Genome-Wide Analysis of Basic Helix–Loop–Helix Superfamily Members Reveals Organization and Chilling-Responsive Patterns in Cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata L.)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sequence Retrieval in the B. oleracea Genome
2.2. Phylogenetic Analysis and Genomic Location of BobHLH Genes
2.3. The Expression Patterns of BobHLH Genes in Different Organs/tissues
2.4. Plant Materials, Growth Conditions, and Chilling Treat
2.5. The Characteristics Analysis, Conserved Motifs, and Gene Structure of the BobHLH Genes
2.6. Characterization of Putative Cis-Acting Elements in the Promoter Regions of BobHLH Genes
2.7. Construction and Localization of Subcellular Localization Vector
3. Results
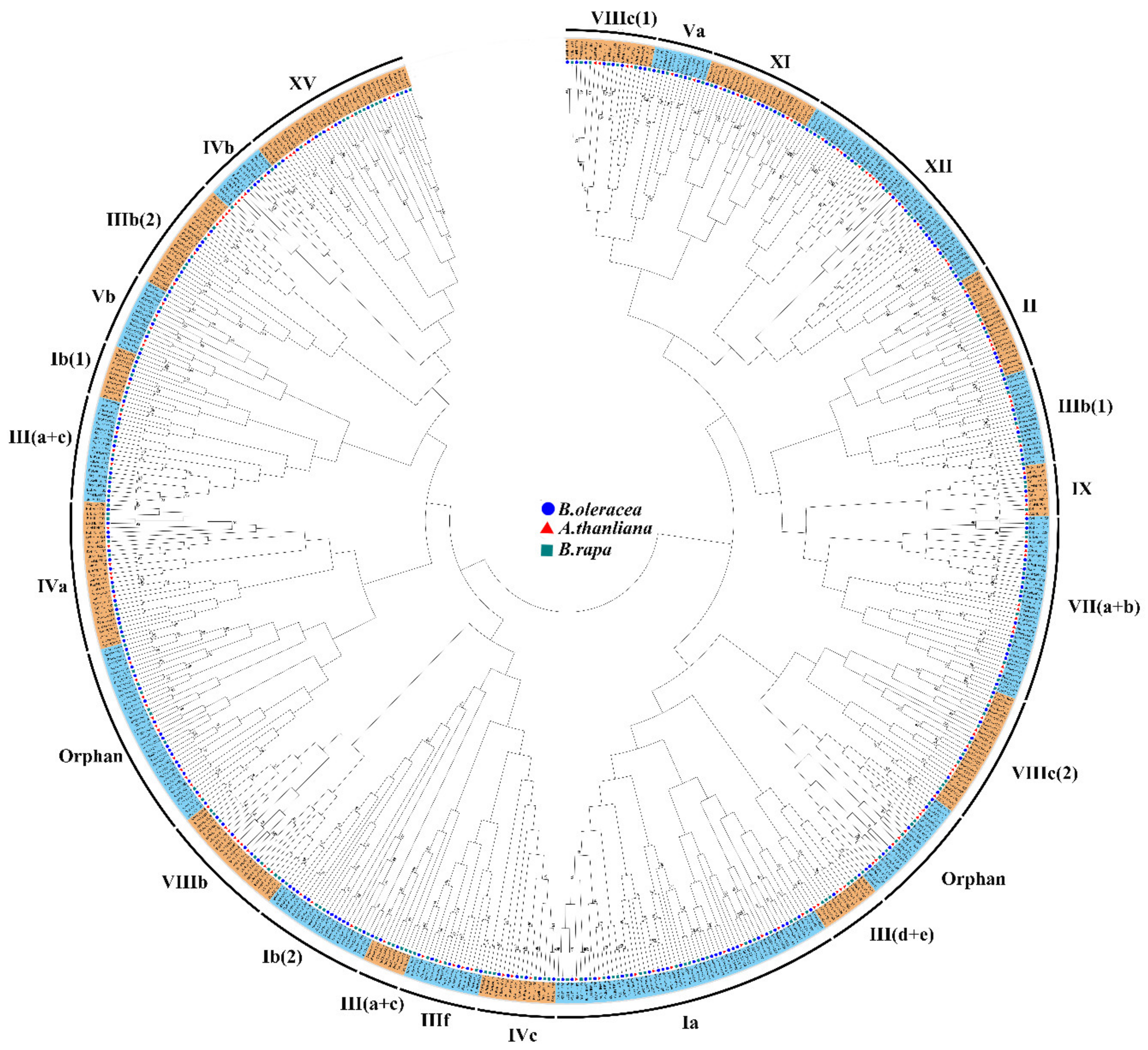
3.1. Identification and Phylogenetic Analysis of BobHLH Genes in B. oleracea
3.2. Chromosomal Localization of the BobHLH Genes in Cabbage
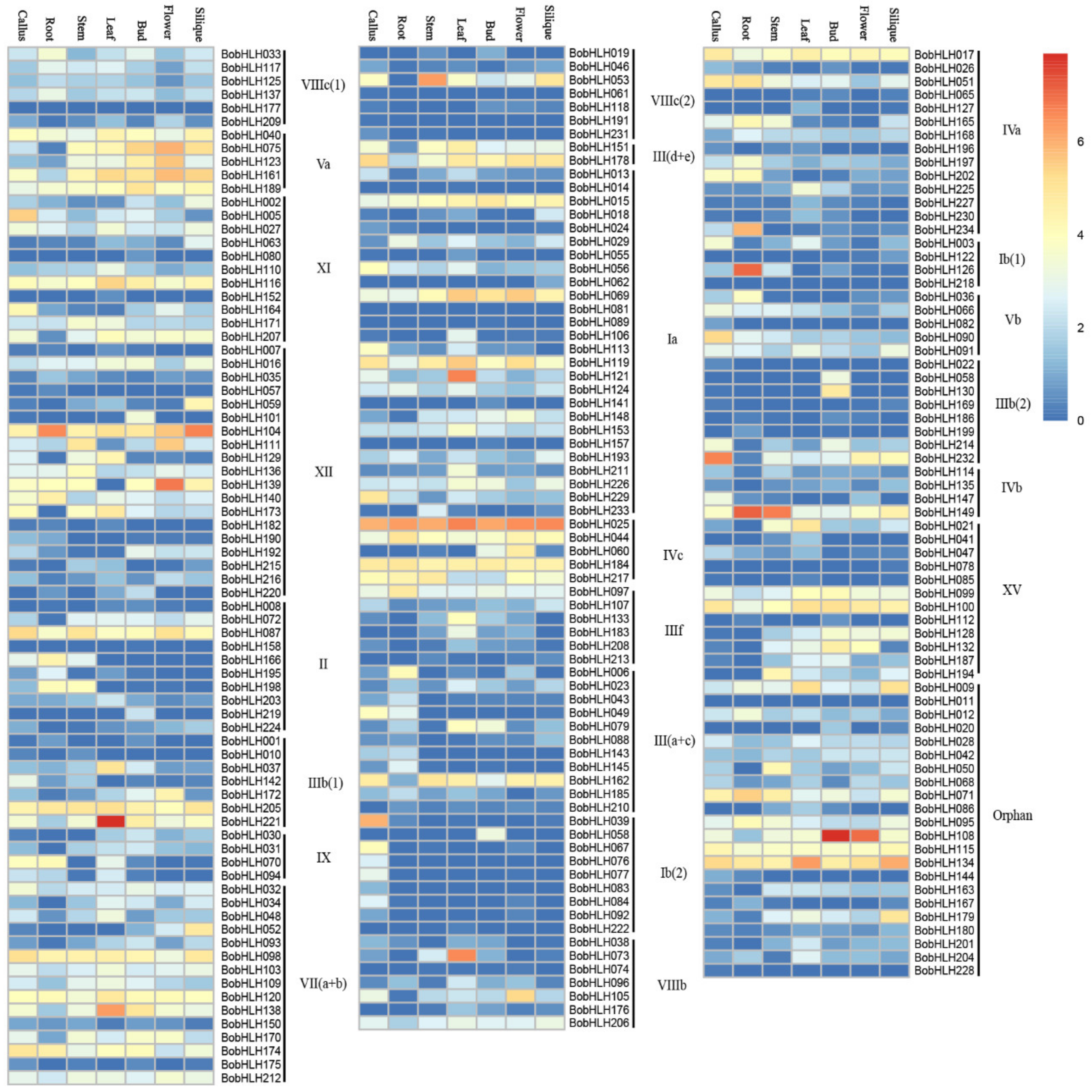
3.3. Expression Patterns of BobHLH Genes in Different Organs/Tissues
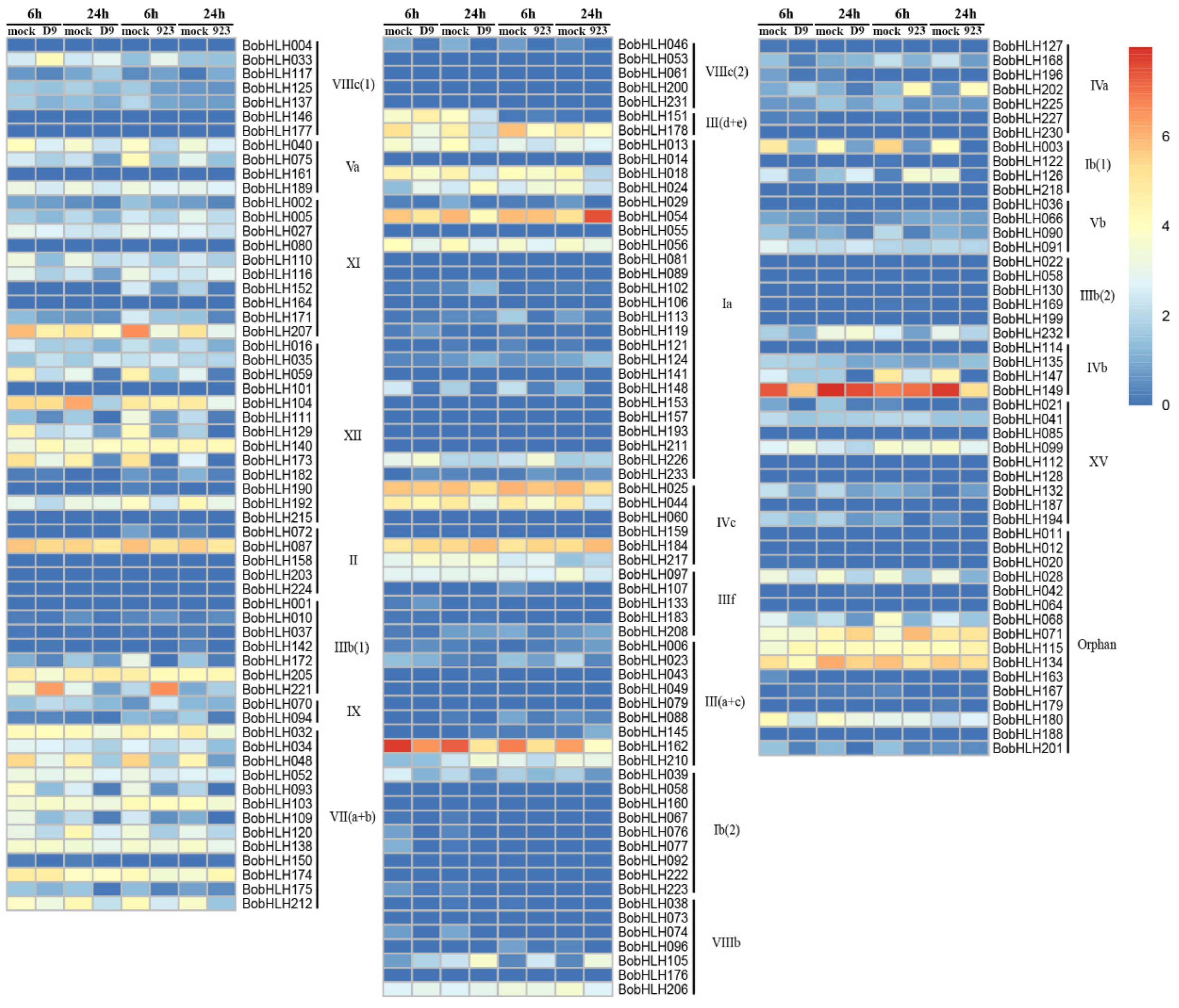
3.4. Expression Analysis of BobHLH Genes in Response to Chilling Stress
3.5. Characteristics, Protein Motifs, and Gene Structures of BobHLH Genes
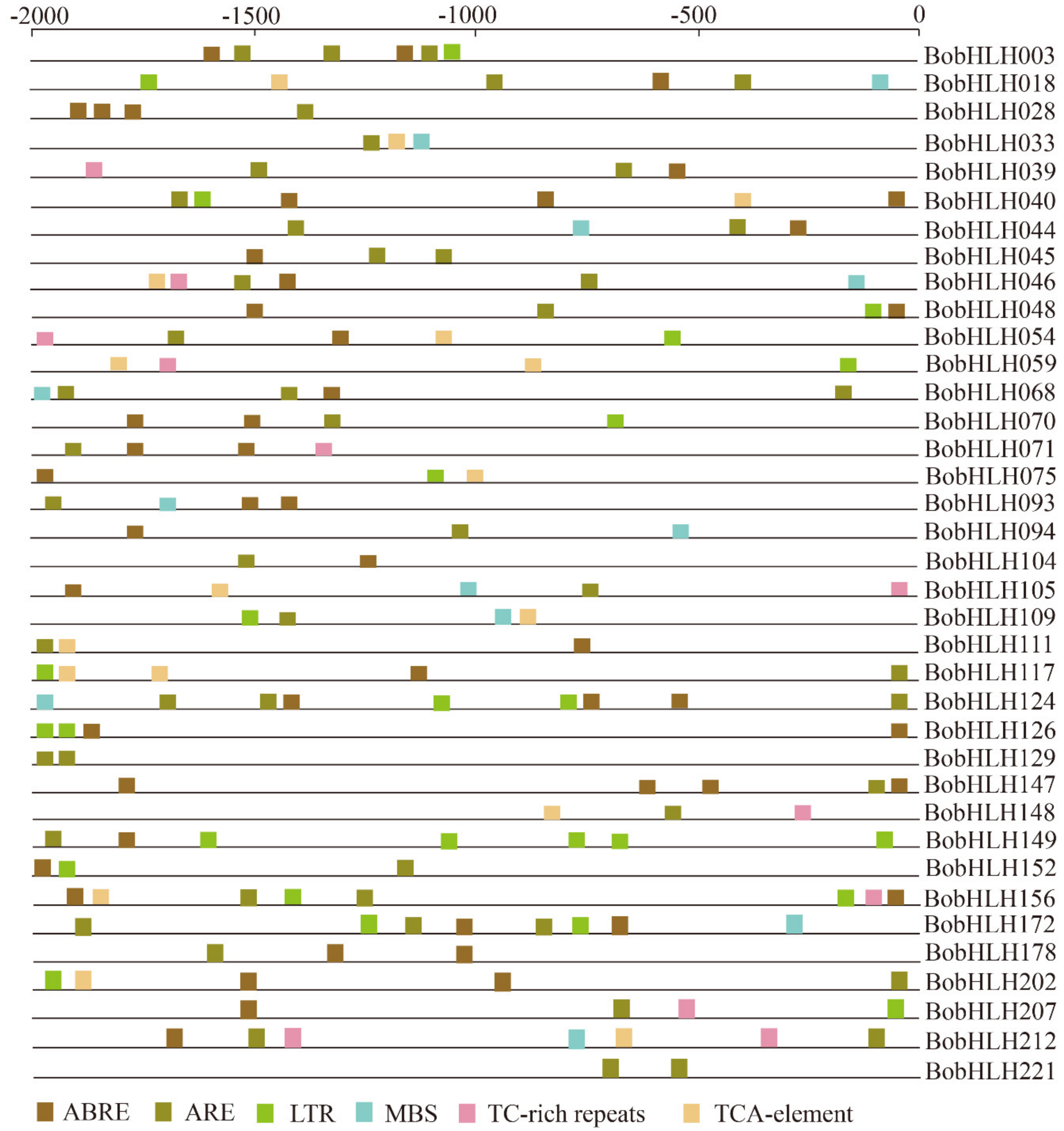
3.6. Characterization of Stress-Related Cis-Acting Elements Among the Chilling-Responsive BobHLH Genes
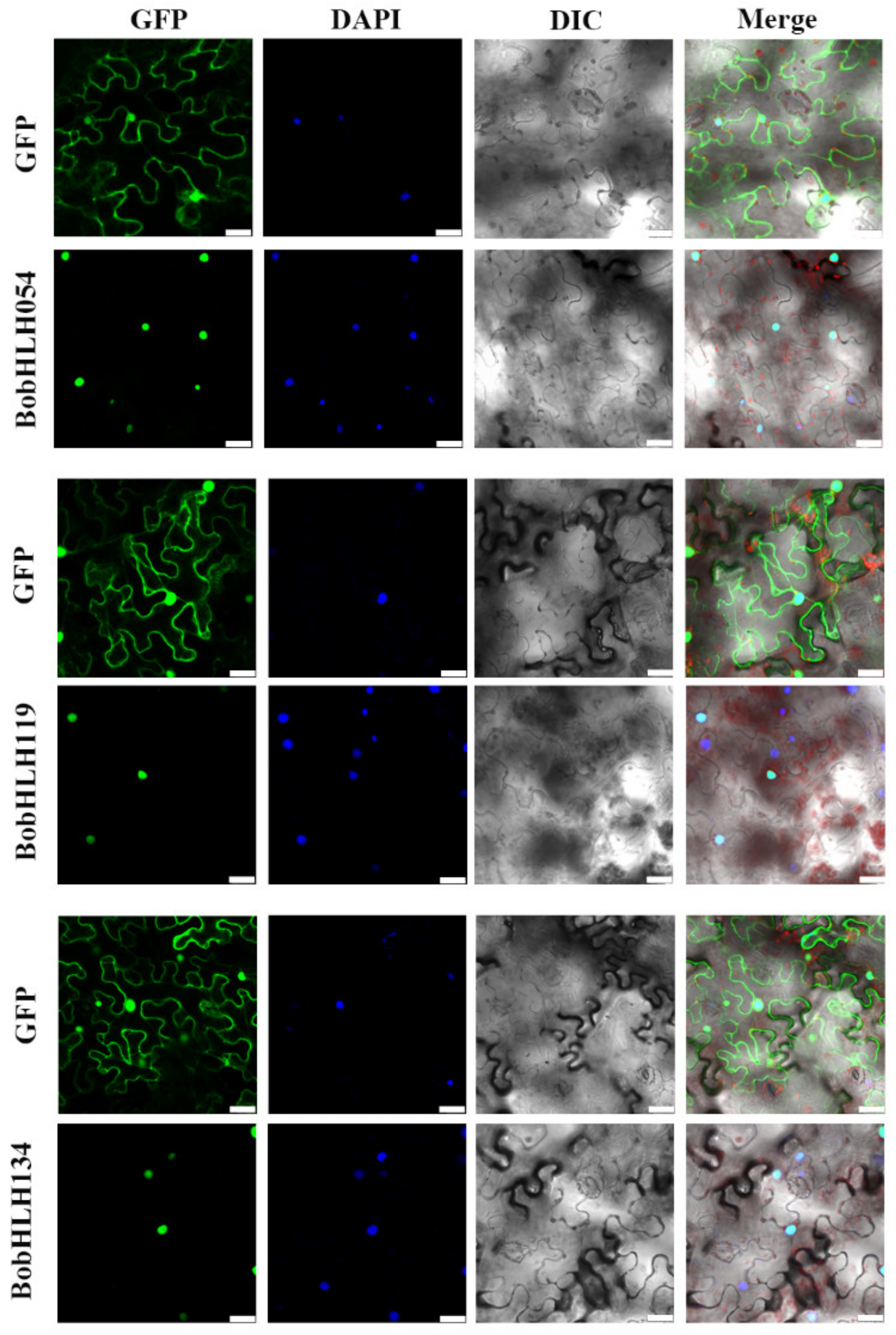
3.7. Subcellular Localization Analysis of the BobHLH Proteins
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X.; Tong, C.; Edwards, D.; Parkin, I.A.P.; Zhao, M.; Ma, J.; Yu, J.; Huang, S.; et al. The Brassica oleracea genome reveals the asymmetrical evolution of polyploid genomes. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Sun, R.; Wu, J.; Liu, S.; Bai, Y.; Mun, J.H.; Bancroft, I.; Cheng, F.; et al. The genome of the mesopolyploid crop species Brassica rapa. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 1035–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, P.K.; Agarwal, P.; Reddy, M.K.; Sopory, S.K. Role of DREB transcription factors in abiotic and biotic stress tolerance in plants. Plant Cell Rep. 2006, 25, 1263–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feller, A.; Machemer, K.; Braun, E.L.; Grotewold, E. Evolutionary and comparative analysis of MYB and bHLH plant transcription factors. Plant J. 2011, 66, 94–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, S.; Mahmood, T. Functional role of DREB and ERF transcription factors: Regulating stress-responsive network in plants. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2015, 37, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Fan, H.-J.; Ling, H.-Q. Genome-wide identification and characterization of the bHLH gene family in tomato. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavas, M.; Baloglu, M.C.; Atabay, E.S.; Ziplar, U.T.; Daşgan, H.Y.; Unver, T. Genome-wide characterization and expression analysis of common bean bHLH transcription factors in response to excess salt concentration. