Leucocyte Telomere Length and Glucose Tolerance Status in Mixed-Ancestry South Africans
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics
2.2. Study Design and Clinical Procedures
2.3. Blood Collection and Biochemical Assays
2.4. Glycaemic Status Classification
2.5. DNA Extraction and Freeze Thawing Procedures
2.6. Telomere Length Measurement
2.7. The Standard Curve for Human Single Copy Gene (SCG), 36B4
2.8. Calculation of the Genome Copy Number
2.9. q-PCR for Absolute Telomere Length (aTL)
2.10. Quality Control
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. General Characteristics of Participants at Baseline and Three Year Follow Up
3.2. Correlation between Telomere Length and Glucose Metabolic Parameters
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oeseburg, H.; De Boer, R.A.; Van Gilst, W.H.; Van Der Harst, P. Telomere biology in healthy aging and disease. Pflugers Archiv. Eur. J. Physiol. 2010, 459, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blackburn, E.H. Switching and signaling at the telomere. Cell 2001, 106, 661–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, D.; Fairall, L.; Simonsson, T.; Court, R.; Chapman, L. Telomere architecture. EMBO Rep. 2002, 3, 1139–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lange, T. Protection of mammalian telomeres. Oncogene 2002, 21, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shammas, M.A. Telomeres, lifestyle, cancer, and aging. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2011, 14, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Yeh, J.-K. Telomeres and Telomerase in Cardiovascular Diseases. Genes 2016, 7, 58. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, J.Y.Y.; De Vivo, I.; Lin, X.; Fang, S.C.; Christiani, D.C. The Relationship between Inflammatory Biomarkers and Telomere Length in an Occupational Prospective Cohort Study. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, K.; Kim, J.; Kim, G.W.; Choi, C. Oxidative Stress-Induced Necrotic Cell Death via Mitochondira-Dependent Burst of Reactive Oxygen Species. Curr. Neurovascular Res. 2009, 6, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, Y.; Takubo, K.; Aida, J.; Araki, A.; Ito, H. Telomere attrition and diabetes mellitus. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2016, 16, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, S8–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lam, K.S.L.; Kraegen, E.W.; Sweeney, G.; Zhang, J.; Tso, A.W.K.; Chow, W.S.; Wat, N.M.S.; Xu, J.Y.; Hoo, R.L.C.; et al. Lipocalin-2 is an inflammatory marker closely associated with obesity, insulin resistance, and hyperglycemia in humans. Clin. Chem. 2007, 53, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Rao, X.; Zhong, J. Role of T Lymphocytes in Type 2 Diabetes and Diabetes-Associated Inflammation. Biol. Proced. Online 2017, 6494795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willeit, P.; Raschenberger, J.; Heydon, E.E.; Tsimikas, S.; Haun, M.; Mayr, A.; Weger, S.; Witztum, J.L.; Butterworth, A.S.; Willeit, J.; et al. Leucocyte telomere length and risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus: New prospective cohort study and literature-based meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wit, E.; Delport, W.; Rugamika, C.E.; Meintjes, A.; Möller, M.; van Helden, P.D.; Seoighe, C.; Hoal, E.G. Genome-wide analysis of the structure of the South African Coloured Population in the Western Cape. Hum. Genet. 2010, 128, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erasmus, R.T.; Soita, D.J.; Hassan, M.S.; Blanco-Blanco, E.; Vergotine, Z.; Kengne, A.P.; Matsha, T.E. High prevalence of diabetes mellitus and metabolic syndrome in a South African coloured population: Baseline data of a study in Bellville, Cape Town. S. Afr. Med. J. 2012, 102, 841–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statistics South Africa. Provincial Profile: Western Cape. Report No: 03-01-70 (2011); 2011. Available online: www.statssa.gov.za/publications/Report-03-01-70/Report-03-01-702011 (accessed on 9 December 2018).
