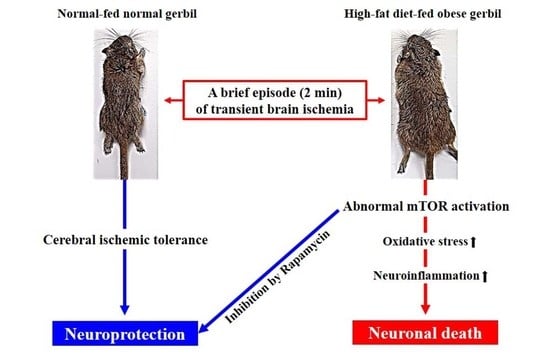
A 2-Min Transient Ischemia Confers Cerebral Ischemic Tolerance in Non-Obese Gerbils, but Results in Neuronal Death in Obese Gerbils by Increasing Abnormal mTOR Activation-Mediated Oxidative Stress and Neuroinflammation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
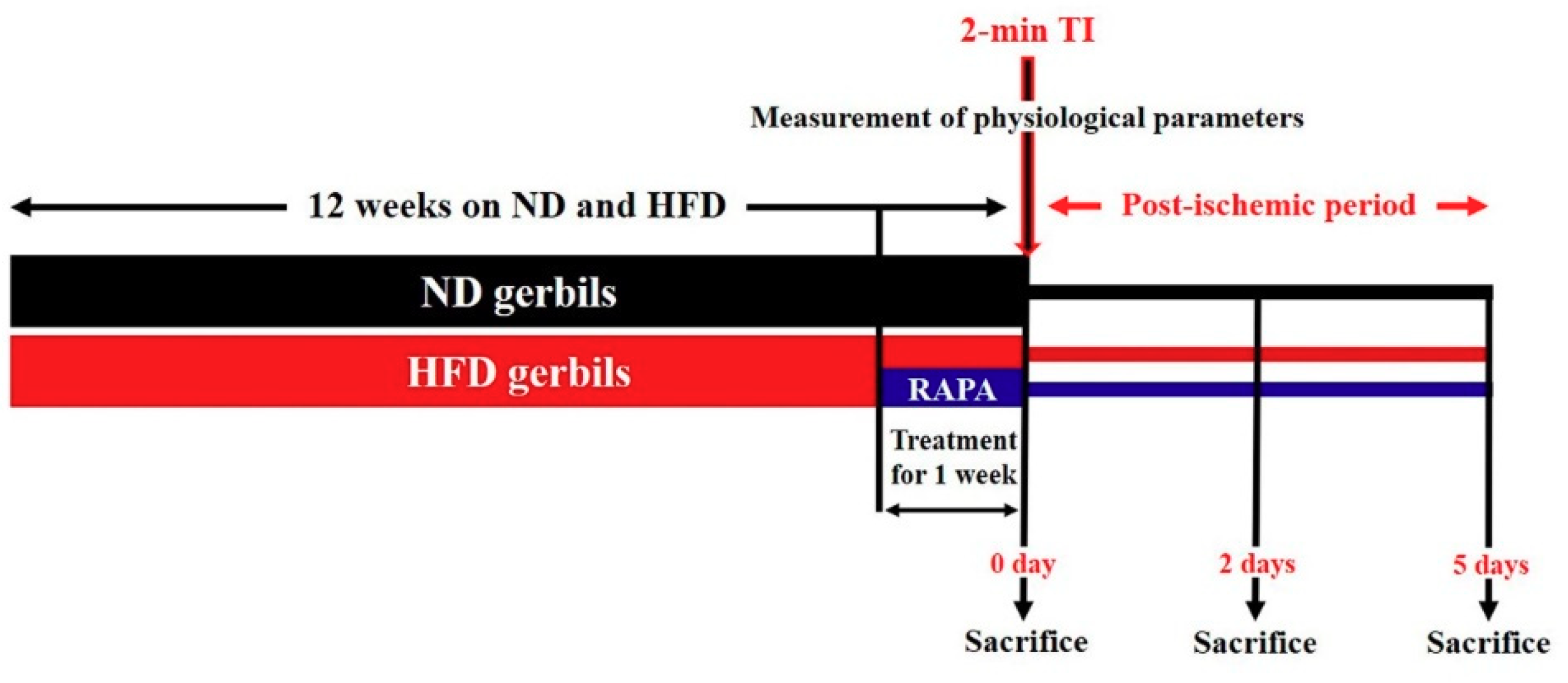
2.1. Experimental Animals and Diets
2.2. Treatment with RAPA
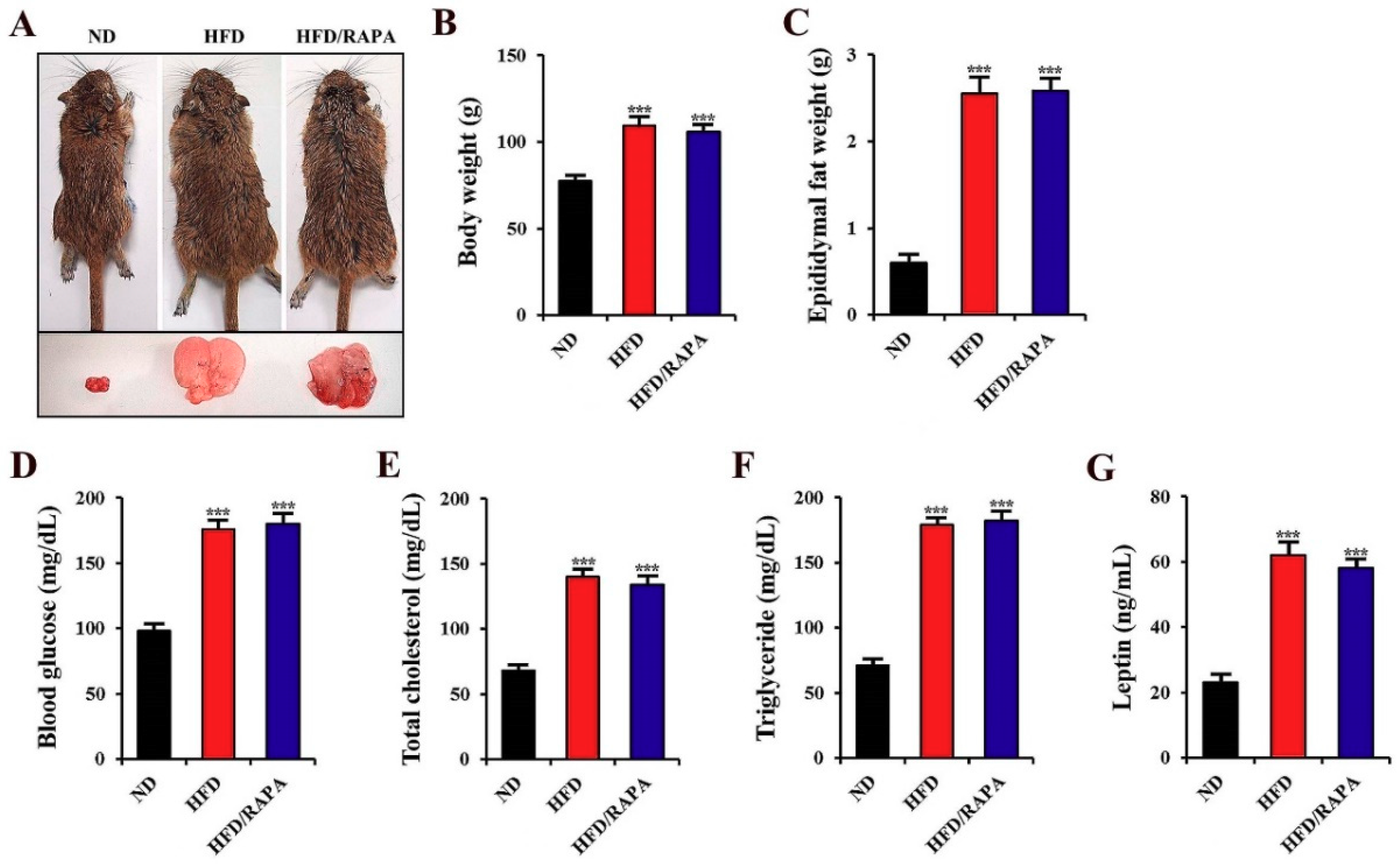
2.3. Analyses of Glucose Levels, and Lipid and Leptin Profiles
2.4. Induction of 2-min TI
2.5. Tissue Section for Histology
2.6. Cresyl Violet Staining
2.7. NeuN Immunofluorescence and F-J B Histofluorescence Staining
2.8. Immunohistochemistry
2.9. Dihydroethidium Fluorescence Staining
2.10. Western Blot Analysis
2.11. Data Analyses
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Changes in Physiological Parameters
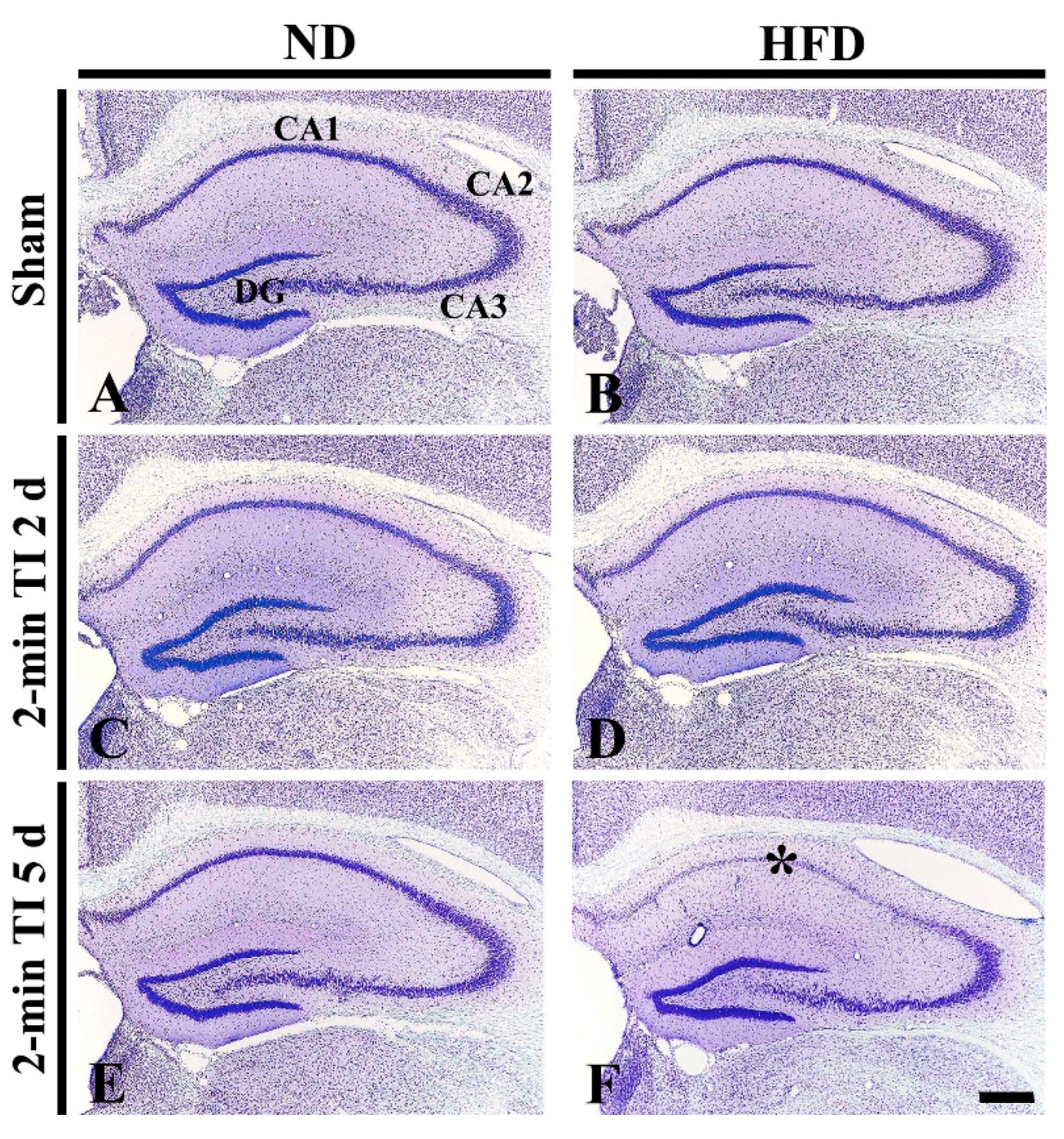
3.2. Neuronal Death by 2 Min of TI in HFD-Fed, Obese Gerbils
CV+ Cells
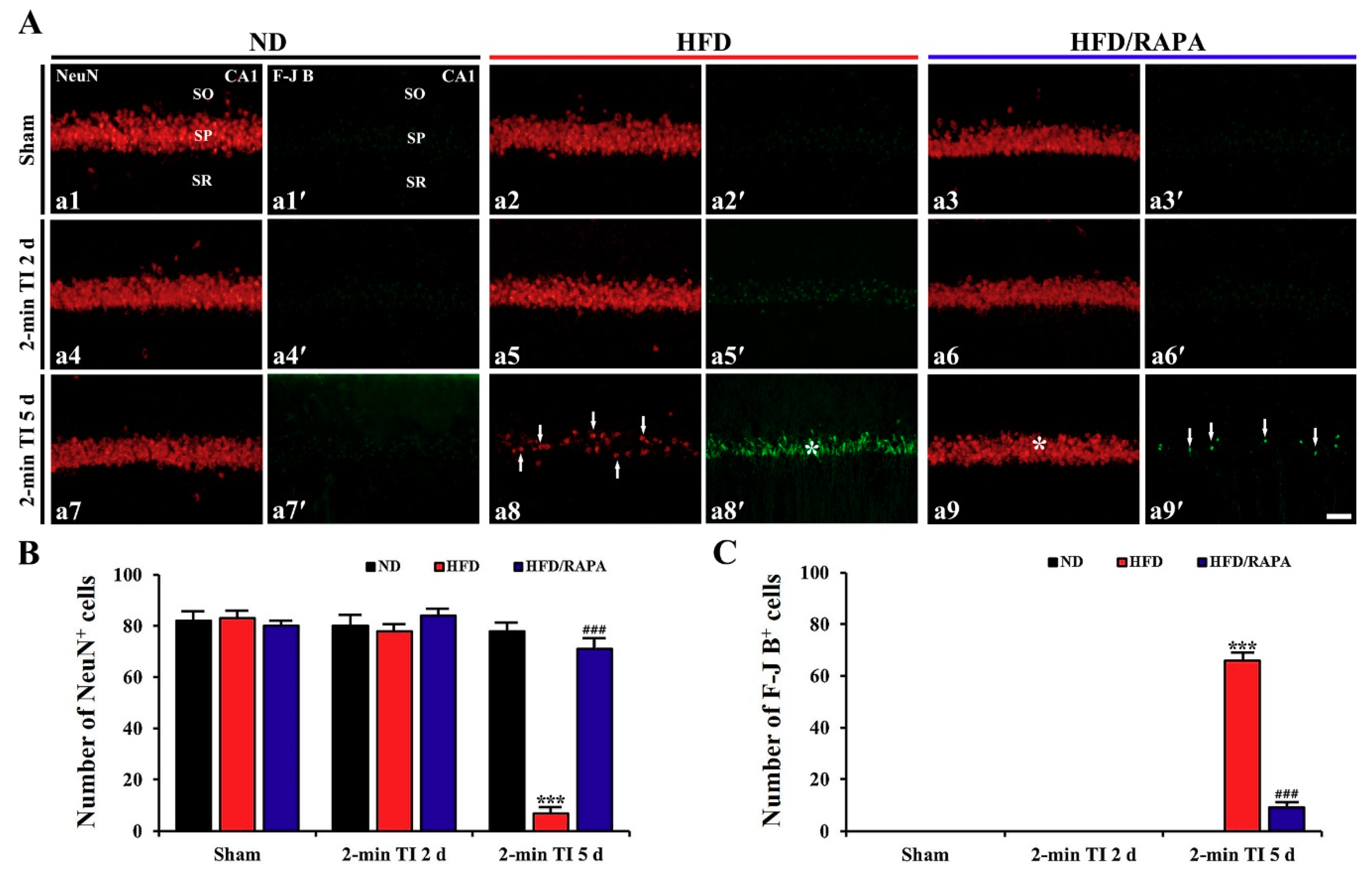
3.3. Neuroprotection by RAPA in HFD-Fed, Obese Gerbils
NeuN+ and F-J B+ Cells
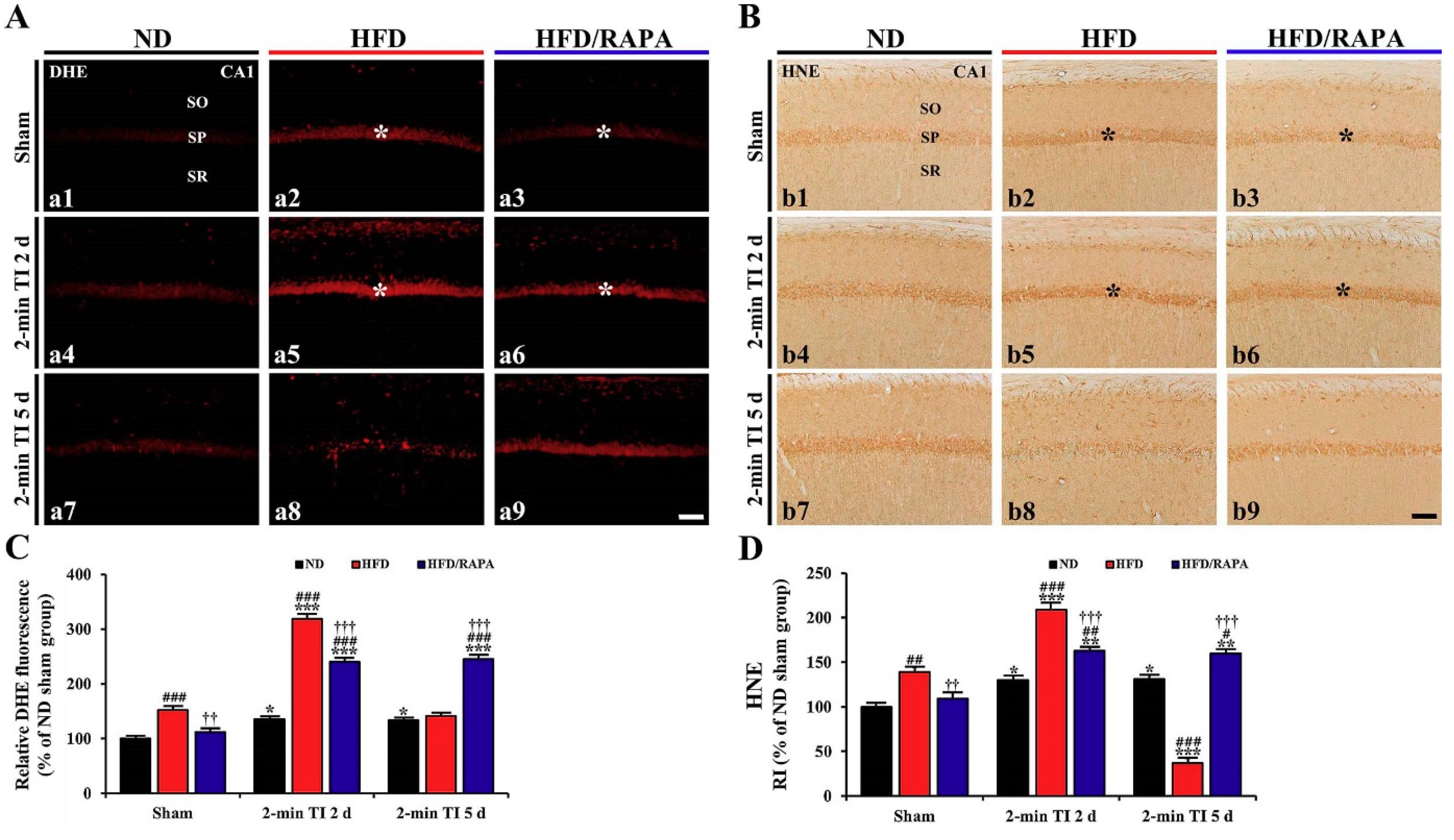
3.4. Attenuation of Oxidative Stress by RAPA in HFD-fed Group
3.4.1. DHE Fluorescence
3.4.2. HNE Immunoreactivity
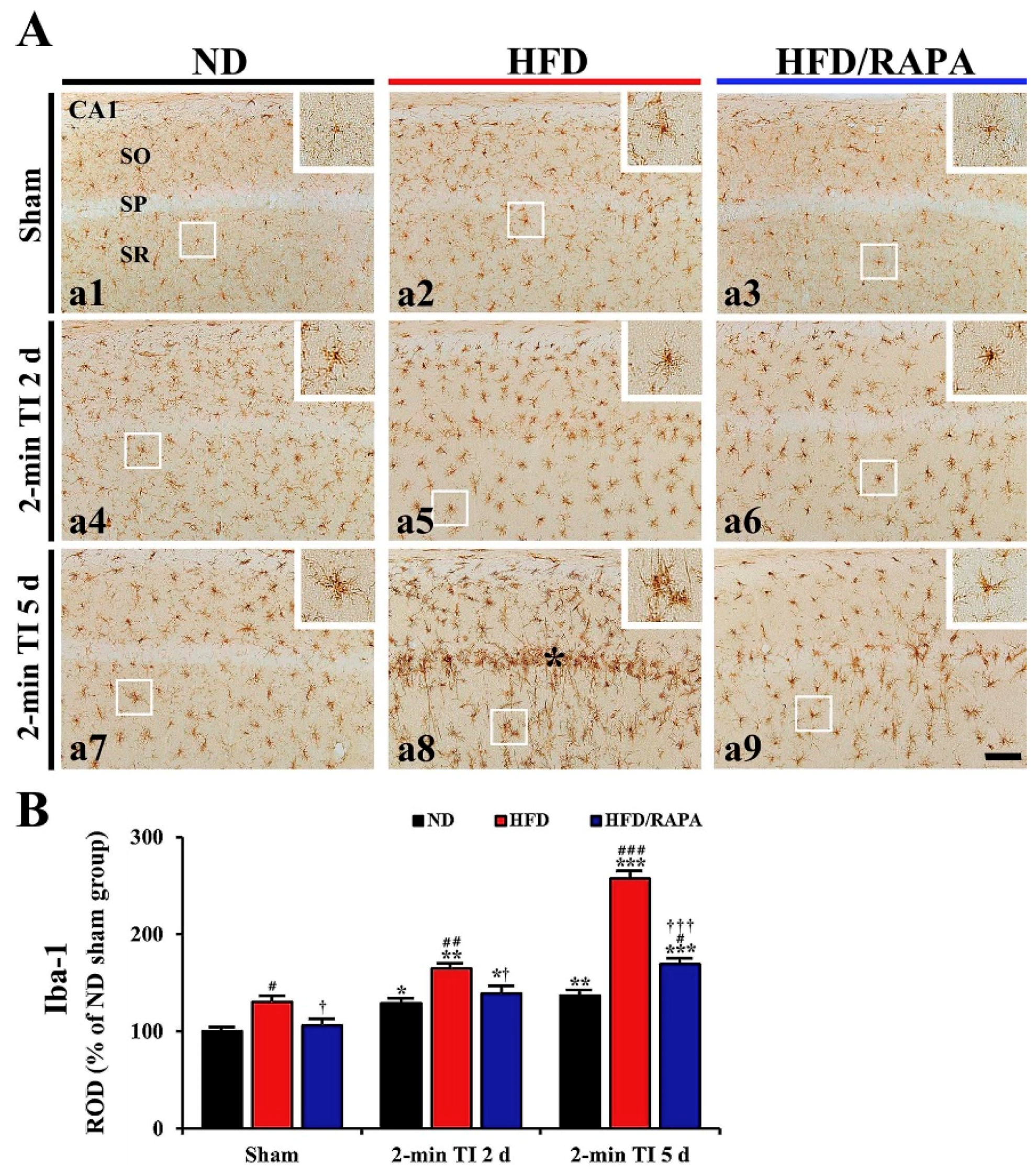
3.5. Reduction of Neuroinflammation by RAPA in HFD-fed Group
3.5.1. Iba-1+ Microglia
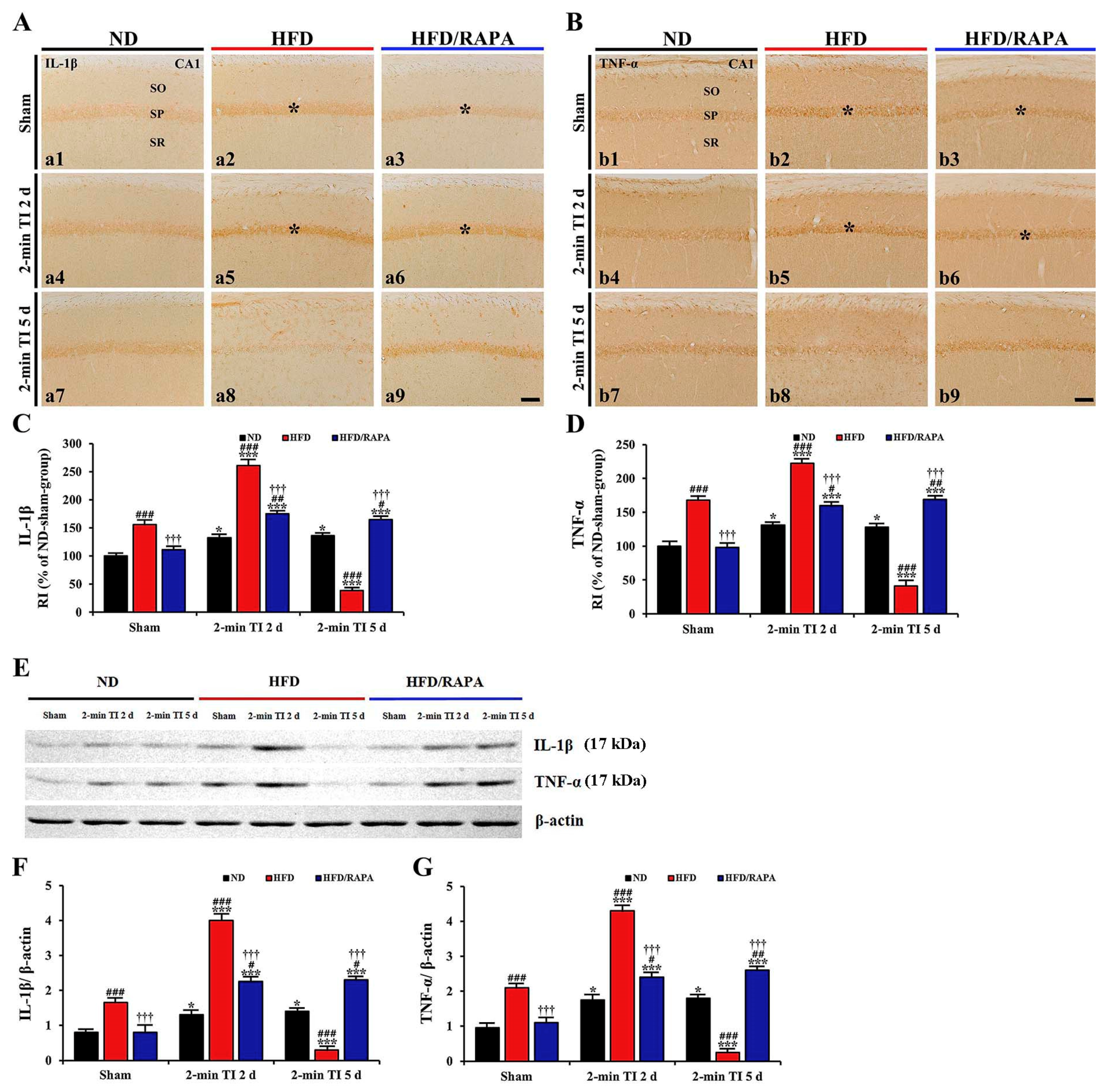
3.5.2. IL-1β and TNF-α Immunoreactivity
3.5.3. IL-1β and TNF-α Protein Levels
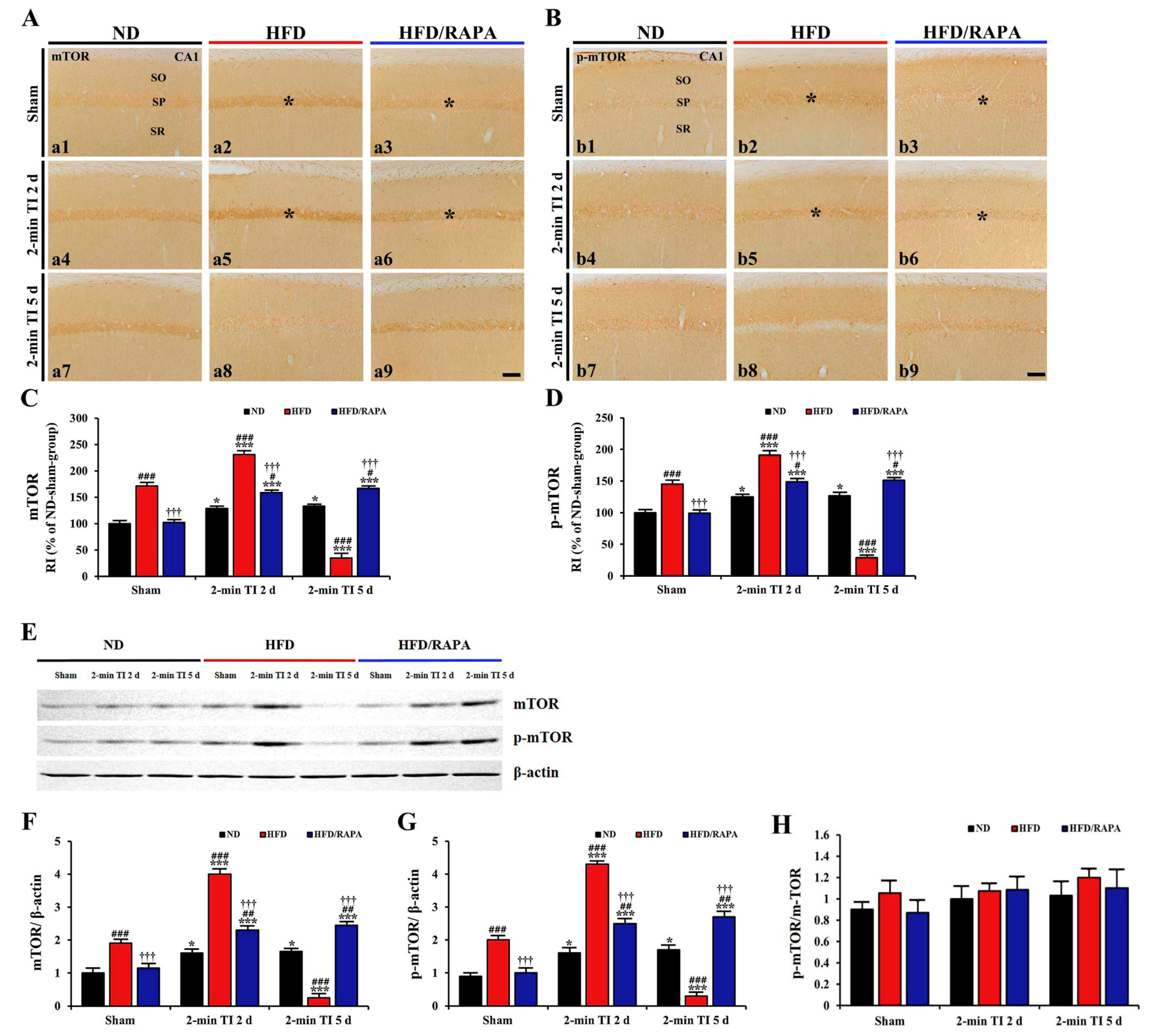
3.6. Inhibition of Abnormal mTOR Activation by RAPA in HFD-fed Group
3.6.1. mTOR and p-mTOR Immunoreactivity
3.6.2. mTOR and p-mTOR Protein Levels
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Globus, M.Y.; Busto, R.; Martinez, E.; Valdes, I.; Dietrich, W.D.; Ginsberg, M.D. Comparative effect of transient global ischemia on extracellular levels of glutamate, glycine, and gamma-aminobutyric acid in vulnerable and nonvulnerable brain regions in the rat. J. Neurochem. 1991, 57, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.S.; Polsky, K.; Nadler, J.V.; Crain, B.J. Selective neocortical and thalamic cell death in the gerbil after transient ischemia. Neuroscience 1990, 35, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.C.; Park, J.H.; Ahn, J.H.; Kim, I.H.; Cho, J.H.; Choi, J.H.; Yoo, K.Y.; Lee, C.H.; Hwang, I.K.; Cho, J.H.; et al. New GABAergic Neurogenesis in the Hippocampal CA1 Region of a Gerbil Model of Long-Term Survival after Transient Cerebral Ischemic Injury. Brain Pathol. 