Cardiac Rhythm and Molecular Docking Studies of Ion Channel Ligands with Cardiotoxicity in Zebrafish
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Alterations in Cardiac Structure and Function by Drugs
1.2. Zebrafish as Cardiotoxicity Animal Model
1.3. Evaluation of Cardiovascular Toxicity Mechanism by In Silico Molecular Docking
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Zebrafish Maintenance and Embryo Collection
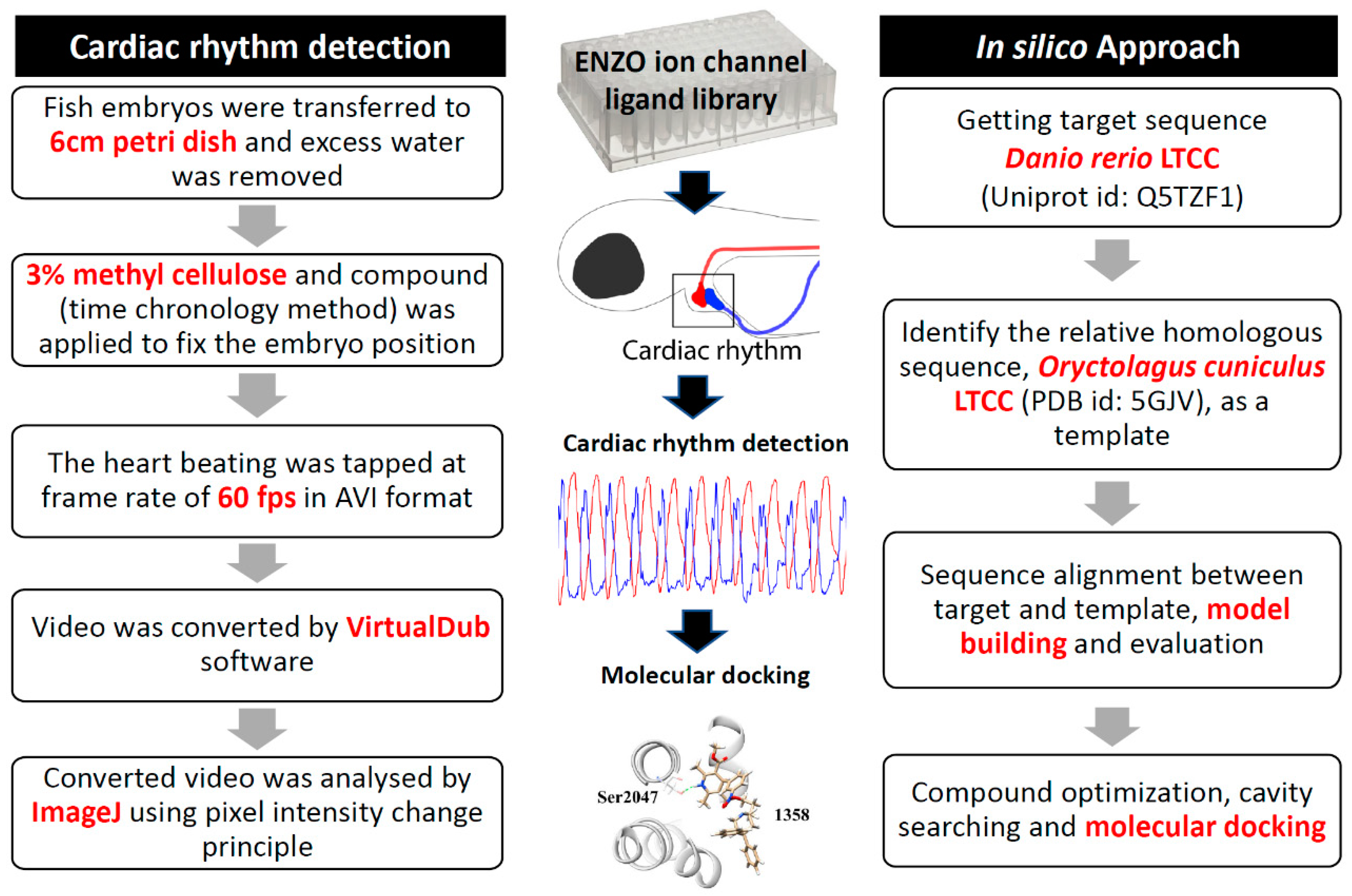
2.2. Video Recording, Processing, and Analysis
2.3. Drug Treatment
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Structure-Based Molecular Simulation for the Binding of Selected Ligands with Danio Rerio LTCC
3. Results
3.1. Overview of Experimental Design and Workflow
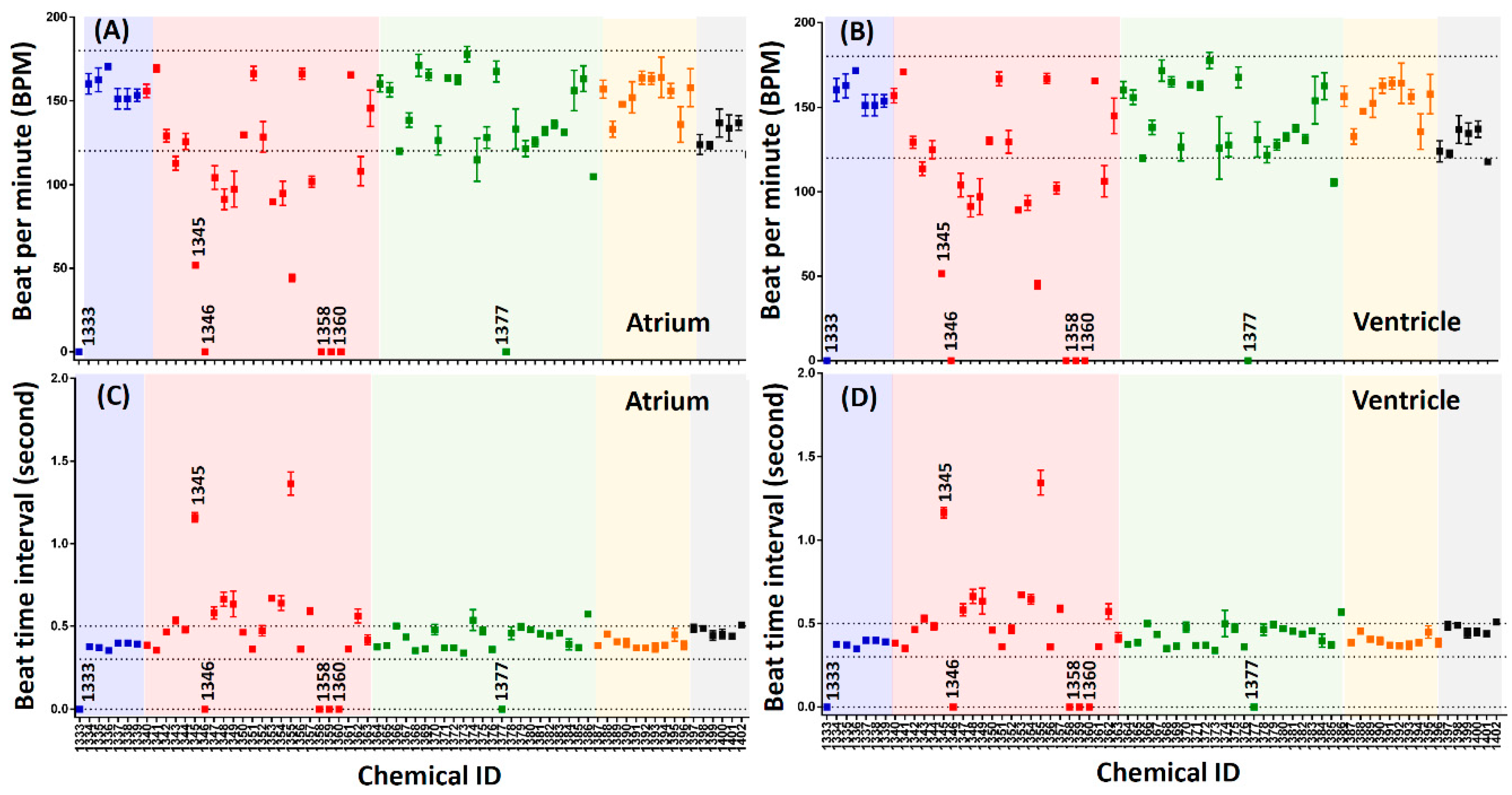
3.2. Evaluation of Chemical Cardiotoxicity by End-Point Method
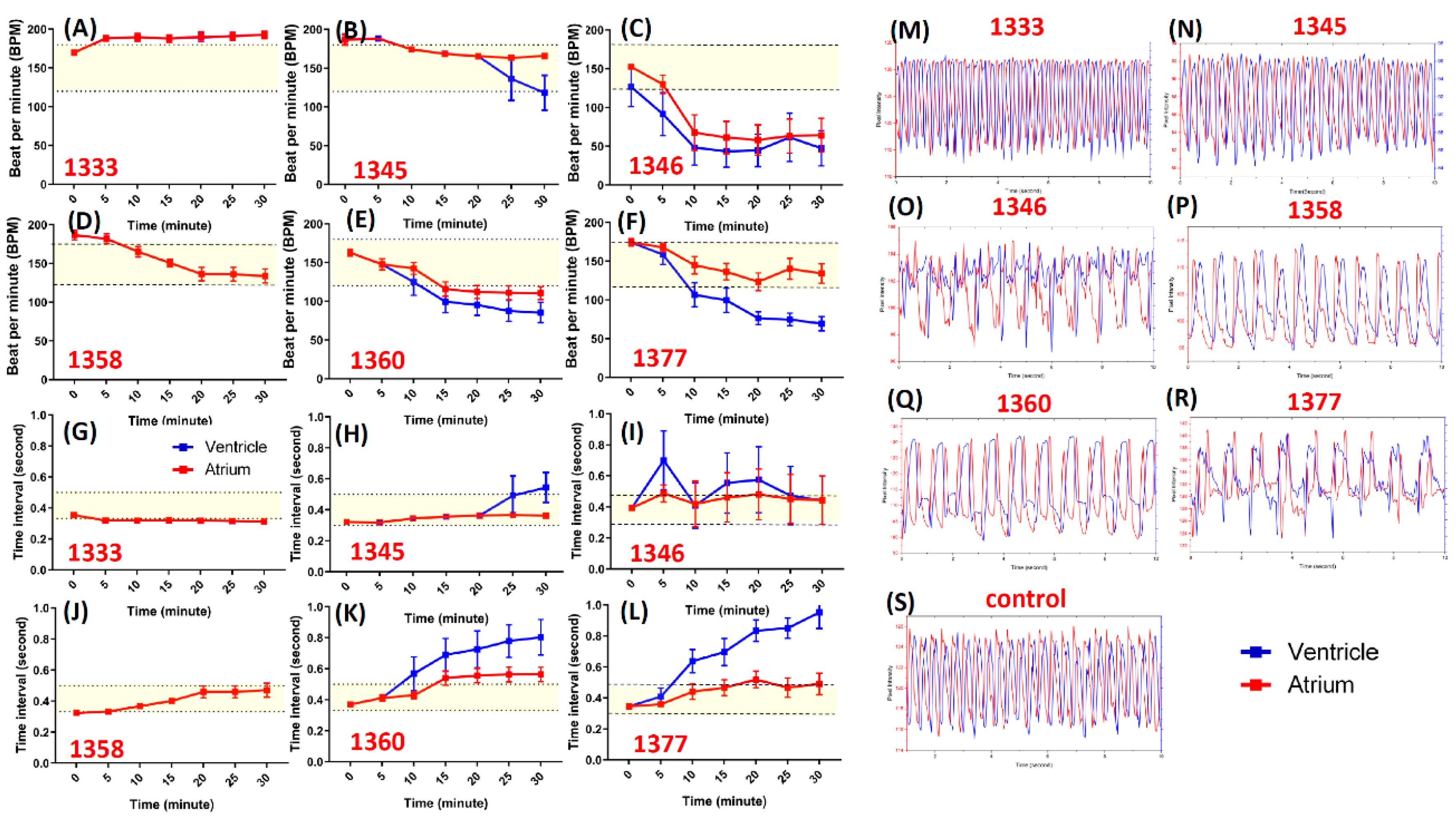
3.3. Validation of Primary Screen Data by Chronology Method
3.4. Molecular Docking Using the Danio Rerio Cav1.2 Homology Modeling Structure
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A


References
- Anson, B.D.; Kolaja, K.; Kamp, T.J. Opportunities for use of human ips cells in predictive toxicology. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 89, 754–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rémuzat, C.; Toumi, M.; Falissard, B. New drug regulations in france: What are the impacts on market access? Part 1–overview of new drug regulations in france. J. Mark. Access Health Policy 2013, 1, 20891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrias, A.; Jie, X.; Romero, L.; Bishop, M.; Bernabeu, M.; Pueyo, E.; Rodriguez, B. Arrhythmic risk biomarkers for the assessment of drug cardiotoxicity: From experiments to computer simulations. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2010, 368, 3001–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braam, S.R.; Tertoolen, L.; van de Stolpe, A.; Meyer, T.; Passier, R.; Mummery, C.L. Prediction of drug-induced cardiotoxicity using human embryonic stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes. Stem Cell Res. 2010, 4, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alderton, P.M.; Gross, J.; Green, M.D. Comparative study of doxorubicin, mitoxantrone, and epirubicin in combination with icrf-187 (adr-529) in a chronic cardiotoxicity animal model. Cancer Res. 1992, 52, 194–201. [Google Scholar]
