ORCAE-AOCC: A Centralized Portal for the Annotation of African Orphan Crop Genomes
Abstract
1. Introduction
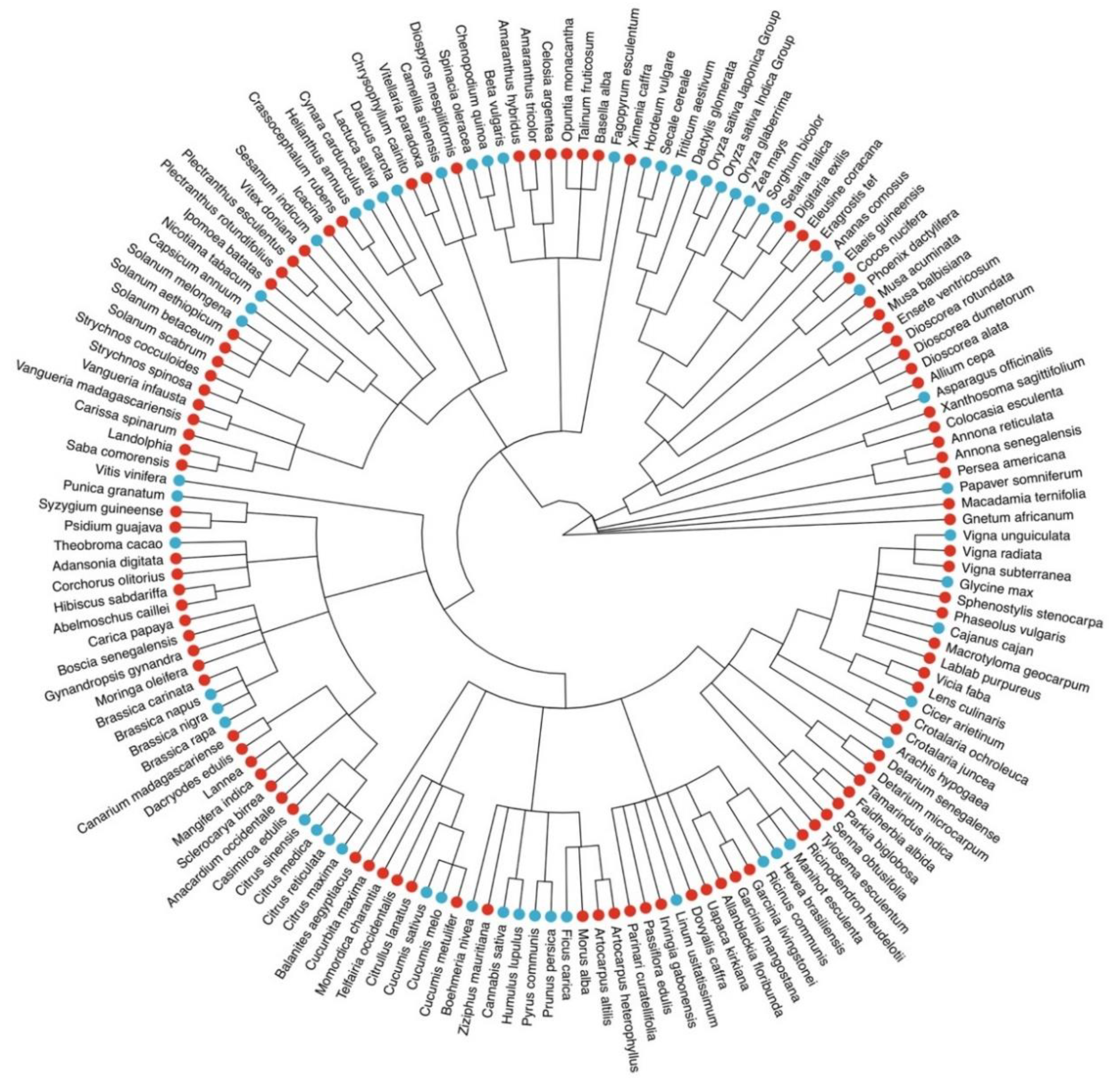
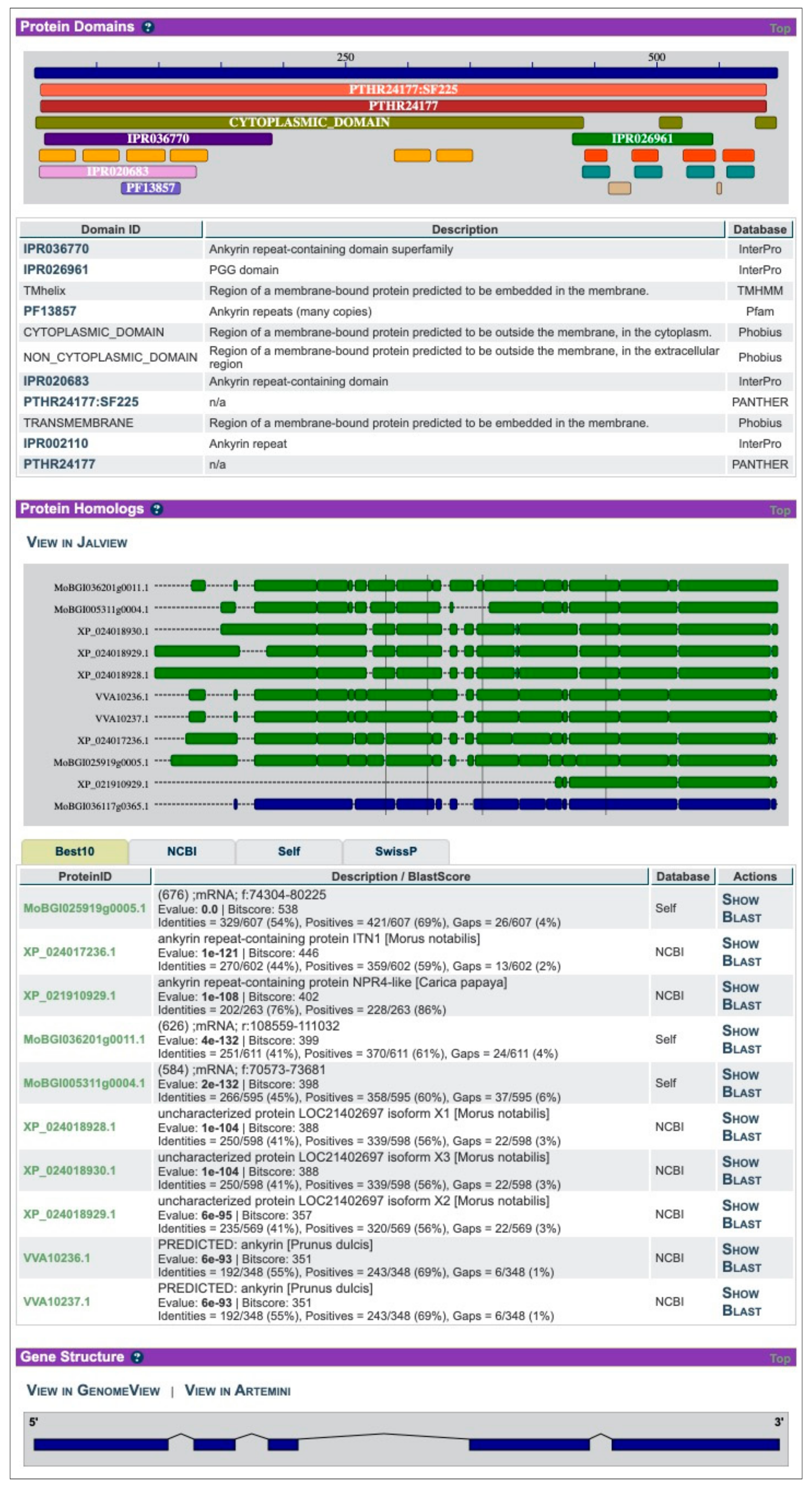
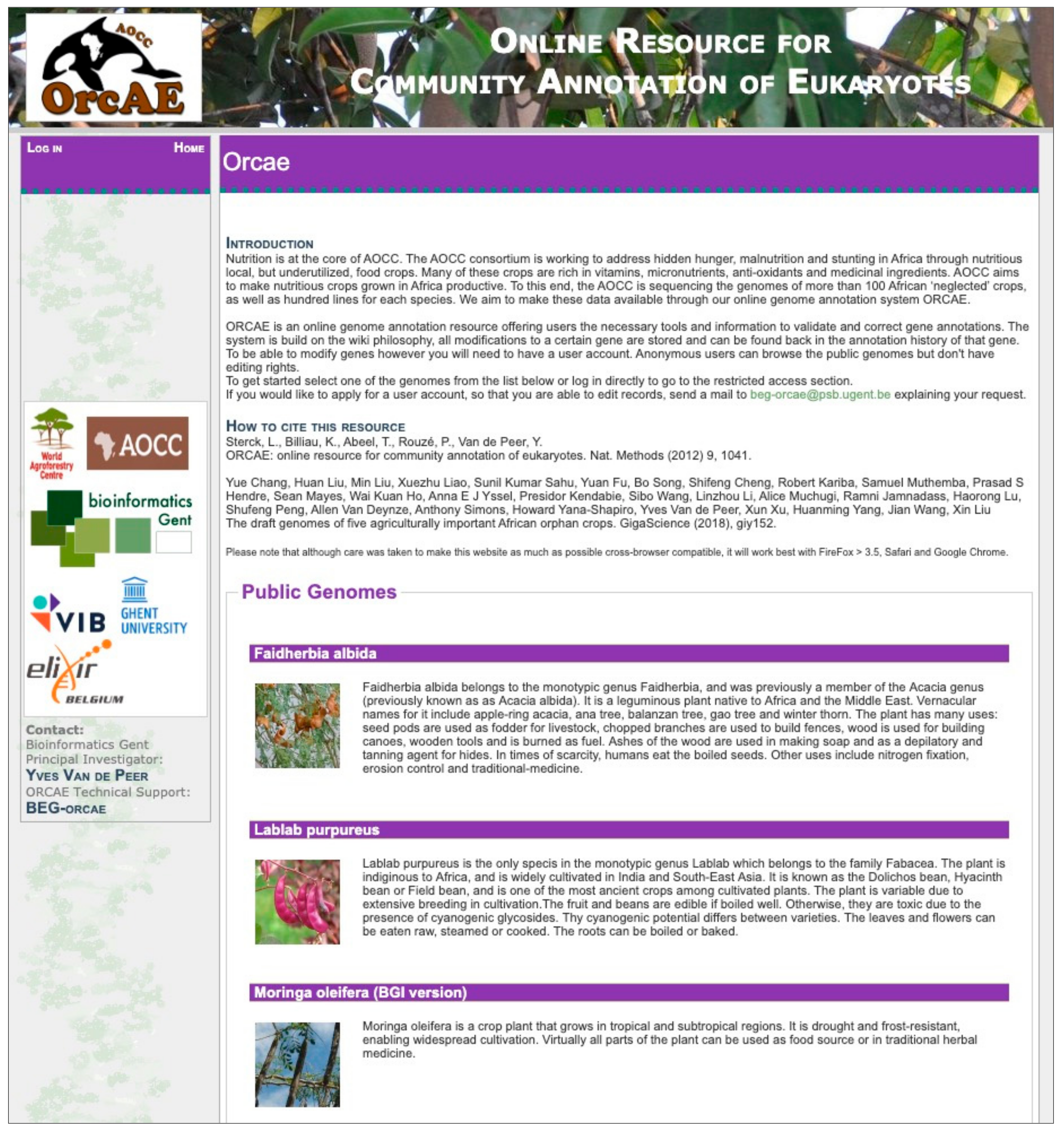
2. ORCAE-AOCC and the Currently Deployed Genomes
3. Concluding Remarks and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Godfray, H.C.J.; Beddington, J.R.; Crute, I.R.; Haddad, L.; Lawrence, D.; Muir, J.F.; Pretty, J.; Robinson, S.; Thomas, S.M.; Toulmin, C. Food security: The challenge of feeding 9 billion people. Science 2010, 327, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayes, S.; Massawe, F.J.; Alderson, P.G.; Roberts, J.A.; Azam-Ali, S.N.; Hermann, M. The potential for underutilized crops to improve security of food production. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 1075–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- African Orphan Crops Consortium—Healthy Africa through Nutritious, Diverse and Local Food Crops. Available online: http://africanorphancrops.org/ (accessed on 19 November 2019).