2016, 26, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nitatori, T.; Sato, N.; Waguri, S.; Karasawa, Y.; Araki, H.; Shibanai, K.; Kominami, E.; Uchiyama, Y. Delayed neuronal death in the CA1 pyramidal cell layer of the gerbil hippocampus following transient ischemia is apoptosis. J. Neurosci. 1995, 15, 1001–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakhan, S.E.; Kirchgessner, A.; Hofer, M. Inflammatory mechanisms in ischemic stroke: Therapeutic approaches. J. Transl. Med. 2009, 7, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.C.; Park, J.H.; Kim, I.H.; Cho, G.S.; Ahn, J.H.; Tae, H.J.; Choi, S.Y.; Cho, J.H.; Kim, D.W.; Kwon, Y.G.; et al. Neuroprotection of ischemic preconditioning is mediated by thioredoxin 2 in the hippocampal CA1 region following a subsequent transient cerebral ischemia. Brain Pathol. 2017, 27, 276–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.P.; Shi, Y.W.; Tang, M.; Zhang, X.C.; Gu, Y.; Liang, X.M.; Wang, Z.W.; Ding, F. Isoquercetin Ameliorates Cerebral Impairment in Focal Ischemia Through Anti-Oxidative, Anti-Inflammatory, and Anti-Apoptotic Effects in Primary Culture of Rat Hippocampal Neurons and Hippocampal CA1 Region of Rats. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 2126–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dirnagl, U.; Becker, K.; Meisel, A. Preconditioning and tolerance against cerebral ischaemia: From experimental strategies to clinical use. Lancet Neurol. 2009, 8, 398–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegener, S.; Gottschalk, B.; Jovanovic, V.; Knab, R.; Fiebach, J.B.; Schellinger, P.D.; Kucinski, T.; Jungehulsing, G.J.; Brunecker, P.; Muller, B.; et al. Transient ischemic attacks before ischemic stroke: Preconditioning the human brain? A multicenter magnetic resonance imaging study. Stroke 2004, 35, 616–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.S.; Cho, K.O.; Kim, E.J.; Sung, K.W.; Kim, S.Y. Ischemic preconditioning in the rat hippocampus increases antioxidant activities but does not affect the level of hydroxyl radicals during subsequent severe ischemia. Exp. Mol. Med. 2007, 39, 556–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, T.; Hata, R.; Kondo, T.; Takenaka, S. Proteomic analysis of the hippocampus in naive and ischemic-preconditioned rat. J. Neurol. Sci. 2015, 358, 158–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, C.