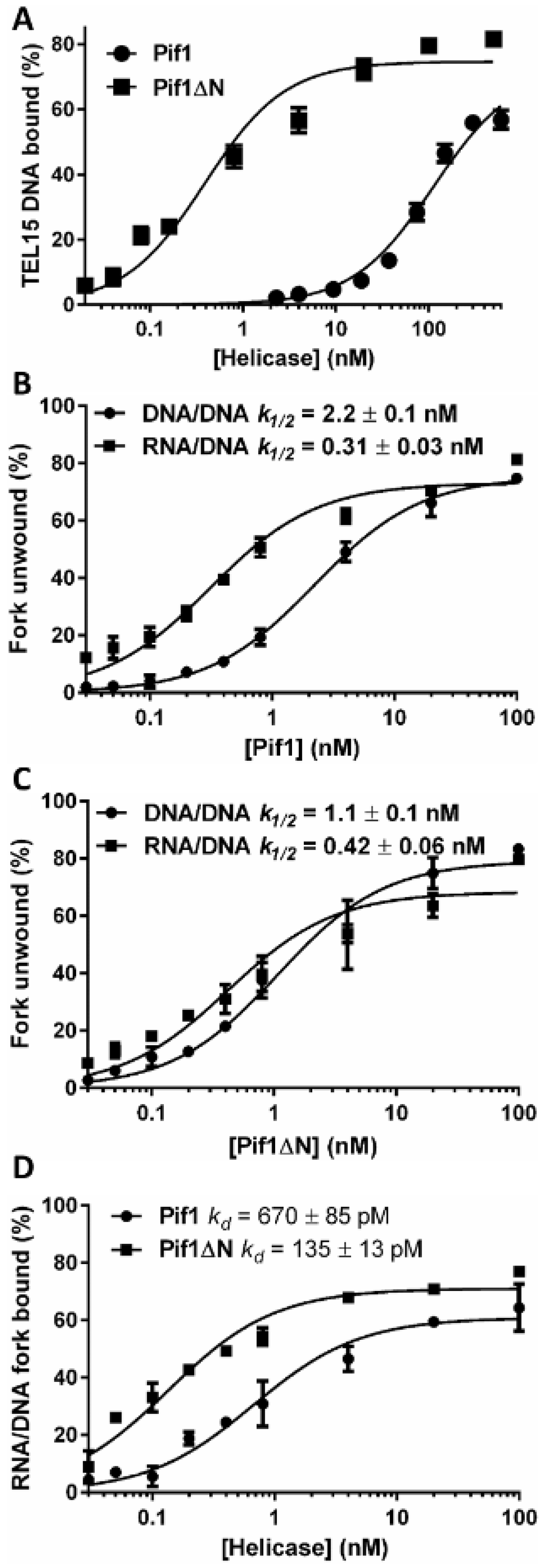
3.5. Truncation of the Pif1 N-Terminus Affects DNA Binding and Unwinding by the Helicase
3.6. Is the Pif1 NTD Necessary to Interact with Hrq1?
4. Discussion
4.1. The Pif1 NTD Is Involved in Regulating Telomerase Activity
4.2. Is the Pif1 NTD a Site of Protein–Protein Interaction?
4.3. Is the Pif1 NTD a Site of Nucleic Acid Interaction?
4.4. PIF1 Perspectives
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abdelhaleem, M. Helicases: An overview. Methods Mol. Biol. 2010, 587, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bochman, M.L. Roles of DNA helicases in the maintenance of genome integrity. Mol. Cell. Oncol. 2014, 1, e963429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Eki, T. Genome-wide survey and comparative study of helicase superfamily members in sequences genomes. In Advances in Genetics Research; Urbano, K.V., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2010; Volume 3, pp. 168–203. [Google Scholar]
- Berger, J.M. Snapshot: Nucleic acid helicases and translocases. Cell 2008, 134, 888–888.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Li, B.; Gray, M.D.; Oshima, J.; Mian, I.S.; Campisi, J. The premature ageing syndrome protein, wrn, is a 3′-->5′ exonuclease. Nat. Genet. 1998, 20, 114–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, C.M.; Wang, J.C.; Noguchi, H.; Imasaki, T.; Takagi, Y.; Bochman, M.L. Yeast hrq1 shares structural and functional homology with the disease-linked human recq4 helicase. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 5217–5230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, K.A.; Gangloff, S.; Rothstein, R. The recq DNA helicases in DNA repair. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2010, 44, 393–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y. Rothmund-thomson syndrome helicase, recq4: On the crossroad between DNA replication and repair. DNA Repair 2010, 9, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bochman, M.L.; Sabouri, N.; Zakian, V.A. Unwinding the functions of the pif1 family helicases. DNA Repair 2010, 9, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochman, M.L.; Judge, C.P.; Zakian, V.A. The pif1 family in prokaryotes: What are our helicases doing in your bacteria? Mol. Biol. Cell 2011, 22, 1955–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bessler, J.B.; Zakian, V.A. The amino terminus of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae DNA helicase rrm3p modulates protein function altering replication and checkpoint activity. Genetics 2004, 168, 1205–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andis, N.M.; Sausen, C.W.; Alladin, A.; Bochman, M.L. The wyl domain of the pif1 helicase from the thermophilic bacterium thermotoga elfii is an accessory single-stranded DNA binding module. Biochemistry 2018, 57, 1108–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Douglas, N.W.; Heine, M.J.; Williams, G.M.; Winther-Larsen, H.C.; Meaden, P.G. The stl1 gene of saccharomyces cerevisiae is predicted to encode a sugar transporter-like protein. Gene 1994, 146, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickens, D.G.; Rogers, C.M.; Bochman, M.L. The saccharomyces cerevisiae hrq1 and pif1 DNA helicases synergistically modulate telomerase activity in vitro. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 14481–14496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sikorski, R.S.; Hieter, P. A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 1989, 122, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Paeschke, K.; Bochman, M.L.; Garcia, P.D.; Cejka, P.; Friedman, K.L.; Kowalczykowski, S.C.; Zakian, V.A. Pif1 family helicases suppress genome instability at g-quadruplex motifs. Nature 2013, 497, 458–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Adkins, C.J.; Cartwright, B.R.; Friedman, K.L. Yeast est2p affects telomere length by influencing association of rap1p with telomeric chromatin. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2008, 28, 2380–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Rogers, C.M.; Bochman, M.L. Saccharomyces cerevisiae hrq1 helicase activity is affected by the sequence but not the length of single-stranded DNA. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 486, 1116–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boule, J.; Vega, L.; Zakian, V. The yeast pif1p helicase removes telomerase from DNA. Nature 2005, 438, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boule, J.B.; Zakian, V.A. Characterization of the helicase activity and anti-telomerase properties of yeast pif1p in vitro. In Helicases Methods and Protocols, Methods in Molecular Biology Series; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2009; Volume 587, pp. 359–376. 1p. [Google Scholar]
- Gietz, R.D.; Schiestl, R.H.; Willems, A.; Woods, R. Studies on the transformation of intact yeast cells by the liac/ss-DNA/peg procedure. Yeast 1995, 11, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osburn, K.; Amaral, J.; Metcalf, S.R.; Nickens, D.M.; Rogers, C.M.; Sausen, C.; Caputo, R.; Miller, J.; Li, H.; Tennessen, J.M.; et al. Primary souring: A novel bacteria-free method for sour beer production. Food Microbiol. 2018, 70, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochman, M.L.; Paeschke, K.; Chan, A.; Zakian, V.A. Hrq1, a homolog of the human recq4 helicase, acts catalytically and structurally to promote genome integrity. Cell Rep. 2014, 6, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, M.; Luke, B.; Kraft, C.; Li, Z.; Peter, M.; Lingner, J.; Rothstein, R. Telomerase is essential to alleviate pif1-induced replication stress at telomeres. Genetics 2009, 183, 779–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosoy, D.; Lue, N.F. Yeast telomerase is capable of limited repeat addition processivity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Jones, D.T.; Cozzetto, D. Disopred3: Precise disordered region predictions with annotated protein-binding activity. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 857–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wellinger, R.J.; Zakian, V.A. Everything you ever wanted to know about saccharomyces cerevisiae telomeres: Beginning to end. Genetics 2012, 191, 1073–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.-Q.; Monson, E.M.; Teng, S.-C.; Schulz, V.P.; Zakian, V.A. The pif1p helicase, a catalytic inhibitor of telomerase lengthening of yeast telomeres. Science 2000, 289, 771–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, S.B.; Hall, D.W. Spontaneous mutations in diploid saccharomyces cerevisiae: More beneficial than expected. Genetics 2004, 168, 1817–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, V.P.; Zakian, V.A. The saccharomyces pif1 DNA helicase inhibits telomere elongation and de novo telomere formation. Cell 1994, 76, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chib, S.; Byrd, A.K.; Raney, K.D. Yeast helicase pif1 unwinds RNA:DNA hybrids with higher processivity than DNA:DNA duplexes. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 5889–5901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, J.H.; Shoemaker, B.A.; Garbuzynskiy, S.O.; Lobanov, M.Y.; Galzitskaya, O.V.; Panchenko, A.R. Intrinsic disorder in protein interactions: Insights from a comprehensive structural analysis. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2009, 5, e1000316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makovets, S.; Blackburn, E.H. DNA damage signalling prevents deleterious telomere addition at DNA breaks. Nat. Cell. Biol. 2009, 11, 1383–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasianovich, Y.; Harrington, L.A.; Makovets, S. Break-induced replication requires DNA damage-induced phosphorylation of pif1 and leads to telomere lengthening. