Expression of FGFR1–4 in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Tissue and Corresponding Cell Lines and its Relationship to Patient Survival and FGFR Inhibitor Sensitivity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clinical Samples
2.2. Immunohistochemistry
2.3. Cell Lines
2.4. Generation of Cell Blocks
2.5. Drug Treatment
2.6. Quantitative Real-Time Reverse Transcription PCR (qRT-PCR)
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
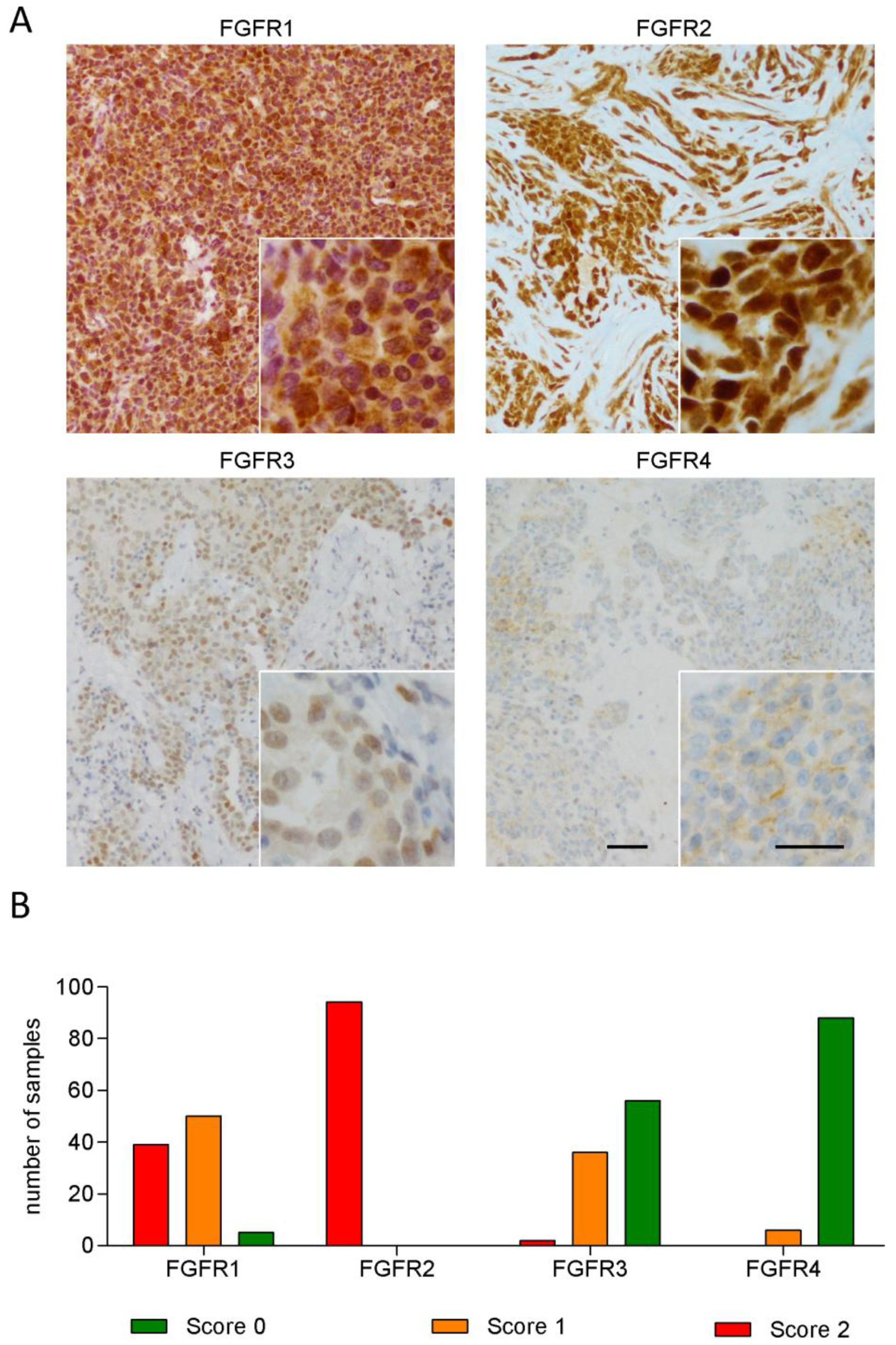
3.1. FGFR1 and FGFR2 Show Strong Staining in MPM Tissue
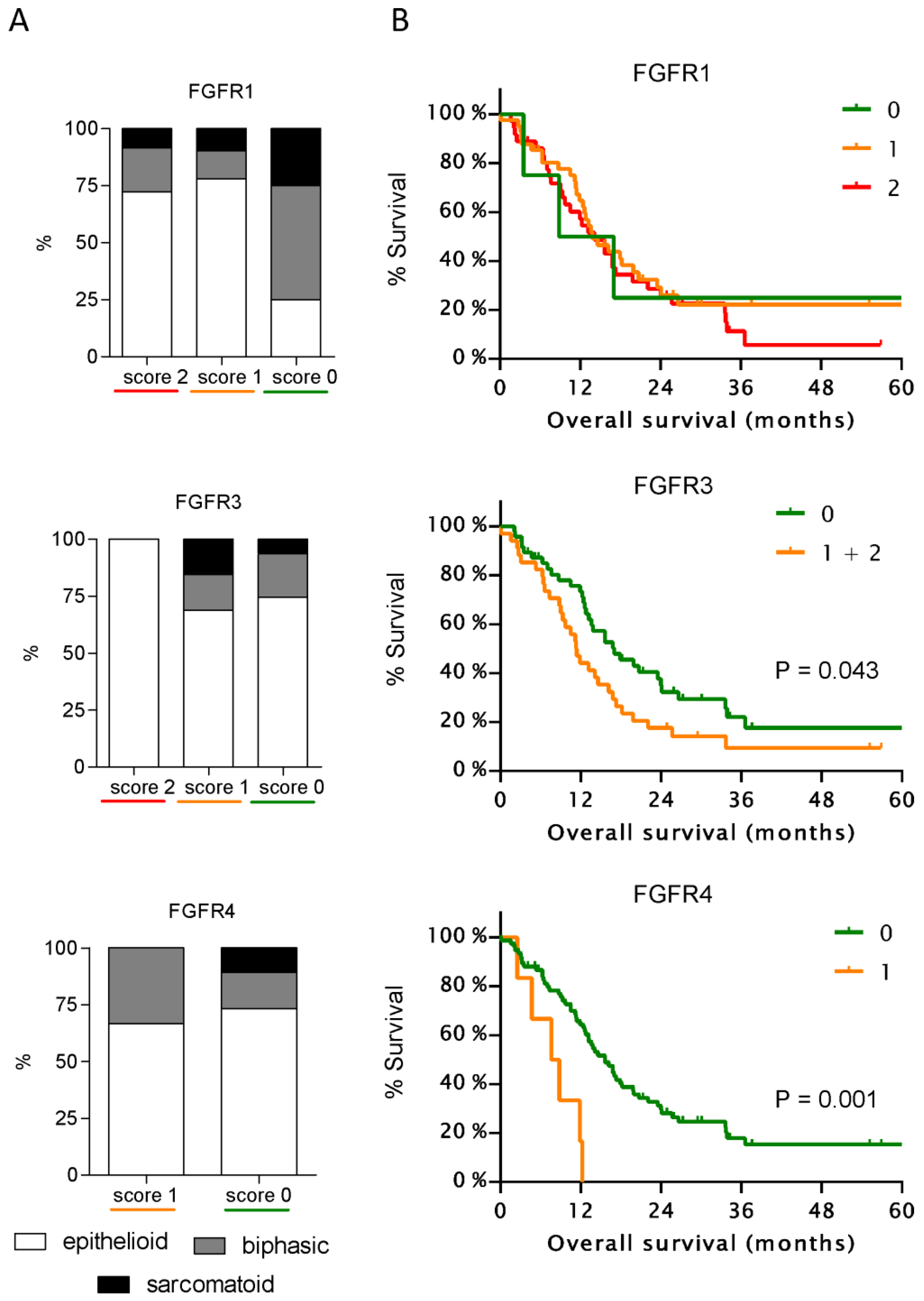
3.2. Expression of FGFR3 and FGFR4 But Not of Other FGFRs Correlates with Patient Survival
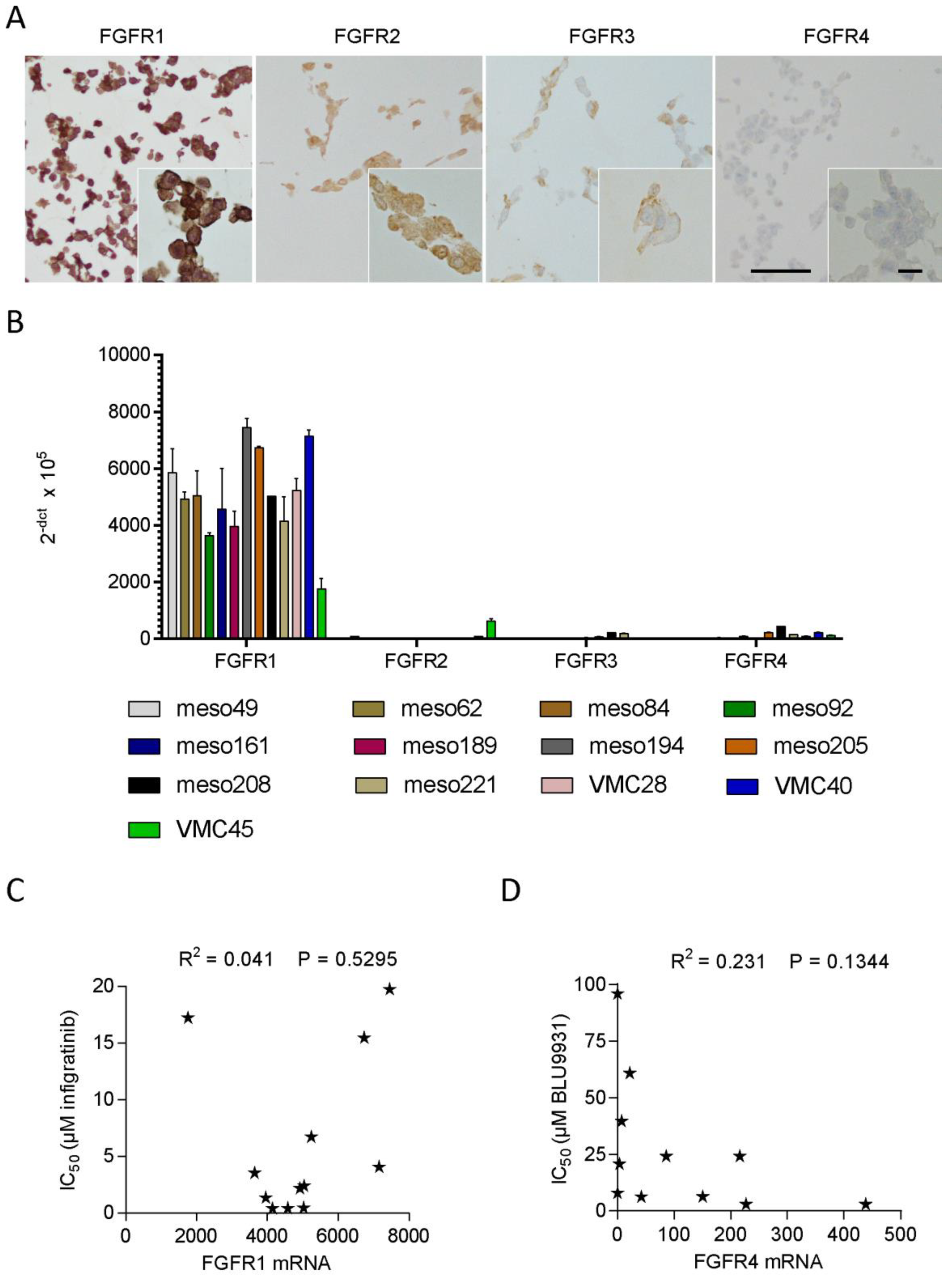
3.3. FGFR Inhibitor Sensitivity in Patient-Derived Cell Lines
3.4. FGFR Expression in Patient-Derived Cell Lines
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yap, T.A.; Aerts, J.G.; Popat, S.; Fennell, D.A. Novel insights into mesothelioma biology and implications for therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 475–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stayner, L.; Welch, L.S.; Lemen, R. The worldwide pandemic of asbestos-related diseases. Annu. Rev. Public Health 2013, 34, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutti, L.; Peikert, T.; Robinson, B.W.S.; Scherpereel, A.; Tsao, A.S.; de Perrot, M.; Woodard, G.A.; Jablons, D.M.; Wiens, J.; Hirsch, F.R.; et al. Scientific Advances and New Frontiers in Mesothelioma Therapeutics. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 1269–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherpereel, A.; Mazieres, J.; Greillier, L.; Lantuejoul, S.; Do, P.; Bylicki, O.; Monnet, I.; Corre, R.; Audigier-Valette, C.; Locatelli-Sanchez, M.; et al. Nivolumab or nivolumab plus ipilimumab in patients with relapsed malignant pleural mesothelioma (IFCT-1501 MAPS2): A multicentre, open-label, randomised, non-comparative, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, R.; Stawiski, E.W.; Goldstein, L.D.; Durinck, S.; De Rienzo, A.; Modrusan, Z.; Gnad, F.; Nguyen, T.T.; Jaiswal, B.S.; Chirieac, L.R.; et al. Comprehensive genomic analysis of malignant pleural mesothelioma identifies recurrent mutations, gene fusions and splicing alterations. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hmeljak, J.; Sanchez-Vega, F.; Hoadley, K.A.; Shih, J.; Stewart, C.; Heiman, D.; Tarpey, P.; Danilova, L.; Drill, E.; Gibb, E.A.; et al. Integrative Molecular Characterization of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 1548–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuno, T.; Murakami, H.; Fujii, M.; Ishiguro, F.; Tanaka, I.; Kondo, Y.; Akatsuka, S.; Toyokuni, S.; Yokoi, K.; Osada, H.; et al. YAP induces malignant mesothelioma cell proliferation by upregulating transcription of cell cycle-promoting genes. Oncogene 2012, 31, 5117–5122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekido, Y. Targeting the Hippo Pathway Is a New Potential Therapeutic Modality for Malignant Mesothelioma. Cancers 2018, 10, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altomare, D.A.; You, H.; Xiao, G.H.; Ramos-Nino, M.E.; Skele, K.L.; De Rienzo, A.; Jhanwar, S.C.; Mossman, B.T.; Kane, A.B.; Testa, J.R. Human and mouse mesotheliomas exhibit elevated AKT/PKB activity, which can be targeted pharmacologically to inhibit tumor cell growth. Oncogene 2005, 24, 6080–6089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marek, L.A.; Hinz, T.K.; von Massenhausen, A.; Olszewski, K.A.; Kleczko, E.K.; Boehm, D.; Weiser-Evans, M.C.; Nemenoff, R.A.; Hoffmann, H.; Warth, A.; et al. Nonamplified FGFR1 is a growth driver in malignant pleural mesothelioma. Mol. Cancer Res. 2014, 12, 1460–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schelch, K.; Hoda, M.A.; Klikovits, T.; Munzker, J.; Ghanim, B.; Wagner, C.; Garay, T.; Laszlo, V.; Setinek, U.; Dome, B.; et al. Fibroblast growth factor receptor inhibition is active against mesothelioma and synergizes with radio- and chemotherapy. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 190, 763–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blackwell, C.; Sherk, C.; Fricko, M.; Ganji, G.; Barnette, M.; Hoang, B.; Tunstead, J.; Skedzielewski, T.; Alsaid, H.; Jucker, B.M.; et al. Inhibition of FGF/FGFR autocrine signaling in mesothelioma with the FGF ligand trap, FP-1039/GSK3052230. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 39861–39871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schelch, K.; Kirschner, M.B.; Williams, M.; Cheng, Y.Y.; van Zandwijk, N.; Grusch, M.; Reid, G. A link between the fibroblast growth factor axis and the miR-16 family reveals potential new treatment combinations in mesothelioma. Mol. Oncol. 