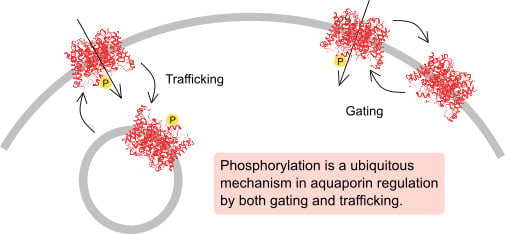
Phosphorylation-Dependent Regulation of Mammalian Aquaporins
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods Used to Study Phosphorylation Sites in Aquaporins
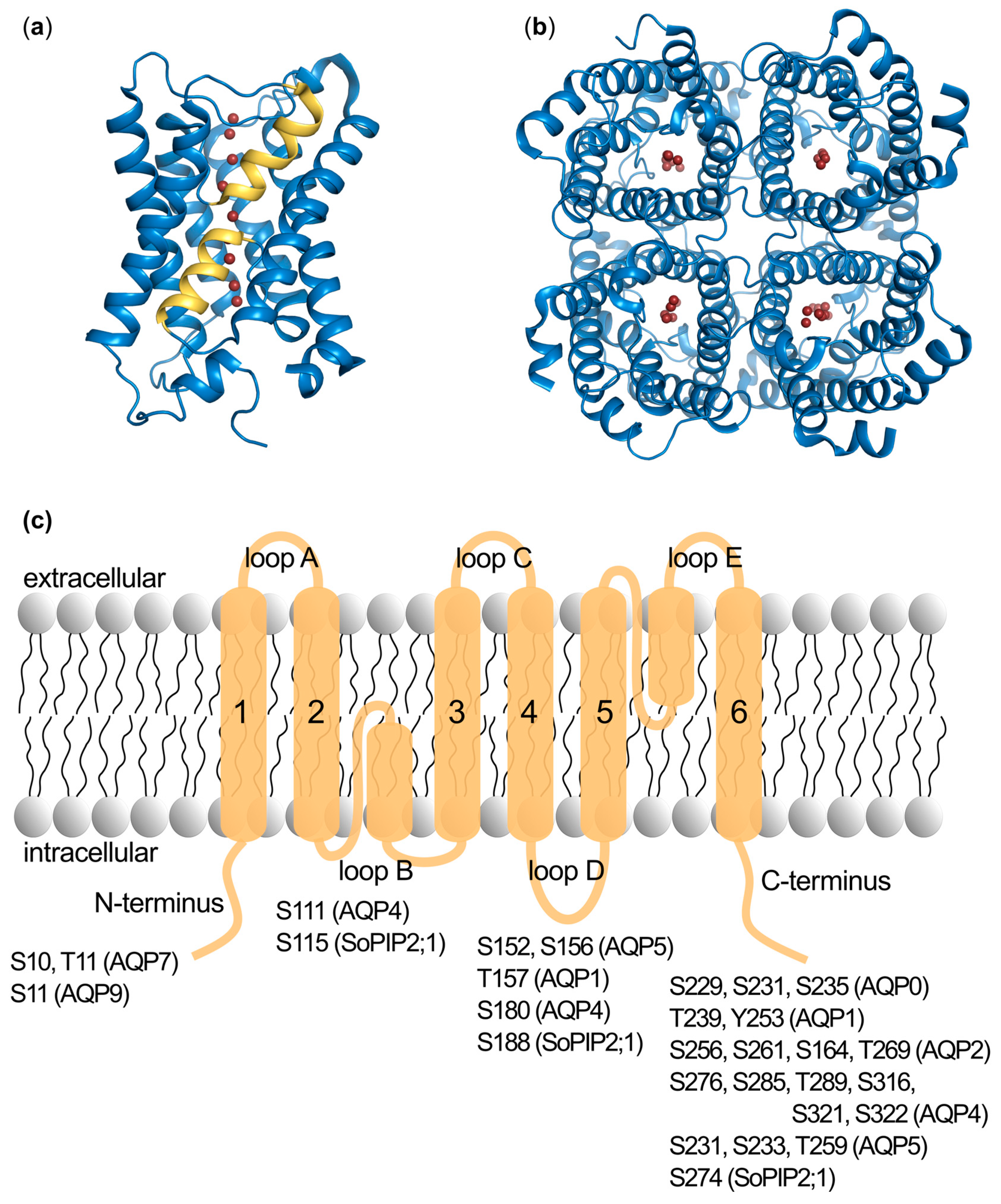
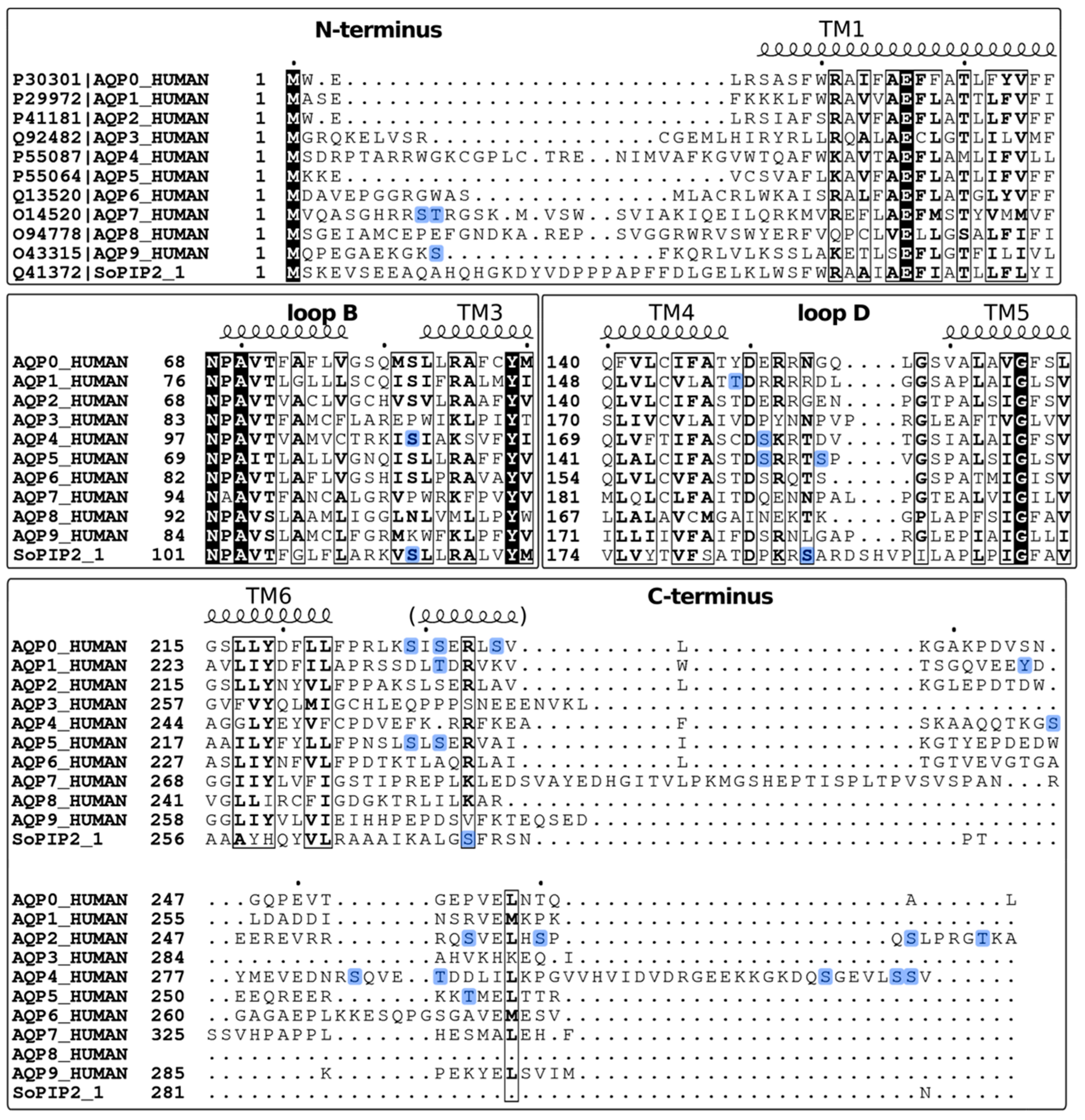
2.1. Identification of Phosphorylation Sites
2.2. Phosphorylation Site Mutations
2.3. Functional Effects of Phosphorylation at Specific Sites
3. Kinases and Phosphatases in Human AQP Regulation
4. Modulation of Protein-Protein Interactions upon Phosphorylation
5. Phosphorylation-Dependent Aquaporin Gating
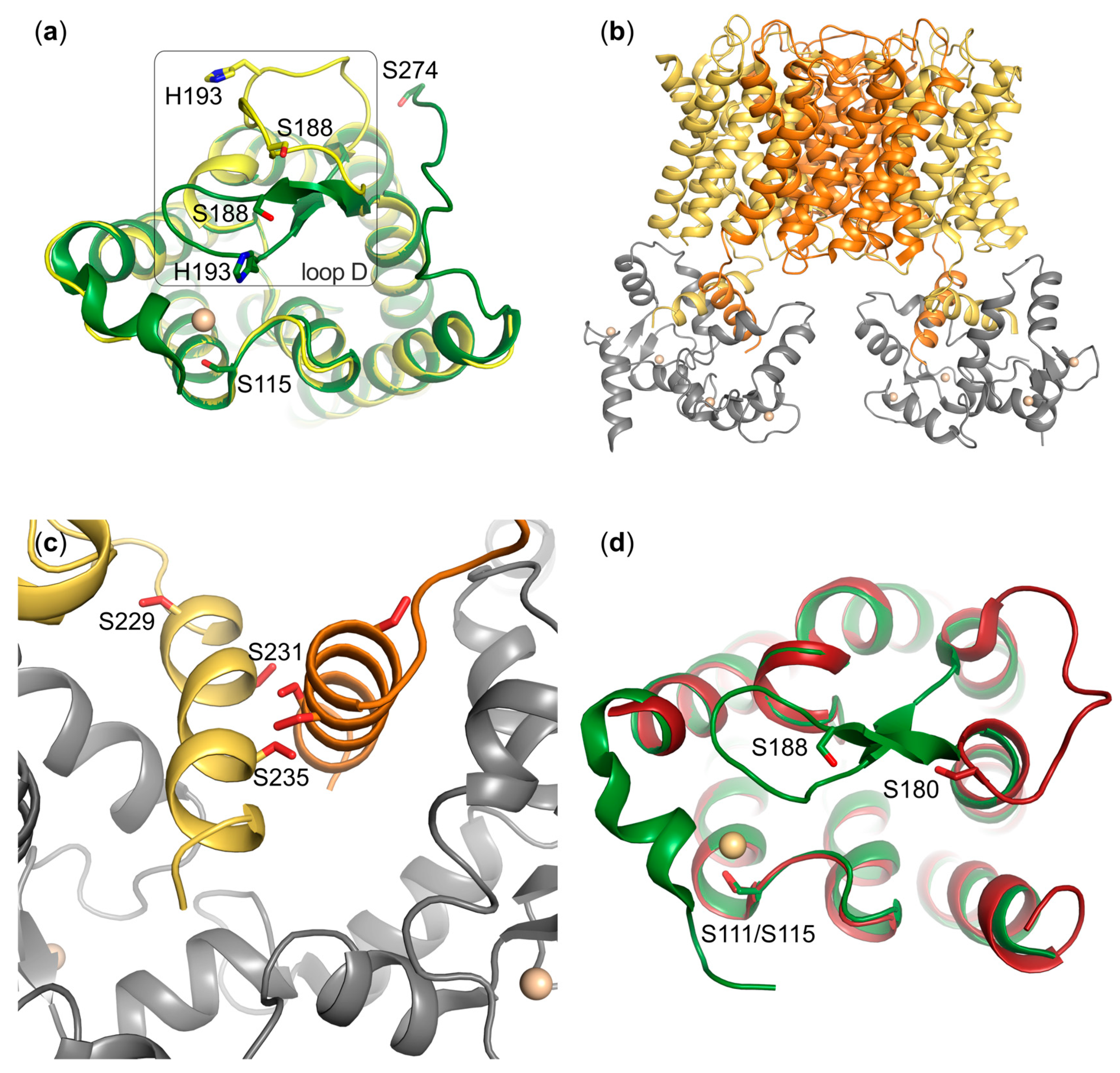
5.1. AQP0
5.2. AQP4
5.3. AQP1
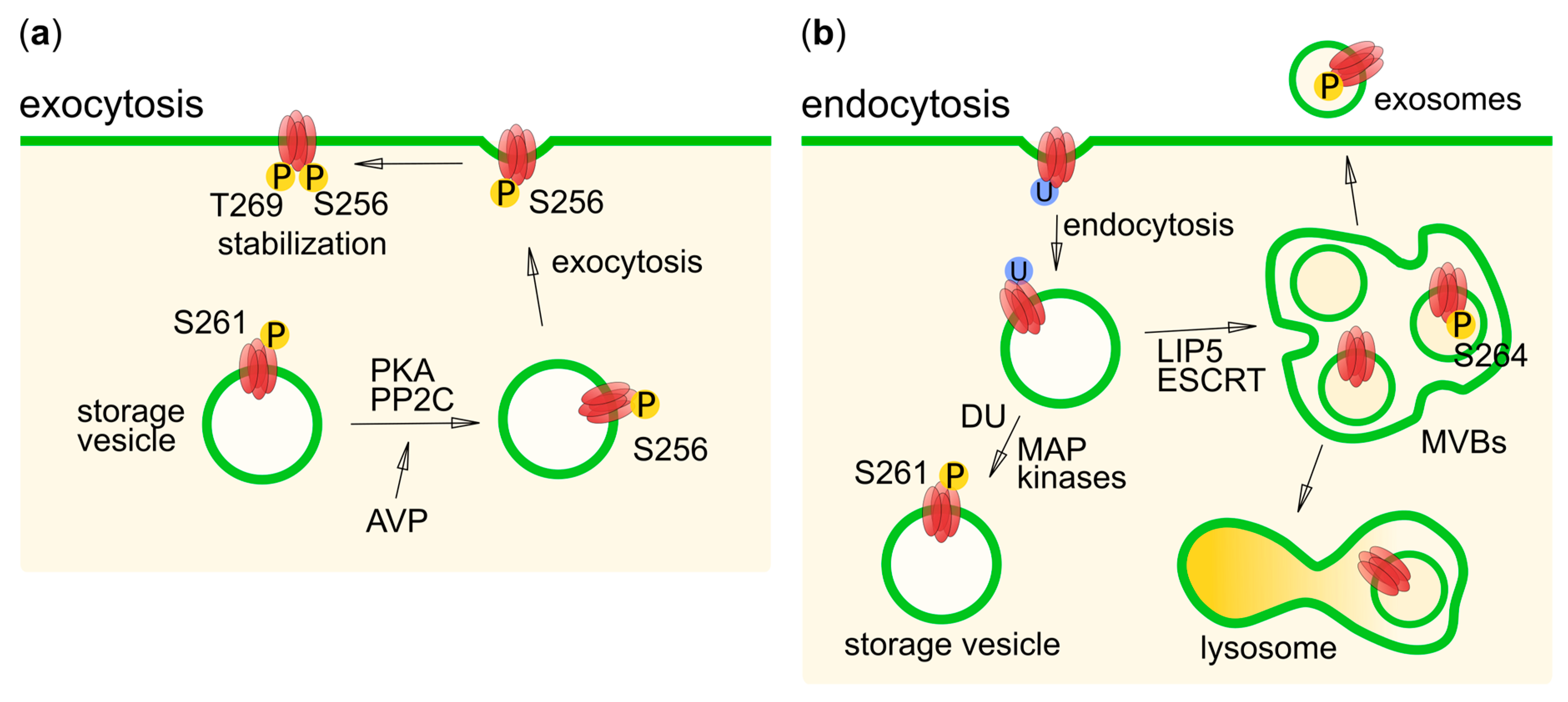
6. Phosphorylation in Human Aquaporin Trafficking
6.1. AQP1
6.2. AQP2
6.3. AQP4
6.4. AQP5
7. Concluding Remarks
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cohen, P. The Origins of Protein Phosphorylation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2002, 4, E127–E130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huttlin, E.L.; Jedrychowski, M.P.; Elias, J.E.; Goswami, T.; Rad, R.; Beausoleil, S.A.; Villén, J.; Haas, W.; Sowa, M.E.; Gygi, S.P. A Tissue-Specific Atlas of Mouse Protein Phosphorylation and Expression. Cell 2010, 143, 1174–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conner, A.C.; Bill, R.M.; Conner, M.T. An Emerging Consensus on Aquaporin Translocation as a Regulatory Mechanism. Mol. Membr. Biol. 2013, 30, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreida, S.; Törnroth-Horsefield, S. Structural Insights into Aquaporin Selectivity and Regulation. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2015, 33, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitchen, P.; Day, R.E.; Salman, M.M.; Conner, M.T.; Bill, R.M.; Conner, A.C. Beyond Water Homeostasis: Diverse Functional Roles of Mammalian Aquaporins. BBA Gen. Subj. 2015, 1850, 2410–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishibashi, K.; Tanaka, Y.; Morishita, Y. The Role of Mammalian Superaquaporins inside the Cell. BBA Gen. Subj. 2014, 1840, 1507–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, L.S.; Kozono, D.; Agre, P. From Structure to Disease: The Evolving Tale of Aquaporin Biology. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004, 5, 687–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morishita, Y.; Sakube, Y.; Sasaki, S.; Ishibashi, K. Molecular Mechanisms and Drug Development in Aquaporin Water Channel Diseases: Aquaporin Superfamily (Superaquaporins): Expansion of Aquaporins Restricted to Multicellular Organisms. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2004, 96, 276–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Törnroth-Horsefield, S.; Hedfalk, K.; Fischer, G.; Lindkvist-Petersson, K.; Neutze, R. Structural Insights into Eukaryotic Aquaporin Regulation. FEBS Lett. 2010, 584, 2580–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roche, J.V.; Törnroth-Horsefield, S. Aquaporin Protein-Protein Interactions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, C.D.; Toker, A. Using Phospho-Motif Antibodies to Determine Kinase Substrates. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. 2013, 101, 18–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blom, N.; Sicheritz-Pontén, T.; Gupta, R.; Gammeltoft, S.; Brunak, S. Prediction of Post-Translational Glycosylation and Phosphorylation of Proteins from the Amino Acid Sequence. Proteomics 2004, 4, 1633–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundby, A.; Secher, A.; Lage, K.; Nordsborg, N.B.; Dmytriyev, A.; Lundby, C.; Olsen, J.V. Quantitative Maps of Protein Phosphorylation Sites across 14 Different Rat Organs and Tissues. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 810–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Zitron, E.; Hömme, M.; Kihm, L.; Morath, C.; Scherer, D.; Hegge, S.; Thomas, D.; Schmitt, C.P.; Zeier, M.; et al. Aquaporin-1 Channel Function Is Positively Regulated by Protein Kinase C. