Clinical Actionability of the Genomic Landscape of Metastatic Castration Resistant Prostate Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
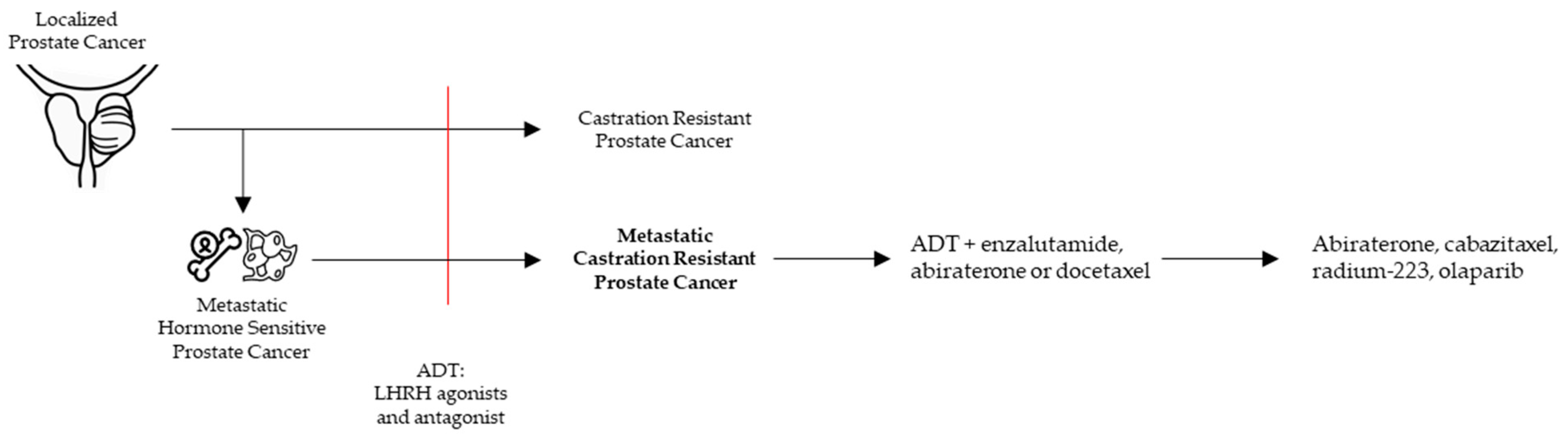
2. mCRPC in the Clinic
2.1. Approved Treatments in Clinic
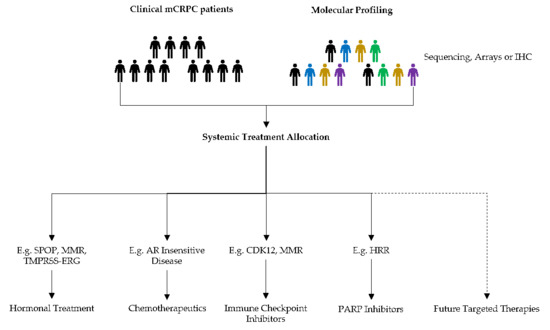
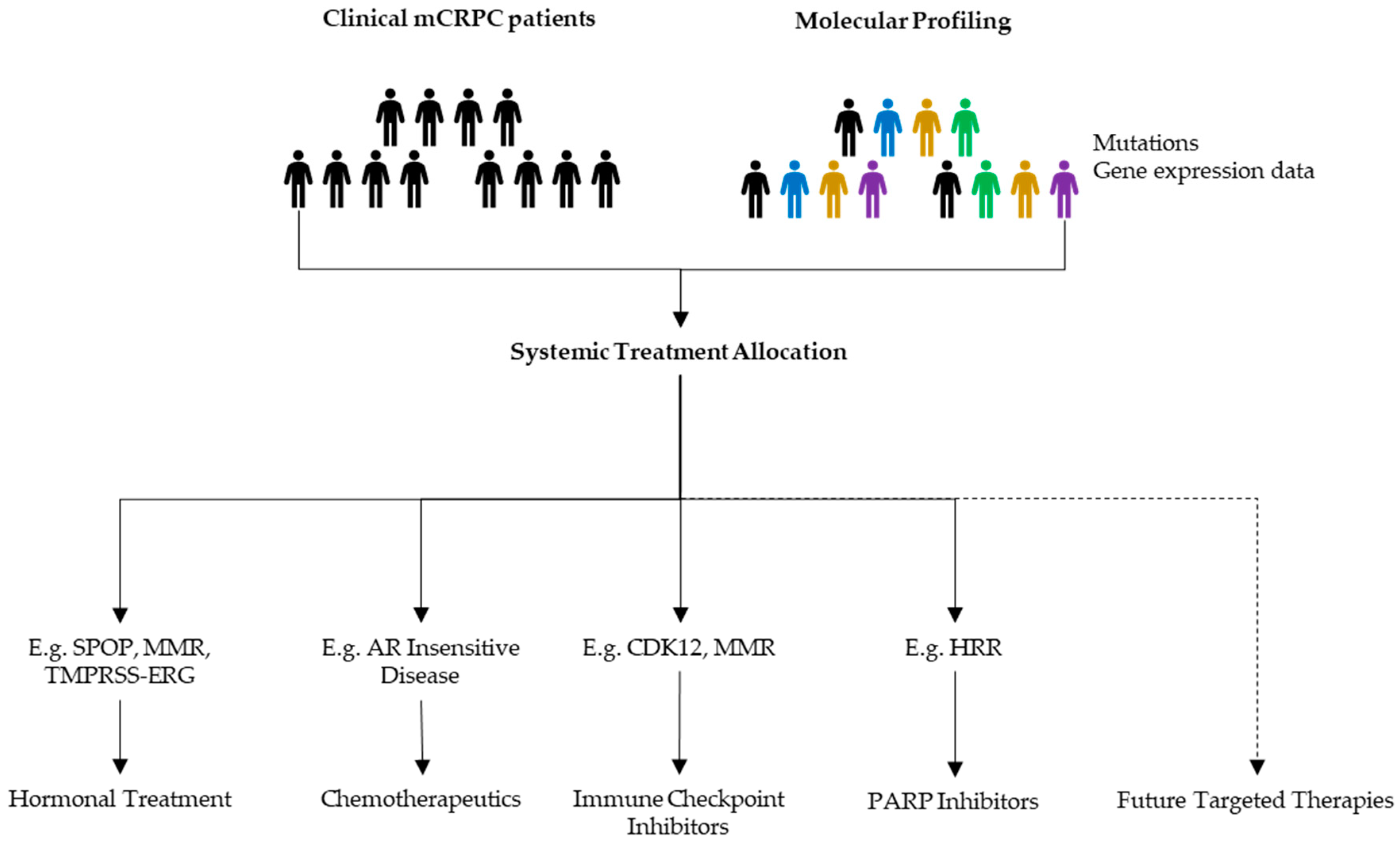
2.2. Treatment Allocation and Decision Making
2.3. Role of Genetic Sequencing
3. PCa Biology and Markers
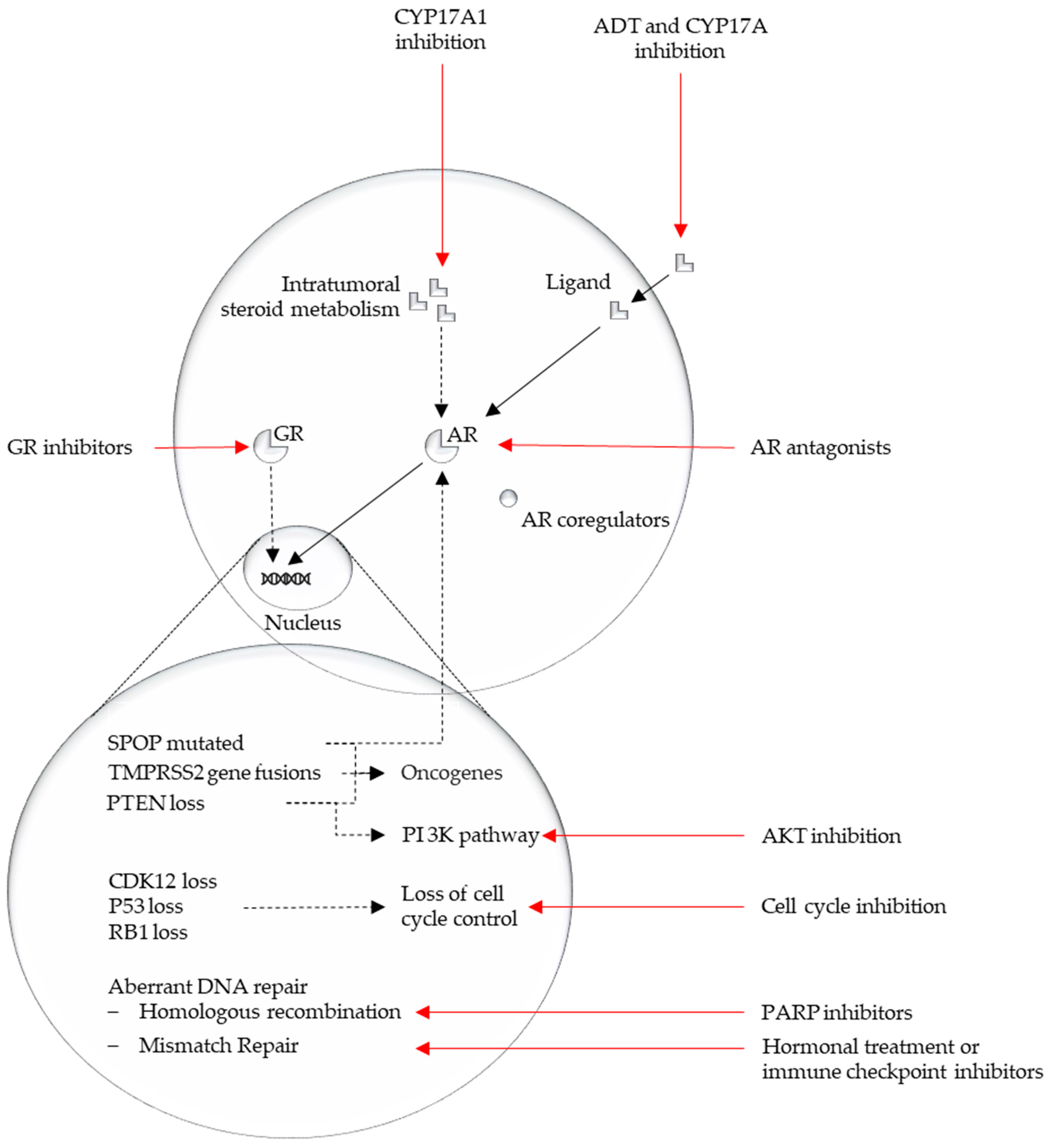
3.1. Genomic and Transcriptomic Pathways in PCa
3.1.1. AR Pathway
3.1.2. PI3K–AKT–MAPK Pathway—PTEN Loss
3.1.3. DNA Repair
3.1.4. Neuroendocrine Differentiation
3.2. Biomarkers
3.3. Prospects
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sehgal, P.D.; Bauman, T.M.; Nicholson, T.M.; Vellky, J.E.; Ricke, E.A.; Tang, W.; Xu, W.; Huang, W.; Ricke, W.A. Tissue-specific quantification and localization of androgen and estrogen receptors in prostate cancer. Hum. Pathol. 2019, 89, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EAU Guidelines. EAU Annual Congress; EAU Guidelines Office: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Mottet, N.; Gillessen, S.; Mottet, N. EAU Guidelines: Prostate Cancer|Uroweb. 2020. Available online: https://uroweb.org/guideline/prostate-cancer/ (accessed on 7 August 2020).
- Francini, E.; Gray, K.P.; Shaw, G.K.; Evan, C.P.; Hamid, A.A.; Perry, C.E.; Kantoff, P.W.; Taplin, M.-E.; Sweeney, C.J. Impact of new systemic therapies on overall survival of patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer in a hospital-based registry. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2019, 22, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Bono, J.S.; Mateo, J.; Fizazi, K.; Saad, F.; Shore, N.; Sandhu, S.; Chi, K.N.; Sartor, O.; Agarwal, N.; Olmos, D.; et al. Olaparib for Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2091–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carceles-Cordon, M.; Kelly, W.K.; Gomella, L.; Knudsen, K.E.; Rodriguez-Bravo, V.; Domingo-Domenech, J. Cellular rewiring in lethal prostate cancer: The architect of drug resistance. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2020, 17, 292–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hovelson, D.H.; Tomlins, S.A. The Role of Next-Generation Sequencing in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer Treatment. Cancer J. 2016, 22, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohr, J.G.; Adalsteinsson, V.A.; Cibulskis, K.; Choudhury, A.D.; Rosenberg, M.; Cruz-Gordillo, P.; Francis, J.M.; Zhang, C.-Z.; Shalek, A.K.; Satija, R.; et al. Whole-exome sequencing of circulating tumor cells provides a window into metastatic prostate cancer. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Coleman, I.; Morrissey, C.; Zhang, X.; True, L.D.; Gulati, R.; Etzioni, R.; Bolouri, H.; Montgomery, B.; White, T.; et al. Substantial interindividual and limited intraindividual genomic diversity among tumors from men with metastatic prostate cancer. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, D.; van Allen, E.M.; Wu, Y.M.; Schultz, N.; Lonigro, R.J.; Mosquera, J.M. Integrative clinical genomics of advanced prostate cancer. Cell 2015, 161, 1215–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, N.A.; Zibelman, M.; Lindsay, T.; Feldman, R.; Saul, M.; Gatalica, Z.; Korn, W.M.; Heath, E.I. An Emerging Landscape for Canonical and Actionable Molecular Alterations in Primary and Metastatic Prostate Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2020, 19, 1373–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasso, C.S.; Wu, Y.-M.; Robinson, D.R.; Cao, X.; Dhanasekaran, S.M.; Khan, A.P.; Quist, M.J.; Jing, X.; Lonigro, R.J.; Brenner, J.C.; et al. The mutational landscape of lethal castration-resistant prostate cancer. Nat. Cell Biol. 2012, 487, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Research. The Molecular Taxonomy of Primary Prostate Cancer. Cell 2015, 163, 1011–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheler, J.J.; Janku, F.; Naing, A.; Li, Y.; Stephen, B.; Zinner, R.; Subbiah, V.; Fu, S.; Karp, D.; Falchook, G.S.; et al. Cancer Therapy Directed by Comprehensive Genomic Profiling: A Single Center Study. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 3690–3701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claessens, F.; Helsen, C.; Prekovic, S.; Broeck, T.V.D.; Spans, L.; van Poppel, H.; Joniau, S. Emerging mechanisms of enzalutamide resistance in prostate cancer. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2014, 11, 712–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viswanathan, S.R.; Ha, G.; Hoff, A.M.; Wala, J.A.; Carrot-Zhang, J.; Whelan, C.W.; Haradhvala, N.J.; Freeman, S.S.; Reed, S.C.; Rhoades, J.; et al. Structural Alterations Driving Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer Revealed by Linked-Read Genome Sequencing. Cell 2018, 174, 433–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veldscholte, J.; Ris-Stalpers, C.; Kuiper, G.; Jenster, G.; Berrevoets, C.; Claassen, E. A mutation in the ligand binding domain of the androgen receptor of human LNCaP cells affects steroid binding characteristics and response to anti-androgens. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1990, 173, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumiyoshi, T.; Mizuno, K.; Yamasaki, T.; Miyazaki, Y.; Makino, Y.; Okasho, K.; Li, X.; Utsunomiya, N.; Goto, T.; Kobayashi, T.; et al. Clinical utility of androgen receptor gene aberrations in circulating cell-free DNA as a biomarker for treatment of castration-resistant prostate cancer. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balbas, M.D.; Evans, M.J.; Hosfield, D.J.; Wongvipat, J.; Arora, V.K.; Watson, P.A.; Chen, Y.; Greene, G.L.; Shen, Y.; Sawyers, C.L. Overcoming mutation-based resistance to antiandrogens with rational drug design. eLife 2013, 2, e00499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prekovic, S.; van Royen, M.E.; Voet, A.R.; Geverts, B.; Houtman, R.; Melchers, D.; Zhang, K.Y.; Broeck, T.V.D.; Smeets, E.; Spans, L.; et al. The Effect of F877L and T878A Mutations on Androgen Receptor Response to Enzalutamide. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15, 1702–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moilanen, A.-M.; Riikonen, R.; Oksala, R.; Ravanti, L.; Aho, E.; Wohlfahrt, G.; Nykänen, P.S.; Törmäkangas, O.P.; Palvimo, J.J.; Kallio, P.J. Discovery of ODM-201, a new-generation androgen receptor inhibitor targeting resistance mechanisms to androgen signaling-directed prostate cancer therapies. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, srep12007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handle, F.; Claessens, F. AR variants: Lost in translation to clinical practice? Nat. Rev. Urol. 2019, 16, 451–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczorowski, A.; Chen, X.; Herpel, E.; Merseburger, A.S.; Kristiansen, G.; Bernemann, C.; Hohenfellner, M.; Cronauer, M.V.; Duensing, S. Antibody selection influences the detection of AR-V7 in primary prostate cancer. Cancer Treat. Res. Commun. 2020, 24, 100186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, S.C.; Li, Y.; Dehm, S.M. Androgen Receptor Splice Variants Activate Androgen Receptor Target Genes and Support Aberrant Prostate Cancer Cell Growth Independent of Canonical Androgen Receptor Nuclear Localization Signal. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 19736–19749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernemann, C.; Schnoller, T.J.; Luedeke, M.; Steinestel, K.; Boegemann, M.; Schrader, A.J.; Steinestel, J. Expression of AR-V7 in Circulating Tumour Cells Does Not Preclude Response to Next Generation Androgen Deprivation Therapy in Patients with Castration Resistant Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2017, 71, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thadani-Mulero, M.; Portella, L.; Sun, S.; Sung, M.; Matov, A.; Vessella, R.L.; Corey, E.; Nanus, D.M.; Plymate, S.R.; Giannakakou, P. Androgen Receptor Splice Variants Determine Taxane Sensitivity in Prostate Cancer. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 2270–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abiraterone Acetate, Niclosamide, and Prednisone in Treating Patients with Hormone-Resistant Prostate Cancer—Full Text View—ClinicalTrials.gov. 2020. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02807805 (accessed on 7 August 2020).
- Enzalutamide and Niclosamide in Treating Patients with Recurrent or Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer—Full Text View—ClinicalTrials.gov. 2020. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03123978 (accessed on 7 August 2020).