2018, 12, 58–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schelch, K.; Wagner, C.; Hager, S.; Pirker, C.; Siess, K.; Lang, E.; Lin, R.; Kirschner, M.B.; Mohr, T.; Brcic, L.; et al. FGF2 and EGF induce epithelial-mesenchymal transition in malignant pleural mesothelioma cells via a MAPKinase/MMP1 signal. Carcinogenesis 2018, 39, 534–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quispel-Janssen, J.M.; Badhai, J.; Schunselaar, L.; Price, S.; Brammeld, J.; Iorio, F.; Kolluri, K.; Garnett, M.; Berns, A.; Baas, P.; et al. Comprehensive Pharmacogenomic Profiling of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Identifies a Subgroup Sensitive to FGFR Inhibition. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusch, V.W. A proposed new international TNM staging system for malignant pleural mesothelioma. From the International Mesothelioma Interest Group. Chest 1995, 108, 1122–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanna-Cherchi, S.; Sampogna, R.V.; Papeta, N.; Burgess, K.E.; Nees, S.N.; Perry, B.J.; Choi, M.; Bodria, M.; Liu, Y.; Weng, P.L.; et al. Mutations in DSTYK and dominant urinary tract malformations. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saucedo, L.; Buffa, G.N.; Rosso, M.; Guillardoy, T.; Gongora, A.; Munuce, M.J.; Vazquez-Levin, M.H.; Marin-Briggiler, C. Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptors (FGFRs) in Human Sperm: Expression, Functionality and Involvement in Motility Regulation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Streit, S.; Mestel, D.S.; Schmidt, M.; Ullrich, A.; Berking, C. FGFR4 Arg388 allele correlates with tumour thickness and FGFR4 protein expression with survival of melanoma patients. Br. J. Cancer 2006, 94, 1879–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauglhofer, C.; Sagmeister, S.; Schrottmaier, W.; Fischer, C.; Rodgarkia-Dara, C.; Mohr, T.; Stattner, S.; Bichler, C.; Kandioler, D.; Wrba, F.; et al. Up-regulation of the fibroblast growth factor 8 subfamily in human hepatocellular carcinoma for cell survival and neoangiogenesis. Hepatology 2011, 53, 854–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagmeister, S.; Eisenbauer, M.; Pirker, C.; Mohr, T.; Holzmann, K.; Zwickl, H.; Bichler, C.; Kandioler, D.; Wrba, F.; Mikulits, W.; et al. New cellular tools reveal complex epithelial-mesenchymal interactions in hepatocarcinogenesis. Br. J. Cancer 2008, 99, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Laszlo, V.; Valko, Z.; Kovacs, I.; Ozsvar, J.; Hoda, M.A.; Klikovits, T.; Lakatos, D.; Czirok, A.; Garay, T.; Stiglbauer, A.; et al. Nintedanib Is Active in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Cell Models and Inhibits Angiogenesis and Tumor Growth In Vivo. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 3729–3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guagnano, V.; Kauffmann, A.; Wohrle, S.; Stamm, C.; Ito, M.; Barys, L.; Pornon, A.; Yao, Y.; Li, F.; Zhang, Y.; et al. FGFR genetic alterations predict for sensitivity to NVP-BGJ398, a selective pan-FGFR inhibitor. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 1118–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabernero, J.; Bahleda, R.; Dienstmann, R.; Infante, J.R.; Mita, A.; Italiano, A.; Calvo, E.; Moreno, V.; Adamo, B.; Gazzah, A.; et al. Phase I Dose-Escalation Study of JNJ-42756493, an Oral Pan-Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor Inhibitor, in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 3401–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledermann, J.A.; Hackshaw, A.; Kaye, S.; Jayson, G.; Gabra, H.; McNeish, I.; Earl, H.; Perren, T.; Gore, M.; Persic, M.; et al. Randomized phase II placebo-controlled trial of maintenance therapy using the oral triple angiokinase inhibitor BIBF 1120 after chemotherapy for relapsed ovarian cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 3798–3804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlumberger, M.; Jarzab, B.; Cabanillas, M.E.; Robinson, B.; Pacini, F.; Ball, D.W.; McCaffrey, J.; Newbold, K.; Allison, R.; Martins, R.G.; et al. A Phase II Trial of the Multitargeted Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Lenvatinib (E7080) in Advanced Medullary Thyroid Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reck, M.; Kaiser, R.; Mellemgaard, A.; Douillard, J.Y.; Orlov, S.; Krzakowski, M.; von Pawel, J.; Gottfried, M.; Bondarenko, I.; Liao, M.; et al. Docetaxel plus nintedanib versus docetaxel plus placebo in patients with previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer (LUME-Lung 1): A phase 3, double-blind, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dienstmann, R.; Rodon, J.; Prat, A.; Perez-Garcia, J.; Adamo, B.; Felip, E.; Cortes, J.; Iafrate, A.J.; Nuciforo, P.; Tabernero, J. Genomic aberrations in the FGFR pathway: Opportunities for targeted therapies in solid tumors. Ann. Oncol. 2014, 25, 552–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, B.C.; Engels, M.; Annala, M.; Zhang, W. Emergence of FGFR family gene fusions as therapeutic targets in a wide spectrum of solid tumours. J. Pathol. 