Cyclin D1 in Cancer: A Molecular Connection for Cell Cycle Control, Adhesion and Invasion in Tumor and Stroma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Cyclin D1-Mediated Mechanisms and Alterations in Human Cancer
2.1. CDK-Dependent and -Independent Mechanisms
2.2. Amplification or Overexpression of Cyclin D1
3. Cyclin D1: Role as Cell Cycle Regulator in Tumor Behavior
3.1. Cyclin D1 in Breast Cancer
3.2. Cyclin D1 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
3.3. Cyclin D1 in Ovary Cancer
3.4. Cyclin D1 in Lung Cancer
4. Membrane Associated and Cytoplasmatic Cyclin D1: Linking Cell Cycle Control, Adhesion and Invasion
5. Cyclin D1 Role in the Tumor Microenvironment
6. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kato, J.; Matsushime, H.; Hiebert, S.W.; Ewen, M.E.; Sherr, C.J. Direct binding of cyclin D to the retinoblastoma gene product (pRb) and pRb phosphorylation by the cyclin D-dependent kinase CDK4. Genes Dev. 1993, 7, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lundberg, A.S.; Weinberg, R.A. Functional Inactivation of the Retinoblastoma Protein Requires Sequential Modification by at Least Two Distinct Cyclin-cdk Complexes. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1998, 18, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, Z.; Lu, Y.; Du, R.; Katiyar, S.; Yang, J.; Fu, M.; Leader, J.E.; Quong, A.; Phyllis, M.; et al. Cyclin D1 repression of nuclear respiratory factor 1 integrates nuclear DNA synthesis and mitochondrial function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 11567–11572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamaki, T.; Casimiro, M.C.; Ju, X.; Quong, A.A.; Katiyar, S.; Liu, M.; Jiao, X.; Li, A.; Zhang, X.; Lu, Y.; et al. Cyclin D1 Determines Mitochondrial Function In Vivo. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2006, 26, 5449–5469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hulit, J.; Bash, T.; Fu, M.; Galbiati, F.; Albanese, C.; Sage, D.R.; Schlegel, A.; Zhurinsky, J.; Shtutman, M.; Ben-Ze’ev, A.; et al. The Cyclin D1 Gene Is Transcriptionally Repressed by Caveolin-1. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 21203–21209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bienvenu, F.; Jirawatnotai, S.; Elias, J.E.; Meyer, C.A.; Mizeracka, K.; Marson, A.; Frampton, G.M.; Cole, M.F.; Odom, D.T.; Odajima, J.; et al. Transcriptional role of cyclin D1 in development revealed by a genetic–proteomic screen. Nature 2010, 463, 374–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agami, R.; Bernards, R. Distinct Initiation and Maintenance Mechanisms Cooperate to Induce G1 Cell Cycle Arrestin Response to DNA Damage. Cell 2000, 102, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inaba, T.; Matsushime, H.; Valentine, M.; Roussel, M.F.; Sherr, C.J.; Look, A.T. Genomic Organization, Chromosomal Localization, and Independent Expression of Human Cyclin D Genes. Genomics 1992, 13, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchakarskaa, G.; Sola, B. The double dealing of cyclin D1. Cell Cycle 2020, 19, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodrug, S.E.; Warner, B.J.; Bath, M.L.; Lindeman, G.J.; Harris, A.W.; Adams, J.M. Cyclin D1 transgene impedes lymphocyte maturation and collaborates in lymphomagenesis with the myc gene. EMBO J. 1994, 13, 2124–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovec, H.; Grzeschiczek, A.; Kowalski, M.B.; Moroy, T. Cyclin D1/bcl-1 cooperates with myc genes in the generation of B-cell lymphoma in transgenic mice. EMBO J. 1994, 13, 3487–3495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.C.; Cardiff, R.D.; Zukerberg, L.; Lees, E.; Arnold, A.; Schmidt, E.V. Mammary hyperplasia and carcinoma in MMTV-cyclin D1 transgenic mice. Nature 1994, 369, 669–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, R.J.; Albanese, C.; Fu, M.; D’Amico, M.; Lin, B.; Watanabe, G.; Haines, G.K.; Siegel, P.M.; Hung, M.C.; Yarden, Y.; et al. Cyclin D1 is required for transformation by activated Neu and is induced through an E2F-dependent signaling pathway. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 672–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Q.; Geng, Y.; Sicinski, P. Specific protection against breast cancers by cyclin D1 ablation. Nature 2001, 411, 1017–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosokawa, Y.; Papanikolaou, A.; Cardiff, R.D.; Yoshimoto, K.; Bernstein, M.; Wang, T.C.; Schmidt, E.V.; Arnold, A. In vivo analysis of mammary and non-mammary tumorigenesis in MMTV-cyclin D1 transgenic mice deficient in p53. Transgenic Res. 2001, 10, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Fan, S.; Li, Z.; Fu, M.; Rao, M.; Ma, Y.; Lisanti, M.P.; Albanese, C.; Katzenellenbogen, B.S.; Kushner, P.J.; et al. Cyclin D1 Antagonizes BRCA1 Repression of Estrogen Receptor α Activity. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 6557–6567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Q.; Hu, Z.; Li, Q.; Yi, T.; Li, J.; Yang, H. Cyclin D1 silencing impairs DNA double strand break repair, sensitizes BRCA1 wildtype ovarian cancer cells to olaparib. Gynecol. Oncol. 2019, 152, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casimiro, M.C.; Di Sante, G.; Di Rocco, A.; Loro, E.; Pupo, C.; Pestell, T.G.; Bisetto, S.; Velasco-Vel_azquez, M.A.; Jiao, X.; Li, Z.; et al. Cyclin D1 Restrains Oncogene-Induced Autophagy by Regulating the AMPK–LKB1 Signaling Axis. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 3391–3405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.-Y.; Lan, S.-H.; Wu, S.-R.; Chiu, Y.-C.; Lin, X.-Z.; Su, I.-J.; Tsai, T.-F.; Yen, C.-J.; Lu, T.-H.; Liang, F.-W.; et al. Hepatocellular Carcinoma–Related Cyclin D1 Is Selectively Regulated by Autophagy Degradation System. Hepatology 2018, 68, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumeister, P.; Pixley, F.J.; Xiong, Y.; Xie, H.; Wu, K.; Ashton, A.; Cammer, M.; Chan, A.; Symons, M.; Stanley, E.R.; et al. Cyclin D1 governs adhesion and motility of macrophages. Mol. Biol. Cell 2003, 14, 2005–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Jiao, X.; Ashton, A.; Di Rocco, A.; Pestell, T.G.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, J.; Casimiro, M.C.; Li, Z.; Lisanti, M.P.; et al. The membrane-associated form of cyclin D1 enhances cellular invasion. Oncogenesis 2020, 18, 9–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, H.; Tian, L.; Zhou, J.; Li, Z.; Jiao, X.; Li, W.W.; Plomann, M.; Xu, Z.; Lisanti, M.P.; Wang, C.; et al. PACSIN 2 represses cellular migration through direct association with cyclin D1 but not its alternate splice form cyclin D1b. Cell Cycle 2011, 10, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Wang, C.; Jiao, X.; Lu, Y.; Fu, M.; Quong, A.A.; Dye, C.; Yang, J.; Dai, M.; Ju, X.; et al. Cyclin D1 regulates cellular migration through the inhibition of thrombospondin 1 and ROCK signaling. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2006, 26, 4240–4256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Wang, C.; Prendergast, G.C.; Pestell, R.G. Cyclin D1 functions in cell migration. Cell Cycle 2006, 5, 2440–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cemeli, T.; Guasch-Vallés, M.; Nàger, M.; Felip, I.; Cambray, S.; Santacana, M.; Gatius, S.; Pedraza, N.; Dolcet, X.; Ferrezuelo, F.; et al. Cytoplasmic cyclin D1 regulates glioblastoma dissemination. J. Pathol. 