- Matsha, T.E.; Soita, D.J.; Hassan, M.S.; Hon, G.M.; Yako, Y.Y.; Kengne, A.P.; Erasmus, R.T. Three-year’s changes in glucose tolerance status in the Bellville South cohort: Rates and phenotypes associated with progression. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2013, 99, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization, Department of Noncommunicable Disease Surveillance. Definition, Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus and Its Complications: Report of a WHO Consultation. 1999, pp. 1–59. Available online: http://www.who.int/iris/handle/10665/66040 (accessed on 22 April 2019).
- O’Callaghan, N.J.; Fenech, M. A quantitative PCR method for measuring absolute telomere length. Biol. Proced. Online 2011, 13, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riethman, H. Human Telomere Structure and Biology. Ann. Rev. Geno. Hum. Genet. 2008, 9, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aubert, G.; Lansdorp, P.M. Telomeres and Aging. Physiol Rev. 2008, 88, 557–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sethi, I.; Bhat, G.R.; Singh, V.; Kumar, R.; Bhanwer, A.J.S.; Bamezai, R.N.K.; Sharma, S.; Rai, E. Role of telomeres and associated maintenance genes in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A review. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2016, 122 (Suppl. C), 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adaikalakoteswari, A.; Balasubramanyam, M.; Mohan, V. Telomere shortening occurs in Asian Indian Type 2 diabetic patients. Diabet. Med. 2005, 22, 1151–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampson, M.J.; Winterbone, M.S.; Hughes, J.C.; Dozio, N.; Hughes, D.A. Monocyte Telomere Shortening and Oxidative DNA Damage in Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivieri, F.; Lorenzi, M.; Antonicelli, R.; Testa, R.; Sirolla, C.; Cardelli, M.; Mariotti, S.; Marchegiani, F.; Marra, M.; Spazzafumo, L.; et al. Leukocyte telomere shortening in elderly Type2DM patients with previous myocardial infarction. Atherosclerosis 2009, 206, 588–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salpea, K.D.; Humphries, S.E. Telomere length in atherosclerosis and diabetes. Atherosclerosis 2010, 209, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Q.; Zhao, X.; Yu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, D.; Kan, M.; Zhang, D.; Cao, L.; Xing, Q.; Yang, Y.; et al. Association of Leukocyte Telomere Length with Type 2 Diabetes in Mainland Chinese Populations. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, 1371–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, N.Y.; Chen, B.H.; Song, Y.; Lu, X.; Chen, Y.; Manson, J.E.; Kang, M. A Prospective Study of Leukocyte Telomere Length and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes in Postmenopausal Women. Diabetes 2012, 61, 2998–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Zhu, W.; Hu, S.; Yu, X.; Yang, Y. Association between oxidative stress and telomere length in Type 1 and Type 2 diabetic patients. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2013, 36. [Google Scholar]
- Testa, R.; Olivieri, F.; Sirolla, C.; Spazzafumo, L.; Rippo, M.R.; Marra, M.; Bonfigli, A.R.; Ceriello, A.; Antonicelli, R.; Franceschi, C.; et al. Leukocyte telomere length is associated with complications of Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabet. Med. 2011, 28, 1388–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilani, S.; Alemao, N.N.; Prabhu, M.; Ambar, S.; Chugh, Y.; Chugh, A.K. Correlation of the telomere length with type 2 diabetes mellitus in patients with ischemic heart disease. Indian Heart, J. 2018, 70, S173–S176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosa, E.C.C.C.; dos Santos, R.R.C.; Fernandes, L.F.A.; Neves, F.D.A.R.; Coelho, M.S.; Amato, A.A. Leukocyte telomere length correlates with glucose control in adults with recently diagnosed type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 135, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cawthon, R.M. Telomere length measurement by a novel monochrome multiplex quantitative PCR method. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hultdin, M.; Grönlund, E.; Norrback, K.; Eriksson-Lindström, E.; Just, T.; Roos, G. Telomere analysis by fluorescence in situ hybridization and flow cytometry. Nucleic Acids Res. 1998, 26, 3651–3656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montpetit, A.J.; Alhareeri, A.A.; Montpetit, M.; Starkweather, A.R.; Elmore, L.W.; Filler, K.; Mohanraj, L.; Burton, C.W.; Menzies, V.S.; Lyon, D.E.; et al. Telomere length: A review of methods for measurement. Nurs. Res. 2014, 63, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Chen, S.; Lin, J.; Matsuguchi, T.; Blackburn, E.; Yeh, F.; Best, L.G.; Devereux, R.B.; Lee, E.T.; Howard, B.V.; et al. Short leukocyte telomere length predicts incidence and progression of carotid atherosclerosis in American Indians: The strong heart family study. Aging 2014, 6, 414–427. [Google Scholar]
