A New Integrated Lab-on-a-Chip System for Fast Dynamic Study of Mammalian Cells under Physiological Conditions in Bioreactor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Mammalian Cell Cultivation
2.2. Design of the Microfluidic System
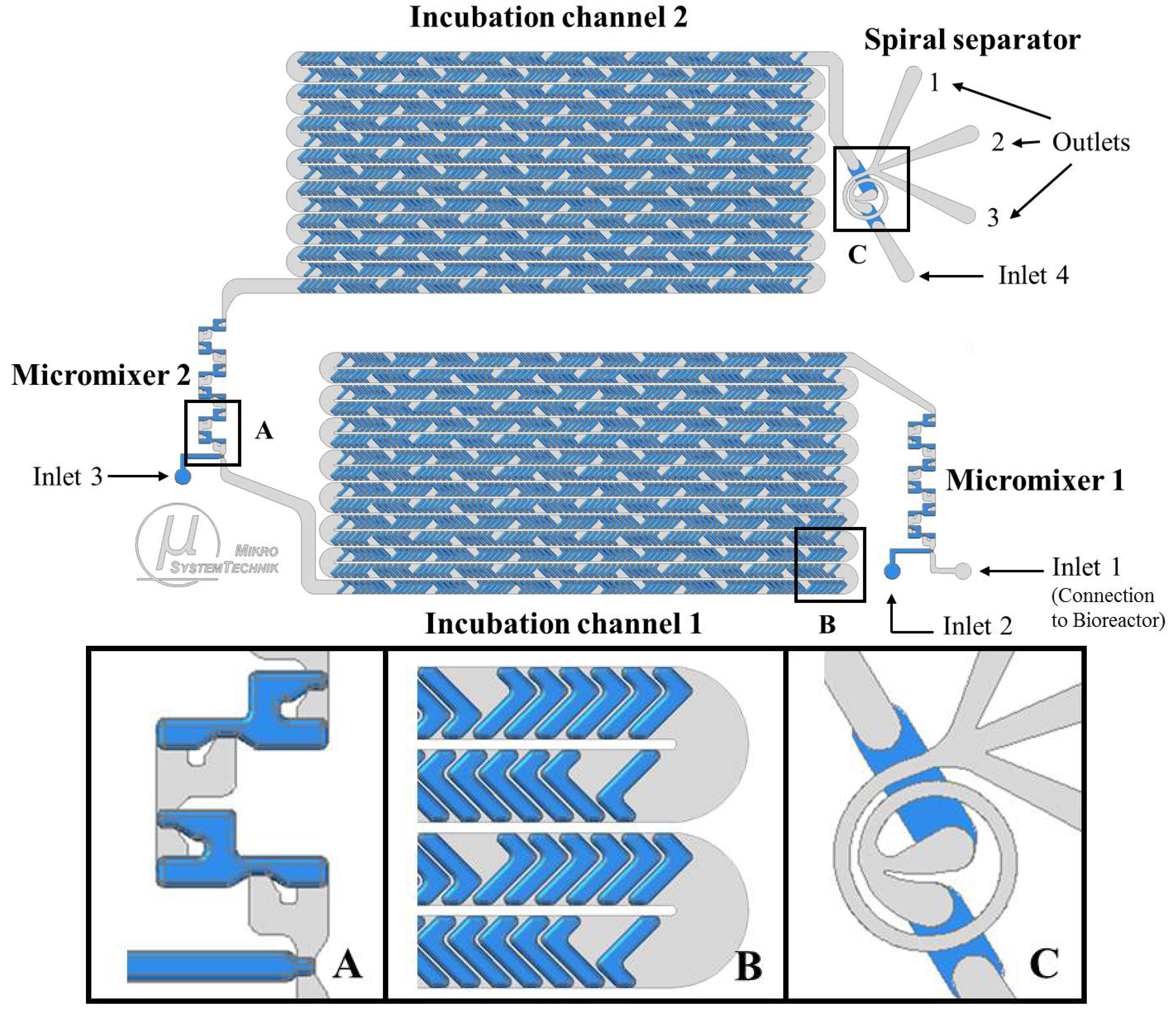
2.3. LoaC Fabrication
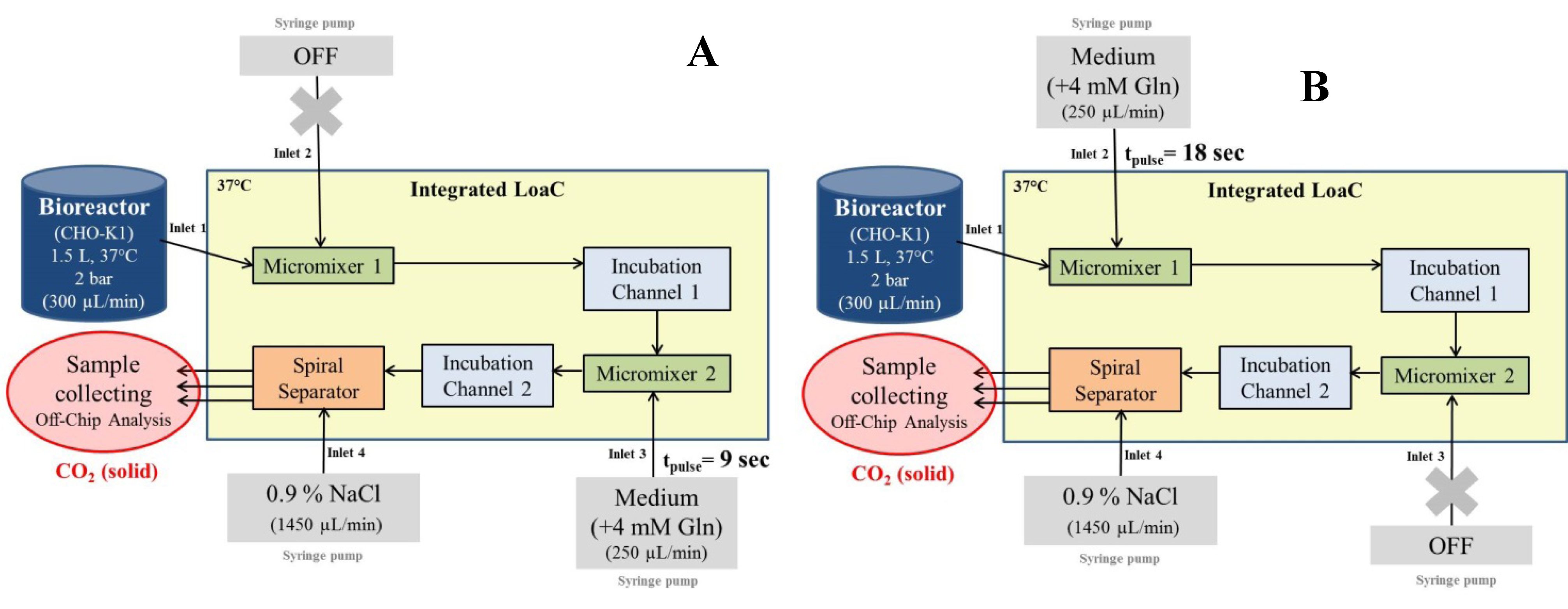
2.4. Integrated Microchip-Bioreactor: Experimental Setup

- Inlet 2 (pulse medium or reagent): 250 µL/min
- Inlet 3 (pulse medium or reagent): 250 µL/min
- Inlet 4 (wash or quenching medium): 1450 µL/min
2.5. Glutamine Pulse Experiments
2.6. Cell Density and Viability
2.7. Analysis of Glucose Concentration
2.8. Fluorescence Staining of CHO-K1 Cells
3. Results and Discussion
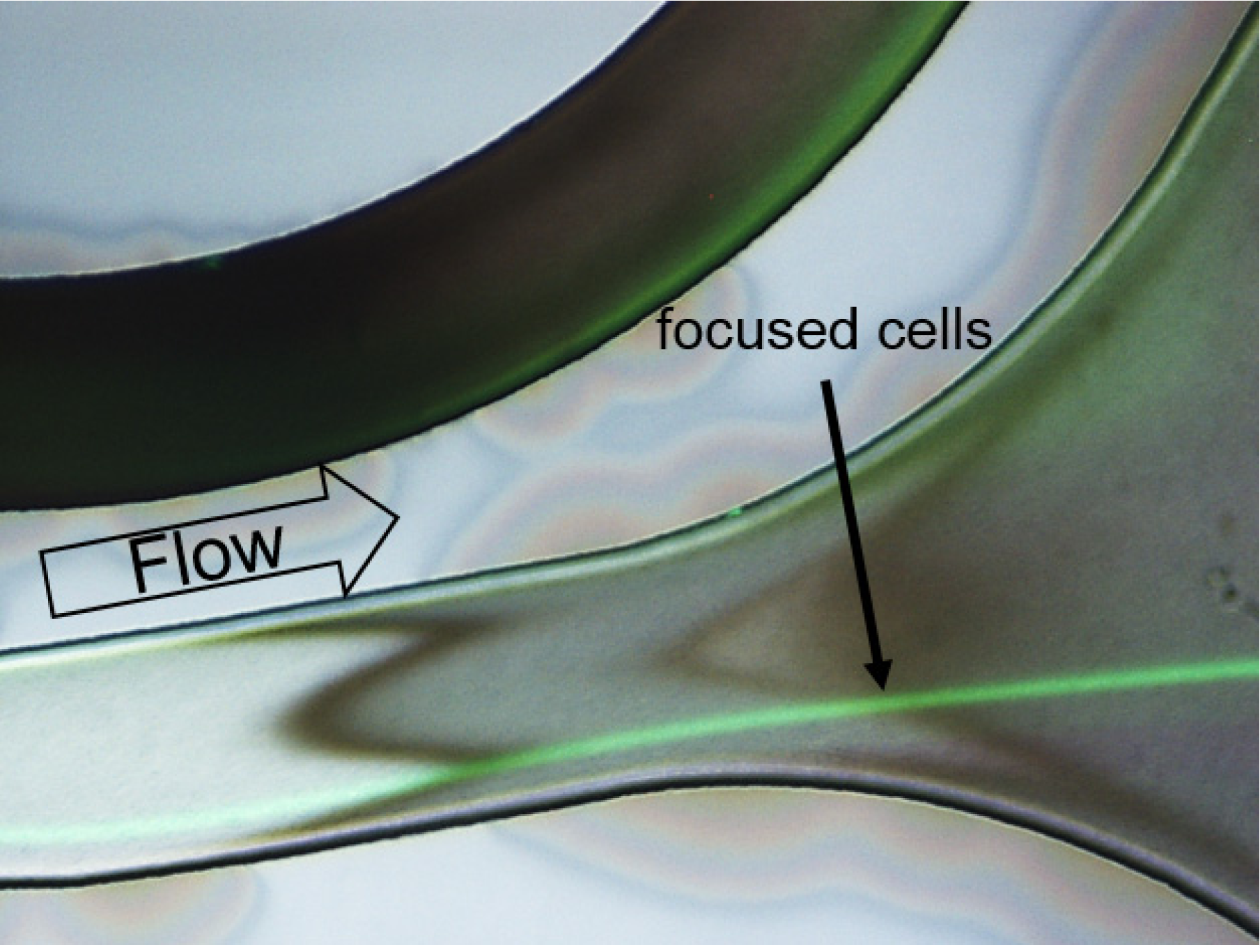
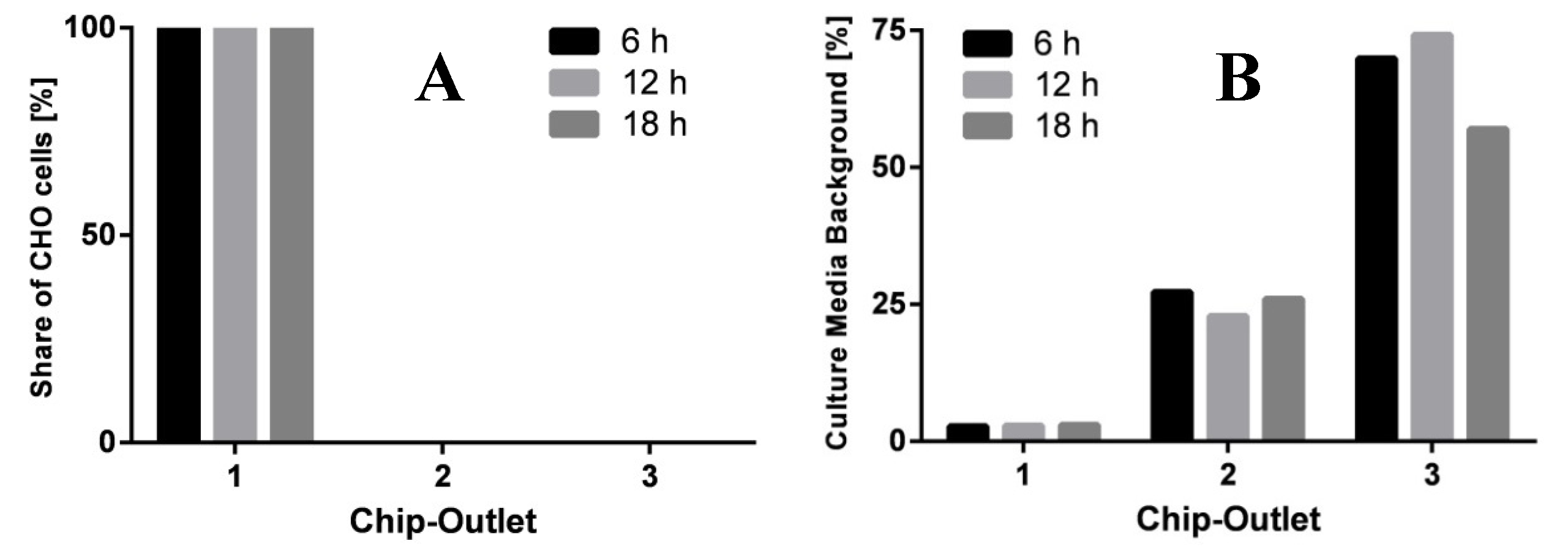
3.1. Medium Exchange and Separation of CHO-K1 Cells

3.2. Biological Application: Dynamic Pulse experiments
