Abstract
The JAK/STAT3 signaling pathway plays an essential role in various types of cancers. Activation of this pathway leads to increased tumorigenic and metastatic ability, the transition of cancer stem cells (CSCs), and chemoresistance in cancer via enhancing the epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT). EMT acts as a critical regulator in the progression of cancer and is involved in regulating invasion, spread, and survival. Furthermore, accumulating evidence indicates the failure of conventional therapies due to the acquisition of CSC properties. In this review, we summarize the effects of JAK/STAT3 activation on EMT and the generation of CSCs. Moreover, we discuss cutting-edge data on the link between EMT and CSCs in the tumor microenvironment that involves a previously unknown function of miRNAs, and also discuss new regulators of the JAK/STAT3 signaling pathway.
1. Introduction
The Janus kinase (JAK)/signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) pathway played a crucial role in many biological functions during the multistep development of human tumors, including proliferation, inflammation, and survival. The JAK/STAT signaling pathway comprises of the receptor and adaptor proteins of interleukin 6 (IL-6), interferon-alpha (IFN-α), and interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) that mediate pleiotropic functions upon binding to their respective ligands [1,2].
The IL-6 family of cytokine comprises IL-6, IL-11, IL-27, IL-31, oncostatin M (OSM), cardiotrophin 1 (CT-1), ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF), cardiotrophin-like cytokine factor 1 (CLCF1), and leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF). Elevated expression of the cytokines belonging to this family is implicated in the development of various human diseases [3,4]. Upon binding IL-6, the IL-6 receptor-α (IL-6R) forms a complex with glycoprotein 130 (IL-6Rβ), and subsequently, triggers the activation of receptor-associated JAK1, JAK2, and tyrosine-protein kinase 2 (TYK2) pathways [4,5].
There are four JAK family non-receptor tyrosine kinases, JAK1, JAK2, JAK3, and TYK2. JAK1, JAK2, and TYK2 are ubiquitously expressed, whereas JAK3 is predominantly expressed in hematopoietic cells [6]. The JAK family is characterized by the presence of four unique domains, four-point-one, ezrin, radixin, moesin (FERM); Src homology 2 (SH2); pseudokinase; and kinase domains. The FERM and SH2 domains facilitate association with cytokine receptors and regulate the catalytic activity [7]. The pseudokinase domain, which interacts with the kinase domain, acts as a suppressor of the kinase domain’s catalytic activity and subsequently activates STAT1, 3, and 5 [8].
Until now, seven members of the STAT family (STATs 1–4, 5α, 5β, and 6) have been identified. Each of the STAT proteins shares highly conserved domains, including amino-terminal, coiled-coil, DNA binding, SH2, and transactivation domains [9]. The Asp170 residue in the helix α1 of the coiled-coil domain of STAT3 interacts with other transcription factors [10], and tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT3 by IL-6 is required for its receptor binding, dimerization, nuclear translocation, and DNA binding [11]. The SH2 domain is essential for STAT-cytokine receptor interactions as it recognizes the tyrosine residues in the cytokine receptors and forms stable homo- or heterodimers with other STAT proteins [12,13]. Cytokines induce the dimerization of STAT3 through the acetylation of Lys685 in the SH2 domain of STAT3, which is associated with the histone acetyltransferase p300 [14]. Besides, the N-terminal domain of STAT3 has multiple functions, including STAT3 tetramer stabilization, cooperative DNA binding, nuclear translocation, and protein–protein interactions [15] (Figure 1).
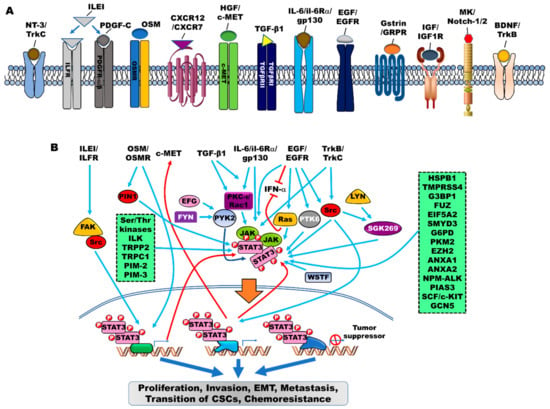
Figure 1.
The contribution of signaling pathways that activate JAK/STAT3 signaling in cancer. Cytokines, growth factors, intracellular proteins, including non-receptor kinases (tyrosine or serine/threonine), can cooperate to induce the JAK/STAT3 signaling. (A) Various cytokines, peptide hormones, growth factors, and chemokines contribute to the activation of the JAK/STAT3 signaling to promote the progression of cancer. (B) The JAK/STAT3 signaling activated by tyrosine receptors and their cognate ligands, including neurotrophic receptors (TrkA, and TrkC), ILE/ILFR, PDGF-C/PDGFR, OSM/OSMR, CXCR12/CXCR7, HGF/c-MET, TGF-β/TGF receptors, IL-6/IL-6Rα/gp130, EGF/EGFR, Gastrin/GRPR, IGF/IGF1R, and Mk/Notch-1/2. Also, potential mechanisms by which tyrosine or serine/threonine kinases activate the JAK/STAT3 signaling through direct binding to JAK/STAT3 or indirect regulation of JAK/STAT3 activation. Once activated, phosphorylated and dimerized STAT3 enters the nucleus through importin-β1 and promotes the transcriptional expression of target genes to promote various cellular processes that are required for maintenance of survival in cancer.
2. Role of IL-6/JAK/STAT3 in the Induction of EMT
STAT proteins are differentially implicated in cancer tumorigenesis. Although STAT1 is known to be involved in mediating the anti-tumor immunity and other STAT families are known to be involved in the promotion of cancer development, it is STAT3 that is most well studied as a significant intrinsic transcription factor in the induction of the EMT and in the pathogenesis of cancer (Figure 2) [16]. IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 activation enhances metastasis via induction of EMT by the upregulation of EMT-inducing transcription factors (EMT-TFs; Snail, Zeb1, JUNB, and Twist-1) and increases cell motility via focal adhesion kinase (FAK) activation [17,18,19,20]. In prostate cancer, paracrine IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 stimulates the autocrine IL-6 loop, and IGF-IR activation induced by both IL-6 and IGF enhances EMT through induction of the STAT3/NANOG/Slug axis [21,22].
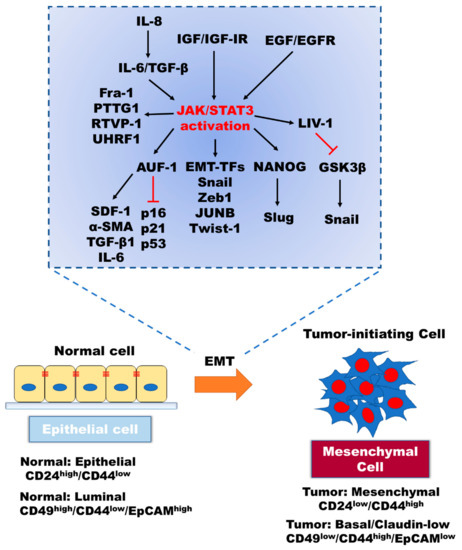
Figure 2.
The contributions of intracellular signaling components to the inducing of EMT through activation of the JAK/STAT signaling. EMT program in cancer is associated with morphological and physiological changes of cancer, including the detachment of epithelial cells, enhanced invasiveness, tumor-initiating ability, and drug resistance. Enhanced EMT through upregulation of EMT-inducing transcription factors via the canonical and non-canonical JAK/STAT3 signaling leads to the downregulation of apoptotic signaling pathways, resistance to anticancer drugs and immunotherapy, induced cell proliferation, and CSC population.
STAT3 acts as a transcriptional activator through binding to the promoter of target genes in a tyrosine phosphorylation-dependent manner [23]. For instance, once activated, STAT3, in combination with estrogen receptor (ER), binds to the LIV-1 promoter leading to the induction of LIV-1 expression, followed by proteolytic N-terminal cleavage of the LIV-1 protein and its subsequent translocation to the plasma membrane. Subsequently, LIV-1 stabilizes Snail through inactivation of GSK3β [24,25,26]. In addition, RANKL is known to enhance EMT in prostate cancer through the STAT3/LIV-1 axis [27]. Moreover, IL-8-mediated production of IL-6 and TGF-β1 promotes binding of STAT3 to AUF-1 promoter, leading to the activation of breast stromal fibroblasts through the reduction of p16, p21, and p53 levels in a paracrine manner. In turn, elevated AUF-1 levels lead to enhanced EMT due to increased expression of SDF-1, α-SMA, TGF-β1, and IL-6 that results from binding of AUF1 to their respective promoters [28,29]. Furthermore, increased expression of Fra-1 [30] and PTTG1 [31] due to the binding of STAT3 to their promoters induce invasion and facilitates resistance to androgen deprivation therapy (AR). Additionally, induced RTVP-1 expression via binding of both C/EBPβ and STAT3 to the RTVP-1 promoter results in maintenance of the stemness property of glioblastoma cells and is associated with poor clinical outcomes in patients [32]. Besides, STAT3 induces UHRF1 expression via direct binding to its promoter. This is especially important in the context of cancer biology as the PHD and SRA domains of UHRF1 are involved in silencing the tumor suppressor genes in CRC cells [33]. The hallmarks of cancer coordinated by the STAT3-dependent transcriptional regulation of target proteins directly underpin the cellular responses.
3. Critical Modulators of the JAK2/STAT3 Signaling Pathway in EMT
The activation of JAK2/STAT3 signaling is triggered by various hormones, cytokines (including the IL-6 family), and growth factors through a variety of molecular mechanisms. OSM, another IL-6 cytokine family member, is crucial for JAK/STAT activation. It interacts with the extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins, and OSM/OSM receptor (OSMR)-mediated JAK2/STAT3/FAK/Src activation promotes EMT and CSC production [34,35,36,37,38,39]. Other pro-inflammatory cytokines, IL-32β and IL-23, are highly expressed in cancers. STAT3 activation by IL-23/IL23R and via IL-32β-induced VEGF leads to increased migration and invasion of breast cancer (BC) and gastric cancer (GC) cells [40,41]. Additionally, the FAM3 family of created cytokines, ILEI-induced PDGF-C/PDGF-Rβ [42], or PDGF-Rα activation [43], enhance EMT and aggressiveness by increasing p-STAT3 via Src activation. Repression of hnRNP E1 by non-canonical TGF-β-induced Akt2 increases ILEI expression, and ILEI/ILFR promotes EMT and CSC generation [44,45].
Hormones, growth factors, and chemokines are associated with JAK/STAT3 activation. The gastrointestinal (GI) peptide hormone, gastrin, promotes the invasiveness of cancer cells by the induction of MMP-1, -2, and -9 secretion [46]. Gastrin-mediated activation of JAK2/STAT3 and PI3K/AKT pathways inhibit cell–cell adhesion and cell motility [47]. Furthermore, gastrin and its receptor, GRPR, promote EMT by increasing Snail and reducing E-cadherin expression [9]. However, polyclonal antibody stimulator (PAS), an anti-gastrin cancer vaccine, inhibits tumor formation, metastases of pancreatic cancer, and gastrin-induced EMT [48]. CXCL12-induced CXCR7 receptor results in increased IL-8 and VEGF levels, and subsequently, EMT by induction of Snail through the activation of AKT, ERK, and STAT3 in bladder cancer and BC [49,50].
The heparin-binding growth factor, Midkine (MK), induces EMT via activating the nuclear accumulation of the Notch-2 receptor through the formation of the MK-Notch-22 complex [51]. In addition, after the formation of the MK-high affinity receptor, this complex is associated with JAK1/JAK2 and subsequently activates JAK/STAT signaling [52]. Moreover, MK engenders a cross-talk between the Notch signaling and JAK2/STAT3 signaling by inducing an interaction between the JAK2/STAT3 complex and Hes1, which is the downstream target of Notch-2 [51,53]. Recent studies have demonstrated that induced MK is significantly associated with chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer via the activation of NF-κB signaling and Hes1-induced JAK2/STAT3 signaling through cleavage and activation of MK-mediated Notch signaling [54,55]. Intriguingly, the binding of estradiol (E2) to ERβ results in the activated ER-β binding to the estrogen response element within the MK promoter, thereby leading to the induction of MK transcription, which enhances the EMT [56]. Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), its splice variant, and its receptor (c-MET) contribute to the activation of STAT3 and its downstream cascades. Following HGF binding, the docking motif within the C-terminal end of activated c-MET associates with the SH2 domain of STAT3 and phosphorylates STAT3 [57,58]. However, suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS)-1 reduces STAT3 activation by proteasomal degradation of c-MET through direct interaction with c-Met [59,60].
Non-canonical Wnt signaling, which is independent of the β-catenin/TCF pathway, induces EMT through STAT3 activation. Upregulated Wnt5a/b and its receptor, Wnt receptor, Frizzled2 (Fzd2), induce cell migration by non-canonical pathways, and activation of STAT3 by the Fzd2/Fyn/STAT3 complex upregulates STAT3 target genes [61].
