Role of Brain Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Decoding Sex Differences Associated with Nicotine Self-Administration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
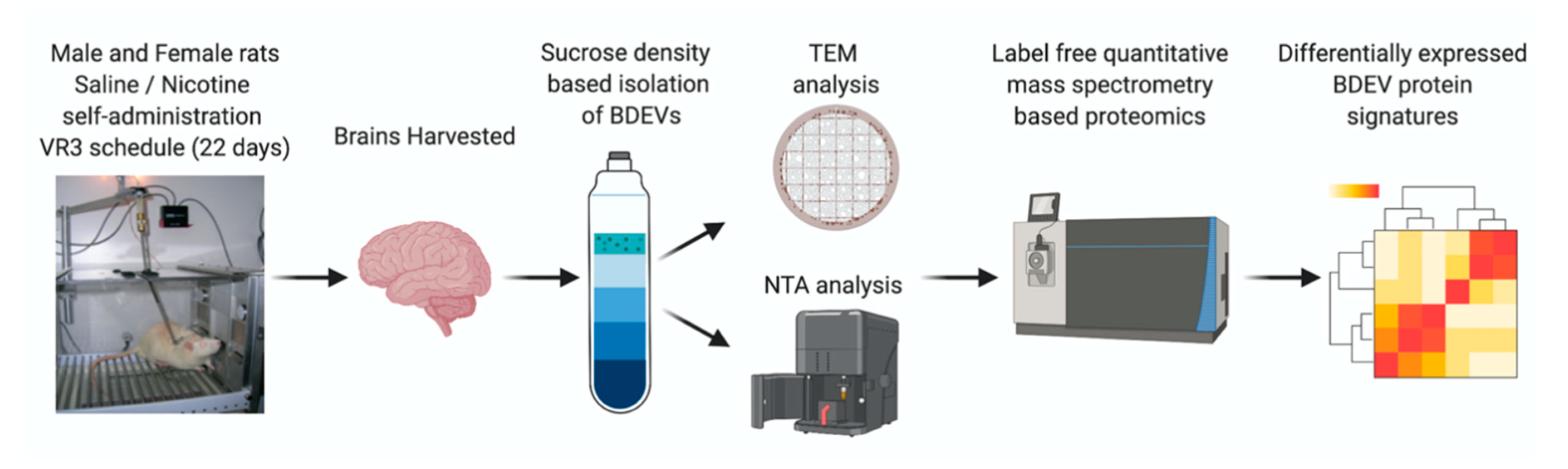
2.1. Self-Administration and Brain Tissue Collection
2.2. BDEV Isolation
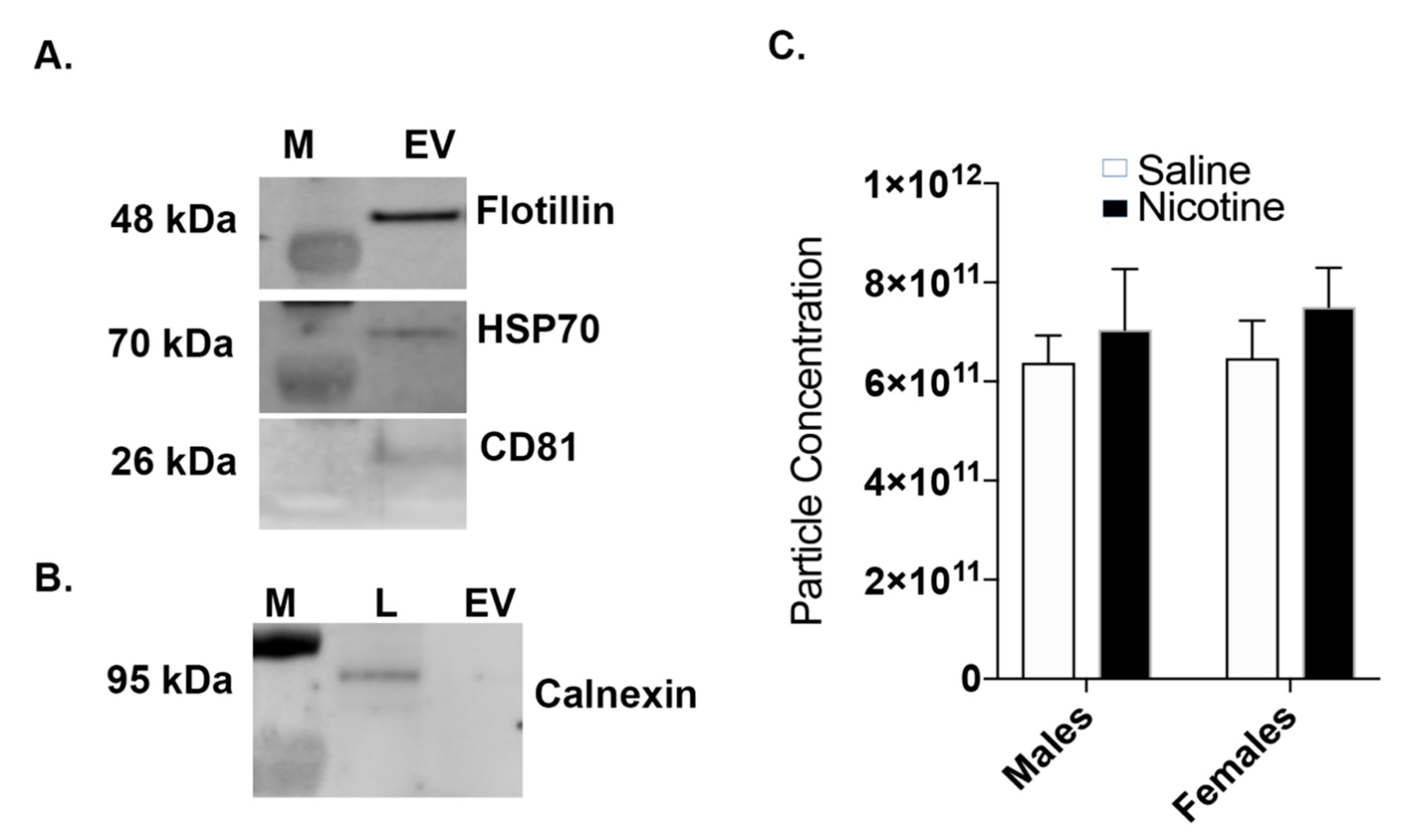
2.3. Western Blot: BDEV Marker Validation
2.4. Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA)
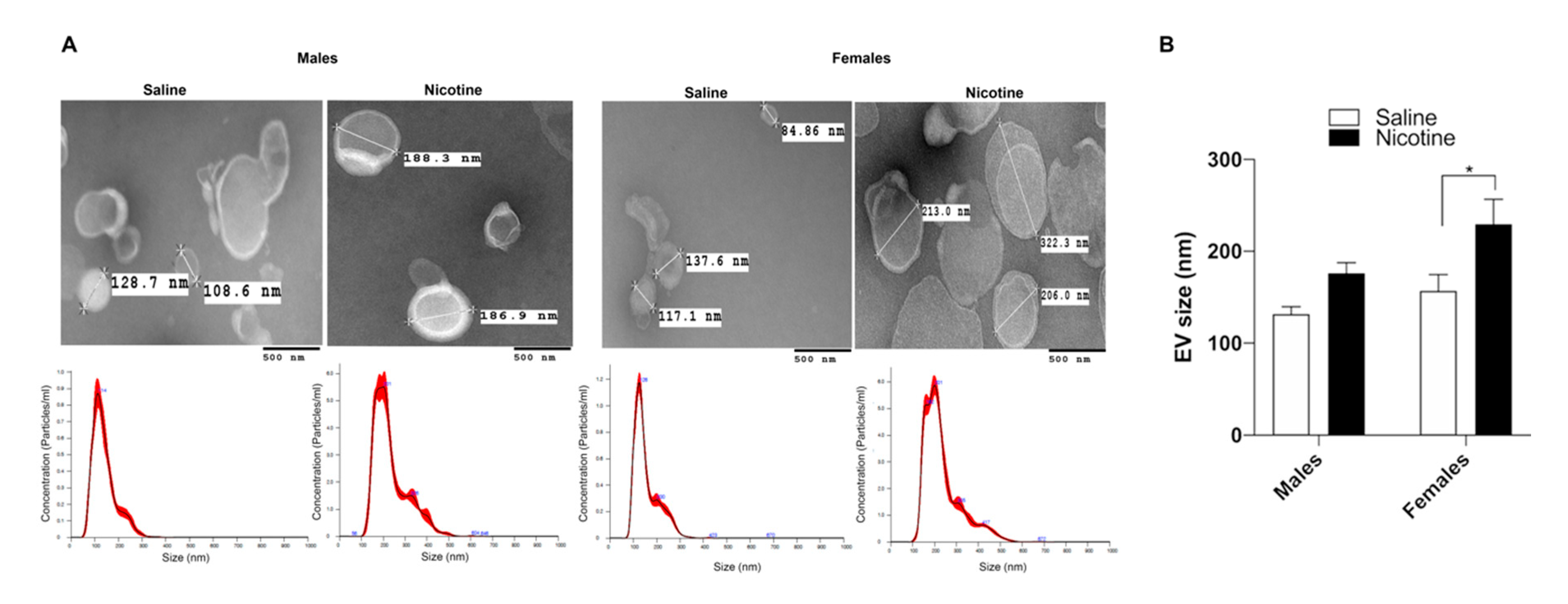
2.5. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.6. Total RNA Isolation, cDNA Preparation, and Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.7. Mass Spectrometry/Proteomics
2.8. Bioinformatics Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Nicotine Exposure Increases BDEV Size Which Is More Pronounced in Females
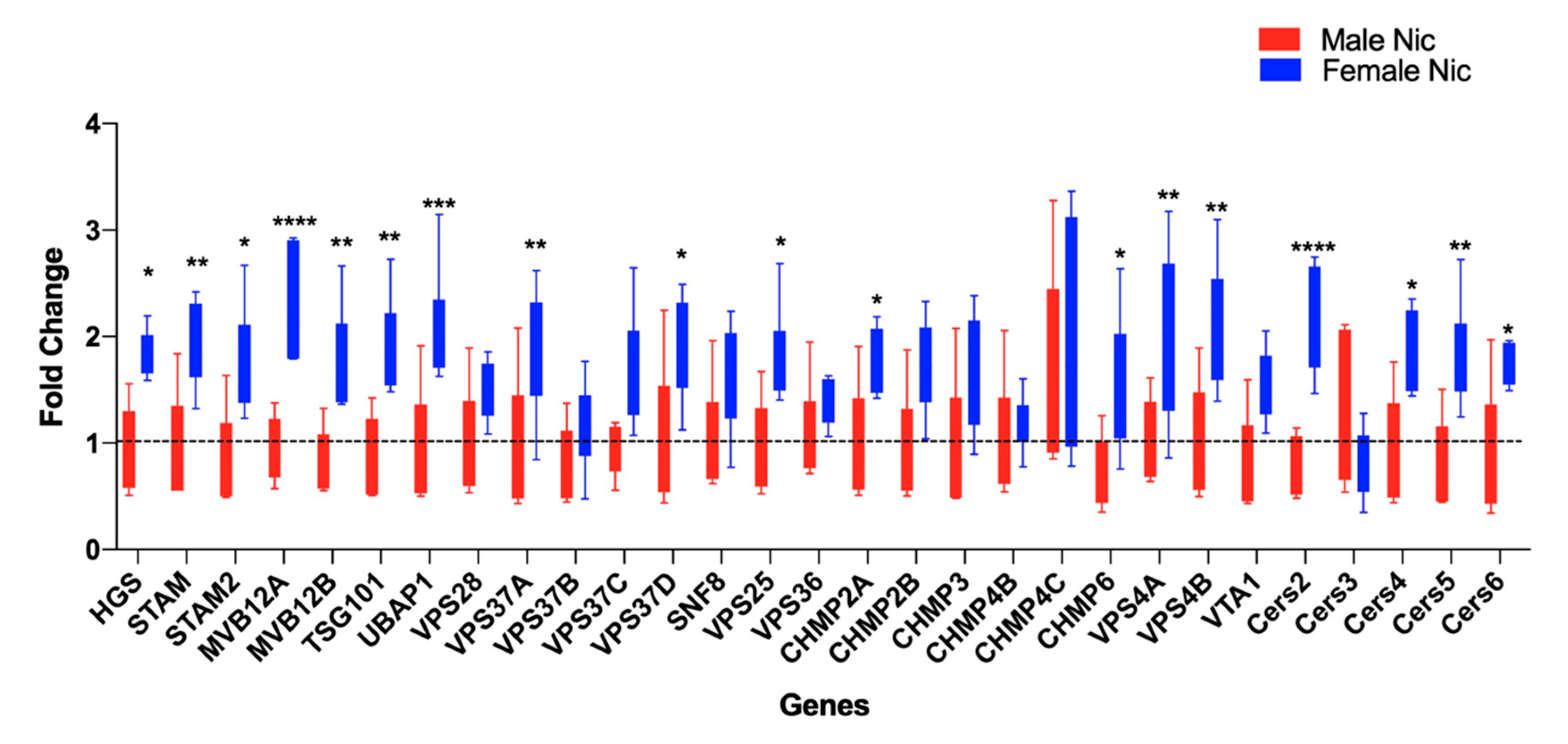
3.2. Nicotine Increases BDEV Biogenesis Which Are More Pronounced in Females
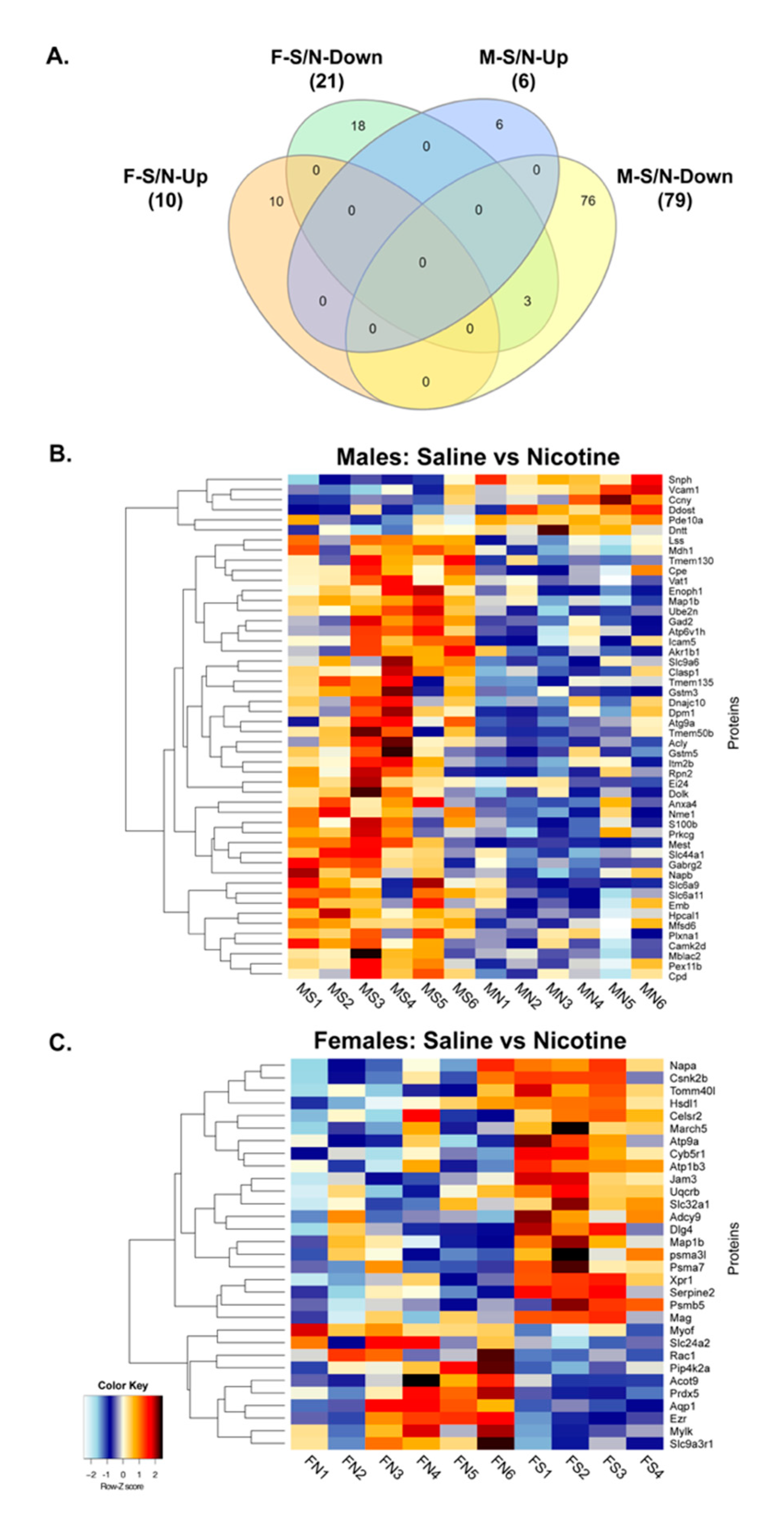
3.3. Proteomics and Bioinformatics Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, X.; Bishop, E.E.; Kennedy, S.M.; Simpson, S.A.; Pechacek, T.F. Annual healthcare spending attributable to cigarette smoking: An update. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2015, 48, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benowitz, N.L. Nicotine addiction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 2295–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benowitz, N.L. Pharmacology of nicotine: Addiction, smoking-induced disease, and therapeutics. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2009, 49, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkins, K.A. Smoking cessation in women. Special considerations. CNS Drugs 2001, 15, 391–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiffman, S.; Paton, S.M. Individual differences in smoking: Gender and nicotine addiction. Nicotine Tob. Res. 1999, 1, S153–S157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, A.M.; Scheuermann, T.S.; Nollen, N.; Hatsukami, D.; Ahluwalia, J.S. Gender differences in smoking behavior and dependence motives among daily and nondaily smokers. Nicotine Tob. Res. 2016, 18, 1408–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, K.A.; Scott, J. Sex differences in long-term smoking cessation rates due to nicotine patch. Nicotine Tob. Res. 2008, 10, 1245–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, R.I.; Hertsgaard, L.A.; Dermody, S.S.; Luo, X.; Moua, L.; Allen, S.; al’Absi, M.; Hatsukami, D.K. Sex differences in response to reduced nicotine content cigarettes. Addict. Behav. 2014, 39, 1197–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittenger, S.T.; Swalve, N.; Chou, S.; Smith, M.D.; Hoonakker, A.J.; Pudiak, C.M.; Fleckenstein, A.E.; Hanson, G.R.; Bevins, R.A. Sex differences in neurotensin and substance P following nicotine self-administration in rats. Synapse 2016, 70, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, S.J.; Linker, K.E.; Leslie, F.M. Sex-dependent effects of nicotine on the developing brain. J. Neurosci. Res. 2017, 95, 