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2016, 291, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, S. An overview of the basic helix-loop-helix proteins. Genome Boil. 2004, 5, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo-Ortiz, G.; Huq, E.; Quail, P.H. The Arabidopsis basic/helix-loop-helix transcription factor family. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 1749–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atchley, W.R.; Fitch, W.M. A natural classification of the basic helix-loop-helix class of transcription factors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 5172–5176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, N.; Dolan, L. Origin and diversification of basic-helix-loop-helix proteins in plants. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2010, 27, 862–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Huang, Z.N.; Duan, W.K.; Ren, J.; Liu, T.K.; Li, Y.; Hou, X.L. Genome-wide analysis of the bHLH transcription factor family in Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa ssp. pekinensis). Mol. Genet. Genom. 2014, 289, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Luo, H.; Xu, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Ji, A.; Song, J.; Chen, S. Genome-wide characterisation and analysis of bHLH transcription factors related to tanshinone biosynthesis in Salvia miltiorrhiza. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Zhang, N.; Jiao, Y.; Li, R.; Xiao, D.; Wang, Z. The grapevine basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) transcription factor positively modulates CBF-pathway and confers tolerance to cold-stress in Arabidopsis. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 41, 5329–5342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-Y.; Li, M.-Y.; Wu, X.-J.; Huang, Y.; Ma, J.; Xiong, A.-S. Genome-wide analysis of basic helix-loop-helix family transcription factors and their role in responses to abiotic stress in carrot. Mol. Breed. 2015, 35, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.; Guan, Y.; Chen, S.; Li, H. Genome-wide analysis of basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) transcription factors in Brachypodium distachyon. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledent, V.; Vervoort, M. The Basic Helix-Loop-Helix Protein Family: Comparative Genomics and Phylogenetic Analysis. Genome Res. 2001, 11, 754–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simionato, E.; Ledent, V.; Richards, G.; Thomas-Chollier, M.; Kerner, P.; Coornaert, D.; Degnan, B.M.; Vervoort, M. Origin and diversification of the basic helix-loop-helix gene family in metazoans: Insights from comparative genomics. BMC Evol. Boil. 2007, 7, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sailsbery, J.K.; Dean, R.A. Accurate discrimination of bHLH domains in plants, animals, and fungi using biologically meaningful sites. BMC Evol. Boil. 2012, 12, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carretero-Paulet, L.; Galstyan, A.; Roig-Villanova, I.; Martínez-García, J.F.; Bilbao-Castro, J.R.; Robertson, D.L. Genome-Wide Classification and Evolutionary Analysis of the bHLH Family of Transcription Factors in Arabidopsis, Poplar, Rice, Moss, and Algae. Plant Physiol. 