Predicting MiRNA-Disease Association by Latent Feature Extraction with Positive Samples
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Disease Semantic Similarity Network
2.2. miRNAs-Disease Association Network
2.3. miRNAs Functional Similarity Network
2.4. Data Fusion
2.5. Loss Function
2.6. Optimization
2.7. Prediction
3. Results and Discussion
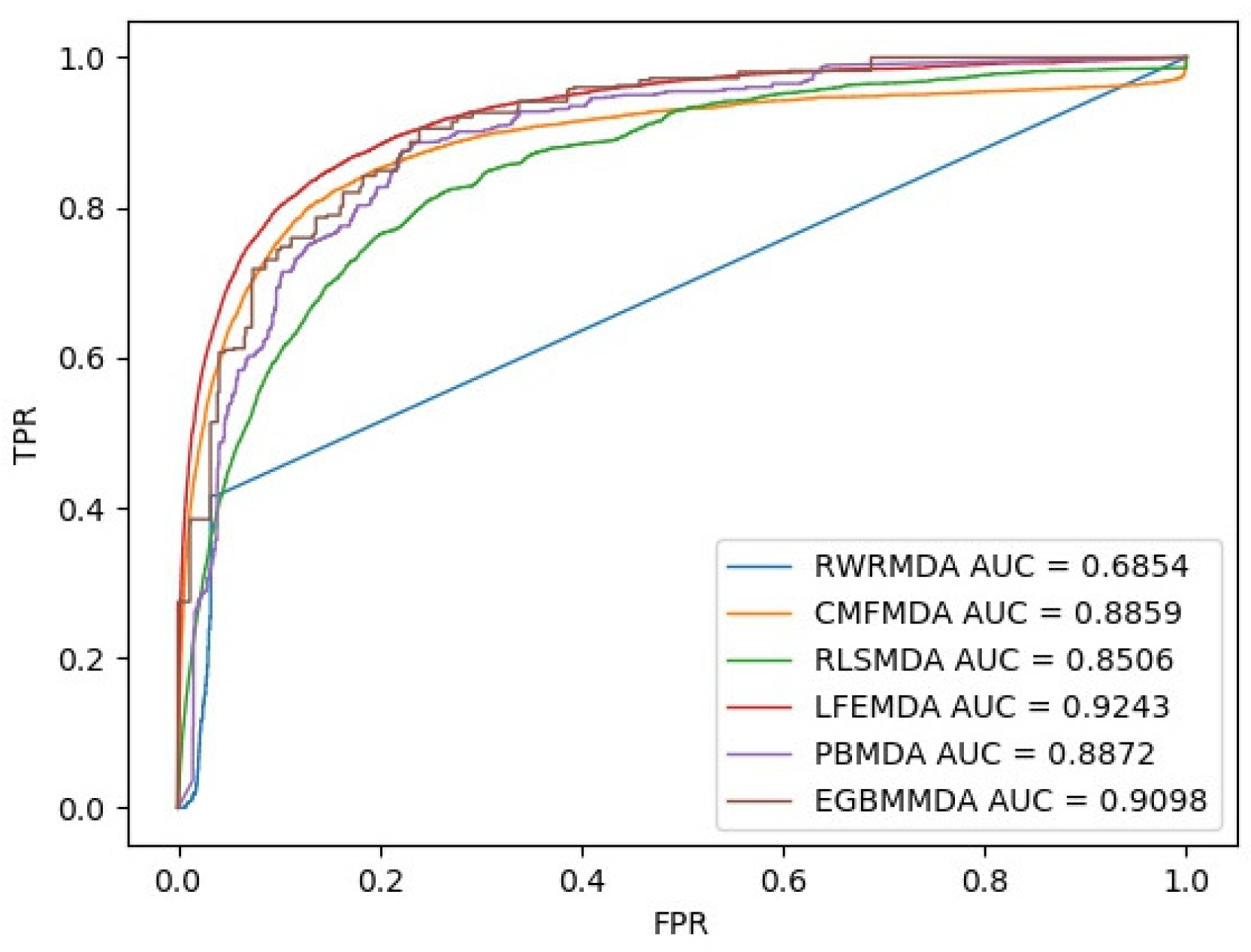
3.1. Performance Evaluation
| Algorithm 1: LFEMDA, predicting miRNA-disease association by latent feature extraction with positive samples |
| Input:MS: m*m miRNAs functional similarity matrix DS: d*d disease semantic similarity matrix R: the experimentally confirmed miRNAs-disease association matrix Paramter: k: hidden space dimension : second normal form regularization coefficient : the distance coefficient between expression matrix inner product of miRNAs on the hidden space and MS : the distance coefficient between expression matrix inner product of diseases on the hidden space and DS : the distance coefficient between expression matrix of miRNAs on the hidden space and auxiliary matrix X : the distance coefficient between expression matrix of diseases on the hidden space and auxiliary matrix Y |
| Output:: the predicted miRNAs-disease association matrix Initialize the vector matrices M, D, and the auxiliary vectors X, Y of miRNAs and diseases , while Δ>ε: update M, given current D, X and Y, using Formula (11) update D, given current M, X and Y, using Formula (12) calculate current X based on the new M calculate current Y based on the new D calculate loss_new using Formula (9) End while |
3.2. Case Study
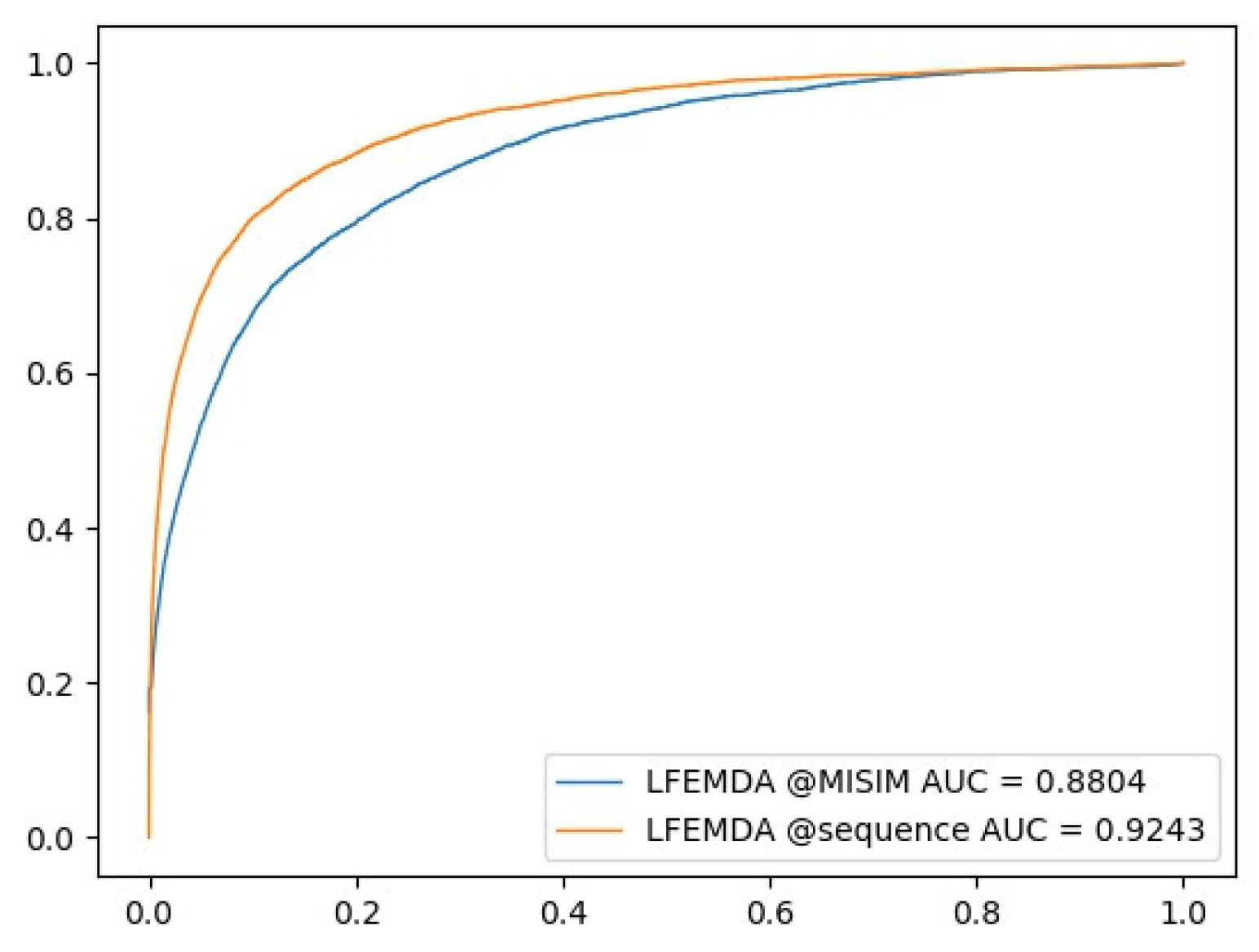
3.3. Control Experiment with Different miRNA Functional Similarity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ambros, V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 2004, 431, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Hannon, G.J. MicroRNAs: Small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2004, 5, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Yan, C.C.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Deng, L.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, Q. RBMMMDA: Predicting multiple types of disease-microRNA associations. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 2009, 136, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miska, E.A. How microRNAs control cell division, differentiation and death. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2005, 15, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, A.M.; Byrom, M.W.; Shelton, J.; Ford, L.P. Antisense inhibition of human miRNAs and indications for an involvement of miRNA in cell growth and apoptosis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 1290–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karp, X.; Ambros, V. Developmental biology. Encountering microRNAs in cell fate signaling. Science 2005, 310, 1288–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Q.; Yu, Z.; Purisima, E.O.; Wang, E. Principles of microRNA regulation of a human cellular signaling network. Mol. Syst. Boil. 2006, 2, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Rajewsky, N. Natural selection on human microRNA binding sites inferred from SNP data. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, M.A.; Liang, H.; Li, W.H. Human polymorphism at microRNAs and microRNA target sites. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 3300–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sethupathy, P.; Collins, F.S. MicroRNA target site polymorphisms and human disease. Trends Genet. 2008, 24, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, C.H.; Chang, N.W.; Shrestha, S.; Hsu, S.D.; Lin, Y.L.; Lee, W.H.; Yang, C.D.; Hong, H.C.; Wei, T.Y.; Tu, S.J.; et al. miRTarBase 2016: Updates to the experimentally validated miRNA-target interactions database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 44, D239–D247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, P.; Luo, J.; Xiao, Q.; Chen, X. A path-based measurement for human miRNA functional similarities using miRNA-disease associations. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.; Zhang, X.; Zou, Q. Integrative approaches for predicting microRNA function and prioritizing disease-related microRNA using biological interaction networks. Brief. Bioinform. 2016, 17, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Hao, Y.; Wang, G.; Juan, L.; Zhang, T.; Teng, M.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y. Prioritization of disease microRNAs through a human phenome-microRNAome network. BMC Syst. Biol. 2010, 4, S2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Q.; Wang, G.; Wang, Y. An approach for prioritizing disease-related microRNAs based on genomic data integration. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Informatics, Yantai, China, 16–18 October 2010; pp. 2270–2274. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Liu, M.X.; Yan, G.Y. RWRMDA: Predicting novel human microRNA–disease associations. Mol. BioSyst. 2012, 8, 2792–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, Z. Similarity-based methods for potential human microRNA-disease association prediction. BMC Med. Genom. 2013, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Xu, J.; Zhang, G.; Xu, L.; Li, C.; Wang, L.; Zhao, Z.; Jiang, W.; Guo, Z.; Li, X. Walking the interactome to identify human miRNA-disease associations through the functional link between miRNA targets and disease genes. BMC Syst. Boil. 2013, 7, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, P.; Han, K.; Guo, M.; Guo, Y.; Li, J.; Ding, J.; Liu, Y.; Dai, Q.; Li, J.; Teng, Z.; et al. Prediction of microRNAs associated with human diseases based on weighted k most similar neighbors. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Ping, Y.; Li, X.; Zhao, H.; Wang, L.; Fan, H.; Xiao, Y.; Li, X. Prioritizing candidate disease miRNAs by integrating phenotype associations of multiple diseases with matched miRNA and mRNA expression profiles. Mol. BioSyst. 2014, 10, 2800–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mørk, S.; Pletscher-Frankild, S.; Palleja Caro, A.; Gorodkin, J.; Jensen, L.J. Protein-driven inference of miRNA–disease associations. Bioinformatics 2013, 30, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, D.; Li, A.; Feng, H.; Wang, M. NTSMDA: Prediction of miRNA–disease associations by integrating network topological similarity. Mol. BioSyst. 2016, 12, 2224–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Xu, J.; Li, Y. Prioritizing Candidate Disease miRNAs by Topological Features in the miRNA-Target Dysregulated Network. In Systems Biology in Cancer Research and Drug Discovery; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 289–306. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Q.; Wang, G.; Jin, S.; Li, Yu.; Wang, Y. Predicting human microRNA-disease associations based on support vector machine. Int. J. Data Min. Bioinform. 2013, 8, 282–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Yan, G.Y. Semi-supervised learning for potential human microRNA-disease associations inference. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, Z.H.; Huang, Z.A.; Zhu, Z.; Yan, G.Y.; Li, Z.W.; Wen, Z.; Chen, X. PBMDA: A novel and effective path-based computational model for miRNA-disease association prediction. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2017, 13, e1005455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, C.; Li, H.; Edwin, W. LRSSLMDA: Laplacian Regularized Sparse Subspace Learning for MiRNA-Disease Association prediction. PLOS Comput. Biol. 2017, 13, e1005912. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Z.; Zhang, Y.H.; Han, K.; Nandi, A.K.; Honig, B.; Huang, D.S. miRNA-Disease Association Prediction with Collaborative Matrix Factorization. Complexity 2017, 2017, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Huang, L.; Xie, D.; Zhao, Q. EGBMMDA: Extreme Gradient Boosting Machine for MiRNA-Disease Association prediction. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wang, J.; Lu, M.; Song, F.; Cui, Q. Inferring the human microRNA functional similarity and functional network based on microRNA-associated diseases. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 1644–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Zhang, Q.; Deng, M.; Miao, J.; Guo, Y.; Gao, W.; Cui, Q. An Analysis of Human MicroRNA and Disease Associations. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Wu, L.; Wang, A.; Tang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, H.; Teschendorff, A.E. dbDEMC 2.0: Updated database of differentially expressed miRNAs in human cancers. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D812–D818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Hao, Y.; Juan, L.; Teng, M.; Zhang, X.; Li, M.; Wang, G.; Liu, Y. miR2Disease: A manually curated database for microRNA deregulation in human disease. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, D98–D104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Name | Associations | LFEMDA | RLSMDA | CMFMDA | RWRMDA | PBMDA | EGBMMDA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carcinoma, Hepatocellular | 209 | 0.777074623 | 0.562371401 | 0.726182159 | 0.718837107 | 0.726162356 | 0.751014475 |
| Breast Neoplasms | 188 | 0.825615501 | 0.575863451 | 0.779712619 | 0.785302831 | 0.744000495 | 0.83387968 |
| Stomach Neoplasms | 166 | 0.781357444 | 0.596336681 | 0.730033905 | 0.415019763 | 0.742491394 | 0.783024957 |
| Colorectal Neoplasms | 143 | 0.815816439 | 0.577177998 | 0.771634237 | 0.726338286 | 0.764776478 | 0.806896074 |
| Melanoma | 133 | 0.837661607 | 0.627245105 | 0.775708519 | 0.809683177 | 0.758005237 | 0.820990175 |
| Lung Neoplasms | 125 | 0.907236486 | 0.593028386 | 0.860728224 | 0.636684303 | 0.79835514 | 0.880834891 |
| Heart Failure | 118 | 0.807582407 | 0.570803132 | 0.718811527 | 0.5 | 0.747054568 | 0.820457834 |
| Neoplasms | 116 | 0.919919468 | 0.641564425 | 0.873431701 | 0.691700345 | 0.82531348 | 0.82318139 |
| Ovarian Neoplasms | 113 | 0.891470921 | 0.626313211 | 0.843754711 | 0.839827262 | 0.768077812 | 0.798872832 |
| Prostatic Neoplasms | 111 | 0.856723686 | 0.628673046 | 0.810308089 | 0.795159194 | 0.741024607 | 0.914524556 |
| Carcinoma, Renal Cell | 100 | 0.843903179 | 0.605379769 | 0.786606069 | 0.5 | 0.735028902 | 0.904940339 |
| Glioblastoma | 99 | 0.816009776 | 0.587858911 | 0.785139551 | 0.485119944 | 0.791925014 | 0.799697261 |
| Pancreatic Neoplasms | 98 | 0.907911933 | 0.626861054 | 0.866743742 | 0.733275142 | 0.799173118 | 0.924964814 |
| Carcinoma, Non-Small-Cell Lung | 92 | 0.869584575 | 0.596822501 | 0.83466099 | 0.843493976 | 0.768944977 | 0.860077377 |
| Urinary Bladder Neoplasms | 89 | 0.855515442 | 0.624616265 | 0.796487867 | 0.607213439 | 0.735907846 | 0.795801467 |
| Colonic Neoplasms | 82 | 0.873166319 | 0.630208504 | 0.801865631 | 0.5 | 0.764004288 | 0.855367194 |
| Carcinoma, Squamous Cell | 78 | 0.878461503 | 0.579512281 | 0.832002776 | 0.5 | 0.761775362 | 0.815635452 |
| Glioma | 73 | 0.91383381 | 0.630672274 | 0.816208746 | 0.5 | 0.786771457 | 0.787616145 |
| Esophageal Neoplasms | 68 | 0.780247066 | 0.558603262 | 0.761111226 | 0.5 | 0.704365079 | 0.790071584 |
| Leukemia, Myeloid, Acute | 67 | 0.860503335 | 0.604397968 | 0.827720767 | 0.5 | 0.818965857 | 0.816735049 |