- Mabhaudhi, T.; Chimonyo, V.G.P.; Hlahla, S.; Massawe, F.; Mayes, S.; Nhamo, L.; Modi, A.T. Prospects of orphan crops in climate change. Planta 2019, 250, 695–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Scheben, A.; Edwards, D. Advances in Integrating Genomics and Bioinformatics in the Plant. Breeding Pipeline. Agriculture-Basel 2018, 8, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claros, M.G.; Bautista, R.; Guerrero-Fernández, D.; Benzerki, H.; Seoane, P.; Fernández-Pozo, N. Why assembling plant genome sequences is so challenging. Biology 2012, 1, 439–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, M.; Warr, A. Errors in long-read assemblies can critically affect protein prediction. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 124–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaattovaara, A.; Leppälä, J.; Salojärvi, J.; Wrzaczek, M. High-throughput sequencing data and the impact of plant gene annotation quality. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 1069–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salzberg, S.L. Next-generation genome annotation: We still struggle to get it right. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanke, M.; Diekhans, M.; Baertsch, R.; Haussler, D. Using native and syntenically mapped cDNA alignments to improve de novo gene finding. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, M.E.; Arsova, B.; Usadel, B. Plant genome and transcriptome annotations: From misconceptions to simple solutions. Brief. Bioinform. 2018, 19, 437–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleator, R.D. An overview of the current status of eukaryote gene prediction strategies. Gene 2010, 461, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolker, E.; Makarova, K.S.; Shabalina, S.; Picone, A.F.; Purvine, S.; Holzman, T.; Cherny, T.; Armbruster, D.; Munson, R.S., Jr.; Kolesov, G.; et al. Identification and functional analysis of ‘hypothetical’ genes expressed in Haemophilus influenzae. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 2353–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolker, E.; Picone, A.F.; Galperin, M.Y.; Romine, M.F.; Higdon, R.; Makarova, K.S.; Kolker, N.; Anderson, G.A.; Qiu, X.; Auberry, K.J.; et al. Global profiling of Shewanella oneidensis MR-1: Expression of hypothetical genes and improved functional annotations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 2099–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, S.; Zhu, W.; Hamilton, J.; Lin, H.; Campbell, M.; Childs, K.; Thibaud-Nissen, F.; Malek, R.L.; Lee, Y.; Zheng, L.; et al. The TIGR Rice Genome Annotation Resource: Improvements and new features. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, D883–D887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.Y.; Christoffels, A.; Ramamoorthy, R.; Ramachandran, S. Expansion mechanisms and functional annotations of hypothetical genes in the rice genome. Plant Physiol. 2009, 150, 1997–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveed, M.; Chaudhry, Z.; Ali, Z.; Amjad, M. Annotation and curation of hypothetical proteins: Prioritizing targets for experimental study. Adv. Life Sci. 2018, 5, 73–87. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Y.L.; Malik, M.; Whitelaw, C.A.; Town, C.D. Cloning and sequencing of cDNAs for hypothetical genes from chromosome 2 of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2002, 130, 2118–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Xiao, Y.L.; Smith, S.R.; Ishmael, N.; Redman, J.C.; Kumar, N.; Monaghan, E.L.; Ayele, M.; Haas, B.J.; Wu, H.C.; Town, C.D. Analysis of the cDNAs of hypothetical genes on Arabidopsis chromosome 2 reveals numerous transcript variants. Plant Physiol. 2005, 139, 1323–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Loveland, J.E.; Gilbert, J.G.; Griffiths, E.; Harrow, J.L. Community gene annotation in practice. Database 2012, 2012, bas009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VEGA. Available online: http://vega.sanger.ac.uk (accessed on 19 November 2019).
- WTSI. Available online: http://www.sanger.ac.uk (accessed on 19 November 2019).
- TAIR. Available online: http://arabidopsis.org (accessed on 19 November 2019).
- Lamesch, P.; Berardini, T.Z.; Li, D.; Swarbreck, D.; Wilks, C.; Sasidharan, R.; Muller, R.; Dreher, K.; Alexander, D.L.; Garcia-Hernandez, M.; et al. The Arabidopsis Information Resource (TAIR): Improved gene annotation and new tools. Nucleic. Acids Res. 2012, 40, D1202–D1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maize GDB. Available online: https://www.maizegdb.org (accessed on 19 November 2019).
- Portwood, J.L.; Woodhouse, M.R.; Cannon, E.K.; Gardiner, J.M.; Harper, L.C.; Schaeffer, M.L.; Walsh, J.R.; Sen, T.Z.; Cho, K.T.; Schott, D.A.; et al. MaizeGDB 2018: The maize multi-genome genetics and genomics database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D1146–D1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- RAP-DB. Available online: https://rapdb.dna.affrc.go.jp (accessed on 19 November 2019).
- Sakai, H.; Lee, S.S.; Tanaka, T.; Numa, H.; Kim, J.; Kawahara, Y.; Wakimoto, H.; Yang, C.; Iwamoto, M.; Abe, T.; et al. Rice Annotation Project Database (RAP-DB): An integrative and interactive database for rice genomics. Plant Cell Physiol. 2013, 54, e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawahara, Y.; de la Bastide, M.; Hamilton, J.P.; Kanamori, H.; McCombie, W.R.; Ouyang, S.; Schwartz, D.C.; Tanaka, T.; Wu, J.; Zhou, S.; et al. Improvement of the Oryza sativa Nipponbare reference genome using next generation sequence and optical map data. Rice 2013, 6, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IWGSC. Available online: https://www.wheatgenome.org (accessed on 19 November 2019).
