Adipose Tissue Stem Cells (ASCs) and ASC-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Prevent the Development of Experimental Peritoneal Fibrosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Adipose-Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells
2.3. Isolation of EVs
2.4. Characterization of EVs
2.5. Experimental Design
2.6. GC Toxicity on ASCs
2.7. PM Histomorphometry
2.8. Immunohistochemistry and Immunofluorescence
2.9. Quantitative Assessment of Angiogenesis
2.10. Real-Time Quantitative PCR
2.11. Peritoneal Function
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Isolation and Characterization of ASCs and EVs
3.2. ASC Viability
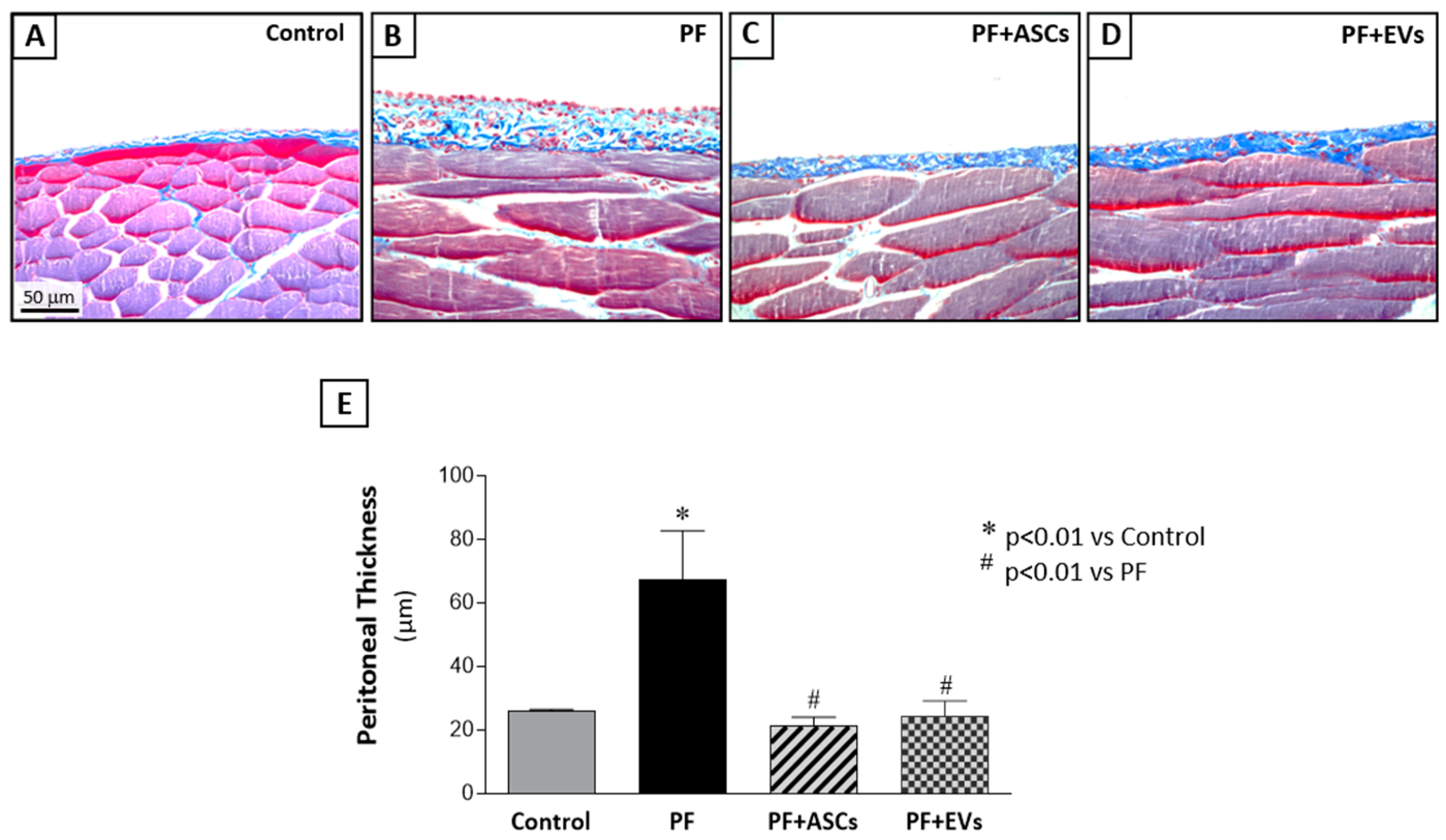
3.3. PF Experimental Model
3.4. ASC and EV Treatments Were Equally Efficient in Protecting the Development of FP
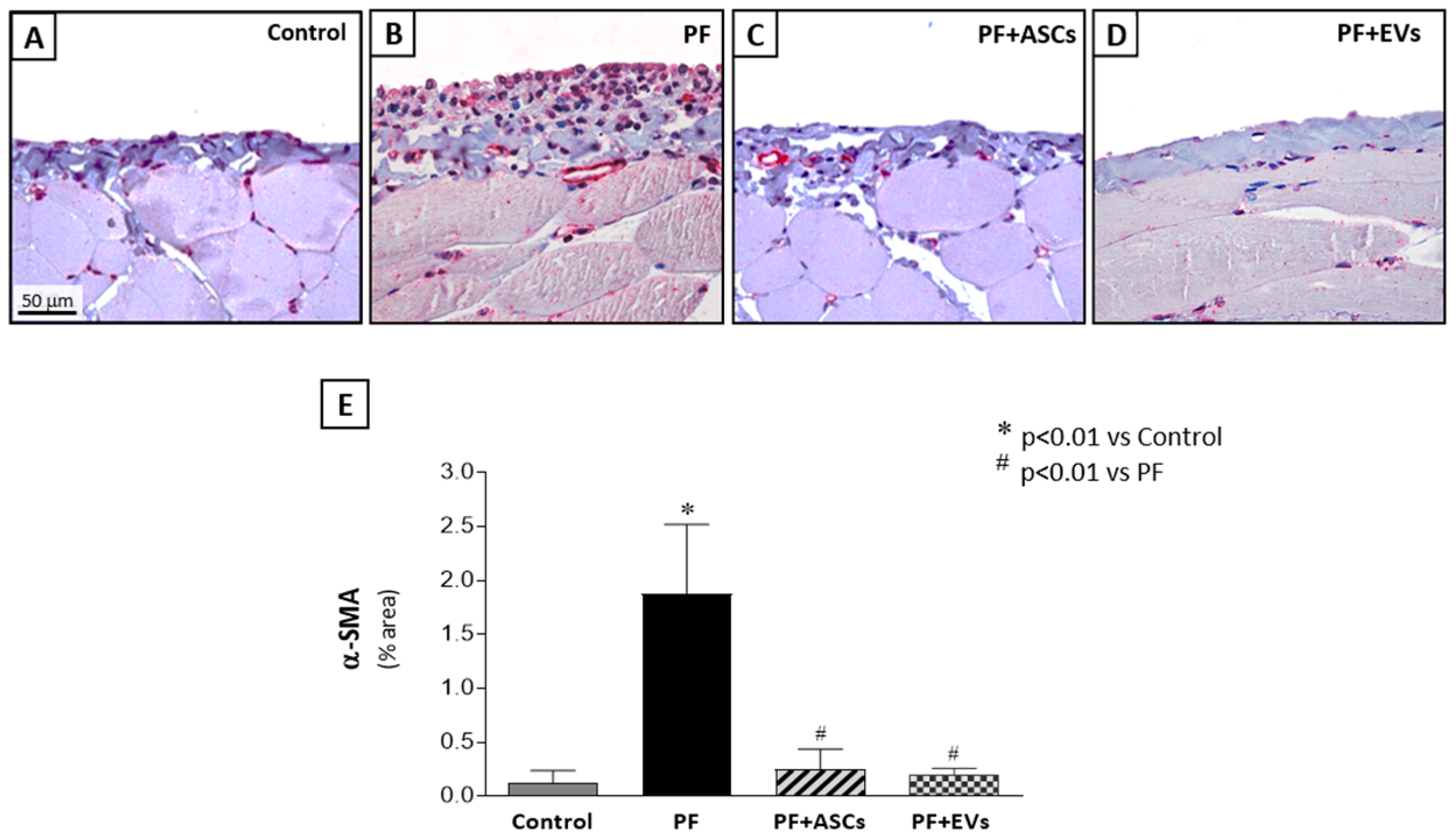
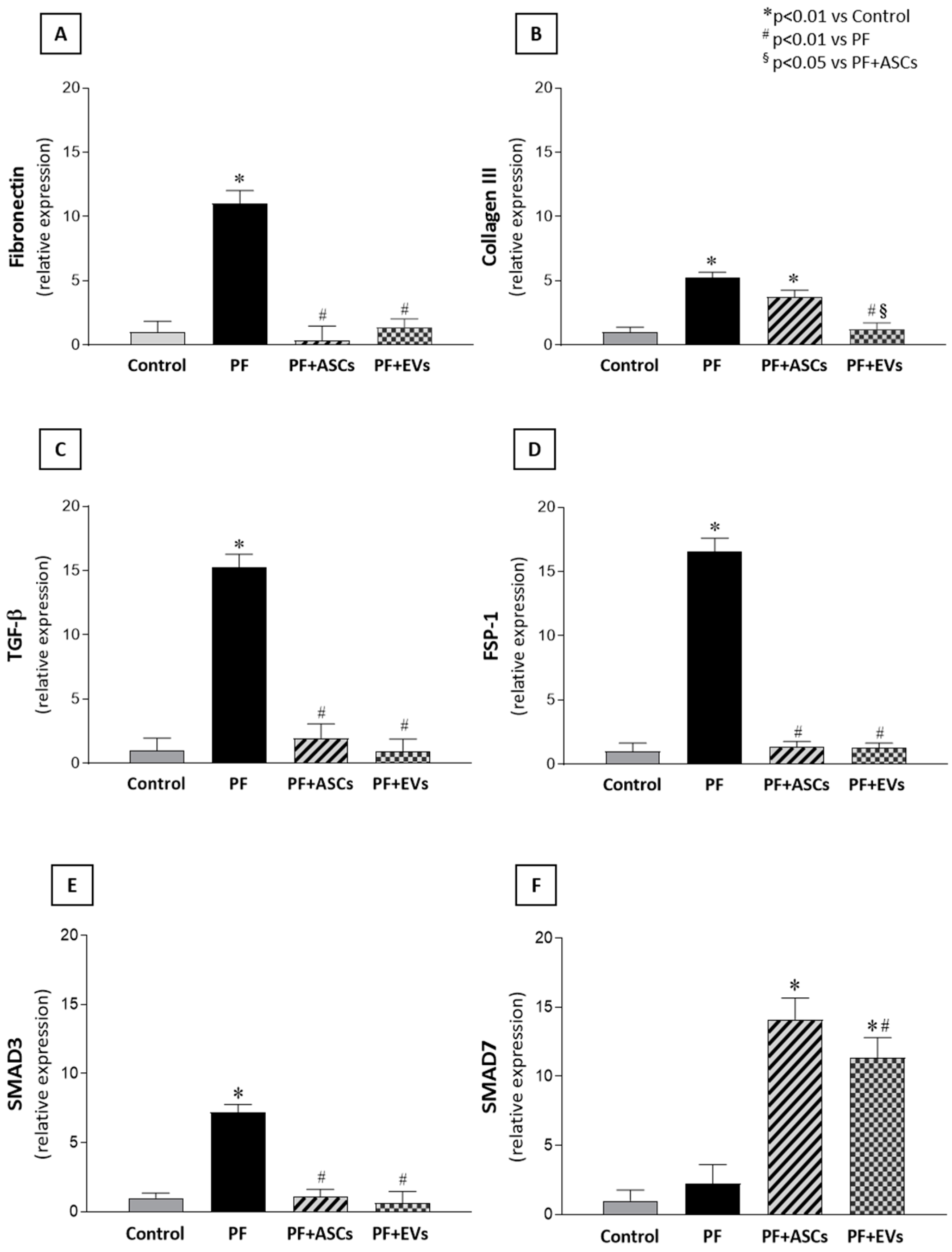
3.5. Administration of ASC or EV Decreased the Number of Myofibroblasts and Reduced the Expression of Factors Involved in PF
3.6. Anti-Fibrotic Effects of ASCs and EVs Are Mediated by the TGF-β/Smad Pathway
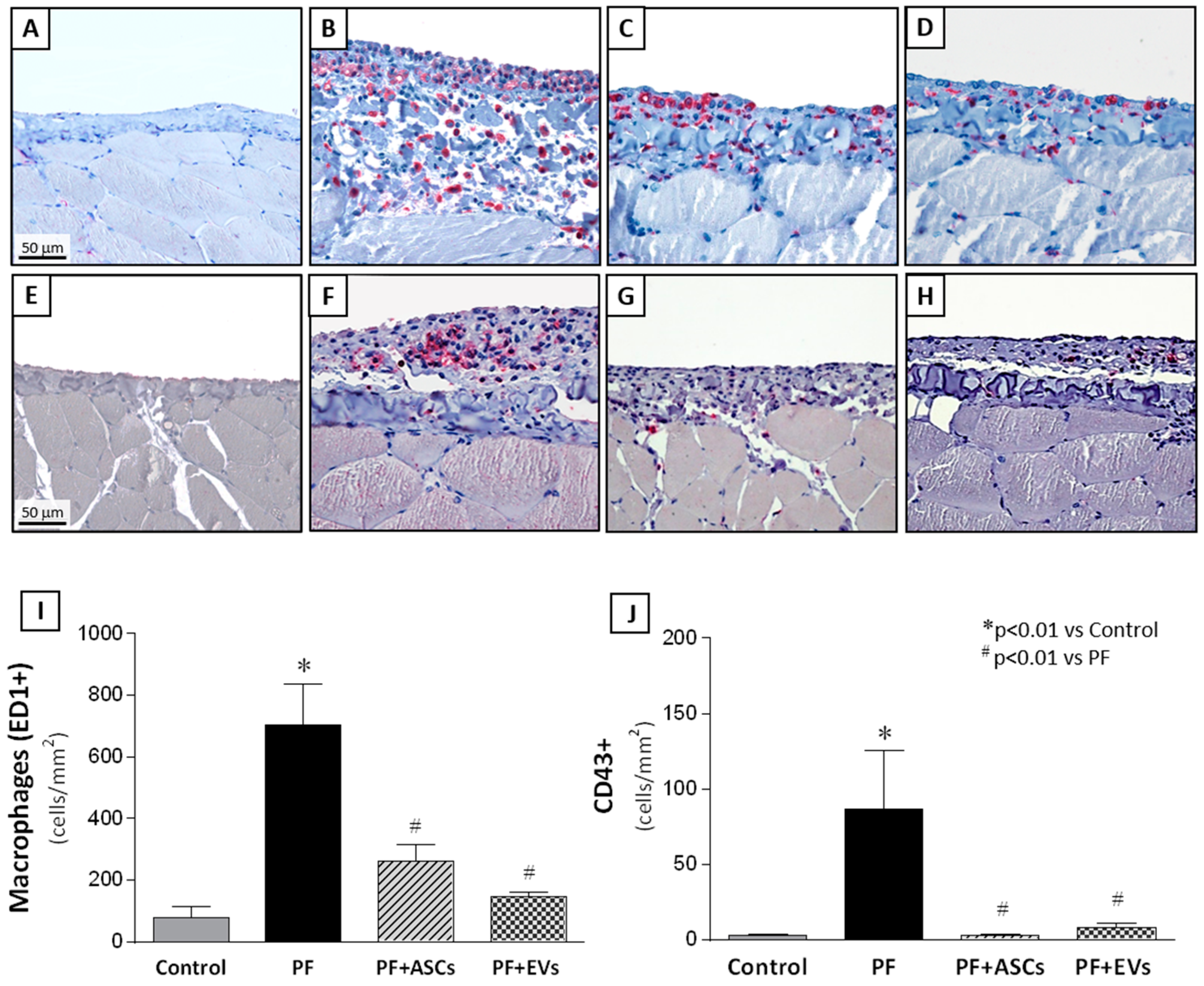
3.7. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of ASCs and EVs
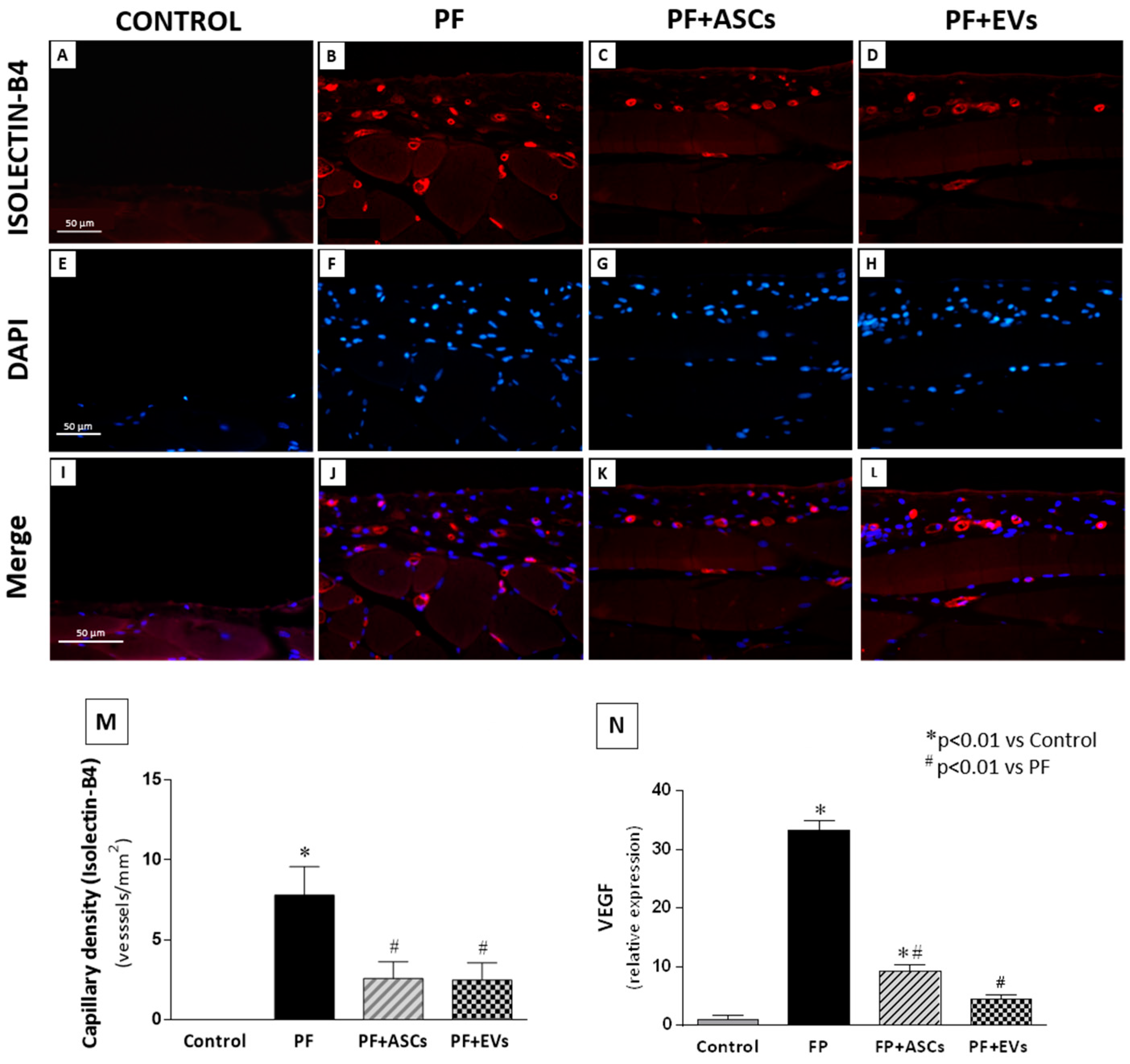
3.8. Effects of ASCs and EVs on PM Angiogenesis
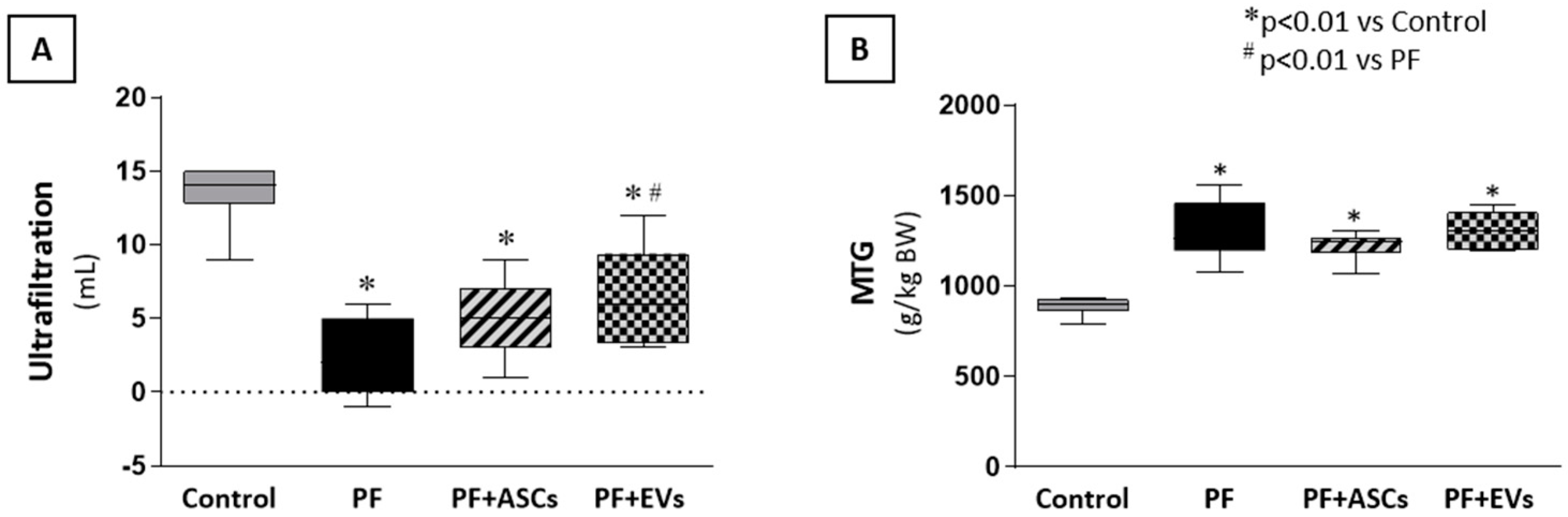
3.9. ASCs and EVs Preserved PM Function
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Himmelfarb, J.; Vanholder, R.; Mehrotra, R.; Tonelli, M. The current and future landscape of dialysis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2020, 16, 573–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devuyst, O.; Margetts, P.J.; Topley, N. The pathophysiology of the peritoneal membrane. