Syncytiotrophoblast of Placentae from Women with Zika Virus Infection Has Altered Tight Junction Protein Expression and Increased Paracellular Permeability
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Patient Selection and Specimens
2.3. Cell Culture
2.4. Immunofluorescence
2.5. Relative Mean Fluorescence Intensity Measurements
2.6. Western Blot
2.7. Histochemical Staining
2.8. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.9. Measurement of Transepithelial Electrical Resistance (TER)
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Trophoblast of Chorionic Villi in Human Placentae Expressed E-cadherin and a Wide Array of TJ Proteins
3.2. E-cadherin Stained the Basal Membrane of the STB and Its Expression was not Affected in ZIKV-Infected Placentae
3.3. The Expression of Claudin-1 Slightly Increased in Placentae Derived from ZIKV-Infected Women
3.4. The Expression of Claudin-3 was Strong in Placental Vessels and Faint at the STB Layer of Both Control and ZIKV-Infected Placentae
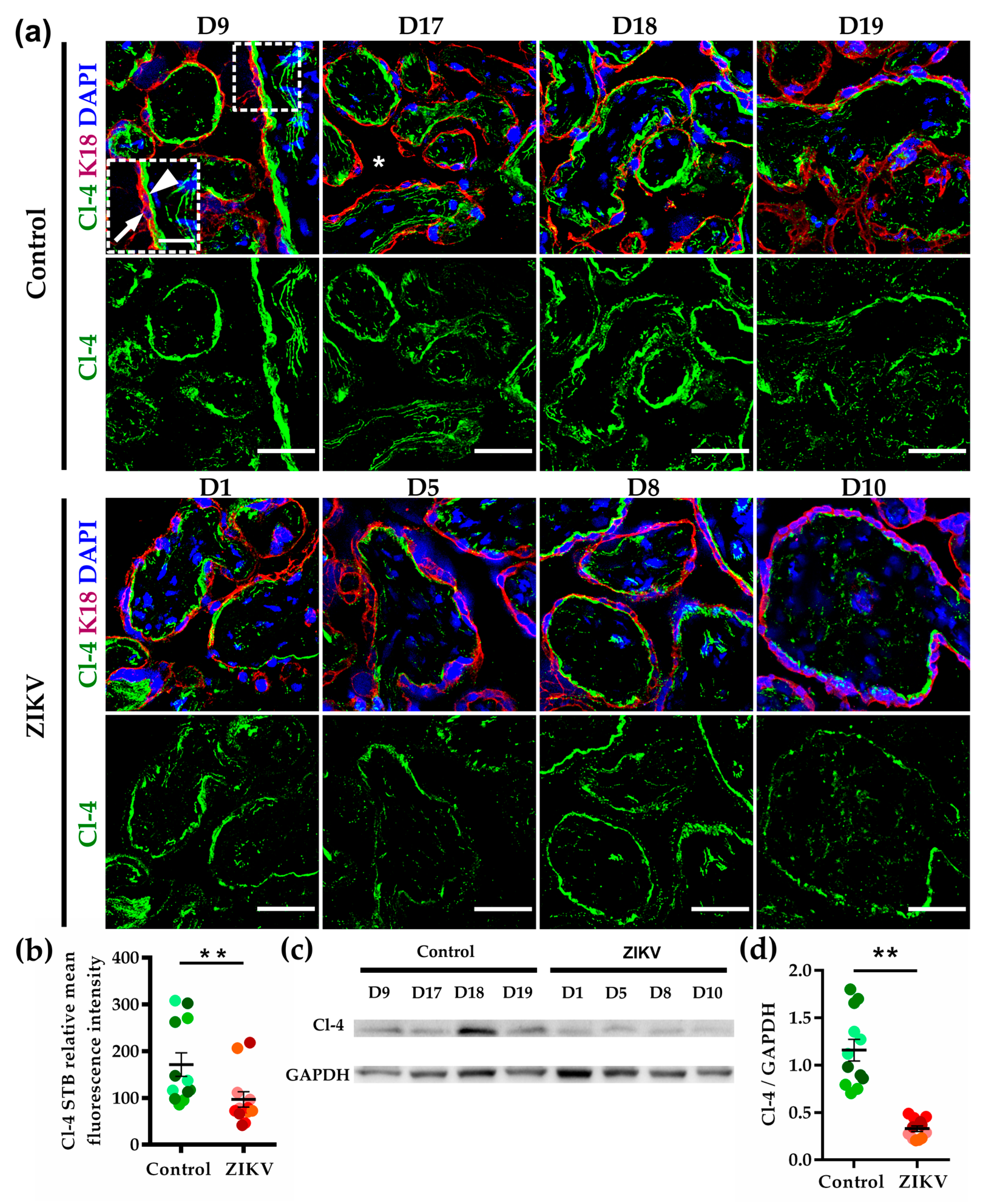
3.5. The Expression of Claudin-4 at the Basolateral Membrane of STB Diminished in ZIKV-Infected Placentae
3.6. Claudin-5 Strong Expression in the Vessels of Chorionic Villi and Faint Stain in STB Cells Did not Change with ZIKV Infection
3.7. Claudin-7 Expression at the Basal Surface of STB Cells was not Altered by ZIKV Infection
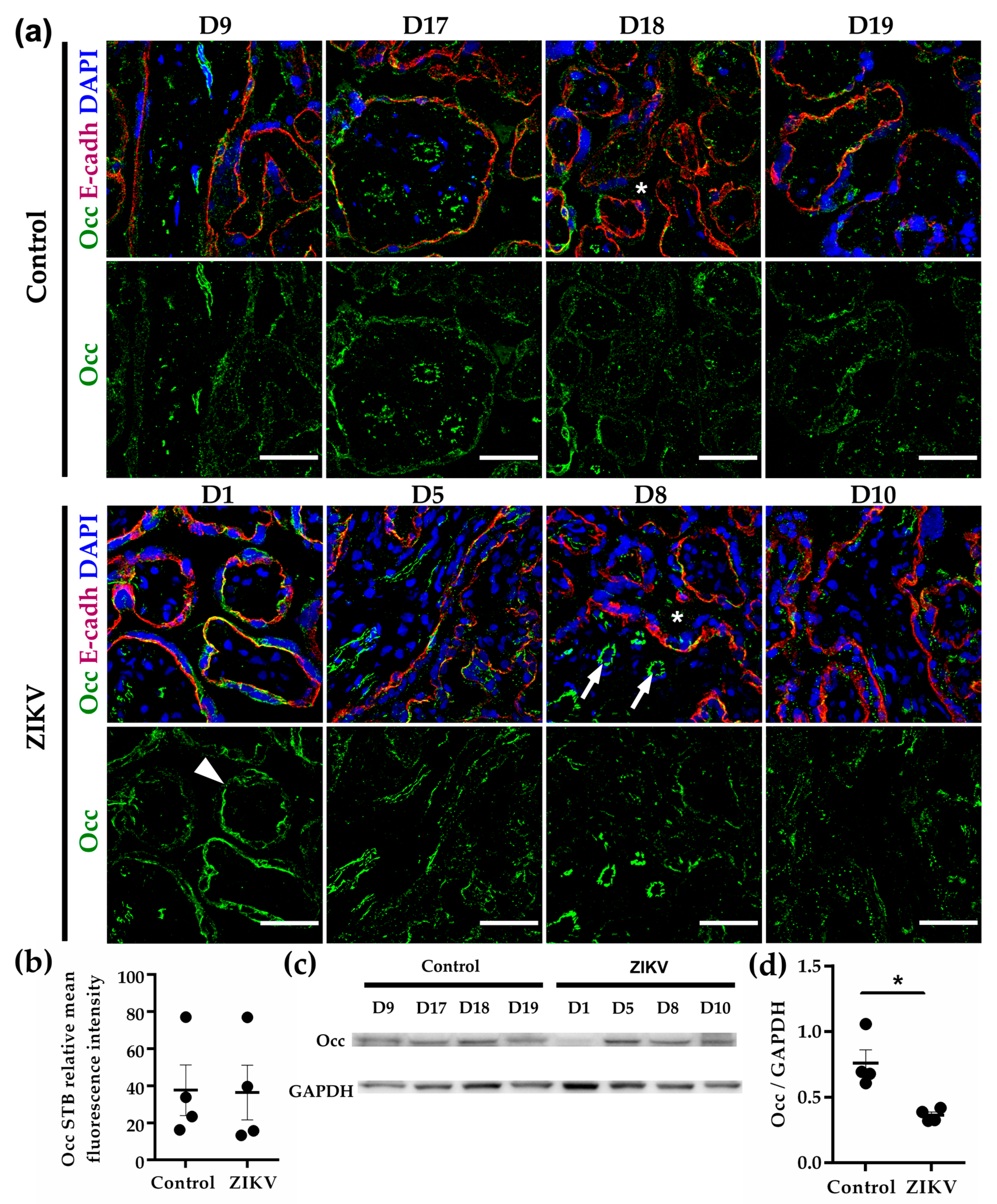
3.8. Occludin Expression in the STB was Low and not Affected by ZIKV Infection
3.9. The Expression of ZO-1 was Higher in Chorionic Vessels than in the STB and was not Affected by ZIKV Infection
