Bcl3 Deficiency Leads to Hyperinflammation in Zebrafish
Highlights
- The establishment of zebrafish as a vertebrate model for dissecting Bcl3 mediated immune reaction.
- Anti-inflammatory treatment effectively alleviated inflammation and improved survival.
- Bcl3 functions as a key negative regulator of immune activation in vivo.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Zebrafish Maintenance
2.3. Bcl3 Knockout Generation
2.4. DNA Extraction and Genotyping
2.5. Calculation of Body Surface Area (BSA) and Body Mass Index (BMI)
2.6. Survival Analysis
2.7. Food Intake Assay
2.8. Motility Assay
2.9. Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) Staining
2.10. RNA Extraction and RT-qPCR
2.11. RNA Sequencing (RNA-seq)
2.12. LPS and Poly(I:C) Injection
2.13. Immersion of LPS-Injected Larvae in Dex Solution
2.14. Dex Injections in WT and bcl3−/− Zebrafish
2.15. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Bcl3 Deficiency Leads to Reduced Growth and Survival in Zebrafish
3.2. Bcl3 Deficiency Impairs Feeding Behavior and Motility in Zebrafish
3.3. Loss of Bcl3 Compromises Immune Organ Integrity and Immune Cell Function
3.4. Transcriptomic Analyses Reveals Systemic Immune Hyperactivation in bcl3 Deficient Zebrafish
3.5. Bcl3 Deficiency Exacerbates Inflammatory and Antiviral Responses to LPS and Poly(I:C) Stimulation
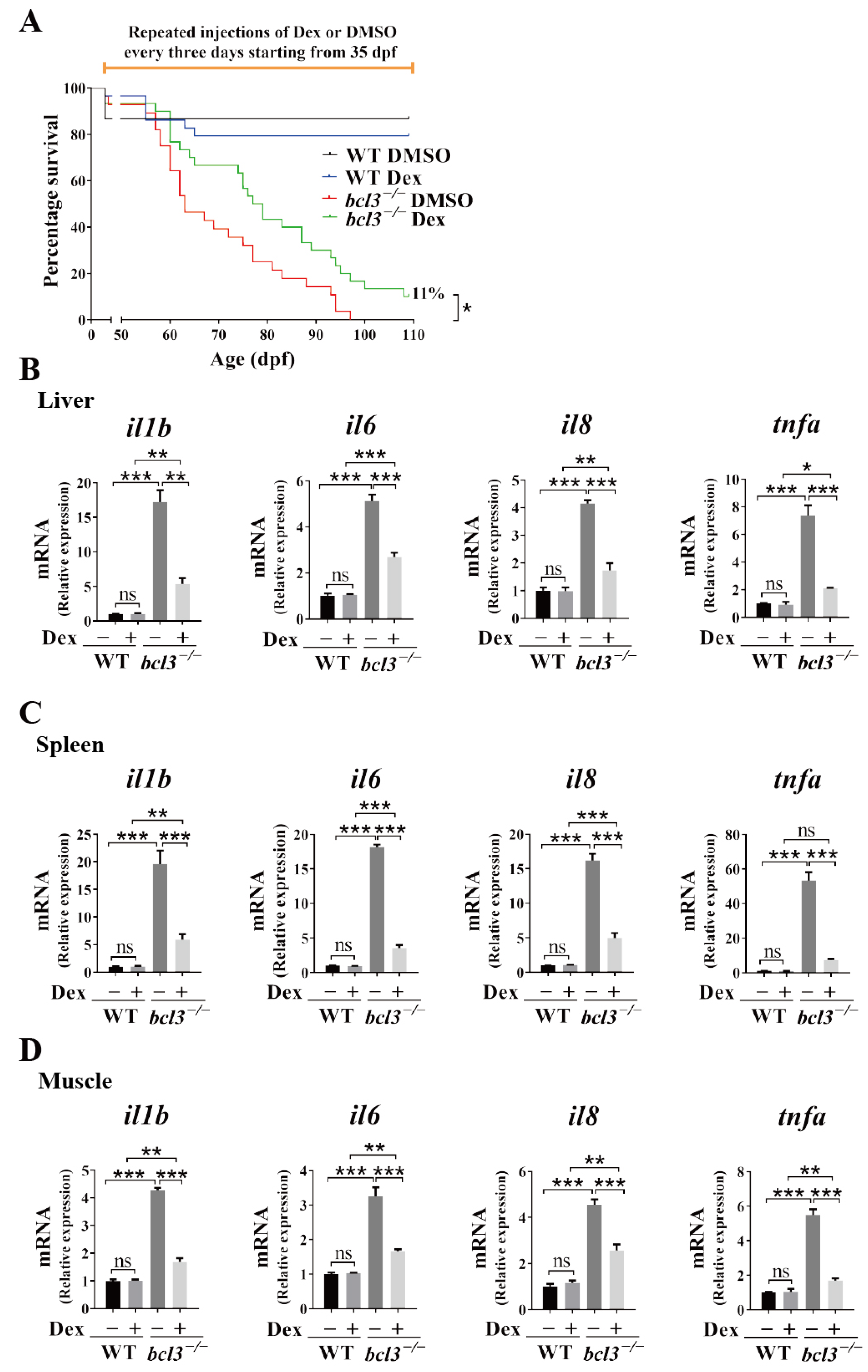
3.6. Anti-Inflammatory Treatment Improves the Survival of bcl3−/− Zebrafish
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ohno, H.; Doi, S.; Yabumoto, K.; Fukuhara, S.; McKeithan, T.W. Molecular characterization of the t(14;19)(q32;q13) translocation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 1993, 7, 2057–2063. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Paun, A.; Claudio, E.; Wang, H.; Siebenlist, U. The tumor promoter and NF-kappaB modulator Bcl-3 regulates splenic B cell development. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 5984–5992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westerheide, S.D.; Mayo, M.W.; Anest, V.; Hanson, J.L.; Baldwin, A.S., Jr. The putative oncoprotein Bcl-3 induces cyclin D1 to stimulate G1 transition. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2001, 21, 8428–8436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turnham, D.J.; Yang, W.W.; Davies, J.; Varnava, A.; Ridley, A.J.; Conlan, R.S.; Clarkson, R.W.E. Bcl-3 promotes multi-modal tumour cell migration via NF-kappaB1 mediated regulation of Cdc42. Carcinogenesis 2020, 41, 1432–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban, B.C.; Collard, T.J.; Eagle, C.J.; Southern, S.L.; Greenhough, A.; Hamdollah-Zadeh, M.; Ghosh, A.; Poulsom, R.; Paraskeva, C.; Silver, A.; et al. BCL-3 expression promotes colorectal tumorigenesis through activation of AKT signalling. Gut 2016, 65, 1151–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornburg, N.J.; Pathmanathan, R.; Raab-Traub, N. Activation of nuclear factor-kappaB p50 homodimer/Bcl-3 complexes in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 8293–8301. [Google Scholar]
- Franzoso, G.; Bours, V.; Park, S.; Tomita-Yamaguchi, M.; Kelly, K.; Siebenlist, U. The candidate oncoprotein Bcl-3 is an antagonist of p50/NF-kappa B-mediated inhibition. Nature 1992, 359, 339–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bours, V.; Franzoso, G.; Azarenko, V.; Park, S.; Kanno, T.; Brown, K.; Siebenlist, U. The oncoprotein Bcl-3 directly transactivates through kappa B motifs via association with DNA-binding p50B homodimers. Cell 1993, 72, 729–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, T.; Nolan, G.P.; Liou, H.C.; Scott, M.L.; Baltimore, D. The candidate proto-oncogene bcl-3 encodes a transcriptional coactivator that activates through NF-kappa B p50 homodimers. Genes Dev. 1993, 7, 1354–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, J.; Takahara, T.; Akizawa, T.; Hino, O. Bcl-3, a member of the I kappa B proteins, has distinct specificity towards the Rel family of proteins. Oncogene 1993, 8, 2067–2073. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, W.; Deng, L.; Wang, H.; Wang, V.Y. Atypical IkappaB Bcl3 enhances the generation of the NF-kappaB p52 homodimer. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 930619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubelbeck, T.; Wichmann, N.O.; Raj, T.; Raj, C.; Ohnmacht, C.; Hovelmeyer, N.; Kramer, D.; Heissmeyer, V. Regulation and Function of the Atypical IkappaBs-Bcl-3, IkappaB(NS), and IkappaBzeta-in Lymphocytes and Autoimmunity. Eur. J. Immunol. 2025, 55, e202451273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, P.E.; Kiely, P.A.; Carmody, R.J. Inhibition of transcription by B cell Leukemia 3 (Bcl-3) protein requires interaction with nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB) p50. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 7059–7067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dechend, R.; