Delivery of microRNAs by Extracellular Vesicles in Viral Infections: Could the News be Packaged?
Abstract
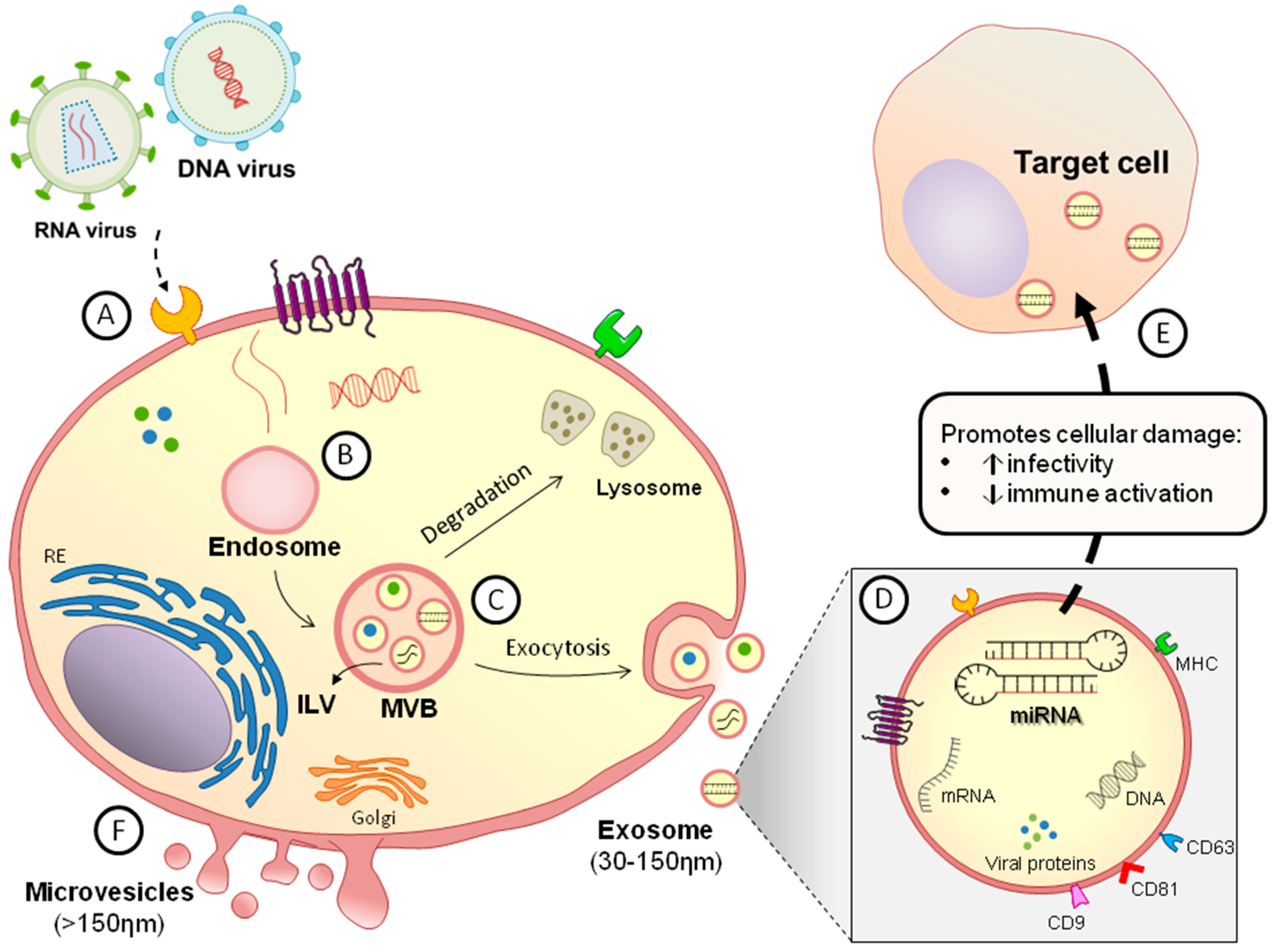
1. Introduction
2. General Features of Extracellular Vesicles
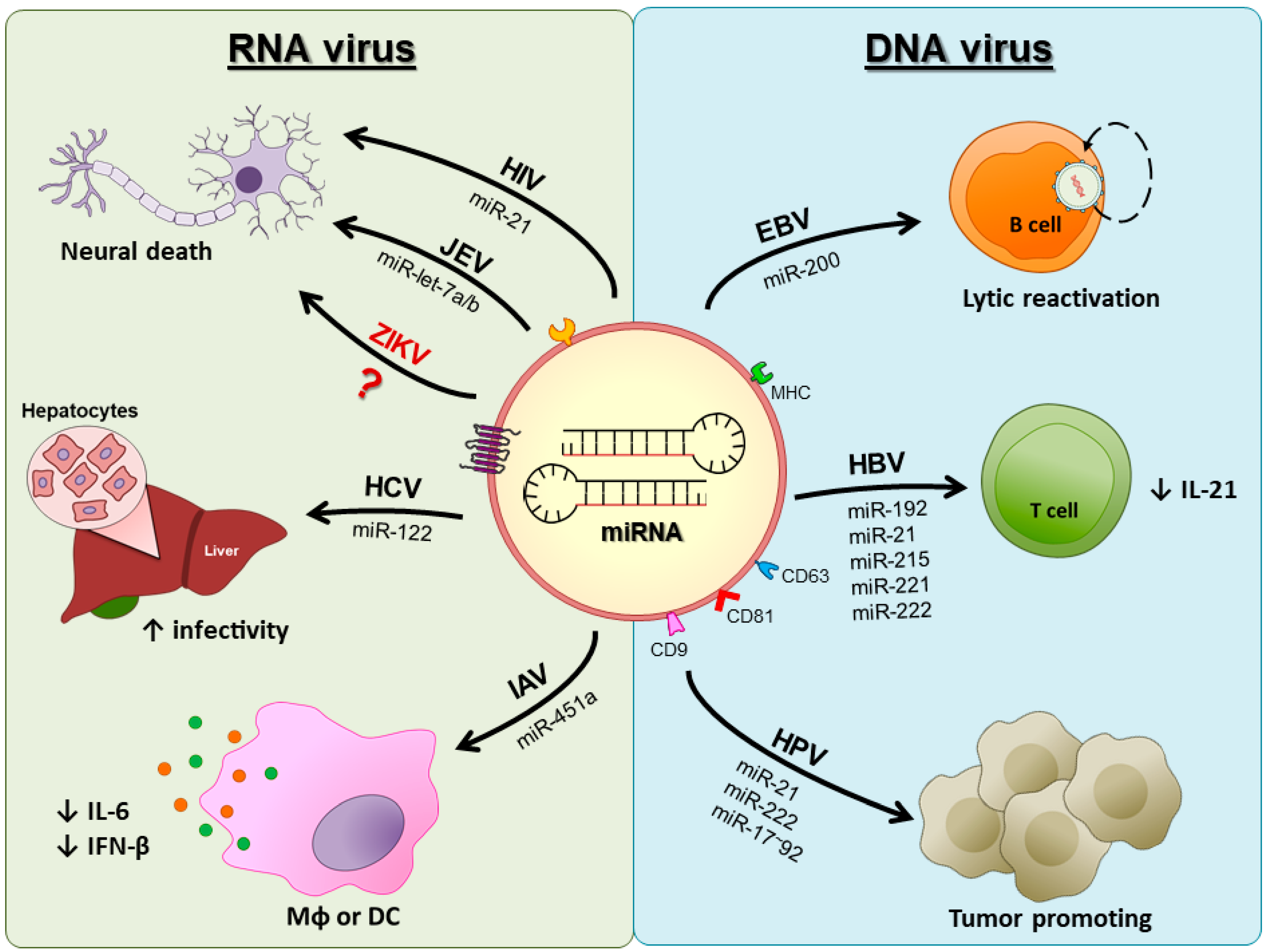
3. DNA Viruses
3.1. Epstein–Barr Virus
3.2. Human Papillomaviruses
3.3. Polyomaviruses
4. RNA Viruses
4.1. Respiratory Viruses
4.2. HIV
4.3. Hepatitis C Virus
4.4. Japanese Encephalitis Virus
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johnstone, R.M.; Adam, M.; Hammond, J.R.; Orr, L.; Turbide, C. Vesicle formation during reticulocyte maturation. Association of plasma membrane activities with released vesicles (exosomes). J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 9412–9420. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Raposo, G.; Stoorvogel, W. Extracellular vesicles: Exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. J. Cell Biol. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowal, J.; Tkach, M.; Théry, C. Biogenesis and secretion of exosomes. Curr. Opin. Cell. Biol. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpintero-Fernández, P.; Fafián-Labora, J.; O’Loghlen, A. Technical Advances to Study Extracellular Vesicles. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shenoda, B.B.; Ajit, S.K. Modulation of Immune Responses by Exosomes Derived from Antigen-Presenting Cells. Clin. Med. Insights Pathol. 2016, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, R.; Gröger, M.; Rauscher, S.; Fendl, B.; Eichhorn, T.; Fischer, M.B.; Spittler, A.; Weber, V. Differential Interaction of Platelet-Derived Extracellular Vesicles with Leukocyte Subsets in Human Whole Blood. Sci. Rep. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tung, S.L.; Boardman, D.A.; Sen, M.; Letizia, M.; Peng, Q.; Cianci, N.; Dioni, L.; Carlin, L.M.; Lechler, R.; Bollati, V.; et al. Regulatory T cell-derived extracellular vesicles modify dendritic cell function. Sci. Rep. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willms, E.; Cabañas, C.; Mäger, I.; Wood, M.J.A.; Vader, P. Extracellular Vesicle Heterogeneity: Subpopulations, Isolation Techniques, and Diverse Functions in Cancer Progression. Front. Immunol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prada, I.; Gabrielli, M.; Turola, E.; Iorio, A.; D’Arrigo, G.; Parolisi, R.; De Luca, M.; Pacifici, M.; Bastoni, M.; Lombardi, M.; et al. Glia-to-neuron transfer of miRNAs via extracellular vesicles: A new mechanism underlying inflammation-induced synaptic alterations. Acta Neuropathol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, S.J.; Booth, A.M.; Hildreth, J.E. The Trojan exosome hypothesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 10592–10597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolte, E.; Cremer, T.; Gallo, R.C.; Margolis, L.B. Extracellular vesicles and viruses: Are they close relatives? Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 9155–9161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Théry, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Aikawa, E.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Anderson, J.D.