3.10. In Chorionic Villi, the Expression of ZO-2 in the STB was Much Higher than in the Mesenchymal Vessels
3.11. ZIKV Infection Had no Impact on the Expression of JAMs -B and -C in the STB of Chorionic Villi
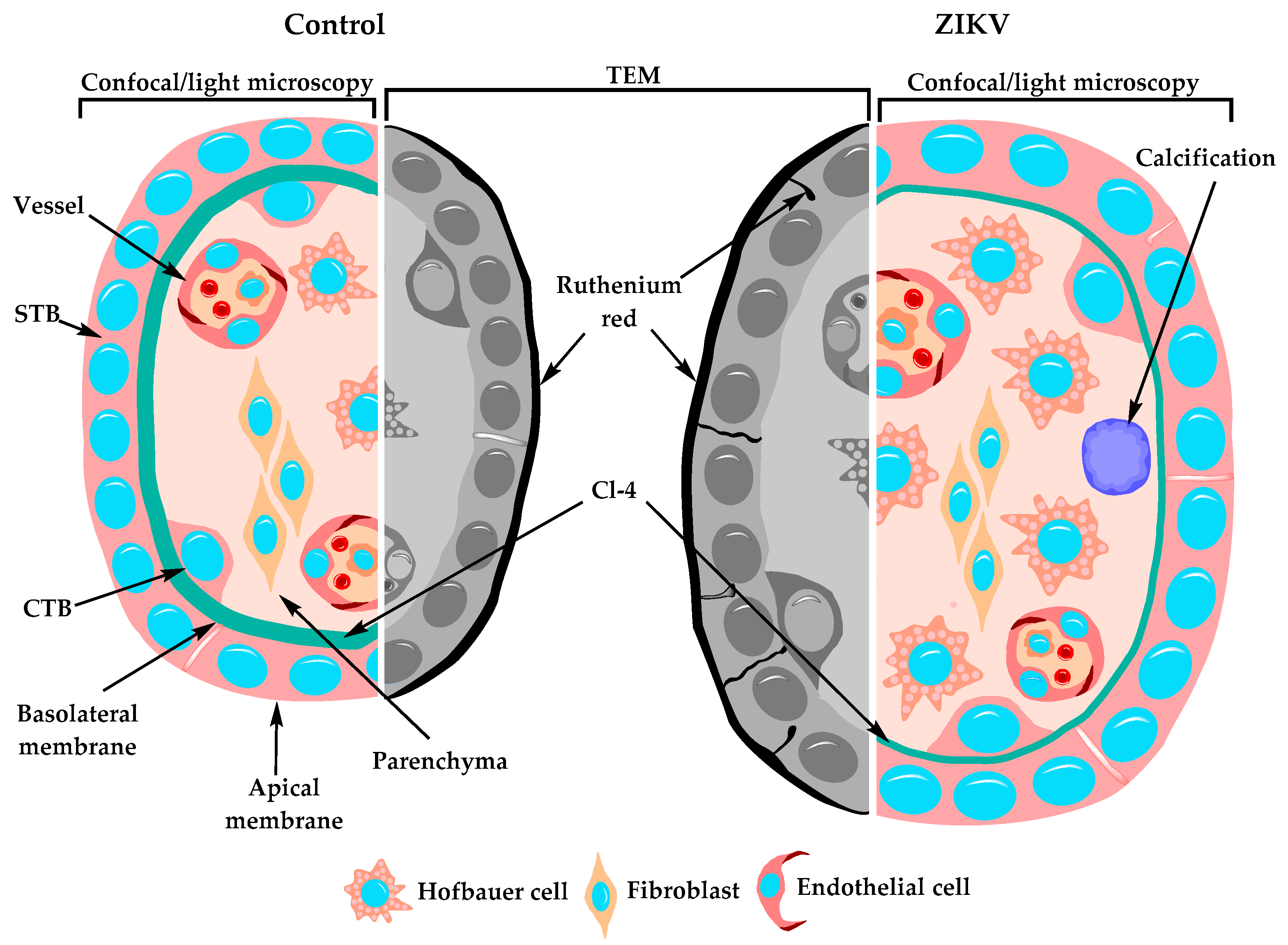
3.12. The STB Layer of Placentae of ZIKV-Infected Women is Permeable to Ruthenium Red
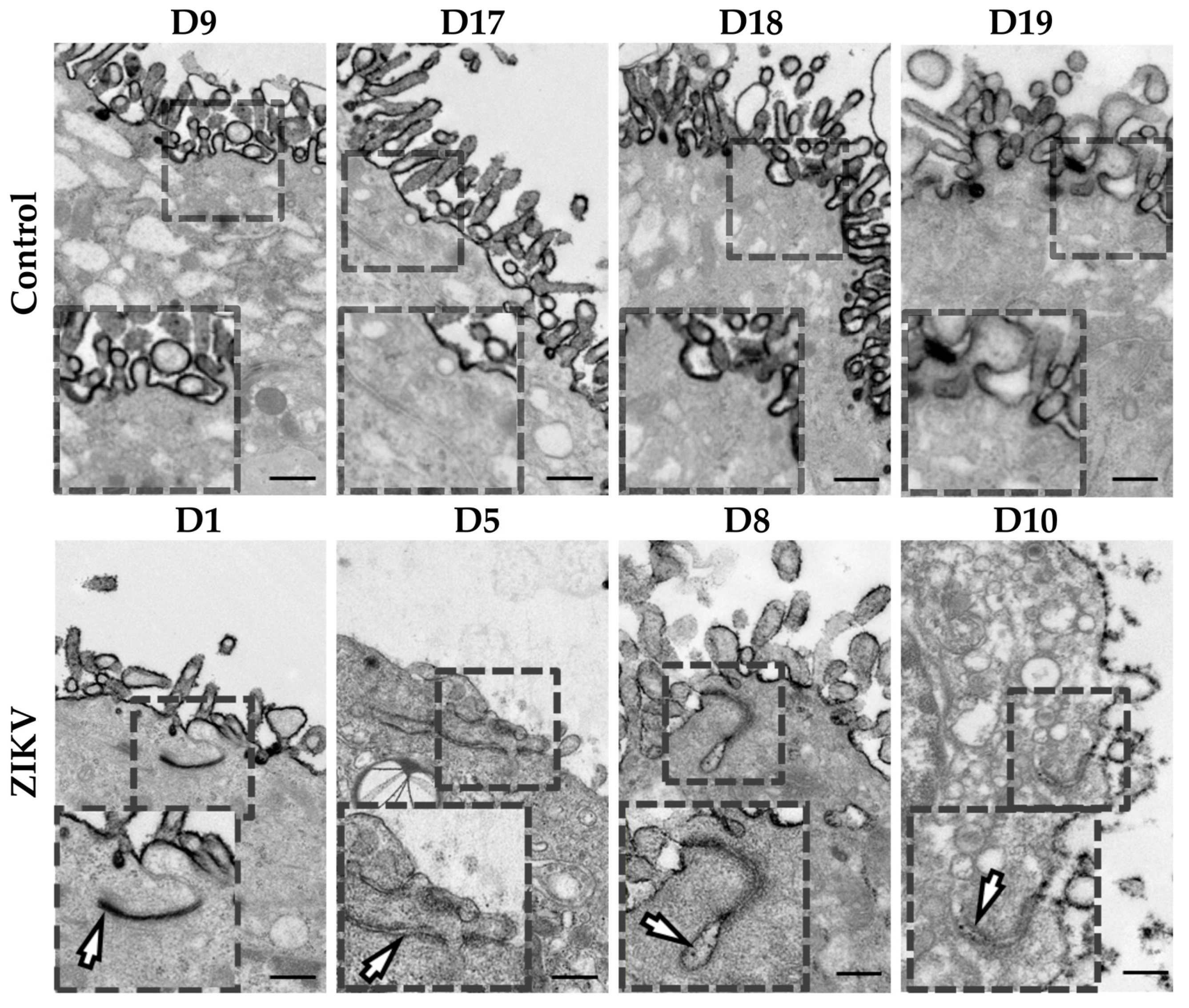
3.13. Hofbauer Cell Hyperplasia, an Increased Diameter of Microvilli and Intravillous Calcifications were Observed in ZIKV-Infected Placentae
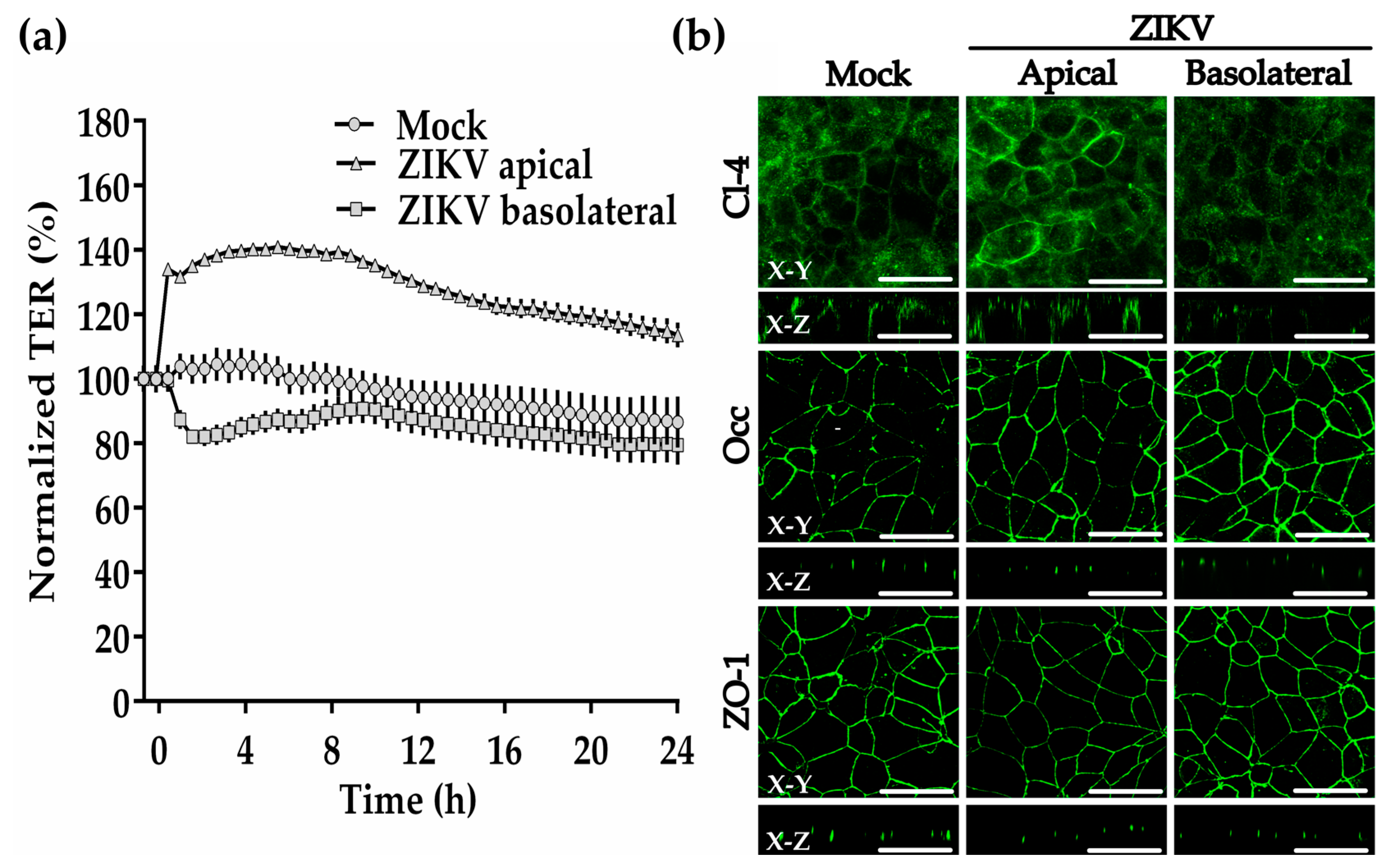
3.14. ZIKV Added to the Basolateral Surface of the Trophoblast-Derived Cell Line BeWo Reduces the Transepithelial Electrical Resistance and Claudin-4 Expression
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Robbins, J.R.; Skrzypczynska, K.M.; Zeldovich, V.B.; Kapidzic, M.; Bakardjiev, A.I. Placental syncytiotrophoblast constitutes a major barrier to vertical transmission of Listeria monocytogenes. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robbins, J.R.; Zeldovich, V.B.; Poukchanski, A.; Boothroyd, J.C.; Bakardjiev, A.I. Tissue barriers of the human placenta to infection with Toxoplasma gondii. Infect. Immun. 2012, 80, 418–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, L. Congenital Viral Infection: Traversing the Uterine-Placental Interface. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2018, 5, 273–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Zika Virus. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/zika-virus (accessed on 6 December 2018).