- Alen, P.; Claessens, F.; Verhoeven, G.; Rombauts, W.; Peeters, B. The Androgen Receptor Amino-Terminal Domain Plays a Key Role in p160 Coactivator-Stimulated Gene Transcription. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1999, 19, 6085–6097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasko, L.M.; Jakob, C.G.; Edalji, R.P.; Qiu, W.; Montgomery, D.; Digiammarino, E.L. Discovery of a selective catalytic p300/CBP inhibitor that targets lineage-specific tumours. Nature 2017, 550, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, L.-G.; Zhu, Y.; Long, Q.-Y.; Li, X.-J.; Lin, X.; Tang, S.-B.; Yin, L.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, X.-H.; Li, L.; et al. SPOP suppresses prostate cancer through regulation of CYCLIN E1 stability. Cell Death Differ. 2019, 26, 1156–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, R.-S. The emerging role of speckle-type POZ protein (SPOP) in cancer development. Drug Discov. Today 2014, 19, 1498–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, C.; Rajapakshe, K.; Shah, S.S.; Shou, J.; Eedunuri, V.K.; Foley, C.; Fiskus, W.; Rajendran, M.; Chew, S.A.; Zimmermann, M.; et al. Androgen receptor is the key transcriptional mediator of the tumor suppressor SPOP in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 5631–5643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, C.; He, B.; Xu, L.; Barbieri, C.E.; Eedunuri, V.K.; Chew, S.A.; Zimmermann, M.; Bond, R.; Shou, J.; Li, C.; et al. Prostate cancer-associated mutations in speckle-type POZ protein (SPOP) regulate steroid receptor coactivator 3 protein turnover. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 6997–7002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blattner, M.; Liu, D.; Robinson, B.D.; Huang, D.; Poliakov, A.; Gao, D.; Nataraj, S.; Deonarine, L.D.; Augello, M.A.; Sailer, V.; et al. SPOP Mutation Drives Prostate Tumorigenesis In Vivo through Coordinate Regulation of PI3K/mTOR and AR Signaling. Cancer Cell 2017, 31, 436–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spans, L.; Clinckemalie, L.; Helsen, C.; Vanderschueren, D.; Boonen, S.; Lerut, E.; Joniau, S.; Claessens, F. The Genomic Landscape of Prostate Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 10822–10851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbieri, C.E.; Baca, S.C.; Lawrence, M.S.; Demichelis, F.; Blattner, M.; Theurillat, J.-P.; White, T.A.; Stojanov, P.; van Allen, E.; Stransky, N.; et al. Exome sequencing identifies recurrent SPOP, FOXA1 and MED12 mutations in prostate cancer. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 685–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Ma, J.; Chang, K.; Ding, D.; Bai, Y.; Gao, K.; Zhang, P.; Mo, R.; Feng, K.; et al. Prostate Cancer-associated SPOP mutations enhance cancer cell survival and docetaxel resistance by upregulating Caprin1-dependent stress granule assembly. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boysen, G.; Rodrigues, D.N.; Rescigno, P.; Seed, G.; Dolling, D.; Riisnaes, R.; Crespo, M.; Zafeiriou, Z.; Sumanasuriya, S.; Bianchini, D.; et al. SPOP-Mutated/CHD1-Deleted Lethal Prostate Cancer and Abiraterone Sensitivity. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 5585–5593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.; Cooper, C.S. ETS gene fusions in prostate cancer. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2009, 6, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reig, Ò.; Marín-Aguilera, M.; Carrera, G.; Jiménez, N.; Paré, L.; García-Recio, S.; Gaba, L.; Pereira, M.V.; Fernandez, P.; Prat, A.; et al. TMPRSS2-ERG in Blood and Docetaxel Resistance in Metastatic Castration-resistant Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2016, 70, 709–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semaan, L.; Mander, N.; Cher, M.L.; Chinni, S.R. TMPRSS2-ERG fusions confer efficacy of enzalutamide in an in vivo bone tumor growth model. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 972–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graff, R.E.; Pettersson, A.; Lis, R.T.; Dupre, N.C.; Jordahl, K.M.; Nuttall, E.; Rider, J.R.; Fiorentino, M.; Sesso, H.D.; Kenfield, S.A.; et al. The TMPRSS2:ERG fusion and response to androgen deprivation therapy for prostate cancer. Prostate 2015, 75, 897–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claessens, F.; Joniau, S.; Helsen, C. Comparing the rules of engagement of androgen and glucocorticoid receptors. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2017, 74, 2217–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efstathiou, E.; Davis, J.W.; Pisters, L.; Li, W.; Wen, S.; McMullin, R.P.; Gormley, M.; Ricci, D.; Titus, M.; Hoang, A.; et al. Clinical and Biological Characterisation of Localised High-risk Prostate Cancer: Results of a Randomised Preoperative Study of a Luteinising Hormone-releasing Hormone Agonist with or Without Abiraterone Acetate plus Prednisone. Eur. Urol. 2019, 76, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowalsky, A.G.; Ye, H.; Bhasin, M.; van Allen, A.T.; Loda, M.; Lis, R.T.; Montaser-Kouhsari, L.; Calagua, C.; Ma, F.; Russo, J.W.; et al. Neoadjuvant-Intensive Androgen Deprivation Therapy Selects for Prostate Tumor Foci with Diverse Subclonal Oncogenic Alterations. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 4716–4730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puhr, M.; Hoefer, J.; Eigentler, A.; Ploner, C.; Handle, F.; Schaefer, G.; Kroon, J.; Leo, A.; Heidegger, I.M.; Eder, I.E.; et al. The Glucocorticoid Receptor Is a Key Player for Prostate Cancer Cell Survival and a Target for Improved Antiandrogen Therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 24, 927–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alyamani, M.; Li, J.; Patel, M.; Taylor, S.; Nakamura, F.; Berk, M.; Przybycin, C.; Posadas, E.; Madan, R.; Gulley, J.; et al. Deep androgen receptor suppression in prostate cancer exploits sexually dimorphic renal expression for systemic glucocorticoid exposure. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taplin, M.-E.; Manola, J.; Oh, W.K.; Kantoff, P.W.; Bubley, G.J.; Smith, M.; Barb, D.; Mantzoros, C.; Gelmann, E.P.; Balk, S.P. A phase II study of mifepristone (RU-486) in castration-resistant prostate cancer, with a correlative assessment of androgen-related hormones. BJU Int. 2008, 101, 1084–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enzalutamide and Mifepristone in Treating Patients with Metastatic Hormone Resistant Prostate Cancer—Full Text View—ClinicalTrials. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02012296 (accessed on 30 June 2020).
