Transcriptomics of Tasmanian Devil (Sarcophilus Harrisii) Ear Tissue Reveals Homogeneous Gene Expression Patterns across a Heterogeneous Landscape
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
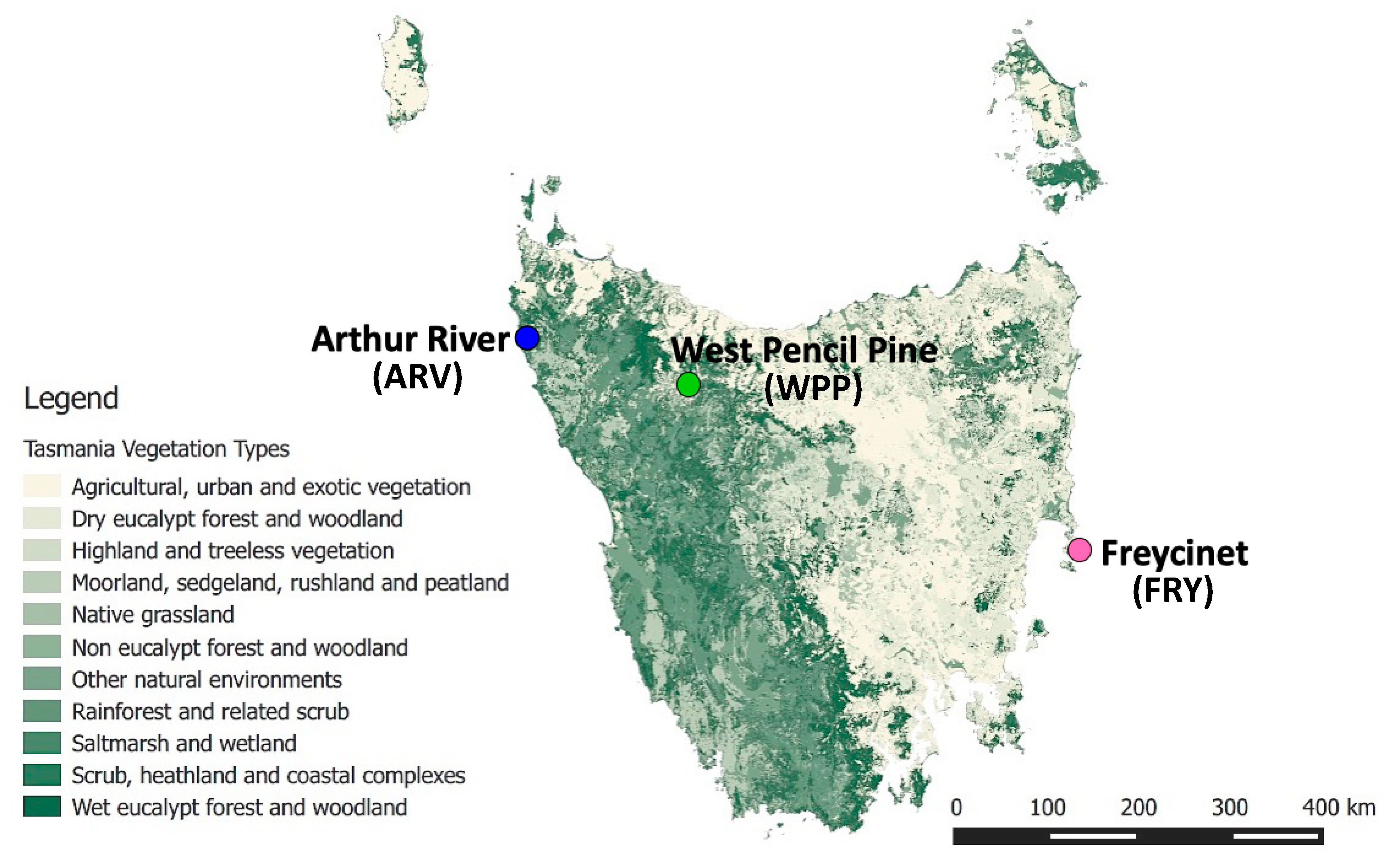
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Library Preparation and Sequencing
2.3. Read Alignment
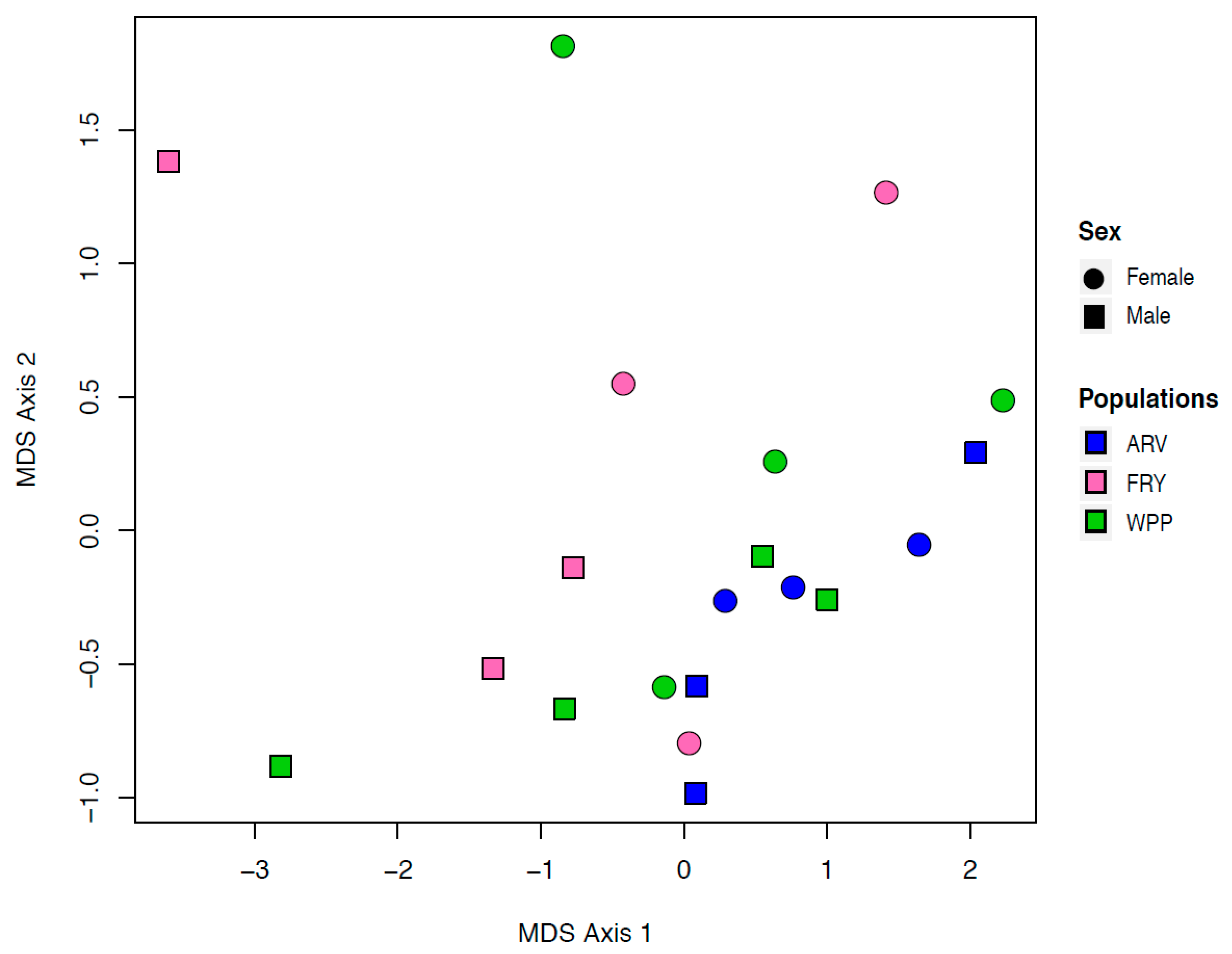
2.4. Multidimensional Scaling (MDS)
2.5. Differential Expression Analysis
2.6. Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis (WGCNA)
2.7. Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA)
2.8. Power Analysis
2.9. Availability of Data and Materials
3. Results
3.1. Sequencing and Alignment
3.2. Multidimensional Scaling Cluster Analysis
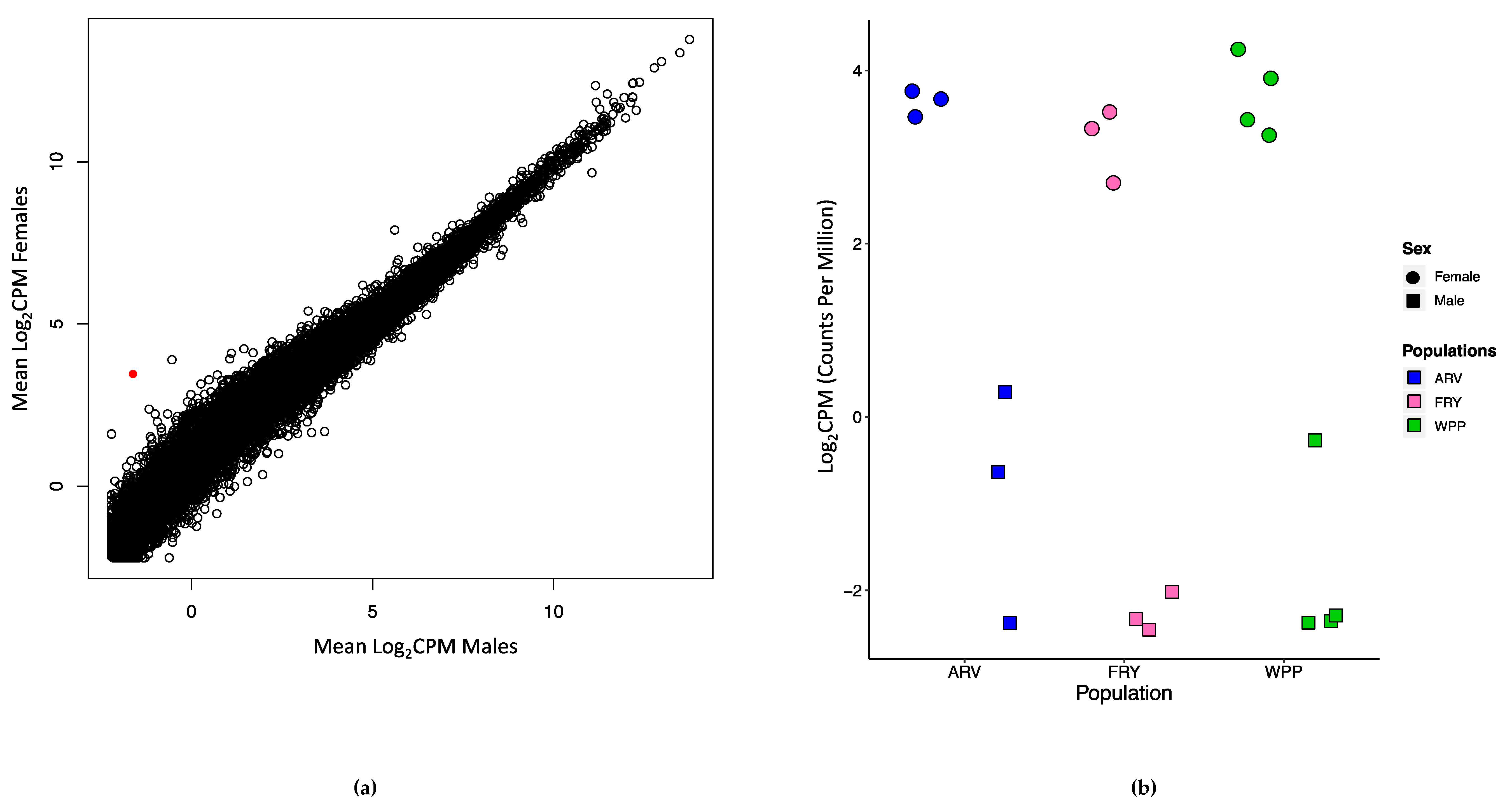
3.3. Identifying Population and Sex-Biased Differential Gene Expression
3.4. Population and Sex-Specific Patterns of Gene Co-Expression
3.5. Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA)
3.6. Power Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Devil Ear Tissue Lacks Transcriptome-Wide Differential Gene Expression
4.2. Differential Expression of Candidate Genes for Local Adaptation
4.3. Gene Co-Expression Patterns Reflect Possible Adaptive Responses to Coastal Environments
4.4. Sex-Biased Expression Patterns
4.5. Choice of Tissue
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Colbourne, J.K.; Pfrender, M.E.; Gilbert, D.; Thomas, W.K.; Tucker, A.; Oakley, T.H.; Tokishita, S.; Aerts, A.; Arnold, G.J.; Basu, M.K.; et al. The ecoresponsive genome of Daphnia pulex. Science 2011, 331, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez, M.; Schrey, A.W.; Richards, C.L. Ten years of transcriptomics in wild populations: What have we learned about their ecology and evolution? Mol. Ecol. 2015, 24, 710–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todd, E.V.; Black, M.A.; Gemmell, N.J. The power and promise of RNA-seq in ecology and evolution. Mol. Ecol. 2016, 25, 1224–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Richards, C.L.; Hanzawa, Y.; Katari, M.S.; Ehrenreich, I.M.; Engelmann, K.E.; Purugganan, M.D. Perspectives on Ecological and Evolutionary Systems Biology. Annu. Plant Rev. Online 2018, 35, 331–349. [Google Scholar]
