Tick-Borne Encephalitis: A Differential Pattern of Intrathecal Humoral Immune Response and Inflammatory Cell Composition Compared with Other Viral CNS Infections
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Inclusion Criteria
2.2. Ethics
2.3. Statistics
2.4. Data Availability
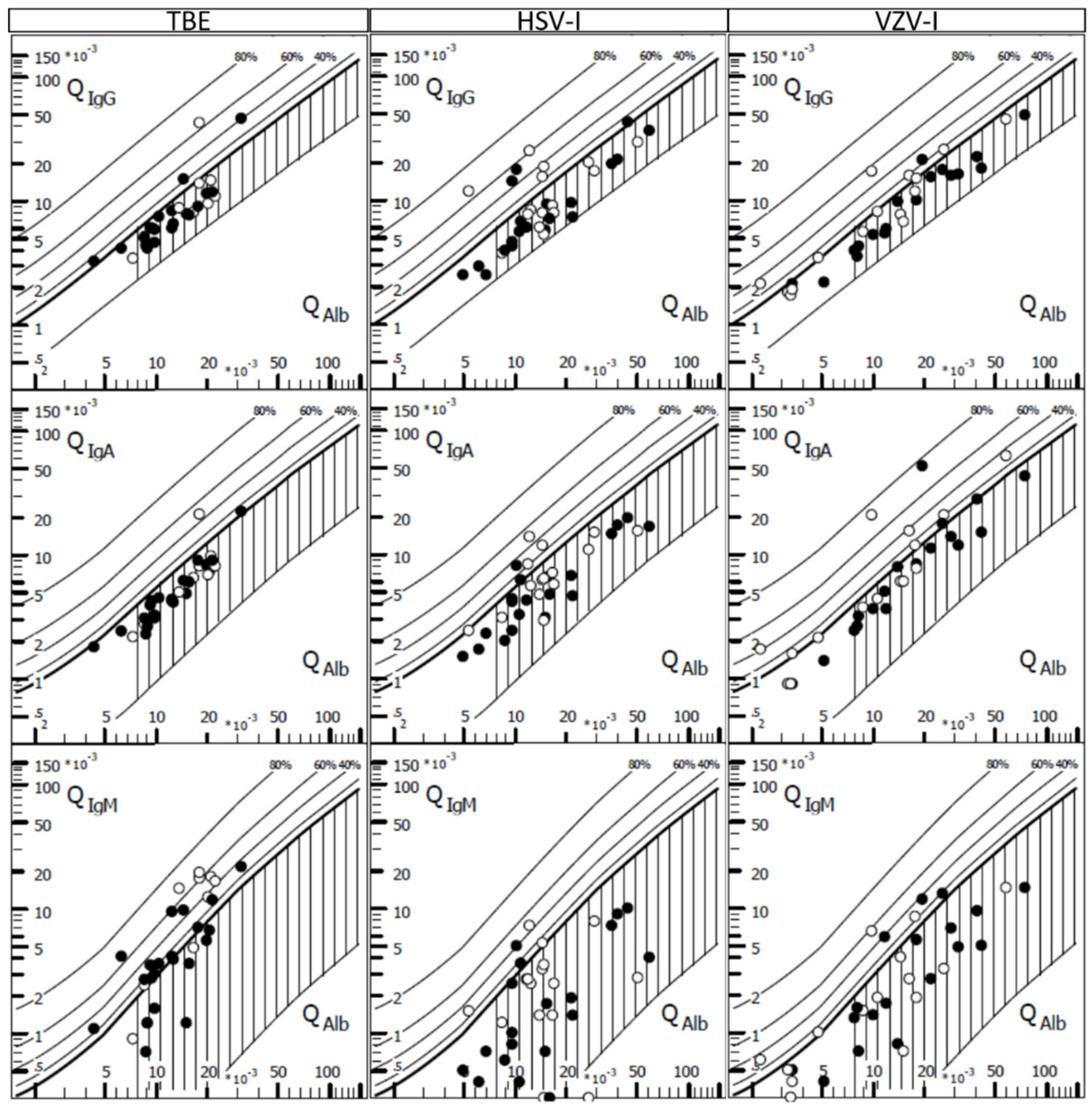
3. Results
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lindquist, L.; Vapalahti, O. Tick-borne encephalitis. Lancet 2008, 371, 1861–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, R. The clinical and epidemiological profile of tick-borne encephalitis in southern Germany 1994–1998. A prospective study of 656 patients. Brain 1999, 122, 2067–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taba, P.; Schmutzhard, E.; Forsberg, P.; Lutsar, I.; Ljøstad, U.; Mygland, Å.; Levchenko, I.; Strle, F.; Steiner, I. EAN consensus review on prevention, diagnosis and management of tick-borne encephalitis. Eur. J. Neurol. 2017, 24, 1214–e61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holding, M.; Dowall, S.; Hewson, R. Detection of tick-borne encephalitis virus in the UK. Lancet 2020, 395, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holding, M.; Dowall, S.D.; Medlock, J.M.; Carter, D.P.; McGinley, L.; Curran-French, M.; Pullan, S.T.; Chamberlain, J.; Hansford, K.M.; Baylis, M.; et al. Detection of new endemic focus of tick-borne encephalitis virus (TBEV), Hampshire/Dorset border, England, September 2019. Eurosurveillance 2019, 24, 1900658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatesan, A.; Tunkel, A.R.; Bloch, K.C.; Lauring, A.S.; Sejvar, J.; Bitnun, A.; Stahl, J.P.; Mailles, A.; Drebot, M.; Rupprecht, C.E.; et al. Case definitions, diagnostic algorithms, and priorities in encephalitis: Consensus statement of the international encephalitis consortium. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 57, 1114–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiber, H.; Lange, P. Quantification of Virus-Specific Antibodies in Cerebrospinal Fluid and Serum: Sensitive and Specific Detection of Antibody Synthesis in Brain. Clin. Chem. 1991, 37, 1153–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senel, M.; Rupprecht, T.A.; Tumani, H.; Pfister, H.W.; Ludolph, A.C.; Brettschneider, J. The