Stability of Alkyl Chain-Mediated Lipid Anchoring in Liposomal Membranes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Dialkyl-Based Anchors
2.2. Synthesis of Amphiphilic Polyethers
2.3. Functionalization of Amphiphilic Polyethers with Propargyl Bromide
2.4. Synthesis of Cholesterol-Based Linear-Hyperbranched Polyethers
2.5. Functionalization of Cholesterol-PEG-hbPG with Propargyl Bromide
2.5.1. Liposome Preparation
2.5.2. Liposome Modification and Purification
2.5.3. Cell Culture and Cell Lines Employed
2.5.4. Flow Cytometry
2.5.5. Microscopy
2.5.6. Dynamic Light Scattering
3. Results
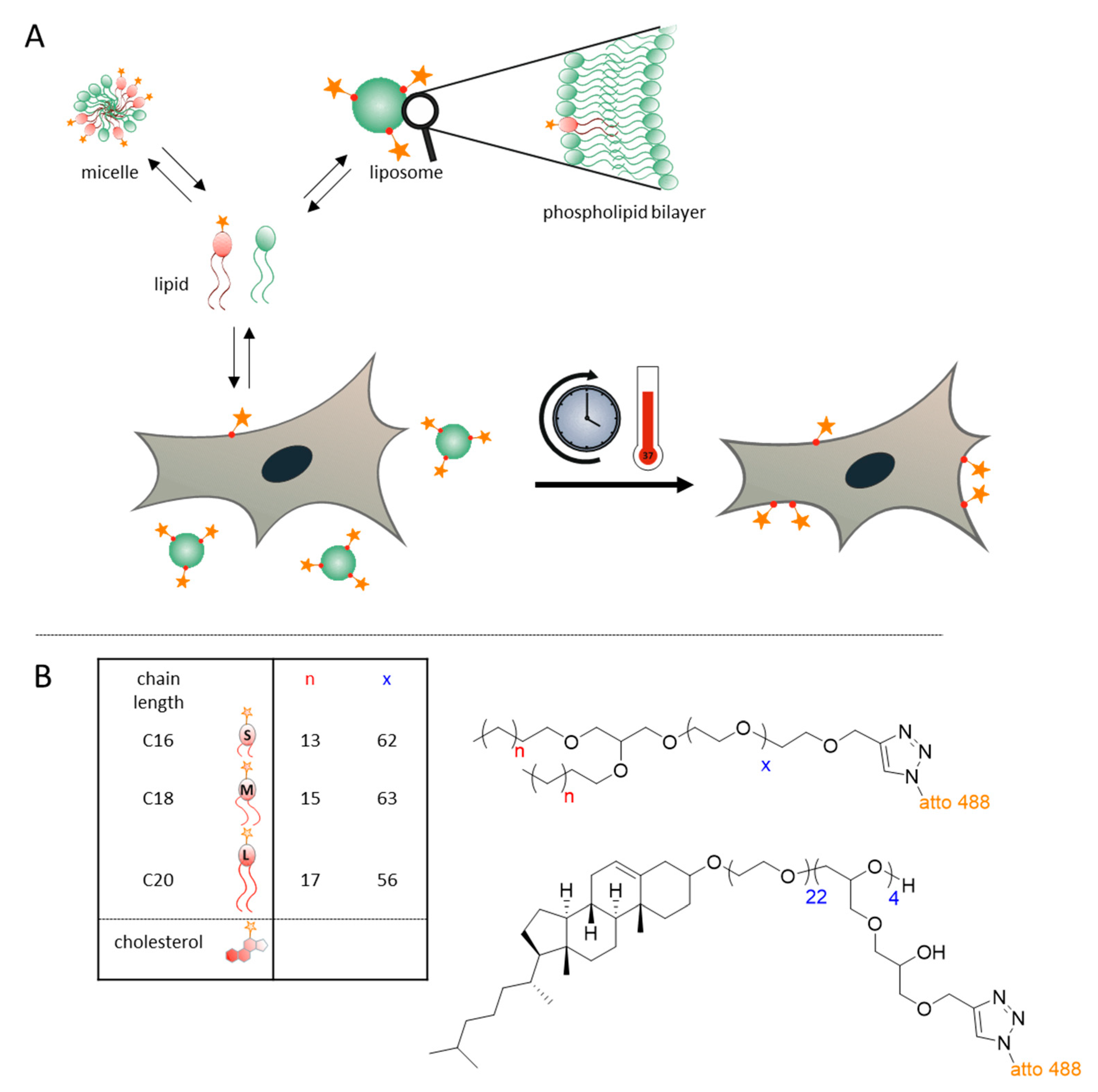
3.1. Concept and Approach
3.2. Experimental Lipids and Liposome Preparation
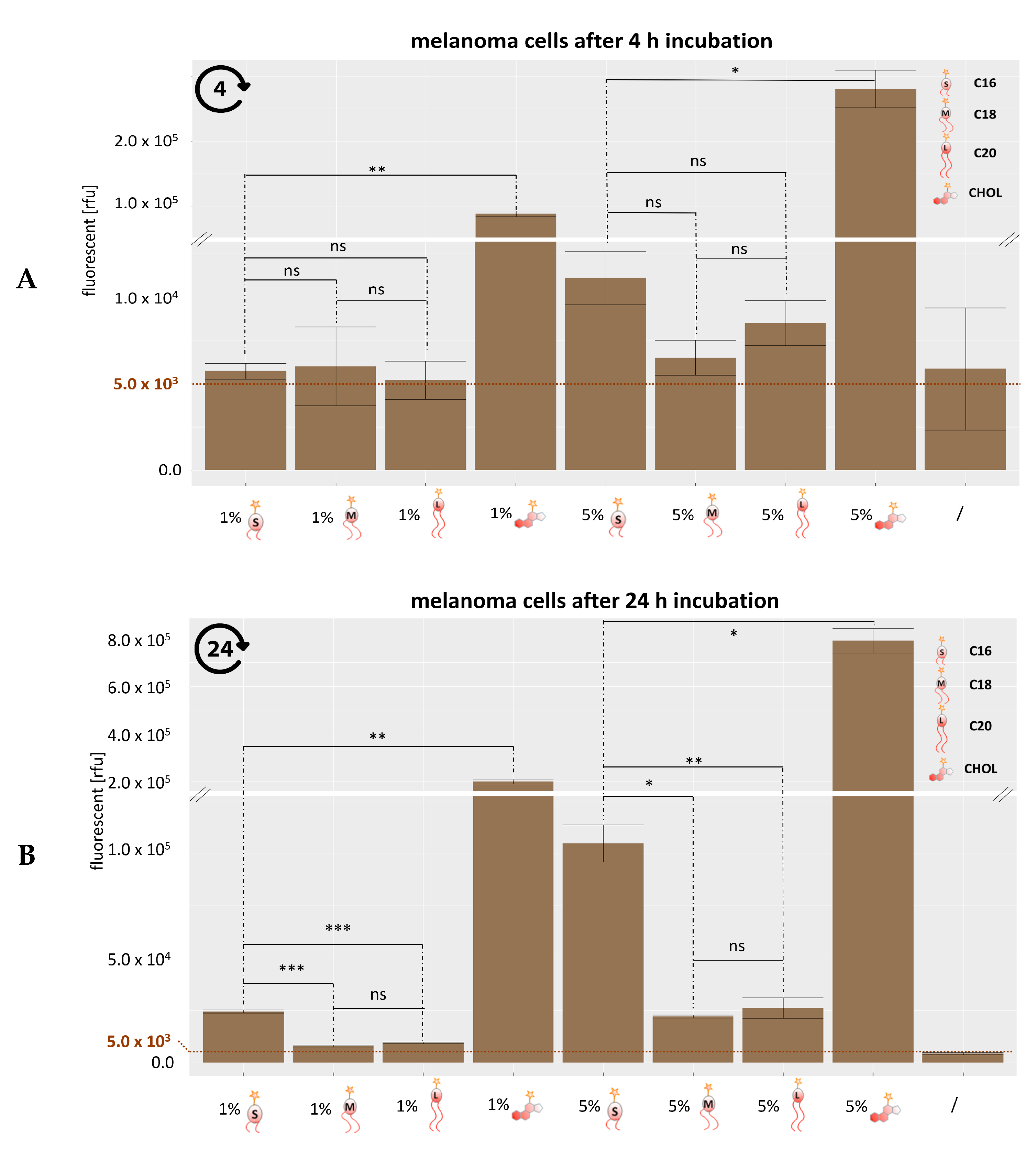
3.3. Analysis of Lipid Exchange Via Flow Cytometry
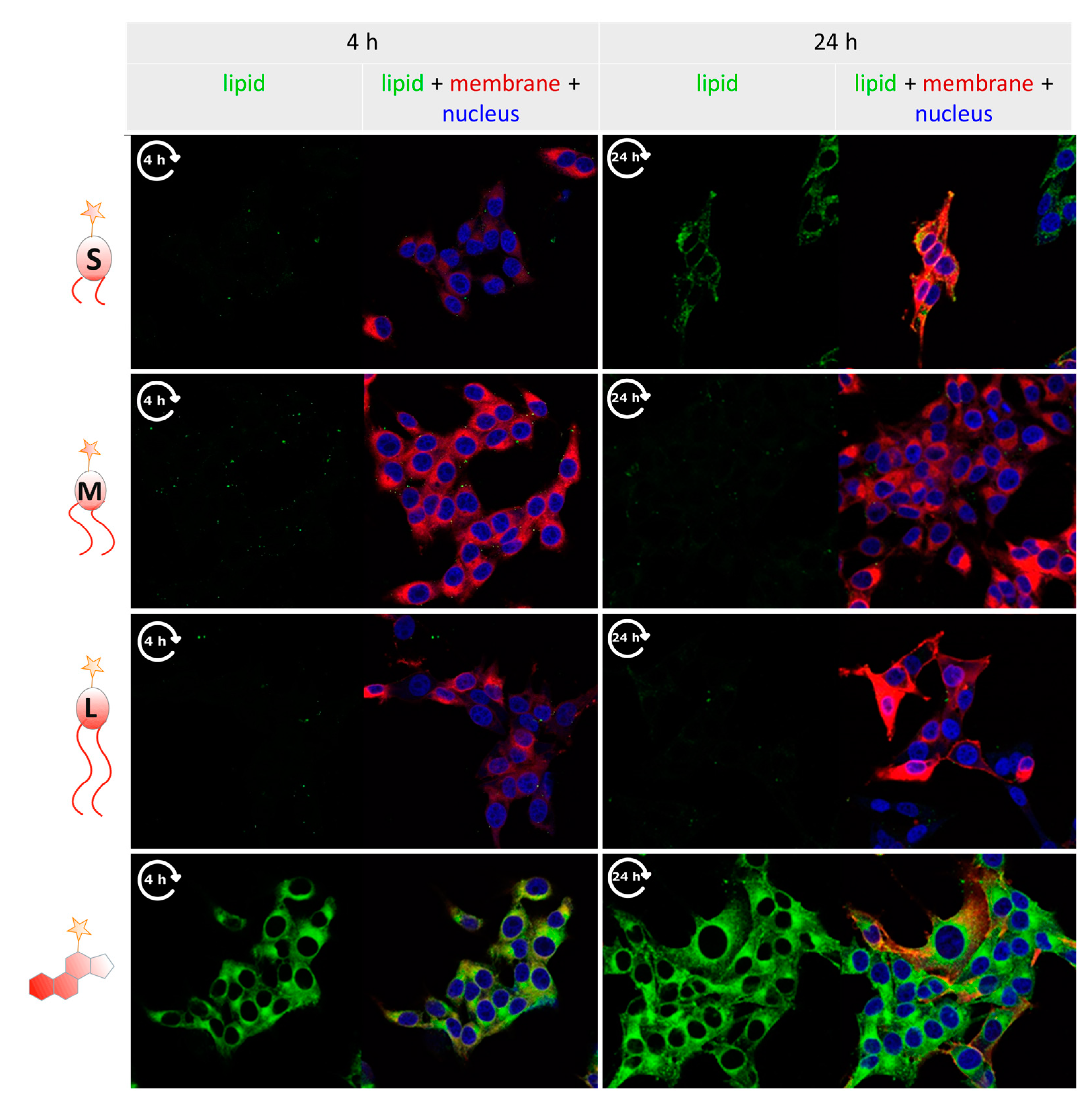
3.4. Tracking Labeled Lipids by Fluorescence Microscopy
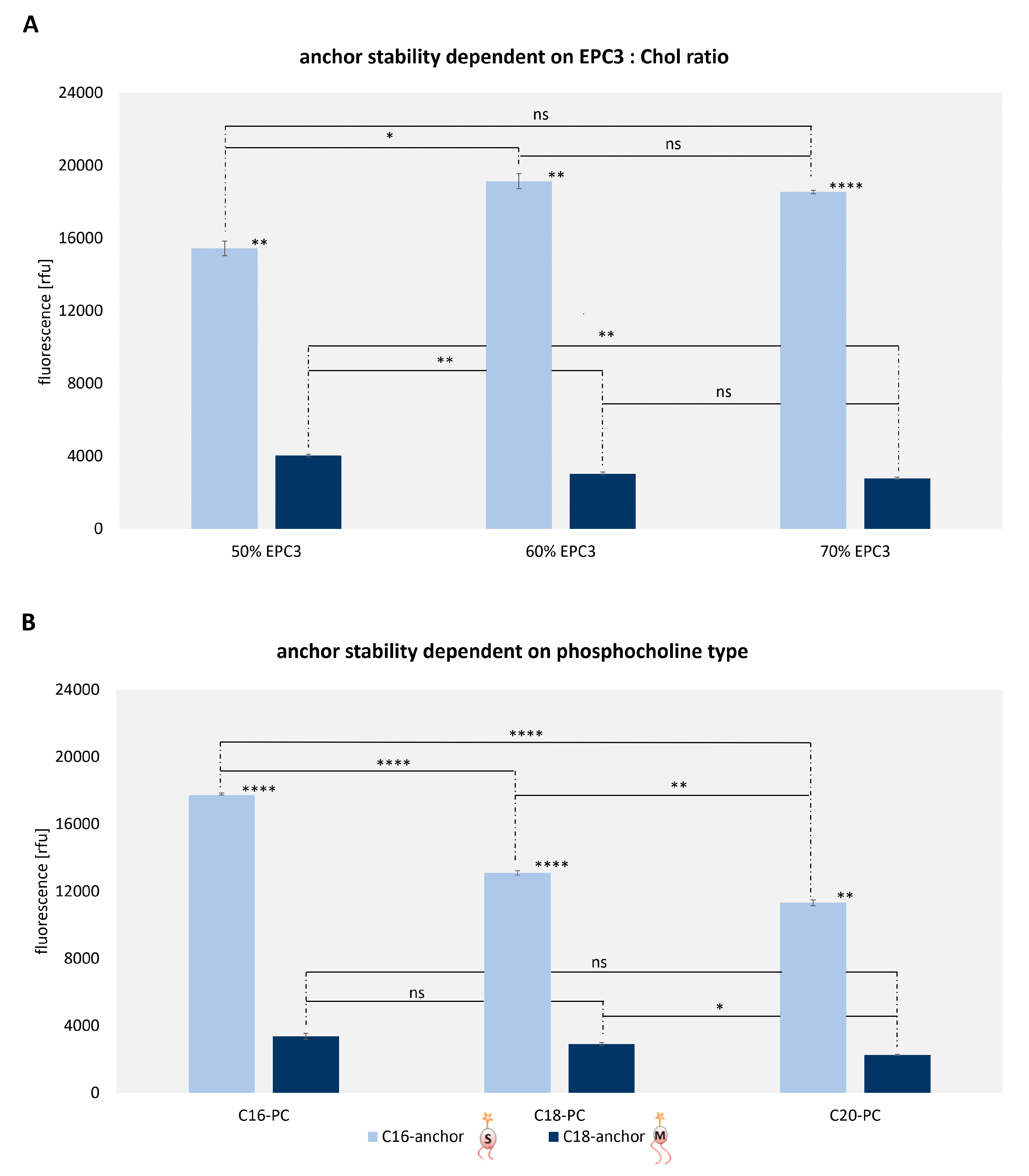
3.5. Analysis of Lipid Exchange Depending on Liposome Composition
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bangham, A.D.; Horne, R.W. Negative Staining of Phospholipids and Their Structural Modification by Surface-Active Agents as Observed in the Electron Microscope. J. Mol. Biol. 1964, 8, 660–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, T.M.; Cullis, P.R. Liposomal Drug Delivery Systems: From Concept to Clinical Applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florence, A. Targeted and Controlled Drug Delivery: Novel Carrier Systems. Int. J. Pharm. 2003, 267, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shashi, K.; Satinder, K.; Bharat, P. A Complete Review on: Liposomes. Int. Res. J. Pharm. 2012, 3, 10–16. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, C.; Voigt, M.; Simon, J.; Danner, A.