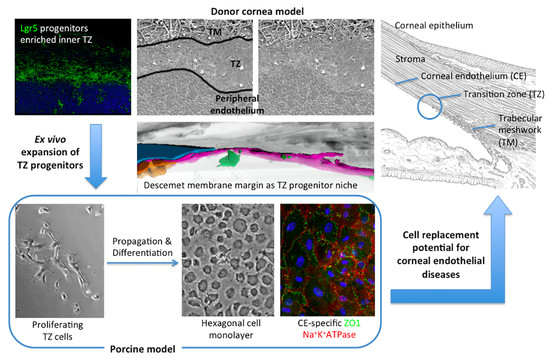
Characterization of Human Transition Zone Reveals a Putative Progenitor-Enriched Niche of Corneal Endothelium
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Human Corneas
2.2. Whole Mount Histochemistry and Immunostaining
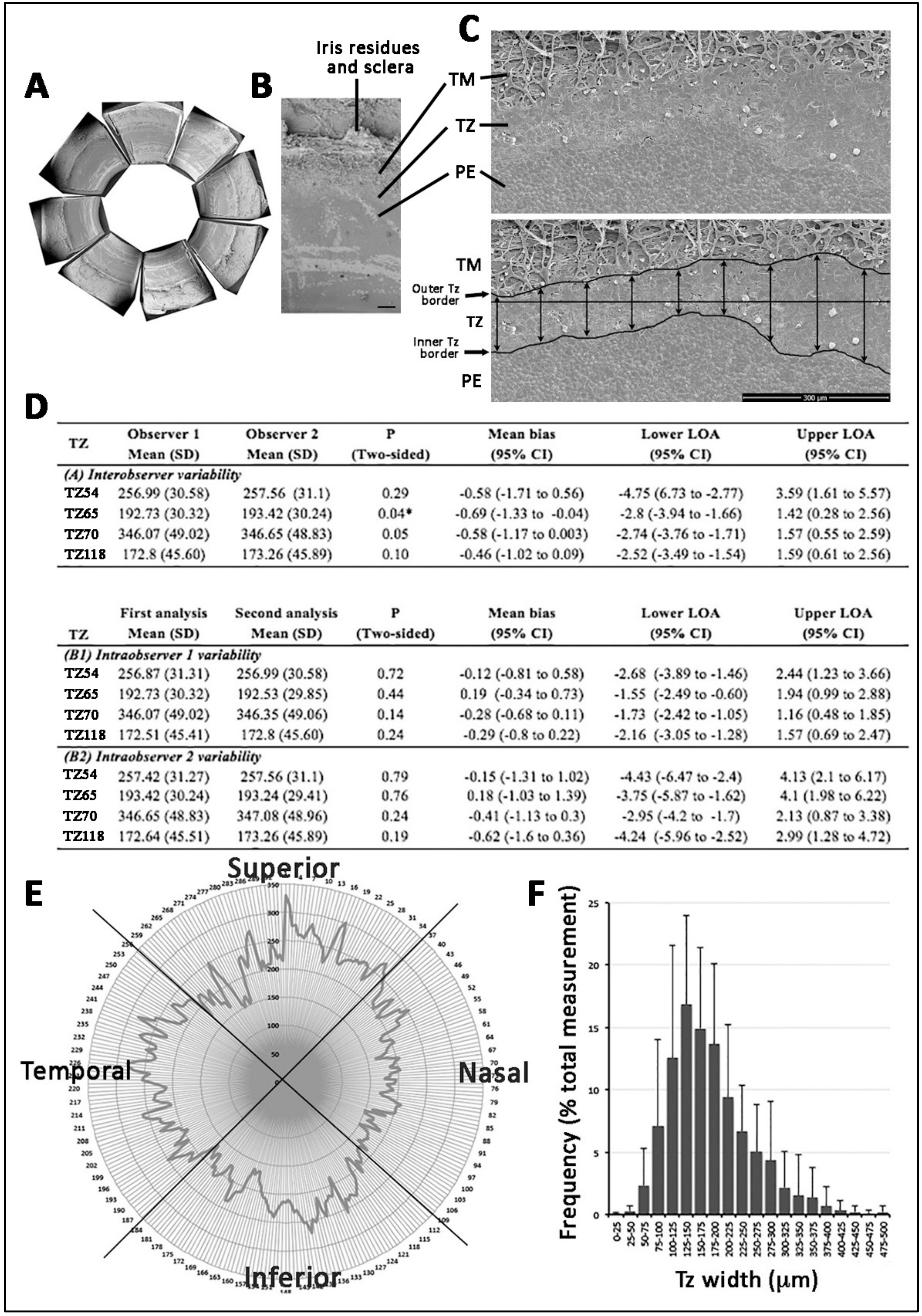
2.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and TZ Width Measurement
2.4. Quantitative Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