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 20933–20940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, J.S.; Krintel, C.; Hernebring, M.; Haataja, T.J.K.; de Marè, S.; Wasserstrom, S.; Kosinska-Eriksson, U.; Palmgren, M.; Holm, C.; Stenkula, K.G.; et al. Perilipin 1 Binds to Aquaporin 7 in Human Adipocytes and Controls Its Mobility via Protein Kinase A Mediated Phosphorylation. Metabolism 2016, 65, 1731–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rust, H.L.; Subramanian, V.; West, G.M.; Young, D.D.; Schultz, P.G.; Thompson, P.R. Using Unnatural Amino Acid Mutagenesis to Probe the Regulation of PRMT1. ACS Chem. Biol. 2014, 9, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyblom, M.; Frick, A.; Wang, Y.; Ekvall, M.; Hallgren, K.; Hedfalk, K.; Neutze, R.; Tajkhorshid, E.; Törnroth-Horsefield, S. Structural and Functional Analysis of SoPIP2;1 Mutants Adds Insight into Plant Aquaporin Gating. J. Mol. Biol. 2009, 387, 653–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tani, K.; Mitsuma, T.; Hiroaki, Y.; Kamegawa, A.; Nishikawa, K.; Tanimura, Y.; Fujiyoshi, Y. Mechanism of Aquaporin-4′s Fast and Highly Selective Water Conduction and Proton Exclusion. J. Mol. Biol. 2009, 389, 694–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitchen, P.; Öberg, F.; Sjöhamn, J.; Hedfalk, K.; Bill, R.M.; Conner, A.C.; Conner, M.T.; Törnroth-Horsefield, S. Plasma Membrane Abundance of Human Aquaporin 5 Is Dynamically Regulated by Multiple Pathways. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalman, K.; Németh-Cahalan, K.L.; Froger, A.; Hall, J.E. Phosphorylation Determines the Calmodulin-Mediated Ca2+response and Water Permeability of AQP0. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 21278–21283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roche, J.V.; Survery, S.; Kreida, S.; Nesverova, V.; Ampah-Korsah, H.; Gourdon, M.; Deen, P.M.T.; Törnroth-Horsefield, S. Phosphorylation of Human Aquaporin 2 (AQP2) Allosterically Controls Its Interaction with the Lysosomal Trafficking Protein LIP5. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 14636–14648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moeller, H.B.; Praetorius, J.; Rutzler, M.R.; Fenton, R.A. Phosphorylation of Aquaporin-2 Regulates Its Endocytosis and Protein-Protein Interactions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 424–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karabasil, M.R.; Hasegawa, T.; Azlina, A.; Purwanti, N.; Purevjav, J.; Yao, C.; Akamatsu, T.; Hosoi, K. Trafficking of GFP-AQP5 Chimeric Proteins Conferred with Unphosphorylated Amino Acids at Their PKA—Target Motif (152SRRTS) in MDCK-II Cells. J. Med. Investig. 2009, 56, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conner, M.T.; Conner, A.C.; Bland, C.E.; Taylor, L.H.J.; Brown, J.E.P.; Parri, H.R.; Bill, R.M. Rapid Aquaporin Translocation Regulates Cellular Water Flow: Mechanism of Hypotonicity-Induced Subcellular Localization of Aquaporin 1 Water Channel. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 11516–11525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitchen, P.; Day, R.E.; Taylor, L.H.J.; Salman, M.M.; Bill, R.M.; Conner, M.T.; Conner, A.C. Identification and Molecular Mechanisms of the Rapid Tonicity-Induced Relocalization of the Aquaporin 4 Channel. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 16873–16881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelenina, M.; Zelenin, S.; Bondar, A.A.; Brismar, H.; Aperia, A. Water Permeability of Aquaporin-4 Is Decreased by Protein Kinase C and Dopamine. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2002, 283, F309–F318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moeller, H.B.; Fenton, R.A.; Zeuthen, T.; MacAulay, N. Vasopressin-Dependent Short-Term Regulation of Aquaporin 4 Expressed in Xenopus Oocytes. Neuroscience 2009, 164, 1674–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCoy, E.S.; Haas, B.R.; Sontheimer, H. Water Permeability through Aquaporin-4 Is Regulated by Protein Kinase C and Becomes Rate-Limiting for Glioma Invasion. Neuroscience 2010, 168, 971–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ampah-Korsah, H.; Anderberg, H.I.; Engfors, A.; Kirscht, A.; Norden, K.; Kjellstrom, S.; Kjellbom, P.; Johanson, U. The Aquaporin Splice Variant NbXIP1;1α Is Permeable to Boric Acid and Is Phosphorylated in the N-Terminal Domain. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eto, K.; Noda, Y.; Horikawa, S.; Uchida, S.; Sasaki, S. Phosphorylation of Aquaporin-2 Regulates Its Water Permeability. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 40777–40784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Wax, M.B.; Patil, R.V. Regulation of Aquaporin-4 Water Channels by Phorbol Ester-Dependent Protein Phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 6001–6004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunnarson, E.; Zelenina, M.; Axehult, G.; Song, Y.; Bondar, A.; Krieger, P.; Brismar, H.; Zelenin, S.; Aperia, A. Identification of a Molecular Target for Glutamate Regulation of Astrocyte Water Permeability. Glia 2008, 56, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustafson, C.E.; Levine, S.; Katsura, T.; McLaughlin, M.; Aleixo, M.D.; Tamarappoo, B.K.; Verkman, A.S.; Brown, D. Vasopressin Regulated Trafficking of a Green Fluorescent Protein- Aquaporin 2 Chimera in LLC-PK1 Cells. Histochem. Cell Biol. 1998, 110, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosugi-Tanaka, C.; Li, X.; Yao, C.; Akamatsu, T.; Kanamori, N.; Hosoi, K. Protein Kinase A-Regulated Membrane Trafficking of a Green Fluorescent Protein-Aquaporin 5 Chimera in MDCK Cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2006, 1763, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moeller, H.B.; Knepper, M.A.; Fenton, R.A. Serine 269 Phosphorylated Aquaporin-2 Is Targeted to the Apical Membrane of Collecting Duct Principal Cells. Kidney Int. 2009, 75, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assentoft, M.; Larsen, B.R.; Olesen, E.T.B.; Fenton, R.A.; MacAulay, N. AQP4 Plasma Membrane Trafficking or Channel Gating Is Not Significantly Modulated by Phosphorylation at COOH-Terminal Serine Residues. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2014, 307, C957–C965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madrid, R.; Le Maout, S.; Barrault, M.-B.; Janvier, K.; Benichou, S.; Mérot, J. Polarized Trafficking and Surface Expression of the AQP4 Water Channel Are Coordinated by Serial and Regulated Interactions with Different Clathrin-Adaptor Complexes. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 7008–7021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, G.; Whyte, D.B.; Martinez, R.; Hunter, T.; Sudarsanam, S. The Protein Kinase Complement of the Human Genome. Science 2002, 298, 1912–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, L.R.; Komander, D.; Alessi, D.R. The Nuts and Bolts of AGC Protein Kinases. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 11, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loitto, V.M.; Huang, C.; Sigal, Y.J.; Jacobson, K. Filopodia Are Induced by Aquaporin-9 Expression. Exp. Cell Res. 2007, 313, 1295–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunnarson, E.; Axehult, G.; Baturina, G.; Zelenin, S.; Zelenina, M.; Aperia, A. Lead Induces Increased Water Permeability in Astrocytes Expressing Aquaporin 4. Neuroscience 2005, 136, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, M.G.; Reichow, S.L.; O’Neill, S.E.; Weisbrod, C.R.; Langeberg, L.K.; Bruce, J.E.; Gonen, T.; Scott, J.D. AKAP2 Anchors PKA with Aquaporin-0 to Support Ocular Lens Transparency. EMBO Mol. Med. 2012, 4, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, L.E.; Garland, D.L.; Crouch, R.K.; Schey, K.L. Post-Translational Modifications of Aquaporin 0 (AQP0) in the Normal Human Lens: Spatial and Temporal Occurrence. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 9856–9865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golestaneh, N.; Fan, J.; Zelenka, P.; Chepelinsky, A.B. PKC Putative Phosphorylation Site Ser235 Is Required for MIP/AQP0 Translocation to the Plasma Membrane. Mol. Vis. 2008, 14, 1006–1014. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Z.; Patil, R.V. Protein Kinase A-Dependent Phosphorylation of Aquaporin-1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 273, 328–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, E.M.; Birdsell, D.N.; Yool, A.J. The Activity of Human Aquaporin 1 as a CGMP-Gated Cation Channel Is Regulated by Tyrosine Phosphorylation in the Carboxyl-Terminal Domain. Mol. Pharmacol. 2012, 81, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Balkom, B.W.M.; Savelkoul, P.J.M.; Markovich, D.; Hofman, E.; Nielsen, S.; Van Der Sluijs, P.; Deen, P.M.T. The Role of Putative Phosphorylation Sites in the Targeting and Shuttling of the Aquaporin-2 Water Channel. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 41473–41479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D.; Hasler, U.; Nunes, P.; Bouley, R.; Lu, H.A.J. Phosphorylation Events and the Modulation of Aquaporin 2 Cell Surface Expression. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2008, 17, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffert, J.D.; Pisitkun, T.; Wang, G.; Shen, R.-F.; Knepper, M.A. Quantitative Phosphoproteomics of Vasopressin-Sensitive Renal Cells: Regulation of Aquaporin-2 Phosphorylation at Two Sites. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 7159–7164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouley, R.; Breton, S.; Sun, T.X.; McLaughlin, M.; Nsumu, N.N.; Lin, H.Y.; Ausiello, D.A.; Brown, D. Nitric Oxide and Atrial Natriuretic Factor Stimulate CGMP-Dependent Membrane Insertion of Aquaporin 2 in Renal Epithelial Cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2000, 106, 1115–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinschen, M.M.; Yu, M.-J.; Wang, G.; Boja, E.S.; Hoffert, J.D.; Pisitkun, T.; Knepper, M.A. Quantitative Phosphoproteomic Analysis Reveals Vasopressin V2-Receptor-Dependent Signaling Pathways in Renal Collecting Duct Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 3882–3887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasui, H.; Kubota, M.; Iguchi, K.; Usui, S.; Kiho, T.; Hirano, K. Membrane Trafficking of Aquaporin 3 Induced by Epinephrine. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 373, 613–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Gunnarson, E. Potassium Dependent Regulation of Astrocyte Water Permeability Is Mediated by Camp Signaling. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmosino, M.; Procino, G.; Tamma, G.; Mannucci, R.; Svelto, M.; Valenti, G. Trafficking and Phosphorylation Dynamics of AQP4 in Histamine-Treated Human Gastric Cells. Biol. Cell 2007, 99, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, J.; Chae, Y.K.; Jang, S.J.; Kim, M.S.; Baek, J.H.; Park, J.C.; Trink, B.; Ratovitski, E.; Lee, T.; Park, B.; et al. Membrane Trafficking of AQP5 and CAMP Dependent Phosphorylation in Bronchial Epithelium. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 366, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, T.; Azlina, A.; Javkhlan, P.; Yao, C.; Akamatsu, T.; Hosoi, K. Novel Phosphorylation of Aquaporin-5 at Its Threonine 259 through CAMP Signaling in Salivary Gland Cells. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2011, 301, C667–C678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, Y.; Iida, H.; Ishida, H. The Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptor-Stimulated Increase in Aquaporin-5 Levels in the Apical Plasma Membrane in Rat Parotid Acinar Cells Is Coupled with Activation of Nitric Oxide/CGMP Signal Transduction. Mol. Pharmacol. 