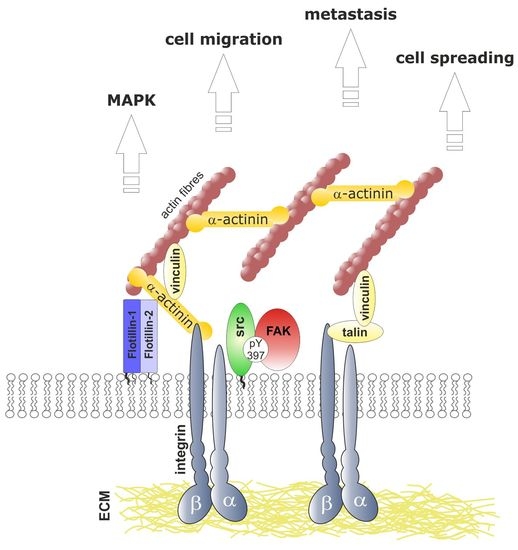
Flotillins Regulate Focal Adhesions by Interacting with α-Actinin and by Influencing the Activation of Focal Adhesion Kinase
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture, Transfection, and RNA Interference
2.2. Antibodies
2.3. Immunofluorescence
2.4. Cell Lysis, Gel Electrophoresis, and Western Blot
2.5. Immunoprecipitation
2.6. GST Pulldown Assay
2.7. Förster Resonance Energy Transfer- Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging (FRET–FLIM)
2.8. Cell Spreading Assay
2.9. Haptotactic Cell Migration Assay
2.10. Wound Healing
2.11. Cell Growth in Soft Agar
2.12. Statistical Analysis and Quantification
3. Results
3.1. Flotillin Knockdown Impairs Cell Migration and Spreading
3.2. Flotillin Expression Enhances Anchorage-Independent Growth
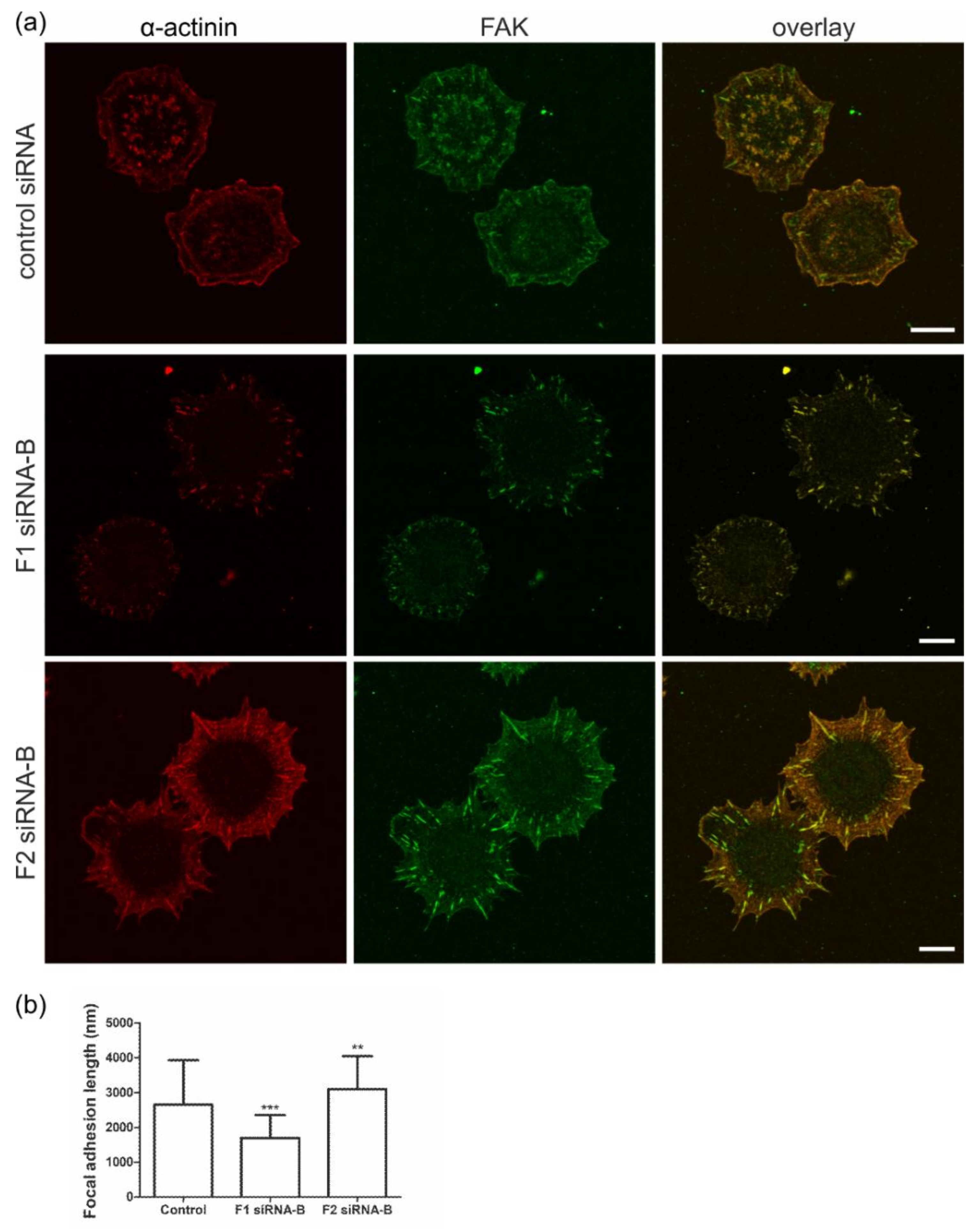
3.3. Flotillin Knockdown Affects Focal Adhesion Morphology
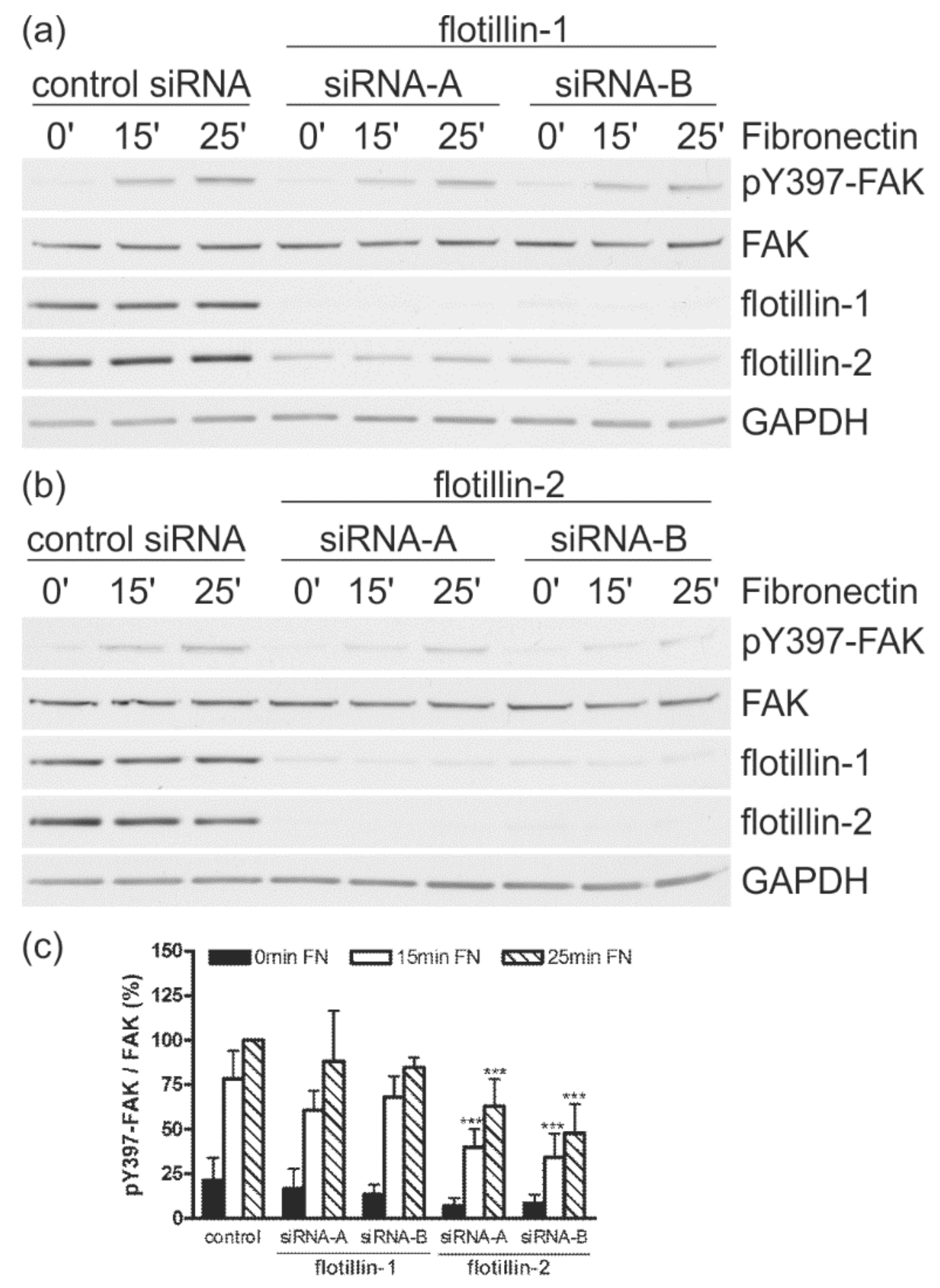
3.4. Flotillin-2 siRNA Results in Reduced FAK Autophosphorylation
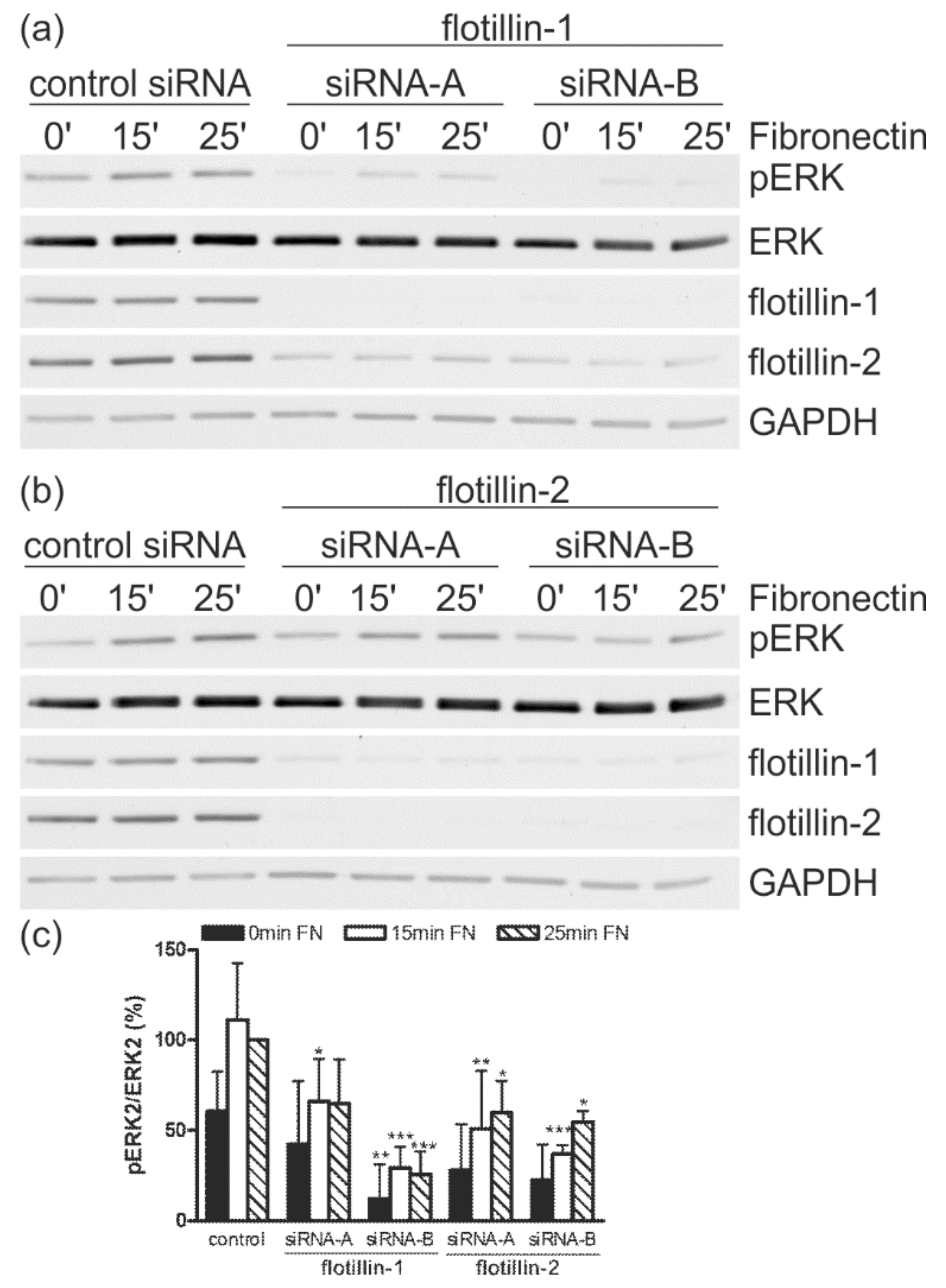
3.5. Flotillin Depletion Impairs ERK Activation during Cell Spreading
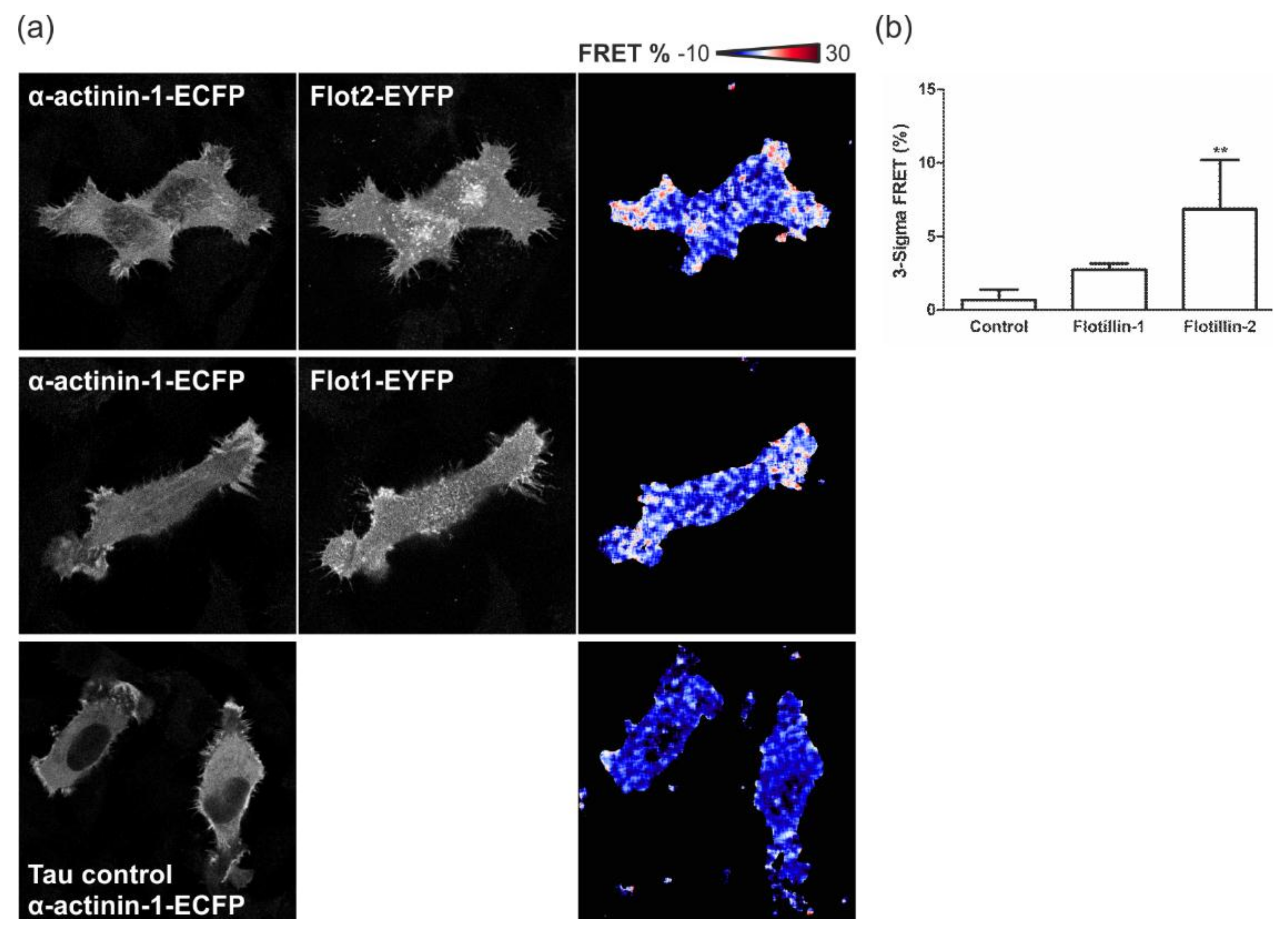
3.6. Flotillins Interact with α-Actinin
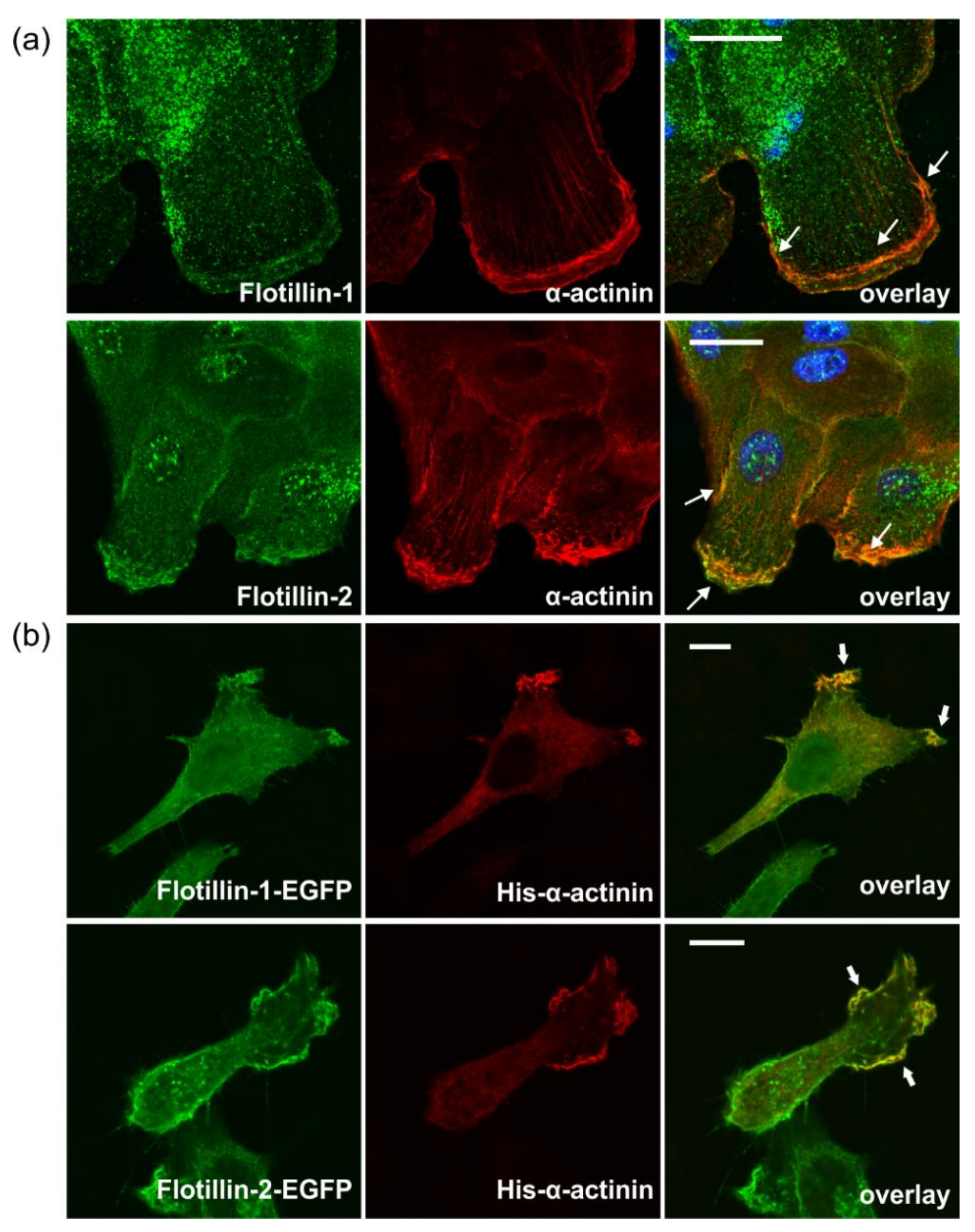
3.7. Flotillins Colocalize and Interact with α-Actinin in Lamellipodia-Like Structures
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lauffenburger, D.A.; Horwitz, A.F. Cell migration: A physically integrated molecular process. Cell 1996, 84, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridley, A.J.; Schwartz, M.A.; Burridge, K.; Firtel, R.A.; Ginsberg, M.H.; Borisy, G.; Parsons, J.T.; Horwitz, A.R. Cell migration: Integrating signals from front to back. Science 2003, 302, 1704–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webb, D.J.; Asmussen, H.; Murase, S.; Horwitz, A.F. Cell migration in slice cultures. Methods Cell Biol. 2002, 69, 341–358. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Geiger, B.; Bershadsky, A.; Pankov, R.; Yamada, K.M. Transmembrane crosstalk between the extracellular matrix--cytoskeleton crosstalk. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001, 2, 793–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Chen, S.C.; Pallen, C.J. Integrin-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of protein-tyrosine phosphatase-alpha is required for cytoskeletal reorganization and cell migration. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 11972–11980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrels, B.; Serrels, A.; Brunton, V.G.; Holt, M.; McLean, G.W.; Gray, C.H.; Jones, G.E.; Frame, M.C. Focal adhesion kinase controls actin assembly via a FERM-mediated interaction with the Arp2/3 complex. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 1046–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, S.K.; Hanson, D.A.; Schlaepfer, D.D. Focal adhesion kinase: In command and control of cell motility. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 6, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brakebusch, C.; Fassler, R. The integrin-actin connection, an eternal love affair. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 2324–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiesner, S.; Legate, K.R.; Fassler, R. Integrin-actin interactions. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2005, 62, 1081–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lietha, D.; Cai, X.; Ceccarelli, D.F.; Li, Y.; Schaller, M.D.; Eck, M.J. Structural basis for the autoinhibition of focal adhesion kinase. Cell 2007, 129, 1177–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlaepfer, D.D.; Hanks, S.K.; Hunter, T.; van der Geer, P. Integrin-mediated signal transduction linked to Ras pathway by GRB2 binding to focal adhesion kinase. Nature 1994, 372, 786–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banning, A.; Tomasovic, A.; Tikkanen, R. Functional aspects of membrane association of reggie/flotillin proteins. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2011, 12, 725–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurrle, N.; John, B.; Meister, M.; Tikkanen, R. Function of Flotillins in Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Signaling and Endocytosis: Role of Tyrosine Phosphorylation and Oligomerization. In Protein Phosphorylation in Human Health; Huang, C., Ed.; Intech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Meister, M.; Tikkanen, R. Endocytic trafficking of membrane-bound cargo: A flotillin point of view. Membranes 2014, 4, 356–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrow, I.C.; Rea, S.; Martin, S.; Prior, I.A.; Prohaska, R.; Hancock, J.F.; James, D.E.; Parton, R.G. Flotillin-1/reggie-2 traffics to surface raft domains via a novel golgi-independent pathway. Identification of a novel membrane targeting domain and a role for palmitoylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 48834–48841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann-Giesen, C.; Falkenbach, B.; Beicht, P.; Claasen, S.; Luers, G.; Stuermer, C.A.; Herzog, V.; Tikkanen, R. Membrane and raft association of reggie-1/flotillin-2: Role of myristoylation, palmitoylation and oligomerization and induction of filopodia by overexpression. Biochem. J. 2004, 378, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babuke, T.; Ruonala, M.; Meister, M.; Amaddii, M.; Genzler, C.; Esposito, A.; Tikkanen, R. Hetero-oligomerization of reggie-1/flotillin-2 and reggie-2/flotillin-1 is required for their endocytosis. Cell. Signal. 