2.5. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.6. Serial Block-Face Scanning Electron Microscopy (SBF-SEM)
2.7. Porcine TZ Cell Culture
2.8. Western Blotting
2.9. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Posterior Limbus Contained Anatomically Distinguishable Regions
3.2. TZ Width Measurement and Distribution in Human Corneas
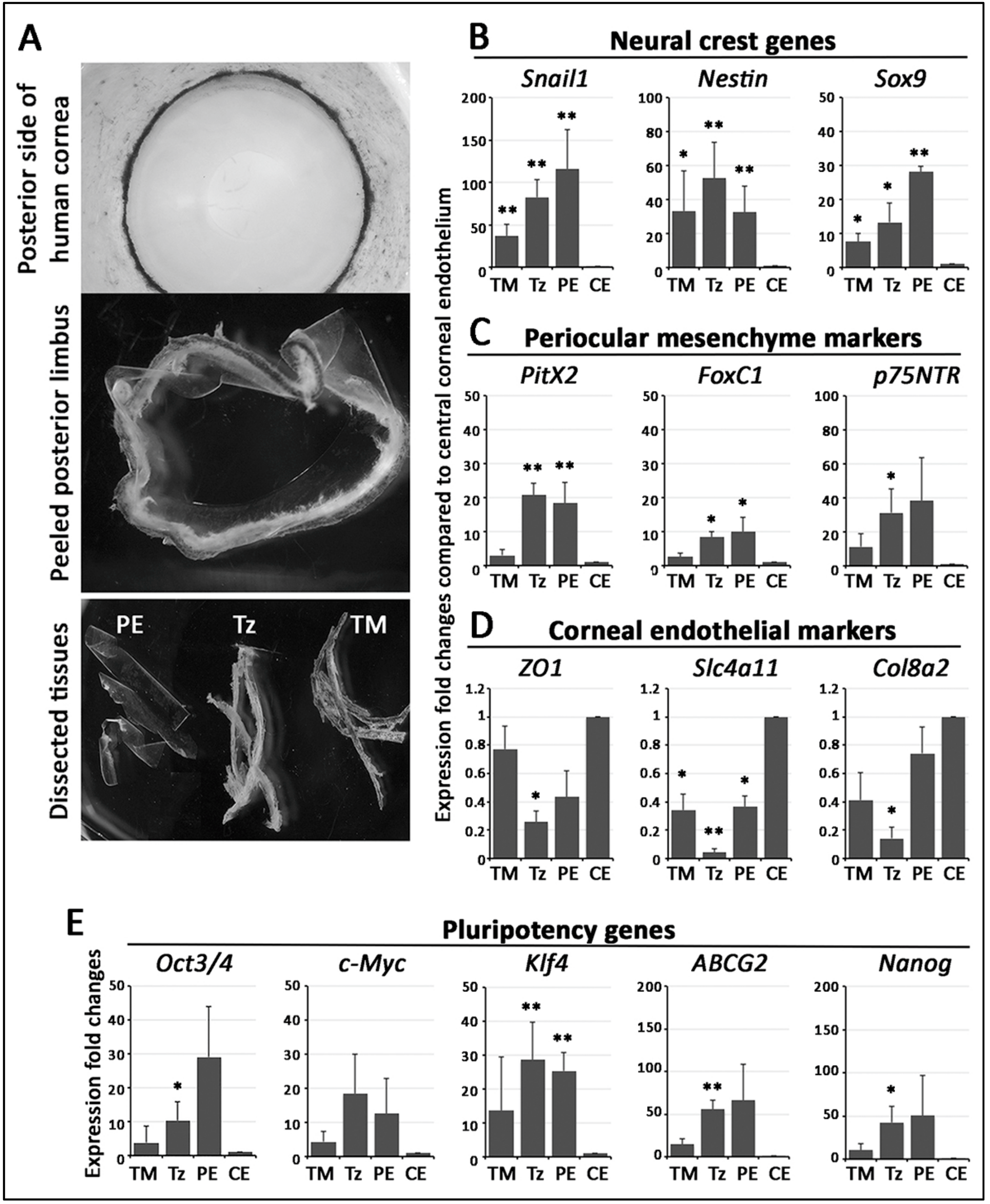
3.3. Stem Cell/Progenitor Gene Expression in TZ
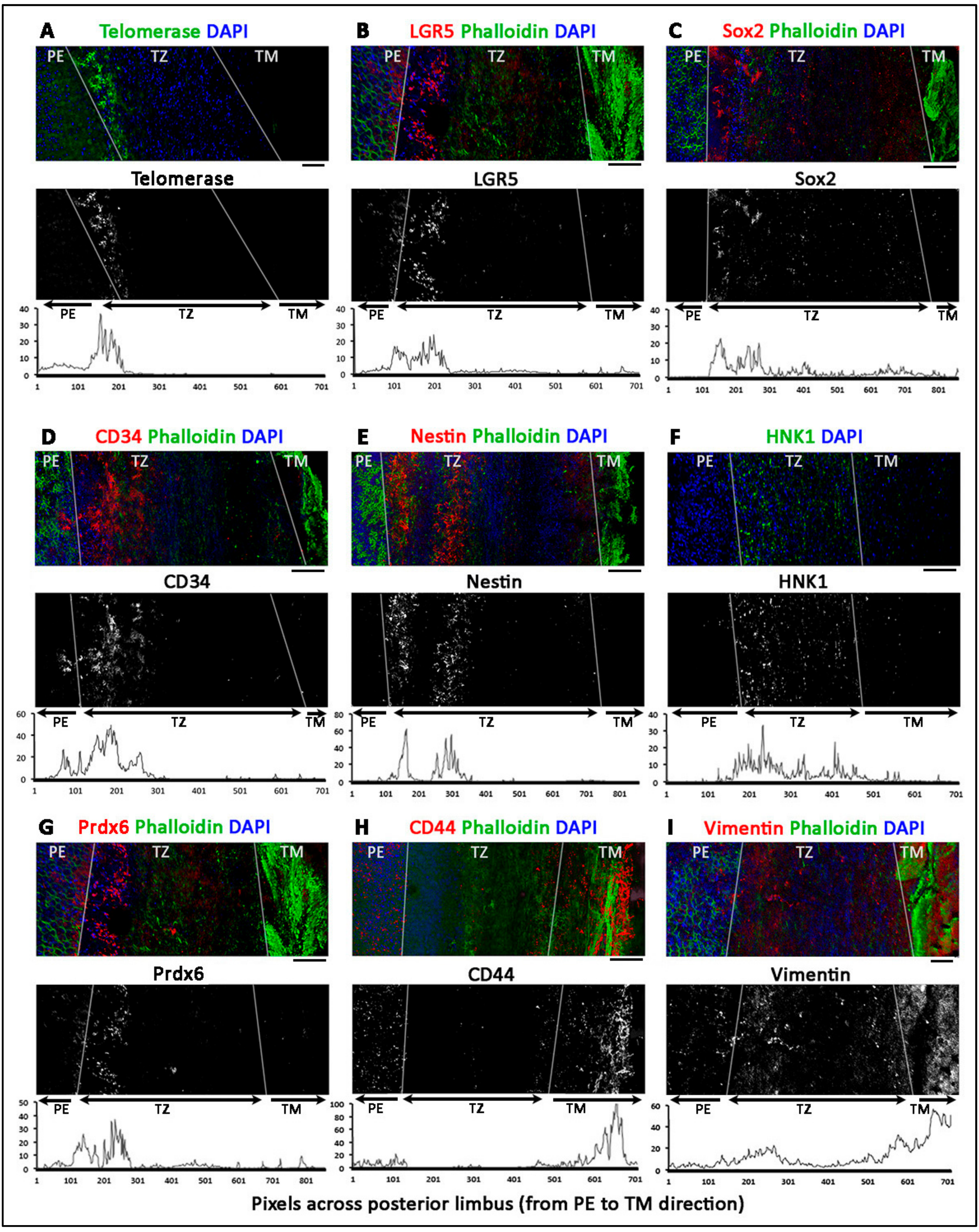
3.4. Phenotypically Distinct Regions Inside TZ
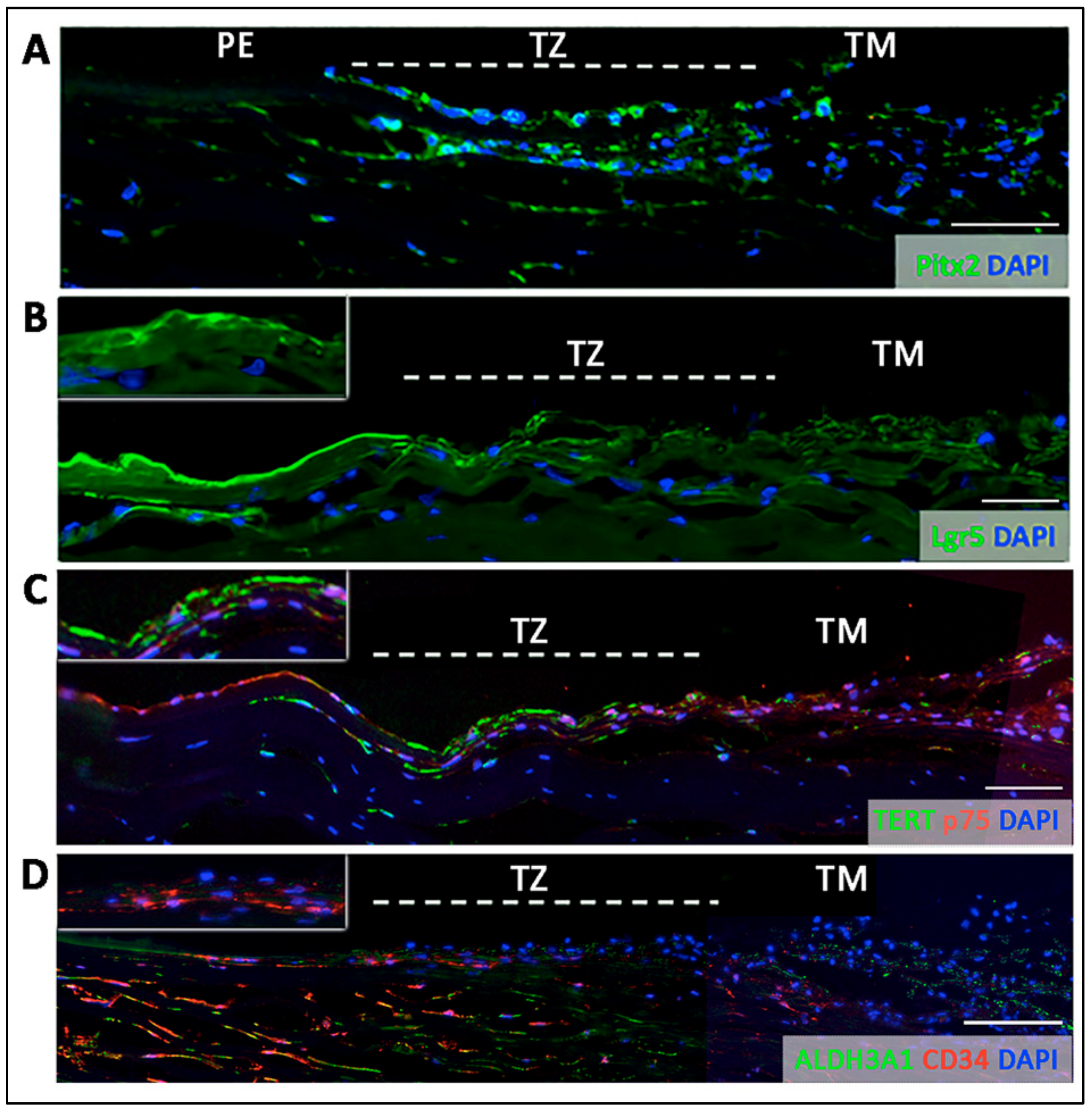
- Entire TZ expression: Vimentin and POM markers (HNK1) were expressed in the entire TZ (Figure 3F,I). While vimentin was also detected in TM and PE, HNK1 was predominantly found in TZ. On cryo-sections of posterior limbus, Pitx2 (POM marker) was distinctly expressed in the entire TZ, with signals colocalized with DAPI-stained nuclei (Figure 4A). The positive cells were located on the TZ surface and in the immediate stromal region. Minimal Pitx2 signal was detected in the TM region.