- McGrath, P.; Li, C.-Q. Zebrafish: A predictive model for assessing drug-induced toxicity. Drug Discov. Today 2008, 13, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zon, L.I.; Peterson, R.T. In vivo drug discovery in the zebrafish. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2005, 4, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parng, C.; Seng, W.L.; Semino, C.; McGrath, P. Zebrafish: A preclinical model for drug screening. Assay Drug Dev. Technol. 2002, 1, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lister, J.A. Development of pigment cells in the zebrafish embryo. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2002, 58, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Ho, N.Y.; Alshut, R.; Legradi, J.; Weiss, C.; Reischl, M.; Mikut, R.; Liebel, U.; Müller, F.; Strähle, U. Zebrafish embryos as models for embryotoxic and teratological effects of chemicals. Reprod. Toxicol. 2009, 28, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alderton, W.; Berghmans, S.; Butler, P.; Chassaing, H.; Fleming, A.; Golder, Z.; Richards, F.; Gardner, I. Accumulation and metabolism of drugs and cyp probe substrates in zebrafish larvae. Xenobiotica 2010, 40, 547–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, F.; Langenbacher, A.D.; Chen, J.-N. Transcriptional regulation of heart development in zebrafish. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2016, 3, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkhard, S.; van Eif, V.; Garric, L.; Christoffels, V.M.; Bakkers, J. On the evolution of the cardiac pacemaker. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2017, 4, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genge, C.E.; Lin, E.; Lee, L.; Sheng, X.; Rayani, K.; Gunawan, M.; Stevens, C.M.; Li, A.Y.; Talab, S.S.; Claydon, T.W. The zebrafish heart as a model of mammalian cardiac function. In Reviews of Physiology, Biochemistry and Pharmacology, vol. 171; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 99–136. [Google Scholar]
- Vornanen, M.; Hassinen, M. Zebrafish heart as a model for human cardiac electrophysiology. Channels 2016, 10, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alday, A.; Alonso, H.; Gallego, M.; Urrutia, J.; Letamendia, A.; Callol, C.; Casis, O. Ionic channels underlying the ventricular action potential in zebrafish embryo. Pharmacol. Res. 2014, 84, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsutsui, H.; Higashijima, S.i.; Miyawaki, A.; Okamura, Y. Visualizing voltage dynamics in zebrafish heart. J. Physiol. 2010, 588, 2017–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. Autodock vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallakyan, S.; Olson, A.J. Small-molecule library screening by docking with pyrx. In Chemical Biology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 243–250. [Google Scholar]