2009, 21, 1287–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solis, G.P.; Hoegg, M.; Munderloh, C.; Schrock, Y.; Malaga-Trillo, E.; Rivera-Milla, E.; Stuermer, C.A. Reggie/flotillin proteins are organized into stable tetramers in membrane microdomains. Biochem. J. 2007, 403, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaddii, M.; Meister, M.; Banning, A.; Tomasovic, A.; Mooz, J.; Rajalingam, K.; Tikkanen, R. Flotillin-1/reggie-2 protein plays dual role in activation of receptor-tyrosine kinase/mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 7265–7278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meister, M.; Tomasovic, A.; Banning, A.; Tikkanen, R. Mitogen-Activated Protein (MAP) Kinase Scaffolding Proteins: A Recount. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 4854–4884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann-Giesen, C.; Fernow, I.; Amaddii, M.; Tikkanen, R. Role of EGF-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of reggie-1/flotillin-2 in cell spreading and signaling to the actin cytoskeleton. J. Cell Sci. 2007, 120, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riento, K.; Frick, M.; Schafer, I.; Nichols, B.J. Endocytosis of flotillin-1 and flotillin-2 is regulated by Fyn kinase. J. Cell Sci. 2009, 122, 912–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otto, G.P.; Nichols, B.J. The roles of flotillin microdomains--endocytosis and beyond. J. Cell Sci. 2011, 124, 3933–3940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, B.A.; Meister, M.; Banning, A.; Tikkanen, R. Flotillins bind to the dileucine sorting motif of beta-site amyloid precursor protein-cleaving enzyme 1 and influence its endosomal sorting. FEBS J. 2014, 281, 2074–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meister, M.; Banfer, S.; Gartner, U.; Koskimies, J.; Amaddii, M.; Jacob, R.; Tikkanen, R. Regulation of cargo transfer between ESCRT-0 and ESCRT-I complexes by flotillin-1 during endosomal sorting of ubiquitinated cargo. Oncogenesis 2017, 6, e344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meister, M.; Zuk, A.; Tikkanen, R. Role of dynamin and clathrin in the