Characterization of In Vitro 3D Cell Model Developed from Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HepG2) Cell Line
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Cell Culture and Formation of 3D Spheroids
2.3. Monitoring the Growth and Morphology of Spheroids
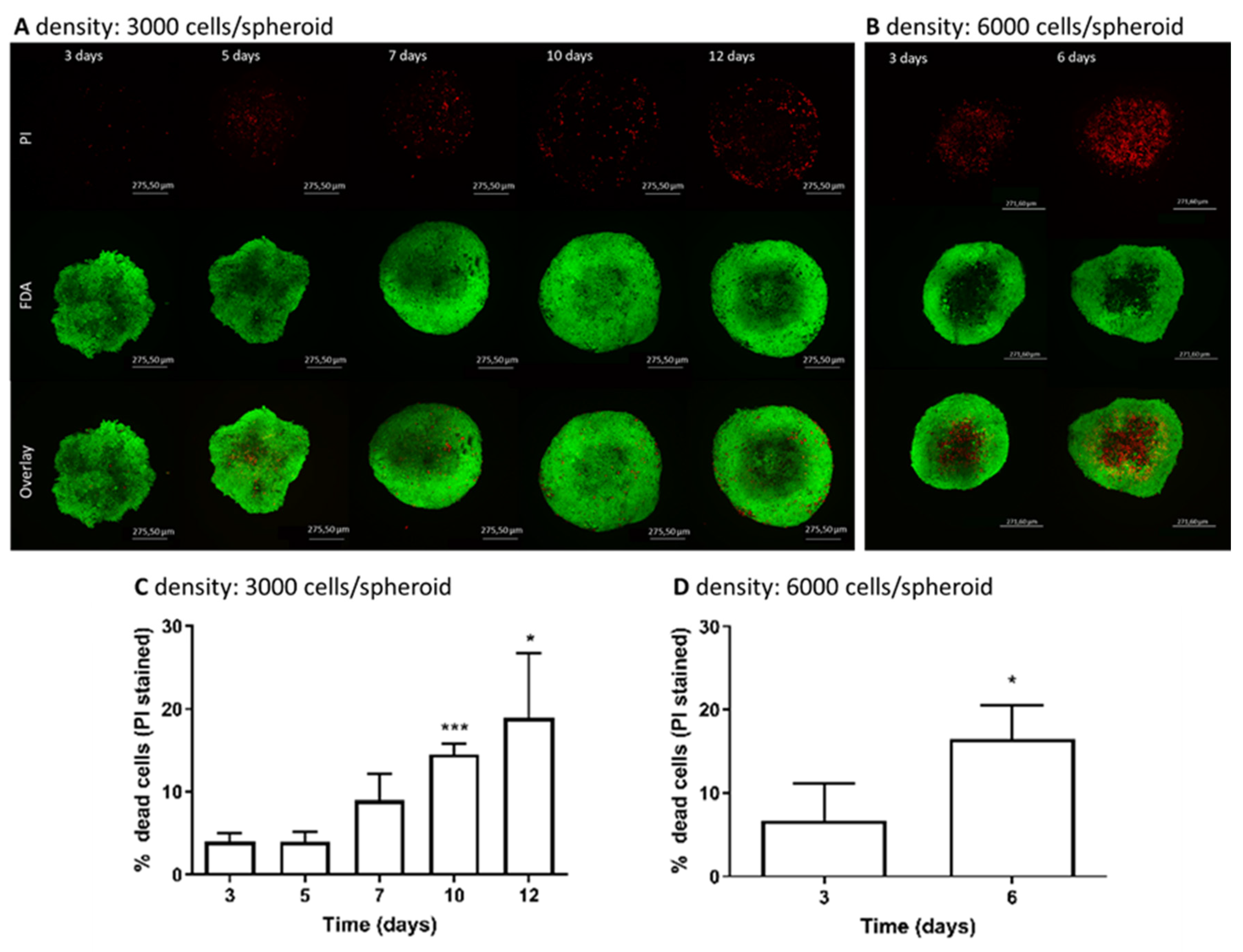
2.4. Quantification and Viability Determination of the Whole Spheroid by Live/Dead Staining
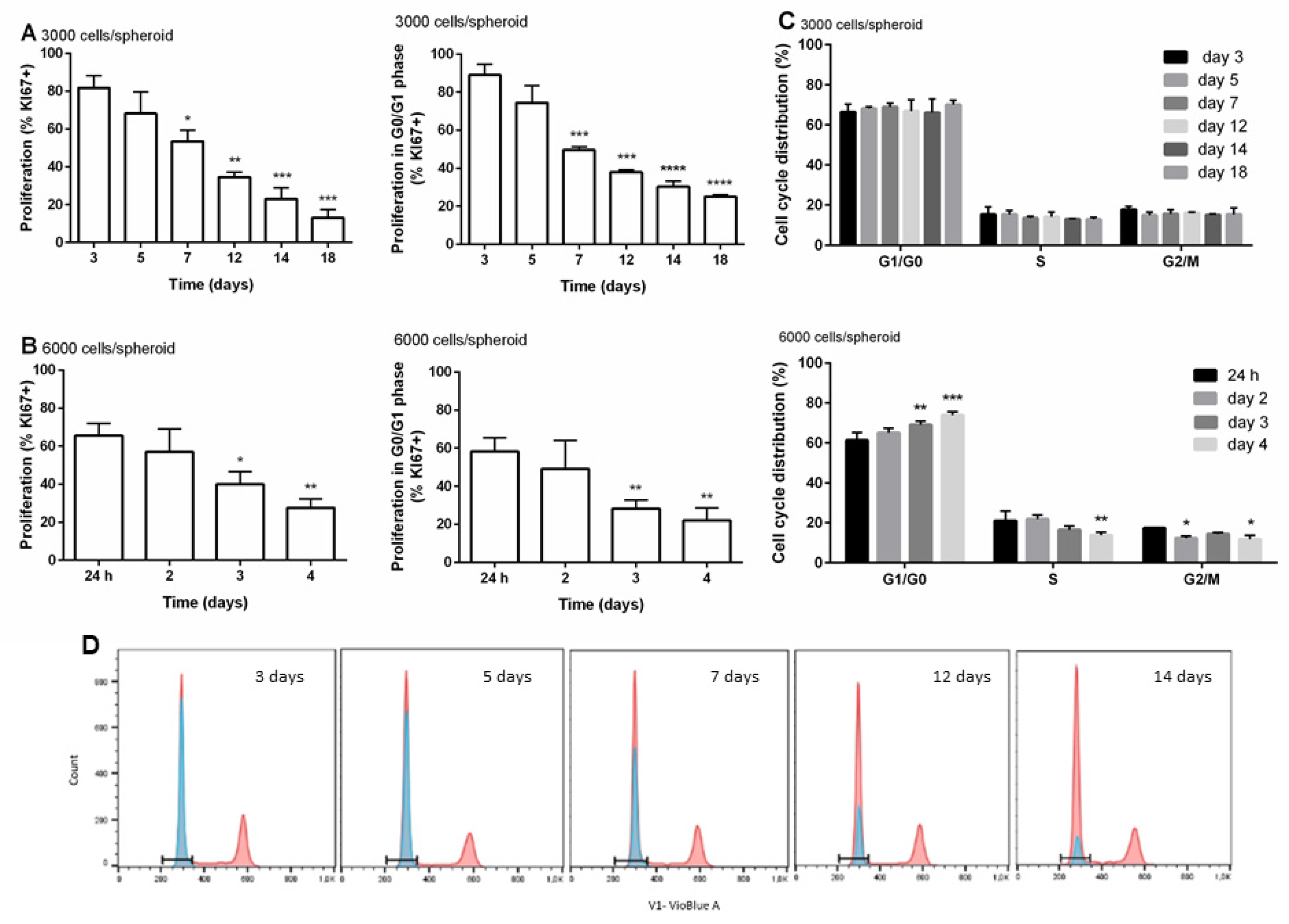
2.5. Analyses of Cell Cycle and Cell Proliferation by Flow Cytometry
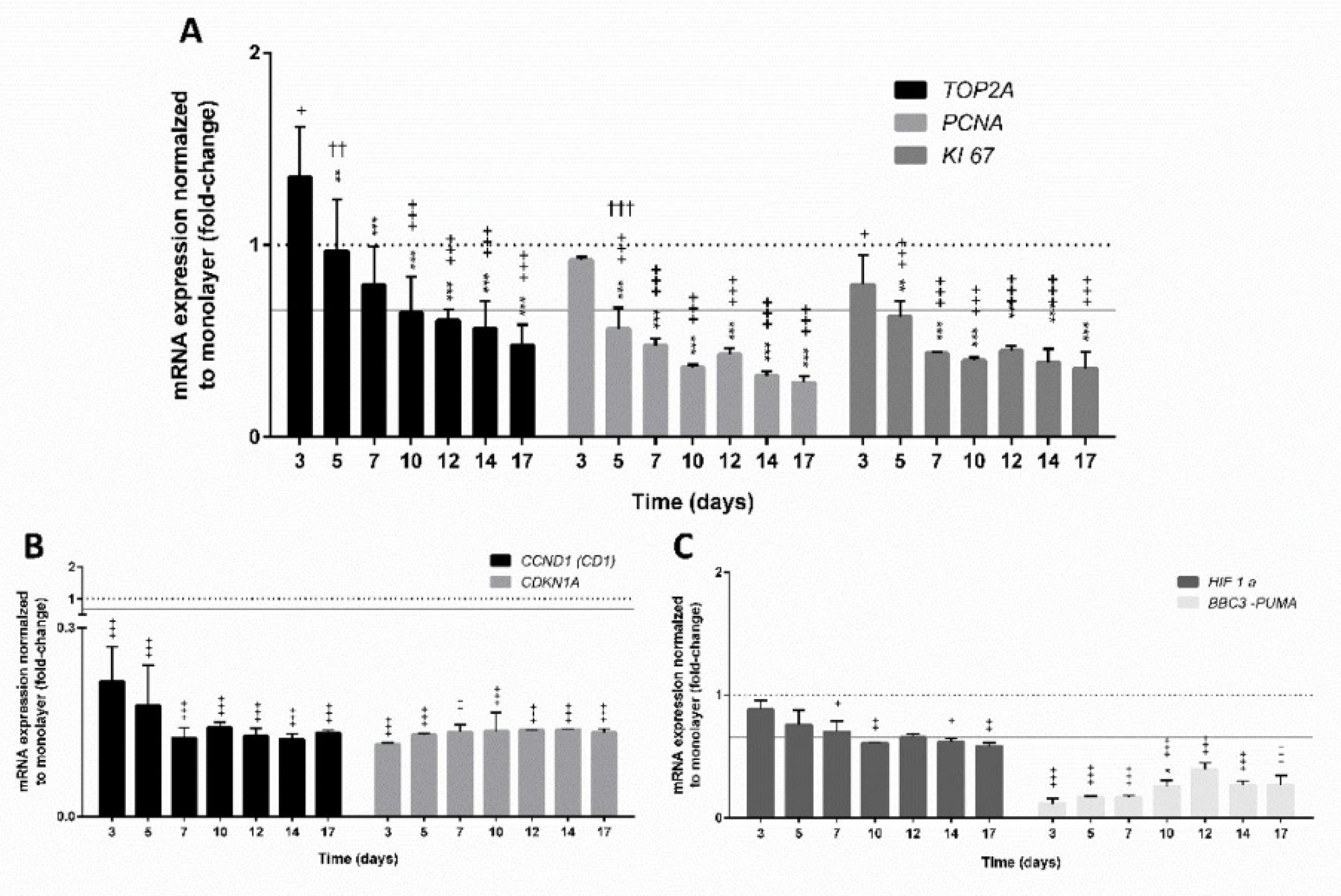
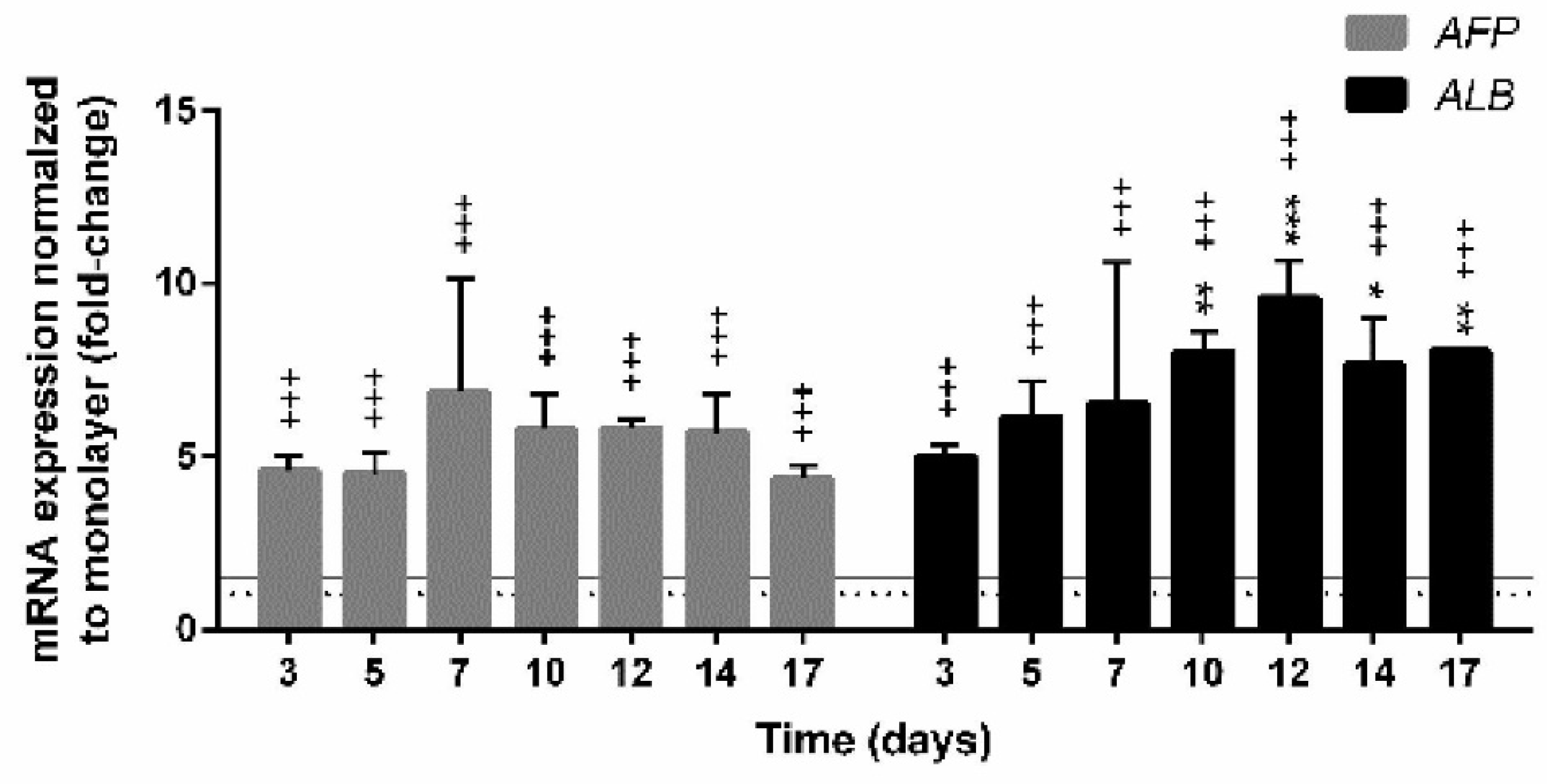
2.6. The qPCR Analyses of the Expression of Selected Genes
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Effects on Growth and Morphological Changes over Time
3.2. Determination of Live/Dead Cells in Spheroids over Cultivation Time
3.3. Distribution of Cells within the Cell Cycle and Cell Proliferation during the Time of Cultivation
3.4. Gene Expression in Spheroids
3.4.1. Expression of Genes Involved in Cell Proliferation
3.4.2. Expression of Genes Encoding Hepatic Markers
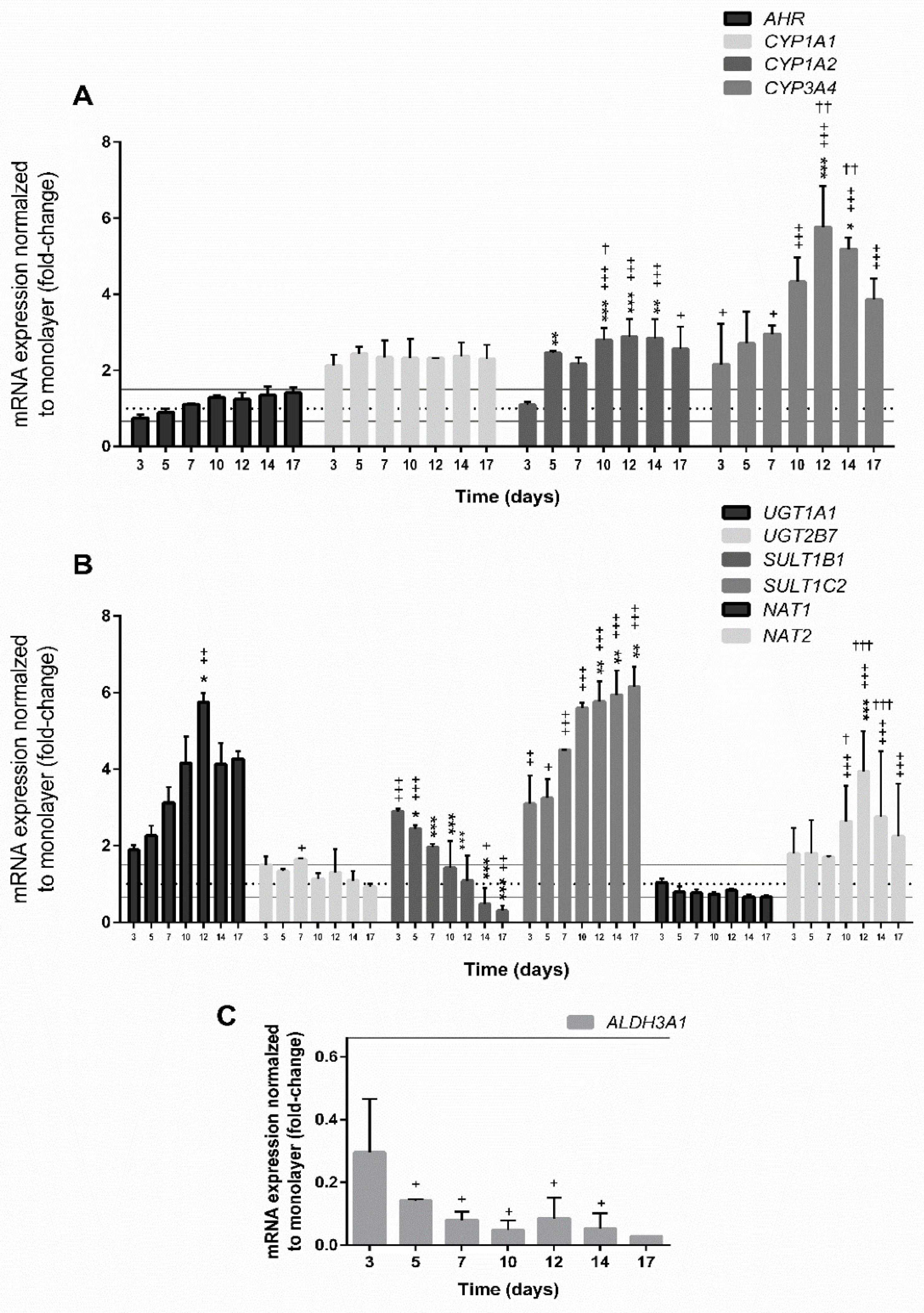
3.4.3. Expression of Genes Involved in the Xenobiotic Metabolism
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thummel, K. Factors influencing drug metabolism. In xPharm: The Comprehensive Pharmacology Reference; Elservier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 1–18. ISBN 9780080552323. [Google Scholar]
- Croom, E. Metabolism of xenobiotics of human environments. In Progress in Molecular Biology and Translational Science; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; Volume 112, pp. 31–88. [Google Scholar]
- Corvi, R.; Madia, F. In vitro genotoxicity testing–Can the performance be enhanced? Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 106, 600–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfuhler, S.; Van Benthem, J.; Curren, R.; Doak, S.H.; Dusinska, M.; Hayashi, M.; Heflich, R.H.; Kidd, D.; Kirkland, D.; Luan, Y.; et al. Use of in vitro 3D tissue models in genotoxicity testing: Strategic fit, validation status and way forward. Report of the working group from the 7th International Workshop on Genotoxicity Testing (IWGT). Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2020, 850–851, 503135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyffin, J.A.; Sharma, P.; Leedale, J.A.; Colley, H.; Murdoch, C.; Mistry, P.; Webb, S.D. Impact of cell types and culture methods on the functionality of in vitro liver systems—A review of cell systems for hepatotoxicity assessment. Toxicol. In Vitr. 2018, 48, 262–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godoy, P.; Hewitt, N.J.; Albrecht, U.; Andersen, M.E.; Ansari, N.; Bhattacharya, S.; Bode, J.G.; Bolleyn, J.; Borner, C.; Böttger, J.; et al. Recent advances in 2D and 3D in vitro systems using primary hepatocytes, alternative hepatocyte sources and non-parenchymal liver cells and their use in investigating mechanisms of hepatotoxicity, cell signaling and ADME. Arch. Toxicol. 2013, 87, 1315–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, A.J.; Dial, S.L.; A Casciano, D. Comparison of basal gene expression profiles and effects of hepatocarcinogens on gene expression in cultured primary human hepatocytes and HepG2 cells. Mutat. Res. Mol. Mech. Mutagen. 