G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) and human GH (hGH) have been reported to be involved in the regulation of JAK/STAT signaling in cancer. Activation of PAF/platelet-activating factor receptor (PAFR) promotes lung cancer progression via the activation of Src/STAT3 or JAK2/STAT3 [62]. Moreover, hGH, which acts as a central endocrine regulator, enhances the oncogenicity of endometrial carcinoma via the activation of STAT3 in a JAK2/src-dependent manner [63]. Critical modulator-mediated JAK/STAT signaling showed a mechanistic link to EMT, invasiveness, malignancy, recurrence, anticancer drug resistance, and generation of cancer stem cells (Figure 1A).
4. Orchestrators of JAK2/STAT3 Activation in EMT
The contribution of intracellular signaling components to the induction of EMT through the activation of the JAK/STAT signaling in cancer progression has been extensively studied (Figure 1B).
4.1. Tyrosine and Serine/Threonine Kinases as Orchestrators
Potential mechanisms by which tyrosine or serine/threonine kinases activate the JAK/STAT3 signaling. Nuclear interactions, as well as cytoplasmic interactions between EGFR and STAT3, increase the expression of iNOS, cyclin D1, and c-fos via direct binding of EGFR/STAT3 complex to their promoters [64]. Moreover, aberrant EGF/EGFR signaling enhances EMT and cisplatin-resistance through the activation of JAK2/STAT3 via the following: increasing IL-6 and LIF production [65], src-induced Zeb1 and Zeb2 upregulation [66], and increasing Twist-1 expression via binding of STAT3 to the promoter of Twist-1 [67,68]. PTK6 interacts with the EGFR family—including EGFR, HER2, HER3—and aggravates cancer through activation of RAS/MAPK, PI3K/AKT, and STAT3 [69]. Besides, IFN-α induces apoptosis by activating JNK and p38 MAPK signaling. Additionally, IFN-α induces apoptosis via promotion of caspase 3-mediated degradation of gelsolin and inhibiting STAT3 activity. However, EGF/EGFR signaling inhibits IFN-α-mediated apoptosis via activation of Ras/ERK signaling and inhibition of caspase-3 activation [70,71,72]. In addition, Fyn-, EFG-, and TGFβ1-mediated PYK2 activation are involved in the progression and survival of BC patients via activation of STAT3, and subsequently, PYK2-induced STAT3 increases PYK2 and c-MET via activation of the positive feedback loop [73,74]. Moreover, Src- and Lyn induces the activation of Sgk269 (PEAK1), a cytoplasmic pseudokinase that is highly expressed in a basal subtype of BC and promotes EMT through both STAT3 and ERK activation [75,76]. Another pseudokinase, Sgk223 (Pragmin), promotes invasion and EMT in pancreatic cancer via activation of JAK1/STAT3 by the formation of Sgk223-STAT3 complex [77]. Interestingly, neurotrophin receptors, TrkB and TrkC, are regulators of JAK/STAT3 signaling. Both TrkB and TrkC increase JAK2 stability through inhibition of SOCS-3-mediated JAK2 degradation via direct interaction with JAK2, thereby resulting in the induction of EMT and metastasis of BC [78,79]. Additionally, William’s syndrome transcription factor (WSTF), a tyrosine kinase, promotes tumor growth via activation of AKT and STAT3 in lung cancer [80].
Serine/threonine kinases as the components of the ion channel are involved in STAT3 activation. The production of calcium signal by EGF induces EMT via activation of STAT3 by increasing the levels of TRPM7, a serine/threonine kinase [81]. Another serine/threonine kinase, ILK, induces EMT by increasing the activation of JAK2/STAT3 [82] and upregulation of SMOC-2 [83]. Mesenchymal cells resistant to EGFR inhibitors showed increased AKT and STAT3 activation; this was mediated via elevated levels of ILK [84]. Moreover, ILK enhances EMT and angiogenesis through induction of the MUC1-C oncoprotein by IL6/STAT3 and by the inhibition of MUC1-C degradation through the reduction of PKCδ, which is involved in ubiquitin-dependent degradation of MUC1-C [85]. Subsequently, MUC1-C and activated STAT3 induce MUC1 transcription by binding to the MUC1 promoter [86]. Furthermore, TRPP2 and TRPC1, which are involved in enhancing Ca2+ permeability, enhance metastasis by induction of EMT through increased STAT3 expression [87]. TRPC1-induced AKT and STAT3 activation increase Snail levels through the upregulation of HIF-1α and LC3BII (a hypoxia-induced autophagy marker) [88]. Increased interleukin production (IL-1α and IL-8) due to the action of PIM-3 [89] and PIM-2 as other serine/threonine kinases promotes the metastasis of BC via STAT3 activation and activated STAT3 upregulates PIM-2 expression by forming a positive feedback loop [90]. Furthermore, IL-6/JAK/STAT3 activation induces c-Myc expression through the upregulation of PIM-1 to enhance EMT and stemness [91].
4.2. Other Proteins as Orchestrators
Several proteins regulate STAT3 activation through direct interaction with STAT3. Pin1 is highly expressed in a majority of cancers [92,93], and elevation in Pin1 levels by either OSM or IL-6 involves the activation of both STAT3 and NF-κB through direct binding with the pSer/Thr-Pro motifs of STAT3 and p65 in the nucleus that results in promotion of STAT3 transcriptional activation [94,95]. The activation of RAC1 (RAC1–GTP) by TGF-β-induced PKC-ι results in STAT3 activation via RAC1–GTP-mediated triggering of the IL-6/JAK and Rac1–JNK pathways, or via its interaction with STAT3 [96,97,98,99]. Additionally, the ATP-independent chaperone Hsp27 (HSPB1) interacts with STAT3 in response to cellular stress-mediated [100], and both HSPB1 and TMPRSS4, induce EMT through the activation of the IL-6/STAT3/Twist-1 axis [100,101].
Diverse proteins are upregulated during cancer progression and facilitate constitutive JAK/STAT activation. The levels of G3BP1, which plays a critical role in stress granule (SG) formation, are increased in renal cell carcinoma (RCC) and promote IL6/STAT3 activation [102]. FUZ is a critical regulator of cilia structure, whose expression is associated with poor prognosis in lung cancer patients; this effect of FUZ is mediated through the activation of ERK1/2 and JAK2/STAT3 signaling via the formation of the FUZ–BNIP3 complex [103]. Moreover, EIF5A2 increases STAT3 stabilization, which via binding to the TGF-β1 promoter, enhances TGF-β1 expression [104,105]. Furthermore, SMYD3 induces STAT3 activation by increasing JAK1 and JAK2 expression via binding to their promoter regions. Furthermore, SMYD3 is a component of the SMYD3/H3K4Me3/RNA pol-II complex that enhances the transcription of genes that are involved in cancer-related pathways [106].
The activation of fundamental components of cellular metabolism and DNA methylation involves tumor progression by regulation of STAT3 activity. Upregulation of G6PD, an enzyme involved in the pentose phosphate pathway, and PKM2, the key enzyme catalyzing the final step of glucose metabolism is correlated with metastasis and poor survival of patients with HCC and ESCC and promotion of EMT via STAT3 and STAT5 [107,108]. Moreover, a lysine methyltransferase, EZH2 as a part of the EZH2-containing PRC2 complex, maintain gene silencing through hypermethylation of tumor suppressors [109,110], and p-AKT-induced EZH enhances tumor progression through activation and methylation of STAT3 by direct association [111]. Moreover, IL-6/STAT3-induced DNMT1 enhances the metastatic potential and reduces radiosensitization in AR-prostate cancer [112] and accumulates myeloid-derived suppressor cells, all of which are responsible for the accelerated tumor growth [113].
The Annexin (Anx) family contains calcium-dependent phospholipid-binding proteins and is associated with the invasiveness of cancer. AnxA1 induces invasiveness, drug-resistance, and generation of CSCs in prostate and pancreatic cancer by increasing the p-STAT3 level [114]. In addition, EGF/EGFR and TGF-β induce AnxA2 activation, following which p-AnxA2 directly interacts with STAT3 and subsequently enhances EMT in BC and CRC [115,116].
Hypoxia-responsive proteins are involved in STAT3-mediated EMT induction. Non-canonical TGF-β and EGF signaling induce the accumulation and upregulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α) in the nucleus. During this process, the degradation of HIF-1α is blocked by the formation of STAT3-HIF-1α complex, and this is followed by induction of Twist-1 expression by binding of both STAT3 and HIF-1α to the Twist-1 and VEGF promoters [117,118,119,120]. Moreover, hypoxia-inducible ERO1α significantly correlates with poor prognosis and metastasis of HCC and enhances the metastatic ability and EMT via activation of S1PR1/STAT3/VEGF-A signaling [121].
Direct activation of STAT3 by the NPM-ALK chimeric protein, which plays a central pathogenic role in anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL), promotes invasiveness of ALK-positive ALCL through induction of Twist-1 [122]. The kinase activity of IGFR induced by NPM-ALK-IGFR complex activates STAT3 and its downstream proteins (AKT, FKHR) that regulate cell survival [123]. Moreover, NPM–ALK suppresses STAT1-mediated interference with STAT3 signaling by promoting the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway-mediated degradation of STAT1 in a STAT3-dependent manner. Furthermore, the NPM-ALK complex eventually inhibits IFN-γ-mediated STAT1 pathway-induced suppression of tumor growth [124].
JAK/STAT3 signaling also can be induced by oncoproteins, including RPL34 [125], HOXB8 [126], CD146 [127], and Akirin2 [128]. This recently recognized regulation of new oncogenes involved in activating JAK/STAT3/VEGFA, NF-κB, and ERK signaling might provide crucial targets to block the cancer progression.
Recently, it was reported that inhibition of the canonical TGF-β signaling due to loss of SMAD4 might be associated with cancer progression and drug resistance. Loss of SMAD4 induces constitutive activation of STAT3 in pancreatic cancer, which cooperates with non-canonical TGF-β signaling to promote cancer progression [129]. Screening via siRNAs identified STAT3 as a transcription factor, which is required for TGF-β and EGF-induced Snail production. TGF-β decreases the binding of PIAS3 to p-STAT3 through increasing the following: TGF-β-mediated formation of the PIAS3-SMAD3 complex and PIAS3-PAI-1 complex, resulting in Snail production via p-STAT3 [130,131,132]. Induction of stem cell factor (SCF)/c-KIT signaling by binding of SMAD2 to its promoter activates STAT3, which, in turn, induces TGF-β1 expression by binding to STB-2 region of TGF-β1 promoter via a positive feedback loop [133]. Moreover, TGF-β-induced histone acetyltransferase (GCN5) enhances EMT by activation of STAT3 and AKT and induces the transcriptional activity of TGF-β1 by interacting with R-Smads [134,135]. Intracellular signaling components such as receptors, non-receptor kinases, and other proteins instigate cancer-specific pleiotropic responses through JAK/STAT-mediated transcriptional regulation in cancer progression and aggressiveness.
5. Targeting the JAK2/STAT3 Signaling Pathway in EMT
There are multiple intrinsic regulators, which can prevent inappropriately sustained STAT3 activation (Figure 3A). Nitric oxide (NO) acts as a critical protector, and high secretion of NO, which is produced by NO synthase enzymes (NOS), blocks the induction of EMT by inhibiting TGF-β induced STAT3 activation in HCC [136]. Additionally, PPAR-γ and its agonists in combination with other drugs—such as type I interferons, gemcitabine, and COX-2 inhibitors—inhibit the survival of pancreatic cancer cells via IFN-β-induced activation of STAT-3, MAPK, and AKT [137,138].
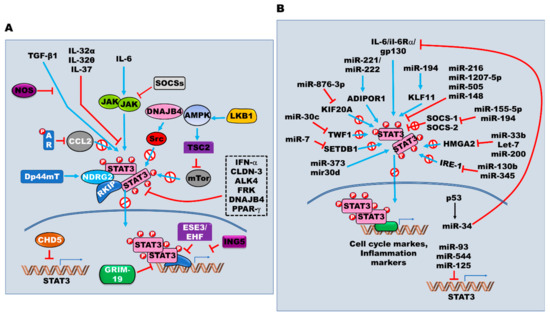
Figure 3.
The regulation of the JAK/STAT3 signaling. (A) The multiple intrinsic proteins also involved in positive or negative regulation of JAK/STAT3 signaling with tyrosine receptors, their cognate ligands, and non-receptor kinases through ubiquitination, acetylation, regulation of STAT3 expression, regulation of STAT3 binding to the promoter of target genes, and direct physical interactions with STAT3. (B) MicroRNAs-mediated regulation of the JAK/STAT3 activation. In addition to being regulated by multiple oncogenes and suppressors, the expression and activation of JAK/STAT3 are directly or indirectly controlled by microRNAs, which are endogenous small non-coding RNAs that function to the regulation of gene expression at transcriptional or post-transcriptional levels.
AMPK has been implicated in the inhibition of tumor proliferation via suppression of STAT3 activation. AMPK suppresses tumor survival through inhibition of mTOR by increasing the expression of p-TSC2, a tumor suppressor gene [139], and leads to the inactivation of AKT and lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 signaling in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) [140]. In addition, activation of the LKB1/AMPK pathway by metformin which is the first-line treatment for type 2 diabetes, suppresses IL-6-induced STAT3 expression and NF-κB activation in various cancers [141,142,143,144].
