Imeglimin Inhibits Macrophage Foam Cell Formation and Atherosclerosis in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic ApoE-Deficient Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Treatment
2.2. Cholesterol Efflux Assay
2.3. Western Blotting
2.4. Animal Protocols
2.5. Blood Sample Assay
2.6. En Face Plaque Area Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
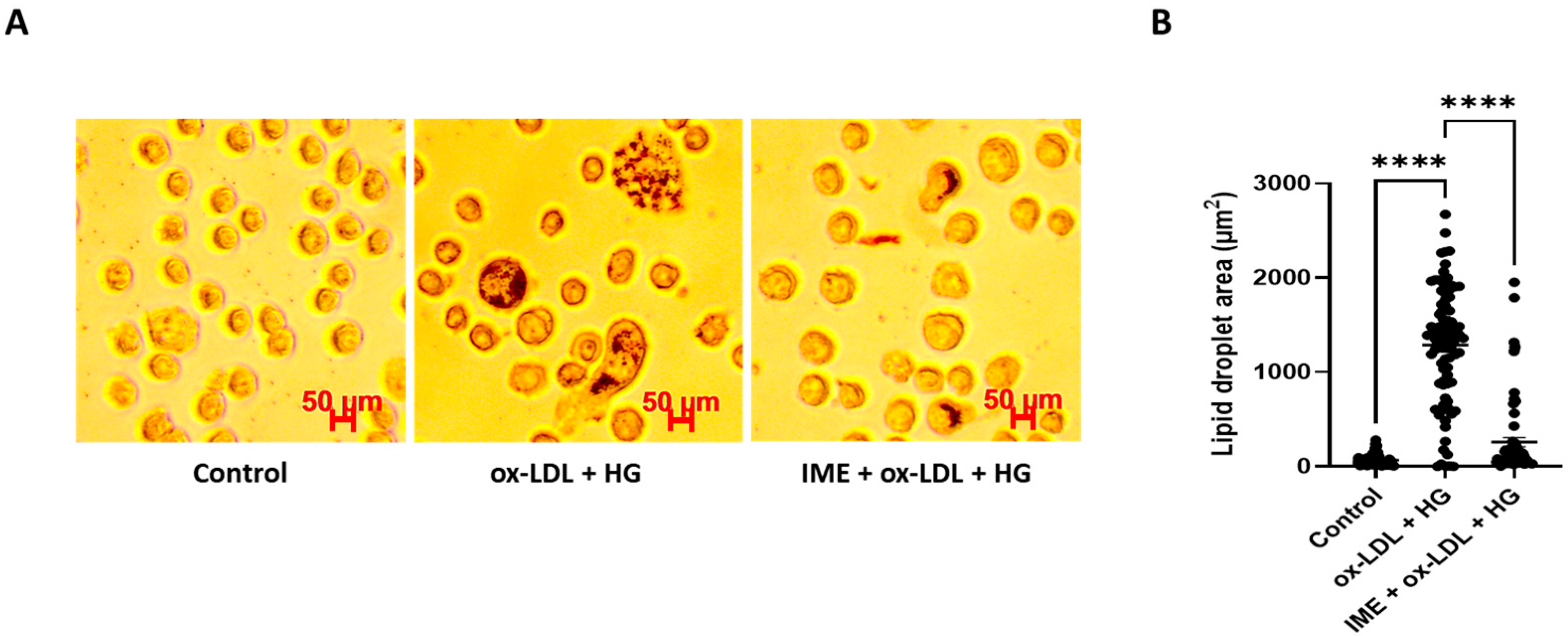
3.1. Imeglimin Inhibits Foam Cell Formation and Promotes Cholesterol Efflux in ox-LDL/HG-Treated THP-1 Macrophages
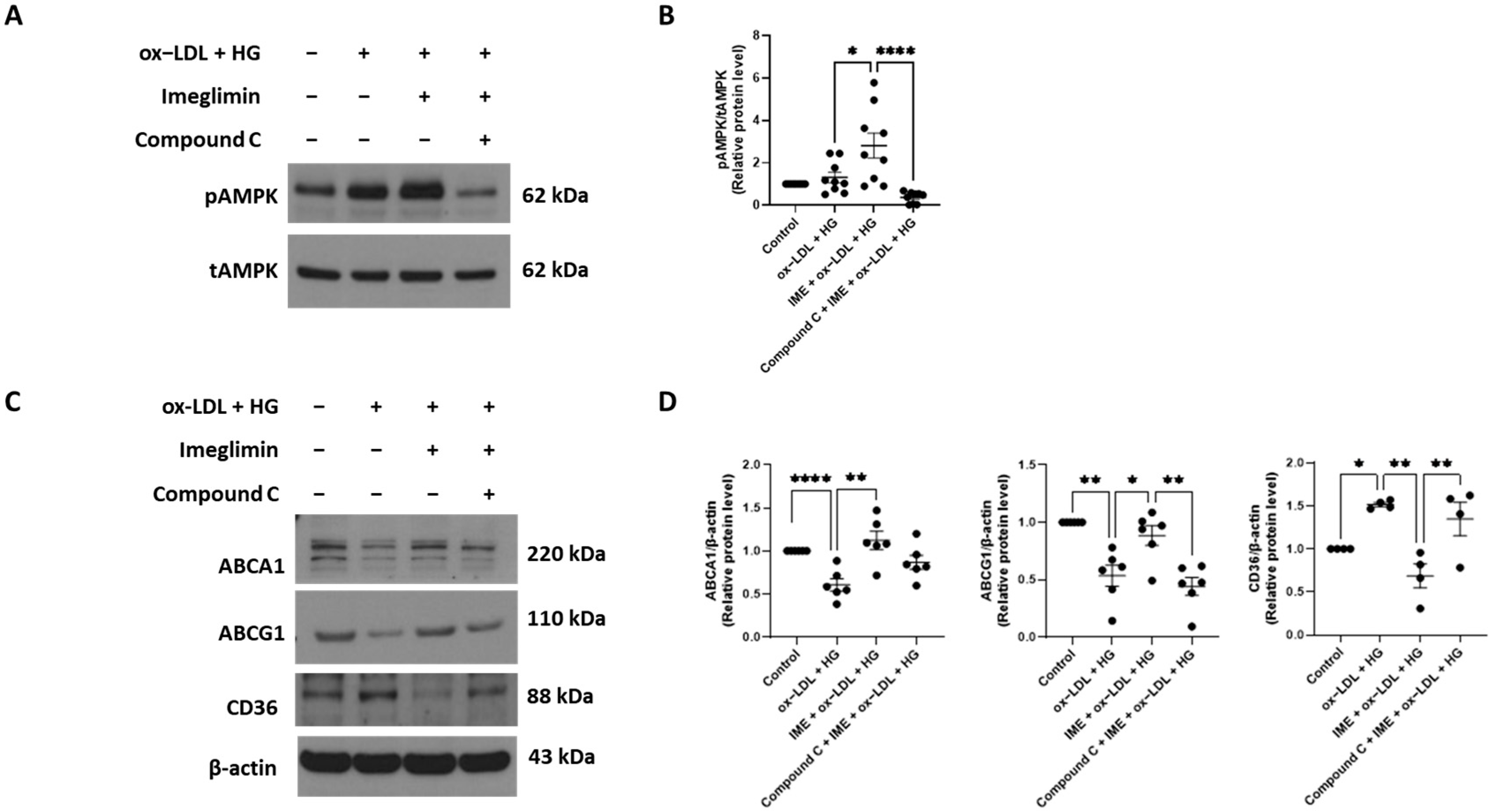
3.2. Imeglimin Upregulates the Expression of ABCA1 and ABCG1 and Inhibits That of CD36 in ox-LDL/HG-Treated THP-1 Macrophages
3.3. Imeglimin Regulates the Expression of ABCG1 and CD36 via Adenosine Monophosphate-Activated Protein Kinase (AMPK) Activation in ox-LDL/HG-Treated THP-1 Macrophages
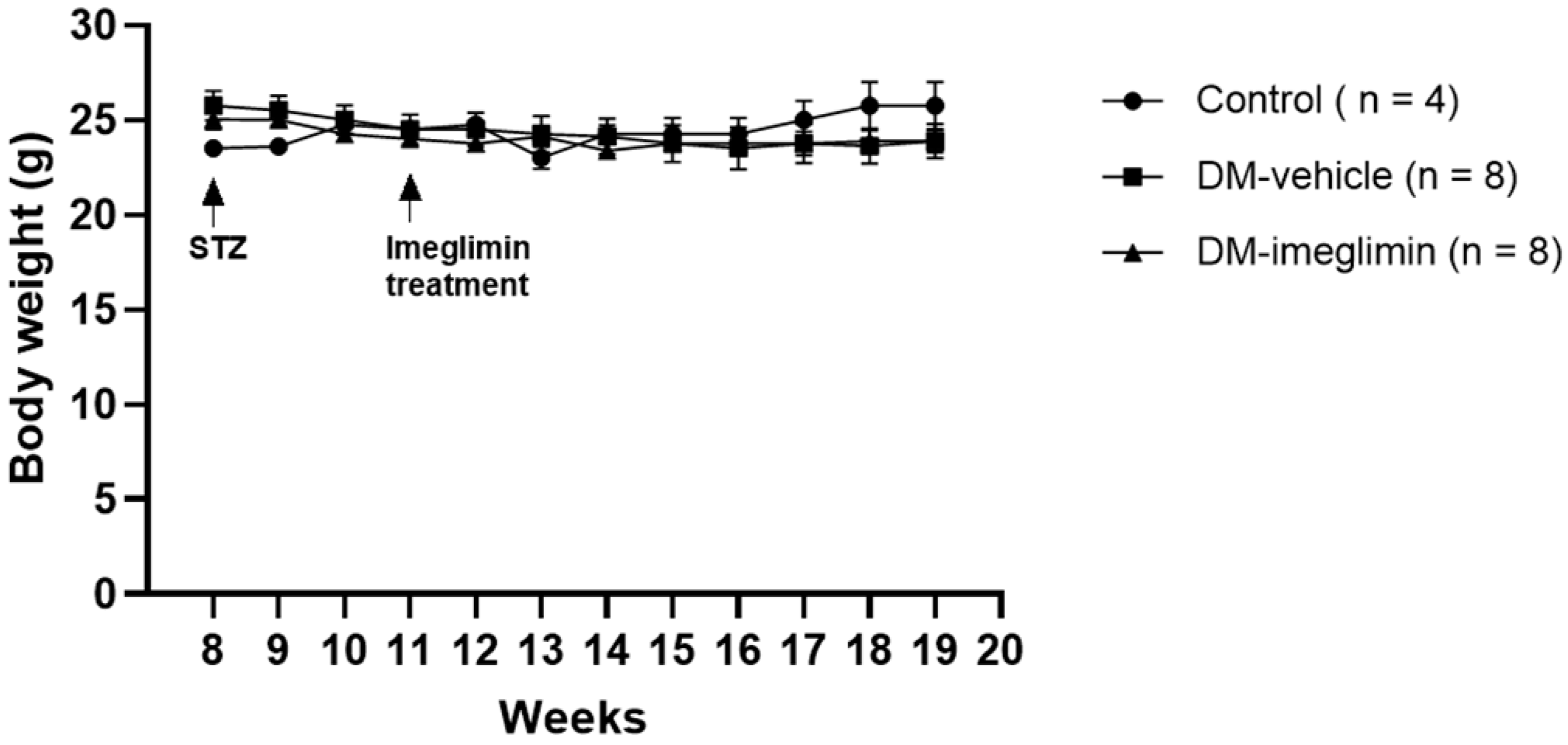
3.4. Effect of Imeglimin on Body Weight and Serum Biochemical Parameters in Diabetic ApoE−/− Mice
3.5. Imeglimin Alleviates Atherosclerotic Plaque Formation in Diabetic ApoE−/− Mice
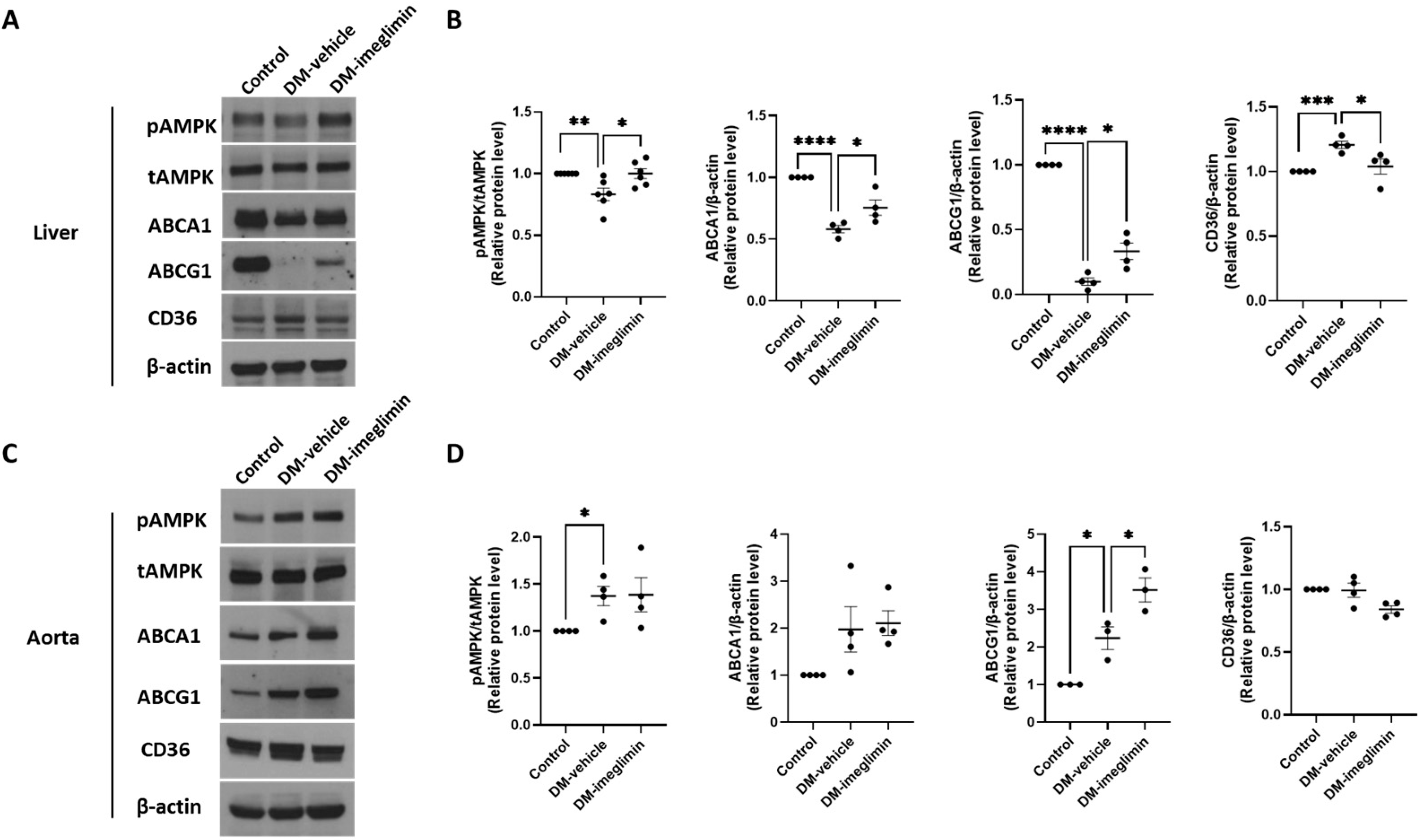
3.6. Effects of Imeglimin on ABCA1, ABCG1, and CD36 Expression, and AMPK Activation in the Liver and Aorta of Diabetic ApoE−/− Mice
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Beckman, J.A.; Creager, M.A.; Libby, P. Diabetes and atherosclerosis: Epidemiology, pathophysiology, and management. JAMA 2002, 287, 2570–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, E.; Song, S.O.; Kim, H.S.; Son, K.J.; Jee, S.H.; Cha, B.S.; Lee, B.W. Improvement in Age at Mortality and Changes in Causes of Death in the Population with Diabetes: An Analysis of Data from the Korean National Health Insurance and Statistical Information Service, 2006 to 2018. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 37, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; Li, L.; Wang, M.; Ma, Q.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, J.; Li, B.; Zhang, B.; Liu, H.; et al. Diabetes Mellitus Promotes the Development of Atherosclerosis: The Role of NLRP3. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 900254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chistiakov, D.A.; Melnichenko, A.A.; Myasoedova, V.A.; Grechko, A.V.; Orekhov, A.N. Mechanisms of foam cell formation in atherosclerosis. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 95, 1153–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Daugherty, A. Atherosclerosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2015, 35, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahaman, S.O.; Lennon, D.J.; Febbraio, M.; Podrez, E.A.; Hazen, S.L.; Silverstein, R.L. A CD36-dependent signaling cascade is necessary for macrophage foam cell formation. Cell Metab. 2006, 4, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, M. ABCA1 and ABCG1 as potential therapeutic targets for the prevention of atherosclerosis. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2022, 148, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lou, N.; Liu, X.; Zhuang, X.; Chen, S. Exploring new mechanisms of Imeglimin in diabetes treatment: Amelioration of mitochondrial dysfunction. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 175, 116755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubourg, J.; Fouqueray, P.; Thang, C.; Grouin, J.M.; Ueki, K. Efficacy and Safety of Imeglimin Monotherapy Versus Placebo in Japanese Patients With Type 2 Diabetes (TIMES 1): A Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Parallel-Group, Multicenter Phase 3 Trial. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, 952–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubourg, J.; Fouqueray, P.; Quinslot, D.; Grouin, J.M.; Kaku, K. Long-term safety and efficacy of imeglimin as monotherapy or in combination with existing antidiabetic agents in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes (TIMES 2): A 52-week, open-label, multicentre phase 3 trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2022, 24, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reilhac, C.; Dubourg, J.; Thang, C.; Grouin, J.M.; Fouqueray, P.; Watada, H. Efficacy and safety of imeglimin add-on to insulin monotherapy in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes (TIMES 3): A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial with a 36-week open-label extension period. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2022, 24, 838–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallakou-Bozec, S.; Vial, G.; Kergoat, M.; Fouqueray, P.; Bolze, S.; Borel, A.L.; Fontaine, E.; Moller, D.E. Mechanism of action of Imeglimin: A novel therapeutic agent for type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2021, 23, 664–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Final Guidance for Industry: Guidance for Industry: Diabetes Mellitus–Evaluating Cardiovascular Risk in New Antidiabetic Therapies to Treat Type 2 Diabetes; U.S. Department of Health and Human Resources: Washington, WA, USA, 2008.
- Detaille, D.; Vial, G.; Borel, A.L.; Cottet-Rouselle, C.; Hallakou-Bozec, S.; Bolze, S.; Fouqueray, P.; Fontaine, E. Imeglimin prevents human endothelial cell death by inhibiting mitochondrial permeability transition without inhibiting mitochondrial respiration. Cell Death Discov. 2016, 2, 15072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachaux, M.; Soulie, M.; Hamzaoui, M.; Bailly, A.; Nicol, L.; Remy-Jouet, I.; Renet, S.; Vendeville, C.; Gluais-Dagorn, P.; Hallakou-Bozec, S.; et al. Short-and long-term administration of imeglimin counters cardiorenal dysfunction in a rat model of metabolic syndrome. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. 2020, 3, e00128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Kang, Y.; Jeon, J.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, D.J.; Lee, K.W.; Han, S.J. Imeglimin attenuates NLRP3 inflammasome activation by restoring mitochondrial functions in macrophages. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2024, 155, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, H.; Iwashita, K.; Iwasa, M.; Kato, S.; Yamakage, H.; Suganami, T.; Tanaka, M.; Satoh-Asahara, N. Imeglimin Exhibits Novel Anti-Inflammatory Effects on High-Glucose-Stimulated Mouse Microglia through ULK1-Mediated Suppression