- Pavey, S.A.; Bernatchez, L.; Aubin-Horth, N.; Landry, C.R. What is needed for next-generation ecological and evolutionary genomics? Trends Ecol. Evol. 2012, 27, 673–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connon, R.E.; Jeffries, K.M.; Komoroske, L.M.; Todgham, A.E.; Fangue, N.A. The utility of transcriptomics in fish conservation. J. Exp. Biol. 2018, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoban, S.; Kelley, J.L.; Lotterhos, K.E.; Antolin, M.F.; Bradburd, G.; Lowry, D.B.; Poss, M.L.; Reed, L.K.; Storfer, A.; Whitlock, M.C. Finding the genomic basis of local adaptation: Pitfalls, practical solutions, and future directions. Am. Nat. 2016, 188, 379–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, D.B.; Hoban, S.; Kelley, J.L.; Lotterhos, K.E.; Reed, L.K.; Antolin, M.F.; Storfer, A. Breaking RAD: An evaluation of the utility of restriction site-associated DNA sequencing for genome scans of adaptation. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2017, 17, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, D.B.; Hoban, S.; Kelley, J.L.; Lotterhos, K.E.; Reed, L.K.; Antolin, M.F.; Storfer, A. Responsible RAD: Striving for best practices in population genomic studies of adaptation. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2017, 17, 366–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storfer, A.; Hohenlohe, P.A.; Margres, M.J.; Patton, A.; Fraik, A.K.; Lawrance, M.; Ricci, L.E.; Stahlke, A.R.; McCallum, H.I.; Jones, M.E. The devil is in the details: Genomics of transmissible cancers in Tasmanian devils. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murchison, E.P.; Schulz-Trieglaff, O.B.; Ning, Z.; Alexandrov, L.B.; Bauer, M.J.; Fu, B.; Hims, M.; Ding, Z.; Ivakhno, S.; Stewart, C.; et al. Genome sequencing and analysis of the Tasmanian devil and its transmissible cancer. Cell 2012, 148, 780–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margres, M.J.; Jones, M.E.; Epstein, B.; Kerlin, D.H.; Comte, S.; Fox, S.; Fraik, A.K.; Hendricks, S.A.; Huxtable, S.; Lachish, S.; et al. Large-effect loci affect survival in Tasmanian devils (Sarcophilus harrisii) infected with a transmissible cancer. Mol. Ecol. 2018, 27, 4189–4199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margres, M.J.; Ruiz-Aravena, M.; Hamede, R.; Jones, M.E.; Lawrance, M.F.; Hendricks, S.A.; Patton, A.; Davis, B.W.; Ostrander, E.A.; McCallum, H.; et al. The Genomic Basis of Tumor Regression in Tasmanian Devils (Sarcophilus harrisii). Genome Biol. Evol. 2018, 10, 3012–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hewavisenti, R.V.; Morris, K.M.; O’Meally, D.; Cheng, Y.; Papenfuss, A.T.; Belov, K. The identification of immune genes in the milk transcriptome of the Tasmanian devil (Sarcophilus harrisii). PeerJ 2016, 4, e1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, W.; Hayes, V.M.; Ratan, A.; Petersen, D.C.; Wittekindt, N.E.; Miller, J.; Walenz, B.; Knight, J.; Qi, J.; Zhao, F.; et al. Genetic diversity and population structure of the endangered marsupial Sarcophilus harrisii (Tasmanian devil). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 12348–12353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brüniche-Olsen, A.; Burridge, C.P.; Austin, J.J.; Jones, M.E. Disease induced changes in gene flow patterns among Tasmanian devil populations. Biol. Conserv. 2013, 165, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruniche-Olsen, A.; Jones, M.E.; Austin, J.J.; Burridge, C.P.; Holland, B.R. Extensive population decline in the Tasmanian devil predates European settlement and devil facial tumour disease. Biol. Lett. 2014, 10, 20140619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddle, H.V.; Kreiss, A.; Tovar, C.; Yuen, C.K.; Cheng, Y.; Belov, K.; Swift, K.; Pearse, A.M.; Hamede, R.; Jones, M.E.; et al. Reversible epigenetic down-regulation of MHC molecules by devil facial tumour disease illustrates immune escape by a contagious cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 5103–5108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lachish, S.; McCallum, H.; Jones, M. Demography, disease and the devil: Life-history changes in a disease-affected population of Tasmanian devils (Sarcophilus harrisii). J. Anim. Ecol. 2009, 78, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, B.; Willet, C.E.; Hamede, R.; Jones, M.; Belov, K.; Wade, C.M. Variants in the host genome may inhibit tumour growth in devil facial tumours: Evidence from genome-wide association. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraik, A.K.; Margres, M.J.; Epstein, B.; Barbosa, S.; Jones, M.; Hamede, R.; Veillet, A.; McCallum, H.; Lopez-Contreras, E.; Kallinen, S.J.; et al. Disease swamps molecular signatures of genetic-environmental associations to abiotic factors in Tasmanian devil (Sarcophilus harrisii) populations. bioRxiv 2019, 780122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.E.; Rose, R.K. Preliminary Assessment of Distribution and Habitat Associations of the Spotted-Tailed Quoll (Dasyurus maculatus maculatus) and Eastern Quoll (D. viverrinus) in Tasmania to Determine Conservation and Reservation Status; Tasmanian Public Land Use Commission: Hobart, Australia, 1996; pp. 65–67. [Google Scholar]
- Rounsevell, D.; Taylor, R.; Hocking, G. Distribution records of native terrestrial mammals in Tasmania. Wildl. Res. 1991, 18, 699–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.E.; Barmuta, L.A. Niche differentiation among sympatric Australian dasyurid carnivores. J. Mammal. 