- Appels, R.; Eversole, K.; Stein, N.; Feuillet, C.; Keller, B.; Rogers, J.; Pozniak, C.J.; Choulet, F.; Distelfeld, A.; Poland, J.; et al. Shifting the limits in wheat research and breeding using a fully annotated reference genome. Science 2018, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheat@URGI. Available online: https://wheat-urgi.versailles.inra.fr (accessed on 19 November 2019).
- Alaux, M.; Rogers, J.; Letellier, T.; Flores, R.; Alfama, F.; Pommier, C.; Mohellibi, N.; Durand, S.; Kimmel, E.; Michotey, C.; et al. Linking the International Wheat Genome Sequencing Consortium bread wheat reference genome sequence to wheat genetic and phenomic data. Genome Biol. 2018, 19, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ORCAE. Available online: https://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/orcae/ (accessed on 19 November 2019).
- Sterck, L.; Billiau, K.; Abeel, T.; Rouze, P.; Van de Peer, Y. ORCAE: Online resource for community annotation of eukaryotes. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimplet, J.; Adam-Blondon, A.F.; Bert, P.F.; Bitz, O.; Cantu, D.; Davies, C.; Delrot, S.; Pezzotti, M.; Rombauts, S.; Cramer, G.R. The grapevine gene nomenclature system. BMC Genomics 2014, 15, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, J.L.; Rouzé, P.; Verhelst, B.; Lin, Y.C.; Bayer, T.; Collen, J.; Dattolo, E.; De Paoli, E.; Dittami, S.; Maumus, F.; et al. The genome of the seagrass Zostera marina reveals angiosperm adaptation to the sea. Nature 2016, 530, 331–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unver, T.; Wu, Z.; Sterck, L.; Turktas, M.; Lohaus, R.; Li, Z.; Yang, M.; He, L.; Deng, T.; Escalante, F.J.; et al. Genome of wild olive and the evolution of oil biosynthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E9413–E9422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Clerck, O.; Kao, S.M.; Bogaert, K.A.; Blomme, J.; Foflonker, F.; Kwantes, M.; Vancaester, E.; Vanderstraeten, L.; Aydogdu, E.; Boesger, J.; et al. Insights into the Evolution of Multicellularity from the Sea Lettuce Genome. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, 2921–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeel, T.; Van Parys, T.; Saeys, Y.; Galagan, J.; Van de Peer, Y. GenomeView: A next-generation genome browser. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, P.; Binns, D.; Chang, H.Y.; Fraser, M.; Li, W.; McAnulla, C.; McWilliam, H.; Maslen, J.; Mitchell, A.; Nuka, G.; et al. InterProScan 5: Genome-scale protein function classification. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1236–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heiko, S. AHRD. Available online: https://github.com/groupschoof/AHRD (accessed on 19 November 2019).
- ORCAE-AOCC. Available online: https://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/orcae/aocc/ (accessed on 19 November 2019).
- Chang, Y.; Liu, H.; Liu, M.; Liao, X.; Sahu, S.K.; Fu, Y.; Song, B.; Cheng, S.; Kariba, R.; Muthemba, S.; et al. The draft genomes of five agriculturally important African orphan crops. Gigascience 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camacho, C.; Coulouris, G.; Avagyan, V.; Ma, N.; Papadopoulos, J.; Bealer, K.; Madden, T.L. BLAST+: Architecture and applications. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yssel, A.E.J.; Kao, S.-M.; Van de Peer, Y.; Sterck, L. ORCAE-AOCC: A Centralized Portal for the Annotation of African Orphan Crop Genomes. Genes 2019, 10, 950. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10120950
Yssel AEJ, Kao S-M, Van de Peer Y, Sterck L. ORCAE-AOCC: A Centralized Portal for the Annotation of African Orphan Crop Genomes. Genes. 2019; 10(12):950. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10120950
Chicago/Turabian StyleYssel, Anna E. J., Shu-Min Kao, Yves Van de Peer, and Lieven Sterck. 2019. "ORCAE-AOCC: A Centralized Portal for the Annotation of African Orphan Crop Genomes" Genes 10, no. 12: 950. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10120950
APA StyleYssel, A. E. J., Kao, S.-M., Van de Peer, Y., & Sterck, L. (2019). ORCAE-AOCC: A Centralized Portal for the Annotation of African Orphan Crop Genomes. Genes, 10(12), 950. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10120950