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 21, 1077–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.K.; Chow, K.M.; Van de Luijtgaarden, M.W.M.; Johnson, D.W.; Jager, K.J.; Mehrotra, R.; Naicker, S.; Pecoits-Filho, R.; Yu, X.Q.; Lameire, N. Changes in the worldwide epidemiology of peritoneal dialysis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2017, 13, 90–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Bajo, M.; del Peso, G.; Yu, X.; Selgas, R. Preventing peritoneal membrane fibrosis in peritoneal dialysis patients. Kidney Int. 2016, 90, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, F.M.O.; Costalonga, E.C.; Silva, C.; Carreira, A.C.O.; Gomes, S.A.; Sogayar, M.C.; Fanelli, C.; Noronha, I.L. Tamoxifen and bone morphogenic protein-7 modulate fibrosis and inflammation in the peritoneal fibrosis model developed in uremic rats. Mol. Med. 2019, 25, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, P.; Sekiguchi, Y.; Oh, K.; Patterson, S.E.; Kolb, M.R.J.; Margetts, P.J. Smad3-dependent and -independent pathways are involved in peritoneal membrane injury. Kidney Int. 2010, 77, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.; Yu, X.; Huang, X.; Yu, J.; Lan, H.Y. Opposing roles for Smad2 and Smad3 in peritoneal fibrosis in vivo and in vitro. Am. J. Pathol. 2014, 184, 2275–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Leung, J.C.K.; Lam, M.F.; Chan, L.Y.Y.; Tsang, A.W.L.; Lan, H.Y.; Lai, K.N. Smad7 transgene attenuates peritoneal fibrosis in uremic rats treated with peritoneal dialysis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 18, 2689–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baştuğ, F.; Gündüz, Z.; Tülpar, S.; Torun, Y.A.; Akgün, H.; Dörterler, E.; Düşünsel, R.; Poyrazoğlu, H.; Baştuğ, O.; Dursun, İ. Compare the effects of intravenous and intraperitoneal mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on ultrafiltration failure in a rat model of chronic peritoneal dialysis. Ren. Fail. 2014, 36, 1428–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-Y.; Chang, P.-Y.; Chen, J.-Y.; Wu, B.-S.; Yang, A.-H.; Lee, O.K.-S. