Role of HMGB1/TLR4 Axis in Ischemia/Reperfusion-Impaired Extracellular Glutamate Clearance in Primary Astrocytes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Culture of Primary Astrocytes
2.3. Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation/Reoxygenation
2.4. Preparation of OGD/R Conditioned Medium
2.5. LDH Release Assay
2.6. Assay for Astrocytic Glutamate Clearance
2.7. siRNA and Cell Transfection
2.8. Western Blot Assay
2.9. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
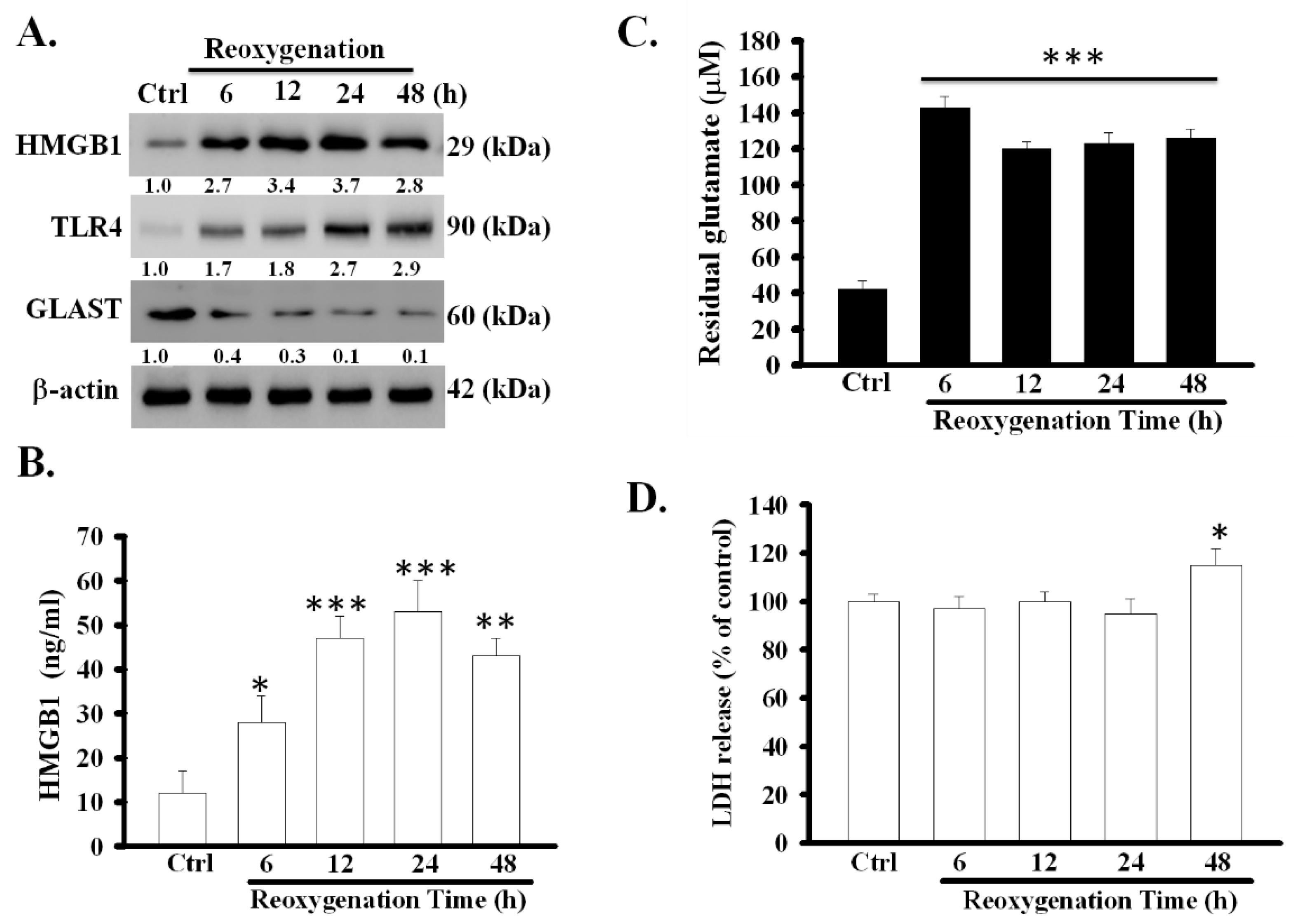
3.1. OGD/R Increased the Expression and Release of HMGB1 Protein and Decreased the Function of Glutamate Clearance in Primary Astrocytes
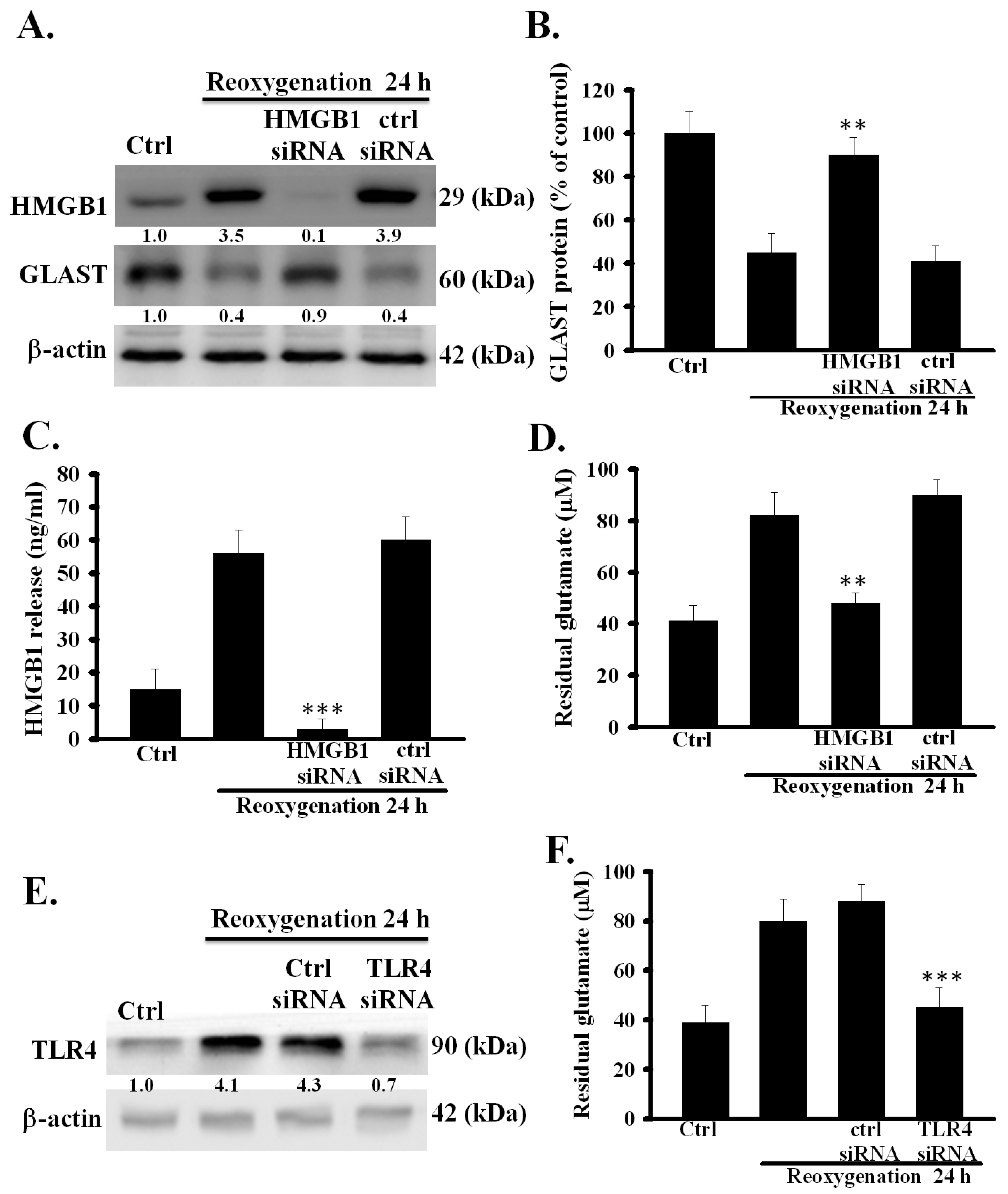
3.2. HMGB1 Knockdown Prevented Dysfunction of Astrocytic Glutamate Clearance Induced by OGD/R
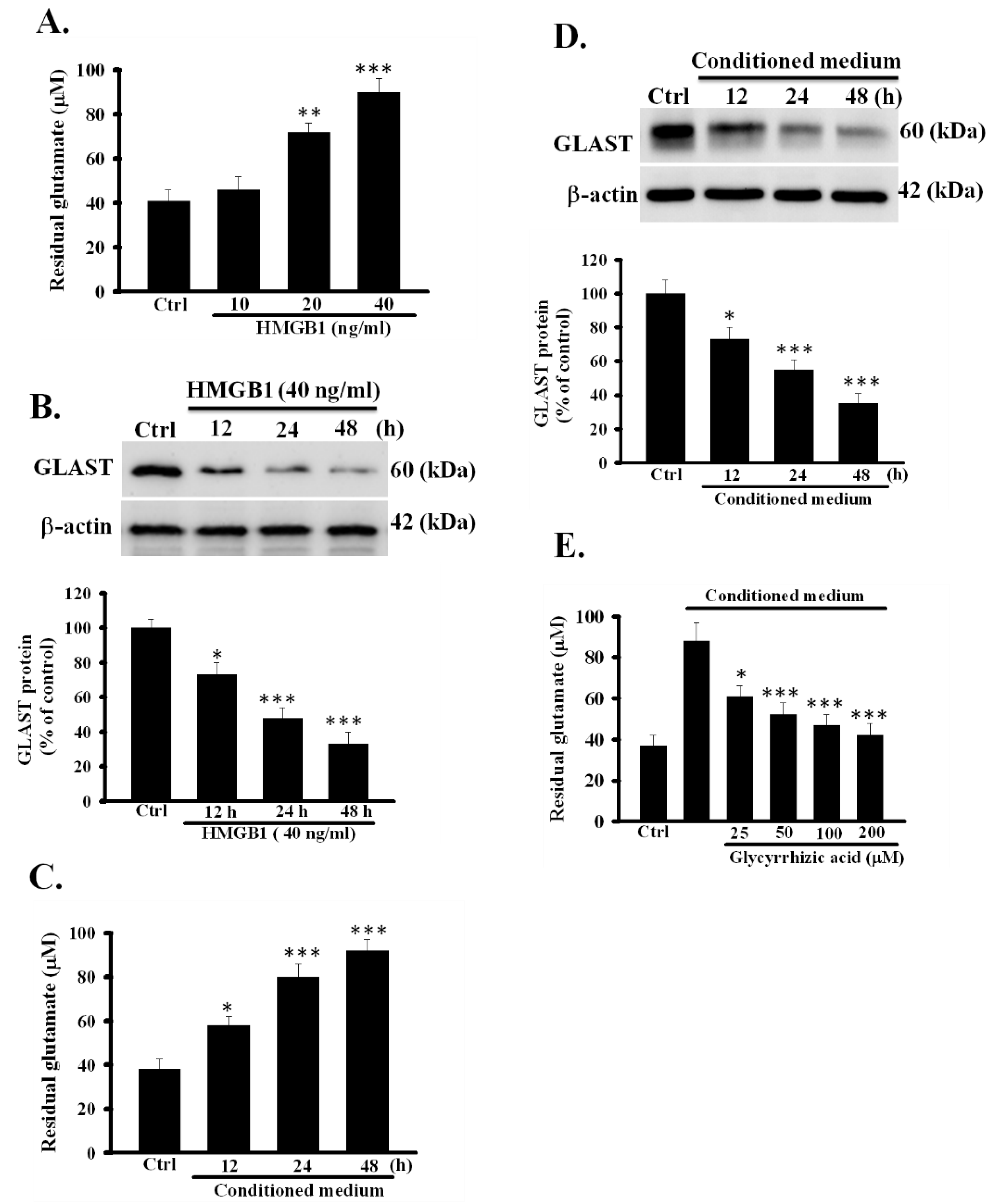
3.3. Exogeneous Recombinant HMGB1 Inhibited the Activity of Glutamate Clearance in Primary Astrocytes
3.4. Conditioned Medium Inhibited the Function of Astrocytic Glutamate Clearance
3.5. TLR4 Was Involved in OGD/R-Induced Dysfunction of Astrocytic Glutamate Clearance
3.6. Inhibition of TLR4 Prevented rHMGB1-Induced Inhibition of the Function of Astrocytic Glutamate Clearance
3.7. Inhibition of TLR4 Prevented CM-Induced Inhibition of the Activity of Astrocytic Glutamate Clearance
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CM | conditioned medium; |
| GLAST | glutamate aspartate transporter; |
| GLT-1 | glutamate transporter 1; |
| HMGB1 | high-mobility group box 1; |
| OGD/R | oxygen-glucose deprivation /reoxygenation; |
| TLR4 | toll-like receptor 4; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s modified eagle medium; |
| FBS | fetal bovine serum; |
| BSS | balanced salt solution; |
| CM | conditioned medium; |
| SEM | standard error of the mean; |
| LPS-RS | lipopolysaccharide from Rhodobacter sphaeroides |
References