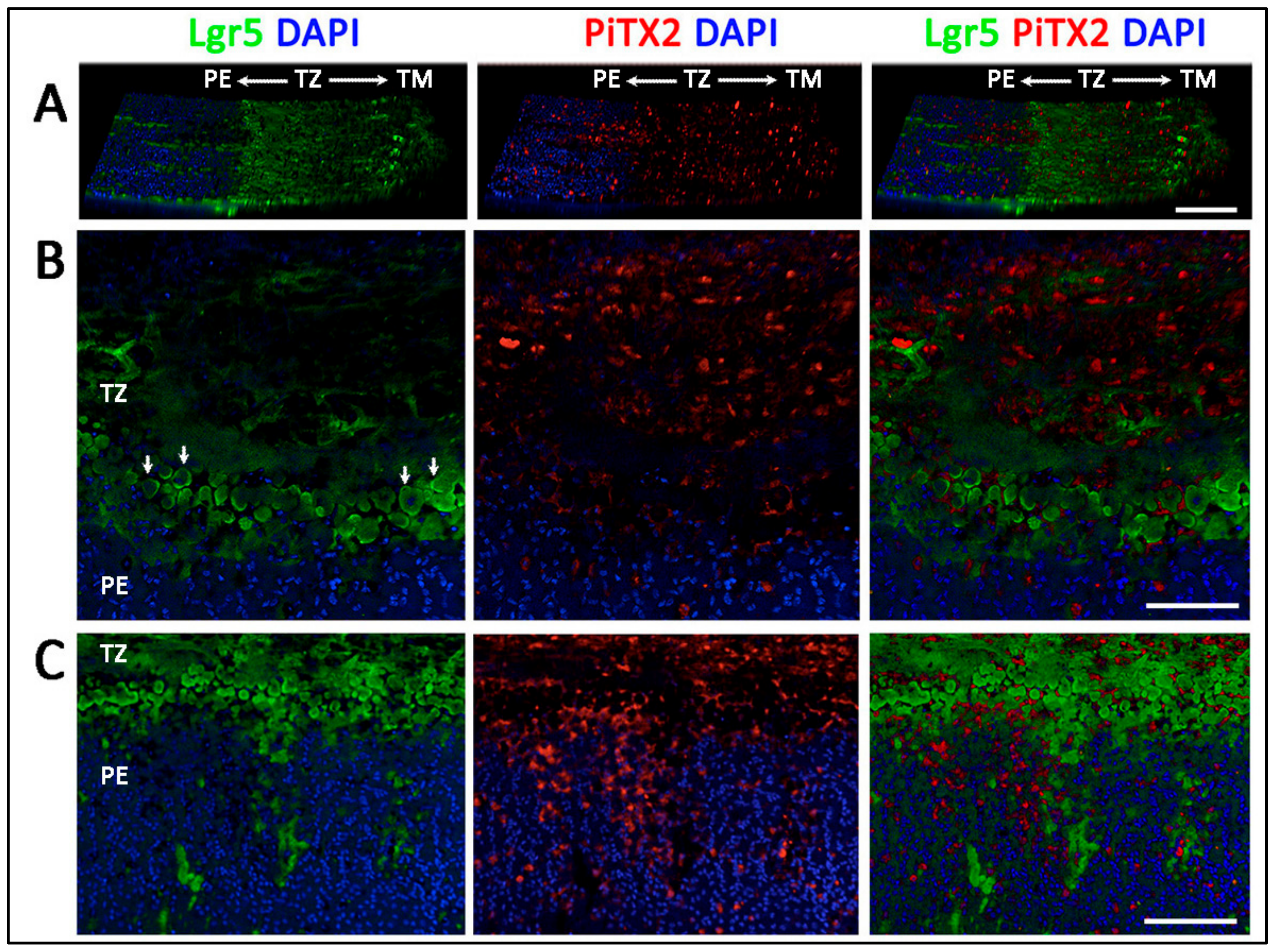
- Inner TZ expression: A number of stem/progenitor markers (TERT, Sox2, CD34, nestin) were expressed in the inner TZ (immediately adjacent to PE) (Figure 3A,C,D,E). The signal profiles showed that intensities were stronger in the inner TZ than in the outer TZ (next to TM), TM and PE regions. Moreover, Lgr5 and Prdx6 (TAG2A12) were detected in the inner TZ and PE, but not in the outer TZ (Figure 3B,G). On cryo-sections of posterior limbus, Lgr5 was distinctly expressed in inner TZ and PE (Figure 4B), of which the cells showed the surface Lgr5 labeling (inset in Figure 4B). We confirmed this result with silver-enhanced immunogold scanning EM (Supplementary Figure S5). Clusters of electron opaque dots detected under secondary electron mode were brightened when shifted to back-scattered electron imaging mode, representing Lgr5 labeling. We observed cell surface Lgr5 expression on cells inside the inner TZ and PE, but not in the outer TZ. Similarly, TERT was clearly expressed in the inner TZ with positive signals found in cells on the TZ surface and in the immediate stromal region (Figure 4C). The staining of CD34, a marker of diverse progenitors and quiescent corneal stromal keratocytes [24], was visualized in some inner TZ cells. They were different to corneal stromal keratocytes, which co-expressed both CD34 and aldehyde dehydrogenase 3A1 (ALDH3A1, a keratocyte marker) (Figure 4D).
- Outer TZ expression: We detected CD44 expression (mesenchymal stem cell marker) in the outer TZ (Figure 3H).
