Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia-Induced Humoral Immunosuppression: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia—Diagnosis, Clinical Features and Prognostic Factors
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Objective
3.2. Search Strategies
3.3. Selection Criteria
3.3.1. Included Criteria
- Studies evaluating the humoral immunodeficiency in chronic lymphocytic leukemia, pathogenesis or treatment;
- Articles published in the last twenty-five years with the latest information and novel guidelines.
3.3.2. Exclusion Criteria
- Restrictions on document type: technical report, editorial, letter, conference summary;
- Articles in a language other than English or Polish;
- The research contained incomplete content or full text of the article was not available;
- Studies that strictly evaluate only animal-related research.
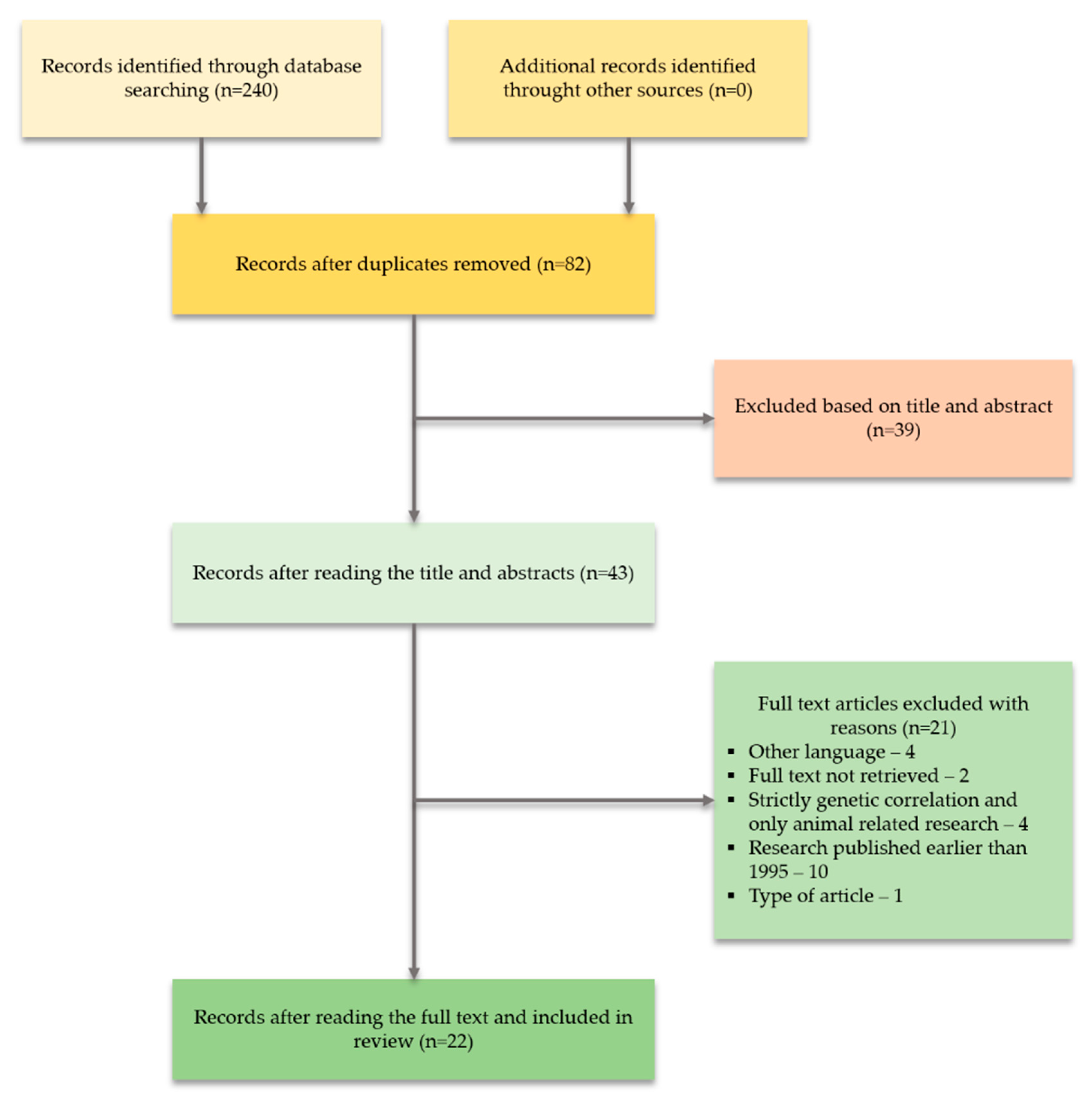
4. Results
Literature Search
5. Discussion
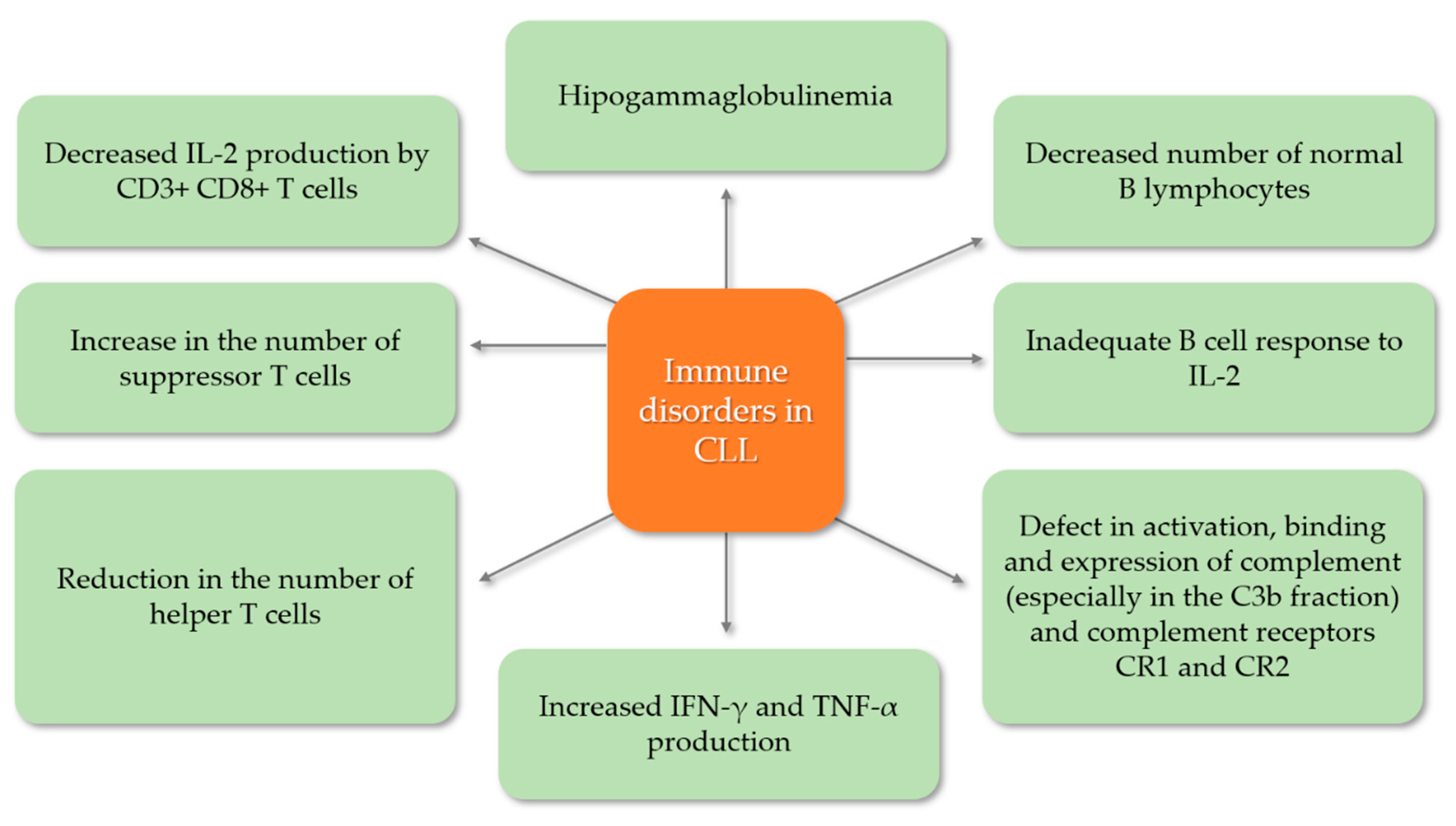
5.1. Secondary Immunodeficiency Disorders in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
5.2. Humoral Immunodefficiency—Clinical Implications
5.3. Hummoral Immunodefficiency—Pathogenesis
5.4. Treatment
5.4.1. Prophylactic Antibiotics
5.4.2. The Use of Immunoglobulin Replacement Therapy
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hallek, M. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia: 2015 Update on diagnosis, risk stratification, and treatment. Am. J. Hematol. 2015, 90, 446–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friman, V.; Winqvist, O.; Blimark, C.; Langerbeins, P.; Chapel, H.; Dhalla, F. Secondary immunodeficiency in lymphoproliferative malignancies. Hematol. Oncol. 2016, 34, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campo, E.; Swerdlow, S.H.; Harris, N.L.; Pileri, S.; Stein, H.; Jaffe, E.S. The 2008 WHO classification of lymphoid neoplasms and beyond: Evolving concepts and practical applications. Blood 2011, 117, 5019–5032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Cancer Institute (NIH). Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia-Cancer Stat Facts. SEER n.d. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/clyl.html (accessed on 16 August 2020).