- Mahmoud, S.; Gharagozloo, M.; Simard, C.; Gris, D. Astrocytes maintain glutamate homeostasis in the CNS by controlling the balance between glutamate uptake and release. Cells 2019, 8, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giaume, C.; Kirchhoff, F.; Matute, C.; Reichenbach, A.; Verkhratsky, A. Glia: The fulcrum of brain diseases. Cell Death Differ. 2007, 14, 1324–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, T.W.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.T. Excitotoxicity and stroke: Identifying novel targets for neuroprotection. Prog. Neurobiol. 2014, 115, 157–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puig, B.; Brenna, S.; Magnus, T. Molecular communication of a dying neuron in stroke. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitchen, P.; Salman, M.M.; Halsey, A.M.; Clarke-Bland, C.; MacDonald, J.A.; Ishida, H.; Vogel, H.J.; Almutiri, S.; Logan, A.; Kreida, S. Targeting Aquaporin-4 Subcellular Localization to Treat Central Nervous System Edema. Cell 2020, 181, 784–799.e719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bak, L.K.; Schousboe, A.; Waagepetersen, H.S. The glutamate/GABA-glutamine cycle: Aspects of transport, neurotransmitter homeostasis and ammonia transfer. J. Neurochem. 2006, 98, 641–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Petersen, K.F.; Behar, K.L.; Brown, P.; Nixon, T.W.; Mason, G.F.; Petroff, O.A.; Shulman, G.I.; Shulman, R.G.; Rothman, D.L. Determination of the rate of the glutamate/glutamine cycle in the human brain by in vivo 13C NMR. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 8235–8240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnewald, U.; Schousboe, A. Introduction to the glutamate–glutamine cycle. In The Glutamate/GABA-Glutamine Cycle; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.-M.; Grabb, M.C.; Zipfel, G.J.; Choi, D.W. Brain tissue responses to ischemia. J. Clin. Investig. 