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, X.; Huang, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Tong, X.; Wang, J.; Wu, J. Ischemic Preconditioning Mediates Neuroprotection against Ischemia in Mouse Hippocampal CA1 Neurons by Inducing Autophagy. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duszczyk, M.; Ziembowicz, A.; Gadamski, R.; Wieronska, J.M.; Smialowska, M.; Lazarewicz, J.W. Changes in the NPY immunoreactivity in gerbil hippocampus after hypoxic and ischemic preconditioning. Neuropeptides 2009, 43, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.C.; Tae, H.J.; Kim, I.H.; Cho, J.H.; Lee, T.K.; Park, J.H.; Ahn, J.H.; Choi, S.Y.; Bai, H.C.; Shin, B.N.; et al. Roles of HIF-1alpha, VEGF, and NF-kappaB in Ischemic Preconditioning-Mediated Neuroprotection of Hippocampal CA1 Pyramidal Neurons Against a Subsequent Transient Cerebral Ischemia. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 6984–6998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, C.L.; Bayraktutan, U. Risk factors for ischaemic stroke. Int. J. Stroke 2008, 3, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, M.; Fleming, T.; Robinson, M.; Thomson, B.; Graetz, N.; Margono, C.; Mullany, E.C.; Biryukov, S.; Abbafati, C.; Abera, S.F.; et al. Global, regional, and national prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adults during 1980–2013: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 2014, 384, 766–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bas, D.F.; Ozdemir, A.O. The effect of metabolic syndrome and obesity on outcomes of acute ischemic stroke patients treated with systemic thrombolysis. J. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 383, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langdon, K.D.; Clarke, J.; Corbett, D. Long-term exposure to high fat diet is bad for your brain: Exacerbation of focal ischemic brain injury. Neuroscience 2011, 182, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Prakash, R.; Chawla, D.; Du, W.; Didion, S.P.; Filosa, J.A.; Zhang, Q.; Brann, D.W.; Lima, V.V.; Tostes, R.C.; et al. Early effects of high-fat diet on neurovascular function and focal ischemic brain injury. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2013, 304, R1001–R1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Tolhurst, A.T.; Cho, S. Deregulation of inflammatory response in the diabetic condition is associated with increased ischemic brain injury. J. Neuroinflamm. 