Graph Convolutional Network and Convolutional Neural Network Based Method for Predicting lncRNA-Disease Associations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dataset for lncRNA-Disease Association Prediction
2.2. Prediction Method Based on Graph Convolutional Network and Convolutional Neural Network
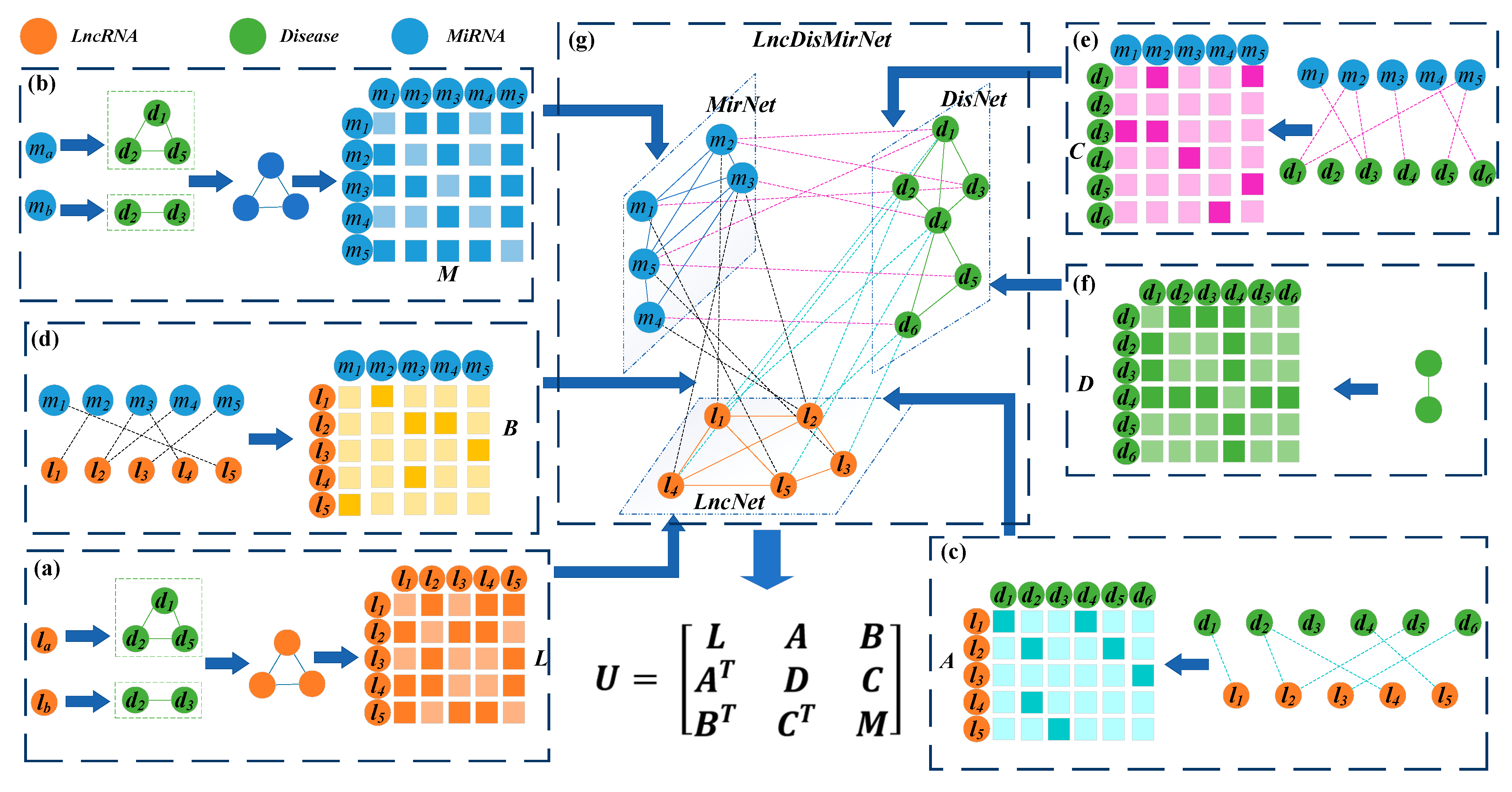
2.2.1. Construction of the lncRNA-Disease-miRNA Network
2.2.2. Construction of the lncRNA, miRNA, and Disease Networks
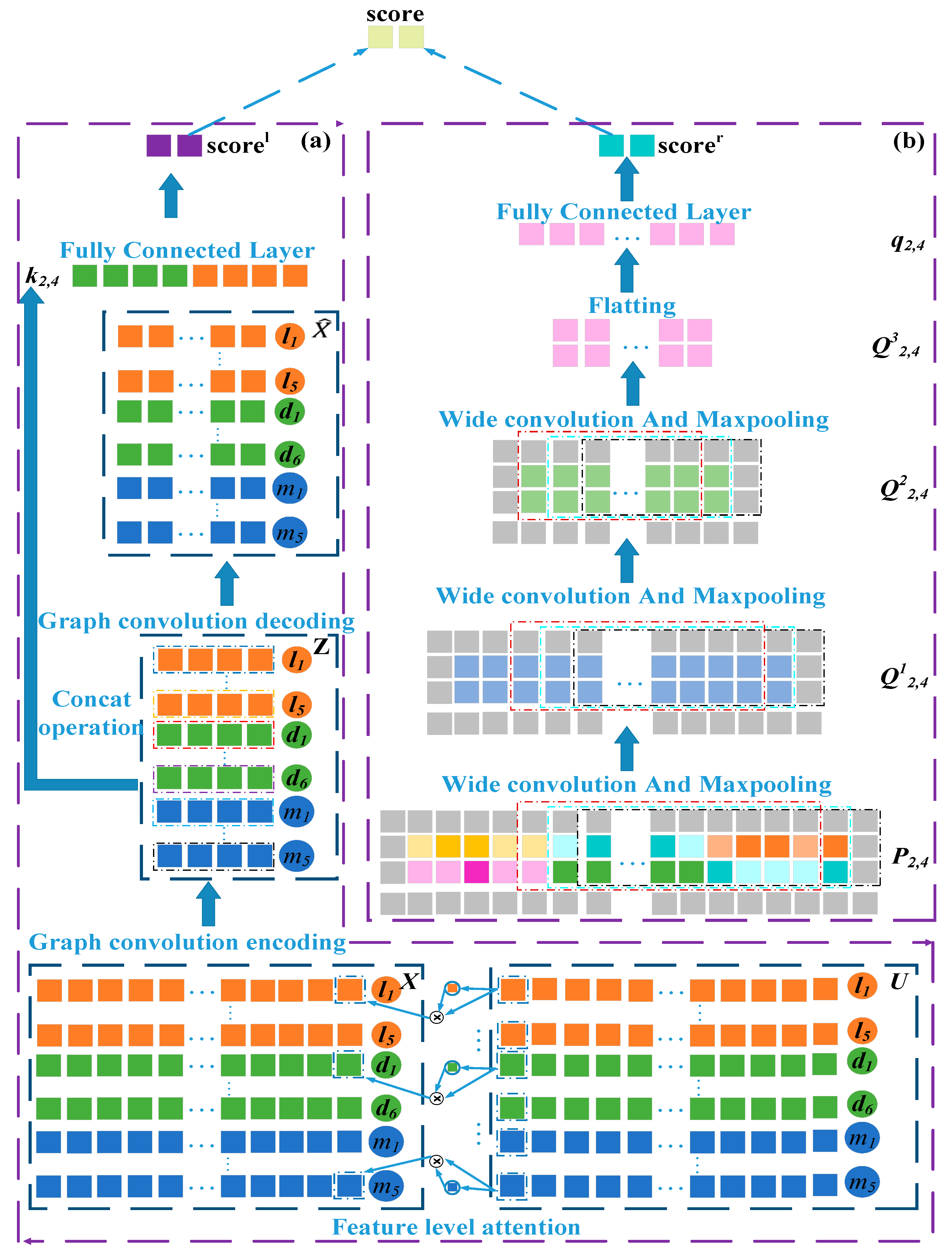
2.2.3. Attention Mechanism on the Left Side of the Framework
2.2.4. Graph Convolutional Network Module on the Right Side of the Framework
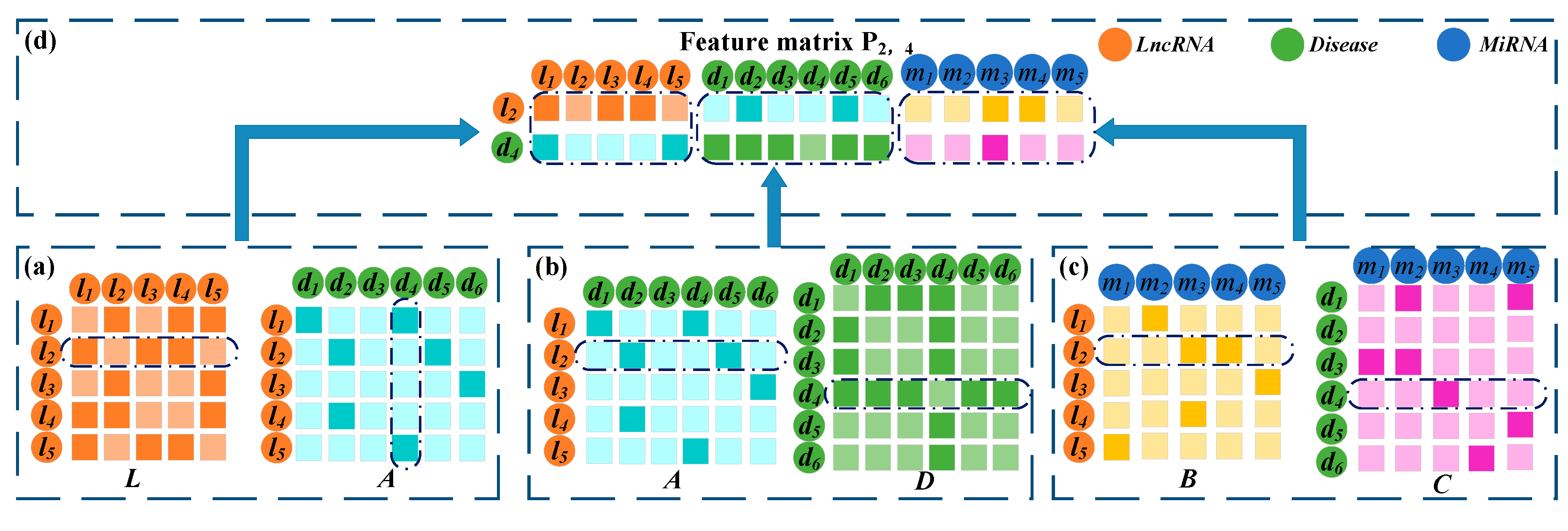
2.2.5. Construction of the Embedding Matrix of lncRNA-Disease Node Pairs
2.2.6. Convolutional Neural Networks Module on the Left Side of the Framework
2.3. Combination Strategy
2.4. Reducing Overfitting
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Performance Evaluation Metrics
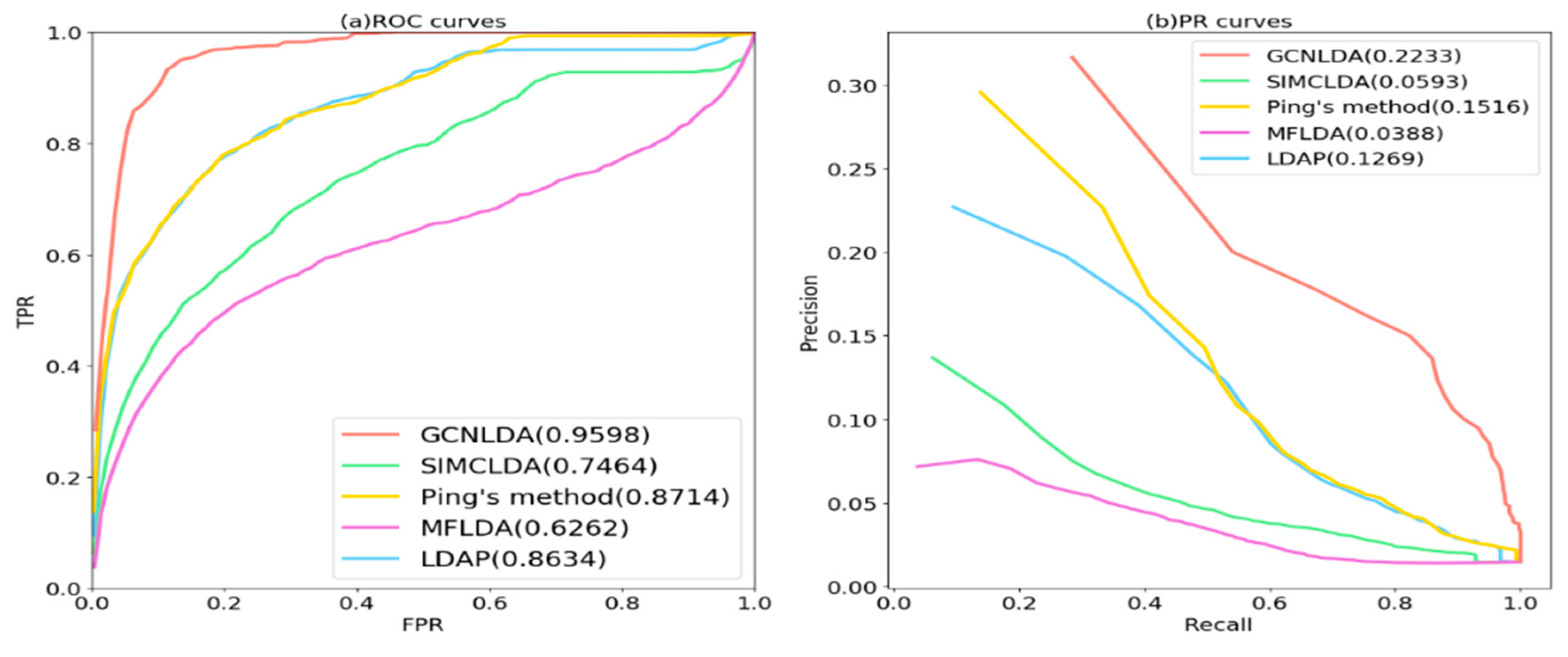
3.2. Comparison with Other Methods
3.3. Case Studies on Stomach Cancer, Osteosarcoma, and Lung Cancer
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Taft, R.J.; Pang, K.C.; Mercer, T.R.; Dinger, M.E.; Mattick, J.S. Non-coding RNAs: Regulators of disease. J. Pathol. 2010, 220, 126–139. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Yan, C.C.; Zhang, X.; You, Z.H. Long non-coding RNAs and complex diseases: From experimental results to computational models. Briefings Bioinform. 2017, 18, 558. [Google Scholar]
- Harrow, J.; Frankish, A.; Gonzalez, J.M.; Tapanari, E.; Diekhans, M.; Kokocinski, F.; Aken, B.L.; Barrell, D.; Zadissa, A.; Searle, S. GENCODE: The reference human genome annotation for the ENCODE project. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 1760–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcia, G.; Danielle, M.; Buddy, S.H.; Dorssers, L.C.J.; Ton, V.A. Characterization of BCAR4, a novel oncogene causing endocrine resistance in human breast cancer cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2011, 226, 1741–1749. [Google Scholar]