- Stanbrough, M.; Bubley, G.J.; Ross, K.; Golub, T.R.; Rubin, M.A.; Penning, T.M.; Febbo, P.G.; Balk, S.P. Increased Expression of Genes Converting Adrenal Androgens to Testosterone in Androgen-Independent Prostate Cancer. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 2815–2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hearn, J.W.; AbuAli, G.; Reichard, C.A.; Reddy, C.A.; Magi-Galluzzi, C.; Chang, K.-H.; Carlson, R.; Rangel, L.; Reagan, K.; Davis, B.J.; et al. HSD3B1 and resistance to androgen-deprivation therapy in prostate cancer: A retrospective, multicohort study. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 1435–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabharwal, N.; Sharifi, N. HSD3B1 Genotypes Conferring Adrenal-Restrictive and Adrenal-Permissive Phenotypes in Prostate Cancer and Beyond. Endocrinology 2019, 160, 2180–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostaghel, E.A.; Zhang, A.; Hernandez, S.; Marck, B.T.; Zhang, X.; Tamae, D.; Biehl, H.E.; Tretiakova, M.S.; Bartlett, J.; Burns, J.F.; et al. Contribution of Adrenal Glands to Intratumor Androgens and Growth of Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 25, 426–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimoto, M.; Cunha, I.; Coudry, R.; Fonseca, F.; Torres, C.; Soares, F.; Squire, J. MP-17.17: FISH analysis of 107 prostate cancers shows that PTEN genomic deletion is associated with poor clinical outcome. Urology 2007, 70, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotan, T.L.; Gurel, B.; Sutcliffe, S.; Esopi, D.; Liu, W.; Xu, J.; Hicks, J.L.; Park, B.H.; Humphreys, E.; Partin, A.W.; et al. PTEN Protein Loss by Immunostaining: Analytic Validation and Prognostic Indicator for a High Risk Surgical Cohort of Prostate Cancer Patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 6563–6573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köksal, I.T.; Dirice, E.; Yasar, D.; Sanlioglu, A.D.; Ciftcioglu, A.; Gulkesen, K.H.; O Ozes, N.; Baykara, M.; Luleci, G.; Sanlioglu, S. The assessment of PTEN tumor suppressor gene in combination with Gleason scoring and serum PSA to evaluate progression of prostate carcinoma. Urol. Oncol. Semin. Orig. Investig. 2004, 22, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaux, A.; Peskoe, S.B.; Gonzalez-Roibon, N.; Schultz, L.; Albadine, R.; Hicks, J.; de Marzo, A.M.; Platz, E.A.; Netto, G. Loss of PTEN expression is associated with increased risk of recurrence after prostatectomy for clinically localized prostate cancer. Mod. Pathol. 2012, 25, 1543–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKay, R.R.; Ye, H.; Xie, W.; Lis, R.; Calagua, C.; Zhang, Z.; Trinh, Q.-D.; Chang, S.L.; Harshman, L.C.; Ross, A.E.; et al. Evaluation of Intense Androgen Deprivation Before Prostatectomy: A Randomized Phase II Trial of Enzalutamide and Leuprolide With or Without Abiraterone. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 923–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilson, C.; Ingleby, F.; Gilbert, D.C.; Parry, M.A.; Atako, N.B.; Ali, A.; Hoyle, A.; Clarke, N.W.; Gannon, M.; Wanstall, C.; et al. Genomic Profiles of De Novo High- and Low-Volume Metastatic Prostate Cancer: Results From a 2-Stage Feasibility and Prevalence Study in the STAMPEDE Trial. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2020, 2020, 882–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gevaert, T.; Montironi, R.; Lopez-Beltran, A.; van Leenders, G.; Allory, Y.; de Ridder, D.; Claessens, F.; Kockx, M.; Akand, M.; Joniau, S.; et al. Genito-urinary genomics and emerging biomarkers for immunomodulatory cancer treatment. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2018, 52, 216–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, J.C.; Xu, J.; Wongvipat, J.; Hieronymus, H.; Carver, B.S.; Leung, D.H.; Taylor, B.S.; Sander, C.; Cardiff, R.D.; Couto, S.S.; et al. Cooperativity of TMPRSS2-ERG with PI3-kinase pathway activation in prostate oncogenesis. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 524–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Sampath, D.; Nannini, M.; Lee, B.B.; Degtyarev, M.; Oeh, J.; Savage, H.; Guan, Z.; Hong, R.; Kassees, R.; et al. Targeting Activated Akt with GDC-0068, a Novel Selective Akt Inhibitor That Is Efficacious in Multiple Tumor Models. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 1760–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carver, B.S.; Chapinski, C.; Wongvipat, J.; Hieronymus, H.; Chen, Y.; Chandarlapaty, S.; Arora, V.K.; Le, C.; Koutcher, J.; Scher, H.; et al. Reciprocal Feedback Regulation of PI3K and Androgen Receptor Signaling in PTEN-Deficient Prostate Cancer. Cancer Cell 2011, 19, 575–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roche, H.-L. Ipatasertib Plus Abiraterone Plus Prednisone/Prednisolone, Relative to Placebo Plus Abiraterone Plus Prednisone/Prednisolone in Adult Male Patients with Metastatic Castrate-Resistant Prostate Cancer (IPATential150). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03072238 (accessed on 7 August 2020).
- Robinson, D.R.; Wu, Y.-M.; Lonigro, R.J.; Vats, P.; Cobain, E.; Everett, J.; Cao, X.; Rabban, E.; Kumar-Sinha, C.; Raymond, V.; et al. Integrative clinical genomics of metastatic cancer. Nat. Cell Biol. 2017, 548, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, C.C.; Mateo, J.; Walsh, M.F.; de Sarkar, N.; Abida, W.; Beltran, H.; Garofalo, A.; Gulati, R.; Carreira, S.; Eeles, R.; et al. Inherited DNA-Repair Gene Mutations in Men with Metastatic Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abida, W.; Campbell, D.; Patnaik, A.; Shapiro, J.D.; Sautois, B.; Vogelzang, N.J.; Voog, E.G.; Bryce, A.; McDermott, R.; Ricci, F.; et al. Non-BRCA DNA Damage Repair Gene Alterations and Response to the PARP Inhibitor Rucaparib in Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer: Analysis From the Phase II TRITON2 Study. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 2487–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, D.T.; Uram, J.N.; Wang, H.; Bartlett, B.R.; Kemberling, H.; Eyring, A. PD-1 Blockade in Tumors with Mismatch-Repair Deficiency. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 2509–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonarakis, E.S.; Shaukat, F.; Velho, P.I.; Kaur, H.; Shenderov, E.; Pardoll, D.M.; Lotan, T.L. Clinical Features and Therapeutic Outcomes in Men with Advanced Prostate Cancer and DNA Mismatch Repair Gene Mutations. Eur. Urol. 2019, 75, 378–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonarakis, E.S.; Velho, P.I.; Fu, W.; Wang, H.; Agarwal, N.; Santos, V.S.; Maughan, B.L.; Pili, R.; Adra, N.; Sternberg, C.N.; et al. CDK12-Altered Prostate Cancer: Clinical Features and Therapeutic Outcomes to Standard Systemic Therapies, Poly (ADP-Ribose) Polymerase Inhibitors, and PD-1 Inhibitors. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2020, 4, 370–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.-M.; Cieślik, M.; Lonigro, R.J.; Vats, P.; Reimers, M.A.; Cao, X.; Ning, Y.; Wang, L.; Kunju, L.P.; de Sarkar, N.; et al. Inactivation of CDK12 Delineates a Distinct Immunogenic Class of Advanced Prostate Cancer. Cell 2018, 173, 1770–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ci, X.; Hao, J.; Dong, X.; Xue, H.; Wu, R.; Choi, S.Y.C.; Haegert, A.; Collins, C.C.; Liu, X.; Lin, D.; et al. Conditionally Reprogrammed Cells from Patient-Derived Xenograft to Model Neuroendocrine Prostate Cancer Development. Cells 2020, 9, 1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faugeroux, V.; Pailler, E.; Oulhen, M.; Deas, O.; Brulle-Soumare, L.; Hervieu, C.; Marty, V.; Alexandrova, K.; Andree, K.C.; Stoecklein, N.H.; et al. Genetic characterization of a unique neuroendocrine transdifferentiation prostate circulating tumor cell-derived eXplant model. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostano, P.; Mello-Grand, M.; Sesia, D.; Gregnanin, I.; Peraldo-Neia, C.; Guana, F.; Jachetti, E.; Farsetti, A.; Chiorino, G. Gene Expression Signature Predictive of Neuroendocrine Transformation in Prostate Adenocarcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachostergios, P.J.; Puca, L.; Beltran, H. Emerging Variants of Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 19, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, P.A.; Arora, V.K.; Sawyers, C.L. Emerging mechanisms of resistance to androgen receptor inhibitors in prostate cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 15, 701–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, M.A.; Stoyanova, T. Biomarkers for Diagnosis and