2014, 11, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maysami, S.; Haley, M.J.; Gorenkova, N.; Krishnan, S.; McColl, B.W.; Lawrence, C.B. Prolonged diet-induced obesity in mice modifies the inflammatory response and leads to worse outcome after stroke. J. Neuroinflamm. 2015, 12, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Kim, D.S.; Kang, S.; Kwon, D.Y. Ischemic hippocampal cell death induces glucose dysregulation by attenuating glucose-stimulated insulin secretion which is exacerbated by a high fat diet. Life Sci. 2011, 88, 766–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wullschleger, S.; Loewith, R.; Hall, M.N. TOR signaling in growth and metabolism. Cell 2006, 124, 471–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.C.; Gao, X.X.; Chen, L.; You, X.Q. Rapamycin suppresses Abeta25-35-or LPS-induced neuronal inflammation via modulation of NF-kappaB signaling. Neuroscience 2017, 355, 188–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Yang, J.; Yang, L. Insights for Oxidative Stress and mTOR Signaling in Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury under Diabetes. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 6437467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catania, C.; Binder, E.; Cota, D. mTORC1 signaling in energy balance and metabolic disease. Int. J. Obes. (Lond.) 2011, 35, 751–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, M. Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathways in neurological diseases. Biomed. J. 2013, 36, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginsberg, M.D.; Busto, R. Rodent models of cerebral ischemia. Stroke 1989, 20, 1627–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hei, C.; Liu, P.; Yang, X.; Niu, J.; Li, P.A. Inhibition of mTOR signaling Confers Protection against Cerebral Ischemic Injury in Acute Hyperglycemic Rats. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 13, 878–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, M.; Ahn, J.H.; Kim, H.; Kim, D.W.; Lee, T.K.; Lee, J.C.; Kim, Y.M.; Lee, C.H.; Hwang, I.K.; Yan, B.C.; et al. Chronic high-fat diet-induced obesity in gerbils increases pro-inflammatory cytokines and mTOR activation, and elicits neuronal death in the striatum following brief transient ischemia. Neurochem. Int. 2018, 121, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H.; Park, C.W.; Ahn, J.H.; Choi, S.Y.; Shin, M.C.; Cho, J.H.; Lee, T.K.; Kim, I.H.; Cho, J.H.; Lee, J.C.; et al. Neuroprotection and reduced gliosis by pre-and post-treatments of hydroquinone in a gerbil model of transient cerebral ischemia. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2017, 278, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radtke-Schuller, S.; Schuller, G.; Angenstein, F.; Grosser, O.S.; Goldschmidt, J.; Budinger, E. Brain atlas of the Mongolian gerbil (Meriones unguiculatus) in CT/MRI-aided stereotaxic coordinates. Brain Struct. Funct. 2016, 221, 1–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, K.B.; Lemberg, L. Obesity and the metabolic syndrome. Am. J. Crit. Care 2003, 12, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moon, S.M.; Choi, G.M.; Yoo, D.Y.; Jung, H.Y.; Yim, H.S.; Kim, D.W.; Hwang, I.K.; Cho, B.M.; Chang, I.B.; Cho, S.M.; et al. Differential Effects of Pioglitazone in the Hippocampal CA1 Region Following Transient Forebrain Ischemia in Low-and High-Fat Diet-Fed Gerbils. Neurochem. Res. 2015, 40, 1063–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventura, L.L.; Fortes, N.C.; Santiago, H.C.; Caliari, M.V.; Gomes, M.A.; Oliveira, D.R. Obesity-induced diet leads to weight gain, systemic metabolic alterations, adipose tissue inflammation, hepatic steatosis, and oxidative stress in gerbils (Meriones unguiculatus). PeerJ 2017, 5, e2967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, M.G., Jr.; Leibel, R.L.; Seeley, R.J.; Schwartz, M.W. Obesity and leptin resistance: Distinguishing cause from effect. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 21, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutsch, C.; Portik-Dobos, V.; Smith, A.D.; Ergul, A.; Dorrance, A.M. Diet-induced obesity causes cerebral vessel remodeling and increases the damage caused by ischemic stroke. Microvasc. Res. 2009, 78, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Zhang, J.; Feng, C.; Xiong, L.; Zuo, Z. Critical role of matrix metalloprotease-9 in chronic high fat diet-induced cerebral vascular remodelling and increase of ischaemic brain injury in micedagger. Cardiovasc. Res. 2014, 103, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElAli, A.; Doeppner, T.R.; Zechariah, A.; Hermann, D.M. Increased blood-brain barrier permeability and brain edema after focal cerebral ischemia induced by hyperlipidemia: Role of lipid peroxidation and calpain-1/2, matrix metalloproteinase-2/9, and RhoA overactivation. Stroke 2011, 42, 3238–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheon, S.H.; Yan, B.C.; Chen, B.H.; Park, J.H.; Ahn, J.H.; Kim, I.H.; Lee, J.C.; Park, Y.S.; Kim, M.J.; Lee, Y.L.; et al. Accelerated and exacerbated