3.5. Projection of Progenitors from Transition Zone to Peripheral Endothelium
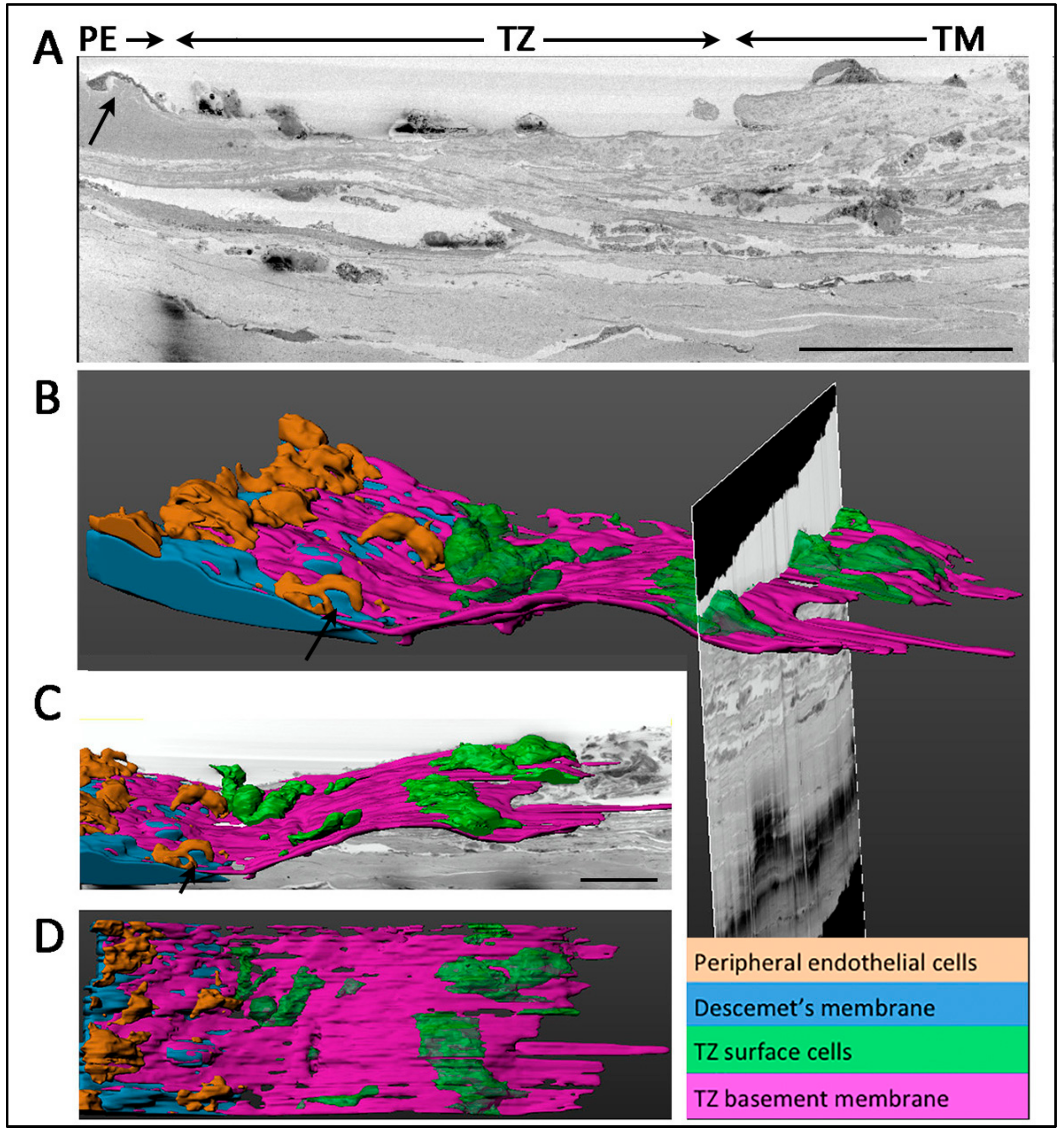
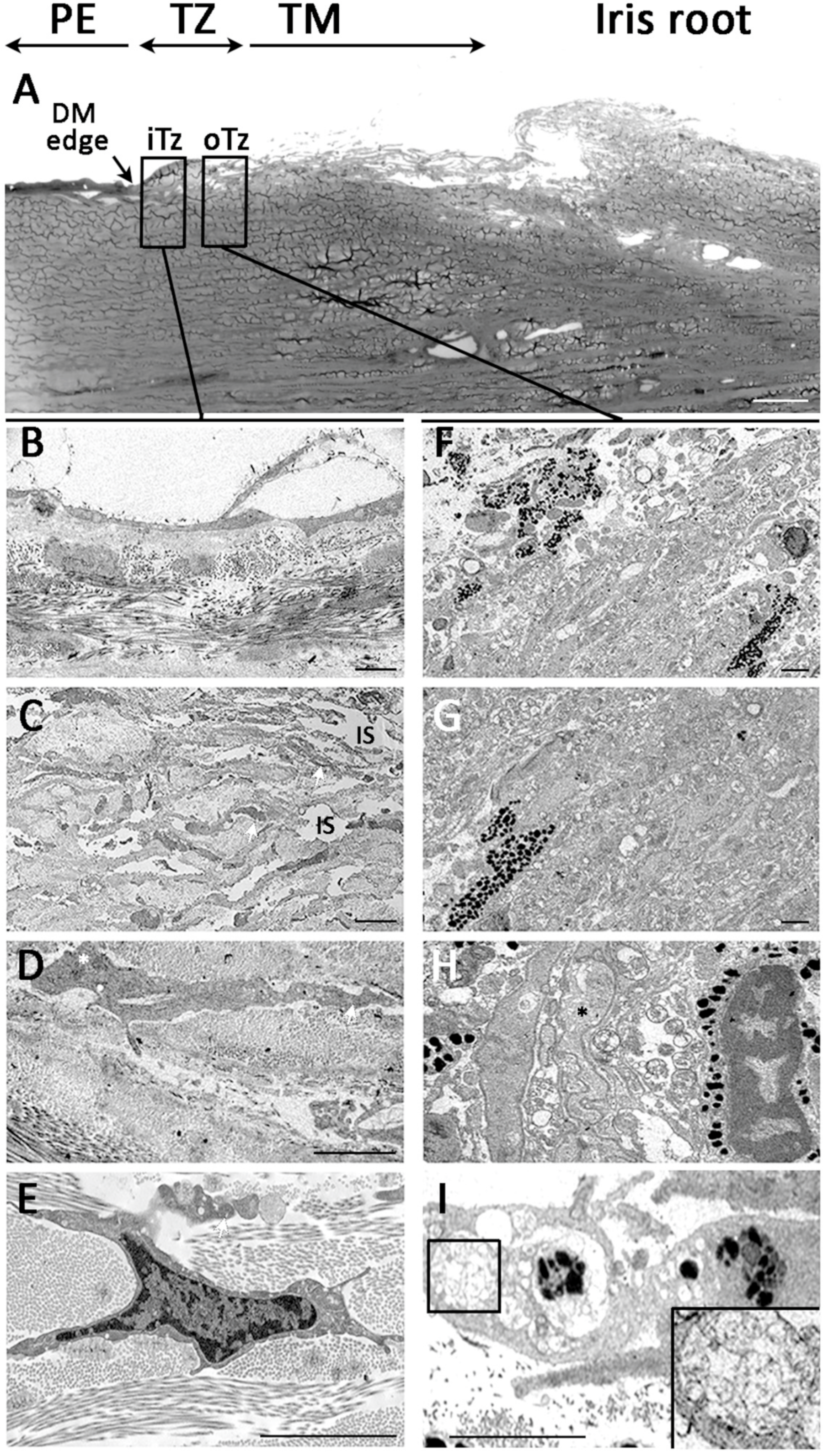
3.6. Ultrastructural Morphology of Transition Zone
3.7. Termination of Descemet’s Membrane Beneath the TZ Surface
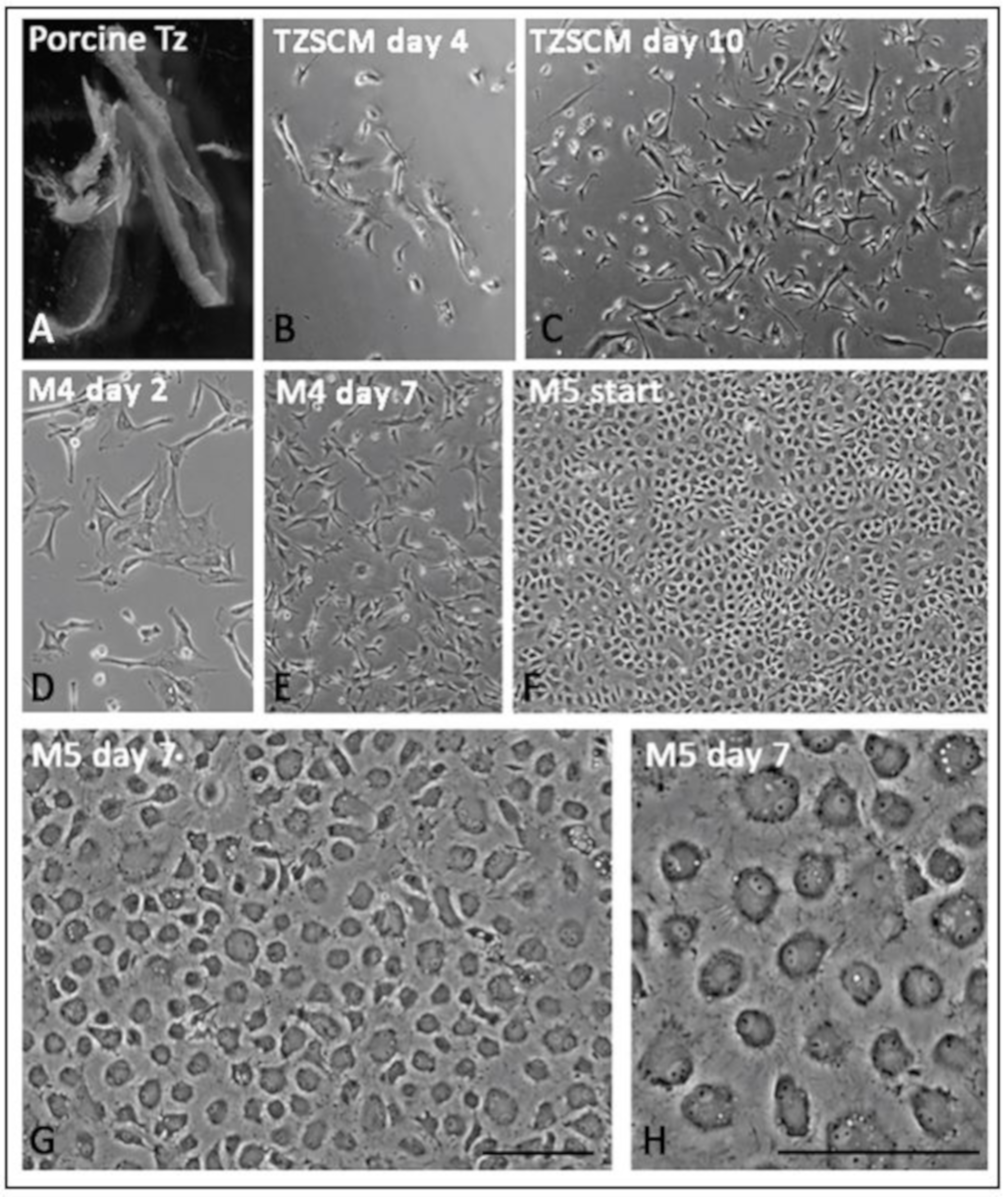
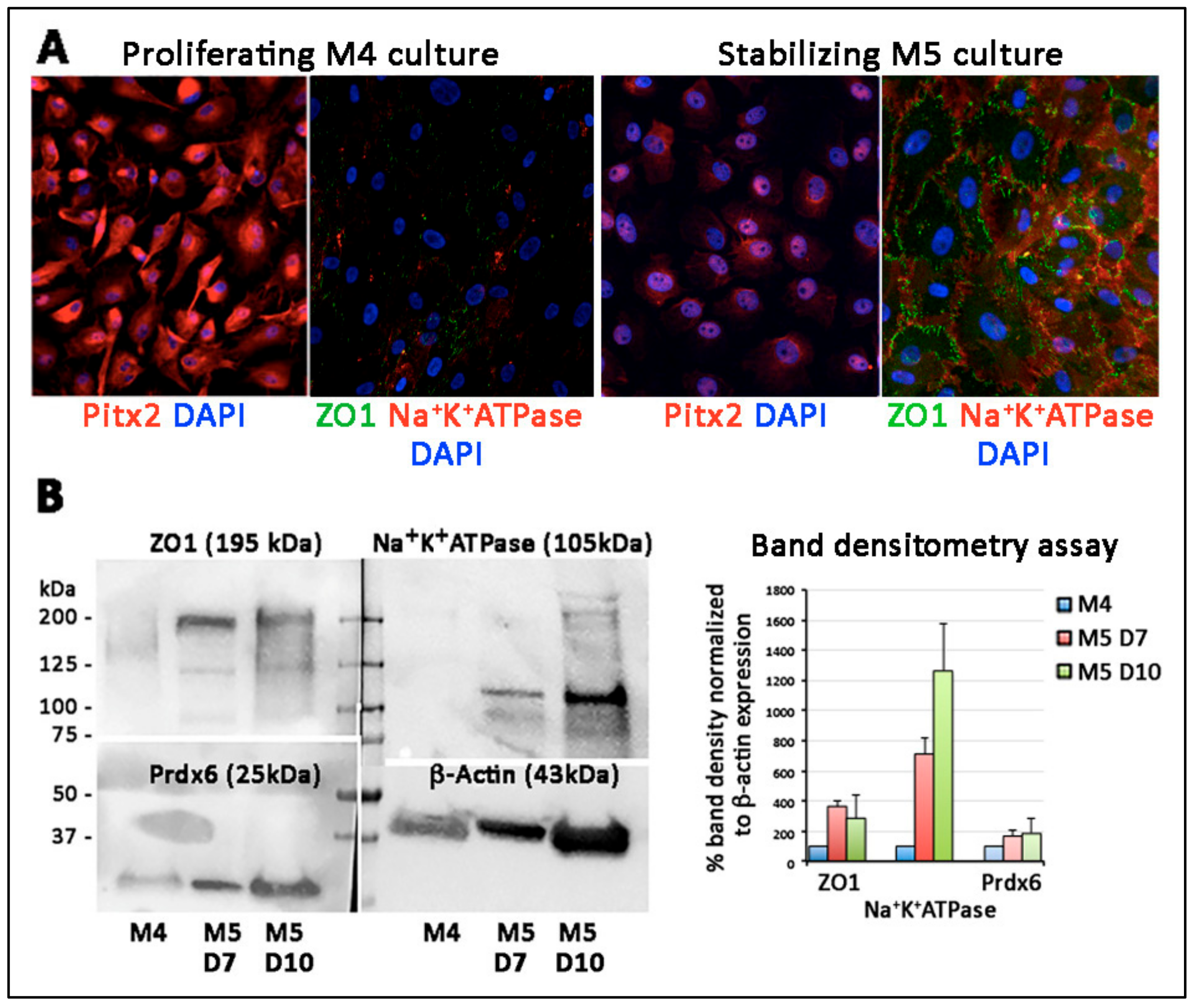
3.8. Primary Culture of Porcine TZ Cells to Corneal Endothelial Cells
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tuft, S.J.; Coster, D.J. The corneal endothelium. Eye 1990, 4, 389–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonanno, J.A. Molecular mechanisms underlying the corneal endothelial pump. Exp. Eye Res. 2012, 95, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourne, W.M. Biology of the corneal endothelium in health and disease. Eye 2003, 17, 912–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worner, C.H.; Olguin, A.; Ruiz-Garcia, J.L.; Garzon-Jimenez, N. Cell pattern in adult human corneal endothelium. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peh, G.S.; Beuerman, R.W.; Colman, A.; Tan, D.T.; Mehta, J.S. Human corneal endothelial cell expansion for corneal endothelium transplantation: An overview. Transplantation 2011, 91, 811–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahlig, S.; Yam, G.H.; Chong, W.; Seah, X.Y.; Kocaba, V.; Ang, M.; Htoon, H.M.; Tun, T.A.; Ong, H.S.; Mehta, J.S. Quantification of the posterior cornea using Swept Source Optical Coherence Tomography. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2018, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.Y.; Sheridan, C.; Grierson, I.; Mason, S.; Kearns, V.; Lo, A.C.; Wong, D. Progenitors for the corneal endothelium and trabecular meshwork: A potential source for personalized stem cell therapy in corneal endothelial diseases and glaucoma. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2011, 2011, 412743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breazzano, M.P.; Fikhman, M.; Abraham, J.L.; Barker-Griffith, A.E. Analysis of Schwalbe’s line (limbal smooth zone) by scanning electron microscopy and optical coherence tomography in human eye bank eyes. J. Ophthalmic Vis. Res. 2013, 8, 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, W.Y.; Grierson, I.; Sheridan, C.; Lo, A.C.; Wong, D.S. Bovine posterior limbus: An evaluation of an alternative source for corneal endothelial and trabecular meshwork stem/progenitor cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2015, 24, 624–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartakova, A.; Kunzevitzky, N.J.; Goldberg, J.L. Regenerative