Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 and IGF Binding Proteins Predict All-Cause Mortality and Morbidity in Older Adults
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Human Cohort Data Acquisition
2.2. Biochemical Measurements
2.3. Disease Definitions
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics of Study Cohort
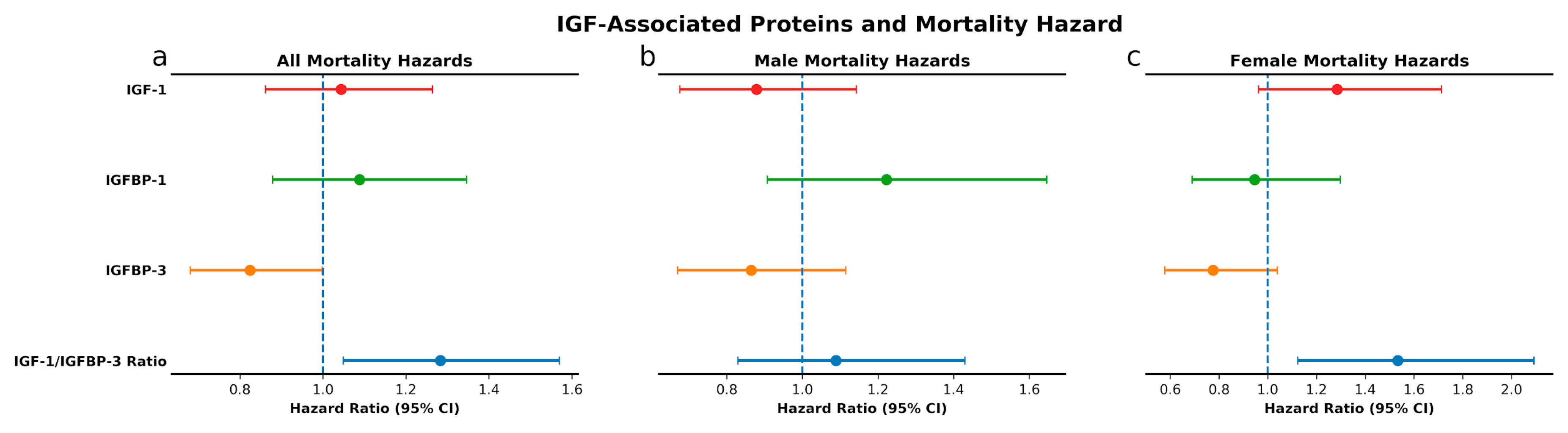
3.2. IGF-Associated Proteins and Mortality: Low IGFBP-3 and High IGF-1/IGFBP-3 Molar Ratio Predict Mortality Risk
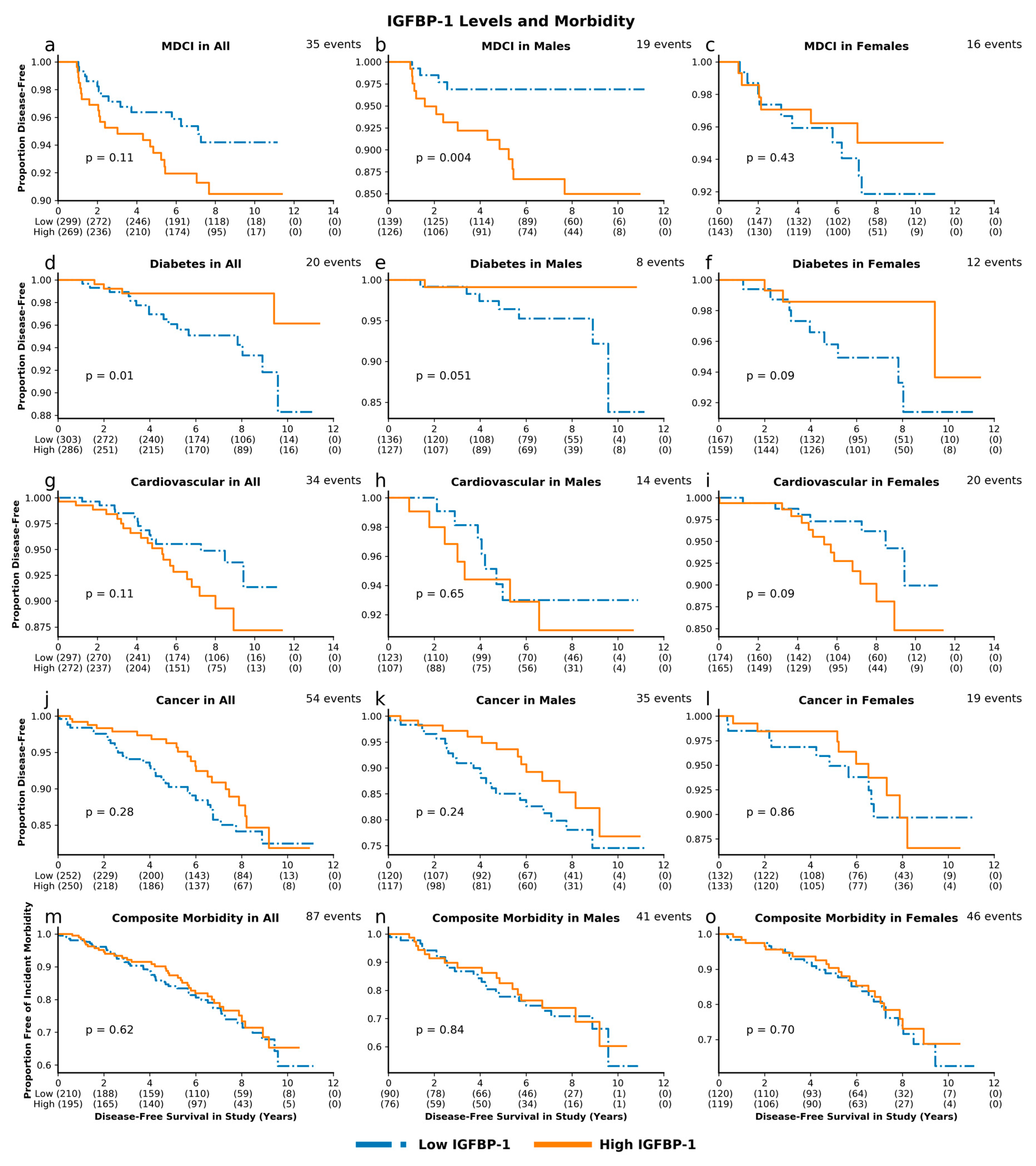
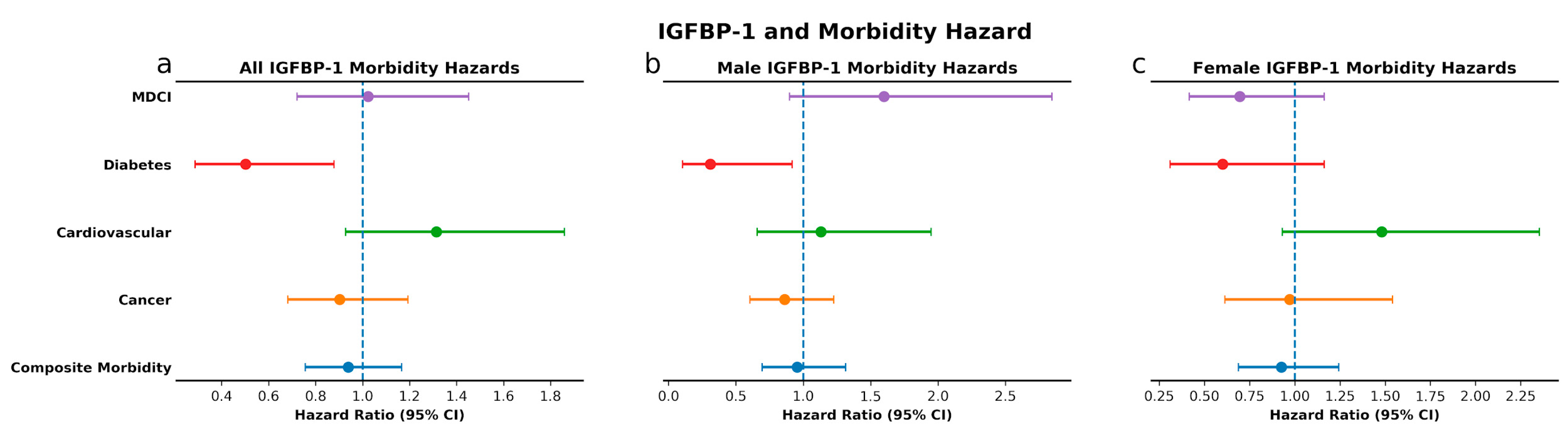
3.3. IGF-Associated Proteins and Morbidity: High IGF-1 Predicts Risk for MDCI and Age-Related Composite Morbidity while Low IGFBP-1 Predicts Risk for Diabetes
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nikolich-Zugich, J.; Goldman, D.P.; Cohen, P.R.; Cortese, D.; Fontana, L.; Kennedy, B.K.; Mohler, M.J.; Olshansky, S.J.; Perls, T.; Perry, D.; et al. Preparing for an Aging World: Engaging Biogerontologists, Geriatricians, and the Society. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2016, 71, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guarente, L.; Kenyon, C. Genetic pathways that regulate ageing in model organisms. Nature 2000, 408, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonntag, W.E.; Csiszar, A.; deCabo, R.; Ferrucci, L.; Ungvari, Z. Diverse roles of growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor-1 in mammalian aging: Progress and controversies. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2012, 67, 587–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenyon, C.; Chang, J.; Gensch, E.; Rudner, A.; Tabtiang, R. A C. elegans mutant that lives twice as long as wild type. Nature 1993, 366, 461–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broughton, S.J.; Piper, M.D.; Ikeya, T.; Bass, T.M.; Jacobson, J.; Driege, Y.; Martinez, P.; Hafen, E.; Withers, D.J.; Leevers, S.J.; et al. Longer lifespan, altered metabolism, and stress resistance in Drosophila from ablation of cells making insulin-like ligands. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 3105–3110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown-Borg, H.M.; Borg, K.E.; Meliska, C.J.; Bartke, A. Dwarf mice and the ageing process. Nature 1996, 384, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeno, Y.; Bronson, R.T.; Hubbard, G.B.; Lee, S.; Bartke, A. Delayed occurrence of fatal neoplastic diseases in ames dwarf mice: Correlation to extended longevity. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2003, 58, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flurkey, K.; Papaconstantinou, J.; Miller, R.A.; Harrison, D.E. Lifespan extension and delayed immune and collagen aging in mutant mice with defects in growth hormone production. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 6736–6741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coschigano, K.T.; Clemmons, D.; Bellush, L.L.; Kopchick, J.J. Assessment of growth parameters and life span of GHR/BP gene-disrupted mice. Endocrinology 2000, 141, 2608–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzenberger, M.; Dupont, J.; Ducos, B.; Leneuve, P.; Geloen, A.; Even, P.C.; Cervera, P.; Le Bouc, Y. IGF-1 receptor regulates lifespan and resistance to oxidative