- Brownlee, M. Biochemistry and molecular cell biology of diabetic complications. Nature 2001, 414, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceriello, A. New Insights on Oxidative Stress and Diabetic Complications May Lead to a “Causal” Antioxidant Therapy. Diabetes Care. 2003, 26, 1589–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, S.M. Reactive Oxygen and Nitrogen Species in Pathogenesis of Vascular Complications of Diabetes. Diabetes Metab. J. 2012, 36, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aouacheri, O.; Saka, S.; Krim, M. The Investigation of the Oxidative Stress-Related Parameters in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Can. J. Diabetes. 2015, 39, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, R.; Zhang, L.-N.; Zhang, T.-T.; Pang, H.-Y.; Chen, L.-F.; Shen, Z.-J.; Liu, Z.-Y.; Fang, Q.; Zhang, S.-Y. Association between Oxidative Stress and Peripheral Leukocyte Telomere Length in Patients with Premature Coronary Artery Disease. Med. Sci. Monit. 2017, 4382–4390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denham, J.; O’Brien, B.J.; Charchar, F.J. Telomere Length Maintenance and Cardio-Metabolic Disease Prevention through Exercise Training. Sports Med. 2016, 46, 1213–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hovatta, I.; de Mello, V.D.F.; Kananen, L.; Lindström, J.; Eriksson, J.G.; Ilanne-Parikka, P.; Keinänen-Kiukaanniemi, S.; Peltonen, M.; Tuomilehto, J.; Uusitupa, M. Leukocyte Telomere Length in the Finnish Diabetes Prevention Study. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavanello, S.; Hoxha, M.; Dioni, L.; Bertazzi, P.A.; Snenghi, R.; Nalesso, A.; Ferrara, S.D.; Montisci, M.; Baccarelli, A. Shortened telomeres in individuals with abuse in alcohol consumption. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 129, 983–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanditha, A.; Jagannathan, R.; Sundaram, S.; Susairaj, P.; Shetty, A.S.; Snehalatha, C.; Ian, G.F.; Johnston, D.G.; Ramachandran, A. Combining fasting plasma glucose with gammaglutamyl transferase improves the sensitivity to predict incident diabetes in asian indian men with impaired glucose tolerance. J. Assoc. Physicians India 2014, 62, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.S.; Cho, Y.; Burgess, S.; Davey Smith, G.; Relton, C.L.; Shin, S.-Y.; Shin, M.-J. Serum gamma-glutamyl transferase and risk of type 2 diabetes in the general Korean population: A Mendelian randomization study. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2016, 25, 3877–3886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsha, T.E.; Macharia, M.; Yako, Y.Y.; Erasmus, R.T.; Hassan, M.S.; Kengne, A.P. Gamma-glutamyltransferase, insulin resistance and cardiometabolic risk profile in a middle-aged African. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2014, 21, 1541–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, L.; Needham, B.; Ailshire, J. Telomere Length Among Older, U.S. Adults: Differences by Race/Ethnicity, Gender, and Age. J. Aging Health 2017, 29, 1350–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Total N205 | Normoglycemia N77 | Pre-Diabetes N43 | New Diabetes N44 | Known Diabetes N41 | p-Value | Total N205 | Normoglycemia N91 | Pre-Diabetes N37 | New Diabetes N13 | Known Diabetes N64 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | Three-Year Follow-Up | |||||||||||
| Age (Years) | 57.0 (48.0; 62.0) | 55.0 (46.0; 61.0) | 55.0 (45.0; 62.0) | 56.0 (47.5; 62.5) | 59.0 (54.0; 64.0) | 0.0869 | 59.0 (51.0;66.0) | 58.0 (47.0;65.0) | 57.0 (48.0;64.0) | 60.0 (53.0;65.0) | 61.5 (55.0;67.5) | 0.0579 |
| BMI | 31.7 (27.4;36.5) | 29.4 (25.0;33.4) | 32.5 (28.7;36.3) | 35.0 (30.5;38.1) | 31.1 (26.5;37.3) | 0.0002 | 31.3 (27.0;36.6) | 29.4 (24.6;35.3) | 34.5 (29.2;37.0) | 32.9 (30.3;40.3) | 31.9 (28.5;36.4) | 0.0023 |
| WC (cm) | 101.5 (93.0;111.0) | 96.0 (87.5;106.0) | 105.0 (97.0;112.0) | 107.7 (101.0;117.5) | 101.0 (93.0;114.5) | 0.0001 | 97.3 (88.3;107.0) | 92.5 (81.1;105.0) | 101.5 (92.3;108.0) | 100.0 (99.3;117.3) | 98.3 (91.5;109.0) | 0.0047 |
| HP (cm) | 112.0 (104.0;122.7) | 109.0 (103.0;116.0) | 115.0 (108.0;122.7) | 116.5 (108.7;127.0) | 111.0 (99.8;125.5) | 0.0036 | 108.8 (98.3;119.3) | 105.1 (96.5;113.4) | 114.7 (106.1;121.6) | 110.7 (104.1;116.0) | 110.0 (100.0;120.6) | 0.0190 |
| WHR | 0.89 (0.85;0.95) | 0.88 (0.84;0.92) | 0.89 (0.83;0.95) | 0.90 (0.86;0.98) | 0.92 (0.86;0.96) | 0.0371 | 0.88 (0.83;0.94) | 0.88 (0.82;0.93) | 0.87 (0.82;0.92) | 0.94 (0.88;1.01) | 0.91 (0.84;0.96) | 0.0098 |
| SBP (mmHg) | 123.0 (112.0;135.0) | 119.0 (111.0;129.0) | 121.0 (112.0;132.0) | 130.5 (116.0;140.5) | 127.0 (114.0;142.0) | 0.0259 | 136.0 (123.0;155.0) | 131.0 (120.0;150.0) | 142.0 (130.0;157.0) | 130.0 (124.0;167.0) | 139.0 (126.0;159.0) | 0.0264 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 76.0 (68.0;83.0) | 76.0 (67.0;85.0) | 76.0 (68.0;82.0) | 77.5 (69.0;86.0) | 74.0 (68.0;83.0) | 0.7670 | 82.0 (74.0;90.0) | 80.0 (72.0;85.0) | 87.0 (77.0;93.0) | 84.0 (79.0;97.0) | 81.0 (75.0;90.0) | 0.0286 |