Tyrosine phosphatase is involved in the negative modulation of STAT3 activity. SHP-1 promotes the inactivation of JAK/STAT3 [145,146], and the STAT3/DNMT1/HDAC1 complex reduces SHP-1 expression by binding to the SHP-1 promoter [147]. Several other proteins negatively regulate JAK/STAT3 activation by inducing JAK degradation. SOCS-1 [148], SOCS-2 [149], and SOCS-3 [150] lead to proliferation and metastasis by suppression of JAK/STAT3 and p38 MAPK activation. In addition, SOCS-2 interacts with IGF1R and inhibits IGF1/IGF1R/JAK/STAT signaling [149].
Some negative regulators inhibit IL-6/JAK/STAT signaling by downregulating the expression of these proteins. ESE3/EHF, ETS transcription factor, inactivates IL6/JAK/STAT3 signaling through the transcriptional repression of IL-6 by direct binding to the IL-6 promoter [151]. Frequently methylated CHD5 also inhibits the invasion of RCC by suppression of oncogenes such as STAT3, epigenetic masters, and stem cell marker expression through direct binding to their promoters [152]. Moreover, apoptosis inducer, ING5, inhibits EGFR and IL-6 production, inactivates JAK/STAT3 and AKT pathways through inactivation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway, and eventually prevents metastasis of lung cancer [153,154].
Alongside the transcriptional repression, critical negative regulation occurs via inhibition of IL-6/JAK/STAT3 activation. Mucosal barrier disruption by loss of CLDN-3 promotes CRC malignancy through induction of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling by activation of IL-6/JAK/STAT3 signaling. In contrast, the upregulation of CLDN-17 activates Tyk2/STAT3 signaling to promote malignancy in HCC [155,156]. In particular, the androgen receptor (AR) decreases macrophage recruitment by reduction of CCL2. Furthermore, AR loss enhances the EMT and invasion of cancer through induction of CCL2/CCR2/STAT3 axis [157]. However, STAT activation upregulates IL-6 and chemokine CCL2 expression, which significantly enhances the induction of EMT [158]. Moreover, high levels of GRIM-19 inhibit hypoxia-induced autophagy in CRC cells by repression of the activation of the STAT3/HIF-1α/VEGF axis under hypoxic conditions [159]. Furthermore, JAK2/STAT3 inactivation by ALK4 and FRK results in reduced cell survival and aggressiveness of different types of cancer. [160,161].
Recent studies have identified that other negative regulators inhibit JAK/STAT3 activation by interfering with the interaction between STAT3 and downstream targets or non-receptor tyrosine kinase. DNA JB4 inhibits Src phosphorylation by direct binding to the SH3 domain of c-Src and suppresses invasion of cancer by disrupting the interaction between Src and Src-downstream targets such as EGFR, FAK, and STAT3 [162]. RKIP inhibits the metastatic potential of cancer through the reduction of IL-6, Raf, or c-Src-mediated STAT3 activation by direct interaction with STAT3 [163,164]. NDRG2 suppresses the invasion abilities of cancer cells through the inhibition of EGF-induced STAT3/Snail signaling by inhibiting the binding of STAT3 to the Snail promoter [165]. Inhibition of IL-6-induced STAT3 activation by Dp44mT-induced NDRG2 attenuates TGF-β1-induced EMT in HCC [166].
Cytokines secreted by either cancer cells or surrounding stromal cells act as negative regulators. For instance, IL-32α and IL-32θ inhibit TGFβ-induced EMT, metastasis, and self-renewal in various cancer cells by inhibition of STAT3 activation [167,168]. Additionally, IL-37b enhances the survival of HCC patients and inhibits HCC progression by suppression of IL-6/STAT3 signaling and Gankyrin expression [169].
6. Link between JAK2/STAT3 Activation and the Transition of Cancer Stem Cells
Cancer stem cells have been proposed to explain cancer progression and therapeutic resistance. Multiple extracellular stimuli and intracellular signaling pathways have been implicated in the activation of the JAK/STAT signaling pathway or in the induction of cross-talk between various JAK/STAT pathways to promote the generation of cancer stem cells and acquisition of drug resistance [170,171]. Of the 28 cytokines and growth factors, OSM is the most potent inducer of CSC properties, and STAT3 activation is essential for OSM-induced EMT and generation of CSCs. Members of the IL-6 cytokine family—including IL-6, CNTF, CT-1, CLCF1, LIF, and OSM—significantly increase STAT3 activation and the subpopulation of CSCs. Additionally, OSM-induced JAK2/STAT3 activation increases Snail and HAS2 levels, which act as CD44 ligands and induce nuclear accumulation of p-SMAD3 by STAT3/SMAD3 complex, and subsequently, facilitate EMT and generation of CSCs [35,172]. The STAT3–SMAD3 complex suppresses TGF-β1-mediated antiproliferative signaling by inhibiting the interaction between SMAD3 and SMAD4 [173]. Moreover, induction and activation of Src by interaction with CD44 promote the survival of cancer cells in the matrix via the activation of integrin β1 in lipid rafts [174]. Additionally, the CD44/acetylated STAT3/p300 complex upregulates STAT3-mediated transcriptional activity of cyclin D1 [175]. After the formation of the CD44–STAT3 complex, STAT3 is activated and gets translocated into the nucleus. Several studies have demonstrated that NF-κB bound to STAT3 induces hTERT expression via binding to the hTERT promoter, which is significantly associated with aggressiveness and poor survival of patients with cancer [176,177]. Furthermore, the CD44/acetylated STAT3 complex increases the expression of stem cell markers (c-Myc, SOX2, and OCT4) [178]; SOX2 induces Slug expression via activation of STAT3/HIF-1α signaling [179]. Besides, the upregulation of IL-6 in CRC-derived mesenchymal stem cells (CC-MSCs) results in enhanced metastasis and survival of patients with CRC; this is attributed to the activation of PI3K/AKT via IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 signaling [180].
Osteopontin (OPN)/integrin complex upregulates the expression of CD44 variants. OPN binding to CD44 enhances metastasis and generation of CSC through activation of STAT3 [181,182,183]. Additionally, OPN as a tumor biomarker is induced through the TM4SF4/GSK3β/β-catenin axis, JAK2/STAT3, and FAK/STAT3 signaling, and is additionally regulated via formation of positive feedback autocrine loop that results in cells acquiring CSC-like properties [183].
JAK/STAT3 activation by positive regulators is involved in drug- or radiation-resistance. CXCR4-mediated STAT3 activation induces gefitinib-resistance and transition into stem-like cancer cells, which possess self-renewal capacity and radiation resistance [184]. Additionally, TM4SF5 expression induces EMT and drug resistance via the activation of FAK and promotion of self-renewal properties in HCC by repressing CD24, and interaction with CD44 to activate c-Src/STAT3/Twit-1/Bim1 signaling to induce sphere formation [185]. Moreover, drug resistance, acquired due to the prolonged trastuzumab treatment of GC, is associated with the remarkable increase in autocrine IL-6 production via IL-6-mediated STAT3 activation. Notably, both activation of JAK/STAT and Notch signaling by IL-6-induce Jagged-1, Hey1, and Hey2, leading to enhanced patient survival, accumulation of CSCs, and drug resistance in cancer [186]. Furthermore, Ras-induced Prx II enhances the self-renewal properties of cancer cells through the activation of VEGFR2/STAT3 signaling in HCC [187].
7. Role of microRNAs and JAK/STAT3 Activation in EMT and Transition into Cancer Stem Cells
7.1. MicroRNAs as Positive Regulators
In addition to JAK2/STAT3 signaling, which is mainly regulated by proteins (positive or negative modulators), the expression and functions of JAK/STAT are also controlled by other regulatory mechanisms. Notably, many studies have established a link between non-coding microRNAs (miRNAs) and JAK/STAT signaling.
JAK/STAT3 signaling induces miRNAs to regulate the target genes. For instance, the loss of p53, IL-6, and LIF induces mTOR and STAT3 activation [188,189,190], leading to the increase in mir-21 levels, thereby inducing tumorigenesis [191], resistance to chemotherapy [192], induction of EMT by upregulation of CDK5 [193], and repression of PIAS3 [194]. Upregulation of miR-96/182/183 in BC patients due to autocrine/paracrine HGH-induced STAT3 and STAT5 activation enables tumor progression by BRMS1L [195]. The levels of miR-143 and miR-145 are increased in response to STAT3 activation. These miRNAs induce EMT by enabling the upregulation of EMT-TFs, Snail, and Slug through TGF-β, and downregulating epithelial cell markers and transcription factors, such as Creb, c-Fos, and Egr1 [196].
miRNAs are upregulated in response to STAT activation, and the JAK/STAT3, in turn, is often activated by miRNAs. miR-221/222 induces the EMT via activation of IL-6-dependent NF-κB and STAT3 through suppression of adiponectin receptor 1 (ADIPOR1) [197,198]. Additionally, miR-373 enhances CRC progression through the upregulation of cell cycle markers (CDK2, CDC2, and CCND2) and inflammation markers (NOS2, TGFβ1, CHI3L1, and TFPI) by induction of p-STAT3 [199]. Moreover, enhanced cell survival and tumorigenesis in BC are dependent on the activation of STAT3 by miR-30d-induced expression of KLF-11 [200].
Besides, increasing the stabilization of STAT3 through SOCS-1 or SOCS-2—both of which are downregulated by miR-155-5p or miR-194—promotes the spread of prostate cancer [201] and is associated with the poor survival of patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) [202].
7.2. MicroRNAs as Negative Regulators
miRNAs lead to the inactivation of the JAK/STAT signaling pathway through several different mechanisms. They act as negative regulators by suppressing the expression of IL-6/JAK/STAT3. miR-93 prevents the generation of CSCs and metastasis through the downregulation of multiple stem cell regulatory genes, including JAK1 and STAT3 [203]. Additionally, p53-induced miR-34a suppresses cancer metastasis by suppressing the expression of IL6R [204]. However, IL-6 or HIF-1A-induce STAT3 and InH3 expression, resulting in the induction of invasion and metastasis of CRC by repression of miR-34a [205]. Moreover, miR-216 inhibits the activation of JAK2/STAT3 signaling by reducing JAK2 expression [206], and miR-544 suppresses the expression of both Bcl6 and STAT3 by direct targeting [207]. Furthermore, miR-26a inhibits metastasis through the downregulation of IL-6 expression by reducing the expression of Lin-28 homolog B (LIN28B), HMGA1, and MITF as a direct target and through the restoration of LIN28B-reduced let7d expression [208,209]. Finally, miR-125a suppresses metastasis and cisplatin resistance in several types of cancer through repression of c-Myc, matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2, and MMP-9 by directly inhibiting STAT3 expression [210,211].
Additionally, miRNAs act as negative regulators by direct or indirect suppression of IL-6/JAK/STAT3 activation. miR-876-3p inhibits glioma progression, including EMT, by inhibiting JAK2/STAT3 activation via suppression of KIF20A expression [212]. GATA3-induced miR-30c decreases TWF1-induced IL-11/STAT3 activation through the downregulation of twinfilin 1 (TWF1) and vimentin (VIM) and correlates with poor survival and endocrine therapy resistance [213]. miR-126 inhibits the progression of osteosarcoma via targeting Zeb1 and inhibition of JAK1/STAT3 activation [214]. miR-7 inhibits SETDB1 expression and suppresses EMT and is involved in the generation of CSCs and dissemination of cancer via the inactivation of SETDB1-induced STAT3 signaling, which results in reduced c-Myc and Twist-1 levels due to the absence of STAT3 binding to the promoters of c-Myc and Twist-1 [215]. miR-33b inhibits EMT through repression of HMGA2 by deactivation of STAT3 [216]. miR-1207-5p, 505, and 148a also suppress cancer metastasis by suppressing the expression of corresponding genes via inhibition of AKT and STAT3 activation [217,218,219].
TCF-4/KIFC1-mediated HMGA1 induces the expression of STAT3, MMP2, and Twist-1 by binding to their promoters [220]. Additionally, HMGA2 directly induces the expression of IL-11, which promotes invasion in a STAT3 activation-dependent manner [221], but upregulation of the let-7 and miR-200 results in marked suppression of their target proteins, such as HMGA2 and Zab1. OSM-induced STAT3 activation restores the expression of HMGA2 and Zab1 through reducing let-7 and miR-200 levels. Moreover, STAT3 activation induces EMT by blocking let-7 maturation via the upregulation of Lin-28, which binds to STAT3 promoter [222].
The upregulation of thyroid hormone (T3) and its receptor (TR) in HCC suppresses miR-130b expression. However, increased miR-130b and miR-345 levels result in the upregulation of interferon regulatory factor 1 (IRF1) via T3/TR, which controls cell migration and invasion and represses the expression of p-mTOR, p-STAT3, p-AKT, and p-ERK1/2 [223,224]. The findings of many studies have highlighted the essential roles played by non-coding miRNAs in the regulation of the JAK/STAT signaling pathway (Figure 3B).