422–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donny, E.C.; Caggiula, A.R.; Rowell, P.P.; Gharib, M.A.; Maldovan, V.; Booth, S.; Mielke, M.M.; Hoffman, A.; McCallum, S. Nicotine self-administration in rats: Estrous cycle effects, sex differences and nicotinic receptor binding. Psychopharmacology 2000, 151, 392–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grebenstein, P.; Burroughs, D.; Zhang, Y.; LeSage, M.G. Sex differences in nicotine self-administration in rats during progressive unit dose reduction: Implications for nicotine regulation policy. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2013, 114–115, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pogun, S.; Yararbas, G.; Nesil, T.; Kanit, L. Sex differences in nicotine preference. J. Neurosci. Res. 2017, 95, 148–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezvani, A.H.; Eddins, D.; Slade, S.; Hampton, D.S.; Christopher, N.C.; Petro, A.; Horton, K.; Johnson, M.; Levin, E.D. Neonatal 6-hydroxydopamine lesions of the frontal cortex in rats: Persisting effects on locomotor activity, learning and nicotine self-administration. Neuroscience 2008, 154, 885–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Han, W.; Wang, B.; Jiang, Q.; Solberg-Woods, L.C.; Palmer, A.A.; Chen, H. Propensity for social interaction predicts nicotine-reinforced behaviors in outbred rats. Genes Brain Behav. 2014, 13, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Belluzzi, J.D.; Loughlin, S.E.; Dao, J.M.; Chen, Y.; Leslie, F.M. Locomotor and stress responses to nicotine differ in adolescent and adult rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2010, 96, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preedy, V.R. Neuroscience of Nicotine: Mechanisms and Treatment; Academic Press: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Antonyak, M.A.; Cerione, R.A. Emerging picture of the distinct traits and functions of microvesicles and exosomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 3589–3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieu, M.; Martin-Jaular, L.; Lavieu, G.; Thery, C. Specificities of secretion and uptake of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles for cell-to-cell communication. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 21, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porro, C.; Trotta, T.; Panaro, M.A. Microvesicles in the brain: Biomarker, messenger or mediator? J. Neuroimmunol. 2015, 288, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maas, S.L.N.; Breakefield, X.O.; Weaver, A.M. Extracellular Vesicles: Unique Intercellular Delivery Vehicles. Trends Cell Biol. 2017, 27, 172–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposo, G.; Stoorvogel, W. Extracellular vesicles: Exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 200, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valadi, H.; Ekström, K.; Bossios, A.; Sjöstrand, M.; Lee, J.J.; Lötvall, J.O. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Xu, X.; Qian, Z.; Zhang, C.; Niu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Sun, J.; Zhang, X.; Yu, Y. The biological functions and clinical applications of exosomes in lung cancer. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 76, 4613–4633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosaka, T.; Yamashita, T.; Tamaoka, A.; Kwak, S. Extracellular RNAs as biomarkers of sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and other neurodegenerative diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Gu, Y.; Du, Y.; Liu, J. Exosomes: Diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic delivery vehicles for cancer. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 3333–3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, R.; Patel, T.; Freedman, J.E. Circulating extracellular vesicles in human disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 958–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Wang, G.; Hu, W.; Yao, Y.; Yu, X.F. Emerging roles and therapeutic value of exosomes in cancer metastasis. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittenger, S.T.; Schaal, V.L.; Moore, D.; Guda, R.S.; Koul, S.; Yelamanchili, S.V.; Bevins, R.A.; Pendyala, G. MicroRNA cluster miR199a/214 are differentially expressed in female and male rats following nicotine self-administration. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, E.B.; Hochfelder, C.G.; Lamberty, B.G.; Meays, B.M.; Morsey, B.M.; Kelso, M.L.; Fox, H.S.; Yelamanchili, S.V. Traumatic brain injury increases levels of miR-21 in extracellular vesicles: Implications for neuroinflammation. FEBS Open Bio 2016, 6, 835–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahjin, F.; Guda, R.S.; Schaal, V.L.; Odegaard, K.; Clark, A.; Gowen, A.; Xiao, P.; Lisco, S.J.; Pendyala, G.; Yelamanchili, S.V. Brain-derived extracellular vesicle microrna signatures associated with in utero and postnatal oxycodone exposure. Cells 2019, 9, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yelamanchili, S.V.; Lamberty, B.G.; Rennard, D.A.; Morsey, B.M.; Hochfelder, C.G.; Meays, B.M.; Levy, E.; Fox, H.S. MiR-21 in Extracellular vesicles leads to neurotoxicity via TLR7 signaling in SIV neurological disease. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1005032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mary, B.; Maurya, S.; Kumar, M.; Bammidi, S.; Kumar, V.; Jayandharan, G.R. Molecular engineering of adeno-associated virus capsid improves its therapeutic gene transfer in murine models of hemophilia and retinal degeneration. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 4738–4750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bindea, G.; Mlecnik, B.; Hackl, H.; Charoentong, P.; Tosolini, M.; Kirilovsky, A.; Fridman, W.H.; Pagès, F.; Trajanoski, Z.; Galon, J. ClueGO: A Cytoscape plug-in to decipher functionally grouped gene ontology and pathway annotation networks. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1091–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhri, N.; Caggiula, A.R.; Donny, E.C.; Booth, S.; Gharib, M.A.; Craven, L.A.; Allen, S.S.; Sved, A.F.; Perkins, K.A. Sex differences in the contribution of nicotine and nonpharmacological stimuli to nicotine self-administration in rats. Psychopharmacology 2005, 180, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Zou, S.; Coen, K.; Funk, D.; Shram, M.J.; Lê, A.D. Sex differences in yohimbine-induced increases in the reinforcing efficacy of nicotine in adolescent rats. Addict. Biol. 2014, 19, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, W.J. Sex and ovarian hormones influence vulnerability and motivation for nicotine during adolescence in rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2009, 94, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Théry, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Aikawa, E.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Anderson, J.D.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Antoniou, A.; Arab, T.; Archer, F.; Atkin-Smith, G.K.K.; et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, M.; Moita, C.; van Niel, G.; Kowal, J.; Vigneron, J.; Benaroch, P.; Manel, N.; Moita, L.F.; Thery, C.; Raposo, G. Analysis of ESCRT functions in exosome biogenesis, composition and secretion highlights the heterogeneity of extracellular vesicles. J. Cell Sci. 2013, 126, 5553–5565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan, T.; Furthauer, M. Biogenesis and function of ESCRT-dependent extracellular vesicles. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2018, 74, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trajkovic, K.; Hsu, C.; Chiantia, S.; Rajendran, L.; Wenzel, D.; Wieland, F.; Schwille, P.; Brugger, B.; Simons, M. Ceramide triggers budding of exosome vesicles into multivesicular endosomes. Science 2008, 319, 1244–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barile, L.; Vassalli, G. Exosomes: Therapy delivery tools and biomarkers of diseases. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 174, 63–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soung, Y.H.; Ford, S.; Zhang, V.; Chung, J. Exosomes in cancer diagnostics. Cancers 2017, 9, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zomer, A.; Vendrig, T.; Hopmans, E.S.; van Eijndhoven, M.; Middeldorp, J.M.; Pegtel, D.M. Exosomes: Fit to deliver small RNA. Commun. Integr. Biol. 2010, 3, 447–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrahari, V.; Agrahari, V.; Burnouf, P.A.; Chew, C.H.; Burnouf, T. Extracellular microvesicles as new industrial therapeutic frontiers. Trends Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 707–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burnouf, T.; Agrahari, V.; Agrahari, V. Extracellular vesicles as nanomedicine: Hopes and hurdles in clinical translation. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 8847–8859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Yin, Z.; Yang, L.; Fan, J.; Xu, J.; Jin, Y.; Yu, J.; Zhang, D.; Yang, G. Smoking induced extracellular vesicles release and their distinct properties in non-small cell lung cancer. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 3435–3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedikter, B.J.; Volgers, C.; van Eijck, P.H.; Wouters, E.F.M.; Savelkoul, P.H.M.; Reynaert, N.L.; Haenen, G.; Rohde, G.G.U.; Weseler, A.R.; Stassen, F.R.M. Cigarette smoke extract induced exosome release is mediated by depletion of exofacial thiols and can be inhibited by thiol-antioxidants. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 108, 334–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsello, T.; Kudlicki, A.S.; Garofalo, R.P.; Casola, A. Cigarette smoke condensate exposure changes RNA content of extracellular vesicles released from small airway epithelial cells. Cells 2019, 8, 1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobarrez, F.; Antoniewicz, L.; Hedman, L.; Bosson, J.A.; Lundback, M. Electronic cigarettes containing nicotine increase endothelial and platelet derived extracellular vesicles in healthy volunteers. Atherosclerosis 2020, 301, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, J.B.; Hu, M. Sex differences in drug abuse. Front. Neuroendocr. 2008, 29, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Becker, J.B. Acquisition of cocaine self-administration in ovariectomized female rats: Effect of estradiol dose or chronic estradiol administration. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2008, 94, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sell, S.L.; Dillon, A.M.; Cunningham, K.A.; Thomas, M.L. Estrous cycle influence on individual differences in the response to novelty and cocaine in female rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2005, 161, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, Q.D.; Cabassa, J.; Kaplan, K.A.; Li, S.T.; Haroon, J.; Spohr, H.A.; Kuhn, C.M. Sex differences in cocaine-stimulated motor behavior: Disparate effects of gonadectomy. Neuropsychopharmacology 2001, 25, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, D.C.; Bennett, S.A.; Vickers, G.J. The estrous cycle affects cocaine self-administration on a progressive ratio schedule in rats. Psychopharmacology 1989, 98, 408–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vietri, M.; Radulovic, M.; Stenmark, H. The many functions of ESCRTs. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 25–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abels, E.R.; Breakefield, X.O. Introduction to extracellular vesicles: Biogenesis, RNA cargo selection, content, release, and uptake. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 36, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henne, W.M.; Buchkovich, N.J.; Emr, S.D. The ESCRT pathway. Dev. Cell 2011, 21, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raiborg, C.; Stenmark, H. The ESCRT machinery in endosomal sorting of ubiquitylated membrane proteins. Nature 2009, 458, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babst, M.; Katzmann, D.J.; Snyder, W.B.; Wendland, B.; Emr, S.D. Endosome-associated complex, ESCRT-II, recruits transport machinery for protein sorting at the multivesicular body. Dev. Cell 2002, 3, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, Y.J.; Wollert, T.; Boura, E.; Hurley, J.H. Structure and function of the ESCRT-II-III interface in multivesicular body biogenesis. Dev. Cell 2009, 17, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuffers, S.; Sem Wegner, C.; Stenmark, H.; Brech, A. Multivesicular