- Castellucci, M.; Kaufmann, P. Basic Structure of the Villous Trees. In Pathology of the Human Placenta; Benirschke, K., Kaufmann, P., Baergen, R.N., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 50–99. [Google Scholar]
- De Virgiliis, G.; Sideri, M.; Fumagalli, G.; Remotti, G. The junctional pattern of the human villous trophoblast. A freeze-fracture study. Gynecol. Obstet. Investig. 1982, 14, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Schneider, J. Cellular junctions on the free surface of human placental syncytium. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 1987, 240, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metz, J.; Weihe, E.; Heinrich, D. Intercellular junctions in the full term human placenta. Brain Struct. Funct. 1979, 158, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liévano, S.; Alarcón, L.; Chávez–Munguía, B.; González–Mariscal, L. Endothelia of term human placentae display diminished expression of tight junction proteins during preeclampsia. Cell Tissue Res. 2006, 324, 433–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzioni, D. Expression of ZO-1 and occludin in normal human placenta and in hydatidiform moles. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2001, 7, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirinen, E.; Soini, Y. A survey of zeb1, twist and claudin 1 and 4 expression during placental development and disease. APMIS 2014, 122, 530–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabata, T.; Petitt, M.; Puerta-Guardo, H.; Michlmayr, D.; Wang, C.; Fang-Hoover, J.; Harris, E.; Pereira, L. Zika Virus Targets Different Primary Human Placental Cells, Suggesting Two Routes for Vertical Transmission. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 20, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, G.J.; Casasnovas, J.M.; Umetsu, D.T.; DeKruyff, R.H. TIM genes: A family of cell surface phosphatidylserine receptors that regulate innate and adaptive immunity. Immunol. Rev. 2010, 235, 172–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabata, T.; Petitt, M.; Puerta-Guardo, H.; Michlmayr, D.; Harris, E.; Pereira, L. Zika Virus Replicates in Proliferating Cells in Explants From First-Trimester Human Placentas, Potential Sites for Dissemination of Infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 217, 1202–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Noronha, L.; Zanluca, C.; Azevedo, M.L.V.; Luz, K.G.; Dos Santos, C.N.D. Zika virus damages the human placental barrier and presents marked fetal neurotropism. Memórias do Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2016, 111, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirohi, D.; Kuhn, R.J. Zika Virus Structure, Maturation, and Receptors. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 216, S935–S944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priyamvada, L.; Quicke, K.M.; Hudson, W.H.; Onlamoon, N.; Sewatanon, J.; Edupuganti, S.; Pattanapanyasat, K.; Chokephaibulkit, K.; Mulligan, M.J.; Wilson, P.C.; et al. Human antibody responses after dengue virus infection are highly cross-reactive to Zika virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 7852–7857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, M.G.; Quicke, K.M.; O’Neal, J.T.; Arora, N.; Machiah, D.; Priyamvada, L.; Kauffman, R.C.; Register, E.; Adekunle, O.; Swieboda, D.; et al. Cross-Reactive Dengue Virus Antibodies Augment Zika Virus Infection of Human Placental Macrophages. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 24, 731–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halai, U.-A.; Nielsen-Saines, K.; Moreira, M.L.; De Sequeira, P.C.; Junior, J.P.P.; Zin, A.D.A.; Cherry, J.; Gabaglia, C.R.; Gaw, S.L.; Adachi, K.; et al. Maternal Zika Virus Disease Severity, Virus Load, Prior Dengue Antibodies, and Their Relationship to Birth Outcomes. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 65, 877–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, R.W.; Freimuth, P.; Moninger, T.O.; Ganske, I.; Zabner, J.; Welsh, M.J. Adenovirus Fiber Disrupts CAR-Mediated Intercellular Adhesion Allowing Virus Escape. Cell 2002, 110, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sufiawati, I.; Tugizov, S.M. HIV-Associated Disruption of Tight and Adherens Junctions of Oral Epithelial Cells Facilitates HSV-1 Infection and Spread. PLoS ONE 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiala, M.; Looney, D.J.; Stins, M.; Way, D.D.; Zhang, L.; Gan, X.; Chiappelli, F.; Schweitzer, E.S.; Shapshak, P.; Weinand, M.; et al. TNF-alpha opens a paracellular route for HIV-1 invasion across the blood-brain barrier. Mol. Med. 1997, 3, 553–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roe, K.; Kumar, M.; Lum, S.; Orillo, B.; Nerurkar, V.R.; Verma, S. West Nile virus-induced disruption of the blood-brain barrier in mice is characterized by the degradation of the junctional complex proteins and increase in multiple matrix metalloproteinases. J. Gen. Virol. 2012, 93, 1193–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velandia-Romero, M.L.; Calderón-Peláez, M.-A.; Castellanos, J.E. In Vitro Infection with Dengue Virus Induces Changes in the Structure and Function of the Mouse Brain Endothelium. PLoS ONE 2016, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Mariscal, L.; Garay, E.; Quirós, M. Identification of Claudins by Western Blot and Immunofluorescence in Different Cell Lines and Tissues. Adv. Struct. Saf. Stud. 2011, 762, 213–231. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelhalim, N.Y.; Shehata, M.H.; Gadallah, H.N.; Sayed, W.M.; Othman, A.A. Morphological and ultrastructural changes in the placenta of the diabetic pregnant Egyptian women. Acta Histochem. 2018, 120, 490–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega-Olvera, J.M.; Winkler, R.; Quintanilla-Vega, B.; Shibayama, M.; Chávez-Munguía, B.; Martín-Tapia, D.; Alarcón, L.; González-Mariscal, L.; Quitanilla-Vega, B. The organophosphate pesticide methamidophos opens the blood-testis barrier and covalently binds to ZO-2 in mice. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2018, 360, 257–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bancher-Todesca, D.; Hefler, L.; Zeisler, H.; Schatten, C.; Husslein, P.; Heinze, G.; Tempfer, C. Placental expression of cytokeratin 18 and serum levels of tissue polypeptide antigen in women with pregnancy-induced hypertension. Hypertens. Pregnancy 2001, 20, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nitta, T.; Hata, M.; Gotoh, S.; Seo, Y.; Sasaki, H.; Hashimoto, N.; Furuse, M.; Tsukita, S. Size-selective loosening of the blood-brain barrier in claudin-5–deficient mice. J. Cell Boil. 2003, 161, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Itallie, C.; Rahner, C.; Anderson, J.M. Regulated expression of claudin-4 decreases paracellular conductance through a selective decrease in sodium permeability. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 107, 1319–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, J.; Renigunta, A.; Yang, J.; Waldegger, S. Claudin-4 forms paracellular chloride channel in the kidney and requires claudin-8 for tight junction localization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 18010–18015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Itallie, C.M.; Fanning, A.S.; Anderson, J.M. Reversal of charge selectivity in cation or anion-selective epithelial lines by expression of different claudins. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2003, 285, F1078–F1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayer, A.; Lennemann, N.J.; Ouyang, Y.; Bramley, J.C.; Morosky, S.; Marques, E.T.D.A.; Cherry, S.; Sadovsky, Y.; Coyne, C.B. Type III Interferons Produced by Human Placental Trophoblasts Confer Protection against Zika Virus Infection. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 19, 705–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capaldo, C.T.; Farkas, A.E.; Hilgarth, R.S.; Krug, S.M.; Wolf, M.F.; Benedik, J.K.; Fromm, M.; Koval, M.; Parkos, C.; Nusrat, A. Proinflammatory cytokine-induced tight junction remodeling through dynamic self-assembly of claudins. Mol. Biol. Cell 2014, 25, 2710–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schumann, S.; Buck, V.U.; Classen-Linke, I.; Wennemuth, G.; Grümmer, R. Claudin-3, claudin-7, and claudin-10 show different distribution patterns during decidualization and trophoblast invasion in mouse and human. Histochem. Cell Boil. 2015, 144, 571–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, C.; Yang, H.; Lee, D.; An, B.-S.; Jeung, E.-B. Placental claudin expression and its regulation by endogenous sex steroid hormones. Steroids 2015, 100, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pidoux, G.; Gerbaud, P.; Gnidehou, S.; Grynberg, M.; Geneau, G.; Guibourdenche, J.; Carette, D.; Cronier, L.; Evain-Brion, D.; Malassine, A.; et al. ZO-1 is involved in trophoblastic cell differentiation in human placenta. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2010, 298, C1517–C1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leach, L.; Lammiman, M.; Babawale, M.; Hobson, S.; Bromilou, B.; Lovat, S.; Simmonds, M. Molecular Organization of Tight and Adherens Junctions in the Human Placental Vascular Tree. Placenta 2000, 21, 547–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsuno, T.; Umeda, K.; Matsui, T.; Hata, M.; Tamura, A.; Itoh, M.; Takeuchi, K.; Fujimori, T.; Nabeshima, Y.-I.; Noda, T.; et al. Deficiency of Zonula Occludens-1 Causes Embryonic Lethal Phenotype Associated with Defected Yolk Sac Angiogenesis and Apoptosis of Embryonic Cells. Mol. Boil. Cell 2008, 19, 2465–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Anuar, F.; Ali, S.M.; Ng, M.Y.; Phua, D.C.; Hunziker, W. Zona Occludens-2 Is Critical for Blood–Testis Barrier Integrity and Male Fertility. Mol. Boil. Cell 2009, 20, 4268–4277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuse, M.; Furuse, K.; Sasaki, H.; Tsukita, S. Conversion of Zonulae Occludentes from Tight to Leaky Strand Type by Introducing Claudin-2 into Madin-Darby Canine Kidney I Cells. J. Cell Boil. 2001, 153, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paria, B.C.; Zhao, X.; Das, S.K.; Dey, S.K.; Yoshinaga, K. Zonula Occludens-1 and E-cadherin Are Coordinately Expressed in the Mouse Uterus with the Initiation of Implantation and Decidualization. Dev. Boil. 1999, 208, 488–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Matsumoto, H.; Zhao, X.; Das, S.K.; Paria, B.C. Embryonic signals direct the formation of tight junctional permeability barrier in the decidualizing stroma during embryo implantation. J. Cell Sci. 2004, 117, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Peña, A.A.; Rivera-Baños, J.; Méndez-Carrillo, L.L.; Ramírez-Solano, M.I.; Galindo-Bustamante, A.; Páez-Franco, J.C.; Morimoto, S.; González-Mariscal, L.; Cruz, M.E.; Mendoza-Rodríguez, C.A.; et al. Perinatal administration of bisphenol A alters the expression of tight junction proteins in the uterus and reduces the implantation rate. Reprod. Toxicol. 