chemokine CXCL13 in acute neuroborreliosis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2010, 81, 929–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, P.G.E.; Quan, P.L.; Lipkin, W.I. Viral encephalitis of unknown cause: Current perspective and recent advances. Viruses 2017, 9, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granerod, J.; Dphil, A.; Clewley, J.P.; Walsh, A.L.; Morgan, D.; Brown Frcpath, W.G.; Granerod, J.; Ambrose, H.E.; Davies, N.W.S.; Clewley, J.P.; et al. Causes of encephalitis and diff erences in their clinical presentations in England: A multicentre, population-based prospective study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2010, 10, 835–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, I.; Schmutzhard, E.; Sellner, J.; Chaudhuri, A.; Kennedy, P.G.E. EFNS-ENS guidelines for the use of PCR technology for the diagnosis of infections of the nervous system. Eur. J. Neurol. 2012, 19, 1278–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| TBE | HSV-I | VZV-I | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (female/male) | 21 (5/16) | 20 (12/8) | 18 (8/10) | 0.064 |
| Age (years), median | 47 (33–66) | 58 (53–71) | 59 (34–77) | 0.280 |
| Onset of neurological symptoms (days) | 7 (5–14) | 3 (1–8) p = 0.002 | 4 (2–6) p = 0.005 | 0.002 |
| Meningitis n [%] | 11 [52.4] | 2 [10.0] p = 0.006 | 10 [55.6] p = 1.00 | 0.004 |
| Encephalitis n [%] | 1 [4.8] | 13 [65.0] p < 0.001 | 2 [11.1] p = 0.586 | <0.001 |
| Meningoencephalitis n [%] | 9 [42.9] | 5 [25.0] | 5 [27.8] | 0.471 |
| Inflammatory changes in brain MRI n [%] | 3 [14.3] | 14 [70.0] p = < 0.001 | 2 [11.8] p = 1.00 | <0.001 |
| Abnormal EEG * n [%] | 5 [23.8] | 12 [63.2] | 6 [33.3] | 0.416 |
| TBE n = 21 | HSV-I n = 20 | VZV-I n = 18 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leucocyte count (/µL) Pleocytosis with >20% granulocytes n [%] | 65 (33–120) 10 [47.6] | 91 (20–285) p = 0.648 3 [15.0] p = 0.043 | 243 (70–302) p = 0.007 1 [5.6] p = 0.005 | 0.037 0.007 |
| Q albumin (×10−3) | 12.6 (9.1–15.9) | 11.5 (9.8–21.9) | 16.2 (8.4–28.8) | 0.540 |
| Total protein | 922 (610–1039) | 865 (676–1355) | 1240 (610–1950) | 0.308 |
| Blood-CSF-barrier dysfunction n [%] | 18 [85.7] | 17 [85.0] | 15 [83.3] | 1.00 |