2010, 153, 1398–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duek, P.D.; Fankhauser, C. HFR1, a putative bHLH transcription factor, mediates both phytochrome A and cryptochrome signalling. Plant J. 2003, 34, 827–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillon, A.; Shen, H.; Huq, E. Phytochrome Interacting Factors: Central players in phytochrome-mediated light signaling networks. Trends Plant Sci. 2007, 12, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedrichsen, D.M.; Nemhauser, J.; Muramitsu, T.; Maloof, J.N.; Alonso, J.; Ecker, J.R.; Furuya, M.; Chory, J. Three redundant brassinosteroid early response genes encode putative bHLH transcription factors required for normal growth. Genetics 2002, 162, 1445–1456. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kiribuchi, K.; Jikumaru, Y.; Kaku, H.; Minami, E.; Hasegawa, M.; Kodama, O.; Seto, H.; Okada, K.; Nojiri, H.; Yamane, H. Involvement of the Basic Helix-Loop-Helix Transcription Factor RERJ1 in Wounding and Drought Stress Responses in Rice Plants. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2005, 69, 1042–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, W.; Ohmori, T.; Kageyama, K.; Miyazaki, C.; Saito, A.; Murata, M.; Noda, K.; Maekawa, M. The Purple leaf (Pl) Locus of Rice: The Plw Allele has a Complex Organization and Includes Two Genes Encoding Basic Helix-Loop-Helix Proteins Involved in Anthocyanin Biosynthesis. Plant Cell Physiol. 2001, 42, 982–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnaud, N.; Girin, T.; Sorefan, K.; Fuentes, S.; Wood, T.A.; Lawrenson, T.; Sablowski, R.; Østergaard, L. Gibberellins control fruit patterning in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genes Dev. 2010, 24, 2127–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, K.; Maekawa, M.; Ujiie, S.; Satake, Y.; Furutani, I.; Okamoto, H.; Shimamoto, K.; Kyozuka, J. Major regulators of shoot branching in rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 11765–11770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiefelbein, J. Cell-fate specification in the epidermis: A common patterning mechanism in the root and shoot. Curr. Opin. Plant Boil. 2003, 6, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.-M.; Zhao, Q.; Zhao, L.-L.; Qiao, Y.; Xie, X.-B.; Li, H.-F.; Yao, Y.-X.; You, C.-X.; Hao, Y.-J. The cold-induced basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor gene MdCIbHLH1 encodes an ICE-like protein in apple. BMC Plant Boil. 2012, 12, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Z. Functional profiling of EcaICE1 transcription factor gene from Eucalyptus camaldulensis involved in cold response in tobacco plants. J. Plant Biochem. Biot. 2014, 23, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Jiao, Y.; Li, R.; Zhang, N.; Xiao, D.; Ding, X.; Wang, Z. Chinese