Prognosis of Prostate Cancer. Prostatectomy 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggener, S.E.; Rumble, R.B.; Armstrong, A.J.; Morgan, T.M.; Crispino, T.; Cornford, P.; van der Kwast, T.; Grignon, D.J.; Rai, A.J.; Agarwal, N.; et al. Molecular Biomarkers in Localized Prostate Cancer: ASCO Guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 1474–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mian, O.Y.; Tendulkar, R.D.; Abazeed, M.E. The evolving role of molecular profiling in prostate cancer: Basal and luminal subtyping transcends tissue of origin. Transl. Cancer Res. 2017, 6, S1441–S1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.G.; Chang, S.L.; Erho, N.; Yu, M.; Lehrer, J.; Alshalalfa, M.; Speers, C.; Cooperberg, M.R.; Kim, W.; Ryan, C.J.; et al. Associations of Luminal and Basal Subtyping of Prostate Cancer With Prognosis and Response to Androgen Deprivation Therapy. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 1663–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Small, E.J.; Aggarwal, R.R.; Den, R.B.; Lehrer, J.; Zhang, L.; Youngren, J.; Goldstein, T.C.; Alumkal, J.J.; Gleave, M.; et al. Luminal and basal subtyping of metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) and its clinical implications. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehr, E.; Masry, P.; Lis, R.; Loda, M.; Taplin, M.-E.; Hirsch, M.S. Detecting metastatic prostate carcinoma in pelvic lymph nodes following neoadjuvant hormone therapy: The eyes have it! Histopathology 2015, 68, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfandy, H.; Armenia, J.; Pederzoli, F.; Pullman, E.; Pértega-Gomes, N.; Schultz, N.; Viswanathan, K.; Vosoughi, A.; Blattner, M.; Stopsack, K.H.; et al. Genetic and Epigenetic Determinants of Aggressiveness in Cribriform Carcinoma of the Prostate. Mol. Cancer Res. 2018, 17, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SUO 2019: Genomic Umbrella Neoadjuvant Study and other Biomarker Trials. 2020. Available online: https://www.urotoday.com/conference-highlights/suo-2019/suo-2019-prostate-cancer/117559-suo-2019-guns-and-other-biomarker-trials.html (accessed on 7 August 2020).
- Case Medical Research ProBio: A Biomarker Driven Study in Patients with Metastatic Castrate Resistant Prostate Cancer. Case Med Res. 2019. [CrossRef]
- Broeck, T.V.D.; Moris, L.; Gevaert, T.; Tosco, L.; Smeets, E.; Fishbane, N.; Liu, Y.; Helsen, C.; Margrave, J.; Buerki, C.; et al. Validation of the Decipher Test for Predicting Distant Metastatic Recurrence in Men with High-risk Nonmetastatic Prostate Cancer 10 Years After Surgery. Eur. Urol. Oncol. 2019, 2, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carm, K.T.; Hoff, A.M.; Bakken, A.C.; Axcrona, U.; Axcrona, K.; Lothe, R.A.; Skotheim, R.I.; Løvf, M. Interfocal heterogeneity challenges the clinical usefulness of molecular classification of primary prostate cancer. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Devlies, W.; Eckstein, M.; Cimadamore, A.; Devos, G.; Moris, L.; Van den Broeck, T.; Montironi, R.; Joniau, S.; Claessens, F.; Gevaert, T. Clinical Actionability of the Genomic Landscape of Metastatic Castration Resistant Prostate Cancer. Cells 2020, 9, 2494. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9112494
Devlies W, Eckstein M, Cimadamore A, Devos G, Moris L, Van den Broeck T, Montironi R, Joniau S, Claessens F, Gevaert T. Clinical Actionability of the Genomic Landscape of Metastatic Castration Resistant Prostate Cancer. Cells. 2020; 9(11):2494. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9112494
Chicago/Turabian StyleDevlies, Wout, Markus Eckstein, Alessia Cimadamore, Gaëtan Devos, Lisa Moris, Thomas Van den Broeck, Rodolfo Montironi, Steven Joniau, Frank Claessens, and Thomas Gevaert. 2020. "Clinical Actionability of the Genomic Landscape of Metastatic Castration Resistant Prostate Cancer" Cells 9, no. 11: 2494. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9112494
APA StyleDevlies, W., Eckstein, M., Cimadamore, A., Devos, G., Moris, L., Van den Broeck, T., Montironi, R., Joniau, S., Claessens, F., & Gevaert, T. (2020). Clinical Actionability of the Genomic Landscape of Metastatic Castration Resistant Prostate Cancer. Cells, 9(11), 2494. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9112494