2019, 248, 501–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musgrove, E.A.; Caldon, C.E.; Barraclough, J.; Stone, A.; Sutherlan, R.L. Cyclin D as a therapeutic target in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 558–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaloglou, C.; Crafter, C.; Siersbaek, R.; Delpuech, O.; Curwen, J.O.; Carnevalli, L.S.; Staniszewska, A.D.; Polanska, U.M.; Cheraghchi-Bashi, A.; Lawson, M.; et al. Combined Inhibition of mTOR and CDK4/6 Is Required for Optimal Blockade of E2F Function and Long-term Growth Inhibition in Estrogen Receptor–positive Breast Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2018, 17, 908–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelivianski, S.; Cooley, A.; Kall, R.; Jeruss, J.S. Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 4–Mediated Phosphorylation Inhibits Smad3 Activity in Cyclin D–Overexpressing Breast Cancer Cells. Mol. Cancer Res. 2010, 8, 1375–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, L.; Kel, N.; Hydbring, P.; Choi, Y.J.; Widlund, H.R.; Chick, J.M.; Zhai, H.; Vidal, M.; Gygi, S.P.; Braun, S.; et al. A Systematic Screen for CDK4/6 Substrates Links FOXM1 Phosphorylation to Senescence Suppression in Cancer Cells. Cancer Cell 2011, 20, 620–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, C.; Tuangporn, S.; Di Renzo, J.; Ewen, M.E. P/CAF associates with cyclin D1 and potentiates its activation of the estrogen receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 5382–5387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reutens, A.T.; Fu, M.; Wang, C.; Albanese, C.; McPhaul, M.J.; Sun, Z.; Balk, S.P.; Jänne, O.A.; Palvimo, J.J.; Pestell, R.G. Cyclin D1 Binds the Androgen Receptor and Regulates Hormone-Dependent Signaling in a p300/CBP-Associated Factor (P/CAF)-Dependent Manner. Mol. Endocrinol. 2001, 15, 797–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, K.; Fry, E.A. Aberrant expression of cyclin D1 in cancer. Signal Transduct. Insights 2015, 4, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Chen, Y.; Xu, H. Expression of B-catenin, cyclinD1 and Erα in breast cancer tissues. Prev. Med. 2010, 7, 1502–1504. [Google Scholar]
- Lamb, J.; Ladha, M.H.; Mcmahon, C.; Sutherland, R.L.; Ewen, M.E. Regulation of the Functional Interaction between Cyclin D1 and the Estrogen Receptor. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 8667–8675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudsen, K.E.; Cavenee, W.K.; Arden, K.C. D-Type Cyclins Complex with the Androgen Receptor and Inhibit Its Transcriptional Transactivation Ability. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 2297–2301. [Google Scholar]
- Comstock, C.E.S.; Augello, M.A.; Schiewer, M.J.; Karch, J.; Burd, C.J.; Ertel, A.; Knudsen, E.S.; Jessen, W.J.; Aronow, B.J.; Knudsen, K.E. Cyclin D1 Is a Selective Modifier of Androgen-dependent Signaling and Androgen Receptor Function. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 8117–8127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.M.; Zhao, L.; Cheng, S.Y. Cyclin D1 Is a Ligand-independent Co-repressor for Thyroid Hormone Receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 28733–28741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, M.; Rao, M.; Bouras, T.; Wang, C.; Wu, K.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Yao, T.; Pestell, R.G. Cyclin D1 inhibits peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma-mediated adipogenesis through histone deacetylase recruitment. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 16934–16941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamarajugadda, S.; Becker, J.R.; Hanse, E.A.; Mashek, D.G.; Mashek, M.T.; Hendrickson, A.M.; Mullany, L.K.; Albrecht, J.H. Cyclin D1 represses peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha and inhibits fatty acid oxidation. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 47674–47686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diehl, J.A.; Zindy, F.; Sherr, C.J. Inhibition of cyclin D1 phosphorylation on threonine-286 prevents its rapid degradation via the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Genes Dev. 1997, 11, 957–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieche, I.; Olivi, M.; Nogues, C.; Vidaud, M.; Lidereau, R. Prognostic value of CCND1 gene status in sporadic breast tumours, as determined by realtime quantitative PCR assays. Br. J. Cancer 2002, 86, 580–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qie, S.; Diehl, J.A. Cyclin D1, Cancer Progression and Opportunities in Cancer Treatment. J. Mol. Med. (Berl.) 2016, 94, 1313–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Liu, S.; Jakulin, A.; Yilamu, D.; Wang, B.; Yan, J. Positive expression of cyclin D1 is an indicator for the evaluation of the prognosis of breast cancer. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 18656–18664. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bosone, I.; Cavalla, P.; Chiadò-Piat, L.; Di Vito, N.; Schiffer, D. Cyclin D1 expression in normal oligodendroglia and microglia cells: Its use in the differential diagnosis of oligodendrogliomas. Neuropathology 2001, 21, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundgren, K.; Brown, M.; Pineda, S.; Cuzick, J.; Salter, J.; Zabaglo, L.; Howell, A.; Dowsett, M.; Landberg, G.; Trans, A. Effects of cyclin D1 gene amplification and protein expression on time to recurrence in postmenopausal breast cancer patients treated with anastrozole or tamoxifen: A TransATAC study. Breast Cancer Res. 2012, 14, R57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beca, F.; Pereira, M.; Cameselle-Teijeiro, J.F.; Martins, D.; Schmitt, F. Altered PPP2R2A and Cyclin D1 expression defines a subgroup of aggressive luminal-like breast cancer. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, H.; Cheng, S.; Liao, C.; Wang, H.; Huang, S. Amplification of the EGFR and CCND1 Are Coordinated and Play Important Roles in the Progression of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinomas. Cancers 2019, 11, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, K.; Imbeaud, S.; Letouzé, E.; Alexandrov, L.B.; Calderaro, J.; Rebouissou, S.; Couchy, G.; Meiller, C.; Shinde, J.; Soysouvanh, J.; et al. Exome sequencing of hepatocellular carcinomas identifies new mutational signatures and potential therapeutic targets. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.S.; Crown, J.P.; Lang, I.; Boer, K.; Bondarenko, I.M.; Kulyk, S.O.; Ettl, J.; Patel, R.; Pinter, T.; Schmidt, M.; et al. The cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitor palbociclib in combination with letrozole versus letrozole alone as first-line treatment of oestrogen receptor-positive, HER2-negative, advanced breast cancer (PALOMA-1/TRIO-18): A randomised phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernas, S.; Tolaney, S.M.; Winer, E.P.; Goel, S. CDK4/6 inhibition in breast cancer: Current practice and future directions. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2018, 10, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickey, T.E.; Robinson, J.L.; Carroll, J.S.; Tilley, W.D. Minireview: The androgen receptor in breast tissues: Growth inhibitor, tumor suppressor, oncogene? J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2012, 26, 1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanzino, M.; De Amicis, F.; McPhaul, M.J.; Marsico, S.; Panno, M.L.; Andò, S. Endogenous Coactivator ARA70 Interacts with Estrogen Receptor α (ERα) and Modulates the Functional ERα/Androgen Receptor Interplay in MCF-7 Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 20421–20430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ando, S.; De Amicis, F.; Rago, V.; Carpino, A.; Maggiolini, M.; Panno, M.L.; Lanzino, M. Breast cancer: From estrogen to androgen receptor. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2002, 193, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
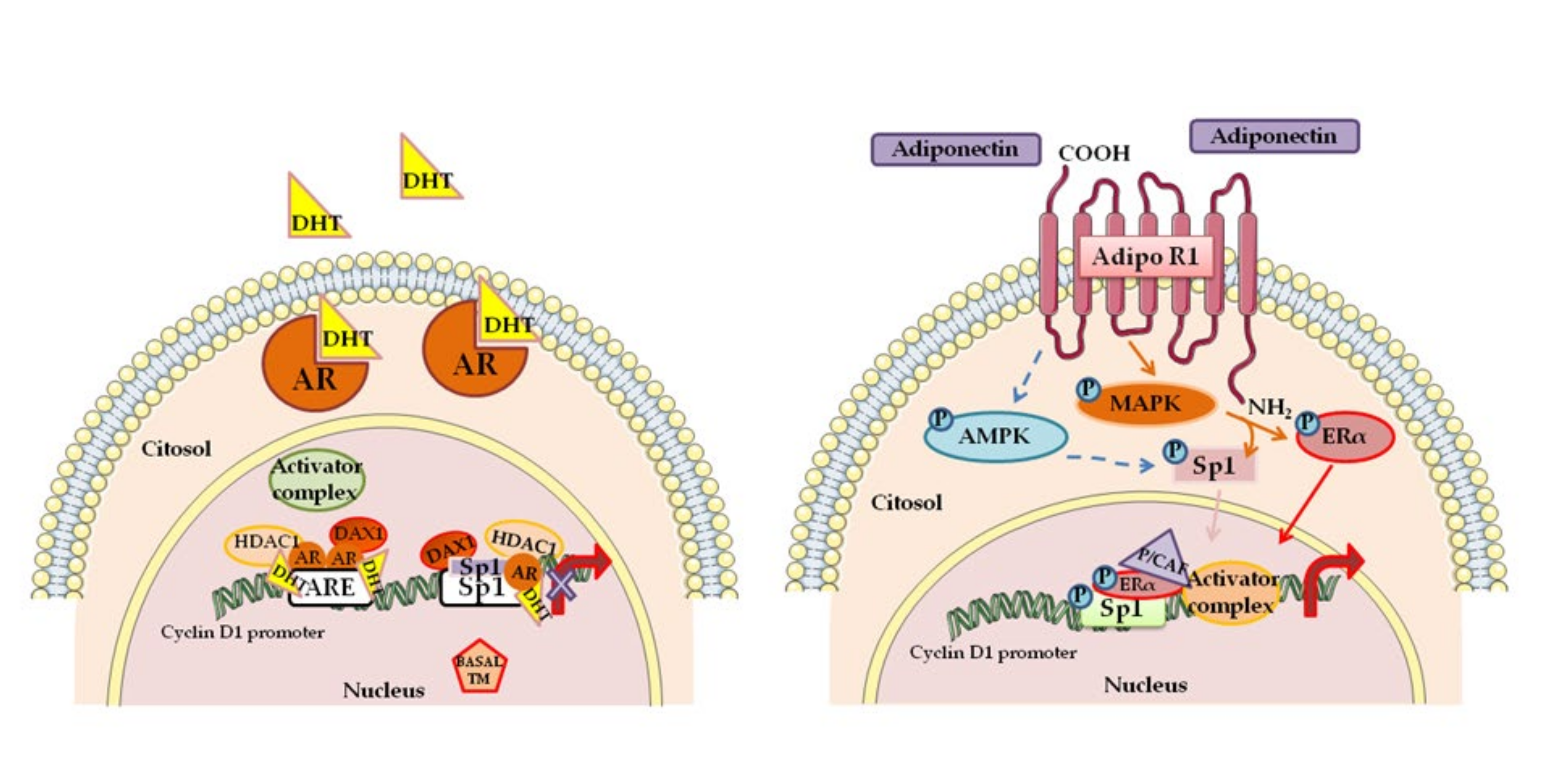
- Lanzino, M.; Sisci, D.; Morelli, C.; Garofalo, C.; Catalano, S.; Casaburi, I.; Capparelli, C.; Giordano, C.; Giordano, F.; Maggiolini, M.; et al. Inhibition of cyclin D1 expression by androgen receptor in breast cancer cells-identification of a novel androgen response element. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, 5351–5365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauro, L.; Pellegrino, M.; Giordano, F.; Ricchio, E.; Rizza, P.; De Amicis, F.; Catalano, S.; Bonofiglio, D.; Panno, M.L.; Ando, S. Estrogen receptor-alpha drives adiponectin effects on cyclin D1 expression in breast cancer cells. FASEB J. 2015, 29, 2150–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Amicis, F.; Chiodo, C.; Morelli, C.; Casaburi, I.; Marsico, S.; Bruno, R.; Sisci, D.; Andò, S.; Lanzino, M. AIB1 sequestration by androgen receptor inhibits estrogen-dependent cyclin D1 expression in breast cancer cells. Cancer 2019, 19, 1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landskroner-Eiger, S.; Qian, B.; Muise, E.S.; Nawrocki, A.R.; Berger, J.P.; Fine, E.J.; Koba, W.; Deng, Y.; Pollard, J.W.; Scherer, P.E. Proangiogenic contribution of adiponectin toward mammary tumor growth in vivo. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 3265–3276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bockmeyer, C.L.; Christgen, M.; Müller, M.; Fischer, S.; Ahrens, P.; Länger, F.; Kreipe, H.; Lehmannet, U. MicroRNA profiles of healthy basal and luminal mammary epithelial cells are distinct and reflected in different breast cancer subtypes. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2011, 130, 735–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, D.P.; Kerin, M.J.; Dwyer, R.M. Exosome-encapsulated microRNAs as circulating biomarkers for breast cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 139, 1443–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Thomson, J.M.; Hemann, M.T.; Hernando-Monge, E.; Mu, D.; Goodson, S.; Powers, S.; Cordon-Cardo, C.; Lowe, S.W.; Hannon, G.J.; et al. A microRNA polycistron as a potential human oncogene. Nature 2005, 435, 828–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Wang, C.; Wang, M.; Li, Z.; Casimiro, M.C.; Liu, M.; Wu, K.; Whittle, J.; Ju, X.; Hyslop, T.; et al. A cyclin D1/microRNA 17/20 regulatory feedback loop in control of breast cancer cell proliferation. J. Cell. Biol. 2008, 182, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, C.; Ju, X.; Wang, M.; Chen, K.; Loro, E.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, K.; et al. Cyclin D1 induction of Dicer governs microRNA processing and expression in breast cancer. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Gormley, M.; Qiao, J.