wild-growing Vitis amurensis ICE1 and ICE2 encode MYC-type bHLH transcription activators that regulate cold tolerance in Arabidopsis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e0102303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodstein, D.; Shu, S.; Russell, H.; Rochak, N.; Hayes, R.D.; Fazo, J.; Mitros, T.; Dirks, W.; Hellsten, U.; Putnam, N.H.; et al. Phytozome: A comparative platform for green plant genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 1178–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Wang, C.; Han, X.; Tang, S.; Liu, S.; Xia, X.; Yin, W. A novel bHLH transcription factor PebHLH35 from Populus euphratica confers drought tolerance through regulating stomatal development, photosynthesis and growth in Arabidopsis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 450, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Tai, H.; Li, S.; Gao, W.; Zhao, M.; Xie, C.; Li, W. bHLH122 is important for drought and osmotic stress resistance in Arabidopsis and in the repression of ABA catabolism. New Phytol. 2014, 201, 1192–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, B.; Li, M.; Feng, D.; Jin, H.; Wang, P.; Liu, J.; Xiong, F.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.-B. The bHLH Transcription Factor bHLH104 Interacts with IAA-LEUCINE RESISTANT3 and Modulates Iron Homeostasis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2015, 27, 787–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurt, F.; Filiz, E.; Kurt, F. Genome-wide and comparative analysis of bHLH38, bHLH39, bHLH100 and bHLH101 genes in Arabidopsis, tomato, rice, soybean and maize: Insights into iron (Fe) homeostasis. BioMetals 2018, 31, 489–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Ai, Q.; Liang, G.; Yu, D. Two bHLH Transcription Factors, bHLH34 and bHLH104, Regulate Iron Homeostasis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol. 2016, 170, 2478–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnusamy, V.; Ohta, M.; Kanrar, S.; Lee, B.-H.; Hong, X.; Agarwal, M.; Zhu, J.-K. ICE1: A regulator of cold-induced transcriptome and freezing tolerance in Arabidopsis. Genome Res. 2003, 17, 1043–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmour, S.J.; Zarka, D.G.; Stockinger, E.J.; Salazar, M.P.; Houghton, J.M.; Thomashow, M.F. Low temperature regulation of the Arabidopsis CBF family of AP2 transcriptional activators as an early step in cold-induced COR gene expression. Plant J. 1998, 16, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Ding, Y.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; Gong, Z.; Yang, S. MPK3- and MPK6-Mediated ICE1 Phosphorylation Negatively Regulates ICE1 Stability and Freezing Tolerance in Arabidopsis. Dev. Cell 2017, 43, 630–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, J. MAPping kinase regulation of ICE1 in freezing tolerance. Trends Plant Sci. 2018, 23, 91–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buck, M.J.; Atchley, W.R. Phylogenetic Analysis of Plant Basic Helix-Loop-Helix Proteins. J. Mol. Evol. 2003, 56, 742–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miura, K.; Jin, J.B.; Lee, J.; Yoo, C.Y.; Stirm, V.; Miura, T.; Ashworth, E.N.; Bressan, R.A.; Yun, D.