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Antoniou, A.; Arab, T.; Archer, F.; Atkin-Smith, G.K.; et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hergenreider, E.; Heydt, S.; Tréguer, K.; Boettger, T.; Horrevoets, A.J.; Zeiher, A.M.; Scheffer, M.P.; Frangakis, A.S.; Yin, X.; Mayr, M.; et al. Atheroprotective communication between endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells through miRNAs. Nat. Cell Biol. 2012, 14, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoorvogel, W.; Kleijmeer, M.J.; Geuze, H.J.; Raposo, G. The biogenesis and functions of exosomes. Traffic 2002, 3, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocucci, E.; Meldolesi, J. Ectosomes and exosomes: Shedding the confusion between extracellular vesicles. Trends Cell Biol. 2015, 25, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Niel, G.; Porto-Carreiro, I.; Simoes, S.; Raposo, G. Exosomes: A common pathway for a specialized function. J. Biochem. 2006, 140, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, H.L.; Francis, S.E.; Dower, S.K.; Crossman, D.C. Secretion of intracellular IL-1 receptor antagonist (type 1) is dependent on P2X7 receptor activation. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 1202–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obregon, C.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B.; Gitahi, S.K.; Gehr, P.; Nicod, L.P. Exovesicles from human activated dendritic cells fuse with resting dendritic cells, allowing them to present alloantigens. Am. J. Pathol. 2006, 169, 2127–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meldolesi, J. Exosomes and Ectosomes in Intercellular Communication. Curr. Biol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Properzi, F.; Logozzi, M.; Fais, S. Exosomes: The future of biomarkers in medicine. Biomark. Med. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurunathan, S.; Kang, M.H.; Jeyaraj, M.; Qasim, M.; Kim, J.H. Review of the Isolation, Characterization, Biological Function, and Multifarious Therapeutic Approaches of Exosomes. Cells 2019, 8, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeppesen, D.K.; Fenix, A.M.; Franklin, J.L.; Higginbotham, J.N.; Zhang, Q.; Zimmerman, L.J.; Liebler, D.C.; Ping, J.; Liu, Q.; Evans, R.; et al. Reassessment of Exosome Composition. Cell 2019, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dongen, H.M.; Masoumi, N.; Witwer, K.W.; Pegtel, D.M. Extracellular Vesicles Exploit Viral Entry Routes for Cargo Delivery. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2016, 80, 369–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenhill, C. Hepatitis: New route of HCV transmission. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Z.; Hensley, L.; McKnight, K.L.; Hu, F.; Madden, V.; Ping, L.; Jeong, S.H.; Walker, C.; Lanford, R.E.; Lemon, S.M. A pathogenic picornavirus acquires an envelope by hijacking cellular membranes. Nature 2013, 496, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ota, M.; Serada, S.; Naka, T.; Mori, Y. MHC class I molecules are incorporated into human herpesvirus-6 viral particles and released into the extracellular environment. Microbiol. Immunol. 2014, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izquierdo-Useros, N.; Lorizate, M.; Puertas, M.C.; Rodriguez-Plata, M.T.; Zangger, N.; Erikson, E.; Pino, M.; Erkizia, I.; Glass, B.; Clotet, B.; et al. Siglec-1 is a novel dendritic cell receptor that mediates HIV-1 trans-infection through recognition of viral membrane gangliosides. PLoS Biol. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 2009, 136, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croce, C.M. Causes and consequences of microRNA dysregulation in cancer. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 704–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eacker, S.M.; Dawson, T.M.; Dawson, V.L. Understanding microRNAs in neurodegeneration. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2009, 10, 837–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raab-Traub, N.; Dittmer, D.P. Viral effects on the content and function of extracellular vesicles. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 15, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valadi, H.; Ekström, K.; Bossios, A.; Sjöstrand, M.; Lee, J.J.; Lötvall, J.O. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shurtleff, M.J.; Temoche-Diaz, M.M.; Karfilis, K.V.; Ri, S.; Schekman, R. Y-box protein 1 is required to sort microRNAs into exosomes in cells and in a cell-free reaction. eLife 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cha, D.J.; Franklin, J.L.; Dou, Y.; Liu, Q.; Higginbotham, J.N.; Demory Beckler, M.; Weaver, A.M.; Vickers, K.; Prasad, N.; Levy, S.; et al. KRAS-dependent sorting of miRNA to exosomes. eLife 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouillet, J.F.; Ouyang, Y.; Bayer, A.; Coyne, C.B.; Sadovsky, Y. The role of trophoblastic microRNAs in placental viral infection. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delorme-Axford, E.; Donker, R.B.; Mouillet, J.F.; Chu, T.; Bayer, A.; Ouyang, Y.; Wang, T.; Stolz, D.B.; Sarkar, S.N.; Morelli, A.E.; et al. Human placental trophoblasts confer viral resistance to recipient cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 12048–12053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, H.; Kwong, Y.L. EBV Viral Loads in Diagnosis, Monitoring, and Response Assessment. Front. Oncol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forte, E.; Luftig, M.A. The role of microRNAs in Epstein-Barr virus latency and lytic reactivation. Microbes Infect. 2011, 13, 1156–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegtel, D.M.; Cosmopoulos, K.; Thorley-Lawson, D.A.; van Eijndhoven, M.A.; Hopmans, E.S.; Lindenberg, J.L.; de Gruijl, T.D.; Würdinger, T.; Middeldorp, J.M. Functional delivery of viral miRNAs via exosomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canitano, A.; Venturi, G.; Borghi, M.; Ammendolia, M.G.; Fais, S. Exosomes released in vitro from Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-infected cells contain EBV-encoded latent phase mRNAs. Cancer Lett. 2013, 337, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meckes, D.G.; Gunawardena, H.P.; Dekroon, R.M.; Heaton, P.R.; Edwards, R.H.; Ozgur, S.; Griffith, J.D.; Damania, B.; Raab-Traub, N. Modulation of B-cell exosome proteins by gamma herpesvirus infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, C.; Kim, J.; Park, G.; Kim, S.; Kim, D.; Hur, D.Y.; Kim, B.; Kim, Y.S. Delivery of miR-155 to retinal pigment epithelial cells mediated by Burkitt’s lymphoma exosomes. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.; Swan, K.; Zhang, X.; Cao, S.; Brett, Z.; Drury, S.; Strong, M.J.; Fewell, C.; Puetter, A.; Wang, X.; et al. Secreted Oral Epithelial Cell Membrane Vesicles Induce Epstein-Barr Virus Reactivation in Latently Infected B Cells. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 3469–3479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoshina, S.; Sekizuka, T.; Kataoka, M.; Hasegawa, H.; Hamada, H.; Kuroda, M.; Katano, H. Profile of Exosomal and Intracellular microRNA in Gamma-Herpesvirus-Infected Lymphoma Cell Lines. PLoS ONE 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meckes, D.G.; Shair, K.H.; Marquitz, A.R.; Kung, C.P.; Edwards, R.H.; Raab-Traub, N. Human tumor virus utilizes exosomes for intercellular communication. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gourzones, C.; Gelin, A.; Bombik, I.; Klibi, J.; Vérillaud, B.; Guigay, J.; Lang, P.; Témam, S.; Schneider, V.; Amiel, C.; et al. Extra-cellular release and blood diffusion of BART viral micro-RNAs produced by EBV-infected nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Virol. J. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourzones, C.; Ferrand, F.R.; Amiel, C.; Vérillaud, B.; Barat, A.; Guérin, M.; Gattolliat, C.H.; Gelin, A.; Klibi, J.; Chaaben, A.B.; et al. Consistent high concentration of the viral microRNA BART17 in plasma samples from nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients--evidence of non-exosomal transport. Virol. J. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo, A.; Vella, S.; Miele, M.; Timoneri, F.; Di Bella, M.; Bosi, S.; Sciveres, M.; Conaldi, P.G. Global profiling of viral and cellular non-coding RNAs in Epstein-Barr virus-induced lymphoblastoid cell lines and released exosome cargos. Cancer Lett. 2017, 388, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komabayashi, Y.; Kishibe, K.; Nagato, T.; Ueda, S.; Takahara, M.; Harabuchi, Y. Circulating Epstein-Barr virus-encoded micro-RNAs as potential biomarkers for nasal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 35, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramayanti, O.; Verkuijlen, S.A.W.M.; Novianti, P.; Scheepbouwer, C.; Misovic, B.; Koppers-Lalic, D.; van Weering, J.; Beckers, L.; Adham, M.; Martorelli, D.; et al. Vesicle-bound EBV-BART13-3p miRNA in circulation distinguishes nasopharyngeal from other head and neck cancer and asymptomatic EBV-infections. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toussirot, E.; Roudier, J. Epstein-Barr virus in autoimmune diseases. Best Pract Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2008, 22, 883–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo, A.; Jang, S.I.; Ong, H.L.; Perez, P.; Tandon, M.; Ambudkar, I.; Illei, G.; Alevizos, I. Targeting the Ca(2+) Sensor STIM1 by Exosomal Transfer of Ebv-miR-BART13-3p is Associated with Sjögren’s Syndrome. EBioMedicine 2016, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Huang, X.; Zhang, Y. Involvement of Human Papillomaviruses in Cervical Cancer. Front. Microbiol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yim, E.K.; Park, J.S. The role of HPV E6 and E7 oncoproteins in HPV-associated cervical carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. Treat. 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shishodia, G.; Verma, G.; Das, B.C.; Bharti, A.C. miRNA as viral transcription tuners in HPV-mediated cervical carcinogenesis. Front. Biosci. 2018, 10, 21–47. [Google Scholar]
- Chiantore, M.V.; Mangino, G.; Iuliano, M.; Zangrillo, M.S.; De Lillis, I.; Vaccari, G.; Accardi, R.; Tommasino, M.; Columba Cabezas, S.; Federico, M.; et al. Human papillomavirus E6 and E7 oncoproteins affect the expression of cancer-related microRNAs: Additional evidence in HPV-induced tumorigenesis. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 142, 1751–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honegger, A.; Schilling, D.; Bastian, S.; Sponagel, J.; Kuryshev, V.; Sültmann, H.; Scheffner, M.; Hoppe-Seyler, K.; Hoppe-Seyler, F. Dependence of intracellular and exosomal microRNAs on viral E6/E7 oncogene expression in HPV-positive tumor cells. PLoS Pathog 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harden, M.E.; Munger, K. Human papillomavirus 16 E6 and E7 oncoprotein expression alters microRNA expression in extracellular vesicles. Virology 2017, 508, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peacock, B.; Rigby, A.; Bradford, J.; Pink, R.; Hunter, K.; Lambert, D.; Hunt, S. Extracellular vesicle microRNA cargo is correlated with HPV status in oropharyngeal carcinoma. J. Oral. Pathol. Med. 2018, 47, 954–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cokarić Brdovčak, M.; Zubković, A.; Jurak, I. Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Deregulation of Host MicroRNAs. Noncoding RNA 2018, 4, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalamvoki, M.; Du, T.; Roizman, B. Cells infected with herpes simplex virus 1 export to uninfected cells exosomes containing STING, viral mRNAs, and microRNAs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elphick, G.F.; Querbes, W.; Jordan, J.A.; Gee, G.V.; Eash, S.; Manley, K.; Dugan, A.; Stanifer, M.; Bhatnagar, A.; Kroeze, W.K.; et al. The human polyomavirus, JCV, uses serotonin receptors to infect cells. Science 2004, 306, 1380–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagatie, O.; Tritsmans, L.; Stuyver, L.J. The miRNA world of polyomaviruses. Virol. J. 2013, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giovannelli, I.; Clausi, V.; Nukuzuma, S.; Della Malva, N.; Nosi, D.; Giannecchini, S. Polyomavirus JC microRNA expression after infection in vitro. Virus Res. 2016, 213, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pakfetrat, M.; Yaghobi, R.; Salmanpoor, Z.; Roozbeh, J.; Torabinezhad, S.; Kadkhodaei, S. Frequency of Polyomavirus BK Infection in Kidney Transplant Patients Suspected to Nephropathy. Int. J. Organ. Transplant. Med. 2015, 6, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.H.; Lee, Y.H.; Seo, J.W.; Moon, H.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, Y.G.; Jeong, K.H.; Moon, J.Y.; Lee, T.W.; Ihm, C.G.; et al. Urinary exosomal viral microRNA as a marker of BK virus nephropathy in kidney transplant recipients. PLoS ONE 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Ree, M.H.; Jansen, L.; Kruize, Z.; van Nuenen, A.C.; van Dort, K.A.; Takkenberg, R.B.; Reesink, H.W.; Kootstra, N.A. Plasma MicroRNA Levels Are Associated With Hepatitis B e Antigen Status and Treatment Response in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 215, 1421–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enomoto, Y.; Takagi, R.; Naito, Y.; Kiniwa, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Hamada-Tsutsumi, S.; Kawano, M.; Matsushita, S.; Ochiya, T.; Miyajima, A. Identification of the novel 3′UTR sequences of human IL-21 mRNA as potential targets of miRNAs. Sci Rep. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahar, H.S.; Bao, X.; Casola, A. Exosomes and Their Role in the Life Cycle and Pathogenesis of RNA Viruses. Viruses 2015, 7, 2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, M.J.; Gomez, J.L.; Perez, G.F.; Pancham, K.; Val, S.; Pillai, D.K.; Giri, M.; Ferrante, S.; Freishtat, R.; Rose, M.C.; et al. Airway Secretory microRNAome Changes during Rhinovirus Infection in Early Childhood. PLoS ONE 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, M.; Fukushima, Y.; Kouwaki, T.; Daito, T.; Kohara, M.; Kida, H.; Oshiumi, H. MicroRNA-451a in extracellular, blood-resident vesicles attenuates macrophage and dendritic cell responses to influenza whole-virus vaccine. J. Biol. Chem. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheller, N.; Herold, S.; Kellner, R.; Bertrams, W.; Jung, A.L.; Janga, H.; Greulich, T.; Schulte, L.N.; Vogelmeier, C.F.; Lohmeyer, J.; et al. Proviral MicroRNAs Detected in Extracellular Vesicles from Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid of Patients With Influenza Virus-Induced Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 219, 540–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellwanger, J.H.; Veit, T.D.; Chies, J.A.B. Exosomes in HIV infection: A review and critical look. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2017, 53, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, W.W.; Huang, M.B.; Addae Konadu, K.; Powell, M.D.; Bond, V.C. Micro RNA in Exosomes from HIV-Infected Macrophages. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 13, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubert, A.; Subra, C.; Jenabian, M.A.; Tremblay Labrecque, P.F.; Tremblay, C.; Laffont, B.; Provost, P.; Routy, J.P.; Gilbert, C. Elevated Abundance, Size, and MicroRNA Content of Plasma Extracellular Vesicles in Viremic HIV-1+ Patients: Correlations with Known Markers of Disease Progression. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2015, 70, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Z.; Muth, D.C.; Eitan, E.; Travers, M.; Learman, L.N.; Lehrmann, E.; Witwer, K.W. Serum extracellular vesicle depletion processes affect release and infectivity of HIV-1 in culture. Sci. Rep. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNamara, R.P.; Costantini, L.M.; Myers, T.A.; Schouest, B.; Maness, N.J.; Griffith, J.D.; Damania, B.A.; MacLean, A.G.; Dittmer, D.P. Nef Secretion into Extracellular Vesicles or Exosomes Is Conserved across Human and Simian Immunodeficiency Viruses. mBio 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stumptner-Cuvelette, P.; Jouve, M.; Helft, J.; Dugast, M.; Glouzman, A.S.; Jooss, K.; Raposo, G.; Benaroch, P. Human immunodeficiency virus-1 Nef expression induces intracellular accumulation of multivesicular bodies and major histocompatibility complex class II complexes: Potential role of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Mol. Biol. Cell 2003, 14, 4857–4870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aqil, M.; Naqvi, A.R.; Mallik, S.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Maulik, U.; Jameel, S. The HIV Nef protein modulates cellular and exosomal miRNA profiles in human monocytic cells. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aqil, M.; Mallik, S.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Maulik, U.; Jameel, S. Transcriptomic Analysis of mRNAs in Human Monocytic Cells Expressing the HIV-1 Nef Protein and Their Exosomes. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aqil, M.; Naqvi, A.R.; Bano, A.S.; Jameel, S. The HIV-1 Nef protein binds argonaute-2 and functions as a viral suppressor of RNA interference. PLoS ONE 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazleton, J.E.; Berman, J.W.; Eugenin, E.A. Novel mechanisms of central nervous system damage in HIV infection. HIV AIDS 2010, 2, 39–49. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Niu, F.; Yao, H.; Liao, K.; Chen, X.; Kook, Y.; Ma, R.; Hu, G.; Buch, S. Exosomal miR-9 Released from HIV Tat Stimulated Astrocytes Mediates Microglial Migration. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2018, 13, 330–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yelamanchili, S.V.; Lamberty, B.G.; Rennard, D.A.; Morsey, B.M.; Hochfelder, C.G.; Meays, B.M.; Levy, E.; Fox, H.S. MiR-21 in Extracellular Vesicles Leads to Neurotoxicity via TLR7 Signaling in SIV Neurological Disease. PLoS Pathog 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Yao, H.; Chaudhuri, A.D.; Duan, M.; Yelamanchili, S.V.; Wen, H.; Cheney, P.D.; Fox, H.S.; Buch, S. Exosome-mediated shuttling of microRNA-29 regulates HIV Tat and morphine-mediated neuronal dysfunction. Cell Death Dis. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, H.; Chinnappan, M.; Agarwal, S.; Dalvi, P.; Gunewardena, S.; O’Brien-Ladner, A.; Dhillon, N.K. Macrophage-derived extracellular vesicles mediate smooth muscle hyperplasia: Role of altered miRNA cargo in response to HIV infection and substance abuse. FASEB J. 2018, 32, 5174–5185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biyani, S.; Garg, R.K.; Jain, A.; Malhotra, H.S.; Kumar, R.; Prakash, S.; Verma, R.; Sharma, P.K. Toll-like receptor-3 gene polymorphism in patients with Japanese encephalitis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2015, 286, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klase, Z.; Kale, P.; Winograd, R.; Gupta, M.V.; Heydarian, M.; Berro, R.; McCaffrey, T.; Kashanchi, F. HIV-1 TAR element is processed by Dicer to yield a viral micro-RNA involved in chromatin remodeling of the viral LTR. BMC Mol. Biol. 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayanan, A.; Iordanskiy, S.; Das, R.; Van Duyne, R.; Santos, S.; Jaworski, E.; Guendel, I.; Sampey, G.; Dalby, E.; Iglesias-Ussel, M.; et al. Exosomes derived from HIV-1-infected cells contain trans-activation response element RNA. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 20014–20033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, C.; Narayanan, S.; Hahn, Y.S. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells: The dark knight or the joker in viral infections? Immunol. Rev. 2013, 255, 210–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampey, G.C.; Saifuddin, M.; Schwab, A.; Barclay, R.; Punya, S.; Chung, M.C.; Hakami, R.M.; Zadeh, M.A.; Lepene, B.; Klase, Z.A.; et al. Exosomes from HIV-1-infected Cells Stimulate Production of Pro-inflammatory Cytokines through Trans-activating Response (TAR) RNA. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 1251–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramakrishnaiah, V.; Thumann, C.; Fofana, I.; Habersetzer, F.; Pan, Q.; de Ruiter, P.E.; Willemsen, R.; Demmers, J.A.; Stalin Raj, V.; Jenster, G.; et al. Exosome-mediated transmission of hepatitis C virus between human hepatoma Huh7.5 cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 13109–13113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bukong, T.N.; Momen-Heravi, F.; Kodys, K.; Bala, S.; Szabo, G. Exosomes from hepatitis C infected patients transmit HCV infection and contain replication competent viral RNA in complex with Ago2-miR122-HSP90. PLoS Pathog 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devhare, P.B.; Sasaki, R.; Shrivastava, S.; Di Bisceglie, A.M.; Ray, R.; Ray, R.B. Exosome-Mediated Intercellular Communication between Hepatitis C Virus-Infected Hepatocytes and Hepatic Stellate Cells. J. Virol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambrecht, J.; Jan Poortmans, P.; Verhulst, S.; Reynaert, H.; Mannaerts, I.; van Grunsven, L.A. Circulating ECV-Associated miRNAs as Potential Clinical Biomarkers in Early Stage HBV and HCV Induced Liver Fibrosis. Front. Pharmacol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tellapuri, S.; Sutphin, P.D.; Beg, M.S.; Singal, A.G.; Kalva, S.P. Staging systems of hepatocellular carcinoma: A review. Indian J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 37, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.H.; Ren, L.N.; Wang, X.; Wang, T.; Zhang, N.; Gao, Y.; Luo, H.; Navarro-Alvarez, N.; Tang, L.J. Combination of exosomes and circulating microRNAs may serve as a promising tumor marker complementary to alpha-fetoprotein for early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma diagnosis in rats. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 141, 1767–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, H.; He, P.; Li, Y.; Si, M.; Jiao, X. Circulating microRNAs as a biomarker to predict therapy efficacy in hepatitis C patients with different genotypes. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 112, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, X.; Fan, Z.; Chen, H.; He, P.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Ke, C. Serum and exosomal miR-122 and miR-199a as a biomarker to predict therapeutic efficacy of hepatitis C patients. J. Med. Virol 2017, 89, 1597–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santangelo, L.; Bordoni, V.; Montaldo, C.; Cimini, E.; Zingoni, A.; Battistelli, C.; D’Offizi, G.; Capobianchi, M.R.; Santoni, A.; Tripodi, M.; et al. Hepatitis C virus direct-acting antivirals therapy impacts on extracellular vesicles microRNAs content and on their immunomodulating properties. Liver Int. 2018, 38, 1741–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, X.; Sun, L.; Zhou, L.; Ma, T.C.; Song, L.; Wu, J.G.; Li, J.L.; Ho, W.Z. Toll-like receptor 3-activated macrophages confer anti-HCV activity to hepatocytes through exosomes. FASEB J. 2016, 30, 4132–4140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, X.; Xu, C.; Fang, S.; Zhao, P.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Yuan, W.; Qi, Z. Exosomal MicroRNAs Derived from Umbilical Mesenchymal Stem Cells Inhibit Hepatitis C Virus Infection. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2016, 5, 1190–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, N.; Lomash, V.; Rao, P.V. Expression profile of Japanese encephalitis virus induced neuroinflammation and its implication in disease severity. J. Clin. Virol. 2010, 49, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rastogi, M.; Srivastava, N.; Singh, S.K. Exploitation of microRNAs by Japanese Encephalitis virus in human microglial cells. J. Med. Virol. 2018, 90, 648–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, S.; Akbar, I.; Kumari, B.; Vrati, S.; Basu, A.; Banerjee, A. Japanese Encephalitis Virus-induced let-7a/b interacted with the NOTCH-TLR7 pathway in microglia and facilitated neuronal death via caspase activation. J. Neurochem. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germano, J.F.; Sawaged, S.; Saadaeijahromi, H.; Andres, A.M.; Feuer, R.; Gottlieb, R.A.; Sin, J. Coxsackievirus B infection induces the extracellular release of miR-590-5p, a proviral microRNA. Virology 2019, 529, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yoshikawa, F.S.Y.; Teixeira, F.M.E.; Sato, M.N.; Oliveira, L.M.d.S. Delivery of microRNAs by Extracellular Vesicles in Viral Infections: Could the News be Packaged? Cells 2019, 8, 611. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8060611
Yoshikawa FSY, Teixeira FME, Sato MN, Oliveira LMdS. Delivery of microRNAs by Extracellular Vesicles in Viral Infections: Could the News be Packaged? Cells. 2019; 8(6):611. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8060611
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoshikawa, Fabio Seiti Yamada, Franciane Mouradian Emidio Teixeira, Maria Notomi Sato, and Luanda Mara da Silva Oliveira. 2019. "Delivery of microRNAs by Extracellular Vesicles in Viral Infections: Could the News be Packaged?" Cells 8, no. 6: 611. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8060611
APA StyleYoshikawa, F. S. Y., Teixeira, F. M. E., Sato, M. N., & Oliveira, L. M. d. S. (2019). Delivery of microRNAs by Extracellular Vesicles in Viral Infections: Could the News be Packaged? Cells, 8(6), 611. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8060611