- Hrdlickova, B.; Almeida, R.C.D.; Borek, Z.; Withoff, S. Genetic variation in the non-coding genome: Involvement of micro-RNAs and long non-coding RNAs in disease. BBA Mol. Basis Dis. 2014, 1842, 1910–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ada, C.; Kei, K.; Ryousuke, O.; Osamu, Y.; Keishi, M.; Eiichiro, Y.; Tatsuo, K.; Hiroshi, K.; Hiroko, Y.; Yasushi, T. Genetic variants at the 9p21 locus contribute to atherosclerosis through modulation of ANRIL and CDKN2A/B. Atherosclerosis 2012, 220, 449–455. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, R. Long non-coding RNAs in Huntington’s disease neurodegeneration. Neurobiol. Dis. 2012, 46, 245–254. [Google Scholar]
- Mamoshina, P.; Vieira, A.; Putin, E.; Zhavoronkov, A. Applications of deep learning in biomedicine. Mol. Pharm. 2016, 13, 1445–1454. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, M.; Xi, J.; Ao, L. LPGNMF: Predicting long non-coding RNA and protein interaction using graph regularized nonnegative matrix factorization. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piro, R.M.; Marsico, A. network-based methods and other approaches for predicting lncRNA functions and disease associations. In Computational Biology of Non-Coding RNA: Methods and Protocols; Lai, X., Gupta, S.K., Vera, J., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 301–321. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, L.; Peng, Q. A deep ensemble model to predict miRNA-disease association. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressin, A.; Schulte-Sasse, R.; Figini, D.; Urdaneta, E.C.; Beckmann, B.M.; Marsico, A. TriPepSVM: De novo prediction of RNA-binding proteins based on short amino acid motifs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 4406–4417. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Heller, D.; Krestel, R.; Ohler, U.; Vingron, M.; Marsico, A. ssHMM: Extracting intuitive sequence-structure motifs from high-throughput RNA-binding protein data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 11004. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Budach, S.; Marsico, A. pysster: Classification of biological sequences by learning sequence and structure motifs with convolutional neural networks. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 3035–3037. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Krakau, S.; Richard, H.; Marsico, A. PureCLIP: Capturing target-specific protein–RNA interaction footprints from single-nucleotide CLIP-seq data. Genome Biol. 2017, 18, 240. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Wang, Z.; Wang, D.; Qiu, C.; Liu, M.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Q.; Yan, G.; Cui, Q.J.N.A.R. LncRNADisease: A database for long-non-coding RNA-associated diseases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 41, 983–986. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.W.; Gao, C.; Wang, Y.C.; Ma, W.; Tu, J.; Wang, J.P.; Chen, Z.Z.; Kong, W.; Cui, Q.H. A bioinformatics method for predicting long noncoding RNAs associated with vascular disease. Sci. China Life Sci. 2014, 57, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ming-Xi, L.; Xing, C.; Geng, C.; Qing-Hua, C.; Gui-Ying, Y. A computational framework to infer human disease-associated long noncoding RNAs. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e84408. [Google Scholar]
- Biswas, A.K.; Zhang, B.; Wu, X.; Gao, J.X. A multi-label classification framework to predict disease associations of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs). In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Communications, Signal Processing, and Systems, Hohot, China, 14–15 July 2014; Springer: Basel, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 821–830. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Yan, G.-Y. Novel human lncRNA-disease association inference based on lncRNA expression profiles. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 2617–2624. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Yan, C.C.; Luo, C.; Ji, W.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, Q. Constructing lncRNA functional similarity network based on lncRNA-disease associations and disease semantic similarity. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11338. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, C.; Yuan, H.; Wang, X.S.; You, Z.H.; Chan, K.C.C. FMLNCSIM: fuzzy measure-based lncRNA functional similarity calculation model. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 45948–45958. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.A.; Chen, X.; You, Z.H.; Huang, D.S.; Chan, K.C.C. ILNCSIM: improved lncRNA functional similarity calculation model. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 25902–25914. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xiaofei, Y.; Lin, G.; Xingli, G.; Xinghua, S.; Hao, W.; Fei, S.; Bingbo, W. A network based method for analysis of lncRNA-disease associations and prediction of lncRNAs implicated in diseases. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87797. [Google Scholar]
- Ping, P.; Wang, L.; Kuang, L.; Ye, S.; Mfb, I.; Pei, T. A novel method for lncRNA-disease association prediction based on an lncRNA-disease association network. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2018, 16, 688–693. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jie, S.; Hongbo, S.; Zhenzhen, W.; Changjian, Z.; Lin, L.; Letian, W.; Weiwei, H.; Dapeng, H.; Shulin, L.; Meng, Z. Inferring novel lncRNA-disease associations based on a random walk model of a lncRNA functional similarity network. Mol. Biosyst. 2014, 10, 2074–2081. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; You, Z.H.; Yan, G.Y.; Gong, D.W. IRWRLDA: Improved random walk with restart for lncRNA-disease association prediction. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 57919–57931. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gu, C.; Liao, B.; Li, X.; Cai, L.; Li, Z.; Li, K.; Yang, J. Global network random walk for predicting potential human lncRNA-disease associations. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, G.; Fu, G.; Chang, L.; Ren, Y.; Wang, J. BRWLDA: Bi-random walks for predicting lncRNA-disease associations. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 60429–60446. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Q.; Wu, L.; Li, J.; Yang, L.G.; Sun, Y.; Li, Z.; He, S.; Feng, F.; Li, H.; Li, Y. Global prioritizing disease candidate lncRNAs via a multi-level composite network. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 39516. [Google Scholar]
- Pooya, Z.; Ben, J.; Raf, V.; Yves, M. Protein fold recognition using geometric kernel data fusion. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1850–1857. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, W.; Li, M.; Zhao, K.; Liu, J.; Wu, F.X.; Pan, Y.; Wang, J. LDAP: A web server for lncRNA-disease association prediction. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 458–460. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, G.; Wang, J.; Domeniconi, C.; Yu, G. Matrix factorization based data fusion for the prediction of lncRNA-disease associations. Bioinformatics 2017, 34, 1529–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.; Yang, M.; Luo, F.; Wu, F.X.; Li, M.; Pan, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, J. Prediction of lncRNA-disease associations based on inductive matrix completion. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 3357–3364. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ning, S.; Zhang, J.; Wang, P.; Zhi, H.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Guo, M.; Yue, M.; Wang, L. Lnc2Cancer: A manually curated database of experimentally supported lncRNAs associated with various human cancers. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 980–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.; Cohen, K.B.; Hunter, L. GeneRIF quality assurance as summary revision. In Proceedings of the Pacific Symposium on Biocomputing, Maui, HI, USA, 3–7 January 2007; National Institutes of Health: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2007; pp. 269–280. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Liu, S.; Zhou, H.; Qu, L.; Yang, J. starBase v2.0: Decoding miRNA-ceRNA, miRNA-ncRNA and protein–RNA interaction networks from large-scale CLIP-Seq data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 92–97. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Qiu, C.; Tu, J.; Geng, B.; Yang, J.; Jiang, T.; Cui, Q. HMDD v2.0: A database for experimentally supported human microRNA and disease associations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 1070–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.; Hu, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhou, M.; Jiang, Q. DincRNA: A comprehensive web-based bioinformatics toolkit for exploring disease associations and ncRNA function. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 1953–1956. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Wang, J.; Lu, M.; Song, F.; Cui, Q. Inferring the human microRNA functional similarity and functional network based on microRNA-associated diseases. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 1644–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kipf, T.N.; Welling, M. Semi-supervised classification with graph convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the ICLR 2017, Toulon, France, 24–26 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zitnik, M.; Agrawal, M.; Leskovec, J. Modeling polypharmacy side effects with graph convolutional networks. Intell. Syst. Mol. Biol. 2018, 34, 258814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Hu, R.; Fung, S.; Long, G.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, C. Learning Graph Embedding with Adversarial Training Methods. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1901.01250 (accessed on 16 June 2019).