2004, 549, 79–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lecluyse, E.L. Human hepatocyte culture systems for the in vitro evaluation of cytochrome P450 expression and regulation. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 13, 343–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fey, S.J.; Wrzesinski, K. Determination of Drug Toxicity Using 3D Spheroids Constructed From an Immortal Human Hepatocyte Cell Line. Toxicol. Sci. 2012, 127, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Luo, X.; Anene-Nzelu, C.; Yu, Y.; Hong, X.; Singh, N.H.; Xia, L.; Liu, S.; Yu, H. HepaRG culture in tethered spheroids as an in vitro three-dimensional model for drug safety screening. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2015, 35, 909–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, M.; Hansen, S.H.; Dalgaard, L.; Dubois, J.; Badolo, L. Development of an in vitro assay for the investigation of metabolism-induced drug hepatotoxicity. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2008, 24, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drewitz, M.; Helbling, M.; Fried, N.; Bieri, M.; Moritz, W.; Lichtenberg, J.; Kelm, J.M. Towards automated production and drug sensitivity testing using scaffold-free spherical tumor microtissues. Biotechnol. J. 2011, 6, 1488–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillouzo, A.; Corlu, A.; Aninat, C.; Glaise, D.; Morel, F.; Guguen-Guillouzo, C. The human hepatoma HepaRG cells: A highly differentiated model for studies of liver metabolism and toxicity of xenobiotics. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2007, 168, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donato, M.; Tolosa, L.; Gómez-Lechón, M.J. Culture and Functional Characterization of Human Hepatoma HepG2 Cells. In Protocols in In Vitro Hepatocyte Research; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 77–93. ISBN 9781493920747. [Google Scholar]
- Wrzesinski, K.; Fey, S.J. After trypsinisation, 3D spheroids of C3A hepatocytes need 18 days to re-establish similar levels of key physiological functions to those seen in the liver. Toxicol. Res. 2013, 2, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldherr, M.; Lundt, N.; Klaas, M.; Betzold, S.; Wurdack, M.; Baumann, V.; Estrecho, E.; Nalitov, A.; Cherotchenko, E.; Cai, H.; et al. Observation of bosonic condensation in a hybrid monolayer MoSe2-GaAs microcavity. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duret, C.; Gerbal-Chaloin, S.; Ramos, J.; Fabre, J.-M.; Jacquet, E.; Navarro, F.; Blanc, P.; Cunha, A.S.; Maurel, P.; Daujat-Chavanieu, M.; et al. Isolation, Characterization, and Differentiation to Hepatocyte-Like Cells of Nonparenchymal Epithelial Cells from Adult Human Liver. STEM CELLS 2007, 25, 1779–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurrell, T.; Lilley, K.S.; Cromarty, A.D. Proteomic responses of HepG2 cell monolayers and 3D spheroids to selected hepatotoxins. Toxicol. Lett. 2019, 300, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazou, D.; Coakley, W.; Hayes, A.; Jackson, S. Long-term viability and proliferation of alginate-encapsulated 3-D HepG2 aggregates formed in an ultrasound trap. Toxicol. Vitr. 2008, 22, 1321–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkening, S.; Stahl, F.; Bader, A. Comparison of primary human hepatocytes and hepatoma cell line HepG2 with regard to their biotransformation properties. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2003, 31, 1035–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, K.; Kato, N.; Aizawa, K.; Mizutani, R.; Yamauchi, J.; Tanoue, A. Expression of albumin and cytochrome P450 enzymes in HepG2 cells cultured with a nanotechnology-based culture plate with microfabricated scaffold. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2011, 36, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.T.; Hughes-Fulford, M. Monolayer and Spheroid Culture of Human Liver Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Line Cells Demonstrate Distinct Global Gene Expression Patterns and Functional Phenotypes. Tissue Eng. Part A 2009, 15, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerets, H.H.J.; Tilmant, K.; Gerin, B.; Chanteux, H.; Depelchin, B.O.; Dhalluin, S.; Atienzar, F.A. Characterization of primary human hepatocytes, HepG2 cells, and HepaRG cells at the mRNA level and CYP activity in response to inducers and their predictivity for the detection of human hepatotoxins. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2012, 28, 69–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, B. Industry concern over EU hepatotoxicity guidance. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, C.C.; Hendriks, D.F.G.; Moro, S.M.L.; Ellis, E.; Walsh, J.; Renblom, A.; Puigvert, L.F.; Dankers, A.C.A.; Jacobs, F.; Snoeys, J.; et al. Characterization of primary human hepatocyte spheroids as a model system for drug-induced liver injury, liver function and disease. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravi, M.; Paramesh, V.; Kaviya, S.; Anuradha, E.; Solomon, F.P. 3D Cell Culture Systems: Advantages and Applications. J. Cell. Physiol. 2015, 230, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breslin, S.; O’Driscoll, L. Three-dimensional cell culture: The missing link in drug discovery. Drug Discov. Today 2013, 18, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, U.-K.; Mallia, J.D.O.; Singh, N.; Chapman, K.E.; Doak, S.H.; Jenkins, G. A three-dimensional in vitro HepG2 cells liver spheroid model for genotoxicity studies. Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2018, 825, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.-L.; Tian, T.; Nan, K.-J.; Zhao, N.; Guo, Y.H.; Cui, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, W.G. Survival advantages of multicellular spheroids vs. monolayers of HepG2 cells in vitro. Oncol. Rep. 2008, 20, 1465–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aucamp, J.; Calitz, C.; Bronkhorst, A.J.; Wrzesinski, K.; Hamman, J.; Gouws, C.; Pretorius, P.J. Cell-free DNA in a three-dimensional spheroid cell culture model: A preliminary study. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2017, 89, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaiahgari, S.C.; Braver, M.W.D.; Herpers, B.; Terpstra, V.; Commandeur, J.N.; Van De Water, B.; Price, L.S. A 3D in vitro model of differentiated HepG2 cell spheroids with improved liver-like properties for repeated dose high-throughput toxicity studies. Arch. Toxicol. 