effects of high dietary fat on neuronal damage induced by transient cerebral ischemia in the gerbil septum. Endocrinol. Metab. (Seoul) 2014, 29, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.C.; Park, J.H.; Ahn, J.H.; Kim, I.H.; Lee, J.C.; Yoo, K.Y.; Choi, J.H.; Hwang, I.K.; Cho, J.H.; Kwon, Y.G.; et al. Effects of high-fat diet on neuronal damage, gliosis, inflammatory process and oxidative stress in the hippocampus induced by transient cerebral ischemia. Neurochem. Res. 2014, 39, 2465–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hye Kim, I.; Lee, J.C.; Ha Park, J.; Hyeon Ahn, J.; Cho, J.H.; Hui Chen, B.; Na Shin, B.; Chun Yan, B.; Rueol Ryu, D.; Hong, S.; et al. Time interval after ischaemic preconditioning affects neuroprotection and gliosis in the gerbil hippocampal CA1 region induced by transient cerebral ischaemia. Neurol. Res. 2016, 38, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moskowitz, M.A.; Lo, E.H.; Iadecola, C. The science of stroke: Mechanisms in search of treatments. Neuron 2010, 67, 181–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, K.; Yin, B.; Wang, J.; Peng, G.; Liang, H.; Xu, Z.; Du, Y.; Fang, M.; Xia, Q.; Luo, B. Inhibition of P2X7 receptor ameliorates transient global cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury via modulating inflammatory responses in the rat hippocampus. J. Neuroinflamm. 2012, 9, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leak, R.K.; Li, P.; Zhang, F.; Sulaiman, H.H.; Weng, Z.; Wang, G.; Stetler, R.A.; Shi, Y.; Cao, G.; Gao, Y.; et al. Apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 upregulation reduces oxidative DNA damage and protects hippocampal neurons from ischemic injury. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2015, 22, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtsuki, T.; Matsumoto, M.; Kuwabara, K.; Kitagawa, K.; Suzuki, K.; Taniguchi, N.; Kamada, T. Influence of oxidative stress on induced tolerance to ischemia in gerbil hippocampal neurons. Brain Res. 1992, 599, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtsuki, T.; Ruetzler, C.A.; Tasaki, K.; Hallenbeck, J.M. Interleukin-1 mediates induction of tolerance to global ischemia in gerbil hippocampal CA1 neurons. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 1996, 16, 1137–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haley, M.J.; Lawrence, C.B. Obesity and stroke: Can we translate from rodents to patients? J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2016, 36, 2007–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savini, I.; Catani, M.V.; Evangelista, D.; Gasperi, V.; Avigliano, L. Obesity-associated oxidative stress: Strategies finalized to improve redox state. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 10497–10538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajiluian, G.; Abbasalizad Farhangi, M.; Nameni, G.; Shahabi, P.; Megari-Abbasi, M. Oxidative stress-induced cognitive impairment in obesity can be reversed by vitamin D administration in rats. Nutr. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, B.T.; Jeong, E.A.; Shin, H.J.; Lee, Y.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, H.J.; Kang, S.S.; Cho, G.J.; Choi, W.S.; Roh, G.S. Resveratrol attenuates obesity-associated peripheral and central inflammation and improves memory deficit in mice fed a high-fat diet. Diabetes 2012, 61, 1444–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.L.; Du, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, J.T.; Hu, X.M. Hyperlipidemia exacerbates cerebral injury through oxidative stress, inflammation and neuronal apoptosis in MCAO/reperfusion rats. Exp. Brain Res. 2015, 233, 2753–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Hei, C.; Liu, P.; Song, Y.; Thomas, T.; Tshimanga, S.; Wang, F.; Niu, J.; Sun, T.; Li, P.A. Inhibition of mTOR Pathway by Rapamycin Reduces Brain Damage in Rats Subjected to Transient Forebrain Ischemia. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2015, 11, 1424–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, A.; Sharma, U.; Jagannathan, N.R.; Reeta, K.H.; Gupta, Y.K. Rapamycin protects against middle cerebral artery occlusion induced focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2011, 225, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, L.; Sun, F.; Wang, J.; Mao, X.; Xie, L.; Yang, S.H.; Su, D.M.; Simpkins, J.W.; Greenberg, D.A.; Jin, K. mTOR signaling inhibition modulates macrophage/microglia-mediated neuroinflammation and secondary injury via regulatory T cells after focal ischemia. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 6009–6019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, J.; Lu, J. Effects of mTOR on Neurological Deficits after Transient Global Ischemia. Transl. Neurosci. 