- Den Berg, R.V.; Kipf, T.N.; Welling, M. Graph convolutional matrix completion. In Proceedings of the KDD’18 Deep Learning Day, London, UK, 20 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Torng, W.; Altman, R.B. Graph convolutional neural networks for predicting drug-target interactions. bioRxiv 2018, 473074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinton, G.E.; Srivastava, N.; Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Salakhutdinov, R.R. Improving Neural Networks by Preventing Co-Adaptation of Feature Detectors. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1207.0580v1 (accessed on 16 June 2019).
- Bahari, F.; Emadibaygi, M.; Nikpour, P. miR-17-92 host gene, uderexpressed in gastric cancer and its expression was negatively correlated with the metastasis. Indian J. Cancer 2015, 52, 22–25. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.; Liu, S.; Li, Y.; Tang, Q.; Xie, Y.; Zhai, R. Long noncoding RNA AFAP1-AS1 enhances cell proliferation and invasion in osteosarcoma through regulating miR-4695-5p/TCF4-β-catenin signaling. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 18, 1616–1622. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, B.; Yang, N. Long non-coding RNA MIR155HG promotes proliferation, migration and invasion of A549 human lung cancer cells. J. Chongqing Med. Univ. 2017. In Chinese. [Google Scholar]

| Disease Name | AUC | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GCNLDA | SIMCLDA | Ping’s Method | MFLDA | LDAP | |
| Average AUC on 405 diseases | 0.959 | 0.746 | 0.871 | 0.626 | 0.863 |
| respiratory system cancer | 0.948 | 0.789 | 0.911 | 0.719 | 0.891 |
| organ system cancer | 0.992 | 0.82 | 0.95 | 0.729 | 0.884 |
| intestinal cancer | 0.966 | 0.811 | 0.909 | 0.559 | 0.905 |
| prostate cancer | 0.944 | 0.873 | 0.826 | 0.553 | 0.71 |
| lung cancer | 0.961 | 0.79 | 0.911 | 0.676 | 0.883 |
| breast cancer | 0.963 | 0.742 | 0.871 | 0.517 | 0.83 |
| reproductive organ cancer | 0.962 | 0.707 | 0.818 | 0.74 | 0.742 |
| gastrointestinal system cancer | 0.977 | 0.784 | 0.896 | 0.582 | 0.867 |
| liver cancer | 0.978 | 0.799 | 0.91 | 0.634 | 0.898 |
| hepatocellular carcinoma | 0.983 | 0.765 | 0.903 | 0.688 | 0.902 |
| Disease Name | AUPR | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GCNLDA | SIMCLDA | Ping’s Method | MFLDA | LDAP | |
| Average AUC on 405 diseases | 0.223 | 0.166 | 0.219 | 0.095 | 0.066 |
| respiratory system cancer | 0.465 | 0.149 | 0.414 | 0.072 | 0.303 |
| organ system cancer | 0.950 | 0.411 | 0.765 | 0.338 | 0.628 |
| intestinal cancer | 0.697 | 0.141 | 0.252 | 0.042 | 0.246 |
| prostate cancer | 0.594 | 0.176 | 0.333 | 0.095 | 0.297 |
| lung cancer | 0.600 | 0.138 | 0.334 | 0.008 | 0.094 |
| breast cancer | 0.623 | 0.445 | 0.803 | 0.476 | 0.629 |
| reproductive organ cancer | 0.625 | 0.047 | 0.403 | 0.031 | 0.396 |
| gastrointestinal system cancer | 0.812 | 0.130 | 0.271 | 0.104 | 0.238 |
| liver cancer | 0.671 | 0.201 | 0.526 | 0.086 | 0.498 |
| hepatocellular carcinoma | 0.787 | 0.096 | 0.239 | 0.082 | 0.303 |