2000, 106, 723–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.H.; Hazell, A.S. Excitotoxic mechanisms and the role of astrocytic glutamate transporters in traumatic brain injury. Neurochem. Int. 2006, 48, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Wang, Y.X.; Dou, F.F.; Lu, H.Z.; Ma, Z.W.; Lu, P.H.; Xu, X.M. Glutamine synthetase down-regulation reduces astrocyte protection against glutamate excitotoxicity to neurons. Neurochem. Int. 2010, 56, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.H.; You, J.R.; Wei, K.C.; Gean, P.W. Stimulating ERK/PI3K/NFκB signaling pathways upon activation of mGluR2/3 restores OGD-induced impairment in glutamate clearance in astrocytes. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2014, 39, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.B.; Choi, J.S.; Yu, Y.M.; Nam, K.; Piao, C.S.; Kim, S.W.; Lee, M.H.; Han, P.L.; Park, J.S.; Lee, J.K. HMGB1, a novel cytokine-like mediator linking acute neuronal death and delayed neuroinflammation in the postischemic brain. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 6413–6421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, J.; Crews, F.T. Glutamate/NMDA excitotoxicity and HMGB1/TLR4 neuroimmune toxicity converge as components of neurodegeneration. AIMS Mol. Sci. 2015, 2, 77–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollica, L.; De Marchis, F.; Spitaleri, A.; Dallacosta, C.; Pennacchini, D.; Zamai, M.; Agresti, A.; Trisciuoglio, L.; Musco, G.; Bianchi, M.E. Glycyrrhizin binds to high-mobility group box 1 protein and inhibits its cytokine activities. Chem. Biol. 2007, 14, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.W.; Jin, Y.; Shin, J.H.; Kim, I.D.; Lee, H.K.; Park, S.; Han, P.L.; Lee, J.K. Glycyrrhizic acid affords robust neuroprotection in the postischemic brain via anti-inflammatory effect by inhibiting HMGB1 phosphorylation and secretion. Neurobiol. Dis. 2012, 46, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Li, M.; Ma, X.; Feng, H.; Song, J.; Lv, C.; He, Y. Inhibition of HMGB1 reduces rat spinal cord astrocytic swelling and AQP4 expression after oxygen-glucose deprivation and reoxygenation via TLR4 and NF-kappaB signaling in an IL-6-dependent manner. J. Neuroinflamm. 