stress in mice. Nature 2003, 421, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selman, C.; Lingard, S.; Choudhury, A.I.; Batterham, R.L.; Claret, M.; Clements, M.; Ramadani, F.; Okkenhaug, K.; Schuster, E.; Blanc, E.; et al. Evidence for lifespan extension and delayed age-related biomarkers in insulin receptor substrate 1 null mice. FASEB J. 2008, 22, 807–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinney, B.A.; Meliska, C.J.; Steger, R.W.; Bartke, A. Evidence that Ames dwarf mice age differently from their normal siblings in behavioral and learning and memory parameters. Horm. Behav. 2001, 39, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeno, Y.; Hubbard, G.B.; Lee, S.; Cortez, L.A.; Lew, C.M.; Webb, C.R.; Berryman, D.E.; List, E.O.; Kopchick, J.J.; Bartke, A. Reduced incidence and delayed occurrence of fatal neoplastic diseases in growth hormone receptor/binding protein knockout mice. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2009, 64, 522–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spadaro, O.; Goldberg, E.L.; Camell, C.D.; Youm, Y.H.; Kopchick, J.J.; Nguyen, K.Y.; Bartke, A.; Sun, L.Y.; Dixit, V.D. Growth Hormone Receptor Deficiency Protects against Age-Related NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation and Immune Senescence. Cell Rep. 2016, 14, 1571–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, E.; Kahnt, E.; Ehrlein, J.; Hermanns, W.; Brem, G.; Wanke, R. Effects of long-term elevated serum levels of growth hormone on life expectancy of mice: Lessons from transgenic animal models. Mech. Ageing Dev. 1993, 68, 71–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartke, A.; Chandrashekar, V.; Bailey, B.; Zaczek, D.; Turyn, D. Consequences of growth hormone (GH) overexpression and GH resistance. Neuropeptides 2002, 36, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guevara-Aguirre, J.; Balasubramanian, P.; Guevara-Aguirre, M.; Wei, M.; Madia, F.; Cheng, C.W.; Hwang, D.; Martin-Montalvo, A.; Saavedra, J.; Ingles, S.; et al. Growth hormone receptor deficiency is associated with a major reduction in pro-aging signaling, cancer, and diabetes in humans. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 70ra13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colao, A.; Ferone, D.; Marzullo, P.; Lombardi, G. Systemic complications of acromegaly: Epidemiology, pathogenesis, and management. Endocr. Rev. 2004, 25, 102–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal, J.; Leisner, M.Z.; Hermansen, K.; Farkas, D.K.; Bengtsen, M.; Kistorp, C.; Nielsen, E.H.; Andersen, M.; Feldt-Rasmussen, U.; Dekkers, O.M.; et al. Cancer Incidence in Patients With Acromegaly: A Cohort Study and Meta-Analysis of the Literature. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 103, 2182–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekkers, O.M.; Biermasz, N.R.; Pereira, A.M.; Romijn, J.A.; Vandenbroucke, J.P. Mortality in acromegaly: A metaanalysis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, N.; Wolthers, O.D.; Arafat, A.M.; Emeny, R.T.; Spranger, J.; Roswall, J.; Kratzsch, J.; Grabe, H.J.; Hübener, C.; Pfeiffer, A.F.H.; et al. Age- and Sex-Specific Reference Intervals Across Life Span for Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Protein 3 (IGFBP-3) and the IGF-I to IGFBP-3 Ratio Measured by New Automated Chemiluminescence Assays. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, 1675–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milman, S.; Atzmon, G.; Huffman, D.M.; Wan, J.; Crandall, J.P.; Cohen, P.; Barzilai, N. Low insulin-like growth factor-1 level predicts survival in humans with exceptional longevity. Aging Cell 2014, 13, 769–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Spoel, E.; Rozing, M.P.; Houwing-Duistermaat, J.J.; Slagboom, P.E.; Beekman, M.; de Craen, A.J.; Westendorp, R.G.; van Heemst, D. Association analysis of insulin-like growth factor-1 axis parameters with survival and functional status in nonagenarians of the Leiden Longevity Study. Aging (Albany Ny) 2015, 7, 956–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schutte, A.E.; Conti, E.; Mels, C.M.; Smith, W.; Kruger, R.; Botha, S.; Gnessi, L.; Volpe, M.; Huisman, H.W. Attenuated IGF-1 predicts all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in a Black population: A five-year prospective study. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2016, 23, 1690–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourron, O.; Le Bouc, Y.; Berard, L.; Kotti, S.; Brunel, N.; Ritz, B.; Leclercq, F.; Tabone, X.; Drouet, E.; Mulak, G.; et al. Impact of age-adjusted insulin-like growth factor 1 on major cardiovascular events after acute myocardial infarction: Results from the fast-MI registry. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, 1879–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, R.C.; McGinn, A.P.; Pollak, M.N.; Kuller, L.; Strickler, H.D.; Rohan, T.E.; Xue, X.; Kritchevsky, S.B.; Newman, A.B.; Psaty, B.M. Total insulinlike growth factor 1 and insulinlike growth factor binding protein levels, functional status, and mortality in older adults. J. Am. Geriatr Soc. 2008, 56, 652–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juul, A.; Scheike, T.; Davidsen, M.; Gyllenborg, J.; Jorgensen, T. Low serum insulin-like growth factor I is associated with increased risk of ischemic heart disease: A population-based case-control study. Circulation 2002, 106, 939–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saber, H.; Himali, J.J.; Beiser, A.S.; Shoamanesh, A.; Pikula, A.; Roubenoff, R.; Romero, J.R.; Kase, C.S.; Vasan, R.S.; Seshadri, S. Serum Insulin-Like Growth Factor 1 and the Risk of Ischemic Stroke: The Framingham Study. Stroke A J. Cereb. Circ. 2017, 48, 1760–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renehan, A.G.; Zwahlen, M.; Minder, C.; O’Dwyer, S.T.; Shalet, S.M.; Egger, M. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I, IGF binding protein-3, and cancer risk: Systematic review and meta-regression analysis. Lancet 2004, 363, 1346–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, R.C.; McGinn, A.P.; Pollak, M.N.; Kuller, L.H.; Strickler, H.D.; Rohan, T.E.; Cappola, A.R.; Xue, X.; Psaty, B.M. Association of total insulin-like growth factor-I, insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 (IGFBP-1), and IGFBP-3 levels with incident coronary events and ischemic stroke. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 92, 1319–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, R.; Miell, J.; Freeman, E.; Jones, J.; Matthews, D.; Preece, M.; Buchanan, C. Critically ill patients have high basal growth hormone levels with attenuated oscillatory activity associated with low levels of insulin-like growth factor-I. Clin. Endocrinol. 1991, 35, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juul, A. Serum levels of insulin-like growth factor I and its binding proteins in health and disease. Growth Horm. Igf. Res. 2003, 13, 113–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saydah, S.; Graubard, B.; Ballard-Barbash, R.; Berrigan, D. Insulin-like growth factors and subsequent risk of mortality in the United States. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2007, 166, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedrich, N.; Haring, R.; Nauck, M.; Ludemann, J.; Rosskopf, D.; Spilcke-Liss, E.; Felix, S.B.; Dorr, M.; Brabant, G.; Volzke, H.; et al. Mortality and serum insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I and IGF binding protein 3 concentrations. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 1732–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jogie-Brahim, S.; Feldman, D.; Oh, Y. Unraveling insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 actions in human disease. Endocr. Rev. 2009, 30, 417–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allard, J.B.; Duan, C. IGF-Binding Proteins: Why Do They Exist and Why Are There So Many? Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2018, 9, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faix, J.D. Principles and pitfalls of free hormone measurements. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 27, 631–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeap, B.B.; Chubb, S.A.; McCaul, K.A.; Ho, K.K.; Hankey, G.J.; Norman, P.E.; Flicker, L. Associations of IGF1 and IGFBPs 1 and 3 with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in older men: The Health In Men Study. Eur. J. Endocrinol. Eur. Fed. Endocr. Soc. 2011, 164, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laughlin, G.A.; Barrett-Connor, E.; Criqui, M.H.; Kritz-Silverstein, D. The prospective association of serum insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) and IGF-binding protein-1 levels with all cause and cardiovascular disease mortality in older adults: The Rancho Bernardo Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 89, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubbi, S.; Schwartz, E.; Crandall, J.; Verghese, J.; Holtzer, R.; Atzmon, G.; Braunstein, R.; Barzilai, N.; Milman, S. Effect of Exceptional Parental Longevity and Lifestyle Factors on Prevalence of Cardiovascular Disease in Offspring. Am. J. Cardiol. 2017, 120, 2170–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perice, L.; Barzilai, N.; Verghese, J.; Weiss, E.F.; Holtzer, R.; Cohen, P.; Milman, S. Lower circulating insulin-like growth factor-I is associated with better cognition in females with exceptional longevity without compromise to muscle mass and function. Aging (Albany Ny) 2016, 8, 2414–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The UniProt Consortium. UniProt: A worldwide hub of protein knowledge. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D506–D515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinderknecht, E.; Humbel, R.E. The amino acid sequence of human insulin-like growth factor I and its structural homology with proinsulin. J. Biol. Chem. 1978, 253, 2769–2776. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, N.B.; Hayes, L.D.; Brown, K.; Hoo, E.C.; Ethier, K.A. CDC National Health Report: Leading causes of morbidity and mortality and associated behavioral risk and protective factors--United States, 2005–2013. MMWR Suppl. 2014, 63, 3–27. [Google Scholar]