| FBG (mmol/L) | 6.00 (5.00;7.75) | 5.10 (4.80;5.60) | 6.00 (5.00;6.10) | 7.90 (7.10;9.00) | 11.05 (6.40;13.05) | <0.0001 | 5.60 (5.00;7.4) | 5.00 (4.60;5.4) | 5.80 (5.40;6.4) | 8.90 (7.50;11.0) | 8.55 (6.45;10.9) | <0.0001 |
| PostBG (mmol/L) | 7.40 (6.00;10.10) | 6.00 (5.40;6.50) | 8.60 (8.00;9.20) | 13.00 (10.60;17.50) | NA | <0.0001 | 6.50 (5.30;8.10) | 5.70 (4.90;6.60) | 8.40 (7.90;9.00) | 15.10 (11.80;19.00) | NA | <0.0001 |
| Fasting Insulin (mIU/L) | 9.20 (3.80;14.60) | 8.30 (3.80;13.70) | 10.20 (6.00;14.10) | 10.70 (3.60;16.10) | 7.80 (2.40; 14.15) | 0.5562 | 12.20 (6.90;17.80) | 10.40 (5.60;15.10) | 13.20 (6.60;18.80) | 17.90 (14.20;27.70) | 13.20 (8.75;18.85) | 0.0029 |
| FBG/Insulin ratio | 0.71 (0.43;1.62) | 0.60 (0.37;1.24) | 0.56 (0.40;0.95) | 0.74 (0.54;2.22) | 1.16 (0.74;3.16) | 0.0029 | 0.56 (0.33;0.88) | 0.48 (0.34;0.89) | 0.46 (0.30;0.78) | 0.50 (0.23;0.75) | 0.64 (0.34;0.89) | 0.5199 |
| HbA1c (%) | 6.10 (5.70;6.80) | 5.70 (5.40;6.10) | 5.90 (5.80;6.20) | 6.75 (6.25;7.70) | 7.35 (6.50;8.95) | <0.0001 | 6.20 (5.80;7.00) | 5.90 (5.70;6.20) | 6.20 (5.95;6.55) | 7.40 (6.60;8.80) | 7.20 (6.50;8.75) | <0.0001 |
| U-CRP (mg/L) | 5.50 (1.60;10.40) | 4.00 (0.90;7.70) | 7.60 (1.80;14.60) | 7.10 (2.35;16.90) | 4.10 (1.80;8.45) | 0.0050 | 5.30 (2.00;9.20) | 5.30 (1.80;11.80) | 6.50 (3.90;10.10) | 8.20 (4.40;10.40) | 3.90 (1.40;7.00) | 0.0874 |
| GGT (IU/L) | 30.0 (22.0;47.0) | 27.0 (18.0;39.0) | 31.0 (24.0;47.0) | 39.0 (25.0;58.5) | 29.5 (20.0;41.5) | 0.0056 | 27.0 (20.0;45.0) | 26.0 (19.0;45.0) | 27.0 (20.0;46.0) | 42.0 (36.0;47.0) | 27.0 (20.0;41.5) | 0.1010 |
| TC (mmol/L) | 5.56 (4.88;6.33) | 5.52 (4.92;6.16) | 5.53 (4.59;6.30) | 5.82 (5.14;6.74) | 5.43 (4.74;6.30) | 0.3082 | 5.40 (4.71;6.21) | 5.48 (4.76;6.29) | 5.46 (5.00;6.08) | 5.97 (4.85;6.13) | 4.92 (4.53;6.36) | 0.4994 |
| TG (mmol/L) | 1.37 (1.06;1.92) | 1.23 (0.94;1.46) | 1.44 (1.10;1.90) | 1.58 (1.18;1.96) | 1.70 (1.27;2.15) | 0.0003 | 1.36 (0.99;1.75) | 1.23 (0.88;1.69) | 1.28 (1.01;1.68) | 1.53 (1.36;1.94) | 1.43 (1.13;1.95) | 0.0099 |
| HDL (mmol/L) | 1.13 (0.99;1.39) | 1.16 (1.00;1.42) | 1.15 (1.06;1.39) | 1.15 (1.00;1.36) | 1.01 (0.86;1.23) | 0.0212 | 1.33 (1.12;1.61) | 1.39 (1.20;1.68) | 1.21 (1.04;1.46) | 1.34 (1.17;1.49) | 1.25 (1.09;1.54) | 0.0382 |