- Seeliger, D.; de Groot, B.L. Ligand docking and binding site analysis with pymol and autodock/vina. J. Comput. -Aided Mol. Des. 2010, 24, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R.D.; Jewsbury, P.J.; Essex, J.W. A review of protein-small molecule docking methods. J. Comput. -Aided Mol. Des. 2002, 16, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph-McCarthy, D.; Baber, J.C.; Feyfant, E.; Thompson, D.C.; Humblet, C. Lead optimization via high-throughput molecular docking. Curr. Opin. Drug Discov. Dev. 2007, 10, 264–274. [Google Scholar]
- Alonso, H.; Bliznyuk, A.A.; Gready, J.E. Combining docking and molecular dynamic simulations in drug design. Med. Res. Rev. 2006, 26, 531–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lybrand, T.P. Ligand—protein docking and rational drug design. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 1995, 5, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampurna, B.P.; Audira, G.; Juniardi, S.; Lai, Y.-H.; Hsiao, C.-D. A simple imagej-based method to measure cardiac rhythm in zebrafish embryos. Inventions 2018, 3, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avdesh, A.; Chen, M.; Martin-Iverson, M.T.; Mondal, A.; Ong, D.; Rainey-Smith, S.; Taddei, K.; Lardelli, M.; Groth, D.M.; Verdile, G. Regular care and maintenance of a zebrafish (danio rerio) laboratory: An introduction. Jove (J. Vis. Exp.) 2012, e4196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eswar, N.; Webb, B.; Marti-Renom, M.A.; Madhusudhan, M.; Eramian, D.; Shen, M.y.; Pieper, U.; Sali, A. Comparative protein structure modeling using modeller. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2006, 15, 5.6. 1–5.6. 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dassault Systèmes BIOVIA. Discovery Studio Modeling Environment; Dassault Systèmes: San Diego, CA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, M.y.; Sali, A. Statistical potential for assessment and prediction of protein structures. Protein Sci. 2006, 15, 2507–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- John, B.; Sali, A. Comparative protein structure modeling by iterative alignment, model building and model assessment. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3982–3992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatachalam, C.M.; Jiang, X.; Oldfield, T.; Waldman, M. Ligandfit: A novel method for the shape-directed rapid docking of ligands to protein active sites. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2003, 21, 289–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Pei, J.; Lai, L. Binding site detection and druggability prediction of protein targets for structure-based drug design. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 2326–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, B.R.; Bruccoleri, R.E.; Olafson, B.D.; States, D.J.; Swaminathan, S.a.; Karplus, M. Charmm: A program for macromolecular energy, minimization, and dynamics calculations. J. Comput. Chem. 1983, 4, 187–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, U. Chimera–a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Luca, E.; Zaccaria, G.M.; Hadhoud, M.; Rizzo, G.; Ponzini, R.; Morbiducci, U.; Santoro, M.M. Zebrabeat: A flexible platform for the analysis of the cardiac rate in zebrafish embryos. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, R.C.; Tikhonov, D.B.; Zhorov, B.S. Structural model for phenylalkylamine binding to l-type calcium channels. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 28332–28342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hockerman, G.H.; Peterson, B.Z.; Johnson, B.D.; Catterall, W.A. Molecular determinants of drug binding and action on l-type calcium channels. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1997, 37, 361–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Striessnig, J.; Grabner, M.; Mitterdorfer, J.; Hering, S.; Sinnegger, M.J.; Glossmann, H. Structural basis of drug binding to l ca2+ channels. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1998, 19, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Striessnig, J.; Pinggera, A.; Kaur, G.; Bock, G.; Tuluc, P. L-type ca(2+) channels in heart and brain. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Membr. Transp. Signal. 2014, 3, 15–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, L.; Gamal El-Din, T.M.; Swanson, T.M.; Pryde, D.C.; Scheuer, T.; Zheng, N.; Catterall, W.A. Structural basis for inhibition of a voltage-gated ca(2+) channel by ca(2+) antagonist drugs. Nature 2016, 537, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babcock, D.F.; First, N.L.; Lardy, H.A. Action of ionophore a23187 at the cellular level. Separation of effects at the plasma and mitochondrial membranes. J. Biol. Chem. 1976, 251, 3881–3886. [Google Scholar]