cellular trafficking of flotillins. FEBS J. 2014, 281, 2956–2976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodin, S.; Planchon, D.; Rios Morris, E.; Comunale, F.; Gauthier-Rouviere, C. Flotillins in intercellular adhesion—From cellular physiology to human diseases. J. Cell Sci. 2014, 127, 5139–5147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillaume, E.; Comunale, F.; Do Khoa, N.; Planchon, D.; Bodin, S.; Gauthier-Rouviere, C. Flotillin microdomains stabilize cadherins at cell-cell junctions. J. Cell Sci. 2013, 126, 5293–5304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vollner, F.; Ali, J.; Kurrle, N.; Exner, Y.; Eming, R.; Hertl, M.; Banning, A.; Tikkanen, R. Loss of flotillin expression results in weakened desmosomal adhesion and Pemphigus vulgaris-like localisation of desmoglein-3 in human keratinocytes. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoehne, M.; de Couet, H.G.; Stuermer, C.A.; Fischbach, K.F. Loss- and gain-of-function analysis of the lipid raft proteins Reggie/Flotillin in Drosophila: They are posttranslationally regulated, and misexpression interferes with wing and eye development. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2005, 30, 326–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banning, A.; Regenbrecht, C.R.; Tikkanen, R. Increased activity of mitogen activated protein kinase pathway in flotillin-2 knockout mouse model. Cell. Signal. 2014, 26, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, T.; Ueda, T.; Arpaia, E.; Chio, II.; Shirdel, E.A.; Jurisica, I.; Hamada, K.; You-Ten, A.; Haight, J.; Wakeham, A.; et al. Flotillin-2 deficiency leads to reduced lung metastases in a mouse breast cancer model. Oncogene 2013, 32, 4989–4994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwig, A.; Otto, G.P.; Riento, K.; Hams, E.; Fallon, P.G.; Nichols, B.J. Flotillin microdomains interact with the cortical cytoskeleton to control uropod formation and neutrophil recruitment. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 191, 771–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazarika, P.; Dham, N.; Patel, P.; Cho, M.; Weidner, D.; Goldsmith, L.; Duvic, M. Flotillin 2 is distinct from epidermal surface antigen (ESA) and is associated with filopodia formation. J. Cell. Biochem. 1999, 75, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kioka, N.; Ueda, K.; Amachi, T. Vinexin, CAP/ponsin, ArgBP2: A novel adaptor protein family regulating cytoskeletal organization and signal transduction. Cell Struct. Funct. 2002, 27, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandai, K.; Nakanishi, H.; Satoh, A.; Takahashi, K.; Satoh, K.; Nishioka, H.; Mizoguchi, A.; Takai, Y. Ponsin/SH3P12: An l-afadin- and vinculin-binding protein localized at cell-cell and cell-matrix adherens junctions. J. Cell Biol. 1999, 144, 1001–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernow, I.; Tomasovic, A.; Siehoff-Icking, A.; Tikkanen, R. Cbl-associated protein is tyrosine phosphorylated by c-Abl and c-Src kinases. BMC Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langhorst, M.F.; Jaeger, F.A.; Mueller, S.; Sven Hartmann, L.; Luxenhofer, G.; Stuermer, C.A. Reggies/flotillins regulate cytoskeletal remodeling during neuronal differentiation via CAP/ponsin and Rho GTPases. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2008, 87, 921–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munderloh, C.; Solis, G.P.; Bodrikov, V.; Jaeger, F.A.; Wiechers, M.; Malaga-Trillo, E.; Stuermer, C.A. Reggies/flotillins regulate retinal axon regeneration in the zebrafish optic nerve and differentiation of hippocampal and N2a neurons. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 6607–6615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langhorst, M.F.; Reuter, A.; Jaeger, F.A.; Wippich, F.M.; Luxenhofer, G.; Plattner, H.; Stuermer, C.A. Trafficking of the microdomain scaffolding protein reggie-1/flotillin-2. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2008, 87, 211–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomasovic, A.; Traub, S.; Tikkanen, R. Molecular networks in FGF signaling: Flotillin-1 and cbl-associated protein compete for the binding to fibroblast growth factor receptor substrate 2. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e29739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browman, D.T.; Hoegg, M.B.; Robbins, S.M. The SPFH domain-containing proteins: More than lipid raft markers. Trends Cell Biol. 2007, 17, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izaguirre, G.; Aguirre, L.; Hu, Y.P.; Lee, H.Y.; Schlaepfer, D.D.; Aneskievich, B.J.; Haimovich, B. The cytoskeletal/non-muscle isoform of alpha-actinin is phosphorylated on its actin-binding domain by the focal adhesion kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 28676–28685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurrle, N.; Vollner, F.; Eming, R.; Hertl, M.; Banning, A.; Tikkanen, R. Flotillins Directly Interact with gamma-Catenin and Regulate Epithelial Cell-Cell Adhesion. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e84393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazarika, P.; McCarty, M.F.; Prieto, V.G.; George, S.; Babu, D.; Koul, D.; Bar-Eli, M.; Duvic, M. Up-regulation of Flotillin-2 is associated with melanoma progression and modulates expression of the thrombin receptor protease activated receptor 1. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 7361–7369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.Y.; Neel, B.G.; Haimovich, B. Phosphorylated alpha-actinin and protein-tyrosine phosphatase 1B coregulate the disassembly of the focal adhesion kinase × Src complex and promote cell migration. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 1746–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, J.C.; Han, X.; Hsiao, C.T.; Yates, J.R., 3rd; Waterman, C.M. Analysis of the myosin-II-responsive focal adhesion proteome reveals a role for beta-Pix in negative regulation of focal adhesion maturation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banning, A.; Kurrle, N.; Meister, M.; Tikkanen, R. Flotillins in receptor tyrosine kinase signaling and cancer. Cells 2014, 3, 129–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Luo, J.; Wang, B.; Wang, D.; Xie, X.; Yuan, L.; Guo, J.; Xi, S.; Gao, J.; Lin, X.; et al. Microrna-124 targets flotillin-1 to regulate proliferation and migration in breast cancer. Mol. Cancer 2013, 12, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Banning, A.; Babuke, T.; Kurrle, N.; Meister, M.; Ruonala, M.O.; Tikkanen, R. Flotillins Regulate Focal Adhesions by Interacting with α-Actinin and by Influencing the Activation of Focal Adhesion Kinase. Cells 2018, 7, 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells7040028
Banning A, Babuke T, Kurrle N, Meister M, Ruonala MO, Tikkanen R. Flotillins Regulate Focal Adhesions by Interacting with α-Actinin and by Influencing the Activation of Focal Adhesion Kinase. Cells. 2018; 7(4):28. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells7040028
Chicago/Turabian StyleBanning, Antje, Tanja Babuke, Nina Kurrle, Melanie Meister, Mika O. Ruonala, and Ritva Tikkanen. 2018. "Flotillins Regulate Focal Adhesions by Interacting with α-Actinin and by Influencing the Activation of Focal Adhesion Kinase" Cells 7, no. 4: 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells7040028
APA StyleBanning, A., Babuke, T., Kurrle, N., Meister, M., Ruonala, M. O., & Tikkanen, R. (2018). Flotillins Regulate Focal Adhesions by Interacting with α-Actinin and by Influencing the Activation of Focal Adhesion Kinase. Cells, 7(4), 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells7040028