| LDL (mmol/L) | 3.65 (2.92;4.35) | 3.63 (3.02;4.16) | 3.63 (2.82;4.26) | 3.88 (3.16;4.64) | 3.38 (2.81;4.47) | 0.3836 | 3.28 (2.68;4.10) | 3.28 (2.73;4.03) | 3.41 (3.03;4.21) | 3.64 (2.75;4.32) | 3.00 (2.38;4.06) | 0.1795 |
| TC/HDL ratio | 4.78 (3.98;5.70) | 4.52 (3.70;5.39) | 4.51 (3.79;5.12) | 4.89 (4.31;6.07) | 5.05 (4.32;6.39) | 0.0278 | 3.96 (3.13;4.98) | 3.87 (2.97;4.73) | 4.26 (3.27;5.52) | 3.96 (3.40;5.19) | 4.02 (3.19;5.01) | 0.2066 |
| S Cotinine (ng/mL) | 9.00 (9.00;261.0) | 10.00 (9.00;308.0) | 9.00 (9.00;317.0) | 9.00 (9.00;184.5) | 9.00 (9.00;120.0) | 0.0983 | 9.0 (9.0;289.0) | 9.0 (9.0;339.0) | 9.0 (9.0;163.0) | 212.0 (9.0;334.0) | 9.0 (9.0;40.6) | 0.0665 |
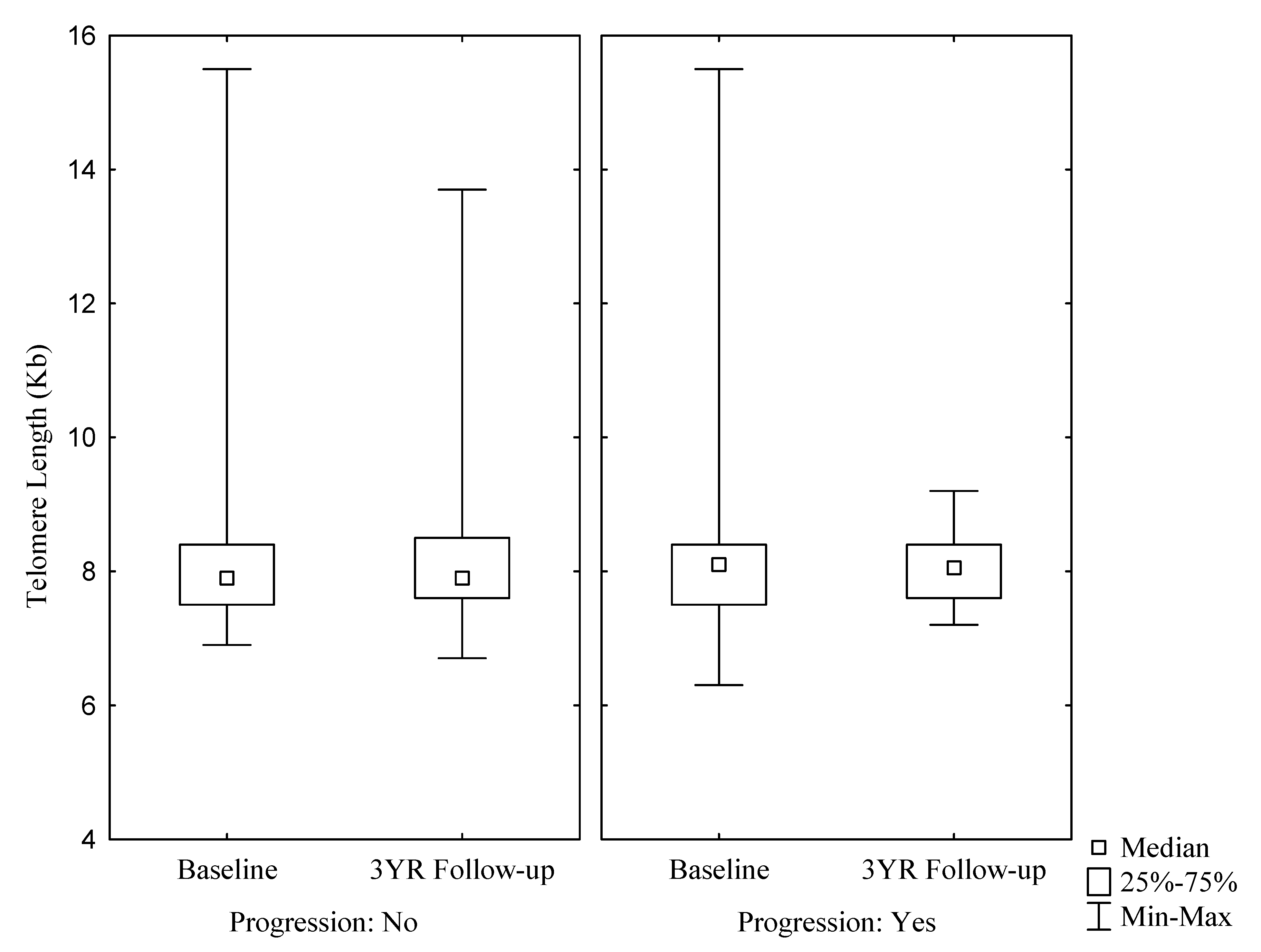
| Telomere length (kb) | 7.80 (7.50; 8.40) | 7.90 (7.50; 8.40) | 7.80 (7.50; 8.30) | 7.80 (7.50; 8.35) | 8.10 (7.50; 8.60) | 0.7618 | 7.90 (7.60; 8.50) | 7.90 (7.60; 8.50) | 7.80 (7.50; 8.40) | 8.40 (8.00; 8.90) | 7.90 (7.60; 8.40) | 0.2204 |
| Glucose Tolerance Status | Telomere Length Baseline | Telomere Length Three-Year Follow-Up | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline to Three-Year Follow-Up | Median (25,75Q) | p-Value | |
| Normoglycemia to Prediabetes, n = 9 | 7.90 (7.50, 8.30) | 7.90 (7.60, 8.20) | 0.8385 |
| Normoglycemia to Diabetes, n = 3 | 8.40 (7.40, 11.10) | 8.40 (8.00, 8.60) | 0.5930 |
| Prediabetes to Diabetes, n = 6 | 8.05 (7.60, 14.80) | 8.15 (7.60, 9.00) | 0.7532 |
| Baseline | Three-Year Follow-Up | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Overall | Prediabetes | Diabetes | Overall | Prediabetes | Diabetes | ||||||
| r | p | r | p | r | p | r | p | r | p | r | p | |
| BMI | −0.005 | 0.944 | −0.007 | 0.937 | 0.134 | 0.397 | 0.044 | 0.538 | 0.123 | 0.198 | −0.010 | 0.976 |
| WC (cm) | −0.014 | 0.846 | −0.001 | 0.993 | 0.238 | 0.130 | 0.022 | 0.753 | 0.112 | 0.243 | −0.084 | 0.805 |
| HP (cm) | 0.012 | 0.868 | −0.002 | 0.981 | 0.072 | 0.650 | 0.020 | 0.778 | 0.044 | 0.650 | 0.362 | 0.304 |
| WHR | −0.048 | 0.499 | −0.003 | 0.977 | 0.198 | 0.209 | −0.003 | 0.968 | 0.095 | 0.330 | −0.487 | 0.154 |
| SBP (mmHg) | 0.003 | 0.966 | 0.037 | 0.677 | 0.348 | 0.024 | −0.065 | 0.358 | 0.020 | 0.836 | −0.389 | 0.237 |
| DBP (mmHg) | −0.021 | 0.763 | −0.012 | 0.897 | 0.228 | 0.146 | 0.038 | 0.593 | 0.124 | 0.194 | −0.154 | 0.650 |
| FBG (mmol/L) | 0.020 | 0.780 | −0.007 | 0.937 | −0.013 | 0.935 | 0.048 | 0.496 | 0.066 | 0.491 | 0.187 | 0.582 |
| PostBG (mmol/L) | −0.023 | 0.772 | −0.073 | 0.506 | −0.151 | 0.339 | 0.146 | 0.091 | 0.216 | 0.149 | −0.044 | 0.897 |