2014, 88, 1083–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elje, E.; Hesler, M.; Rundén-Pran, E.; Mann, P.; Mariussen, E.; Wagner, S.; Dusinska, M.; Kohl, Y. The comet assay applied to HepG2 liver spheroids. Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2019, 845, 403033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loessner, D.; Stok, K.S.; Lutolf, M.P.; Hutmacher, D.W.; Clements, J.A.; Rizzi, S.C. Bioengineered 3D platform to explore cell–ECM interactions and drug resistance of epithelial ovarian cancer cells. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 8494–8506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrzesinski, K. From 2D to 3D—A New Dimension for Modelling the Effect of Natural Products on Human Tissue. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2015, 21, 5605–5616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Štampar, M.; Tomc, J.; Filipič, M.; Žegura, B. Development of in vitro 3D cell model from hepatocellular carcinoma (HepG2) cell line and its application for genotoxicity testing. Arch. Toxicol. 2019, 93, 3321–3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandon, M.; Huet, S.; Dubreil, E.; Fessard, V.; Le Hégarat, L. Three-dimensional HepaRG spheroids as a liver model to study human genotoxicity in vitro with the single cell gel electrophoresis assay. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hercog, K.; Štampar, M.; Štern, A.; Filipič, M.; Žegura, B. Application of advanced HepG2 3D cell model for studying genotoxic activity of cyanobacterial toxin cylindrospermopsin. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 114965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eilenberger, C.; Rothbauer, M.; Ehmoser, E.-K.; Ertl, P.; Küpcü, S. Effect of Spheroidal Age on Sorafenib Diffusivity and Toxicity in a 3D HepG2 Spheroid Model. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinken, M.; Hengstler, J.G. Characterization of hepatocyte-based in vitro systems for reliable toxicity testing. Arch. Toxicol. 2018, 92, 2981–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Lin, C.; Cheng, J.; Su, J.; Zhao, H.; Liu, T.; Wen, X.; Zhao, P. Generation of Multicellular Tumor Spheroids with Microwell-Based Agarose Scaffolds for Drug Testing. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breznik, B.; Motaln, H.; Vittori, M.; Rotter, A.; Turnšek, T.L. Mesenchymal stem cells differentially affect the invasion of distinct glioblastoma cell lines. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 25482–25499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hercog, K.; Maisanaba, S.; Filipič, M.; Sollner-Dolenc, M.; Kač, L.; Zegura, B. Genotoxic activity of bisphenol A and its analogues bisphenol S, bisphenol F and bisphenol AF and their mixtures in human hepatocellular carcinoma (HepG2) cells. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 687, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baebler, Š.; Svalina, M.; Petek, M.; Stare, K.; Rotter, A.; Pompe-Novak, M.; Gruden, K. quantGenius: Implementation of a decision support system for qPCR-based gene quantification. BMC Bioinform. 2017, 18, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witte, R.P.; Kao, W.J. Keratinocyte-fibroblast paracrine interaction: The effects of substrate and culture condition. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 3673–3682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bokhari, M.; Carnachan, R.J.; Cameron, N.R.; Przyborski, S.A. Culture of HepG2 liver cells on three dimensional polystyrene scaffolds enhances cell structure and function during toxicological challenge. J. Anat. 2007, 211, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.-M.; Pohl, J.; Morgan, E.T. Dual Mechanisms of CYP3A Protein Regulation by Proinflammatory Cytokine Stimulation in Primary Hepatocyte Cultures. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2009, 37, 865–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nath, S.; Devi, G.R. Three-dimensional culture systems in cancer research: Focus on tumor spheroid model. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 163, 94–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, G.; Hsiao, A.Y.; Ingram, M.; Luker, G.D.; Takayama, S. Opportunities and challenges for use of tumor spheroids as models to test drug delivery and efficacy. J. Control. Release 2012, 164, 192–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asthana, A.; Kisaalita, W.S. Microtissue size and hypoxia in HTS with 3D cultures. Drug Discov. Today 2012, 17, 810–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrzesinski, K.; Rogowska-Wrzesinska, A.; Kanlaya, R.; Borkowski, K.; Schwämmle, V.; Dai, J.; Joensen, K.E.; Wojdyla, K.; Carvalho, V.B.; Fey, S.J. The Cultural Divide: Exponential Growth in Classical 2D and Metabolic Equilibrium in 3D Environments. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanoni, M.; Piccinini, F.; Arienti, C.; Zamagni, A.; Santi, S.; Polico, R.; Bevilacqua, A.; Tesei, A. 3D tumor spheroid models for in vitro therapeutic screening: A systematic approach to enhance the biological relevance of data obtained. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaskell, H.; Sharma, P.; Colley, H.E.; Murdoch, C.; Williams, D.P.; Webb, S.D. Characterization of a functional C3A liver spheroid model. Toxicol. Res. 2016, 5, 1053–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luckert, C.; Schulz, C.; Lehmann, N.; Thomas, M.; Hofmann, U.; Hammad, S.; Hengstler, J.G.; Braeuning, A.; Lampen, A.; Hessel, S. Comparative analysis of 3D culture methods on human HepG2 cells. Arch. Toxicol. 2017, 91, 393–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.T.; Jiang, G.; Chen, Q.; Zheng, J.N. Ki67 is a promising molecular target in the diagnosis of cancer (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 11, 1566–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerlach, C.; Sakkab, D.Y.; Scholzen, T.; Daßler, R.; Alison, M.R.; Gerdes, J. Ki-67 expression during rat liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy. Hepatology 1997, 26, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Heideman, L.; Chung, C.S.; Pelling, J.C.; Koehler, K.J.; Birt, D.F. Cell-cycle arrest at G2/M and growth inhibition by apigenin in human colon carcinoma cell lines. Mol. Carcinog. 2000, 28, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartek, J.; Lukas, J. Mammalian G1- and S-phase checkpoints in response to DNA damage. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2001, 13, 738–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberts, B.; Johnson, A.; Lewis, J.; Raff, M.; Roberts, K.; Walter, P. Extracellular Control of Cell Division, Cell Growth, and Apoptosis. Mol. Biol. Cell 2002, 91, 40–53. [Google Scholar]