endosome biogenesis in the absence of ESCRTs. Traffic 2009, 10, 925–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsherbini, A.; Bieberich, E. Ceramide and exosomes: A novel target in cancer biology and therapy. Adv. Cancer Res. 2018, 140, 121–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khayrullin, A.; Krishnan, P.; Martinez-Nater, L.; Mendhe, B.; Fulzele, S.; Liu, Y.; Mattison, J.A.; Hamrick, M.W. Very Long-Chain C24:1 Ceramide is increased in serum extracellular vesicles with aging and can induce senescence in bone-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Cells 2019, 8, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, P.; Saleem, M.; Herrmann, N.; Mielke, M.M.; Haughey, N.J.; Oh, P.I.; Kiss, A.; Lanctot, K.L. Ceramide accumulation is associated with declining verbal memory in coronary artery disease patients: An observational study. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2018, 64, 1235–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGrath, E.R.; Himali, J.J.; Xanthakis, V.; Duncan, M.S.; Schaffer, J.E.; Ory, D.S.; Peterson, L.R.; DeCarli, C.; Pase, M.P.; Satizabal, C.L.; et al. Circulating ceramide ratios and risk of vascular brain aging and dementia. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2020, 7, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anand, S.; Samuel, M.; Kumar, S.; Mathivanan, S. Ticket to a bubble ride: Cargo sorting into exosomes and extracellular vesicles. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Proteins Proteom. 2019, 1867, 140203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margolis, L.; Sadovsky, Y. The biology of extracellular vesicles: The known unknowns. PLoS Biol. 2019, 17, e3000363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, T.; Imamura, T.; Ogawa, T.; Minagawa, T.; Domen, T.; Suzuki, T.; Ueno, M.; Ishizuka, O. Nicotine-induced hypoxia in rat urothelium deteriorates bladder storage functions. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2019, 38, 1560–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.R.; Castellano, L.M.; Blendy, J.A. Parallel anxiolytic-like effects and upregulation of neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors following chronic nicotine and varenicline. Nicotine Tob. Res. 2011, 13, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulzer, D. How addictive drugs disrupt presynaptic dopamine neurotransmission. Neuron 2011, 69, 628–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, B.J.; Lester, H.A. Inside-out neuropharmacology of nicotinic drugs. Neuropharmacology 2015, 96, 178–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lester, H.A.; Xiao, C.; Srinivasan, R.; Son, C.D.; Miwa, J.; Pantoja, R.; Banghart, M.R.; Dougherty, D.A.; Goate, A.M.; Wang, J.C. Nicotine is a selective pharmacological chaperone of acetylcholine receptor number and stoichiometry. Implications for drug discovery. AAPS J. 2009, 11, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallejo, Y.F.; Buisson, B.; Bertrand, D.; Green, W.N. Chronic nicotine exposure upregulates nicotinic receptors by a novel mechanism. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 5563–5572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaimarri, A.; Moretti, M.; Riganti, L.; Zanardi, A.; Clementi, F.; Gotti, C. Regulation of neuronal nicotinic receptor traffic and expression. Brain Res. Rev. 2007, 55, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aspera-Werz, R.H.; Ehnert, S.; Heid, D.; Zhu, S.; Chen, T.; Braun, B.; Sreekumar, V.; Arnscheidt, C.; Nussler, A.K. Nicotine and cotinine inhibit catalase and glutathione reductase activity contributing to the Impaired osteogenesis of SCP-1 cells exposed to cigarette smoke. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazzini, C.; Rossetti, V.; Civello, D.A.; Sassone, F.; Vezzoli, V.; Persani, L.; Tiberio, L.; Lanata, L.; Bagnasco, M.; Paulmichl, M.; et al. Short- and long- term effects of cigarette smoke exposure on glutathione homeostasis in human bronchial epithelial cells. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 32, 129–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán, D.; García, E.; Jiménez, F.; Mejía, G.; Olguín, H.; González, J.; Angel, D.; Brizuela, N. Effect of Nicotine on Dopamine and Glutathione Levels in Presence of Oligoelements in Brain Regions of Young Rats——Effect of Nicotine on Brain Regions of Rat. Neurosci. Med. 2012, 3, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mohammed, B.; Al-Thwani, A. Evaluation the effect of nicotine injection on the lungs of mice. J. Rep. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 8, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.K.; Cho, C.H. The pharmacological actions of nicotine on the gastrointestinal tract. J. Pharm. Sci. 2004, 94, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.F.; Chan, R.L.; Lu, L.; Shen, J.; Zhang, L.; Wu, W.K.; Wang, L.; Hu, T.; Li, M.X.; Cho, C.H. Cigarette smoking and gastrointestinal diseases: The causal relationship and underlying molecular mechanisms (review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 34, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, P.; Biswas, K.; Roy, S.; Banerjee, R.K.; Bandyopadhyay, U. Smoking and the pathogenesis of gastroduodenal ulcer—Recent mechanistic update. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2003, 253, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Group, A.-D.N.I.S.; Rhodes, M.; Zijlastra, F.; Bradburn, D.M.; Srivastava, E.; Dijk, A.; Russell, M.; Blankenstein, M.; Wilson, J.; Allen, A.; et al. Effect of Nicotine on Gallbladder Bile. Exp. Gastroenterol. 1994, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.Y.; Chen, Y.C. Role of bile acids in carcinogenesis of pancreatic cancer: An old topic with new perspective. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 7463–7477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brett, K.; Parker, R.; Wittenauer, S.; Hayashida, K.; Young, T.; Vincler, M. Impact of chronic nicotine on sciatic nerve injury in the rat. J. Neuroimmunol. 2007, 186, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, F.D.; Piao, W.H.; Kuo, Y.P.; Campagnolo, D.I.; Vollmer, T.L.; Lukas, R.J. Nicotinic attenuation of central nervous system inflammation and autoimmunity. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 1730–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Group | Accession Number | Gene Name | Fold Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Males | F1MA89 | Cyclin Y | +2.1 |