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells attenuate dialysis-induced peritoneal fibrosis by modulating macrophage polarization via interleukin-6. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2021, 12, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costalonga, E.C.; Fanelli, C.; Garnica, M.R.; Noronha, I.L. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells modulate fibrosis and inflammation in the peritoneal fibrosis model developed in uremic rats. Stem Cells Int. 2020, 2020, 3768718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alatab, S.; Shekarchian, S.; Najafi, I.; Moghadasali, R.; Ahmadbeigi, N.; Pourmand, M.R.; Bolurieh, T.; Jaroughi, N.; Pourmand, G.; Aghdami, N. Systemic infusion of autologous adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells in peritoneal dialysis patients: Feasibility and safety. Cell J. 2019, 20, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafarinia, M.; Alsahebfosoul, F.; Salehi, H.; Eskandari, N.; Ganjalikhani-Hakemi, M. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles: A novel cell-free therapy. Immunol. Investig. 2020, 49, 758–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raposo, G.; Stoorvogel, W. Extracellular vesicles: Exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 200, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yáñez-Mó, M.; Siljander, P.R.-M.; Andreu, Z.; Bedina Zavec, A.; Borràs, F.E.; Buzas, E.I.; Buzas, K.; Casal, E.; Cappello, F.; Carvalho, J.; et al. Biological properties of extracellular vesicles and their physiological functions. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 27066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gnecchi, M.; Zhang, Z.; Ni, A.; Dzau, V.J. Paracrine mechanisms in adult stem cell signaling and therapy. Circ. Res. 2008, 103, 1204–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Tredget, E.E.; Wu, P.Y.G.; Wu, Y. Paracrine factors of mesenchymal stem cells recruit macrophages and endothelial lineage cells and enhance wound healing. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiklander, O.P.B.; Nordin, J.Z.; O’Loughlin, A.; Gustafsson, Y.; Corso, G.; Mäger, I.; Vader, P.; Lee, Y.; Sork, H.; Seow, Y.; et al. Extracellular vesicle in vivo biodistribution is determined by cell source, route of administration and targeting. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 26316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Börger, V.; Bremer, M.; Ferrer-Tur, R.; Gockeln, L.; Stambouli, O.; Becic, A.; Giebel, B. Mesenchymal stem/stromal cell-derived extracellular vesicles and their potential as novel immunomodulatory therapeutic agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collino, F.; Bruno, S.; Incarnato, D.; Dettori, D.; Neri, F.; Provero, P.; Pomatto, M.; Oliviero, S.; Tetta, C.; Quesenberry, P.J.; et al. AKI recovery induced by mesenchymal stromal cell-derived extracellular vesicles carrying microRNAs. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 2349–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grange, C.; Bussolati, B. Extracellular vesicles in kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2022, 18, 499–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.Y.; Kim, T.Y.; Lee, M.; Kim, S.H.; Jhee, J.H.; Lee, Y.K.; Kim, H.J.; Park, H.C. Kidney mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles engineered to express erythropoietin improve renal anemia in mice with chronic kidney disease. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2022, 18, 980–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grange, C.; Tritta, S.; Tapparo, M.; Cedrino, M.; Tetta, C.; Camussi, G.; Brizzi, M.F. Stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles inhibit and revert fibrosis progression in a mouse model of diabetic nephropathy. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, W.; El-Ansary, M.; Sabry, D.; Mostafa, M.A.; Fayad, T.; Kotb, E.; Temraz, M.; Saad, A.