2014, 232, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.G.t.; Cheuk, A.T.; Tsang, P.S.; Chung, J.Y.; Song, Y.K.; Desai, K.; Yu, Y.; Chen, Q.R.; Shah, K.; Youngblood, V.; et al. Identification of FGFR4-activating mutations in human rhabdomyosarcomas that promote metastasis in xenotransplanted models. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 3395–3407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotani, H.; Ebi, H.; Kitai, H.; Nanjo, S.; Kita, K.; Huynh, T.G.; Ooi, A.; Faber, A.C.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; Yano, S. Co-active receptor tyrosine kinases mitigate the effect of FGFR inhibitors in FGFR1-amplified lung cancers with low FGFR1 protein expression. Oncogene 2016, 35, 3587–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golfmann, K.; Meder, L.; Koker, M.; Volz, C.; Borchmann, S.; Tharun, L.; Dietlein, F.; Malchers, F.; Florin, A.; Buttner, R.; et al. Synergistic anti-angiogenic treatment effects by dual FGFR1 and VEGFR1 inhibition in FGFR1-amplified breast cancer. Oncogene 2018, 37, 5682–5693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez-Pascual, A.; Siebzehnrubl, F.A. Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor Functions in Glioblastoma. Cells 2019, 8, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Tang, P.M.K.; Zhou, Y.; Cheng, A.S.L.; Yu, J.; Kang, W.; To, K.F. Targeting the Oncogenic FGF-FGFR Axis in Gastric Carcinogenesis. Cells 2019, 8, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czyz, M. Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor Signaling in Skin Cancers. Cells 2019, 8, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santolla, M.F.; Vivacqua, A.; Lappano, R.; Rigiracciolo, D.C.; Cirillo, F.; Galli, G.R.; Talia, M.; Brunetti, G.; Miglietta, A.M.; Belfiore, A.; et al. GPER Mediates a Feedforward FGF2/FGFR1 Paracrine Activation Coupling CAFs to Cancer Cells toward Breast Tumor Progression. Cells 2019, 8, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pattarozzi, A.; Carra, E.; Favoni, R.E.; Wurth, R.; Marubbi, D.; Filiberti, R.A.; Mutti, L.; Florio, T.; Barbieri, F.; Daga, A. The inhibition of FGF receptor 1 activity mediates sorafenib antiproliferative effects in human malignant pleural mesothelioma tumor-initiating cells. Stem. Cell Res. Ther. 2017, 8, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Brummelen, E.M.J.; Levchenko, E.; Domine, M.; Fennell, D.A.; Kindler, H.L.; Viteri, S.; Gadgeel, S.; Lopez, P.G.; Kostorov, V.; Morgensztern, D.; et al. A phase Ib study of GSK3052230, an FGF ligand trap in combination with pemetrexed and cisplatin