2000, 81, 434–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendricks, S.; Epstein, B.; Schonfeld, B.; Wiench, C.; Hamede, R.; Jones, M.; Storfer, A.; Hohenlohe, P. Conservation implications of limited genetic diversity and population structure in Tasmanian devils (Sarcophilus harrisii). Conserv. Genet. 2017, 18, 977–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Storfer, A.; Epstein, B.; Jones, M.; Micheletti, S.; Spear, S.F.; Lachish, S.; Fox, S. Landscape genetics of the Tasmanian devil: Implications for spread of an infectious cancer. Conserv. Genet. 2017, 18, 1287–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.E.; Paetkau, D.; Geffen, E.L.; Moritz, C. Genetic diversity and population structure of Tasmanian devils, the largest marsupial carnivore. Mol. Ecol. 2004, 13, 2197–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawecki, T.J.; Ebert, D. Conceptual issues in local adaptation. Ecol. Lett. 2004, 7, 1225–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamede, R.K.; McCallum, H.; Jones, M. Biting injuries and transmission of Tasmanian devil facial tumour disease. J. Anim. Ecol. 2013, 82, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pertea, M.; Kim, D.; Pertea, G.M.; Leek, J.T.; Salzberg, S.L. Transcript-level expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with HISAT, StringTie and Ballgown. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 1650–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H. A statistical framework for SNP calling, mutation discovery, association mapping and population genetical parameter estimation from sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2987–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ritchie, M.E.; Phipson, B.; Wu, D.; Hu, Y.; Law, C.W.; Shi, W.; Smyth, G.K. limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. edgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, M.D.; Oshlack, A. A scaling normalization method for differential expression analysis of RNA-seq data. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langfelder, P.; Horvath, S. WGCNA: An R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashburner, M.; Ball, C.A.; Blake, J.A.; Botstein, D.; Butler, H.; Cherry, J.M.; Davis, A.P.; Dolinski, K.; Dwight, S.S.; Eppig, J.T.; et al. Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. Gene Ontol. Consort. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, A.; Tamayo, P.; Mootha, V.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Ebert, B.L.; Gillette, M.A.; Paulovich, A.