| Head and Neck Neoplasms | 63 | 0.876705038 | 0.63878347 | 0.817123175 | 0.800857458 | 0.746404741 | 0.715606114 |
| Name | Associations | LFEMDA | RLSMDA | CMFMDA | RWRMDA | PBMDA | EGBMMDA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Distal Myopathies | 1 | 1 | 0.993258427 | 0.988764045 | 0.5 | 0.943820225 | 0.957303371 |
| Moyamoya Disease | 1 | 0.993258427 | 0.995505618 | 0.08988764 | 0.5 | 0.995505618 | 0.982022472 |
| Hypoxia-Ischemia, Brain | 1 | 0.991011236 | 0.988764045 | 0.096629213 | 0.5 | 0.901123596 | 0.982022472 |
| Hypopharyngeal Neoplasms | 1 | 0.991011236 | 1 | 0.838202247 | 0.5 | 1 | 0.982022472 |
| Hepatitis C, Chronic | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.991011236 | 0.959550562 |
| Lipid Metabolism Disorders | 1 | 0.993258427 | 0.979775281 | 0.914606742 | 0.5 | 0.991011236 | 0.959550562 |
| Liver Diseases, Alcoholic | 1 | 0.930337079 | 0.739325843 | 0.051685393 | 0.5 | 0.824719101 | 0.817977528 |
| Adenoma | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.930337079 | 0.5 | 1 | 0.982022472 |
| Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis | 1 | 0.95505618 | 0.948314607 | 0.11011236 | 0.5 | 0.943820225 | 0.957303371 |
| Keratoconus | 1 | 1 | 0.993258427 | 0.986516854 | 0.5 | 0.912359551 | 0.959550562 |
| Aortic Aneurysm, Abdominal | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.964044944 | 0.5 | 1 | 0.982022472 |
| Carcinoma, Embryonal | 1 | 0.865168539 | 0.838202247 | 0.856179775 | 0.5 | 0.694382022 | 0.817977528 |
| Oligodendroglioma | 1 | 0.907865169 | 0.817977528 | 0.905617978 | 0.5 | 0.84494382 | 0.817977528 |
| Carcinoma, Ductal, Breast | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.914606742 | 0.5 | 1 | 0.982022472 |
| Fanconi Anemia | 1 | 0.824719101 | 0.730337079 | 0.820224719 | 0.5 | 0.471910112 | 0.438202247 |
| Colitis | 1 | 1 | 0.997752809 | 0.898876404 | 0.5 | 0.997752809 | 0.982022472 |
| Eye Abnormalities | 1 | 0.993258427 | 0.82247191 | 0.779775281 | 0.5 | 0.912359551 | 0.959550562 |
| Pemphigus, Benign Familial | 1 | 0.991011236 | 0.993258427 | 0.103370787 | 0.5 | 0.970786517 | 0.982022472 |
| Neuroma, Acoustic | 1 | 0.995505618 | 1 | 0.173033708 | 0.5 | 1 | 0.982022472 |
| Creutzfeldt-Jakob Syndrome | 1 | 1 | 0.997752809 | 0.44494382 | 0.5 | 0.995505618 | 0.982022472 |
| Rank | Name | Evidence | Rank | Name | Evidence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | hsa-mir-21 | HDMM, dbDEMC2, miR2Disease | 26 | hsa-mir-148a | HDMM, dbDEMC2, miR2Disease |
| 2 | hsa-mir-126 | HDMM, dbDEMC2, miR2Disease | 27 | hsa-let-7c | HDMM, dbDEMC2, miR2Disease |
| 3 | hsa-mir-17 | HDMM, dbDEMC2, miR2Disease | 28 | hsa-mir-34b | HDMM, dbDEMC2, miR2Disease |
| 4 | hsa-mir-34a | HDMM, dbDEMC2, miR2Disease | 29 | hsa-mir-182 | HDMM, dbDEMC2, miR2Disease |
| 5 | hsa-mir-155 | HDMM, dbDEMC2, miR2Disease | 30 | hsa-mir-125b-2 | HDMM, dbDEMC2, miR2Disease |