-J.; Hasegawa, P.M. SIZ1-Mediated Sumoylation of ICE1 Controls CBF3/DREB1A Expression and Freezing Tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 1403–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Jiang, L.; Wang, F.; Yu, D. Jasmonate regulates the inducer of cbf expression-C-repeat binding factor/DRE binding factor1 cascade and freezing tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 2907–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Xie, Q.; Gong, Z.; Yang, S. OST1 Kinase Modulates Freezing Tolerance by Enhancing ICE1 Stability in Arabidopsis. Dev. Cell 2015, 32, 278–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Duan, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Mi, G.; Ren, H. Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) over-expressing cold-induced transcriptome regulator ICE1 exhibits changed morphological characters and enhances chilling tolerance. Sci. Hortic. 2010, 124, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, D.-J.; Hu, X.-Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, K.-D. Over-Expression of ICE1 Gene in Transgenic Rice Improves Cold Tolerance. Rice Sci. 2008, 15, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakoby, M.; Werber, M.; Bailey, P.C.; Heim, M.A.; Martin, C.; Weisshaar, B. The Basic Helix-Loop-Helix Transcription Factor Family in Plants: A Genome-Wide Study of Protein Structure and Functional Diversity. Mol. Boil. Evol. 2003, 20, 735–747. [Google Scholar]
- Finn, R.D.; Penelope, C.; Eberhardt, R.Y.; Eddy, S.R.; Jaina, M.; Mitchell, A.L.; Potter, S.C.; Punta, M.; Qureshi, M.; Sangardorvegas, A. The Pfam protein families database: Towards a more sustainable future. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchler-Bauer, A.; Derbyshire, M.K.; Gonzales, N.R.; Lu, S.N.; Chitsaz, F.; Geer, L.Y.; Geer, R.C.; He, J.; Gwadz, M.; Hurwitz, D.I.; et al. CDD: NCBI’s conserved domain database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D222–D226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 6.0. Mol. Boil. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voorrips, R.E. MapChart: Software for the graphical presentation of linkage maps and QTLs. J. Hered. 2002, 93, 77–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, T.L.; Boden, M.; Buske, F.A.; Frith, M.; Grant, C.E.; Clementi, L.; Ren, J.; Li, W.W.; Noble, W.S. MEME SUITE: Tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, W202–W208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, A.-Y. GSDS: A gene structure display server. Hereditas 2007, 29, 1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Jin, J.; Guo, A.Y.; Zhang, H.; Luo, J.; Gao, G. GSDS 2.0: An upgraded gene feature visualization server. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1296–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lescot, M. PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, P.; Park, K.