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Golub, T.R.; Lander, E.S.; et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: A knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15545–15550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mootha, V.K.; Lindgren, C.M.; Eriksson, K.F.; Subramanian, A.; Sihag, S.; Lehar, J.; Puigserver, P.; Carlsson, E.; Ridderstrale, M.; Laurila, E.; et al. PGC-1alpha-responsive genes involved in oxidative phosphorylation are coordinately downregulated in human diabetes. Nat. Genet. 2003, 34, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, S.N.; Therneau, T.M.; Zhang, Y.; Poland, G.A.; Kocher, J.P. Calculating sample size estimates for RNA sequencing data. J. Comput. Biol. 2013, 20, 970–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell-Staton, S.C.; Bare, A.; Losos, J.B.; Edwards, S.V.; Cheviron, Z.A. Physiological and regulatory underpinnings of geographic variation in reptilian cold tolerance across a latitudinal cline. Mol. Ecol. 2018, 27, 2243–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleksiak, M.F.; Churchill, G.A.; Crawford, D.L. Variation in gene expression within and among natural populations. Nat. Genet. 2002, 32, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Grande, F.; Sharma, R.; Meiser, A.; Rolshausen, G.; Budel, B.; Mishra, B.; Thines, M.; Otte, J.; Pfenninger, M.; Schmitt, I. Adaptive differentiation coincides with local bioclimatic conditions along an elevational cline in populations of a lichen-forming fungus. BMC Evol. Biol. 2017, 17, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzo, F.R.; Huff, C.; Myllymaki, M.; Olenchock, B.; Swierczek, S.; Tashi, T.; Gordeuk, V.; Wuren, T.; Ri-Li, G.; McClain, D.A.; et al. A genetic mechanism for Tibetan high-altitude adaptation. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 951–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schoville, S.D.; Barreto, F.S.; Moy, G.W.; Wolff, A.; Burton, R.S. Investigating the molecular basis of local adaptation to thermal stress: Population differences in gene expression across the transcriptome of the copepod Tigriopus californicus. BMC Evol. Biol. 2012, 12, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gleason, L.U.; Burton, R.S. RNA-seq reveals regional differences in transcriptome response to heat stress in the marine snail Chlorostoma funebralis. Mol. Ecol. 2015, 24, 610–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Chen, Z.X.; Oliver, B.; Harbison, S.T. Microenvironmental Gene Expression Plasticity Among Individual Drosophila melanogaster. G3 2016, 6, 4197–4210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Yang, H.; Storey, K.B.; Chen, M. RNA-seq dependent transcriptional analysis unveils gene expression profile in the intestine of sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus during aestivation. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2014, 10, 30–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishikimi, T.; Inaba-Iemura, C.; Ishimura, K.; Tadokoro, K.; Koshikawa, S.; Ishikawa, K.; Akimoto, K.; Hattori, Y.; Kasai, K.; Minamino, N.; et al. Natriuretic peptide/natriuretic peptide receptor-A (NPR-A) system has inhibitory effects in renal fibrosis in mice. Regul. Pept. 2009, 154, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, D.C.; Hughes, M.R. Comparison of renal and salt gland function in three species of wild ducks. J. Exp. Biol. 2003, 206, 3273–3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, C.Y.; Childress, V.; Piao, Y.; Michel, M.; Johnson, A.A.; Kunisada, M.; Ko, M.S.; Kaestner, K.H.; Marmorstein, A.D.; Schlessinger, D. Forkhead transcription factor FoxA1 regulates sweat secretion through Bestrophin 2 anion channel and Na-K-Cl cotransporter 1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 1199–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zacchi, F.L.; de Lima, D.; Flores-Nunes, F.; Mattos, J.J.; Luchmann, K.H.; de Miranda Gomes, C.H.A.; Bicego, M.C.; Taniguchi, S.; Sasaki, S.T.; Dias Bainy, A.C. Transcriptional changes in oysters Crassostrea brasiliana exposed to phenanthrene at different salinities. Aquat. Toxicol. 2017, 183, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deck, C.A.; McKay, S.J.; Fiedler, T.J.; LeMoine, C.M.; Kajimura, M.; Nawata, C.M.; Wood, C.M.; Walsh, P.J. Transcriptome responses in the rectal gland of fed and fasted spiny dogfish shark (Squalus acanthias) determined by suppression subtractive hybridization. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2013, 8, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guiler, E.R. Observations on the Tasmanian devil, Sarcophilus harrisii (Marsupialia:Dasyuridae): I. Numbers, home range, movements, and food in two populations. Aust. J. Zool. 1970, 18, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pemberton, D.; Gales, S.; Bauer, B.; Gales, R.; Lazenby, B.; Medlock, K. The diet of the tasmanian devil, sarcophilus harrisii, as determined from analysis of scat and stomach contents. Pap. Proc. R. Soc. Tasman. 2008, 142, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Flock, K.; Jue, N.; Zhang, M.Y.; Jones, A.; Al Seesi, S.; Mandoiu, I.; Pillai, S.; Hoffman, M.; O’Neill, R.; et al. Dosage Compensation and Gene Expression of the X Chromosome in Sheep. G3-Genes Genomes Genet. 2019, 9, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tarpey, P.; Thomas, S.; Sarvananthan, N.; Mallya, U.; Lisgo, S.; Talbot, C.J.; Roberts, E.O.; Awan, M.; Surendran, M.; McLean, R.J.; et al. Mutations in FRMD7, a newly identified member of the FERM family, cause X-linked idiopathic congenital nystagmus. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 1242–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Self, J.; Haitchi, H.M.; Griffiths, H.; Holgate, S.T.; Davies, D.E.; Lotery, A. Frmd7 expression in developing mouse brain. Eye 2010, 24, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.; Proudlock, F.A.; Sarvananthan, N.; Roberts, E.O.; Awan, M.; McLean, R.; Surendran, M.; Kumar, A.S.; Farooq, S.J.; Degg, C.; et al. Phenotypical characteristics of idiopathic infantile nystagmus with and without mutations in FRMD7. Brain 2008, 131, 1259–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Wei, Y.; Tian, L.; Kang, X. A novel frameshift mutation in FRMD7 causes X-linked infantile nystagmus in a Chinese family. BMC Med. Genet. 2019, 20, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloksgaard, M.; Neess, D.; Faergeman, N.J.; Mandrup, S. Acyl-CoA binding protein and epidermal barrier function. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1841, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, L.; DeBono, C.A.; Campagna, D.R.; Young, D.C.; Moody, D.B.; Fleming, M.D. Loss of the acyl-CoA binding protein (Acbp) results in fatty acid metabolism abnormalities in mouse hair and skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2007, 127, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Aravena, M.; Jones, M.E.; Carver, S.; Estay, S.; Espejo, C.; Storfer, A.; Hamede, R.K. Sex bias in ability to cope with cancer: Tasmanian devils and facial tumour disease. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2018, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mele, M.; Ferreira, P.G.; Reverter, F.; DeLuca, D.S.; Monlong, J.; Sammeth, M.; Young, T.R.; Goldmann, J.M.; Pervouchine, D.D.; Sullivan, T.J.; et al. Human genomics. The human transcriptome across tissues and individuals. Science 2015, 348, 660–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Fuscoe, J.C.; Zhao, C.; Guo, C.; Jia, M.; Qing, T.; Bannon, D.I.; Lancashire, L.; Bao, W.; Du, T.; et al. A rat RNA-Seq transcriptomic BodyMap across 11 organs and 4 developmental stages. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Z.; Chen, G.; Zhu, S.; Zhu, J.; Li, B.; Song, Y.; Li, S.; Shi, L.; Zheng, Y.; Li, M. Expression profiling and functional annotation of noncoding genes across 11 distinct organs in rat development. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, Q.; Cheng, D.; Duan, J.; Wang, G.; Cheng, T.; Zha, X.; Liu, C.; Zhao, P.; Dai, F.