in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma. Investig. New Drugs 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosso, F.; Steele, N.; Novello, S.; Nowak, A.K.; Popat, S.; Greillier, L.; John, T.; Leighl, N.B.; Reck, M.; Taylor, P.; et al. Nintedanib Plus Pemetrexed/Cisplatin in Patients With Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: Phase II Results From the Randomized, Placebo-Controlled LUME-Meso Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 3591–3600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scagliotti, G.V.; Gaafar, R.; Nowak, A.K.; Nakano, T.; van Meerbeeck, J.; Popat, S.; Vogelzang, N.J.; Grosso, F.; Aboelhassan, R.; Jakopovic, M.; et al. Nintedanib in combination with pemetrexed and cisplatin for chemotherapy-naive patients with advanced malignant pleural mesothelioma (LUME-Meso): A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2019, 7, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, H.; Lee, L.Y.; Goh, K.Y.; Ong, R.; Hao, H.X.; Huang, A.; Wang, Y.; Graus Porta, D.; Chow, P.; Chung, A. Infigratinib Mediates Vascular Normalization, Impairs Metastasis, and Improves Chemotherapy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Hepatology 2019, 69, 943–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chioni, A.M.; Grose, R. FGFR1 cleavage and nuclear translocation regulates breast cancer cell behavior. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 197, 801–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gauglhofer, C.; Paur, J.; Schrottmaier, W.C.; Wingelhofer, B.; Huber, D.; Naegelen, I.; Pirker, C.; Mohr, T.; Heinzle, C.; Holzmann, K.; et al. Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4: A putative key driver for the aggressive phenotype of hepatocellular carcinoma. Carcinogenesis 2014, 35, 2331–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagel, M.; Miduturu, C.; Sheets, M.; Rubin, N.; Weng, W.; Stransky, N.; Bifulco, N.; Kim, J.L.; Hodous, B.; Brooijmans, N.; et al. First Selective Small Molecule Inhibitor of FGFR4 for the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinomas with an Activated FGFR4 Signaling Pathway. Cancer Discov. 