2017, 14, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Bianchi, M.E.; Coleman, T.R.; Tracey, K.J.; Al-Abed, Y. Exploring the biological functional mechanism of the HMGB1/TLR4/MD-2 complex by surface plasmon resonance. Mol. Med. 2018, 24, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Jin, T.; Zhang, H.; Xiong, X.; Gu, L. The role of high mobility group box 1 in ischemic stroke. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.-J.; Cheng, J.; Feng, X.; Yu, Y.; Tian, L.; Huang, Q. The dual role and therapeutic potential of high-mobility group box 1 in cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 64534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirillo, P.; Giallauria, F.; Pacileo, M.; Petrillo, G.; D’Agostino, M.; Vigorito, C.; Chiariello, M. Increased high mobility group box-1 protein levels are associated with impaired cardiopulmonary and echocardiographic findings after acute myocardial infarction. J. Card. Fail. 2009, 15, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrassy, M.; Volz, H.C.; Igwe, J.C.; Funke, B.; Eichberger, S.N.; Kaya, Z.; Buss, S.; Autschbach, F.; Pleger, S.T.; Lukic, I.K.; et al. High-mobility group box-1 in ischemia-reperfusion injury of the heart. Circulation 2008, 117, 3216–3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Souza, A.W.; Westra, J.; Limburg, P.C.; Bijl, M.; Kallenberg, C.G. HMGB1 in vascular diseases: Its role in vascular inflammation and atherosclerosis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2012, 11, 909–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayaraj, R.L.; Azimullah, S.; Beiram, R.; Jalal, F.Y.; Rosenberg, G.A. Neuroinflammation: Friend and foe for ischemic stroke. J. Neuroinflammation. 2019, 16, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.B.; Lim, C.M.; Yu, Y.M.; Lee, J.K. Induction and subcellular localization of high-mobility group box-1 (HMGB1) in the postischemic rat brain. J. Neurosci. Res. 2008, 86, 1125–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Mori, S.; Takahashi, H.K.; Tomono, Y.; Wake, H.; Kanke, T.; Sato, Y.; Hiraga, N.; Adachi, N.; Yoshino, T.; et