| p-Value | SIMCLDA | Ping’s Method | MFLDA | LDAP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| p-value of ROC curve | 1.131026 × 10−106 | 1.494908 × 10−44 | 4.534043 × 10−124 | 4.291344 × 10−50 |
| p-value of PR curve | 1.342560 × 10−89 | 2.204929 × 10−29 | 1.567472 × 10−112 | 2.844473 × 10−48 |
| Disease Name | Rank | lncRNA | Evidence | Rank | lncRNA | Evidence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stomach cancer | 1 | MALAT1 | Lnc2Cancer, LncRNADisease | 9 | HULC | Lnc2Cancer, LncRNADisease |
| 2 | NEAT1 | Lnc2Cancer, LncRNADisease | 10 | CCAT2 | Lnc2Cancer, LncRNADisease | |
| 3 | MIR17HG | Literature [47] | 11 | KCNQ1OT1 | Lnc2Cancer | |
| 4 | HOTTIP | Lnc2Cancer, LncRNADisease | 12 | BCYRN1 | LncRNADisease* | |
| 5 | TUG1 | Lnc2Cancer, LncRNADisease | 13 | CASC2 | Lnc2Cancer, LncRNADisease | |
| 6 | HNF1A-AS1 | Lnc2Cancer, LncRNADisease | 14 | PANDAR | Lnc2Cancer, LncRNADisease | |
| 7 | XIST | Lnc2Cancer, LncRNADisease | 15 | PCAT1 | LncRNADisease* | |
| 8 | AFAP1-AS1 | Lnc2Cancer | ||||
| Osteosarcoma | 1 | H19 | Lnc2Cancer, LncRNADisease | 9 | LINC00675 | LncRNADisease* |
| 2 | GAS5 | Lnc2Cancer | 10 | BCYRN1 | LncRNADisease* | |
| 3 | PVT1 | Lnc2Cancer | 11 | CCAT2 | Lnc2Cancer | |
| 4 | NEAT1 | Lnc2Cancer | 12 | CASC2 | Lnc2Cancer | |
| 5 | EWSAT1 | Lnc2Cancer | 13 | CCAT1 | Lnc2Cancer | |
| 6 | AFAP1-AS1 | Literature [48] | 14 | TP73-AS1 | Lnc2Cancer | |
| 7 | CDKN2B-AS1 | LncRNADisease | 15 | PCA3 | LncRNADisease* | |
| 8 | SPRY4-IT1 | Lnc2Cancer | ||||
| Lung cancer | 1 | KCNQ1OT1 | Lnc2Cancer | 9 | IGF2-AS | Lnc2Cancer |
| 2 | HOTTIP | Lnc2Cancer, LncRNADisease | 10 | PCAT1 | LncRNADisease | |
| 3 | SPRY4-IT1 | Lnc2Cancer, LncRNADisease | 11 | CASC2 | Lnc2Cancer, LncRNADisease | |
| 4 | TP73-AS1 | Lnc2Cancer | 12 | ESRG | LncRNADisease* | |
| 5 | MIAT | Lnc2Cancer | 13 | PCA3 | LncRNADisease* | |
| 6 | MIR155HG | Literature [49] | 14 | SNHG12 | Lnc2Cancer | |
| 7 | LINC00675 | LncRNADisease* | 15 | TUSC7 | Lnc2Cancer | |
| 8 | SOX2-OT | LncRNADisease |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xuan, P.; Pan, S.; Zhang, T.; Liu, Y.; Sun, H. Graph Convolutional Network and Convolutional Neural Network Based Method for Predicting lncRNA-Disease Associations. Cells 2019, 8, 1012. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8091012
Xuan P, Pan S, Zhang T, Liu Y, Sun H. Graph Convolutional Network and Convolutional Neural Network Based Method for Predicting lncRNA-Disease Associations. Cells. 2019; 8(9):1012. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8091012
Chicago/Turabian StyleXuan, Ping, Shuxiang Pan, Tiangang Zhang, Yong Liu, and Hao Sun. 2019. "Graph Convolutional Network and Convolutional Neural Network Based Method for Predicting lncRNA-Disease Associations" Cells 8, no. 9: 1012. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8091012
APA StyleXuan, P., Pan, S., Zhang, T., Liu, Y., & Sun, H. (2019). Graph Convolutional Network and Convolutional Neural Network Based Method for Predicting lncRNA-Disease Associations. Cells, 8(9), 1012. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8091012