-K.; Frey, H.; Mailänder, V.; Helm, M.; Morsbach, S.; Landfester, K. Functionalization of Liposomes with Hydrophilic Polymers Results in Macrophage Uptake Independent of the Protein Corona. Biomacromolecules 2019, 20, 2989–2999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geusens, B.; Lambert, J.; De Smedt, S.C.; Buyens, K.; Sanders, N.N.; Van Gele, M. Ultradeformable Cationic Liposomes for Delivery of Small Interfering RNA (SiRNA) into Human Primary Melanocytes. J. Control. Release 2009, 133, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissig, V.; Boddapati, S.V.; Cheng, S.-M.; D’souza, G.G.M. Liposomes and Liposome-like Vesicles for Drug and DNA Delivery to Mitochondria. J. Liposome Res. 2006, 16, 249–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindner, L.H.; Eichhorn, M.E.; Eibl, H.; Teichert, N.; Schmitt-Sody, M.; Issels, R.D.; Dellian, M. Novel Temperature-Sensitive Liposomes with Prolonged Circulation Time. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 2168–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, K.; Hossann, M.; Hirschberger, J.; Troedson, K.; Peller, M.; Schneider, M.; Brühschwein, A.; Meyer-Lindenberg, A.; Wess, G.; Wergin, M.; et al. A Pilot Trial of Doxorubicin Containing Phosphatidyldiglycerol Based Thermosensitive Liposomes in Spontaneous Feline Soft Tissue Sarcoma. Int. J. Hyperth. 2017, 33, 178–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmentier, J.; Hofhaus, G.; Thomas, S.; Cuesta, L.C.; Gropp, F.; Schröder, R.; Hartmann, K.; Fricker, G. Improved Oral Bioavailability of Human Growth Hormone by a Combination of Liposomes Containing Bio-Enhancers and Tetraether Lipids and Omeprazole. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 103, 3985–3993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briuglia, M.-L.; Rotella, C.; McFarlane, A.; Lamprou, D.A. Influence of Cholesterol on Liposome Stability and on in Vitro Drug Release. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2015, 5, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vemuri, S.; Rhodes, C.T. Preparation and Characterization of Liposomes as Therapeutic Delivery Systems: A Review. Pharm. Acta Helv. 1995, 70, 95–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirby, C.; Clarke, J.; Gregoriadis, G. Effect