- Tabert, M.H.; Manly, J.J.; Liu, X.; Pelton, G.H.; Rosenblum, S.; Jacobs, M.; Zamora, D.; Goodkind, M.; Bell, K.; Stern, Y.; et al. Neuropsychological prediction of conversion to Alzheimer disease in patients with mild cognitive impairment. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2006, 63, 916–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jak, A.J.; Bondi, M.W.; Delano-Wood, L.; Wierenga, C.; Corey-Bloom, J.; Salmon, D.P.; Delis, D.C. Quantification of five neuropsychological approaches to defining mild cognitive impairment. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2009, 17, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacNee, W.; Rabinovich, R.A.; Choudhury, G. Ageing and the border between health and disease. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 44, 1332–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreassen, M.; Raymond, I.; Kistorp, C.; Hildebrandt, P.; Faber, J.; Kristensen, L.O. IGF1 as predictor of all cause mortality and cardiovascular disease in an elderly population. Eur. J. Endocrinol. Eur. Fed. Endocr. Soc. 2009, 160, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzilai, N.; Huffman, D.M.; Muzumdar, R.H.; Bartke, A. The critical role of metabolic pathways in aging. Diabetes 2012, 61, 1315–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartke, A.; Darcy, J. GH and ageing: Pitfalls and new insights. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 31, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, Y.; Atzmon, G.; Cho, M.O.; Hwang, D.; Liu, B.; Leahy, D.J.; Barzilai, N.; Cohen, P. Functionally significant insulin-like growth factor I receptor mutations in centenarians. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 3438–3442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Heemst, D.; Beekman, M.; Mooijaart, S.P.; Heijmans, B.T.; Brandt, B.W.; Zwaan, B.J.; Slagboom, P.E.; Westendorp, R.G. Reduced insulin/IGF-1 signalling and human longevity. Aging Cell 2005, 4, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlikowska, L.; Hu, D.; Huntsman, S.; Sung, A.; Chu, C.; Chen, J.; Joyner, A.H.; Schork, N.J.; Hsueh, W.C.; Reiner, A.P.; et al. Association of common genetic variation in the insulin/IGF1 signaling pathway with human longevity. Aging Cell 2009, 8, 460–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgers, A.M.; Biermasz, N.R.; Schoones, J.W.; Pereira, A.M.; Renehan, A.G.; Zwahlen, M.; Egger, M.; Dekkers, O.M. Meta-analysis and dose-response metaregression: Circulating insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) and mortality. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, 2912–2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Diabetes Statistics Report; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, U.S. Dept of Health and Human Services: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2020.