2017, 8, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Cloughesy, T.F.; Yoshimoto, K.; Nghiemphu, P.; Brown, K.; Dang, J.; Zhu, S.; Hsueh, T.; Chen, Y.; Wang, W.; Youngkin, D.; et al. Antitumor activity of rapamycin in a Phase I trial for patients with recurrent PTEN-deficient glioblastoma. PLoS Med. 2008, 5, e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thellung, S.; Corsaro, A.; Nizzari, M.; Barbieri, F.; Florio, T. Autophagy activator drugs: A new opportunity in neuroprotection from misfolded protein toxicity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Yang, X.; Hei, C.; Meli, Y.; Niu, J.; Sun, T.; Li, P.A. Rapamycin Reduced Ischemic Brain Damage in Diabetic Animals Is Associated with Suppressions of mTOR and ERK1/2 Signaling. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2016, 12, 1032–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, J.H.; Ahn, J.H.; Song, M.; Kim, H.; Park, C.W.; Park, Y.E.; Lee, T.-K.; Lee, J.-C.; Kim, D.W.; Lee, C.-H.; et al. A 2-Min Transient Ischemia Confers Cerebral Ischemic Tolerance in Non-Obese Gerbils, but Results in Neuronal Death in Obese Gerbils by Increasing Abnormal mTOR Activation-Mediated Oxidative Stress and Neuroinflammation. Cells 2019, 8, 1126. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8101126
Park JH, Ahn JH, Song M, Kim H, Park CW, Park YE, Lee T-K, Lee J-C, Kim DW, Lee C-H, et al. A 2-Min Transient Ischemia Confers Cerebral Ischemic Tolerance in Non-Obese Gerbils, but Results in Neuronal Death in Obese Gerbils by Increasing Abnormal mTOR Activation-Mediated Oxidative Stress and Neuroinflammation. Cells. 2019; 8(10):1126. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8101126
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Joon Ha, Ji Hyeon Ahn, Minah Song, Hyunjung Kim, Cheol Woo Park, Young Eun Park, Tae-Kyeong Lee, Jae-Chul Lee, Dae Won Kim, Choong-Hyun Lee, and et al. 2019. "A 2-Min Transient Ischemia Confers Cerebral Ischemic Tolerance in Non-Obese Gerbils, but Results in Neuronal Death in Obese Gerbils by Increasing Abnormal mTOR Activation-Mediated Oxidative Stress and Neuroinflammation" Cells 8, no. 10: 1126. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8101126
APA StylePark, J. H., Ahn, J. H., Song, M., Kim, H., Park, C. W., Park, Y. E., Lee, T.-K., Lee, J.-C., Kim, D. W., Lee, C.-H., Hwang, I. K., Yan, B. C., Ryoo, S., Kim, Y.-M., Kang, I. J., Won, M.-H., & Choi, S. Y. (2019). A 2-Min Transient Ischemia Confers Cerebral Ischemic Tolerance in Non-Obese Gerbils, but Results in Neuronal Death in Obese Gerbils by Increasing Abnormal mTOR Activation-Mediated Oxidative Stress and Neuroinflammation. Cells, 8(10), 1126. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8101126