- Molica, S. Infections in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Risk factors, and impact on survival, and treatment. Leuk. Lymphoma 1994, 13, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsiodras, S.; Samonis, G.; Keating, M.J.; Kontoyiannis, D.P. Infection and Immunity in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2000, 75, 1039–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stilgenbauer, S.; Bullinger, L.; Lichter, P.; Döhner, H. Genetics of chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Genomic aberrations and V H gene mutation status in pathogenesis and clinical course. Leukemia 2002, 16, 993–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallek, M. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia: 2017 update on diagnosis, risk stratification, and treatment. Am. J. Hematol. 2017, 92, 946–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seda, V.; Mraz, M. B-cell receptor signalling and its crosstalk with other pathways in normal and malignant cells. Eur. J. Haematol. 2015, 94, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woyach, J.A.; Johnson, A.J.; Byrd, J.C. The B-cell receptor signaling pathway as a therapeutic target in CLL. Blood 2012, 120, 1175–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fais, F.; Ghiotto, F.; Hashimoto, S.; Sellars, B.; Valetto, A.; Allen, S.L.; Schulman, P.; Vinciguerra, V.P.; Rai, K.; Rassenti, L.Z.; et al. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells express restricted sets of mutated and unmutated antigen receptors. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 102, 1515–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamblin, T.J.; Davis, Z.; Gardiner, A.; Oscier, D.G.; Stevenson, F.K. Unmutated Ig V(H) genes are associated with a more aggressive form of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 1999, 94, 1848–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Huynh, L.; Apgar, J.; Tang, L.; Rassenti, L.; Weiss, A.; Kipps, T.J. ZAP-70 enhances IgM signaling independent of its kinase activity in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2008, 111, 2685–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, S.J.; Matthews, C.; Catherwood, M.A.; Alexander, H.D.; Carey, B.S.; Farrugia, J.; Gardiner, A.; Mould, S.; Oscier, D.J.; Copplestone, A.; et al. ZAP-70 expression is associated with enhanced ability to respond to migratory and survival signals in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL). Blood 2006, 107, 3584–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaidano, G.; Rossi, D. The mutational landscape of chronic lymphocytic leukemia and its impact on prognosis and treatment. Hematology Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program 2017, 2017, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döhner, H.; Stilgenbauer, S.; Benner, A.; Leupolt, E.; Kröber, A.; Bullinger, L.; Döhner, K.; Bentz, M.; Lichter, P. Genomic aberrations and survival in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 343, 1910–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landau, D.A.; Tausch, E.; Taylor-Weiner, A.N.; Stewart, C.; Reiter, J.G.; Bahlo, J.; Kluth, S.; Bozic, I.; Lawrence, M.; Böttcher, S.; et al. Mutations driving CLL and their evolution in progression and relapse. Nature 2015, 526, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenz, T.; Eichhorst, B.; Busch, R.; Denzel, T.; Häbe, S.; Winkler, D.; Bühler, A.; Edelmann, J.; Bergmann, M.; Hopfinger, G.; et al. TP53 mutation and survival in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. Off, J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 4473–4479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keating, M.J.; Chiorazzi, N.; Messmer, B.; Damle, R.N.; Allen, S.L.; Rai, K.R.; Ferrarini, M.; Kipps, T.J. Biology and treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program 2003, 2003, 153–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbingi, A.; Innocenti, I.; Tomasso, A.; Pasquale, R.; Visentin, A.; Varettoni, M.; Flospergher, E.; Autore, F.; Morelli, F.; Trentin, L.; et al. Monoclonal gammopathy and serum immunoglobin levels as prognostic factors in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Br. J. Haematol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauro, F.R.; Giannarelli, D.; Galluzzo, C.M.; Vitale, C.; Visentin, A.; Riemma, C.; Rosati, S.; Porrazzo, M.; Pepe, S.; Coscia, M.; et