cell therapy for corneal endothelium. Curr. Ophthalmol. Rep. 2014, 2, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, N.C. Proliferative capacity of corneal endothelial cells. Exp. Eye Res. 2012, 95, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feizi, S. Corneal endothelial cell dysfunction: Etiologies and management. Ther. Adv. Ophthalmol. 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lwigale, P.Y. Corneal development: Different cells from a common progenitor. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2015, 134, 43–59. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lovatt, M.; Yam, G.H.; Peh, G.S.; Colman, A.; Dunn, N.R.; Mehta, J.S. Directed differentiation of periocular mesenchyme from human embryonic stem cells. Differentiation 2018, 99, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGowan, S.L.; Edelhauser, H.F.; Pfister, R.R.; Whikehart, D.R. Stem cell markers in the human posterior limbus and corneal endothelium of unwounded and wounded corneas. Mol. Vis. 2007, 13, 1984–2000. [Google Scholar]
- Whikehart, D.R.; Parikh, C.H.; Vaughn, A.V.; Mishler, K.; Edelhauser, H.F. Evidence suggesting the existence of stem cells for the human corneal endothelium. Mol. Vis. 2005, 11, 816–824. [Google Scholar]
- Yokoo, S.; Yamagami, S.; Yanagi, Y.; Uchida, S.; Mimura, T.; Usui, T.; Amano, S. Human corneal endothelial cell precursors isolated by sphere-forming assay. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2005, 46, 1626–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimura, T.; Yamagami, S.; Yokoo, S.; Usui, T.; Amano, S. Selective isolation of young cells from human corneal endothelium by the sphere-forming assay. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 2010, 16, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walshe, J.; Harkin, D.G. Serial explant culture provides novel insights into the potential location and phenotype of corneal endothelial progenitor cells. Exp. Eye Res. 2014, 127, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katikireddy, K.R.; Schmedt, T.; Price, M.O.; Price, F.W.; Jurkunas, U.V. Existence of neural crest-derived progenitor cells in normal and Fuchs endothelial dystrophy corneal endothelium. Am. J. Pathol. 