- Dillehay, K.L.; Seibel, W.L.; Zhao, D.; Lu, S.; Dong, Z. Target validation and structure–activity analysis of a series of novel PCNA inhibitors. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2015, 3, e00115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Su, H.; Liao, X.; Han, C.; Yu, T.; Zhu, G.; Wang, X.; Winkler, C.A.; O’Brien, S.J.; Peng, T. Marker of proliferation Ki-67 expression is associated with transforming growth factor beta 1 and can predict the prognosis of patients with hepatic B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Manag. Res. 2018, 10, 679–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Liu, E.; Kang, J.; Yang, X.; Liu, H. MiR-3613-3p affects cell proliferation and cell cycle in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 93014–93028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neubauer, E.; Wirtz, R.M.; Kaemmerer, D.; Athelogou, M.; Schmidt, L.; Sänger, J.; Lupp, A. Comparative evaluation of three proliferation markers, Ki-67, TOP2A, and RacGAP1, in bronchopulmonary neuroendocrine neoplasms: Issues and prospects. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 41959–41973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ramaiahgari, S.C.; Waidyanatha, S.; Dixon, D.; DeVito, M.J.; Paules, R.S.; Ferguson, S.S. From the Cover: Three-Dimensional (3D) HepaRG Spheroid Model With Physiologically Relevant Xenobiotic Metabolism Competence and Hepatocyte Functionality for Liver Toxicity Screening. Toxicol. Sci. 2017, 159, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duronio, R.J.; Xiong, Y. Signaling Pathways that Control Cell Proliferation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a008904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snoj, N.; Dinh, P.; Bedard, P.; Sotiriou, C. Molecular Biology of Breast Cancer. In Molecular Pathology: The Molecular Basis of Human Disease; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 501–517. ISBN 9780123744197. [Google Scholar]
- Tamura, R.E.; De Vasconcellos, J.F.; Sarkar, D.; Libermann, A.T.; Fisher, P.B.; Zerbini, L.F. GADD45 Proteins: Central Players in Tumorigenesis. Curr. Mol. Med. 2012, 12, 634–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiemstra, S.; Ramaiahgari, S.C.; Wink, S.; Callegaro, G.; Coonen, M.; Meerman, J.; Jennen, D.; Van Den Nieuwendijk, K.; Dankers, A.; Snoeys, J.; et al. High-throughput confocal imaging of differentiated 3D liver-like spheroid cellular stress response reporters for identification of drug-induced liver injury liability. Arch. Toxicol. 2019, 93, 2895–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, K.; Vousden, K.H. PUMA, a Novel Proapoptotic Gene, Is Induced by p53. Mol. Cell 2001, 7, 683–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieu, J.; Zhou, W.; Xing, Y.; Sperber, H.; Ferreccio, A.; Agoston, Z.; Kuppusamy, K.T.; Moon, R.T.; Ruohola-Baker, H. Hypoxia-Inducible Factors Have Distinct and Stage-Specific Roles during Reprogramming of Human Cells to Pluripotency. Cell Stem Cell 2014, 14, 592–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Li, H.; Li, C.; Wang, S.; Jiang, W.