| A0A0G2K127 | Vascular cell adhesion protein 1 | +1.6 | |
| P62749 | Hippocalcin-like protein 1 | −1.5 | |
| F8WFM2 | Beta-soluble NSF attachment protein | −1.5 | |
| Q5XIE8 | Integral membrane protein 2B | −1.5 | |
| Q9EQX9 | Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 | −1.5 | |
| Q9Z1B2 | Glutathione S-transferase Mu 5 | −1.5 | |
| D3Z981 | Plexin A1 | −1.5 | |
| Q05683 | Glutamate decarboxylase 2 | −1.6 | |
| Q05982 | Nucleoside diphosphate kinase A | −1.6 | |
| P04631 | Protein S100-B | −1.6 | |
| P15205 | Microtubule-associated protein 1B | −1.6 | |
| P31647 | Sodium- and chloride-dependent GABA transporter 3 | −1.6 | |
| A0A0G2K9J2 | V-type proton ATPase subunit H | −1.6 | |
| P08009 | Glutathione S-transferase Yb-3 | −1.6 | |
| Q6PW52 | GABA-A gamma2 long isoform | −1.8 | |
| A0A0G2K5E7 | ATP-citrate synthase | −1.9 | |
| D4A8N1 | Dolichol-phosphate mannosyltransferase subunit 1 | −2.0 | |
| M0R830 | Mesoderm-specific transcript homolog protein | −2.7 | |
| Females | P29975 | Aquaporin-1 | +2.0 |
| A0A0G2K890 | Ezrin | +1.8 | |
| Q9R0I8 | Phosphatidylinositol 5-phosphate 4-kinase type-2 alpha | +1.7 | |
| Q5U2 × 8 | Acyl-CoA thioesterase 9 | +1.6 | |
| G3V7Q6 | Proteasome subunit beta | −1.5 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Koul, S.; Schaal, V.L.; Chand, S.; Pittenger, S.T.; Nanoth Vellichirammal, N.; Kumar, V.; Guda, C.; Bevins, R.A.; Yelamanchili, S.V.; Pendyala, G. Role of Brain Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Decoding Sex Differences Associated with Nicotine Self-Administration. Cells 2020, 9, 1883. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9081883
Koul S, Schaal VL, Chand S, Pittenger ST, Nanoth Vellichirammal N, Kumar V, Guda C, Bevins RA, Yelamanchili SV, Pendyala G. Role of Brain Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Decoding Sex Differences Associated with Nicotine Self-Administration. Cells. 2020; 9(8):1883. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9081883
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoul, Sneh, Victoria L. Schaal, Subhash Chand, Steven T. Pittenger, Neetha Nanoth Vellichirammal, Vikas Kumar, Chittibabu Guda, Rick A. Bevins, Sowmya V. Yelamanchili, and Gurudutt Pendyala. 2020. "Role of Brain Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Decoding Sex Differences Associated with Nicotine Self-Administration" Cells 9, no. 8: 1883. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9081883
APA StyleKoul, S., Schaal, V. L., Chand, S., Pittenger, S. T., Nanoth Vellichirammal, N., Kumar, V., Guda, C., Bevins, R. A., Yelamanchili, S. V., & Pendyala, G. (2020). Role of Brain Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Decoding Sex Differences Associated with Nicotine Self-Administration. Cells, 9(8), 1883. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9081883






_Guda.png)