8. Conclusions
Along with its essential role in the progression of cancer, the IL-6/JAK/STAT3 signaling axis incorporates various unexpected components and miRNAs that contribute to JAK/STAT3 activation in cancer. Unpredicted functions of various components and miRNAs that have been identified as new positive or negative regulators of STAT3 may need further investigations, for us to be able to selectively target JAK/STAT3 signaling for cancer therapy. Thus, therapies that target these proteins or miRNAs, which are currently not thoroughly explored, may be implicated in suppressing invasion, dissemination, and transition into CSCs in the tumor microenvironment. Although small RNA-target based therapy, including miRNAs, is challenging due to the broad off-target effects, studies that investigate the use of small RNAs as medical interventions have expanded the preclinical and clinical applications. Recently, the FDA approved Onpattro (patisiran) for polyneuropathy in patients with hereditary amyloidosis; it is the first FDA approval for an siRNA drug. Thus, miRNAs or novel identified regulatory proteins may serve as potential targets in further clinical developments and represent significant conceptual advances in terms of repression of JAK/STAT3 activation in human diseases, including cancer, diabetes, inflammation, and neurodegenerative disorders. Thus, the development of therapeutic strategies based on the targeting of the JAK/STAT3 pathway is of utmost clinical relevance.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Taga, T.; Hibi, M.; Hirata, Y.; Yamasaki, K.; Yasukawa, K.; Matsuda, T.; Hirano, T.; Kishimoto, T. Interleukin-6 triggers the association of its receptor with a possible signal transducer, gp130. Cell 1989, 58, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darnell, J.E., Jr.; Kerr, I.M.; Stark, G.R. Jak-STAT pathways and transcriptional activation in response to IFNs and other extracellular signaling proteins. Science 1994, 264, 1415–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, C.A.; Jones, S.A. IL-6 as a keystone cytokine in health and disease (vol 16, pg 448, 2015). Nat. Immunol. 2017, 18, 1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, S.A.; Jenkins, B.J. Recent insights into targeting the IL-6 cytokine family in inflammatory diseases and cancer. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 773–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinrich, P.C.; Behrmann, I.; Haan, S.; Hermanns, H.M.; Muller-Newen, G.; Schaper, F. Principles of interleukin (IL)-6-type cytokine signalling and its regulation. Biochem. J. 2003, 374, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haan, C.; Kreis, S.; Margue, C.; Behrmann, I. Jaks and cytokine receptors—An intimate relationship. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2006, 72, 1538–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrao, R.; Lupardus, P.J. The Janus Kinase (JAK) FERM and SH2 Domains: Bringing Specificity to JAK-Receptor Interactions. Front. Endocrinol. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babon, J.J.; Lucet, I.S.; Murphy, J.M.; Nicola, N.A.; Varghese, L.N. The molecular regulation of Janus kinase (JAK) activation. Biochem. J. 2014, 462, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darnell, J.E. STATs and gene regulation. Science 1997, 277, 1630–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.K.; Wrzeszczynska, M.H.; Horvath, C.M.; Darnell, J.E. Interacting regions in Stat3 and c-Jun that participate in cooperative transcriptional activation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1999, 19, 7138–7146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Kee, W.H.; Seow, K.T.; Fung, W.; Cao, X.M. The coiled-coil domain of Stat3 is essential for its SH2 domain-mediated receptor binding and subsequent activation induced by epidermal growth factor and interleukin-6. Mol. Cell Biol. 2000, 20, 7132–7139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heim, M.H.; Kerr, I.M.; Stark, G.R.; Darnell, J.E. Contribution of Stat Sh2 Groups to Specific Interferon Signaling by the Jak-Stat Pathway. Science 1995, 267, 1347–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemmann, U.; Gerhartz, C.; Heesel, B.; Sasse, J.; Kurapkat, G.; Grotzinger, J.; Wollmer, A.; Zhong, Z.; Darnell, J.E.; Graeve, L.; et al. Differential activation of acute phase response factor/Stat3 and Stat1 via the cytoplasmic domain of the interleukin 6 signal transducer gp130.2. Src homology SH2 domains define the specificity of STAT factor activation. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 12999–13007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Z.L.; Guan, Y.J.; Chatterjee, D.; Chin, Y.E. Stat3 dimerization regulated by reversible acetylation of a single lysine residue. Science 2005, 307, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Yeh, J.E.; Pinello, L.; Jacob, J.; Chakravarthy, S.; Yuan, G.C.; Chopra, R.; Frank, D.A. Impact of the N-Terminal Domain of STAT3 in STAT3-Dependent Transcriptional Activity. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2015, 35, 3284–3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Pardoll, D.; Jove, R. STATs in cancer inflammation and immunity: A leading role for STAT3. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 798–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, N.J.; Sasser, A.K.; Axel, A.E.; Vesuna, F.; Raman, V.; Ramirez, N.; Oberyszyn, T.M.; Hall, B.M. Interleukin-6 induces an epithelial-mesenchymal transition phenotype in human breast cancer cells. Oncogene 2009, 28, 2940–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.; Kumar, B.; Datta, J.; Teknos, T.N.; Kumar, P. IL-6 promotes head and neck tumor metastasis by inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition via the JAK-STAT3-SNAIL signaling pathway. Mol. Cancer Res. 2011, 9, 1658–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.; Hong, J.; Du, W.; Lin, Y.W.; Ren, L.L.; Wang, Y.C.; Su, W.Y.; Wang, J.L.; Cui, Y.; Wang, Z.H.; et al. Roles of STAT3 and ZEB1 Proteins in E-cadherin Down-regulation and Human Colorectal Cancer Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 5819–5832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Shen, J.; Fang, Z.; Qiao, L.; Feng, R.; Lin, X.; Li, S. Abnormally expressed JunB transactivated by IL-6/STAT3 signaling promotes uveal melanoma aggressiveness via epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Biosci. Rep. 2018, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, A.; Liu, G.; Coleman, I.; Nelson, P.S.; Zhang, M.; Dash, R.; Fisher, P.B.; Plymate, S.R.; Wu, J.D. IL-6 promotes prostate tumorigenesis and progression through autocrine cross-activation of IGF-IR. Oncogene 2011, 30, 2345–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, C.; Su, L.; Shan, J.; Zhu, C.; Liu, L.; Liu, C.; Xu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Bian, X.; Shao, J.; et al. IGF/STAT3/NANOG/Slug Signaling Axis Simultaneously Controls Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Stemness Maintenance in Colorectal Cancer. Stem Cells 2016, 34, 820–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shuai, K.; Horvath, C.M.; Huang, L.H.T.; Qureshi, S.A.; Cowburn, D.; Darnell, J.E. Interferon Activation of the Transcription Factor Stat91 Involves Dimerization through Sh2-Phosphotyrosyl Peptide Interactions. Cell 1994, 76, 821–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, D.L.; Robertson, J.F.R.; Ellis, I.O.; Elston, C.W.; Mcclelland, R.A.; Gee, J.M.W.; Jones, R.J.; Green, C.D.; Cannon, P.; Blamey, R.W.; et al. Estrogen-Regulated Genes in Breast-Cancer - Association of Pliv1 with Lymph-Node Involvement. Eur. J. Cancer 1994, 30, 675–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogstrand, C.; Kille, P.; Ackland, M.L.; Hiscox, S.; Taylor, K.M. A mechanism for epithelial-mesenchymal transition and anoikis resistance in breast cancer triggered by zinc channel ZIP6 and STAT3 (signal transducer and activator of transcription 3). Biochem. J. 2013, 455, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unno, J.; Satoh, K.; Hirota, M.; Kanno, A.; Hamada, S.; Ito, H.; Masamune, A.; Tsukamoto, N.; Motoi, F.; Egawa, S.; et al. LIV-1 enhances the aggressive phenotype through the induction of epithelial to mesenchymal transition in human pancreatic carcinoma cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2009, 35, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhau, H.E.; Odero-Marah, V.; Lue, H.W.; Nomura, T.; Wang, R.; Chu, G.; Liu, Z.R.; Zhou, B.P.; Huang, W.C.; Chung, L.W. Epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) in human prostate cancer: Lessons learned from ARCaP model. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2008, 25, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hendrayani, S.F.; Al-Khalaf, H.H.; Aboussekhra, A. The Cytokine IL-6 Reactivates Breast Stromal Fibroblasts through Transcription Factor STAT3-dependent Up-regulation of the RNA-binding Protein AUF1. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 30962–30976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khalaf, H.H.; Ghebeh, H.; Inass, R.; Aboussekhra, A. Senescent Breast Luminal Cells Promote Carcinogenesis through Interleukin-8-Dependent Activation of Stromal Fibroblasts. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2019, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Ren, G.P.; Wang, T.Y.; Chen, Y.X.; Gong, C.J.; Bai, Y.F.; Wang, B.; Qi, H.Y.; Shen, J.; Zhu, L.J.; et al. Aberrantly expressed Fra-1 by IL-6/STAT3 transactivation promotes colorectal cancer aggressiveness through epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Carcinogenesis 2015, 36, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.Q.; Liu, Q.; Liao, Q.J.; Wu, Q.J.; Sun, B.S.; Yang, Z.X.; Hu, X.Y.; Tan, M.J.; Li, L.K. Interleukin-6/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 promotes prostate cancer resistance to androgen deprivation therapy via regulating pituitary tumor transforming gene 1 expression. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 678–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giladi, N.D.; Ziv-Av, A.; Lee, H.K.; Finniss, S.; Cazacu, S.; Xiang, C.L.; Ben-Asher, H.W.; Decarvalho, A.; Mikkelsen, T.; Poisson, L.; et al. RTVP-1 promotes mesenchymal transformation of glioma via a STAT-3/IL-6-dependent positive feedback loop. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 22680–22697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, X.Q.; Chen, J.; Xie, W.B.; Brown, S.M.; Cai, Y.; Wu, K.C.; Fan, D.M.; Nie, Y.Z.; Yegnasubramanian, S.; Tiedemann, R.L.; et al. Defining UHRF1 Domains that Support Maintenance of Human Colon Cancer DNA Methylation and Oncogenic Properties. Cancer Cell 2019, 35, 633–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollack, V.; Sarkozi, R.; Banki, Z.; Feifel, E.; Wehn, S.; Gstraunthaler, G.; Stoiber, H.; Mayer, G.; Montesano, R.; Strutz, F.; et al. Oncostatin M-induced effects on EMT in human proximal tubular cells: Differential role of ERK signaling. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2007, 293, F1714–F1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junk, D.J.; Bryson, B.L.; Smigiel, J.M.; Parameswaran, N.; Bartel, C.A.; Jackson, M.W. Oncostatin M promotes cancer cell plasticity through cooperative STAT3-SMAD3 signaling. Oncogene 2017, 36, 4001–4013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, R.E.; Martin, B.; Mellor, L.; Jacob, R.B.; Tawara, K.; McDougal, O.M.; Oxford, J.T.; Jorcyk, C.L. Oncostatin M binds to extracellular matrix in a bioactive conformation: Implications for inflammation and metastasis. Cytokine 2015, 72, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucia-Tran, J.A.; Tulkki, V.; Smith, S.; Scarpini, C.G.; Hughes, K.; Araujo, A.M.; Yan, K.Y.M.; Botthof, J.; Perez-Gomez, E.; Quintanilla, M.; et al. Overexpression of the oncostatin-M receptor in cervical squamous cell carcinoma is associated with epithelial-mesenchymal transition and poor overall survival. Br. J. Cancer 2016, 115, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smigiel, J.M.; Parameswaran, N.; Jackson, M.W. Potent EMT and CSC Phenotypes Are Induced By Oncostatin-M in Pancreatic Cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 2017, 15, 478–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.J.; Li, Z.; Wang, C.C.; Pan, T.; Chang, X.Y.; Wang, X.F.; Zhou, Q.; Wu, X.Y.; Li, J.F.; Zhang, J.P.; et al. Oncostatin M receptor, positively regulated by SP1, promotes gastric cancer growth and metastasis upon treatment with Oncostatin M. Gastric Cancer 2019, 22, 955–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.S.; Choi, S.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, M.; Nam, E.S.; Jeong, A.L.; Lee, S.; Han, S.; Lee, M.S.; Lim, J.S.; et al. Interleukin-32beta stimulates migration of MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7cells via the VEGF-STAT3 signaling pathway. Cell. Oncol. (Dordr.) 2013, 36, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.H.; Yang, C.D.; Chen, J.; Liu, J.Y.; Li, P.A.; Shi, Y.; Yu, P.W. Interleukin-23 promotes the migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells by inducing epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via the STAT3 pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 499, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahsnig, C.; Mikula, M.; Petz, M.; Zulehner, G.; Schneller, D.; van Zijl, F.; Huber, H.; Csiszar, A.; Beug, H.; Mikulits, W. ILEI requires oncogenic Ras for the epithelial to mesenchymal transition of hepatocytes and liver carcinoma progression. Oncogene 2009, 28, 638–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekpe-Adewuyi, E.; Lopez-Campistrous, A.; Tang, X.; Brindley, D.N.; McMullen, T.P. Platelet derived growth factor receptor alpha mediates nodal metastases in papillary thyroid cancer by driving the epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 83684–83700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hussey, G.S.; Link, L.A.; Brown, A.S.; Howley, B.V.; Chaudhury, A.; Howe, P.H. Establishment of a TGFbeta-induced post-transcriptional EMT gene signature. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e52624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woosley, A.N.; Dalton, A.C.; Hussey, G.S.; Howley, B.V.; Mohanty, B.K.; Grelet, S.; Dincman, T.; Bloos, S.; Olsen, S.K.; Howe, P.H. TGF beta promotes breast cancer stem cell self-renewal through an ILEI/LIFR signaling axis. Oncogene 2019, 38, 3794–3811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kermorgant, S.; Lehy, T. Glycine-extended gastrin promotes the invasiveness of human colon cancer cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 285, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrand, A.; Kowalski-Chauvel, A.; Bertrand, C.; Pradayrol, L.; Fourmy, D.; Dufresne, M.; Seva, C. Involvement of JAK2 upstream of the PI 3-kinase in cell-cell adhesion regulation by gastrin. Exp. Cell Res. 2004, 301, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborne, N.; Sundseth, R.; Gay, M.D.; Cao, H.; Tucker, R.D.; Nadella, S.; Wang, S.; Liu, X.; Kroemer, A.; Sutton, L.; et al. Vaccine against gastrin, a polyclonal antibody stimulator, decreases pancreatic cancer metastases. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2019, 317, G682–G693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, M.G.; Zheng, J.H.; Hou, K.L.; Wang, J.L.; Chen, X.S.; Lu, X.J.; Bo, J.J.; Xu, C.; Shen, K.W.; Wang, J.H. Role of chemokine receptor CXCR7 in bladder cancer progression. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 84, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, N.A.; Nasser, M.W.; Ahirwar, D.K.; Zhao, H.L.; Miao, Z.H.; Shilo, K.; Ganju, R.K. C-X-C motif chemokine 12/C-X-C chemokine receptor type 7 signaling regulates breast cancer growth and metastasis by modulating the tumor microenvironment. Breast Cancer Res. 2014, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Hoque, M.O.; Wu, F.; Trink, B.; Sidransky, D.; Ratovitski, E.A. Midkine induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition through Notch2/Jak2-Stat3 signaling in human keratinocytes. Cell Cycle 2008, 7, 1613–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratovitski, E.A.; Kotzbauer, P.T.; Milbrandt, J.; Lowenstein, C.J.; Burrow, C.R. Midkine induces tumor cell proliferation and binds to a high affinity signaling receptor associated with JAK tyrosine kinases. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 3654–3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamakura, S.; Oishi, K.; Yoshimatsu, T.; Nakafuku, M.; Masuyama, N.; Gotoh, Y. Hes binding to STAT3 mediates crosstalk between Notch and JAK-STAT signalling. Nat. Cell Biol. 2004, 6, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gungor, C.; Zander, H.; Effenberger, K.E.; Vashist, Y.K.; Kalinina, T.; Izbicki, J.R.; Yekebas, E.; Bockhorn, M. Notch Signaling Activated by Replication Stress-Induced Expression of Midkine Drives Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Chemoresistance in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 5009–5019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.L.; Yan, B.; Guo, H.H.; Qiu, L.; Sun, X.R.; Wang, X.; Shi, Q.; Bao, Y. Effect of midkine on gemcitabine resistance in biliary tract cancer. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 2003–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.F.; Nie, Y.Z.; Lv, M.M.; He, L.F.; Wang, T.T.; Hou, Y.Y. ER beta-Mediated Estradiol Enhances Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition of Lung Adenocarcinoma through Increasing Transcription of Midkine. Mol. Endocrinol. 2012, 26, 1304–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trusolino, L.; Bertotti, A.; Comoglio, P.M. MET signalling: Principles and functions in development, organ regeneration and cancer. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Bio. 2010, 11, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavone, L.M.; Cattaneo, F.; Rea, S.; De Pasquale, V.; Spina, A.; Sauchelli, E.; Mastellone, V.; Ammendola, R. Intracellular signaling cascades triggered by the NK1 fragment of hepatocyte growth factor in human prostate epithelial cell line PNT1A. Cell. Signal. 2011, 23, 1961–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, Y.; Yeganeh, M.; Donates, Y.C.; Tobelaim, W.S.; Chababi, W.; Mayhue, M.; Yoshimura, A.; Ramanathan, S.; Saucier, C.; Ilangumaran, S. Regulation of MET receptor tyrosine kinase signaling by suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 2015, 34, 5718–5728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, Y.; Khan, M.G.M.; Bobbala, D.; Dubois, C.; Ramanathan, S.; Saucier, C.; Ilangumaran, S. Attenuation of MET-mediated migration and invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma cells by SOCS1. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 6639–6649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gujral, T.S.; Chan, M.; Peshkin, L.; Sorger, P.K.; Kirschner, M.W.; MacBeath, G. A noncanonical Frizzled2 pathway regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis. Cell 2014, 159, 844–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Lan, T.; Zhang, W.M.; Dong, L.J.; Kang, N.; Zhang, S.M.; Fu, M.; Liu, B.; Liu, K.T.; Zhan, Q.M. Feed-Forward Reciprocal Activation of PAFR and STAT3 Regulates Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 4198–4210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.Z.; Kong, X.J.; Banerjee, A.; Muniraj, N.; Pandey, V.; Steiner, M.; Perry, J.K.; Zhu, T.; Liu, D.X.; Lobie, P.E. STAT3 alpha Is Oncogenic for Endometrial Carcinoma Cells and Mediates the Oncogenic Effects of Autocrine Human Growth Hormone. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 4133–4145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, H.W.; Hsu, S.C.; Ali-Seyed, M.; Gunduz, M.; Xia, W.; Wei, Y.; Bartholomeusz, G.; Shih, J.Y.; Hung, M.C. Nuclear interaction of EGFR and STAT3 in the activation of the iNOS/NO pathway. Cancer Cell 2005, 7, 575–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colomiere, M.; Ward, A.C.; Riley, C.; Trenerry, M.K.; Cameron-Smith, D.; Findlay, J.; Ackland, L.; Ahmed, N. Cross talk of signals between EGFR and IL-6R through JAK2/STAT3 mediate epithelial-mesenchymal transition in ovarian carcinomas. Br. J. Cancer 2009, 100, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Li, X.; Song, N.; Li, A.D.; Hou, K.Z.; Qu, X.J.; Che, X.F.; Liu, Y.P. Src promotes EGF-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and migration in gastric cancer cells by upregulating ZEB1 and ZEB2 through AKT. Cell. Biol. Int. 2018, 42, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, H.W.; Hsu, S.C.; Xia, W.Y.; Cao, X.Y.; Shih, J.Y.; Wei, Y.K.; Abbruzzese, J.L.; Hortobagyi, G.N.; Hung, M.C. Epidermal growth factor receptor cooperates with signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 to induce epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer cells via up-regulation of TWIST gene expression. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 9066–9076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, P.; Zhang, X.; Paladino, D.; Sengupta, B.; Ahmad, S.; Holloway, R.W.; Ingersoll, S.B.; Turkson, J. Hyperactive EGF receptor, Jaks and Stat3 signaling promote enhanced colony-forming ability, motility and migration of cisplatin-resistant ovarian cancer cells. Oncogene 2012, 31, 2309–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, M.D.; Liang, K.; Lu, Y.; Qiu, S.B.; Fan, Z. Brk/PTK6 cooperates with HER2 and Src in regulating breast cancer cell survival and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2013, 14, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caraglia, M.; Tagliaferri, P.; Marra, M.; Giuberti, G.; Budillon, A.; Gennaro, E.D.; Pepe, S.; Vitale, G.; Improta, S.; Tassone, P.; et al. EGF activates an inducible survival response via the RAS-> Erk-1/2 pathway to counteract interferon-alpha-mediated apoptosis in epidermoid cancer cells. Cell Death Differ. 2003, 10, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccellino, M.; Giuberti, G.; Quagliuolo, L.; Marra, M.; D’Alessandro, A.M.; Fujita, H.; Giovane, A.; Abbruzzese, A.; Caraglia, M. Apoptosis induced by interferon-alpha and antagonized by EGF is regulated by caspase-3-mediated cleavage of gelsolin in human epidermoid cancer cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2004, 201, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thyrell, L.; Arulampalam, V.; Hjortsberg, L.; Farnebo, M.; Grander, D.; Pokrovskaja Tamm, K. Interferon alpha induces cell death through interference with interleukin 6 signaling and inhibition of STAT3 activity. Exp. Cell. Res. 2007, 313, 4015–4024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, N.; Keinan, O.; Selitrennik, M.; Karn, T.; Filipits, M.; Lev, S. PYK2 sustains endosomal-derived receptor signalling and enhances epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.Z.; Gotz, J. Pyk2 is a Novel Tau Tyrosine Kinase that is Regulated by the Tyrosine Kinase Fyn. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2018, 64, 205–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelber, J.A.; Reno, T.; Kaushal, S.; Metildi, C.; Wright, T.; Stoletov, K.; Weems, J.M.; Park, F.D.; Mose, E.; Wang, Y.C.; et al. KRas Induces a Src/PEAK1/ErbB2 Kinase Amplification Loop That Drives Metastatic Growth and Therapy Resistance in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 2554–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croucher, D.R.; Hochgrafe, F.; Zhang, L.X.; Liu, L.X.; Lyons, R.J.; Rickwood, D.; Tactacan, C.M.; Browne, B.C.; Ali, N.; Chan, H.; et al. Involvement of Lyn and the Atypical Kinase SgK269/PEAK1 in a Basal Breast Cancer Signaling Pathway. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 1969–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tactacan, C.M.; Phua, Y.W.; Liu, L.; Zhang, L.X.; Humphrey, E.S.; Cowley, M.; Pinese, M.; Biankin, A.V.; Daly, R.J. The pseudokinase SgK223 promotes invasion of pancreatic ductal epithelial cells through JAK1/Stat3 signaling. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.S.; Lee, W.S.; Jeong, J.; Kim, S.J.; Jin, W. Induction of metastatic potential by TrkB via activation of IL6/JAK2/STAT3 and PI3K/AKT signaling in breast cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 40158–40171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.S.; Jeong, J.; Seo, J.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, S.J.; Jin, W. Dysregulated JAK2 expression by TrkC promotes metastasis potential, and EMT program of metastatic breast cancer. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Zhang, X.T.; Liu, X.L.; Fan, L.; Li, C.; Sun, Y.; Liang, X.H.; Wang, J.B.; Mei, Q.B.; Zhang, F.; et al. WSTF promotes proliferation and invasion of lung cancer cells by inducing EMT via PI3K/Akt and IL-6/STAT3 signaling pathways. Cell. Signal. 2016, 28, 1673–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, F.M.; Azimi, I.; Faville, R.A.; Peters, A.A.; Jalink, K.; Putney, J.W.; Goodhill, G.J.; Thompson, E.W.; Roberts-Thomson, S.J.; Monteith, G.R. Induction of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in breast cancer cells is calcium signal dependent. Oncogene 2014, 33, 2307–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troussard, A.A.; Mawji, N.M.; Ong, C.; Mui, A.; St Arnaud, R.; Dedhar, S. Conditional knock-out of integrin-linked kinase demonstrates an essential role in protein kinase B/Akt activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 22374–22378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shvab, A.; Haase, G.; Ben-Shmuel, A.; Gavert, N.; Brabletz, T.; Dedhar, S.; Ben-Ze’ev, A. Induction of the intestinal stem cell signature gene SMOC-2 is required for L1-mediated colon cancer progression. Oncogene 2016, 35, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchs, B.C.; Fujii, T.; Dorfman, J.D.; Goodwin, J.M.; Zhu, A.X.; Lanuti, M.; Tanabe, K.K. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and integrin-linked kinase mediate sensitivity to epidermal growth factor receptor inhibition in human hepatoma cells. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 2391–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamoto, S.; Yokoyama, S.; Higashi, M.; Yamada, N.; Takao, S.; Yonezawa, S. MUC1 enhances hypoxia-driven angiogenesis through the regulation of multiple proangiogenic factors. Oncogene 2013, 32, 4614–4621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R.; Rajabi, H.; Kosugi, M.; Joshi, M.D.; Alam, M.; Vasir, B.; Kawano, T.; Kharbanda, S.; Kufe, D. MUC1-C Oncoprotein Promotes STAT3 Activation in an Autoinductive Regulatory Loop. Sci. Signal. 2011, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Shen, B.; Jiang, F.; Xia, L.; Fan, T.; Qin, M.; Yang, L.; Guo, J.; Li, Y.; Zhu, M.; et al. TRPP2 Enhances Metastasis by Regulating Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 39, 2203–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimi, I.; Milevskiy, M.J.G.; Kaemmerer, E.; Turner, D.; Yapa, K.T.D.S.; Brown, M.A.; Thompson, E.W.; Roberts-Thomson, S.J.; Monteith, G.R. TRPC1 is a differential regulator of hypoxia-mediated events and Akt signalling in PTEN-deficient breast cancer cells. J. Cell. Sci. 2017, 130, 2292–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Qu, X.Y.; Shao, L.W.; Hu, Y.; Yu, X.; Lan, P.X.; Guo, Q.; Han, Q.J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, C. Pim-3 enhances melanoma cell migration and invasion by promoting STAT3 phosphorylation. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2018, 19, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, N.; Kim, R.K.; Yoo, K.C.; Kim, Y.H.; Cui, Y.H.; Kim, I.G.; Suh, Y.; Lee, S.J. Persistent activation of STAT3 by PIM2-driven positive feedback loop for epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer. Cancer Sci. 2015, 106, 718–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.A.; Liu, X.P.; Lu, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.; Cao, W.H.; Liu, X.Y.; Hu, H.Y.; Wang, H.B. PIM1 is responsible for IL-6-induced breast cancer cell EMT and stemness via c-myc activation. Breast Cancer-Tokyo 2019, 26, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Wu, Y.R.; Yang, H.Y.; Li, X.Z.; Jie, M.M.; Hu, C.J.; Wu, Y.Y.; Yang, S.M.; Yang, Y.B. Prolyl isomerase Pin1: A promoter of cancer and a target for therapy. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.Z.; Lu, K.P. The isomerase PIN1 controls numerous cancer-driving pathways and is a unique drug target. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 463–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lufei, C.; Koh, T.H.; Uchida, T.; Cao, X. Pin1 is required for the Ser727 phosphorylation-dependent Stat3 activity. Oncogene 2007, 26, 7656–7664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryo, A.; Suizu, F.; Yoshida, Y.; Perrem, K.; Liou, Y.C.; Wulf, G.; Rottapel, R.; Yamaoka, S.; Lu, K.P. Regulation of NF-kappaB signaling by Pin1-dependent prolyl isomerization and ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis of p65/RelA. Mol. Cell. 2003, 12, 1413–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faruqi, T.R.; Gomez, D.; Bustelo, X.R.; Bar-Sagi, D.; Reich, N.C. Rac1 mediates STAT3 activation by autocrine IL-6. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 9014–9019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, A.R.; Vikis, H.G.; Stewart, S.; Fanburg, B.L.; Cochran, B.H.; Guan, K.L. Regulation of STAT3 by direct binding to the Rac1 GTPase. Science 2000, 290, 144–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Rao, J.; Zhou, Z.H.; Yao, X.H.; Wu, F.; Yang, J.; Yang, L.; Zhang, X.; Cui, Y.H.; Bian, X.W.; et al. RAC1-GTP promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and invasion of colorectal cancer by activation of STAT3. Lab. Invest. 2018, 98, 989–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, G.S.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, W.S.; Peng, K.; Zhang, Z.C.; Li, X.S.; Xiao, W.D.; Yang, H. Knockdown on aPKC-iota inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition, migration and invasion of colorectal cancer cells through Rac1-JNK pathway. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2019, 107, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiota, M.; Bishop, J.L.; Nip, K.M.; Zardan, A.; Takeuchi, A.; Cordonnier, T.; Beraldi, E.; Bazov, J.; Fazli, L.; Chi, K.; et al. Hsp27 Regulates Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition, Metastasis, and Circulating Tumor Cells in Prostate Cancer. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 3109–3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.W.; Li, Q.; Xu, Q.Q.; Wang, T.E.; Wang, Q.W. TMPRSS4 Upregulates TWIST1 Expression through STAT3 Activation to Induce Prostate Cancer Cell Migration. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2018, 24, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fu, D.H.; Chen, Y.J.; Su, J.; Wang, Y.T.; Li, X.; Zhai, W.; Niu, Y.J.; Yue, D.; Geng, H. G3BP1 promotes tumor progression and metastasis through IL-6/G3BP1/STAT3 signaling axis in renal cell carcinomas. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.W.; Li, K.Q.; Yu, C.F.; Lv, B.F.; Zhao, N.; Deng, J.H.; Cao, L.L.; Huang, H.; Yin, A.; Shi, T.P.; et al. In vitro study of FUZ as a novel potential therapeutic target in non-small-cell lung cancer. Life Sci. 2018, 197, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.H.; Cao, J.Z.; Zhang, D.; Liao, B.; Zhong, W.M.; Lu, J.; Zhao, H.W.; Zhang, J.X.; Tong, Z.T.; Fan, S.; et al. EIF5A2 predicts outcome in localised invasive bladder cancer and promotes bladder cancer cell aggressiveness in vitro and in vivo. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 1767–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogata, H.; Chinen, T.; Yoshida, T.; Kinjyo, I.; Takaesu, G.; Shiraishi, H.; Iida, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Yoshimura, A. Loss of SOCS3 in the liver promotes fibrosis by enhancing STAT3-mediated TGF-beta1 production. Oncogene 2006, 25, 2520–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarris, M.E.; Moulos, P.; Haroniti, A.; Giakountis, A.; Talianidis, I. Smyd3 Is a Transcriptional Potentiator of Multiple Cancer-Promoting Genes and Required for Liver and Colon Cancer Development. Cancer Cell 2016, 29, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Lu, L.; Dong, Q.Z.; Yu, G.Y.; Chen, J.H.; Qin, L.X.; Wang, L.X.; Zhu, W.W.; Jia, H.L. Elevated G6PD expression contributes to migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Acta Biochem. Biophys. Sin. 2018, 50, 370–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Liu, Q.; Zheng, S.; Liu, T.; Tan, D.; Lu, X. PKM2-regulated STAT3 promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression via TGF-beta1-induced EMT. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 11539–11550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, A.B.; Shen, X.H.; Ma, Q.; Cao, J.J.; von Gise, A.; Zhou, P.Z.; Wang, G.; Marquez, V.E.; Orkin, S.H.; Pu, W.T. PRC2 directly methylates GATA4 and represses its transcriptional activity. Genes Dev. 2012, 26, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.M.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, H.; Kim, K.; Park, H.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, I.S.; Kim, J.; Lee, M.; et al. EZH2 Generates a Methyl Degron that Is Recognized by the DCAF1/DDB1/CUL4 E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Complex. Mol. Cell. 2012, 48, 572–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Kim, M.; Woo, D.H.; Shin, Y.; Shin, J.; Chang, N.; Oh, Y.T.; Kim, H.; Rheey, J.; Nakano, I.; et al. Phosphorylation of EZH2 Activates STAT3 Signaling via STAT3 Methylation and Promotes Tumorigenicity of Glioblastoma Stem-like Cells. Cancer Cell 2013, 23, 839–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.F.; Chen, W.C.; Chang, Y.J.; Wu, C.F.; Wu, C.T. Role of DNA methyltransferase 1 in hormone-resistant prostate cancer. J. Mol. Med. (Berl.) 2010, 88, 953–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.T.; Hsieh, C.C.; Lin, C.C.; Chen, W.C.; Hong, J.H.; Chen, M.F. Significance of IL-6 in the transition of hormone-resistant prostate cancer and the induction of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (vol 90, pg 1343, 2012). J. Mol. Med. 2013, 91, 649–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bizzarro, V.; Belvedere, R.; Milone, M.R.; Pucci, B.; Lombardi, R.; Bruzzese, F.; Popolo, A.; Parente, L.; Budillon, A.; Petrella, A. Annexin A1 is involved in the acquisition and maintenance of a stem cell-like/aggressive phenotype in prostate cancer cells with acquired resistance to zoledronic acid. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 25074–25092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, J.; Tian, R.; Ji, W.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, Y.; Song, W.J.; Zhang, F.; Niu, R.F. Anxa2 binds to STAT3 and promotes epithelial to mesenchymal transition in breast cancer cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 30975–30992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, M.R.; Barcellos-de-Souza, P.; Sousa-Squiavinato, A.C.M.; Fernandes, P.V.; de Oliveira, I.M.; Boroni, M.; Morgado-Diaz, J.A. Annexin A2 overexpression associates with colorectal cancer invasiveness and TGF-ss induced epithelial mesenchymal transition via Src/ANXA2/STAT3. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.H.; Jeong, K.J.; Shin, S.C.; Kang, J.; Park, C.G.; Lee, H.Y. STAT3 mediates TGF-beta1-induced TWIST1 expression and prostate cancer invasion. Cancer Lett. 2013, 336, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.H.; Choi, M.J.; Jeong, K.J.; Kim, J.J.; Hwang, M.H.; Shin, S.C.; Park, C.G.; Lee, H.Y. A ROS/STAT3/HIF-1alpha signaling cascade mediates EGF-induced TWIST1 expression and prostate cancer cell invasion. Prostate 2014, 74, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.E.; Lee, H.G.; Cho, I.H.; Chung, D.H.; Yoon, S.H.; Yang, Y.M.; Lee, J.W.; Choi, S.; Park, J.W.; Ye, S.K.; et al. STAT3 is a potential modulator of HIF-1-mediated VEGF expression in human renal carcinoma cells. FASEB J. 2005, 19, 1296–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.E.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, C.S.; Shin, Y.J.; Kim, Y.N.; Kang, G.H.; Kim, T.Y.; Juhnn, Y.S.; Kim, S.J.; Park, J.W.; et al. STAT3 inhibits the degradation of HIF-1alpha by pVHL-mediated ubiquitination. Exp. Mol. Med. 2008, 40, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.K.; Yang, C.; Yu, F.; Ding, W.B.; Hu, Y.C.; Cheng, F.; Zhang, F.; Guan, B.G.; Wang, X.H.; Lu, L.; et al. Endoplasmic reticulum resident oxidase ERO1-Lalpha promotes hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis and angiogenesis through the S1PR1/STAT3/VEGF-A pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, P.; Wu, F.; Li, M.; Sharon, D.; Ingham, R.J.; Hitt, M.; McMullen, T.P.; Lai, R. Aberrant expression of the transcriptional factor Twist1 promotes invasiveness in ALK-positive anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Cell. Signal. 2012, 24, 852–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, P.; Lai, R.; Lin, Q.; Iqbal, A.S.; Young, L.C.; Kwak, L.W.; Ford, R.J.; Amin, H.M. IGF-IR tyrosine kinase interacts with NPM-ALK oncogene to induce survival of T-cell ALK+ anaplastic large-cell lymphoma cells. Blood 2009, 114, 360–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.S.; Molavi, O.; Zhang, H.F.; Gupta, N.; Alshareef, A.; Bone, K.M.; Gopal, K.; Wu, F.; Lewis, J.T.; Douglas, D.N.; et al. STAT1 is phosphorylated and downregulated by the oncogenic tyrosine kinase NPM-ALK in ALK-positive anaplastic large-cell lymphoma. Blood 2015, 126, 336–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, P.G.; Wang, L.; Liu, J.H.; Mao, P.; Li, R.C.; Jiang, H.T.; Lou, M.; Xu, M.; Yu, X. Knockdown of RPL34 inhibits the proliferation and migration of glioma cells through the inactivation of JAK/STAT3 signaling pathway. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 3259–3267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Lin, F.; Sun, X.; Jiang, L.; Mao, R.; Zhou, S.; Shang, W.; Bi, R.; Lu, F.; Li, S. HOXB8 enhances the proliferation and metastasis of colorectal cancer cells by promoting EMT via STAT3 activation. Cancer Cell. Int. 2019, 19, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xiong, C.; Liu, Z.; Xu, Q.; Feng, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Yan, X. CD146 mediates an E-cadherin-to-N-cadherin switch during TGF-beta signaling-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Lett. 2018, 430, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, K.M.; Xu, Y.; Kang, P.C.; Qin, W.; Cai, H.L.; Wang, H.; Ji, D.L.; Jiang, X.M.; Li, J.L.; Li, Z.L.; et al. Akirin2 is modulated by miR-490-3p and facilitates angiogenesis in cholangiocarcinoma through the IL-6/STAT3/VEGFA signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Venkatasubbarao, K.; Lazor, J.W.; Sperry, J.; Jin, C.; Cao, L.; Freeman, J.W. Inhibition of STAT3 Tyr705 phosphorylation by Smad4 suppresses transforming growth factor beta-mediated invasion and metastasis in pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 4221–4228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitoh, M.; Endo, K.; Furuya, S.; Minami, M.; Fukasawa, A.; Imamura, T.; Miyazawa, K. STAT3 integrates cooperative Ras and TGF-beta signals that induce Snail expression. Oncogene 2016, 35, 1049–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, U.; Suarez, A.A.; Naidu, S.; Wallbillich, J.J.; Bixel, K.; Wanner, R.A.; Bice, J.; Kladney, R.D.; Lester, J.; Karlan, B.Y.; et al. STAT3/PIAS3 Levels Serve as “Early Signature” Genes in the Development of High-Grade Serous Carcinoma from the Fallopian Tube. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 1739–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Lin, B.W.; Chen, X.L.; Zhang, B.L.; Xiao, X.J.; Shi, J.S.; Lin, J.D.; Chen, X. PAI-1/PIAS3/Stat3/miR-34a forms a positive feedback loop to promote EMT-mediated metastasis through Stat3 signaling in Non-small cell lung cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 493, 1464–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas, A.; Zhang, P.; Wang, Y.; Foo, W.C.; Munoz, N.M.; Xiao, L.; Wang, J.; Gores, G.J.; Hung, M.C.; Blechacz, B. A Positive TGF-beta/c-KIT Feedback Loop Drives Tumor Progression in Advanced Primary Liver Cancer. Neoplasia 2016, 18, 371–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahata, K.; Hayashi, M.; Asaka, M.; Hellman, U.; Kitagawa, H.; Yanagisawa, J.; Kato, S.; Imamura, T.; Miyazono, K. Regulation of transforming growth factor-beta and bone morphogenetic protein signalling by transcriptional coactivator GCN5. Genes Cells 2004, 9, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Pang, A.; Li, Y. Function of GCN5 in the TGF-beta1-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 3955–3963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.; Wang, X.; Lei, W.; Min, L.