| Fasting Insulin (mIU/L) | −0.017 | 0.811 | 0.000 | 0.997 | 0.079 | 0.625 | 0.022 | 0.755 | 0.146 | 0.125 | 0.681 | 0.021 |
| FBG/Insulin ratio | −0.044 | 0.536 | −0.040 | 0.662 | −0.037 | 0.818 | −0.010 | 0.888 | −0.036 | 0.707 | −0.123 | 0.719 |
| HbA1c (%) | 0.046 | 0.520 | 0.024 | 0.794 | −0.022 | 0.888 | 0.050 | 0.478 | 0.083 | 0.385 | 0.150 | 0.659 |
| U-CRP (mg/L) | 0.073 | 0.300 | 0.116 | 0.198 | −0.133 | 0.400 | 0.015 | 0.831 | −0.030 | 0.756 | −0.199 | 0.557 |
| GGT (IU/L) | −0.156 | 0.027 | −0.173 | 0.054 | −0.176 | 0.264 | 0.127 | 0.072 | 0.092 | 0.335 | 0.096 | 0.778 |
| TC (mmol/L) | 0.024 | 0.733 | 0.035 | 0.699 | 0.168 | 0.289 | −0.012 | 0.867 | 0.008 | 0.934 | −0.224 | 0.508 |
| TG (mmol/L) | −0.011 | 0.877 | −0.058 | 0.520 | −0.165 | 0.295 | −0.002 | 0.978 | 0.007 | 0.938 | −0.163 | 0.632 |
| HDL (mmol/L) | 0.109 | 0.121 | 0.073 | 0.416 | 0.193 | 0.220 | 0.041 | 0.558 | 0.017 | 0.856 | 0.171 | 0.615 |
| LDL (mmol/L) | −0.003 | 0.969 | 0.043 | 0.637 | 0.224 | 0.153 | −0.028 | 0.693 | 0.005 | 0.961 | −0.223 | 0.510 |
| TC/HDL ratio | −0.039 | 0.579 | −0.001 | 0.989 | −0.034 | 0.829 | −0.040 | 0.573 | −0.027 | 0.781 | −0.337 | 0.310 |
| S Cotinine (ng/mL) | 0.065 | 0.357 | 0.077 | 0.396 | −0.173 | 0.274 | −0.050 | 0.482 | −0.137 | 0.151 | −0.512 | 0.107 |
| S. Creatinine (umol/L) | 0.058 | 0.408 | 0.100 | 0.269 | 0.138 | 0.382 | −0.042 | 0.548 | −0.041 | 0.665 | 0.317 | 0.342 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Weale, C.J.; Davison, G.M.; Hon, G.M.; Kengne, A.P.; Erasmus, R.T.; Matsha, T.E. Leucocyte Telomere Length and Glucose Tolerance Status in Mixed-Ancestry South Africans. Cells 2019, 8, 464. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8050464
Weale CJ, Davison GM, Hon GM, Kengne AP, Erasmus RT, Matsha TE. Leucocyte Telomere Length and Glucose Tolerance Status in Mixed-Ancestry South Africans. Cells. 2019; 8(5):464. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8050464
Chicago/Turabian StyleWeale, Cecil J., Glenda M. Davison, Gloudina M. Hon, Andre P. Kengne, Rajiv T. Erasmus, and Tandi E. Matsha. 2019. "Leucocyte Telomere Length and Glucose Tolerance Status in Mixed-Ancestry South Africans" Cells 8, no. 5: 464. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8050464
APA StyleWeale, C. J., Davison, G. M., Hon, G. M., Kengne, A. P., Erasmus, R. T., & Matsha, T. E. (2019). Leucocyte Telomere Length and Glucose Tolerance Status in Mixed-Ancestry South Africans. Cells, 8(5), 464. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8050464