of the cholesterol content of small unilamellar liposomes on their stability in vivo and in vitro. Biochem. J. 1980, 186, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, N.; Paul, V.; Mahmoud, M.; Sawaftah, N.; Kawak, P.; Al-Sayah, M.; Husseini, G. The Effect of Pegylation and Targeting Moieties on the Ultrasound-Mediated Drug Release from Liposomes. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, D.C.; Meyer, O.; Hong, K.; Kirpotin, D.B.; Papahadjopoulos, D. Optimizing Liposomes for Delivery of Chemotherapeutic Agents to Solid Tumors. Pharmacol. Rev. 1999, 51, 691–743. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moghimipour, E.; Rezaei, M.; Ramezani, Z.; Kouchak, M.; Amini, M.; Angali, K.A.; Dorkoosh, F.A.; Handali, S. Folic Acid-Modified Liposomal Drug Delivery Strategy for Tumor Targeting of 5-Fluorouracil. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 114, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Zhou, L.; Yue, Q.; Liu, Q.; Cai, X.; Xiao, W.; Hai, L.; Guo, L.; Wu, Y. Liposomes Modified with Double-Branched Biotin: A Novel and Effective Way to Promote Breast Cancer Targeting. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2019, 27, 3115–3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.-C.; Chang, D.-K. Peptide-Mediated Liposomal Drug Delivery System Targeting Tumor Blood Vessels in Anticancer Therapy. J. Oncol. 2010, 2010, 723798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heath, T.D.; Fraley, R.T.; Papahdjopoulos, D. Antibody targeting of liposomes: Cell specificity obtained by conjugation of F (ab’) 2 to vesicle surface. Science 1980, 210, 539–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bendas, G.; Krause, A.; Bakowsky, U.; Vogel, J.; Rothe, U. Targetability of Novel Immunoliposomes Prepared by a New Antibody Conjugation Technique. Int. J. Pharm. 1999, 181, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, A.M.; Wurm, F.; Hühn, E.; Nawroth, T.; Langguth, P.; Frey, H. Hyperbranched Polyglycerol-Based Lipids via Oxyanionic Polymerization: Toward Multifunctional Stealth Liposomes. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 568–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohr, K.; Müller, S.S.; Müller, L.K.; Rusitzka, K.; Gietzen, S.; Frey, H.; Schmidt, M. Evaluation of Multifunctional Liposomes in Human Blood Serum by Light Scattering. Langmuir 2014, 30, 14954–14962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagener, K.; Worm, M.; Pektor, S.; Schinnerer, M.; Thiermann, R.; Miederer, M.; Frey, H.; Rösch, F. Comparison of Linear and Hyperbranched Polyether Lipids for Liposome Shielding by (18)F-Radiolabeling and Positron Emission Tomography. Biomacromolecules 2018, 19, 2506–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, R.A. Influence of Increased Membrane Cholesterol on Membrane Fluidity and Cell Function in Human Red Blood Cells. J. Supramol. Struct. 1978, 8, 413–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feingold, K.R.; Grunfeld, C. Introduction to Lipids and Lipoproteins; Feingold, K.R., Anawalt, B., Boyce, A., Chrousos, G., Dungan, K., Grossman, A., Hershman, J.M., Kaltsas, G., Koch, C., Kopp, P., et al., Eds.; South Dartmouth: Dartmouth, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Fritz, T.; Voigt, M.; Worm, M.; Negwer, I.; Müller, S.S.; Kettenbach, K.; Ross, T.L.; Roesch, F.; Koynov, K.; Frey, H.; et al. Orthogonal Click Conjugation to the Liposomal Surface Reveals the Stability of the Lipid Anchorage as Crucial for Targeting. Chem. A Eur. J. 2016, 22, 11578–11582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.R.; Weston, N.; Coombes, A.G.A.; Fitzgerald, M.; Perrie, Y. Liposome Formulation of Poorly Water Soluble Drugs: Optimisation of Drug Loading and ESEM Analysis of Stability. Int. J. Pharm. 2004, 285, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, E.; Gomes, A.C.; Preto, A.; Cavaco-Paulo, A. Design of Liposomal Formulations for Cell Targeting. Coll. Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 136, 514–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stauch, O.; Uhlmann, T.; Fröhlich, M.; Thomann, R.; El-Badry, M.; Kim, Y.-K.; Schubert, R. Mimicking a Cytoskeleton by Coupling Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide) to the Inner Leaflet of Liposomal Membranes: Effects of Photopolymerization on Vesicle Shape and Polymer Architecture. Biomacromolecules 2002, 3, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herzberger, J.; Niederer, K.; Pohlit, H.; Seiwert, J.; Worm, M.; Wurm, F.R.; Frey, H. Polymerization of Ethylene Oxide, Propylene Oxide, and Other Alkylene Oxides: Synthesis, Novel Polymer Architectures, and Bioconjugation. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 2170–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reibel, A.T.; Müller, S.S.; Pektor, S.; Bausbacher, N.; Miederer, M.; Frey, H.; Rösch, F. Fate of Linear and Branched Polyether-Lipids In Vivo in Comparison to Their Liposomal Formulations by 18F-Radiolabeling and Positron Emission Tomography. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 842–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagener, K.; Bros, M.; Krumb, M.; Langhanki, J.; Pektor, S.; Worm, M.; Schinnerer, M.; Montermann, E.; Miederer, M.; Frey, H.; et al. Targeting of Immune Cells with Trimannosylated Liposomes. Adv. Ther. 2020, 3, 1900185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawant, R.; Torchilin, V. Challenges in Development of Targeted Liposomal Therapeutics. AAPS J. 2012, 14, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kainthan, R.K.; Janzen, J.; Levin, E.; Devine, D.V.; Brooks, D.E. Biocompatibility Testing of Branched and Linear Polyglycidol. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 703–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofmann, A.M.; Wurm, F.; Frey, H. Rapid Access to Polyfunctional Lipids with Complex Architecture via Oxyanionic Ring-Opening Polymerization. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 4648–4657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, L.M.; Roth, R.; Heuser, J.E.; Schmid, S.L. Actin Assembly Plays a Variable, but Not Obligatory Role in Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis. Traffic 2000, 1, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribes, S.; Ebert, S.; Regen, T.; Agarwal, A.; Tauber, S.C.; Czesnik, D.; Spreer, A.; Bunkowski, S.; Eiffert, H.; Hanisch, U.-K.; et al. Toll-like receptor stimulation enhances phagocytosis and intracellular killing of nonencapsulated and encapsulated Streptococcus pneumoniae by murine microglia. Infect. Immun. 2010, 78, 865–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, D.; Donaldson, J.G. Search for Inhibitors of Endocytosis. Cell. Logist. 2012, 2, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotecha, N.; Krutzik, P.O.; Irish, J.M. Web-Based Analysis and Publication of Flow Cytometry Experiments. Curr. Protoc. Cytom. 2010, 53, 10.17.1–10.17.24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An Open-Source Platform for Biological-Image Analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, H.C.; Finn, M.G.; Sharpless, K.B. Click Chemistry: Diverse Chemical Function from a Few Good Reactions. Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. 2001, 40, 2004–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massing, U.; Ingebrigtsen, S.G.; Škalko-Basnet, N.; Holsæter, A.M. Dual Centrifugation—A Novel “in-Vial” Liposome Processing Technique. Liposomes 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Jaafari, M.R.; Szoka, F.C., Jr. Disterolphospholipids: Nonexchangeable Lipids and Their Application to Liposomal Drug Delivery. Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 4146–4149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, M.C.; Johnson, W.J.; Rothblat, G.H. Mechanisms and Consequences of Cellular Cholesterol Exchange and Transfer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Biomembr. 