| 6 | hsa-mir-20a | HDMM, dbDEMC2, miR2Disease | 31 | hsa-mir-30a | HDMM, dbDEMC2, miR2Disease |
| 7 | hsa-mir-146a | HDMM, dbDEMC2, miR2Disease | 32 | hsa-mir-19a | HDMM, dbDEMC2, miR2Disease |
| 8 | hsa-mir-34c | HDMM, dbDEMC2, miR2Disease | 33 | hsa-let-7d | HDMM, dbDEMC2, miR2Disease |
| 9 | hsa-mir-29a | HDMM, dbDEMC2, miR2Disease | 34 | hsa-mir-92a-1 | HDMM, dbDEMC2 |
| 10 | hsa-mir-145 | HDMM, dbDEMC2, miR2Disease | 35 | hsa-mir-200a | HDMM, dbDEMC2, miR2Disease |
| 11 | hsa-mir-218-1 | HDMM, dbDEMC2 | 36 | hsa-mir-222 | HDMM, dbDEMC2, miR2Disease |
| 12 | hsa-mir-16-2 | HDMM, dbDEMC2 | 37 | hsa-mir-143 | HDMM, dbDEMC2, miR2Disease |
| 13 | hsa-mir-221 | HDMM, dbDEMC2, miR2Disease | 38 | hsa-mir-210 | HDMM, dbDEMC2, miR2Disease |
| 14 | hsa-let-7b | HDMM, dbDEMC2, miR2Disease | 39 | hsa-mir-31 | HDMM, dbDEMC2, miR2Disease |
| 15 | hsa-mir-16-1 | HDMM, dbDEMC2, miR2Disease | 40 | hsa-mir-375 | HDMM, dbDEMC2, miR2Disease |
| 16 | hsa-mir-125b-1 | HDMM, dbDEMC2, miR2Disease | 41 | hsa-let-7f-2 | HDMM, dbDEMC2, miR2Disease |
| 17 | hsa-mir-146b | HDMM, dbDEMC2, miR2Disease | 42 | hsa-mir-29b-1 | HDMM, dbDEMC2, miR2Disease |
| 18 | hsa-let-7a-2 | HDMM, dbDEMC2, miR2Disease | 43 | hsa-let-7f-1 | HDMM, dbDEMC2, miR2Disease |
| 19 | hsa-mir-10b | HDMM, dbDEMC2, miR2Disease | 44 | hsa-let-7e | HDMM, dbDEMC2, miR2Disease |
| 20 | hsa-mir-200b | HDMM, dbDEMC2, miR2Disease | 45 | hsa-let-7g | HDMM, dbDEMC2, miR2Disease |
| 21 | hsa-mir-200c | HDMM, dbDEMC2, miR2Disease | 46 | hsa-mir-27a | HDMM, dbDEMC2, miR2Disease |
| 22 | hsa-mir-218-2 | HDMM, dbDEMC2, miR2Disease | 47 | hsa-mir-181a-2 | HDMM, dbDEMC2, miR2Disease |
| 23 | hsa-mir-22 | HDMM, dbDEMC2, miR2Disease | 48 | hsa-mir-30c-2 | HDMM, dbDEMC2, miR2Disease |
| 24 | hsa-mir-18a | HDMM, dbDEMC2, miR2Disease | 49 | hsa-mir-25 | HDMM, dbDEMC2, miR2Disease |
| 25 | hsa-mir-133b | HDMM, dbDEMC2, miR2Disease | 50 | hsa-mir-486 | HDMM, dbDEMC2, miR2Disease |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Che, K.; Guo, M.; Wang, C.; Liu, X.; Chen, X. Predicting MiRNA-Disease Association by Latent Feature Extraction with Positive Samples. Genes 2019, 10, 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10020080
Che K, Guo M, Wang C, Liu X, Chen X. Predicting MiRNA-Disease Association by Latent Feature Extraction with Positive Samples. Genes. 2019; 10(2):80. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10020080
Chicago/Turabian StyleChe, Kai, Maozu Guo, Chunyu Wang, Xiaoyan Liu, and Xi Chen. 2019. "Predicting MiRNA-Disease Association by Latent Feature Extraction with Positive Samples" Genes 10, no. 2: 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10020080
APA StyleChe, K., Guo, M., Wang, C., Liu, X., & Chen, X. (2019). Predicting MiRNA-Disease Association by Latent Feature Extraction with Positive Samples. Genes, 10(2), 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10020080