2017, 69, 106–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, C.R.; Swift, J.G.; Mukherjee, T.M.; Rogers, A.W. Effects of ovarian hormones on cell membranes in the rat uterus. Cell Biophys. 1981, 3, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, C.R.; Swift, J.G.; Mukherjee, T.M.; Rogers, A.W. The structure of tight junctions between uterine luminal epithelial cells at different stages of pregnancy in the rat. Cell Tissue Res. 1982, 223, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carson, D.D.; Lagow, E.; Thathiah, A.; Al-Shami, R.; Farach-Carson, M.C.; Vernon, M.; Yuan, L.; Fritz, M.A.; Lessey, B. Changes in gene expression during the early to mid-luteal (receptive phase) transition in human endometrium detected by high-density microarray screening. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2002, 8, 871–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kao, L.C.; Tulac, S.; Lobo, S.; Imani, B.; Yang, J.P.; Germeyer, A.; Osteen, K.; Taylor, R.N.; Lessey, B.A.; Giudice, L.C. Global gene profiling in human endometrium during the window of implantation. Endocrinology 2002, 143, 2119–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riesewijk, A.; Martin, J.; van Os, R.; Horcajadas, J.A.; Polman, J.; Pellicer, A.; Mosselman, S.; Simon, C. Gene expression profiling of human endometrial receptivity on days LH+2 versus LH+7 by microarray technology. Mol. Human Reprod. 2003, 9, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, N.; Zhao, H.; Cui, Y.; Liu, J. Expression of tight junction factors in human placental tissues derived from assisted reproductive technology and natural pregnancy. Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi 2014, 49, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Mariscal, L. Virus interaction with the apical junctional complex. Front. Biosci. 2009, 14, 731–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Evans, M.J.; Von Hahn, T.; Tscherne, D.M.; Syder, A.J.; Panis, M.; Wölk, B.; Hatziioannou, T.; McKeating, J.A.; Bieniasz, P.D.; Rice, C.M. Claudin-1 is a hepatitis C virus co-receptor required for a late step in entry. Nature 2007, 446, 801–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, A.; Yuan, F.; Li, Y.; Zhu, F.; Hou, P.; Li, J.; Song, X.; Ding, M.; Deng, H. Claudin-6 and Claudin-9 Function as Additional Coreceptors for Hepatitis C Virus. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 12465–12471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Waeckerlin, R.; Urbanowski, M.D.; Van Marle, G.; Hobman, T.C. West Nile Virus Infection Causes Endocytosis of a Specific Subset of Tight Junction Membrane Proteins. PLoS ONE 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nava, P.; López, S.; Arias, C.F.; Islas, S.; Gonzalez-Mariscal, L. The rotavirus surface protein VP8 modulates the gate and fence function of tight junctions in epithelial cells. J. Cell Sci. 2004, 117, 5509–5519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, A.; Kondoh, M.; Masuyama, A.; Fujii, M.; Mizuguchi, H.; Horiguchi, Y.; Watanabe, Y. Role of C-terminal regions of the C-terminal fragment of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin in its interaction with claudin-4. J. Control. Release 2005, 108, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonoda, N.; Furuse, M.; Sasaki, H.; Yonemura, S.; Katahira, J.; Horiguchi, Y.; Tsukita, S. Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin fragment removes specific claudins from tight junction strands: Evidence for direct involvement of claudins in tight junction barrier. J. Cell Biol. 1999, 147, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schelhaas, M.; Jansen, M.; Haase, I.; Knebel-Mörsdorf, D. Herpes simplex virus type 1 exhibits a tropism for basal entry in polarized epithelial cells. J. Gen. Virol. 2003, 84, 2473–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marozin, S.; Prank, U.; Sodeik, B. Herpes simplex virus type 1 infection of polarized epithelial cells requires microtubules and access to receptors present at cell-cell contact sites. J. Gen. Virol. 2004, 85, 775–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mee, C.J.; Grove, J.; Harris, H.J.; Hu, K.; Balfe, P.; McKeating, J.A. Effect of cell polarization on hepatitis C virus entry. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baktash, Y.; Madhav, A.; Coller, K.E.; Randall, G. Single Particle Imaging of Polarized Hepatoma Organoids upon Hepatitis C Virus Infection Reveals an Ordered and Sequential Entry Process. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 23, 382–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberg, A.Z.; Yu, W.; Hill, D.A.; Reyes, C.A.; Schwartz, D.A. Placental Pathology of Zika Virus: Viral Infection of the Placenta Induces Villous Stromal Macrophage (Hofbauer Cell) Proliferation and Hyperplasia. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2017, 141, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Noronha, L.; Zanluca, C.; Burger, M.; Suzukawa, A.A.; Azevedo, M.; Rebutini, P.Z.; Novadzki, I.M.; Tanabe, L.S.; Presibella, M.M.; Dos Santos, C.N.D. Zika Virus Infection at Different Pregnancy Stages: Anatomopathological Findings, Target Cells and Viral Persistence in Placental Tissues. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martines, R.B.; Bhatnagar, J.; Keating, M.K.; Silva-Flannery, L.; Muehlenbachs, A.; Gary, J.; Goldsmith, C.; Hale, G.; Ritter, J.; Rollin, D.; et al. Notes from the Field: Evidence of Zika Virus Infection in Brain and Placental Tissues from Two Congenitally Infected Newborns and Two Fetal Losses--Brazil, 2015. MMWR. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2016, 65, 159–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes, L.; Wolfe, B.; Golos, T. Hofbauer Cells: Placental Macrophages of Fetal Origin. In Macrophages: Origin, Functions and Biointervention; Kloc, M., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Houston, TX, USA, 2017; pp. 45–60. [Google Scholar]
- Benirschke, K.; Kaufmann, P.; Baergen, R. Classification of Villous Maldevelopment. In Pathology of the Human Placenta, 5th ed.; Benirschke, K., Kaufmann, P., Baergen, R., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 491–518. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.; Zhang, S.; Nakano, H.; Simmons, D.G.; Wang, S.; Kong, S.; Wang, Q.; Shen, L.; Tu, Z.; Wang, W.; et al. A positive feedback loop involving Gcm1 and Fzd5 directs chorionic branching morphogenesis in the placenta. PLoS Boil. 2013, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Mother | |||||
| Donor | Age (years) | Birth (GW) | Zika Symptoms Onset (GW) | Rash | Pregnancy Complications |
| D1 | 31 | 36.6 | 11.5 | Yes | Preeclampsia |
| D5 | 35 | 35.1 | 7.6 | Yes | Preeclampsia |
| D8 | 30 | 36.0 | 13.0 | Yes | None |
| D10 | 29 | 36.0 | 15.0 | Yes | None |
| Newborn | |||||
| Sex | Weight (kg) | Height (cm) | Apgar | HC (cm) | Outcome |
| F | 2.84 | 47 | 8/9 | 33.0 | Right pulmonary cystic adenomatoid malformation |
| F | 2.92 | 47 | 6/9 | 36.0 | Ventriculomegaly, macrocephaly, hydrocephaly, and hip dysplasia |
| F | 3.00 | 48 | 8/9 | 33.8 | 22q11 deletion syndrome with mielomeningocele, hypotonia and right aortic arch |
| F | 3.03 | 50 | 8/9 | 34.0 | Brachycephaly, low-set ears, short neck, and widely-spaced nipples |
| Mother | |||||||||
| Donor | Age (years) | Birth (GW) | Pregnancy complications | ||||||
| D9 | 32 | 38.0 | Preeclampsia | ||||||
| D17 | 30 | 38.8 | Preeclampsia | ||||||
| D18 | 23 | 40.0 | None | ||||||
| D19 | 34 | 36.0 | None | ||||||
| Newborn | |||||||||
| Sex | Weight (kg) | Height (cm) | Apgar | HC (cm) | Outcome | ||||
| M | 2.20 | 50 | 8/9 | 35.0 | Healthy | ||||
| F | 2.90 | 49 | 8/9 | 34.0 | Healthy | ||||
| M | 3.20 | 51 | 8/9 | 36.0 | Healthy | ||||
| F | 2.97 | 50 | 9/9 | 35.0 | Healthy | ||||
| Protein | STB Distribution | Abundance in Chorionic Vessels | ZIKV-infected vs. Control Placentae |
|---|---|---|---|
| E-cadh | basal | − | = |
| Cl-1 | apical/basal | +++ | = |
| Cl-2 | nd | − | |
| Cl-3 | apical/basal | +++ | = |
| Cl-4 | basal | +++ | ↓ |
| Cl-5 | apical/basal | +++ | = |
| Cl-7 | basal | ± | = |
| Cl-10 | nd | − | |
| JAM-A | nd | − | |
| JAM-B | apical/basal | − | = |
| JAM-C | bd | +++ | = |
| Occ | apical/basal | +++ | = |
| ZO-1 | apical/basal | +++ | = |
| ZO-2 | apical/basal | ± | = |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miranda, J.; Martín-Tapia, D.; Valdespino-Vázquez, Y.; Alarcón, L.; Espejel-Nuñez, A.; Guzmán-Huerta, M.; Muñoz-Medina, J.E.; Shibayama, M.; Chávez-Munguía, B.; Estrada-Gutiérrez, G.; et al. Syncytiotrophoblast of Placentae from Women with Zika Virus Infection Has Altered Tight Junction Protein Expression and Increased Paracellular Permeability. Cells 2019, 8, 1174. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8101174
Miranda J, Martín-Tapia D, Valdespino-Vázquez Y, Alarcón L, Espejel-Nuñez A, Guzmán-Huerta M, Muñoz-Medina JE, Shibayama M, Chávez-Munguía B, Estrada-Gutiérrez G, et al. Syncytiotrophoblast of Placentae from Women with Zika Virus Infection Has Altered Tight Junction Protein Expression and Increased Paracellular Permeability. Cells. 2019; 8(10):1174. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8101174
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiranda, Jael, Dolores Martín-Tapia, Yolotzin Valdespino-Vázquez, Lourdes Alarcón, Aurora Espejel-Nuñez, Mario Guzmán-Huerta, José Esteban Muñoz-Medina, Mineko Shibayama, Bibiana Chávez-Munguía, Guadalupe Estrada-Gutiérrez, and et al. 2019. "Syncytiotrophoblast of Placentae from Women with Zika Virus Infection Has Altered Tight Junction Protein Expression and Increased Paracellular Permeability" Cells 8, no. 10: 1174. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8101174
APA StyleMiranda, J., Martín-Tapia, D., Valdespino-Vázquez, Y., Alarcón, L., Espejel-Nuñez, A., Guzmán-Huerta, M., Muñoz-Medina, J. E., Shibayama, M., Chávez-Munguía, B., Estrada-Gutiérrez, G., Lievano, S., Ludert, J. E., & González-Mariscal, L. (2019). Syncytiotrophoblast of Placentae from Women with Zika Virus Infection Has Altered Tight Junction Protein Expression and Increased Paracellular Permeability. Cells, 8(10), 1174. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8101174