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, M.; Di Sante, G.; Deng, S.; Dong, L.; Pestell, T.; Ju, X.; et al. Cyclin D1-mediated microRNA expression signature predicts breast cancer outcome. Theranostics 2018, 8, 2251–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lü, J.; Zhao, Q.; Ding, X.; Guo, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, Z.; Li, S.; Wang, Z.; Shen, L.; Chen, H.; et al. Cyclin D1 promotes secretion of pro-oncogenic immuno-miRNAs and piRNAs. Clin. Sci. 2020, 134, 791–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, M.A.; Lee, S.A.; Macias, E.; Lam, E.T.; Xu, C.; Jones, K.D.; Ho, C.; Marcelo Rodriguez-Puebla, M.; Chen, X. Role of Cyclin D1 as a Mediator of c-Met– and β-Catenin–Induced Hepatocarcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Lo, C.M.; Poon, R.Y.C.; Tan To Cheung, T.T.; Chan, A.C.Y.; Chen, L.; Yang, S.; Tsao, G.S.W.; Wang, X.Q. Smad inhibitor induces CSC differentiation for effective chemosensitization in cyclin D1- and TGF-β/Smad-regulated liver cancer stem cell-like cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 38811–38824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Fang, Y.; Wang, J.; Yuan, X.; Fan, Y.; Gao, S.; Han, L.; Wang, K. Hypomethylation of the cyclin D1 promoter in hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. Medicine 2020, 99, e20326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orr, S.J.; Gaymes, T.; Ladon, D.; Chronis, C.; Czepulkowski, B.; Wang, R. Reducing MCM levels in human primary T cells during the G(0) →4G(1) transition causes genomic instability during the first cell cycle. Oncogene 2010, 29, 3803–3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malvezzi, M.; Carioli, G.; Rodriguez, T.; Negri, E.; La Vecchia, C. Global trends and predictions in ovarian cancer mortality. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 2017–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, W.; Dong, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Feng, Y.; Ma, D.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, S. Gankyrin is frequently overexpressed in cervical high grade disease and is associated with cervical carcinogenesis and metastasis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95043. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Bai, M.; Ning, C.; Xie, B.; Zhang, J.; Liao, H.; Xiong, J.; Tao, X.; Yan, D.; Xi, X.; et al. Gankyrin facilitates FSH driven OC cell proliferation through phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases (PI3K)/AKT pathway, the central regulator of OC converging on CD1. Oncogene 2015, 35, 2506–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, D.; Berchuck, A.; Birrer, M.; Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Integrated genomic analyses of ovarian carcinoma. Nature 2011, 474, 609–615. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Li, W.; Wang, Z.; Ren, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, P.; Pan, S. Genistein Upregulates Cyclin D1 and CDK4 Expression and Promotes The proliferation of Ovarian Cancer OVCAR-5 Cells; Elsevier B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; Volume S0009-8981, p. 32020-0. [Google Scholar]
- Bali, A.; O’Brien, P.M.; Edwards, L.S.; Sutherland, R.L.; Hacker, N.F.; Henshall, S.M. Cyclin D1, p53, and p21Waf1/Cip1 Expression Is Predictive of Poor Clinical Outcome in Serous Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 5168–5177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, B.; Yang, S.; Liu, T.; Lou, G. miR-211 suppresses epithelial ovarian cance proliferation and cell-cycle progression by targeting Cyclin D1 and CDK6. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanken, H.; Gröbe, A.; Cachovan, G.; Smeets, R.; Simon, R.; Sauter, G.; Heiland, M.; Blessmann, M. CCND1 amplification and cyclin D1 immunohistochemical expression in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Clin. Oral Investig. 