2002, 61, 1423–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gradilone, S.A.; García, F.; Huebert, R.C.; Tietz, P.S.; Larocca, M.C.; Kierbel, A.; Carreras, F.I.; LaRusso, N.F.; Marinelli, R.A. Glucagon Induces the Plasma Membrane Insertion of Functional Aquaporin-8 Water Channels in Isolated Rat Hepatocytes. Hepatology 2003, 37, 1435–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, N.S.; Sang, H.L.; Min, Y.L.; Jung, S.H.; Yu, J.L.; Ho, J.H. High Glucose Induced Translocation of Aquaporin8 to Chicken Hepatocyte Plasma Membrane: Involvement of CAMP, PI3K/Akt, PKC, MAPKs, and Microtubule. J. Cell. Biochem. 2008, 103, 1089–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, I.; Ward, D.T.; Baum, M.A.; Scott, J.D.; Coghlan, V.M.; Hammond, T.G.; Harris, H.W. AQP2 Is a Substrate for Endogenous PP2B Activity within an Inner Medullary AKAP-Signaling Complex. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2001, 281, 958–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gooch, J.L. Loss of Calcineurin A Results in Altered Trafficking of AQP2 and in Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus. J. Cell Sci. 2006, 119, 2468–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Yang, B.; Ruiz, J.A.; Efe, O.; Ilori, T.O.; Sands, J.M.; Klein, J.D. Phosphatase Inhibition Increases AQP2 Accumulation in the Rat IMCD Apical Plasma Membrane. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2016, 311, F1189–F1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzi, J.R.; Sayegh, M.H.; Mallat, S.G. Calcineurin Inhibitors: 40 Years Later, Can’t Live Without…. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 5785–5791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichow, S.L.; Clemens, D.M.; Freites, J.A.; Németh-Cahalan, K.L.; Heyden, M.; Tobias, D.J.; Hall, J.E.; Gonen, T. Allosteric Mechanism of Water-Channel Gating by Ca2+-Calmodulin. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2013, 20, 1085–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traub, L.M. Tickets to Ride: Selecting Cargo for Clathrin-Regulated Internalization. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 583–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjöhamn, J.; Hedfalk, K. Unraveling Aquaporin Interaction Partners. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakazawa, Y.; Oka, M.; Furuki, K.; Mitsuishi, A.; Nakashima, E.; Takehana, M. The Effect of the Interaction between Aquaporin 0 (AQP0) and the Filensin Tail Region on AQP0 Water Permeability. Mol. Vis. 2011, 17, 3191–3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedfalk, K.; Törnroth-Horsefield, S.; Nyblom, M.; Johanson, U.; Kjellbom, P.; Neutze, R. Aquaporin Gating. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2006, 16, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Törnroth-Horsefield, S.; Wang, Y.; Hedfalk, K.; Johanson, U.; Karlsson, M.; Tajkhorshid, E.; Neutze, R.; Kjellbom, P. Structural Mechanism of Plant Aquaporin Gating. Nature 2006, 439, 688–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frick, A.; Järvå, M.; Törnroth-Horsefield, S. Structural Basis for PH Gating of Plant Aquaporins. FEBS Lett. 2013, 587, 989–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Németh-Cahalan, K.L.; Hall, J.E. PH and Calcium Regulate the Water Permeability of Aquaporin 0. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 6777–6782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonen, T.; Sliz, P.; Kistler, J.; Cheng, Y.; Walz, T. Aquaporin-0 Membrane Junctions Reveal the Structure of a Closed Water Pore. Nature 2004, 429, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotfryd, K.; Mósca, A.F.; Missel, J.W.; Truelsen, S.F.; Wang, K.; Spulber, M.; Krabbe, S.; Hélix-nielsen, C.; Laforenza, U.; Soveral, G.; et al. Human Adipose Glycerol Flux Is Regulated by a PH Gate in AQP10. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yool, A.J.; Stamer, W.D.; Regan, J.W. Forskolin Stimulation of Water and Cation Permeability in Aquaporin1 Water Channels. Science 1996, 273, 1216–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, T.L.; Brooks, H.L.; Boassa, D.; Leonov, S.; Yanochko, G.M.; Regan, J.W.; Yool, A.J. Cloned Human Aquaporin-1 Is a Cyclic GMP-Gated Ion Channel. Mol. Pharmacol. 2000, 57, 576–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saparov, S.M.; Kozono, D.; Rothe, U.; Agre, P.; Pohl, P. Water and Ion Permeation of Aquaporin-1 in Planar Lipid Bilayers. Major Differences in Structural Determinants and Stoichiometry. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 31515–31520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boassa, D.; Yool, A.J. A Fascinating Tail: CGMP Activation of Aquaporin-1 Ion Channels. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2002, 23, 558–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.L.; Hamann, S.; Heegaard, S. Aquaporins in the Eye. In Aquaporins. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Yang, B., Ed.; Sprenger: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 969. [Google Scholar]
- Girsch, S.J.; Peracchia, C. Lens Cell-to-Cell Channel Protein: I. Self-Assembly into Liposomes and Permeability Regulation by Calmodulin. J. Membr. Biol. 1985, 83, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girsch, S.J.; Peracchia, C. Calmodulin Interacts with a C-Terminus Peptide from the Lens Membrane Protein MIP26. Curr. Eye Res. 1991, 10, 839–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichow, S.L.; Gonen, T. Noncanonical Binding of Calmodulin to Aquaporin-0: Implications for Channel Regulation. Structure 2008, 16, 1389–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreida, S.; Roche, J.V.; Olsson, C.; Linse, S.; Törnroth-Horsefield, S. Protein–Protein Interactions in AQP Regulation—Biophysical Characterization of AQP0–CaM and AQP2–LIP5 Complex Formation. Faraday Discuss. 2018, 209, 35–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schey, K.L.; Little, M.; Fowler, J.G.; Crouch, R.K. Characterization of Human Lens Major Intrinsic Protein Structure. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2000, 41, 175–182. [Google Scholar]
- Lindsey Rose, K.M.; Wang, Z.; Magrath, G.N.; Hazard, E.S.; Hildebrandt, J.D.; Schey, K.L. Aquaporin 0-Calmodulin Interaction and the Effect of Aquaporin 0 Phosphorylation. Biochemistry 2008, 47, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fields, J.B.; Németh-Cahalan, K.L.; Freites, J.A.; Vorontsova, I.; Hall, J.E.; Tobias, D.J. Calmodulin Gates Aquaporin 0 Permeability through a Positively Charged Cytoplasmic Loop. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.S.; Bhat, R.V.; Preston, G.M.; Guggino, W.B.; Baraban, J.M.; Agre, P. Molecular Characterization of an Aquaporin CDNA from Brain: Candidate Osmoreceptor and Regulator of Water Balance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 13052–13056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbard, J.A.; Hsu, M.S.; Seldin, M.M.; Binder, D.K. Expression of the Astrocyte Water Channel Aquaporin-4 in the Mouse Brain. ASN Neuro 2015, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazzina, G.; Amorini, A.M.; Marmarou, C.R.; Fukui, S.; Okuno, K.; Dunbar, J.G.; Glisson, R.; Marmarou, A.; Kleindienst, A. The Protein Kinase C Activator Phorbol Myristate Acetate Decreases Brain Edema by Aquaporin 4 Downregulation after Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion in the Rat. J. Neurotrauma 2010, 27, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Sayeed, I.; Baronne, L.M.; Hoffman, S.W.; Guennoun, R.; Stein, D.G. Progesterone Administration Modulates AQP4 Expression and Edema after Traumatic Brain Injury in Male Rats. Exp. Neurol. 