2016, 186, 2736–2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Campolmi, N.; Gain, P.; Ha Thi, B.M.; Dumollard, J.M.; Duband, S.; Peoc’h, M.; Piselli, S.; Garraud, O.; Thuret, G. Revisited microanatomy of the corneal endothelial periphery: New evidence for continuous centripetal migration of endothelial cells in humans. Stem Cells 2012, 30, 2523–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peh, G.S.; Chng, Z.; Ang, H.P.; Cheng, T.Y.; Adnan, K.; Seah, X.Y.; George, B.L.; Toh, K.P.; Tan, D.T.; Yam, G.H.; et al. Propagation of human corneal endothelial cells: A novel dual media approach. Cell Transpl. 2015, 24, 287–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peh, G.S.; Toh, K.P.; Wu, F.Y.; Tan, D.T.; Mehta, J.S. Cultivation of human corneal endothelial cells isolated from paired donor corneas. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidney, L.E.; Branch, M.J.; Dunphy, S.E.; Dua, H.S.; Hopkinson, A. Concise review: Evidence for CD34 as a common marker for diverse progenitors. Stem Cells 2014, 32, 1380–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinero, D.P.; Plaza Puche, A.B.; Alio, J.L. Corneal diameter measurements by corneal topography and angle-to-angle measurements by optical coherence tomography: Evaluation of equivalence. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2008, 34, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gage, P.J.; Rhoades, W.; Prucka, S.K.; Hjalt, T. Fate maps of neural crest and mesoderm in the mammalian eye. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2005, 46, 4200–4208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.L.; Bohnsack, B.L. Neural crest derivatives in ocular development: Discerning the eye of the storm. Birth Defects Res. C Embryo Today 2015, 105, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavala, J.; Lopez Jaime, G.R.; Rodriguez Barrientos, C.A.; Valdez-Garcia, J. Corneal endothelium: Developmental strategies for regeneration. Eye 2013, 27, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greaves, M.F.; Brown, J.; Molgaard, H.V.; Spurr, N.K.; Roberston, D.; Delia, D.; Sutherland, D.R. Molecular features of CD34: A hemopoietic progenitor cell-associated molecule. Leukemia 1992, 6 (Suppl. 1), 31–36. [Google Scholar]
- Joseph, A.; Hossain, P.; Jhan, S.; Jones, R.E.; Tighe, P.; Mcintosh, R.S.; Dua, H.S. Expression of CD34 and L-Selectin on human corneal keratocytes. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2003, 44, 4689–4692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosnova, M.; Bradl, M.; Forrester, J.V. CD34+ corneal stromal cells are bone marrow-derived and express haematopoietic stem cell markers. Stem Cells 2005, 23, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrella, G.; Bursini, P.; Spelat, R.; Hossain, P.; Hopkinson, A.; Dua, H.S. Expression of haematopoietic stem cell markers, CD133 and CD34 in human corneal keratocytes. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2007, 91, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, S.J.; Spradling, A.C. Stem cells and niches: Mechanisms that promote stem cell maintenance throughout life. Cell 2008, 132, 598–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, R.A.; Grierson, I. Morphological effects of argon laser trabeculoplasty upon the glaucomatous human meshwork. Eye 1989, 3 Pt 6, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Voog, J.; Jones, D.L. Stem cells and the niche: A dynamic duo. Cell Stem Cell 2010, 6, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vranka, J.A.; Acott, T.S. Pressure-induced expression changes in segmental flow regions of the human trabecular meshwork. Exp. Eye Res. 2017, 158, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Posterior Limbus Regions | Marker Expression |
|---|---|
| Peripheral endothelium (PE) | Lgr5, Prdx6, nestin (sporadic), CD34 (scarce), TERT (sporadic), ZO1, Na+K+ATPase |
| Transition zone (TZ) Entire TZ | Vimentin, HNK1, Pitx2, p75NTR |
| Inner TZ | Lgr5, Prdx6, CD34, TERT, nestin |
| Outer TZ | CD44 |
| Trabecular meshwork (TM) | Vimentin, CD44 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yam, G.H.-F.; Seah, X.; Yusoff, N.Z.B.M.; Setiawan, M.; Wahlig, S.; Htoon, H.M.; Peh, G.S.L.; Kocaba, V.; Mehta, J.S. Characterization of Human Transition Zone Reveals a Putative Progenitor-Enriched Niche of Corneal Endothelium. Cells 2019, 8, 1244. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8101244
Yam GH-F, Seah X, Yusoff NZBM, Setiawan M, Wahlig S, Htoon HM, Peh GSL, Kocaba V, Mehta JS. Characterization of Human Transition Zone Reveals a Putative Progenitor-Enriched Niche of Corneal Endothelium. Cells. 2019; 8(10):1244. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8101244
Chicago/Turabian StyleYam, Gary Hin-Fai, Xinyi Seah, Nur Zahirah Binte M Yusoff, Melina Setiawan, Stephen Wahlig, Hla Myint Htoon, Gary S.L. Peh, Viridiana Kocaba, and Jodhbir S Mehta. 2019. "Characterization of Human Transition Zone Reveals a Putative Progenitor-Enriched Niche of Corneal Endothelium" Cells 8, no. 10: 1244. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8101244
APA StyleYam, G. H.-F., Seah, X., Yusoff, N. Z. B. M., Setiawan, M., Wahlig, S., Htoon, H. M., Peh, G. S. L., Kocaba, V., & Mehta, J. S. (2019). Characterization of Human Transition Zone Reveals a Putative Progenitor-Enriched Niche of Corneal Endothelium. Cells, 8(10), 1244. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8101244