-J.; Obayashi, T.; Fujita, N.; Harada, H.; Adams-Collier, C.; Nakai, K. WoLF PSORT: Protein localization predictor. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W585–W587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, W.-H.; Kim, S.; Lee, H.-A.; Choi, D.; Yeom, S.-I. Genome-wide analysis of Dof transcription factors reveals functional characteristics during development and response to biotic stresses in pepper. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Guo, C.; Shan, H.; Kong, H. Divergence of duplicate genes in exon–intron structure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 1187–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Duan, X.; Jiang, H.; Sun, Y.; Tang, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Guo, J.; Liang, W.; Chen, L.; Yin, J.; et al. Genome-Wide Analysis of Basic/Helix-Loop-Helix Transcription Factor Family in Rice and Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2006, 141, 1167–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narusaka, Y.; Nakashima, K.; Shinwari, Z.K.; Sakuma, Y.; Furihata, T.; Abe, H.; Narusaka, M.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. Interaction between two cis-acting elements, ABRE and DRE, in ABA-dependent expression of Arabidopsis rd29A gene in response to dehydration and high-salinity stresses. Plant J. 2003, 34, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, A.P.C.; Dunn, M.A.; Goddard, N.J.; Hughes, M.A. Identification of a novel low-temperature-response element in the promoter of the barley (Hordeum vulgare L) gene blt101.1. Planta 2001, 213, 770–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, P.S.; Agarwal, P.; Gupta, K.; Agarwal, P.K. Molecular characterization of an MYB transcription factor from a succulent halophyte involved in stress tolerance. AoB PLANTS 2015, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, K.; Dong, Q.; Li, C.; Liu, C.; Ma, F. Genome Wide Identification and Characterization of Apple bHLH Transcription Factors and Expression Analysis in Response to Drought and Salt Stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.; Li, G.; Hu, P.; Zhao, X.; Li, L.; Wei, W.; Feng, J.; Zhou, H. Identification of basic/helix-loop-helix transcription factors reveals candidate genes involved in anthocyanin biosynthesis from the strawberry white-flesh mutant. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Feng, R.; Ma, R.; Shen, Z.; Cai, Z.; Song, Z.; Peng, B.; Yu, M. Genome-wide analysis of basic helix-loop-helix superfamily members in peach. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Wang, F.; Wu, Z.; Li, Y.; Shi, G.; Hu, J.; Hou, X.L. Components of the Arabidopsis CBF Cold-Response Pathway Are Conserved in Non-heading Chinese Cabbage. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2011, 29, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herold, S.; Wanzel, M.; Beuger, V.; Frohme, C.; Beul, D.; Hillukkala, T.; Syvaoja, J.; Saluz, H.