| Lactate (mmol/L) | 2.0 (1.9–2.2) | 2.5 (2.0–3.0) | 2.8 (2.3–3.7) | 0.010 |
| p = 0.050 | p = 0.004 | |||
| Oligoclonal IgG bands n [%] | ||||
| In first LP | 3 [14.3] | 6 [30.0] | 6 [33.3] | 0.364 |
| In follow-up LP * | 9 [90.0] | 12 [80.0] | 13 [86.7] | 0.871 |
| Intrathecal IgG synthesis n [%] | ||||
| In first LP | 2 [9.5] | 3 [15.0] | 1 [5.6] | 0.764 |
| In follow-up LP * | 2 [20.0] | 6 [40.0] | 6 [40.0] | 0.639 |
| Intrathecal IgA synthesis n [%] | ||||
| In first LP | 1 [4.8] | 2 [10.0] | 3 [16.7] | 0.420 |
| In follow-up LP * | 1 [10.0] | 6 [40.0] | 8 [53.3] | 0.107 |
| Intrathecal IgM synthesis n [%] | ||||
| In first LP | 13 [61.9] | 2 [10.0] | 3 [16.7] | 0.001 |
| p = 0.001 | p = 0.008 | |||
| In follow-up LP * | 10 [100.0] | 3 [20.0] | 4 [26.7] | <0.001 |
| p < 0.001 | p = 0.001 | |||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Senel, M.; Rapp, D.; Mayer, B.; Jesse, S.; Süssmuth, S.D.; Otto, M.; Lewerenz, J.; Tumani, H. Tick-Borne Encephalitis: A Differential Pattern of Intrathecal Humoral Immune Response and Inflammatory Cell Composition Compared with Other Viral CNS Infections. Cells 2020, 9, 2169. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9102169
Senel M, Rapp D, Mayer B, Jesse S, Süssmuth SD, Otto M, Lewerenz J, Tumani H. Tick-Borne Encephalitis: A Differential Pattern of Intrathecal Humoral Immune Response and Inflammatory Cell Composition Compared with Other Viral CNS Infections. Cells. 2020; 9(10):2169. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9102169
Chicago/Turabian StyleSenel, Makbule, Daniel Rapp, Benjamin Mayer, Sarah Jesse, Sigurd D. Süssmuth, Markus Otto, Jan Lewerenz, and Hayrettin Tumani. 2020. "Tick-Borne Encephalitis: A Differential Pattern of Intrathecal Humoral Immune Response and Inflammatory Cell Composition Compared with Other Viral CNS Infections" Cells 9, no. 10: 2169. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9102169
APA StyleSenel, M., Rapp, D., Mayer, B., Jesse, S., Süssmuth, S. D., Otto, M., Lewerenz, J., & Tumani, H. (2020). Tick-Borne Encephalitis: A Differential Pattern of Intrathecal Humoral Immune Response and Inflammatory Cell Composition Compared with Other Viral CNS Infections. Cells, 9(10), 2169. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9102169