2006, 198, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunnarson, E.; Zelenina, M.; Aperia, A. Regulation of Brain Aquaporins. Neuroscience 2004, 129, 947–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.D.; Yeh, R.; Sandstrom, A.; Chorny, I.; Harries, W.E.C.; Robbins, R.A.; Miercke, L.J.W.; Stroud, R.M. Crystal Structure of Human Aquaporin 4 at 1.8 A and Its Mechanism of Conductance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 7437–7442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notredame, C.; Higgins, D.G.; Heringa, J. T-Coffee: A Novel Method for Fast and Accurate Multiple Sequence Alignment. J. Mol. Biol. 2000, 302, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, X.; Gouet, P. Deciphering Key Features in Protein Structures with the New ENDscript Server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 320–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assentoft, M.; Kaptan, S.; Fenton, R.A.; Hua, S.Z.; de Groot, B.L.; Macaulay, N. Phosphorylation of Rat Aquaporin-4 at Ser111 Is Not Required for Channel Gating. Glia 2013, 61, 1101–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, C.G.; Cooper, S.T.; Lo, H.P.; Compton, A.G.; Yang, N.; Wintour, E.M.; North, K.N.; Winlaw, D.S. Expression of Aquaporin 1 in Human Cardiac and Skeletal Muscle. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2004, 36, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsunoda, S.P.; Wiesner, B.; Lorenz, D.; Rosenthal, W.; Pohl, P. Aquaporin-1, Nothing but a Water Channel. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 11364–11367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Yool, A.J.; Schulten, K.; Tajkhorshid, E. Mechanism of Gating and Ion Conductivity of a Possible Tetrameric Pore in Aquaporin-1. Structure 2006, 14, 1411–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsura, T.; Verbavatz, J.M.; Farinas, J.; Ma, T.; Ausiello, D.A.; Verkman, A.S.; Brown, D. Constitutive and Regulated Membrane Expression of Aquaporin 1 and Aquaporin 2 Water Channels in Stably Transfected LLC-PK1 Epithelial Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 7212–7216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conner, M.T.; Conner, A.C.; Brown, J.E.P.; Bill, R.M. Membrane Trafficking of Aquaporin 1 Is Mediated by Protein Kinase C via Microtubules and Regulated by Tonicity. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 821–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamsteeg, E.-J.; Hendriks, G.; Boone, M.; Konings, I.B.M.; Oorschot, V.; van der Sluijs, P.; Klumperman, J.; Deen, P.M.T. Short-Chain Ubiquitination Mediates the Regulated Endocytosis of the Aquaporin-2 Water Channel. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 18344–18349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffert, J.D.; Fenton, R.A.; Moeller, H.B.; Simons, B.; Tchapyjnikov, D.; McDill, B.W.; Yu, M.J.; Pisitkun, T.; Chen, F.; Knepper, M.A. Vasopressin-Stimulated Increase in Phosphorylation at Ser269 Potentiates Plasma Membrane Retention of Aquaporin-2. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 24617–24627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, P.W.; Ueberdiek, L.; Day, J.; Bouley, R.; Brown, D. Protein Phosphatase 2C Is Responsible for VP-Induced Dephosphorylation of AQP2 Serine 261. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2017, 313, F404–F413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffert, J.D.; Nielsen, J.; Yu, M.-J.; Pisitkun, T.; Schleicher, S.M.; Nielsen, S.; Knepper, M.A. Dynamics of Aquaporin-2 Serine-261 Phosphorylation in Response to Short-Term Vasopressin Treatment in Collecting Duct. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2007, 292, F691–F700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamma, G.; Robben, J.H.; Trimpert, C.; Boone, M.; Deen, P.M.T. Regulation of AQP2 Localization by S256 and S261 Phosphorylation and Ubiquitination. AJP Cell Physiol. 