- Villarroel, M.A.B.D.; Jen, A. Tables of Summary Health Statistics for U.S. Adults: 2018 National Health Interview Survey. National Center for Health Statistics, 2019. Available online: http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhis/SHS/tables.htm (accessed on 27 April 2020).
- Yamamoto, H.; Sohmiya, M.; Oka, N.; Kato, Y. Effects of aging and sex on plasma insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) levels in normal adults. Acta Endocrinol. 1991, 124, 497–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubbi, S.; Quipildor, G.F.; Barzilai, N.; Huffman, D.M.; Milman, S. 40 YEARS of IGF1: IGF1: The Jekyll and Hyde of the aging brain. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2018, 61, T171–T185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Delaimy, W.K.; von Muhlen, D.; Barrett-Connor, E. Insulinlike growth factor-1, insulinlike growth factor binding protein-1, and cognitive function in older men and women. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2009, 57, 1441–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wennberg, A.M.V.; Hagen, C.E.; Machulda, M.M.; Hollman, J.H.; Roberts, R.O.; Knopman, D.S.; Petersen, R.C.; Mielke, M.M. The association between peripheral total IGF-1, IGFBP-3, and IGF-1/IGFBP-3 and functional and cognitive outcomes in the Mayo Clinic Study of Aging. Neurobiol. Aging. 2018, 66, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumati, S.; Burger, H.; Martens, S.; van der Schouw, Y.T.; Aleman, A. Association between Cognition and Serum Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1 in Middle-Aged & Older Men: An 8 Year Follow-Up Study. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okereke, O.; Kang, J.H.; Ma, J.; Hankinson, S.E.; Pollak, M.N.; Grodstein, F. Plasma IGF-I levels and cognitive performance in older women. Neurobiol. Aging 2007, 28, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.; Cline, G.W.; Macica, C.M. IGF-1 stimulates de novo fatty acid biosynthesis by Schwann cells during myelination. Glia 2007, 55, 632–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieto-Estevez, V.; Defterali, C.; Vicario-Abejon, C. IGF-I: A Key Growth Factor that Regulates Neurogenesis and Synaptogenesis from Embryonic to Adult Stages of the Brain. Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gontier, G.; George, C.; Chaker, Z.; Holzenberger, M.; Aid, S. Blocking IGF Signaling in Adult Neurons Alleviates Alzheimer’s Disease Pathology through Amyloid-beta Clearance. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 11500–11513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sevigny, J.J.; Ryan, J.M.; van Dyck, C.H.; Peng, Y.; Lines, C.R.; Nessly, M.L. Growth hormone secretagogue MK-677: No clinical effect on AD progression in a randomized trial. Neurology 2008, 71, 1702–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedlander, A.L.; Butterfield, G.E.; Moynihan, S.; Grillo, J.; Pollack, M.; Holloway, L.; Friedman, L.; Yesavage, J.; Matthias, D.; Lee, S.; et al. One year of insulin-like growth factor I treatment does not affect bone density, body composition, or psychological measures in postmenopausal women. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 1496–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schedlich, L.J.; Le Page, S.L.; Firth, S.M.; Briggs, L.J.; Jans, D.A.; Baxter, R.C. Nuclear import of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 and -5 is mediated by the importin beta subunit. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 23462–23470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schedlich, L.J.; O’Han, M.K.; Leong, G.M.; Baxter, R.C. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 prevents retinoid receptor heterodimerization: Implications for retinoic acid-sensitivity in human breast cancer cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 314, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.S.; Ling, T.Y.; Tseng, W.F.; Huang, Y.H.; Tang, F.M.; Leal, S.M.; Huang, J.S. Cellular growth inhibition by IGFBP-3 and TGF-beta1 requires LRP-1. FASEB J. 2003, 17, 2068–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, P.; Lamson, G.; Okajima, T.; Rosenfeld, R.G. Transfection of the human insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 gene into Balb/c fibroblasts inhibits cellular growth. Mol. Endocrinol. 1993, 7, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Valentinis, B.; Bhala, A.; DeAngelis, T.; Baserga, R.; Cohen, P. The human insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding protein-3 inhibits the growth of fibroblasts with a targeted disruption of the IGF-I receptor gene. Mol. Endocrinol. 1995, 9, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.L.; Weenink, S.M.; Baxter, R.C. Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 potentiates epidermal growth factor action in MCF-10A mammary epithelial cells. Involvement of p44/42 and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 2969–2976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lofqvist, C.; Chen, J.; Connor, K.M.; Smith, A.C.; Aderman, C.M.; Liu, N.; Pintar, J.E.; Ludwig, T.; Hellstrom, A.; Smith, L.E. IGFBP3 suppresses retinopathy through suppression of oxygen-induced vessel loss and promotion of vascular regrowth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 10589–10594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajpathak, S.N.; He, M.; Sun, Q.; Kaplan, R.C.; Muzumdar, R.; Rohan, T.E.; Gunter, M.J.; Pollak, M.; Kim, M.; Pessin, J.E.; et al. Insulin-like growth factor axis and risk of type 2 diabetes in women. Diabetes 2012, 61, 2248–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersson, U.; Ostgren, C.J.; Brudin, L.; Brismar, K.; Nilsson, P.M. Low levels of insulin-like growth-factor-binding protein-1 (IGFBP-1) are prospectively associated with the incidence of type 2 diabetes and impaired glucose tolerance (IGT): The Soderakra Cardiovascular Risk Factor Study. Diabetes Metab. 2009, 35, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewitt, M.S.; Hilding, A.; Ostenson, C.G.; Efendic, S.; Brismar, K.; Hall, K. Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-1 in the prediction and development of type 2 diabetes in middle-aged Swedish men. Diabetologia 2008, 51, 1135–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suikkari, A.M.; Koivisto, V.A.; Rutanen, E.M.; Yki-Jarvinen, H.; Karonen, S.L.; Seppala, M. Insulin regulates the serum levels of low molecular weight insulin-like growth factor-binding protein. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1988, 66, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, D.K.; Clemmons, D.R. Insulin-dependent regulation of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-1. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1990, 71, 1632–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemmons, D.R. Role of IGF-binding proteins in regulating IGF responses to changes in metabolism. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2018, 61, T139–T169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddals, K.W.; Westwood, M.; Gibson, J.M.; White, A. IGF-binding protein-1 inhibits IGF effects on adipocyte function: Implications for insulin-like actions at the adipocyte. J. Endocrinol. 2002, 174, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkumar, K.; Modric, T.; Murphy, L.J. Impaired adipogenesis in insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 transgenic mice. J. Endocrinol. 1999, 162, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haywood, N.J.; Cordell, P.A.; Tang, K.Y.; Makova, N.; Yuldasheva, N.Y.; Imrie, H.; Viswambharan, H.; Bruns, A.F.; Cubbon, R.M.; Kearney, M.T.; et al. Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Protein 1 Could Improve Glucose Regulation and Insulin Sensitivity Through Its RGD Domain. Diabetes 2017, 66, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheatcroft, S.B.; Kearney, M.T. IGF-dependent and IGF-independent actions of IGF-binding protein-1 and -2: Implications for metabolic homeostasis. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 20, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heald, A.H.; Cruickshank, J.K.; Riste, L.K.; Cade, J.E.; Anderson, S.; Greenhalgh, A.; Sampayo, J.; Taylor, W.; Fraser, W.; White, A.; et al. Close relation of fasting insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 (IGFBP-1) with glucose tolerance and cardiovascular risk in two populations. Diabetologia 2001, 44, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unden, A.L.; Elofsson, S.; Brismar, K. Gender differences in the relation of insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 to cardiovascular risk factors: A population-based study. Clin. Endocrinol. 2005, 63, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Span, J.P.; Pieters, G.F.; Sweep, F.G.; Hermus, A.R.; Smals, A.G. Gender differences in rhGH-induced changes in body composition in GH-deficient adults. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 4161–4165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Frystyk, J. Free insulin-like growth factors -- measurements and relationships to growth hormone secretion and glucose homeostasis. Growth Horm. IGF Res. 2004, 14, 337–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drogan, D.; Schulze, M.B.; Boeing, H.; Pischon, T. Insulin-Like Growth Factor 1 and Insulin-Like Growth Factor-Binding Protein 3 in Relation to the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Results From the EPIC-Potsdam Study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2016, 183, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra-Johnson, J.; Romero-Corral, A.; Somers, V.K.; Lopez-Jimenez, F.; Malarstig, A.; Brismar, K.; Hamsten, A.; Fisher, R.M.; Hellenius, M.L. IGF-I/IGFBP-3 ratio: A mechanistic insight into the metabolic syndrome. Clin. Sci. 2009, 116, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Katki, H.; Graubard, B.; Pollak, M.; Martin, M.; Tao, Y.; Schoen, R.E.; Church, T.; Hayes, R.B.; Greene, M.H.; et al. Serum IGF1, IGF2 and IGFBP3 and risk of advanced colorectal adenoma. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 131, E105–E113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzullo, P.; Di Somma, C.; Pratt, K.L.; Khosravi, J.; Diamandis, A.; Lombardi, G.; Colao, A.; Rosenfeld, R.G. Usefulness of different biochemical markers of the insulin-like growth factor (IGF) family in diagnosing growth hormone excess and deficiency in adults. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 3001–3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soubry, A.; Il’yasova, D.; Sedjo, R.; Wang, F.; Byers, T.; Rosen, C.; Yashin, A.; Ukraintseva, S.; Haffner, S.; D’Agostino, R., Jr. Increase in circulating levels of IGF-1 and IGF-1/IGFBP-3 molar ratio over a decade is associated with colorectal adenomatous polyps. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 131, 512–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Cheng, Y.W.; Idrees, K.; Shattock, R.; Khan, S.A.; Zeng, Z.; Brennan, C.W.; Paty, P.; Barany, F. Loss of imprinting and marked gene elevation are 2 forms of aberrant IGF2 expression in colorectal cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 127, 568–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergman, D.; Halje, M.; Nordin, M.; Engstrom, W. Insulin-like growth factor 2 in development and disease: A mini-review. Gerontology 2013, 59, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, K.; Quipildor, G.F.; Tabrizian, T.; Novaj, A.; Guan, F.; Walters, R.O.; Delahaye, F.; Hubbard, G.B.; Ikeno, Y.; Ejima, K.; et al. Late-life targeting of the IGF-1 receptor improves healthspan and lifespan in female mice. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Lely, A.J.; Kopchick, J.J. Growth hormone receptor antagonists. Neuroendocrinology 2006, 83, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, R.S.; Kahaly, G.J.; Patel, A.; Sile, S.; Thompson, E.H.Z.; Perdok, R.; Fleming, J.C.; Fowler, B.T.; Marcocci, C.; Marino, M.; et al. Teprotumumab for the Treatment of Active Thyroid Eye Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| All | Male | Female | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Individuals, n (%) | 840 | 382 (45.5) | 458 (54.5) | 0.01 |
| Deaths, n (%) | 117 (13.9) | 65 (17.0) | 52 (11.4) | 0.02 |
| Age (years), mean ± SD | 76.1 ± 6.8 | 76.4 ± 7.0 | 76.0 ± 6.7 | 0.39 |
| BMI (kg/m2), mean ± SD, n = 820 | 27.6 ± 4.7 | 27.9 ± 3.9 | 27.3 ± 5.3 | 0.053 |
| Insulin (mIU/L), mean ± SD, n = 801 | 15.4 ± 12.3 | 16.6 ± 15.7 | 14.5 ± 8.3 | 0.02 |
| IGF-1 (ng/mL), mean ± SD, n = 761 | 117 ± 38 | 127 ± 39 | 108 ± 36 | <0.001 |
| IGFBP-1 (ng/mL), mean ± SD, n = 728 | 19 ± 15 | 17 ± 14 | 21 ± 15 | <0.001 |
| IGFBP-3 (mg/L), mean ± SD, n = 828 | 3.9 ± 1.0 | 3.6 ± 0.9 | 4.2 ± 1.0 | <0.001 |
| IGF-1/IGFBP-3 Molar Ratio, n = 749 | 0.13 ± 0.04 | 0.15 ± 0.04 | 0.11 ± 0.03 | <0.001 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, W.B.; Aleksic, S.; Gao, T.; Weiss, E.F.; Demetriou, E.; Verghese, J.; Holtzer, R.; Barzilai, N.; Milman, S. Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 and IGF Binding Proteins Predict All-Cause Mortality and Morbidity in Older Adults. Cells 2020, 9, 1368. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9061368
Zhang WB, Aleksic S, Gao T, Weiss EF, Demetriou E, Verghese J, Holtzer R, Barzilai N, Milman S. Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 and IGF Binding Proteins Predict All-Cause Mortality and Morbidity in Older Adults. Cells. 2020; 9(6):1368. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9061368
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, William B., Sandra Aleksic, Tina Gao, Erica F. Weiss, Eleni Demetriou, Joe Verghese, Roee Holtzer, Nir Barzilai, and Sofiya Milman. 2020. "Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 and IGF Binding Proteins Predict All-Cause Mortality and Morbidity in Older Adults" Cells 9, no. 6: 1368. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9061368
APA StyleZhang, W. B., Aleksic, S., Gao, T., Weiss, E. F., Demetriou, E., Verghese, J., Holtzer, R., Barzilai, N., & Milman, S. (2020). Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 and IGF Binding Proteins Predict All-Cause Mortality and Morbidity in Older Adults. Cells, 9(6), 1368. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9061368