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, S.E.; Ajazi, A.; Carotenuto, W.; Foiani, M.; Giannattasio, M. Rad53-mediated regulation of rrm3 and pif1 DNA helicases contributes to prevention of aberrant fork transitions under replication stress. Cell Rep. 2015, 13, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, B.; Tandon, R.; Attri, P.; Bhatia, R. Chemical crosslinking: Role in protein and peptide science. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2017, 18, 946–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makarova, K.S.; Anantharaman, V.; Grishin, N.V.; Koonin, E.V.; Aravind, L. Carf and wyl domains: Ligand-binding regulators of prokaryotic defense systems. Front. Genet. 2014, 5, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garbacz, M.A.; Lujan, S.A.; Burkholder, A.B.; Cox, P.B.; Wu, Q.; Zhou, Z.X.; Haber, J.E.; Kunkel, T.A. Evidence that DNA polymerase delta contributes to initiating leading strand DNA replication in saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, M.L.; Pike, J.E.; Wang, W.; Burgers, P.M.; Campbell, J.L.; Bambara, R.A. Pif1 helicase directs eukaryotic okazaki fragments toward the two-nuclease cleavage pathway for primer removal. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 27483–27493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chisholm, K.M.; Aubert, S.D.; Freese, K.P.; Zakian, V.A.; King, M.C.; Welcsh, P.L. A genomewide screen for suppressors of alu-mediated rearrangements reveals a role for pif1. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| pRS414 | TRP1, ARS1, CEN4 empty vector [15] |
| pMB282 | Pif1-3xFLAG cloned into pRS414 under the control of the RRM3 regulatory sequences [16] |
| pMB327 | Pif1ΔN-3xFLAG cloned into pRS414 under the control of the RRM3 regulatory sequences [16] |
| pESC-URA | Multi-copy vector enabling epitope tagging of genes cloned under the control of the bidirectional GAL1,10 promoter |
| pUC19(+)TEL | pUC19 harboring yeast telomeric repeat sequence DNA cloned into the EcoRI site [17] |
| pMB526 | Pif1 cloned into pESC-URA, enabling galactose induction and epitope-tagged with FLAG |
| pMB540 | Pif1ΔN cloned into pESC-URA, enabling galactose induction and epitope-tagged with FLAG |
| pSUMO-Pif1 | Nuclear isoform of Pif1 cloned into the pSUMO vector |
| pSUMO-Pif1ΔN | Pif1ΔN cloned into the pSUMO vector |
| Name | Sequence (5′-3′) | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| MB1571 | *rGrGrUrGrUrGrGrUrGrUrGrGrGrUrGrUrGrGrUrGrUrGrGrGrUrCrArCrArGrUrGrArGrUrGrUrArUrCrGrCrArArG | RNA–DNA hybrid fork substrate |
| MB1572 | GAACGCTATGTGAGTGACACTGGGTCACCACACCCACACCACACC | Fork substrates |
| MB1596 | GGTGTGGTGTGGGTGTGGTGTGGGTCACAGTGAGTGTATCGCAAG | DNA–DNA fork substrate |
| Tel15 | TGTGGTGTGTGTGGG | EMSAs and in vitro telomerase assays |
| Tel30 | CGCCATGCTGATCCGTGTGGTGTGTGTGGG | EMSAs |
| Tel50 | GTGTGGGTGTGGTGTGGGTGTGGTGTGGGTGTGTGGTGTGGTGTGTGTGG | In vitro telomerase assays |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nickens, D.G.; Sausen, C.W.; Bochman, M.L. The Biochemical Activities of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae Pif1 Helicase Are Regulated by Its N-Terminal Domain. Genes 2019, 10, 411. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10060411
Nickens DG, Sausen CW, Bochman ML. The Biochemical Activities of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae Pif1 Helicase Are Regulated by Its N-Terminal Domain. Genes. 2019; 10(6):411. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10060411
Chicago/Turabian StyleNickens, David G., Christopher W. Sausen, and Matthew L. Bochman. 2019. "The Biochemical Activities of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae Pif1 Helicase Are Regulated by Its N-Terminal Domain" Genes 10, no. 6: 411. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10060411
APA StyleNickens, D. G., Sausen, C. W., & Bochman, M. L. (2019). The Biochemical Activities of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae Pif1 Helicase Are Regulated by Its N-Terminal Domain. Genes, 10(6), 411. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10060411