al. Anti-high mobility group box 1 monoclonal antibody ameliorates brain infarction induced by transient ischemia in rats. FASEB J. 2007, 21, 3904–3916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Yoon, E.J.; Seo, J.; Kavoussi, A.; Chung, Y.E.; Chung, S.P.; Park, I.; Kim, C.H.; You, J.S. Hypothermia inhibits the propagation of acute ischemic injury by inhibiting HMGB1. Mol. Brain 2016, 9, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhowmick, S.; Moore, J.T.; Kirschner, D.L.; Curry, M.C.; Westbrook, E.G.; Rasley, B.T.; Drew, K.L. Acidotoxicity via ASIC1a mediates cell death during oxygen glucose deprivation and abolishes excitotoxicity. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2017, 8, 1204–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhowmick, S.; Moore, J.T.; Kirschner, D.L.; Drew, K.L. Arctic ground squirrel hippocampus tolerates oxygen glucose deprivation independent of hibernation season even when not hibernating and after ATP depletion, acidosis, and glutamate efflux. J. Neurochem. 2017, 142, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhowmick, S.; Drew, K.L. Arctic ground squirrel resist peroxynitrite-mediated cell death in response to oxygen glucose deprivation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 113, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umahara, T.; Uchihara, T.; Hirokawa, K.; Hirao, K.; Shimizu, S.; Hashimoto, T.; Terasi, H.; Hanyu, H. Time-dependent and lesion-dependent HMGB1-selective localization in brains of patients with cerebrovascular diseases. Histol. Histopathol. 2018, 33, 215–222. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, S.P.; Seehra, R.S.; Heath, P.R.; Hall, B.P.; Bates, J.; Garwood, C.J.; Matuszyk, M.M.; Wharton, S.B.; Simpson, J.E. Transcriptomic Analysis of Human Astrocytes In Vitro Reveals Hypoxia-Induced Mitochondrial Dysfunction, Modulation of Metabolism, and Dysregulation of the Immune Response. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salman, M.M.; Kitchen, P.; Woodroofe, M.N.; Bill, R.M.; Conner, A.C.; Heath, P.R.; Conner, M.T. Transcriptome analysis of gene expression provides new insights into the effect of mild therapeutic hypothermia on primary human cortical astrocytes cultured under hypoxia. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Zhu, Q.; Xu, C.; Li, M.; Li, H.; Yi, P.Q.; Xu, F.F.; Cao, L.; Chen, J.Y. Glycyrrhizin mitigates radiation-induced acute lung injury by inhibiting the HMGB1/TLR4 signalling pathway. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lancaster, M.A.; Huch, M. Disease modelling in human organoids. Dis. Model. Mech. 2019, 12, dmm039347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salman, M.M.; Marsh, G.; Kusters, I.; Delincé, M.; Di Caprio, G.; Upadhyayula, S.; De Nola, G.; Hunt, R.; Ohashi, K.G.; Gray, T. Design and validation of a human brain endothelial microvessel-on-a-chip open microfluidic model enabling advanced optical imaging. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 573775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, C.-H.; Chen, H.-Y.; Wei, K.-C. Role of HMGB1/TLR4 Axis in Ischemia/Reperfusion-Impaired Extracellular Glutamate Clearance in Primary Astrocytes. Cells 2020, 9, 2585. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9122585
Lin C-H, Chen H-Y, Wei K-C. Role of HMGB1/TLR4 Axis in Ischemia/Reperfusion-Impaired Extracellular Glutamate Clearance in Primary Astrocytes. Cells. 2020; 9(12):2585. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9122585
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Chia-Ho, Han-Yu Chen, and Kai-Che Wei. 2020. "Role of HMGB1/TLR4 Axis in Ischemia/Reperfusion-Impaired Extracellular Glutamate Clearance in Primary Astrocytes" Cells 9, no. 12: 2585. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9122585
APA StyleLin, C.-H., Chen, H.-Y., & Wei, K.-C. (2020). Role of HMGB1/TLR4 Axis in Ischemia/Reperfusion-Impaired Extracellular Glutamate Clearance in Primary Astrocytes. Cells, 9(12), 2585. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9122585