of the TXNIP-NLRP3 Axis. Cells 2024, 13, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjurjo, L.; Castelblanco, E.; Julve, J.; Villalmanzo, N.; Tellez, E.; Ramirez-Morros, A.; Alonso, N.; Mauricio, D.; Sarrias, M.R. Contribution of Elevated Glucose and Oxidized LDL to Macrophage Inflammation: A Role for PRAS40/Akt-Dependent Shedding of Soluble CD14. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyandwi, J.B.; Ko, Y.S.; Jin, H.; Yun, S.P.; Park, S.W.; Kim, H.J. Rosmarinic Acid Increases Macrophage Cholesterol Efflux through Regulation of ABCA1 and ABCG1 in Different Mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Hashem, M.; Wiehler, W.B.; Lau, W.; Martin, J.; Reid, J.; Triggle, C. Endothelial dysfunction in the streptozotocin-induced diabetic apoE-deficient mouse. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2005, 146, 1110–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozu, T.; Miyagishi, S.; Ishioh, M.; Takakusaki, K.; Okumura, T. Imeglimin prevents visceral hypersensitivity and colonic hyperpermeability in irritable bowel syndrome rat model. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2023, 153, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; Ling, W.; Feng, X.; Xia, M. Adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase induces cholesterol efflux from macrophage-derived foam cells and alleviates atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 33499–33509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, A.; Wang, J.; Yang, L.; An, Y.; Zhu, H. AMPK activation enhances the anti-atherogenic effects of high density lipoproteins in apoE(−/−) mice. J. Lipid Res. 2017, 58, 1536–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunjathoor, V.V.; Febbraio, M.; Podrez, E.A.; Moore, K.J.; Andersson, L.; Koehn, S.; Rhee, J.S.; Silverstein, R.; Hoff, H.F.; Freeman, M.W. Scavenger receptors class A-I/II and CD36 are the principal receptors responsible for the uptake of modified low density lipoprotein leading to lipid loading in macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 49982–49988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, A.C.; Han, J.; Febbraio, M.; Silversterin, R.L.; Hajjar, D.P. Role of CD36, the macrophage class B scavenger receptor, in atherosclerosis. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2001, 947, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Febbraio, M.; Guy, E.; Silverstein, R.L. Stem cell transplantation reveals that absence of macrophage CD36 is protective against atherosclerosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2004, 24, 2333–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Febbraio, M.; Podrez, E.A.; Smith, J.D.; Hajjar, D.P.; Hazen, S.L.; Hoff, H.F.; Sharma, K.; Silverstein, R.L. Targeted disruption of the class B scavenger receptor CD36 protects against atherosclerotic lesion development in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2000, 105, 1049–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hozumi, K.; Sugawara, K.; Ishihara, T.; Ishihara, N.; Ogawa, W. Effects of imeglimin on mitochondrial function, AMPK activity, and gene expression in hepatocytes. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, N.; Kimura, A.P.; Yoshizaki, T.; Ohmura, K. Imeglimin modulates mitochondria biology and facilitates mitokine secretion in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Life Sci. 2024, 349, 122735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.B.; Zhou, G.; Li, C. AMPK: An emerging drug target for diabetes and the metabolic syndrome. Cell Metab. 2009, 9, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, H.; Sun, W.; Yi, Q. The role of AMPK in macrophage metabolism, function and polarisation. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanada, J.; Kimura, T.; Shimoda, M.; Iwamoto, Y.; Iwamoto, H.; Dan, K.; Fushimi, Y.; Katakura, Y.; Nogami, Y.; Shirakiya, Y.; et al. Protective effects of imeglimin on the development of atherosclerosis in ApoE KO mice treated with STZ. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2024, 23, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubourg, J.; Ueki, K.; Grouin, J.M.; Fouqueray, P. Efficacy and safety of imeglimin in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes: A 24-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging phase 2b trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2021, 23, 800–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Control Group (n = 4) | DM-Vehicle Group (n = 8) | DM-Imeglimin Group (n = 8) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fasting glucose level (mg/dL) | 300 ± 27.58 | 712.4 ± 27.35 | 606.6 ± 27.74 * |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 540 ± 39.53 | 1257 ± 61.20 | 935.5 ± 10.8 * |
| Triglyceride (mg/dL) | 109.5 ± 11.85 | 134.5 ± 15.73 | 98.63 ± 23.80 |
| HDL cholesterol (mg/dL) | 48.25 ± 3.065 | 110.5 ± 11.01 | 84.13 ± 10.64 |
| LDL cholesterol (mg/dL) | 245.5 ± 17.40 | 962.3 ± 60.93 | 697.3 ± 83.07 * |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.175 ± 0.0104 | 0.2588 ± 0.0166 | 0.2263 ± 0.0169 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.Y.; Kang, Y.; Jeon, J.Y.; Han, S.J. Imeglimin Inhibits Macrophage Foam Cell Formation and Atherosclerosis in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic ApoE-Deficient Mice. Cells 2025, 14, 472. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14070472
Lee JY, Kang Y, Jeon JY, Han SJ. Imeglimin Inhibits Macrophage Foam Cell Formation and Atherosclerosis in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic ApoE-Deficient Mice. Cells. 2025; 14(7):472. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14070472
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Ji Yeon, Yup Kang, Ja Young Jeon, and Seung Jin Han. 2025. "Imeglimin Inhibits Macrophage Foam Cell Formation and Atherosclerosis in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic ApoE-Deficient Mice" Cells 14, no. 7: 472. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14070472
APA StyleLee, J. Y., Kang, Y., Jeon, J. Y., & Han, S. J. (2025). Imeglimin Inhibits Macrophage Foam Cell Formation and Atherosclerosis in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic ApoE-Deficient Mice. Cells, 14(7), 472. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14070472