2014, 18, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albero, R.; Enjuanes, A.; Demajo, S.; Castellano, G.; Pinyol, M.; García, N.; Capdevila, C.; Clot, G.; Suárez-Cisneros, H.; Shimada, M.; et al. Cyclin D1 overexpression induces global transcriptional downregulation in lymphoid neoplasms. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 4132–4147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Kim, S.; Lee, B.; Kim, H.; Song, I.; Shin, H.; Han, Y.; Chang, K.; Kim, J.; Lee, D.; et al. Prx I Suppresses K-ras-Driven Lung Tumorigenesis by Opposing Redox-Sensitive ERK/Cyclin D1 Pathway. Antoxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 19, 482–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquila, S.; Santoro, M.; Caputo, A.; Panno, M.L.; Pezzi, V.; De Amicis, F. The Tumor Suppressor PTEN as Molecular Switch Node Regulating Cell Metabolism and Autophagy: Implications in Immune System andTumor Microenvironment. Cells 2020, 9, 1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yin, L.L.; Su, K.L.; Zhang, G.F.; Wang, J. Concomitant depletion of PTEN and p27 and overexpression of cyclin D1 may predict a worse prognosis for patients with post-operative stage II and III colorectal cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2014, 8, 1543–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragoj, M.; Milosevic, Z.; Bankovic, J.; Dinic, J.; Pesic, M.; Tanic, N.; Stankovic, T. Association of CCND1 overexpression with KRAS and PTEN alterations in specific subtypes of non-small cell lung carcinoma and its influence on patients’ outcome. Tumor Biol. 2015, 36, 8773–8780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Song, L.; Ai, T.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Cui, J. Prognostic value of MET, cyclin D1 and MET gene copy number in non-small cell lung cancer. J. Biomed. Res. 2013, 27, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lawson, C.D.; Ridley, A.J. Rho GTPase signaling complexes in cell migration and invasion. J. Cell Biol. 2017, 217, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhaja, E.; Adan, J.; Pagan, R.; Mitjans, F.; Cascalló, M.; Rodríguez, M.; Noé, V.; Ciudad, C.J.; Mazo, A.; Vilaró, S.; et al. Anti-migratory and anti-angiogenic effect of p16: A novel localization at membrane ruffles and lamellipodia in endothelial cells. Angiogenesis 2004, 7, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Yeow, W.-S.; Zou, C.; Wassell, R.; Wang, C.; Pestell, R.G.; Quong, J.N.; Quong, A. Cyclin D1/cyclin-dependent kinase 4 interacts with filamin A and affects the migration and invasion potential of breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 2105–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
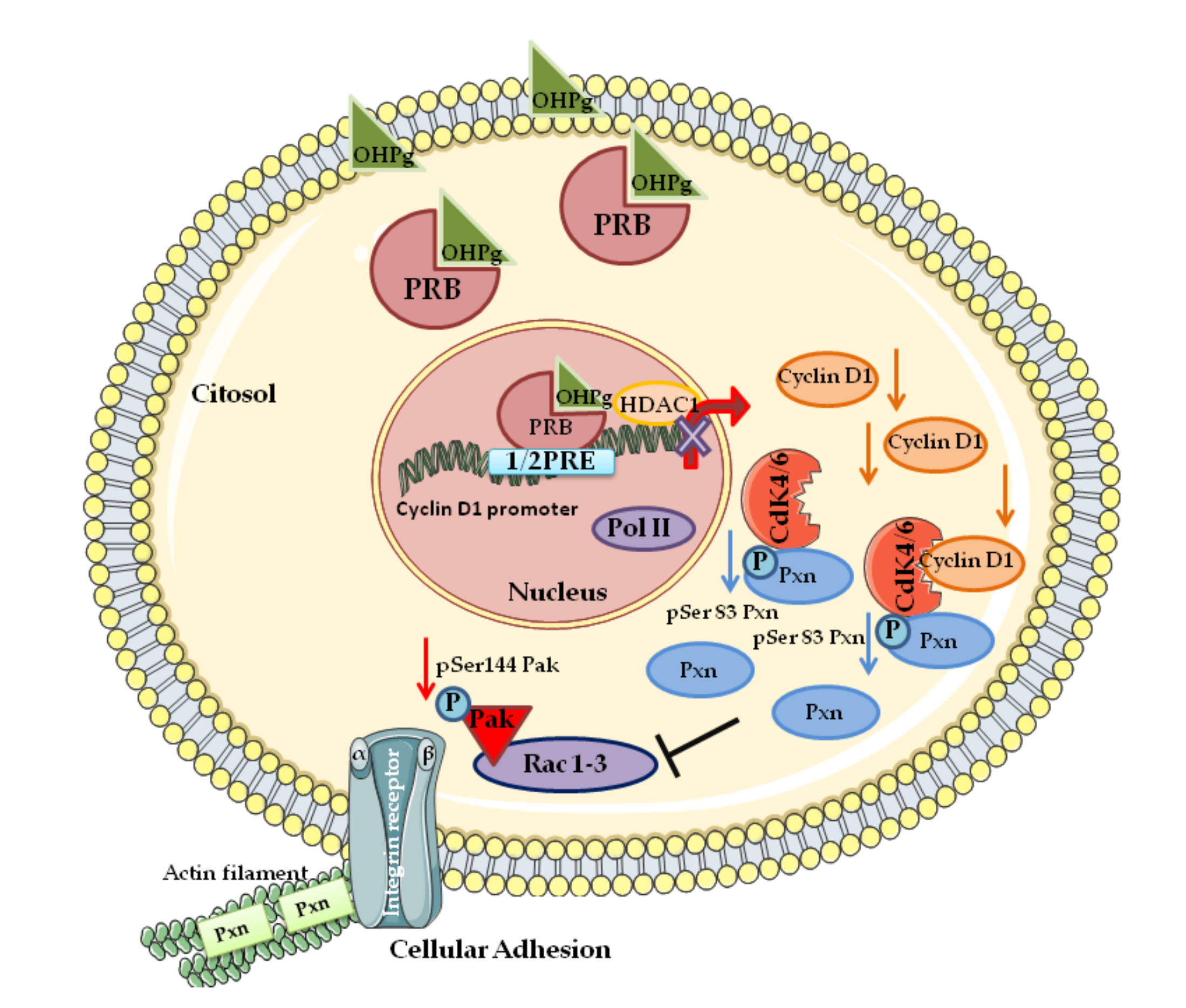
- Fusté, N.P.; Fernández-Hernández, R.; Cemeli, T.; Mirantes, C.; Pedraza, N.; Rafel, M.; Torres-Rosell, J.; Colomina, N.; Ferrezuelo, F.; Dolcet, X.; et al. Cytoplasmic cyclin D1 regulates cell invasion and metastasis through the phosphorylation of paxillin. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, K.; Boudreau, C.G.; Brown, C.M.; Khadra, A. Paxillin phosphorylation at serine 273 and its effects on Rac, Rho and adhesion dynamics. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2018, 14, e1006303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montalto, F.I.; Giordano, F.; Chiodo, C.; Marsico, S.; Mauro, L.; Sisci, D.; Aquila, S.; Lanzino, M.; Panno, M.L.; Andò, S.; et al. Progesterone Receptor B signaling Reduces Breast Cancer Cell Aggressiveness: Role of Cyclin-D1/Cdk4 Mediating Paxillin Phosphorylation. Cancers 2019, 11, 1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusté, N.P.; Castelblanco, E.; Felip, I.; Santacana, M.; Fernández-Hernández, R.; Gatius, S.; Pedraza, N.; Pallarés, J.; Cemeli, T.; Valls, J.; et al. Characterization of