1987, 906, 223–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumann, J.; Leichtle, A.; Thiery, J.; Fuhrmann, H. Fatty Acid and Peptide Profiles in Plasma Membrane and Membrane Rafts of PUFA Supplemented RAW264.7 Macrophages. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, S.K.; Else, P.L.; Atkins, T.A.; Hulbert, A.J. Fatty Acid Composition of Membrane Bilayers: Importance of Diet Polyunsaturated Fat Balance. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2012, 1818, 1309–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Lipid 1 | Percentage | Lipid 2 | Percentage | Lipid 3 | Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPC3 | 50 mol-% | Cholesterol | 45 mol-% | C16 or C18 or C20 or Cholesterol alkyne lipid | 5 mol-% |
| EPC3 | 60 mol-% | Cholesterol | 35 mol-% | ||
| EPC3 | 70 mol-% | Cholesterol | 35 mol-% | C16 or C18 alkyne lipid | 5 mol-% |
| DPPC | 50 mol-% | Cholesterol | 45 mol-% | ||
| DSPC | 50 mol-% | Cholesterol | 45 mol-% | ||
| 20:0 PC | 50 mol-% | Cholesterol | 45 mol-% |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gleue, L.; Schupp, J.; Zimmer, N.; Becker, E.; Frey, H.; Tuettenberg, A.; Helm, M. Stability of Alkyl Chain-Mediated Lipid Anchoring in Liposomal Membranes. Cells 2020, 9, 2213. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9102213
Gleue L, Schupp J, Zimmer N, Becker E, Frey H, Tuettenberg A, Helm M. Stability of Alkyl Chain-Mediated Lipid Anchoring in Liposomal Membranes. Cells. 2020; 9(10):2213. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9102213
Chicago/Turabian StyleGleue, Lukas, Jonathan Schupp, Niklas Zimmer, Eyleen Becker, Holger Frey, Andrea Tuettenberg, and Mark Helm. 2020. "Stability of Alkyl Chain-Mediated Lipid Anchoring in Liposomal Membranes" Cells 9, no. 10: 2213. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9102213
APA StyleGleue, L., Schupp, J., Zimmer, N., Becker, E., Frey, H., Tuettenberg, A., & Helm, M. (2020). Stability of Alkyl Chain-Mediated Lipid Anchoring in Liposomal Membranes. Cells, 9(10), 2213. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9102213