2011, 300, C636–C646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenton, R.A.; Moeller, H.B.; Hoffert, J.D.; Yu, M.-J.; Nielsen, S.; Knepper, M.A. Acute Regulation of Aquaporin-2 Phosphorylation at Ser-264 by Vasopressin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 3134–3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, M.C.; Verkman, A.S. Aquaporin-4 and Brain Edema. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2007, 22, 778–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raina, S.; Preston, G.M.; Guggino, W.B.; Agre, P. Molecular Cloning and Characterization of an Aquaporin CDNA from Salivary, Lacrimal and Respiratory Tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 1908–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Kawedia, J.D.; Menon, A.G. Cyclic AMP Regulates Aquaporin 5 Expression at Both Transcriptional and Post-Transcriptional Levels through a Protein Kinase A Pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 32173–32180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvin, M.N. Subcellular Redistribution of AQP5 by Vasoactive Intestinal Polypeptide in the Brunner’s Gland of the Rat Duodenum. AJP Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2005, 288, G1283–G1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, S.S.; Varadaraj, M.; Yerramilli, V.S.; Menon, A.G.; Varadaraj, K. Spatial Expression of Aquaporin 5 in Mammalian Cornea and Lens, and Regulation of Its Localization by Phosphokinase A. Mol. Vis. 2012, 18, 957–967. [Google Scholar]
- Sidhaye, V.; Hoffert, J.D.; King, L.S. CAMP Has Distinct Acute and Chronic Effects on Aquaporin-5 in Lung Epithelial Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 3590–3596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, J.; Lee, J.; Chae, Y.K.; Kim, M.S.; Baek, J.H.; Park, J.C.; Park, M.J.; Smith, I.M.; Trink, B.; Ratovitski, E.; et al. Overexpression of AQP5, a Putative Oncogene, Promotes Cell Growth and Transformation. Cancer Lett. 2008, 264, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horsefield, R.; Nordén, K.; Fellert, M.; Backmark, A.; Törnroth-Horsefield, S.; Terwisscha van Scheltinga, A.C.; Kvassman, J.; Kjellbom, P.; Johanson, U.; Neutze, R. High-Resolution x-Ray Structure of Human Aquaporin 5. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 13327–13332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| AQP | PKA | PKC | PKG | CK | CaMKII | Other | Unknown |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AQP0 | S235 [42] | S231 [43] S235 [44] | S229 [43] | ||||
| AQP1 | N/A [45] | T157 [14,24] T239 [14,24] | Y253 [46] | ||||
| AQP2 | S256 [47] T269 1 [48] | S264 1 [49] | S256 [50] | S264 1 [48] | S261—MAP kinases [51] | ||
| AQP3 | Indirect [52] | ||||||
| AQP4 | Indirect [53] N/A [54] S276 [25] | S180 [26,27] | S111 [32] | S276 [37] | Indirect [32,41] | S285, S315, S316, S321, S322 [13] | |
| AQP5 | S156 [55] T259 [56] | N/A [57] | |||||
| AQP6 | |||||||
| AQP7 | S10 [15] T11 [15] | ||||||
| AQP8 | N/A 2 [58] | N/A 2 [59] | |||||
| AQP9 | S11 [40] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nesverova, V.; Törnroth-Horsefield, S. Phosphorylation-Dependent Regulation of Mammalian Aquaporins. Cells 2019, 8, 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8020082
Nesverova V, Törnroth-Horsefield S. Phosphorylation-Dependent Regulation of Mammalian Aquaporins. Cells. 2019; 8(2):82. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8020082
Chicago/Turabian StyleNesverova, Veronika, and Susanna Törnroth-Horsefield. 2019. "Phosphorylation-Dependent Regulation of Mammalian Aquaporins" Cells 8, no. 2: 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8020082
APA StyleNesverova, V., & Törnroth-Horsefield, S. (2019). Phosphorylation-Dependent Regulation of Mammalian Aquaporins. Cells, 8(2), 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8020082