-P.; Haenel, F.; Eilers, M. Negative regulation of the mammalian UV response by Myc through association with Miz-1. Mol. Cell 2002, 10, 509–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.K.; Lee, M.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, H.J.; Park, C.M. The unified ICE–CBF pathway provides a transcriptional feedback control of freezing tolerance during cold acclimation in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol. Biol. 2015, 89, 187–201. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, C.-H.; Agarwal, M.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, Q.; Zhu, J.-K. The negative regulator of plant cold responses, HOS1, is a RING E3 ligase that mediates the ubiquitination and degradation of ICE1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 8281–8286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurbidaeva, A.; Ezhova, T.; Novokreshchenova, M. Arabidopsis thaliana ICE2 gene: Phylogeny, structural evolution and functional diversification from ICE1. Plant Sci. 2014, 229, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leivar, P.; Monte, E.; Al-Sady, B.; Carle, C.; Storer, A.; Alonso, J.M.; Ecker, J.R.; Quail, P.H. The Arabidopsis Phytochrome-Interacting Factor PIF7, Together with PIF3 and PIF4, Regulates Responses to Prolonged Red Light by Modulating phyB Levels. Plant Cell 2008, 20, 337–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Gene Name | Gene ID | Subgroup | MW (kD) | PL (aa) | pI | Instability Index | Aliphatic Index | GRAVY |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BobHLH003 | Bol013674 | Ib(1) | 38.02 | 336 | 5.23 | 50.35 | 62.89 | -0.58 |
| BobHLH018 | Bol034680 | Ia | 29.33 | 258 | 7.09 | 43.18 | 69.53 | -0.61 |
| BobHLH028 | Bol028622 | Orphan | 33.56 | 305 | 5.66 | 59.74 | 74.20 | -0.79 |
| BobHLH033 | Bol031047 | VIIIc(1) | 38.22 | 333 | 6.11 | 56.65 | 70.30 | -0.80 |
| BobHLH039 | Bol015349 | Ib(2) | 35.87 | 314 | 6.20 | 54.79 | 81.11 | -0.56 |
| BobHLH040 | Bol008832 | Va | 55.21 | 500 | 7.25 | 64.06 | 59.86 | -0.86 |
| BobHLH044 | Bol027942 | IVc | 26.23 | 240 | 9.08 | 57.23 | 62.62 | -0.69 |
| BobHLH045 | Bol028008 | Ib(1) | 37.16 | 338 | 5.59 | 77.92 | 85.65 | -0.53 |
| BobHLH046 | Bol020475 | VIIIc(2) | 26.70 | 240 | 7.60 | 51.58 | 80.92 | -0.41 |
| BobHLH048 | Bol029437 | VII(a+b) | 46.22 | 414 | 5.75 | 64.00 | 57.22 | -0.83 |
| BobHLH054 | Bol010742 | Ia | 42.56 | 387 | 6.80 | 66.78 | 59.30 | -0.64 |
| BobHLH059 | Bol012482 | XII | 38.43 | 341 | 5.89 | 62.00 | 74.57 | -0.61 |
| BobHLH068 | Bol004843 | Orphan | 36.34 | 325 | 6.18 | 65.72 | 64.22 | -0.80 |
| BobHLH070 | Bol029986 | IX | 34.65 | 319 | 8.52 | 56.00 | 62.41 | -0.62 |
| BobHLH071 | Bol004925 | Orphan | 56.20 | 504 | 5.44 | 50.17 | 77.08 | -0.46 |
| BobHLH075 | Bol011028 | Va | 38.11 | 344 | 6.13 | 49.36 | 69.16 | -0.73 |
| BobHLH093 | Bol021577 | VII(a+b) | 45.76 | 406 | 6.40 | 60.63 | 61.21 | -0.78 |
| BobHLH094 | Bol021588 | IX | 32.94 | 302 | 6.67 | 57.82 | 53.97 | -0.81 |
| BobHLH104 | Bol020888 | XII | 66.30 | 610 | 5.21 | 49.41 | 66.70 | -0.53 |