- Cornet, C.; Calzolari, S.; Miñana-Prieto, R.; Dyballa, S.; van Doornmalen, E.; Rutjes, H.; Savy, T.; D’Amico, D.; Terriente, J. Zeglobaltox: An innovative approach to address organ drug toxicity using zebrafish. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.G.; Rao, G.H.; Gerrard, J.M. Effects of the ionophore a23187 on blood platelets: I. Influence on aggregation and secretion. Am. J. Pathol. 1974, 77, 135. [Google Scholar]
- Holland, D.; Steinberg, M.; Armstrong, W.M. A23187: A calcium lonophore that directly increases cardiac contractility. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1975, 148, 1141–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaffer, S.W.; Safer, B.; Scarpa, A.; Williamson, J.R. Mode of action of the calcium ionophores x-537a and a23187 on cardiac contractility. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1974, 23, 1609–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, W.; Kittner, H.; Regenthal, R.; De Sarro, G. Anticonvulsant profile of flunarizine and relation to na+ channel blocking effects. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2004, 94, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagbemi, O.; Kane, K.; McDonald, F.; Parratt, J.; Rothaul, A. The effects of verapamil, prenylamine, flunarizine and cinnarizine on coronary artery occlusion-induced arrhythmias in anaesthetized rats. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1984, 83, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghais, N.S.; Zhang, Y.; Grace, A.A.; Huang, C.L.H. Arrhythmogenic actions of the ca2+ channel agonist fpl-64716 in langendorff-perfused murine hearts. Exp. Physiol. 2009, 94, 240–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.S.; Palade, P. Effects of fpl 64176 on ca transients in voltage-clamped rat venticular myocytes. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 135, 1495–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Xiao, B.; Zhang, L.; Chen, S.W. Enhanced basal activity of a cardiac ca2+ release channel (ryanodine receptor) mutant associated with ventricular tachycardia and sudden death. Circ. Res. 2002, 91, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stengel, W.; Jainz, M.; Andreas, K. Different potencies of dihydropyridine derivatives in blocking t-type but not l-type ca2+ channels in neuroblastoma-glioma hybrid cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1998, 342, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, R.I.; Takeda, P.; Mason, D.T.; DeMaria, A.N. The effects of calcium channel blocking agents on cardiovascular function. Am. J. Cardiol. 