2015, 5, 424–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raja, A.; Park, I.; Haq, F.; Ahn, S.M. FGF19-FGFR4 Signaling in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cells 2019, 8, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.P.; Feng, H.; Qiao, H.B.; Ren, Z.X.; Zhu, G.D. The prognostic significance of fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 in non-small-cell lung cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 2015, 8, 1157–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Heinzle, C.; Erdem, Z.; Paur, J.; Grasl-Kraupp, B.; Holzmann, K.; Grusch, M.; Berger, W.; Marian, B. Is fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 a suitable target of cancer therapy? Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 2881–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strizzi, L.; Vianale, G.; Catalano, A.; Muraro, R.; Mutti, L.; Procopio, A. Basic fibroblast growth factor in mesothelioma pleural effusions: Correlation with patient survival and angiogenesis. Int. J. Oncol. 2001, 18, 1093–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, L.; Teng, Y. Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 4 Targeting in Cancer: New Insights into Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategies. Cells 2019, 8, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, Z.; Xu, G.; Chen, Y. Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptors (FGFRs): Structures and Small Molecule Inhibitors. Cells 2019, 8, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirker, C.; Bilecz, A.; Grusch, M.; Mohr, T.; Laszlo, V.; Stockhammer, P.; Lötsch, D.; Gojo, J.; Gabler, L.; Spiegl-Kreinecker, S.; et al. Activating TERT promoter mutations in malignant pleural mesothelioma: Association with prognosis and altered genomic signature. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019. under review. [Google Scholar]

| All Patients | n | % | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | <60 | 22 | 27 |
| ≥60 | 59 | 73 | |
| Sex | female | 22 | 27 |
| male | 59 | 73 | |
| Histology | non-epithelioid | 22 | 27 |
| epithelioid | 59 | 73 | |
| Stage | early | 28 | 35 |
| late | 53 | 65 | |
| Treatment overview | BSC | 15 | 19 |
| CHT | 33 | 41 | |
| CHT + RT | 3 | 4 | |
| CHT + S | 11 | 14 | |
| TMT | 19 | 23 | |
| Cell Line | Histology | IC50 (µM) | Cell Block IHC Score | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Infigratinib | FGFR1 | FGFR2 | FGFR3 | FGFR4 | ||