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, S.; Liu, X.; McNutt, M.A.; Li, G. Alpha-fetoprotein: A new member of intracellular signal molecules in regulation of the PI3K/AKT signaling in human hepatoma cell lines. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 128, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedrichs, B. Th. Peters. Jr.: All about Albumin. Biochemistry, Genetics, and Medical Applications. XX and 432 pages, numerous figures and tables. Academic Press, Inc., San Diego, California, 1996. Price: 85.00 US $. Food/Nahrung 1997, 41, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzenbacher, P.; Anzenbacherová, E. Cytochromes P450 and metabolism of xenobiotics. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2001, 58, 737–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jancova, P.; Anzenbacher, P.; Anzenbacherova, E. Phase II drug metabolizing enzymes Activity and expression of detoxification enzymes: Effect of age, obesity induction and administration of plant extracts View project microflora View project PHASE II DRUG METABOLIZING ENZYMES. Biomed. Pap. Med. Fac. Univ. Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2010, 154, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, P.B. Role of Cytochromes P45O in Drug Metabolism and Hepatotoxicity. Semin. Liver Dis. 1990, 10, 235–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikandan, P.; Nagini, S. Cytochrome P450 Structure, Function and Clinical Significance: A Review. Curr. Drug Targets 2018, 19, 38–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donato, M.; Jover, R.; Gómez-Lechón, M. Hepatic Cell Lines for Drug Hepatotoxicity Testing: Limitations and Strategies to Upgrade their Metabolic Competence by Gene Engineering. Curr. Drug Metab. 2013, 14, 946–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štampar, M.; Frandsen, H.S.; Rogowska-Wrzesinska, A.; Wrzesinski, K.; Filipič, M.; Žegura, B. Hepatocellular carcinoma (HepG2/C3A) cell-based 3D model for genotoxicity testing of chemicals. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 143255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, Y.; Hori, Y.; Yamamoto, T.; Urashima, T.; Ohara, Y.; Tanaka, H. 3D spheroid cultures improve the metabolic gene expression profiles of HepaRG cells. Biosci. Rep. 2015, 35, e00208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivertsson, L.; Ek, M.; Darnell, M.; Edebert, I.; Ingelman-Sundberg, M.; Neve, E.P.A. CYP3A4 Catalytic Activity Is Induced in Confluent Huh7 Hepatoma Cells. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2010, 38, 995–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanebratt, K.P.; Andersson, T.B. Evaluation of HepaRG Cells as an in Vitro Model for Human Drug Metabolism Studies. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2008, 36, 1444–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunness, P.; Mueller, D.; Shevchenko, V.; Heinzle, E.; Ingelman-Sundberg, M.; Noor, F. 3D Organotypic Cultures of Human HepaRG Cells: A Tool for In Vitro Toxicity Studies. Toxicol. Sci. 2013, 133, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotiropoulou, M.; Pappas, P.; Marselos, M. Effects of 3-methylcholanthrene and aspirin co-administration on ALDH3A1 in HepG2 cells. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2001, 130–132, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindahl, R. Aldehyde Dehydrogenases and Their Role in Carcinogenesis. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1992, 27, 283–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzio, G.; Maggiora, M.; Paiuzzi, E.; Oraldi, M.; Canuto, R. Aldehyde dehydrogenases and cell proliferation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2012, 52, 735–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, R.S.; Hempel, J. Comparative studies of vertebrate aldehyde dehydrogenase 3: Sequences, structures, phylogeny and evolution. Evidence for a mammalian origin for the ALDH3A1 gene. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2011, 191, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Cui, B.; Xu, Y.; Hu, C.; Liu, Y.; Qu, G.; Li, D.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Quan, S.; et al. Ethyl carbamate induces cell death through its effects on multiple metabolic pathways. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2017, 277, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, M.E. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor: A comparative perspective. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Pharmacol. Toxicol. Endocrinol. 1998, 121, 23–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snykers, S.; De Kock, J.; Rogiers, V.; Vanhaecke, T. In Vitro Differentiation of Embryonic and Adult Stem Cells into Hepatocytes: State of the Art. Stem Cells 2009, 27, 577–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamage, N.; Barnett, A.; Hempel, N.; Duggleby, R.G.; Windmill, K.F.; Martin, J.L.; McManus, M.E. Human Sulfotransferases and Their Role in Chemical Metabolism. Toxicol. Sci. 2006, 90, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altmann, B.; Ahrens, R.; Welle, A.; Dinglreiter, H.; Schneider, M.; Schober, A. Microstructuring of multiwell plates for three-dimensional cell culture applications by ultrasonic embossing. Biomed. Microdevices 2012, 14, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, N.R. Bioactivation of benzylic and allylic alcohols via sulfo-conjugation. Chem. Biol. Interact. 1998, 109, 221–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Štampar, M.; Breznik, B.; Filipič, M.; Žegura, B. Characterization of In Vitro 3D Cell Model Developed from Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HepG2) Cell Line. Cells 2020, 9, 2557. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9122557
Štampar M, Breznik B, Filipič M, Žegura B. Characterization of In Vitro 3D Cell Model Developed from Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HepG2) Cell Line. Cells. 2020; 9(12):2557. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9122557
Chicago/Turabian StyleŠtampar, Martina, Barbara Breznik, Metka Filipič, and Bojana Žegura. 2020. "Characterization of In Vitro 3D Cell Model Developed from Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HepG2) Cell Line" Cells 9, no. 12: 2557. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9122557
APA StyleŠtampar, M., Breznik, B., Filipič, M., & Žegura, B. (2020). Characterization of In Vitro 3D Cell Model Developed from Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HepG2) Cell Line. Cells, 9(12), 2557. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9122557