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Microarray-based gene expression profiles in multiple tissues of the domesticated silkworm, Bombyx mori. Genome Biol. 2007, 8, R162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cribbin, K.M.; Quackenbush, C.R.; Taylor, K.; Arias-Rodriguez, L.; Kelley, J.L. Sex-specific differences in transcriptome profiles of brain and muscle tissue of the tropical gar. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehead, A.; Zhang, S.; Roach, J.L.; Galvez, F. Common functional targets of adaptive micro-and macro-evolutionary divergence in killifish. Mol. Ecol. 2013, 22, 3780–3796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaisers, W.; Boukamp, P.; Stark, H.J.; Schwender, H.; Tigges, J.; Krutmann, J.; Schaal, H. Age, gender and UV-exposition related effects on gene expression in in vivo aged short term cultivated human dermal fibroblasts. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0175657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fraik, A.K.; Quackenbush, C.; Margres, M.J.; Comte, S.; Hamilton, D.G.; Kozakiewicz, C.P.; Jones, M.; Hamede, R.; Hohenlohe, P.A.; Storfer, A.; et al. Transcriptomics of Tasmanian Devil (Sarcophilus Harrisii) Ear Tissue Reveals Homogeneous Gene Expression Patterns across a Heterogeneous Landscape. Genes 2019, 10, 801. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10100801
Fraik AK, Quackenbush C, Margres MJ, Comte S, Hamilton DG, Kozakiewicz CP, Jones M, Hamede R, Hohenlohe PA, Storfer A, et al. Transcriptomics of Tasmanian Devil (Sarcophilus Harrisii) Ear Tissue Reveals Homogeneous Gene Expression Patterns across a Heterogeneous Landscape. Genes. 2019; 10(10):801. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10100801
Chicago/Turabian StyleFraik, Alexandra K., Corey Quackenbush, Mark J. Margres, Sebastien Comte, David G. Hamilton, Christopher P. Kozakiewicz, Menna Jones, Rodrigo Hamede, Paul A. Hohenlohe, Andrew Storfer, and et al. 2019. "Transcriptomics of Tasmanian Devil (Sarcophilus Harrisii) Ear Tissue Reveals Homogeneous Gene Expression Patterns across a Heterogeneous Landscape" Genes 10, no. 10: 801. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10100801
APA StyleFraik, A. K., Quackenbush, C., Margres, M. J., Comte, S., Hamilton, D. G., Kozakiewicz, C. P., Jones, M., Hamede, R., Hohenlohe, P. A., Storfer, A., & Kelley, J. L. (2019). Transcriptomics of Tasmanian Devil (Sarcophilus Harrisii) Ear Tissue Reveals Homogeneous Gene Expression Patterns across a Heterogeneous Landscape. Genes, 10(10), 801. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10100801