| Meso49 | bi | n.i. | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| Meso62 | sarc | 2.18 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| Meso84 | sarc | 2.39 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| Meso92 | bi | 3.53 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| Meso161 | bi | 0.41 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| Meso189 | epi | 1.34 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| Meso194 | epi | 19.76 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| Meso205 | epi | 15.47 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| Meso208 | epi | 0.46 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| Meso221 | epi | 0.39 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| VMC28 | epi | 6.71 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| VMC40 | bi | 4.06 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| VMC45 | epi | 17.24 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vlacic, G.; Hoda, M.A.; Klikovits, T.; Sinn, K.; Gschwandtner, E.; Mohorcic, K.; Schelch, K.; Pirker, C.; Peter-Vörösmarty, B.; Brankovic, J.; et al. Expression of FGFR1–4 in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Tissue and Corresponding Cell Lines and its Relationship to Patient Survival and FGFR Inhibitor Sensitivity. Cells 2019, 8, 1091. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8091091
Vlacic G, Hoda MA, Klikovits T, Sinn K, Gschwandtner E, Mohorcic K, Schelch K, Pirker C, Peter-Vörösmarty B, Brankovic J, et al. Expression of FGFR1–4 in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Tissue and Corresponding Cell Lines and its Relationship to Patient Survival and FGFR Inhibitor Sensitivity. Cells. 2019; 8(9):1091. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8091091
Chicago/Turabian StyleVlacic, Gregor, Mir A. Hoda, Thomas Klikovits, Katharina Sinn, Elisabeth Gschwandtner, Katja Mohorcic, Karin Schelch, Christine Pirker, Barbara Peter-Vörösmarty, Jelena Brankovic, and et al. 2019. "Expression of FGFR1–4 in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Tissue and Corresponding Cell Lines and its Relationship to Patient Survival and FGFR Inhibitor Sensitivity" Cells 8, no. 9: 1091. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8091091
APA StyleVlacic, G., Hoda, M. A., Klikovits, T., Sinn, K., Gschwandtner, E., Mohorcic, K., Schelch, K., Pirker, C., Peter-Vörösmarty, B., Brankovic, J., Dome, B., Laszlo, V., Cufer, T., Rozman, A., Klepetko, W., Grasl-Kraupp, B., Hegedus, B., Berger, W., Kern, I., & Grusch, M. (2019). Expression of FGFR1–4 in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Tissue and Corresponding Cell Lines and its Relationship to Patient Survival and FGFR Inhibitor Sensitivity. Cells, 8(9), 1091. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8091091