-N.; Essa, W.; Adel, H. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells derived extracellular vesicles can safely ameliorate the progression of chronic kidney diseases. Biomater. Res. 2016, 20, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kushiyama, T.; Oda, T.; Yamada, M.; Higashi, K.; Yamamoto, K.; Oshima, N.; Sakurai, Y.; Miura, S.; Kumagai, H. Effects of liposome-encapsulated clodronate on chlorhexidine gluconate-induced peritoneal fibrosis in rats. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2011, 26, 3143–3154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costalonga, E.C.; de Freitas, L.J.; Aragone, D.d.S.P.; Silva, F.M.O.; Noronha, I.L. Anti-fibrotic effects of valproic acid in experimental peritoneal fibrosis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pepineli, R.; Gouveia, P.Q.; Garnica, M.G.; Fanelli, C.; Martini, D.; Andrade, L.; Gomes, S.A.; Noronha, I.L. Mesenchymal stem cells derived from adipose tissue ameliorate chronic allograft rejection in the long term in a rat experimental model of kidney transplantation. J. Stem Cells Res. Dev. Ther. 2020, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caplan, A.I. Mesenchymal stem cells. J. Orthop. Res. 1991, 9, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, F.; Chiu, S.M.; Motan, D.A.L.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, L.; Ji, H.; Tse, H.; Fu, Q.; Lian, Q. Mesenchymal stem cells and immunomodulation: Current status and future prospects. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nargesi, A.A.; Lerman, L.O.; Eirin, A. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles for kidney repair: Current status and looming challenges. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2017, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ornellas, F.M.; Ramalho, R.J.; Fanelli, C.; Garnica, M.R.; Malheiros, D.M.A.C.; Martini, S.V.; Morales, M.M.; Noronha, I.L. Mesenchymal stromal cells induce podocyte protection in the puromycin injury model. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandeira, E.; Oliveira, H.; Silva, J.D.; Menna-Barreto, R.F.S.; Takyia, C.M.; Suk, J.S.; Witwer, K.W.; Paulaitis, M.E.; Hanes, J.; Rocco, P.R.M.; et al. Therapeutic effects of adipose-tissue-derived mesenchymal stromal cells and their extracellular vesicles in experimental silicosis. Respir. Res. 2018, 19, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margetts, P.J.; Bonniaud, P. Basic mechanisms and clinical implications of peritoneal fibrosis. Perit. Dial. Int. 2003, 23, 530–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosanović, M.; Llorente, A.; Glamočlija, S.; Valdivielso, J.M.; Bozic, M. Extracellular vesicles and renal fibrosis: An odyssey toward a new therapeutic approach. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, K.Y.; Jacobsen, M.; Schrøder, H.D.; Aagaard, P.; Nielsen, J.L.; Jørgensen, A.N.; Boyle, E.; Bech, R.D.; Rosmark, S.; Diederichsen, L.P.; et al. THE immune system in sporadic inclusion body myositis patients is not compromised by blood-flow restricted exercise training. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2019, 21, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Li, Z.; Sun, W.; Yang, G.; Xing, C.; Yuan, L. Delivery efficacy differences of intravenous and intraperitoneal injection of exosomes: Perspectives from tracking dye labeled and miRNA encapsulated exosomes. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2020, 17, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruno, S.; Grange, C.; Collino, F.; Deregibus, M.C.; Cantaluppi, V.; Biancone, L.; Tetta, C.; Camussi, G. Microvesicles derived from mesenchymal stem cells enhance survival in a lethal model of acute kidney injury. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Wang, Y.; Sun, S.; Yu, M.; Wang, C.; Pei, X.; Zhu, B.; Wu, J.; Zhao, W.; Bruno, S.; et al. Bone marrow stem cells-derived microvesicles protect against renal injury in the mouse remnant kidney model. Nephrology 2012, 17, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, X.; Zhang, G.; Cheng, Z.; Yin, D.; Du, T.; Ju, G.; Miao, S.; Liu, G.; Lu, M.; Zhu, Y. Microvesicles derived from human Wharton’s jelly mesenchymal stromal cells ameliorate renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats by suppressing CX3CL1. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2014, 5, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatti, S.; Bruno, S.; Deregibus, M.C.; Sordi, A.; Cantaluppi, V.; Tetta, C.; Camussi, G. Microvesicles derived from human adult mesenchymal stem cells protect against ischaemia-reperfusion-induced acute and chronic kidney injury. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2011, 26, 1474–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, T.; Nakashima, A.; Doi, S.; Kawamoto, T.; Honda, K.; Yokoyama, Y.; Doi, T.; Higashi, Y.; Yorioka, N.; Kato, Y.; et al. Mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate experimental peritoneal fibrosis by suppressing inflammation and inhibiting TGF-Β1 signaling. Kidney Int. 2013, 84, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakabayashi, K.; Hamada, C.; Kanda, R.; Nakano, T.; Io, H.; Horikoshi, S.; Tomino, Y. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells transplantation facilitate experimental peritoneal fibrosis repair by suppressing epithelial–mesenchymal transition. J. Nephrol. 2014, 27, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anders, H.-J.; Ryu, M. Renal microenvironments and macrophage phenotypes determine progression or resolution of renal inflammation and fibrosis. Kidney Int. 2011, 80, 915–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, P.M.-K.; Nikolic-Paterson, D.J.; Lan, H.