al. Response to the conjugate pneumococcal vaccine (PCV13) in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Leukemia 2020, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dighiero, G.; Maloum, K.; Desablens, B.; Cazin, B.; Navarro, M.; Leblay, R.; Leporrier, M.; Jaubert, J.; Lepeu, G.; Dreyfus, B.; et al. Chlorambucil in indolent chronic lymphocytic leukemia. French Cooperative Group on Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 338, 1506–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brion, A.; Mahé, B.; Kolb, B.; Audhuy, B.; Colombat, P.; Maisonneuve, H.; Foussard, C.; Bureau, A.; Ferrand, C.; Lesesve, J.F.; et al. Autologous transplantation in CLL patients with B and C Binet stages: Final results of the prospective randomized GOELAMS LLC 98 trial. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2012, 47, 542–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreger, P.; Schetelig, J.; Andersen, N.; Corradini, P.; van Gelder, M.; Gribben, J.; Kimby, E.; Michallet, M.; Moreno, C.; Stilgenbauer, S.; et al. Managing high-risk CLL during transition to a new treatment era: Stem cell transplantation or novel agents? Blood 2014, 124, 3841–3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arruga, F.; Gyau, B.B.; Iannello, A.; Vitale, N.; Vaisitti, T.; Deaglio, S. Immune Response Dysfunction in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Dissecting Molecular Mechanisms and Microenvironmental Conditions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riches, J.C.; Ramsay, A.G.; Gribben, J.G. Immune reconstitution in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Curr. Hematol. Malig. Rep. 2012, 7, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosari, A. Infectious Complications in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Mediterr. J. Hematol. Infect. Dis. 2012, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.Y.; Carbone, J.; Jolles, S. The Expanding Field of Secondary Antibody Deficiency: Causes, Diagnosis, and Management. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langerbeins, P.; Fürstenau, M.; Gruell, H.; Klein, F.; Persigehl, T.; Rybniker, J.; Seeger-Nukpezah, T.; Kochanek, M.; Hallek, M.; Eichhorst, B.; et al. COVID-19 complicated by parainfluenza co-infection in a patient with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Eur. J. Haematol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadhwa, P.D.; Morrison, V.A. Infectious complications of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Semin. Oncol. 2006, 33, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molica, S.; Levato, D.; Levato, L. Infections in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Analysis of incidence as a function of length of follow-up. Haematologica 1993, 78, 374–377. [Google Scholar]
- Alexandrescu, D.T.; Wiernik, P.H. Serum globulins as marker of immune restoration after treatment with high-dose rituximab for chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Med. Oncol. 2008, 25, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Severin, F.; Frezzato, F.; Visentin, A.; Martini, V.; Trimarco, V.; Carraro, S.; Tibaldi, E.; Brunati, A.M.; Piazza, F.; Semenzato, G.; et al. In Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia the JAK2/STAT3 Pathway Is Constitutively Activated and Its Inhibition Leads to CLL Cell Death Unaffected by the Protective Bone Marrow Microenvironment. Cancers 2019, 11, 1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabhan, C.; Rosen, S.T. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia: A clinical review. JAMA 2014, 312, 2265–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichhorst, B.F.; Busch, R.; Hopfinger, G.; Pasold, R.; Hensel, M.; Steinbrecher, C.; Siehl, S.; Jäger, U.; Bergmann, M.; Stilgenbauer, S.; et al. Fludarabine plus cyclophosphamide versus fludarabine alone in first-line therapy of younger patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2006, 107, 885–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, S.M.; Keating, M.J.; Mocarski, E.S. Updated guidelines on the management of cytomegalovirus reactivation in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia treated with alemtuzumab. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma. 2006, 7, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visentin, A.; Gurrieri, C.; Imbergamo, S.; Lessi, F.; di Maggio, S.A.; Frezzato, F.; Adami, F.; Zambello, R.; Piazza, F.; Semenzato, G.; et al. Epidemiology and risk factors of invasive fungal infections in a large cohort of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 35, 925–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamblin, A.D.; Hamblin, T.J. The immunodeficiency of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Br. Med. Bull. 2008, 87, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marbello, L.; Nosari, A.; Carrafiello, G.; Anghilieri, M.; Cesana, C.; Cafro, A.M.; D’Avanzo, G.; Morra, E. Successful treatment with voriconazole of cerebral aspergillosis in an hematologic patient. Haematologica 2003, 88, ECR05. [Google Scholar]
- Parikh, S.A.; Leis, J.F.; Chaffee, K.G.; Call, T.G.; Hanson, C.A.; Ding, W.; Chanan-Khan, A.A.; Bowen, D.; Conte, M.; Schwager, S.; et al. Hypogammaglobulinemia in Newly Diagnosed Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Natural History, Clinical Correlates and Outcomes. Cancer 2015, 121, 2883–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinisalo, M.; Aittoniemi, J.; Käyhty, H.; Vilpo, J. Vaccination against infections in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leuk. Lymphoma 2003, 44, 649–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, N.E.; Perri, R.T. Evidence that large granular lymphocytes from B-CLL patients with hypogammaglobulinemia down-regulate B-cell immunoglobulin synthesis. Blood 1989, 73, 1016–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheson, B.D.; Bennett, J.M.; Grever, M.; Kay, N.; Keating, M.J.; O’Brien, S.; Rai, K.R. National Cancer Institute-sponsored Working Group guidelines for chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Revised guidelines for diagnosis and treatment. Blood 1996, 87, 4990–4997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampalo, A.; Brieva, J.A. Humoral immunodeficiency in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Role of CD95/CD95L in tumoral damage and escape. Leuk. Lymphoma 2002, 43, 881–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tinhofer, I.; Marschitz, I.; Kos, M.; Henn, T.; Egle, A.; Villunger, A.; Greil, R. Differential sensitivity of CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes to the killing efficacy of Fas (Apo-1/CD95) ligand+ tumor cells in B chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 1998, 91, 4273–4281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, S.; Golstein, P. The Fas death factor. Science 1995, 267, 1449–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampalo, A.; Navas, G.; Medina, F.; Segundo, C.; Cámara, C.; Brieva, J.A. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells inhibit spontaneous Ig production by autologous bone marrow cells: Role of CD95-CD95L interaction. Blood 2000, 96, 3168–3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerutti, A.; Kim, E.C.; Shah, S.; Schattner, E.J.; Zan, H.; Schaffer, A.; Casali, P. Dysregulation of CD30+ T cells by leukemia impairs isotype switching in normal B cells. Nat. Immunol. 2001, 2, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantwell, M.; Hua, T.; Pappas, J.; Kipps, T.J. Acquired CD40-ligand deficiency in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Nat. Med. 1997, 3, 984–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oscier, D.; Dearden, C.; Erem, E.; Fegan, C.; Follows, G.; Hillmen, P.; Illidge, T.; Matutes, E.; Milligan, D.W.; Pettitt, A.; et al. Guidelines on the diagnosis, investigation and management of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Br. J. Haematol. 2012, 159, 541–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhalla, F.; Lucas, M.; Schuh, A.; Bhole, M.; Jain, R.; Patel, S.Y.; Misbah, S.; Chapel, H. Antibody deficiency secondary to chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Should patients be treated with prophylactic replacement immunoglobulin? J. Clin. Immunol. 2014, 34, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaveri, S.V.; Maddur, M.S.; Hegde, P.; Lacroix-Desmazes, S.; Bayry, J. Intravenous immunoglobulins in immunodeficiencies: More than mere replacement therapy. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2011, 164, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazatchkine, M.D.; Kaveri, S.V. Immunomodulation of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases with intravenous immune globulin. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 747–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochsenbein, A.F.; Fehr, T.; Lutz, C.; Suter, M.; Brombacher, F.; Hengartner, H.; Zinkernagel1, R.M. Control of early viral and bacterial distribution and disease by natural antibodies. Science 1999, 286, 2156–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayry, J.; Lacroix-Desmazes, S.; Kazatchkine, M.D.; Kaveri, S.V. Intravenous immunoglobulin for infectious diseases: Back to the pre-antibiotic and passive prophylaxis era? Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2004, 25, 306–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boughton, B.J.; Jackson, N.; Lim, S.; Smith, N. Randomized trial of intravenous immunoglobulin prophylaxis for patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia and secondary hypogammaglobulinaemia. Clin. Lab. Haematol. 1995, 17, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molica, S.; Musto, P.; Chiurazzi, F.; Specchia, G.; Brugiatelli, M.; Cicoira, L.; Levato, D.; Nobile, F.; Carotenuto, M.; Liso, V.; et al. Prophylaxis against infections with low-dose intravenous immunoglobulins (IVIG) in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Results of a crossover study. Haematologica 1996, 81, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ammann, E.M.; Jones, M.P.; Link, B.K.; Carnahan, R.M.; Winiecki, S.K.; Torner, J.C.; McDowell, B.D.; Fireman, B.H.; Chrischilles, E.A. Intravenous immune globulin and thromboembolic adverse events in patients with hematologic malignancy. Blood 2016, 127, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compagno, N.; Malipiero, G.; Cinetto, F.; Agostini, C. Immunoglobulin Replacement Therapy in Secondary Hypogammaglobulinemia. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Medicines Agency, Science Medicines Health. Core Summary of Product Characteristics for Human Normal Immunoglobulin Intravenous Administration (IVIg). Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/core-summary-product-characteristics-human-normal-immunoglobulin-intravenous-administration-ivig (accessed on 16 August 2020).
- European Medicines Agency, Science Medicines Health. Clinical Investigation of Human Normal Immunoglobulin for Subcutaneous and/or Intramuscular Administration (SCIg/IMIg). Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/clinical-investigation-human-normal-immunoglobulin-subcutaneous-andor-intramuscular-administration (accessed on 16 August 2020).
- Eichhorst, B.; Robak, T.; Montserrat, E.; Ghia, P.; Hillmen, P.; Hallek, M.; Buske, C.; ESMO Guidelines Committee. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up†. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, v78–v84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grywalska, E.; Zaborek, M.; Łyczba, J.; Hrynkiewicz, R.; Bębnowska, D.; Becht, R.; Sosnowska-Pasiarska, B.; Smok-Kalwat, J.; Pasiarski, M.; Góźdź, S.; et al. Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia-Induced Humoral Immunosuppression: A Systematic Review. Cells 2020, 9, 2398. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9112398
Grywalska E, Zaborek M, Łyczba J, Hrynkiewicz R, Bębnowska D, Becht R, Sosnowska-Pasiarska B, Smok-Kalwat J, Pasiarski M, Góźdź S, et al. Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia-Induced Humoral Immunosuppression: A Systematic Review. Cells. 2020; 9(11):2398. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9112398
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrywalska, Ewelina, Monika Zaborek, Jakub Łyczba, Rafał Hrynkiewicz, Dominika Bębnowska, Rafał Becht, Barbara Sosnowska-Pasiarska, Jolanta Smok-Kalwat, Marcin Pasiarski, Stanisław Góźdź, and et al. 2020. "Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia-Induced Humoral Immunosuppression: A Systematic Review" Cells 9, no. 11: 2398. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9112398
APA StyleGrywalska, E., Zaborek, M., Łyczba, J., Hrynkiewicz, R., Bębnowska, D., Becht, R., Sosnowska-Pasiarska, B., Smok-Kalwat, J., Pasiarski, M., Góźdź, S., Roliński, J., & Niedźwiedzka-Rystwej, P. (2020). Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia-Induced Humoral Immunosuppression: A Systematic Review. Cells, 9(11), 2398. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9112398