1982, 49, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Wang, L.; Cai, F.; Rampe, D. High affinity blockade of the herg cardiac k+ channel by the neuroleptic pimozide. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 392, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desta, Z.; Kerbusch, T.; Flockhart, D.A. Effect of clarithromycin on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of pimozide in healthy poor and extensive metabolizers of cytochrome p450 2d6 (cyp2d6). Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1999, 65, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spedding, M.; Kenny, B.; Chatelain, P. New drug binding sites in ca2+ channels. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1995, 16, 139–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.T.; Lu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.-N. Zebrafish as a model for cardiovascular development and disease. Drug Discov. Today Dis. Models 2008, 5, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Siepmann, J.; Peppas, N. Modeling of drug release from delivery systems based on hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (hpmc). Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sampurna, B.P.; Santoso, F.; Lee, J.-H.; Yu, W.-H.; Wu, C.-C.; Audira, G.; Juniardi, S.; Chen, J.-R.; Lin, Y.-T.; Hsiao, C.-D. Cardiac Rhythm and Molecular Docking Studies of Ion Channel Ligands with Cardiotoxicity in Zebrafish. Cells 2019, 8, 566. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8060566
Sampurna BP, Santoso F, Lee J-H, Yu W-H, Wu C-C, Audira G, Juniardi S, Chen J-R, Lin Y-T, Hsiao C-D. Cardiac Rhythm and Molecular Docking Studies of Ion Channel Ligands with Cardiotoxicity in Zebrafish. Cells. 2019; 8(6):566. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8060566
Chicago/Turabian StyleSampurna, Bonifasius Putera, Fiorency Santoso, Jia-Hau Lee, Wen-Hao Yu, Chin-Chung Wu, Gilbert Audira, Stevhen Juniardi, Jung-Ren Chen, Ying-Ting Lin, and Chung-Der Hsiao. 2019. "Cardiac Rhythm and Molecular Docking Studies of Ion Channel Ligands with Cardiotoxicity in Zebrafish" Cells 8, no. 6: 566. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8060566
APA StyleSampurna, B. P., Santoso, F., Lee, J.-H., Yu, W.-H., Wu, C.-C., Audira, G., Juniardi, S., Chen, J.-R., Lin, Y.-T., & Hsiao, C.-D. (2019). Cardiac Rhythm and Molecular Docking Studies of Ion Channel Ligands with Cardiotoxicity in Zebrafish. Cells, 8(6), 566. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8060566