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflict of Interest
References and Notes
- Groussac, E.; Ortiz, M.; François, J. Improved protocols for quantitative determination of metabolites from biological samples using high performance ionic-exchange chromatography with conductimetric and pulsed amperometric detection. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2000, 26, 715–723. [Google Scholar]
- Fell, D. Understanding the Control of Metabolism, 1st ed; Portland Press: Portland, OR, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Oldiges, M.; Lütz, S.; Pflug, S.; Schroer, K.; Stein, N.; Wiendahl, C. Metabolomics: Current state and evolving methodologies and tools. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 76, 495–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurm, M.; Zeng, A.-P. Mechanical disruption of mammalian cells in a microfluidic system and its numerical analysis based on computational fluid dynamics. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsutsui, H.; Ho, C.-M. Cell separation by non-inertial force fields in microfluidic systems. Mech. Res. Commun. 2009, 36, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuntaegowdanahalli, S.S.; Bhagat, A.A.S.; Kumar, G.; Papautsky, I. Inertial microfluidics for continuous particle separation in spiral microchannels. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitesides, G.M. The origins and the future of microfluidics. Nature 2006, 442, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beebe, D.J.; Mensing, G.A.; Walker, G.M. Physics and applications of microfluidics in biology. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2002, 4, 261–286. [Google Scholar]
- Tabeling, P. Introduction to Microfluidics; Oxford University Press: Oxford, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- El-Ali, J.; Sorger, P.K.; Jensen, K.F. Cells on chips. Nature 2006, 442, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, S.; Gao, D.; Liu, W.; Wei, H.; Lin, J.-M. Imitation of drug metabolism in human liver and cytotoxicity assay using a microfluidic device coupled to mass spectrometric detection. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, J.-M. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of tumor cell metabolism via stable isotope labeling assisted microfluidic chip electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 1695–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabi, N.; Bahnemann, J.; Tzeng, T.-N.; Zeng, A.-P.; Müller, J. Microfluidic device for the continuous preparation of eukaryotic cells for metabolic analysis. In Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS), Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE 26th International Conference on, Taipei, Taiwan, 20–24 January 2013; pp. 259–262.
- Rajabi, N.; Bahnemann, J.; Wahrheit, J.; Heinzle, E.; Zeng, A.-P.; Müller, J. Inertia-based media exchange and quenching of cells for the continuous preparation of cells in a lab-on-a-chip. In proceedings of the 3rd European Conference on Microfluidics, Heidelberg, Germany, 4–5 December 2012.
- Rajabi, N.; Hoffmann, M.; Bahnemann, J.; Zeng, A.-P.; Schlüter, M.; Müller, J. A Chaotic Advection Enhanced Microfluidic Split-and-Recombine Mixer for the Preparation of Chemical and Biological Probes. J. Chem. Eng. Japan 2012, 45, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroock, A.D. Chaotic Mixer for Microchannels. Science 2002, 295, 647–651. [Google Scholar]
- Di Carlo, D. Inertial microfluidics. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackall, J.; Meredith, M.; Lane, M. A mild procedure for the rapid release of cytoplasmic enzymes from cultured animal cells. Anal. Biochem. 1979, 95, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niklas, J.; Melnyk, A.; Yuan, Y.; Heinzle, E. Selective permeabilization for the high-throughput measurement of compartmented enzyme activities in mammalian cells. Anal. Biochem. 2011, 416, 218–227. [Google Scholar]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Bahnemann, J.; Rajabi, N.; Fuge, G.; Barradas, O.P.; Müller, J.; Pörtner, R.; Zeng, A.-P. A New Integrated Lab-on-a-Chip System for Fast Dynamic Study of Mammalian Cells under Physiological Conditions in Bioreactor. Cells 2013, 2, 349-360. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells2020349
Bahnemann J, Rajabi N, Fuge G, Barradas OP, Müller J, Pörtner R, Zeng A-P. A New Integrated Lab-on-a-Chip System for Fast Dynamic Study of Mammalian Cells under Physiological Conditions in Bioreactor. Cells. 2013; 2(2):349-360. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells2020349
Chicago/Turabian StyleBahnemann, Janina, Negar Rajabi, Grischa Fuge, Oscar Platas Barradas, Jörg Müller, Ralf Pörtner, and An-Ping Zeng. 2013. "A New Integrated Lab-on-a-Chip System for Fast Dynamic Study of Mammalian Cells under Physiological Conditions in Bioreactor" Cells 2, no. 2: 349-360. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells2020349
APA StyleBahnemann, J., Rajabi, N., Fuge, G., Barradas, O. P., Müller, J., Pörtner, R., & Zeng, A.-P. (2013). A New Integrated Lab-on-a-Chip System for Fast Dynamic Study of Mammalian Cells under Physiological Conditions in Bioreactor. Cells, 2(2), 349-360. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells2020349