cytoplasmic cyclin D1 as a marker of invasiveness in cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 26979–26991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jirawatnotai, S.; Hu, Y.; Michowski, W.; Elias, J.E.; Becks, L.; Bienvenu, F.; Zagozdzon, A.; Goswami, T.; Wang, Y.E.; Clark, A.B.; et al. A function for cyclin D1 in DNA repair uncovered by protein interactome analyses in human cancers. Nature 2011, 474, 230–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Body, S.; Esteve-Arenys, A.; Miloudi, H.; Recasens-Zorzo, C.; Tchakarska, G.; Moros, A.; Bustany, S.; Vidal-Crespo, A.; Rodriguez, V.; Lavigne, R.; et al. Cytoplasmic cyclin D1 controls the migration and invasiveness of mantle lymphoma cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liotta, L.A.; Kohn, E.C. The microenvironment of the tumour-host interface. Nature 2001, 411, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, P.J.; Mishra, P.J.; Humeniuk, R.; Medina, D.J.; Alexe, G.; Mesirov, J.P.; Ganesan, S.; Glod, J.W.; Banerjee, D. Carcinoma-Associated Fibroblast–Like Differentiation of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 4331–4339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Franco, O.E.; Jiang, M.; Williams, K.; Harold, D.; Love, H.D.; Coleman, I.M.; Peter, S.; Nelson, P.S.; Hayward, S.W. Tissue-Specific Consequences of Cyclin D1 Overexpression in Prostate Cancer Progression. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 8188–8197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciznadija, D.; Liu, Y.; Pyonteck, S.M.; Holland, E.C.; Koff, A. Cyclin D1 and cdk4 mediate development of neurologically destructive oligodendroglioma. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 6174–6183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pestell, T.G.; Jiao, X.; Kumar, M.; Peck, A.R.; Prisco, M.; Deng, S.; Li, Z.; Ertel, A.; Casimiro, M.C.; Ju, X.; et al. Stromal cyclin D1 promotes heterotypic immune signaling and breast cancer growth. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 81754–81775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Huang, Y.; Gao, X.; Li, Y.; Lin, J.; Chen, L.; Chang, L.; Chen, G.; Guan, Y.; Pan, L.K.; et al. CCND1 Amplification Contributes to Immunosuppression and Is Associated With a Poor Prognosis to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Solid Tumors. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, Z.L.; Versaci, S.; Dushyanthen, S.; Caramia, F.; Savas, P.; Mintoff, C.P.; Zethoven, M.; Virassamy, B.; Luen, S.J.; McArthur, G.A.; et al. Combined CDK4/6 and PI3Kα Inhibition Is Synergistic and Immunogenic in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 6340–6352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Montalto, F.I.; De Amicis, F. Cyclin D1 in Cancer: A Molecular Connection for Cell Cycle Control, Adhesion and Invasion in Tumor and Stroma. Cells 2020, 9, 2648. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9122648
Montalto FI, De Amicis F. Cyclin D1 in Cancer: A Molecular Connection for Cell Cycle Control, Adhesion and Invasion in Tumor and Stroma. Cells. 2020; 9(12):2648. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9122648
Chicago/Turabian StyleMontalto, Francesca Ida, and Francesca De Amicis. 2020. "Cyclin D1 in Cancer: A Molecular Connection for Cell Cycle Control, Adhesion and Invasion in Tumor and Stroma" Cells 9, no. 12: 2648. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9122648
APA StyleMontalto, F. I., & De Amicis, F. (2020). Cyclin D1 in Cancer: A Molecular Connection for Cell Cycle Control, Adhesion and Invasion in Tumor and Stroma. Cells, 9(12), 2648. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9122648