-Y. Macrophages: Versatile players in renal inflammation and fibrosis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2019, 15, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Ortega, M.; Rayego-Mateos, S.; Lamas, S.; Ortiz, A.; Rodrigues-Diez, R.R. Targeting the progression of chronic kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2020, 16, 269–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gouveia, P.Q.; Fanelli, C.; Ornellas, F.M.; Garnica, M.R.; Francini, A.L.R.; Murata, G.M.; Matheus, L.H.G.; Morales, M.M.; Noronha, I.L. Adipose Tissue Stem Cells (ASCs) and ASC-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Prevent the Development of Experimental Peritoneal Fibrosis. Cells 2025, 14, 436. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14060436
Gouveia PQ, Fanelli C, Ornellas FM, Garnica MR, Francini ALR, Murata GM, Matheus LHG, Morales MM, Noronha IL. Adipose Tissue Stem Cells (ASCs) and ASC-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Prevent the Development of Experimental Peritoneal Fibrosis. Cells. 2025; 14(6):436. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14060436
Chicago/Turabian StyleGouveia, Priscila Q., Camilla Fanelli, Felipe M. Ornellas, Margoth R. Garnica, Ana L. R. Francini, Gilson M. Murata, Luiz H. G. Matheus, Marcelo M. Morales, and Irene L. Noronha. 2025. "Adipose Tissue Stem Cells (ASCs) and ASC-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Prevent the Development of Experimental Peritoneal Fibrosis" Cells 14, no. 6: 436. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14060436
APA StyleGouveia, P. Q., Fanelli, C., Ornellas, F. M., Garnica, M. R., Francini, A. L. R., Murata, G. M., Matheus, L. H. G., Morales, M. M., & Noronha, I. L. (2025). Adipose Tissue Stem Cells (ASCs) and ASC-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Prevent the Development of Experimental Peritoneal Fibrosis. Cells, 14(6), 436. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14060436