| BobHLH105 | Bol030777 | VIIIb | 29.84 | 263 | 7.79 | 53.77 | 70.11 | -0.75 |
| BobHLH109 | Bol036767 | VII(a+b) | 37.95 | 342 | 6.37 | 65.07 | 60.37 | -0.72 |
| BobHLH111 | Bol007664 | XII | 50.41 | 457 | 6.14 | 57.04 | 64.46 | -0.62 |
| BobHLH117 | Bol023989 | VIIIc(1) | 39.00 | 354 | 5.75 | 63.46 | 69.46 | -0.57 |
| BobHLH124 | Bol040072 | Ia | 36.64 | 324 | 5.42 | 61.33 | 74.94 | -0.75 |
| BobHLH126 | Bol027107 | Ib(1) | 25.08 | 219 | 9.27 | 54.41 | 70.68 | -0.80 |
| BobHLH129 | Bol041503 | XII | 37.75 | 337 | 5.86 | 46.86 | 76.94 | -0.55 |
| BobHLH147 | Bol018679 | IVb | 27.25 | 245 | 5.91 | 47.66 | 76.41 | -0.69 |
| BobHLH148 | Bol018659 | Ia | 29.48 | 257 | 8.79 | 64.19 | 79.61 | -0.64 |
| BobHLH149 | Bol014189 | IVb | 61.79 | 568 | 5.78 | 46.74 | 74.19 | -0.49 |
| BobHLH152 | Bol007436 | XI | 39.69 | 349 | 5.50 | 66.58 | 73.50 | -0.60 |
| BobHLH156 | Bol037257 | II | 36.43 | 328 | 4.93 | 55.42 | 58.57 | -0.76 |
| BobHLH162 | Bol044486 | III(a+c) | 101.68 | 900 | 8.68 | 51.92 | 70.53 | -0.56 |
| BobHLH172 | Bol018435 | IIIb(1) | 32.42 | 282 | 8.80 | 66.89 | 68.44 | -0.69 |
| BobHLH173 | Bol011442 | XII | 34.63 | 310 | 6.15 | 73.35 | 77.71 | -0.57 |
| BobHLH178 | Bol032141 | III(d+e) | 25.37 | 226 | 9.04 | 38.23 | 80.22 | -0.67 |
| BobHLH202 | Bol029707 | IVa | 28.79 | 257 | 8.76 | 60.15 | 89.84 | -0.30 |
| BobHLH207 | Bol016340 | XI | 34.26 | 298 | 6.22 | 66.88 | 78.56 | -0.81 |
| BobHLH212 | Bol009457 | VII(a+b) | 27.15 | 246 | 5.19 | 60.28 | 63.46 | -0.76 |
| BobHLH221 | Bol004364 | IIIb(1) | 40.51 | 359 | 5.08 | 63.80 | 74.40 | -0.57 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shan, X.; Zhang, W.; Yu, F.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Tang, J.; Dai, Z. Genome-Wide Analysis of Basic Helix–Loop–Helix Superfamily Members Reveals Organization and Chilling-Responsive Patterns in Cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata L.). Genes 2019, 10, 914. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10110914
Shan X, Zhang W, Yu F, Wang S, Li J, Tang J, Dai Z. Genome-Wide Analysis of Basic Helix–Loop–Helix Superfamily Members Reveals Organization and Chilling-Responsive Patterns in Cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata L.). Genes. 2019; 10(11):914. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10110914
Chicago/Turabian StyleShan, Xi, Wei Zhang, Fangwei Yu, Shenyun Wang, Jianbin Li, Jun Tang, and Zhongliang Dai. 2019. "Genome-Wide Analysis of Basic Helix–Loop–Helix Superfamily Members Reveals Organization and Chilling-Responsive Patterns in Cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata L.)" Genes 10, no. 11: 914. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10110914
APA StyleShan, X., Zhang, W., Yu, F., Wang, S., Li, J., Tang, J., & Dai, Z. (2019). Genome-Wide Analysis of Basic Helix–Loop–Helix Superfamily Members Reveals Organization and Chilling-Responsive Patterns in Cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata L.). Genes, 10(11), 914. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10110914