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X.; Song, J. Nitric oxide suppresses transforming growth factor-beta1-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and apoptosis in mouse hepatocytes. Hepatology 2009, 50, 1577–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitale, G.; Zappavigna, S.; Marra, M.; Dicitore, A.; Meschini, S.; Condello, M.; Arancia, G.; Castiglioni, S.; Maroni, P.; Bendinelli, P.; et al. The PPAR-gamma agonist troglitazone antagonizes survival pathways induced by STAT-3 in recombinant interferon-beta treated pancreatic cancer cells. Biotechnol. Adv. 2012, 30, 169–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dicitore, A.; Caraglia, M.; Colao, A.; Zappavigna, S.; Mari, D.; Hofland, L.J.; Persani, L.; Vitale, G. Combined treatment with PPAR-gamma agonists in pancreatic cancer: A glimmer of hope for cancer therapy? Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2013, 13, 460–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoki, K.; Zhu, T.Q.; Guan, K.L. TSC2 mediates cellular energy response to control cell growth and survival. Cell 2003, 115, 577–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H.; Hsu, E.C.; Guh, J.H.; Yang, H.C.; Wang, D.S.; Kulp, S.K.; Shapiro, C.L.; Chen, C.S. Targeting Energy Metabolic and Oncogenic Signaling Pathways in Triple-negative Breast Cancer by a Novel Adenosine Monophosphate-activated Protein Kinase (AMPK) Activator. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 39247–39258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Ke, C.; Tang, Q.; Dong, H.; Zheng, X.; Lin, W.; Ke, J.; Huang, J.; Jeung, S.C.J.; Zhang, H. Metformin promotes autophagy and apoptosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by downregulating Stat3 signaling. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.C.; Yeh, H.H.; Huang, W.L.; Yan, J.J.; Lai, W.W.; Su, W.P.; Chen, H.H.W.; Su, W.C. Metformin Enhances Cisplatin Cytotoxicity by Suppressing Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription-3 Activity Independently of the Liver Kinase B1-AMP-Activated Protein Kinase Pathway. Am. J. Resp. Cell. Mol. 2013, 49, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, W.; Zheng, X.; Lin, Y.; Yang, C.S.; Xu, Q.; Carpizo, D.; Huang, H.R.; DiPaola, R.S.; Tan, X.L. Metformin combined with aspirin significantly inhibit pancreatic cancer cell growth in vitro and in vivo by suppressing anti-apoptotic proteins Mcl-1 and Bcl-2. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 21208–21224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esparza-Lopez, J.; Alvarado-Munoz, J.F.; Escobar-Arriaga, E.; Ulloa-Aguirre, A.; de Jesus Ibarra-Sanchez, M. Metformin reverses mesenchymal phenotype of primary breast cancer cells through STAT3/NF-kappaB pathways. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Morales, L.D.; Jang, I.S.; Cho, Y.Y.; Kim, D.J. Protein Tyrosine Phosphatases as Potential Regulators of STAT3 Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.T.; Su, J.C.; Liu, C.Y.; Shiau, C.W.; Chen, K.F. Alteration of SHP-1/p-STAT3 Signaling: A Potential Target for Anticancer Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, H.Y.; Marzec, M.; Raghunath, P.N.; Nagasawa, T.; Wasik, M.A. STAT3- and DNA methyltransferase 1-mediated epigenetic silencing of SHP-1 tyrosine phosphatase tumor suppressor gene in malignant T lymphocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 6948–6953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souma, Y.; Nishida, T.; Serada, S.; Iwahori, K.; Takahashi, T.; Fujimoto, M.; Ripley, B.; Nakajima, K.; Miyazaki, Y.; Mori, M.; et al. Antiproliferative effect of SOCS-1 through the suppression of STAT3 and p38 MAPK activation in gastric cancer cells. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 131, 1287–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Z.L.; Wang, N.; Chen, J.Z.; Zhang, X.; Guo, M.; Zhong, L.J.; Wang, Q. Suppressor of cytokine signalling-2 limits IGF1R-mediated regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in lung adenocarcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuwirt. Suppressor of cytokine signalling-3 is up-regulated by androgen in prostate cancer cell lines and inhibits androgen-mediated proliferation and secretion (vol 14, pg 1007, 2007). Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2008, 15, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albino, D.; Civenni, G.; Rossi, S.; Mitra, A.; Catapano, C.V.; Carbone, G.M. The ETS factor ESE3/EHF represses IL-6 preventing STAT3 activation and expansion of the prostate cancer stem-like compartment. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 76756–76768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Z.F.; Li, L.L.; Huang, X.; Jin, J.; Huang, S.M.; Zhang, Q.; Tao, Q. The epigenetic modifier CHD5 functions as a novel tumor suppressor for renal cell carcinoma and is predominantly inactivated by promoter CpG methylation. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 21618–21630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.L.; Zhang, X.T.; Meng, J.; Zhang, H.F.; Zhao, Y.; Li, C.; Sun, Y.; Mei, Q.B.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, T. ING5 knockdown enhances migration and invasion of lung cancer cells by inducing EMT via EGFR/PI3K/Akt and IL-6/STAT3 signaling pathways. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 54265–54276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.L.; Meng, J.; Zhang, X.T.; Liang, X.H.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, G.R.; Zhang, T. ING5 inhibits lung cancer invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition by inhibiting the WNT/beta-catenin pathway. Thorac. Cancer 2019, 10, 848–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R.; Kumar, B.; Chen, Z.; Chen, X.; Muller, D.; Lele, S.M.; Washington, M.K.; Batra, S.K.; Dhawan, P.; Singh, A.B. Loss of claudin-3 expression induces IL6/gp130/Stat3 signaling to promote colon cancer malignancy by hyperactivating Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Oncogene 2017, 36, 6592–6604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.M.; Feng, L.S.; Cui, J.W. Increased expression of claudin-17 promotes a malignant phenotype in hepatocyte via Tyk2/Stat3 signaling and is associated with poor prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Diagn. Pathol. 2018, 13, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izumi, K.; Fang, L.Y.; Mizokami, A.; Namiki, M.; Li, L.; Lin, W.J.; Chang, C. Targeting the androgen receptor with siRNA promotes prostate cancer metastasis through enhanced macrophage recruitment via CCL2/CCR2-induced STAT3 activation. Embo Mol. Med. 2013, 5, 1383–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Gao, Q.; Han, S.Q.; Pan, F.; Fan, W. The CCL2/CCR2 axis enhances IL-6-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition by cooperatively activating STAT3-Twist signaling. Tumor Biol. 2015, 36, 973–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chu, D.K.; Kawamura, T.; Tanaka, K.; He, S.X. GRIM-19 repressed hypoxia-induced invasion and EMT of colorectal cancer by repressing autophagy through inactivation of STAT3/HIF-1 signaling axis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 12800–12808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.J.; Fan, B.; Xiao, Z.Z. Overexpression of ALK4 inhibits cell proliferation and migration through the inactivation of JAK/STAT3 signaling pathway in glioma. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 98, 440–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunbolude, Y.; Dai, C.L.; Bagu, E.T.; Goel, R.K.; Miah, S.; MacAusland-Berg, J.; Ng, C.Y.; Chibbar, R.; Napper, S.; Raptis, L.; et al. FRK inhibits breast cancer cell migration and invasion by suppressing epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 113034–113065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.H.; Chang, W.H.; Su, K.Y.; Ku, W.H.; Chang, G.C.; Hong, Q.S.; Hsiao, Y.J.; Chen, H.C.; Chen, H.Y.; Wu, R.; et al. HLJ1 is an endogenous Src inhibitor suppressing cancer progression through dual mechanisms. Oncogene 2016, 35, 5674–5685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousuf, S.; Duan, M.; Moen, E.L.; Cross-Knorr, S.; Brilliant, K.; Bonavida, B.; LaValle, T.; Yeung, K.C.; Al-Mulla, F.; Chin, E.; et al. Raf kinase inhibitor protein (RKIP) blocks signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) activation in breast and prostate cancer. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.Y.; Yi, H.M.; Yi, H.; Xiao, T.; Qu, J.Q.; Yuan, L.; Zhu, J.F.; Li, J.Y.; Wang, Y.Y.; Li, L.N.; et al. Reduction of RKIP expression promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma invasion and metastasis by activating Stat3 signaling. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 16422–16436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.J.; Lim, J.; Yang, Y.; Lee, M.S.; Lim, J.S. N-myc downstream-regulated gene 2 (NDRG2) suppresses the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in breast cancer cells via STAT3/Snail signaling. Cancer Lett. 2014, 354, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.B.; Yin, D.L.; Xie, C.M.; Zheng, T.S.; Liang, Y.J.; Hong, X.H.; Lu, Z.Y.; Song, X.; Song, R.P.; Yang, H.Y.; et al. The iron chelator Dp44mT inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis via N-Myc downstream-regulated gene 2 (NDRG2)/gp130/STAT3 pathway. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 8478–8491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bak, Y.; Kwon, T.; Bak, I.S.; Hong, J.; Yu, D.Y.; Yoon, D.Y. IL-32theta inhibits stemness and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of cancer stem cells via the STAT3 pathway in colon cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 7307–7317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, S.; Su, J.; Chu, G.; You, H.; Chen, Z.; Sun, H.; Chen, B.; Zhou, M. Interleukin-32alpha inactivates JAK2/STAT3 signaling and reverses interleukin-6-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition, invasion, and metastasis in pancreatic cancer cells. OncoTargets Ther. 2016, 9, 4225–4237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, X.Y.; Zheng, D.F.; Shen, A.; Gu, H.T.; Wei, X.F.; Mou, T.; Zhang, J.B.; Liu, R. IL-37b suppresses epithelial mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting IL-6/STAT3 signaling. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Dis. Int. 2018, 17, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibue, T.; Weinberg, R.A. EMT, CSCs, and drug resistance: The mechanistic link and clinical implications. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 611–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongre, A.; Weinberg, R.A. New insights into the mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and implications for cancer. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2019, 20, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryson, B.L.; Junk, D.J.; Cipriano, R.; Jackson, M.W. STAT3-mediated SMAD3 activation underlies Oncostatin M-induced Senescence. Cell Cycle 2017, 16, 319–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Yu, Y.; Sun, C.; Liu, T.; Liang, T.; Zhan, L.; Lin, X.; Feng, X.H. STAT3 selectively interacts with Smad3 to antagonize TGF-beta signalling. Oncogene 2016, 35, 4388–4398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.L.; Wang, M.J.; Sudhir, P.R.; Chen, J.Y. CD44 engagement promotes matrix-derived survival through the CD44-Src-integrin axis in lipid rafts. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2008, 28, 5710–5723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.L.; Wang, M.J.; Chen, J.Y. Acetylation and activation of STAT3 mediated by nuclear translocation of CD44. J. Cell. Biol. 2009, 185, 949–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyo, S.; Takakura, M.; Fujiwara, T.; Inoue, M. Understanding and exploiting hTERT promoter regulation for diagnosis and treatment of human cancers. Cancer Sci. 2008, 99, 1528–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, S.S.; Aroh, C.; Vadgama, J.V. Constitutive Activation of STAT3 Signaling Regulates hTERT and Promotes Stem Cell-Like Traits in Human Breast Cancer Cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.J.; Lai, H.M.; Chang, Y.W.; Chen, G.Y.; Lee, J.L. Direct reprogramming of stem cell properties in colon cancer cells by CD44. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 3186–3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Teng, C.; Huang, W.; Peng, J.; Wang, C. SOX2 Promotes the Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition of Esophageal Squamous Cells by Modulating Slug Expression through the Activation of STAT3/HIF-alpha Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 21643–21657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.C.; Hu, F.Y.; Li, G.; Li, G.D.; Yang, X.; Liu, L.; Zhang, R.S.; Zhang, B.X.; Feng, Y.D. Human colorectal cancer-derived mesenchymal stem cells promote colorectal cancer progression through IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 signaling. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wai, P.Y.; Kuo, P.C. Osteopontin: Regulation in tumor metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2008, 27, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kothari, A.N.; Arffa, M.L.; Chang, V.; Blackwell, R.H.; Syn, W.K.; Zhang, J.; Mi, Z.; Kuo, P.C. Osteopontin-A Master Regulator of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. J. Clin. Med. 2016, 5, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.I.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Cho, E.W.; Kim, I.G. Osteopontin production by TM4SF4 signaling drives a positive feedback autocrine loop with the STAT3 pathway to maintain cancer stem cell-like properties in lung cancer cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 101284–101297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, M.J.; Rho, J.K.; Kim, Y.M.; Jung, J.E.; Jin, Y.B.; Ko, Y.G.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, J.C.; Park, M.J. Upregulation of CXCR4 is functionally crucial for maintenance of stemness in drug-resistant non-small cell lung cancer cells. Oncogene 2013, 32, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.; Na, J.; Ryu, J.; Kim, H.J.; Nam, S.H.; Kang, M.; Jung, J.W.; Lee, M.S.; Song, H.E.; Choi, J.; et al. Interaction of tetraspan(in) TM4SF5 with CD44 promotes self-renewal and circulating capacities of hepatocarcinoma cells. Hepatology 2015, 61, 1978–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.Y.; Guo, L.; Liu, D.; Sun, L.M.; Chen, H.Y.; Deng, Q.; Liu, Y.J.; Yu, M.; Ma, Y.F.; Guo, N.; et al. Acquisition of resistance to trastuzumab in gastric cancer cells is associated with activation of IL-6/STAT3/Jagged-1/Notch positive feedback loop. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 5072–5087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, T.; Bak, Y.; Park, Y.H.; Jang, G.B.; Nam, J.S.; Yoo, J.E.; Park, Y.N.; Bak, I.S.; Kim, J.M.; Yoon, D.Y.; et al. Peroxiredoxin II Is Essential for Maintaining Stemness by Redox Regulation in Liver Cancer Cells. Stem Cells 2016, 34, 1188–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.L.; Liu, M.R.; Wang, Y.M.; Mo, Z.Q.; Bi, X.K.; Liu, Z.R.; Fan, Y.M.; Chen, X.; Wu, C.Y. Re-expression of miR-21 contributes to migration and invasion by inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition consistent with cancer stem cell characteristics in MCF-7 cells. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2012, 363, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, F.; Xu, Y.; Ling, M.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, W.C.; Liang, X.; Jiang, R.R.; Wang, B.R.; Bian, Q.; Liu, Q.Z. Arsenite evokes IL-6 secretion, autocrine regulation of STAT3 signaling, and miR-21 expression, processes involved in the EMT and malignant transformation of human bronchial epithelial cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 2013, 273, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.T.; Zhao, Y.H.; Zhang, C.; Li, J.; Liu, Z.; Liu, J.; Hu, W.W. Leukemia inhibitory factor promotes EMT through STAT3-dependent miR-21 induction. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 3777–3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bornachea, O.; Santos, M.; Martinez-Cruz, A.B.; Garcia-Escudero, R.; Duenas, M.; Costa, C.; Segrelles, C.; Lorz, C.; Buitrago, A.; Saiz-Ladera, C.; et al. EMT and induction of miR-21 mediate metastasis development in Trp53-deficient tumours. Sci. Rep.UK 2012, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Mattos-Arruda, L.; Bottai, G.; Nuciforo, P.G.; Di Tommaso, L.; Giovannetti, E.; Peg, V.; Losurdo, A.; Perez-Garcia, J.; Masci, G.; Corsi, F.; et al. MicroRNA-21 links epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and inflammatory signals to confer resistance to neoadjuvant trastuzumab and chemotherapy in HER2-positive breast cancer patients. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 37269–37280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.S.; Zhou, X.; Huang, Y.Y.; Kong, L.P.; Mei, M.; Guo, W.Y.; Zhao, M.H.; Ren, Y.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, L. Targeting STAT3/miR-21 axis inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition via regulating CDK5 in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, S.; Coulter, D.W.; Gray, S.D.; Sughroue, J.A.; Roychoudhury, S.; McIntyre, E.M.; Chaturvedi, N.K.; Bhakat, K.K.; Joshi, S.S.; McGuire, T.R.; et al. Suppression of STAT3 NH2-terminal domain chemosensitizes medulloblastoma cells by activation of protein inhibitor of activated STAT3 via de-repression by microRNA-21. Mol. Carcinogen. 2018, 57, 536–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.J.; Qian, P.X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, M.; Wang, H.; Wu, M.M.; Kong, X.J.; Tan, S.; Ding, K.S.; Perry, J.K.; et al. Autocrine/Paracrine Human Growth Hormone-stimulated MicroRNA 96-182-183 Cluster Promotes Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Invasion in Breast Cancer. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 13812–13829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avalle, L.; Incarnato, D.; Savino, A.; Gai, M.; Marino, F.; Pensa, S.; Barbieri, I.; Stadler, M.B.; Provero, P.; Oliviero, S.; et al. MicroRNAs-143 and-145 induce epithelial to mesenchymal transition and modulate the expression of junction proteins. Cell Death Differ. 2017, 24, 1750–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.K.; Lin, H.Y.; Dou, X.W.; Chen, M.; Wei, X.L.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Wu, Y.; Chen, C.F.; Bai, J.W.; Xiao, Y.S.; et al. MiR-221/222 promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition by targeting Notch3 in breast cancer cell lines. Npj Breast Cancer 2018, 4, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Li, M.; Hu, S.B.; Cheng, X.; Gao, Y.; Jiang, S.; Yu, Q.H.; Zhang, C.; Sun, P.; Xian, W.J.; et al. MiR-221 mediates the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting AdipoR1. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 103, 1054–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyking, A.; Reis, H.; Frank, M.; Gerken, G.; Schmid, K.W.; Cario, E. MiR-205 and MiR-373 Are Associated with Aggressive Human Mucinous Colorectal Cancer. PLoS ONE 2016, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Wang, Y.; Guo, G.; Li, L.; Dou, D.; Ge, X.; Lv, P.; Wang, F.; Gu, Y. microRNA-30d mediated breast cancer invasion, migration, and EMT by targeting KLF11 and activating STAT3 pathway. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 8138–8145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, R.; Gregory, P.A.; Fernandes, R.C.; Denis, I.; Wang, Q.; Townley, S.L.; Zhao, S.G.; Hanson, A.R.; Pickering, M.A.; Armstrong, H.K.; et al. MicroRNA-194 Promotes Prostate Cancer Metastasis by Inhibiting SOCS2. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 1021–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baba, O.; Hasegawa, S.; Nagai, H.; Uchida, F.; Yamatoji, M.; Kanno, N.I.; Yamagata, K.; Sakai, S.; Yanagawa, T.; Bukawa, H. MicroRNA-155-5p is associated with oral squamous cell carcinoma metastasis and poor prognosis. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2016, 45, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.L.; Patel, S.H.; Ginestier, C.; Ibarra, I.; Martin-Trevino, R.; Bai, S.M.; McDermott, S.P.; Shang, L.; Ke, J.; Ou, S.J.; et al. MicroRNA93 Regulates Proliferation and Differentiation of Normal and Malignant Breast Stem Cells. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rokavec, M.; Oner, M.G.; Li, H.; Jackstadt, R.; Jiang, L.; Lodygin, D.; Kaller, M.; Horst, D.; Ziegler, P.K.; Schwitalla, S.; et al. IL-6R/STAT3/miR-34a feedback loop promotes EMT-mediated colorectal cancer invasion and metastasis. J. Clin. Invest. 2014, 124, 1853–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Rokavec, M.; Jiang, L.; Horst, D.; Hermeking, H. Antagonistic Effects of p53 and HIF1A on microRNA-34a Regulation of PPP1R11 and STAT3 and Hypoxia-induced Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 505–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Yang, S.; Wu, Y.; Fang, X.; Wang, Y.; Song, Y.; Han, T. MicroRNA-216a inhibits the metastasis of gastric cancer cells by targeting JAK2/STAT3-mediated EMT process. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 88870–88881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.Z.; Wang, S.Y.; Zhu, J.H.; Yang, Q.F.; Dong, H.M.; Huang, J.K. MicroRNA-544 down-regulates both Bcl6 and Stat3 to inhibit tumor growth of human triple negative breast cancer. Biol. Chem. 2016, 397, 1087–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, H.; Yang, C.; Yang, Y. MicroRNA-26a inhibits the growth and invasiveness of malignant melanoma and directly targets on MITF gene. Cell Death Discov. 2017, 3, 17028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Y.; Chang, J.T.; Ho, Y.F.; Shyu, A.B. MiR-26 down-regulates TNF-alpha/NF-kappaB signalling and IL-6 expression by silencing HMGA1 and MALT1. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 3772–3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Cui, H.; Xu, X.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, X.; Kang, L.; Han, B.; Meng, J.; Yan, Z.; Yan, X.; et al. MiR-125a suppresses tumor growth, invasion and metastasis in cervical cancer by targeting STAT3. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 25266–25280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Ma, K.; Yang, S.J.; Zhang, X.S.; Wang, F.; Zhang, X.Q.; Liu, H.T.; Fan, Q.X. MicroRNA-125a-5p enhances the sensitivity of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells to cisplatin by suppressing the activation of the STAT3 signaling pathway. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 53, 644–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Xu, J.; Zhi, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, R. MiR-876-3p targets KIF20A to block JAK2/STAT3 pathway in glioma. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2019, 11, 4957–4966. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bockhorn, J.; Dalton, R.; Nwachukwu, C.; Huang, S.M.; Prat, A.; Yee, K.; Chang, Y.F.; Huo, D.Z.; Wen, Y.J.; Swanson, K.E.; et al. MicroRNA-30c inhibits human breast tumour chemotherapy resistance by regulating TWF1 and IL-11. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, R.; Zhang, C.; Liu, G.; Gu, R.; Wu, H. MicroRNA-126 Inhibits Proliferation, Migration, Invasion, and EMT in Osteosarcoma by Targeting ZEB1. J. Cell. Biochem. 2017, 118, 3765–3774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Cai, K.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Cheng, K.; Shi, F.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Dou, J. MiR-7, inhibited indirectly by lincRNA HOTAIR, directly inhibits SETDB1 and reverses the EMT of breast cancer stem cells by downregulating the STAT3 pathway. Stem Cells 2014, 32, 2858–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Bai, H.Y.; Liu, G.T.; Wang, H.Y.; Chen, F.; Zhang, B.S.; Zeng, P.Y.; Wu, C.X.; Peng, C.; Huang, C.J.; et al. MicroRNA-33b, upregulated by EF24, a curcumin analog, suppresses the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and migratory potential of melanoma cells by targeting HMGA2 l. Toxicol. Lett. 2015, 234, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.L.; He, W.; Tang, J.Q.; Ye, Q.R.; Dang, W.; Lu, Y.J.; Wang, J.; Li, G.Y.; Yan, Q.; Ma, J. MicroRNAs Provide Feedback Regulation of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Induced by Growth Factors. J. Cell. Physiol. 2016, 231, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, W.; Qin, Z.L.; Fan, S.Q.; Wen, Q.Y.; Lu, Y.J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.M.; Wei, L.Y.; He, W.; Ye, Q.R.; et al. miR-1207-5p suppresses lung cancer growth and metastasis by targeting CSF1. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 32421–32432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.B.; Wu, B.W.; Huang, S.; Peng, X.S.; Li, X.; Huang, X.F.; Zhou, W.; Xie, P.G.; He, P.H. Downregulation of miR-505-3p predicts poor bone metastasis-free survival in prostate cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 41, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, K.; Wei, S.; Zhang, C.; Chen, J.W.; Chen, J.B.; Xiao, K.H.; Liu, J.; Dai, M.M.; Guan, X.Y.; Yun, J.P.; et al. KIFC1 is activated by TCF-4 and promotes hepatocellular carcinoma pathogenesis by regulating HMGA1 transcriptional activity. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.J.; Wang, Y.H.; Xu, X.; Cao, H.; Sahengbieke, S.; Sheng, H.Q.; Huang, Q.; Lai, M.D. Transcriptional activation of FN1 and IL11 by HMGA2 promotes the malignant behavior of colorectal cancer. Carcinogenesis 2016, 37, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Chen, C.; Shi, M.; Wang, F.; Chen, X.; Diao, D.; Hu, M.; Yu, M.; Qian, L.; Guo, N. Stat3-coordinated Lin-28-let-7-HMGA2 and miR-200-ZEB1 circuits initiate and maintain oncostatin M-driven epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Oncogene 2013, 32, 5272–5282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.H.; Wu, M.H.; Liao, C.J.; Huang, Y.H.; Chi, H.C.; Wu, S.M.; Chen, C.Y.; Tseng, Y.H.; Tsai, C.Y.; Chung, I.H.; et al. Repression of microRNA-130b by thyroid hormone enhances cell motility. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, 1328–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.; Xue, H.; Wang, Y.; Shen, Q.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Li, K.; Jia, M.; Jia, J.; Xu, J.; et al. miR-345 inhibits tumor metastasis and EMT by targeting IRF1-mediated mTOR/STAT3/AKT pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Oncol. 2017, 50, 975–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).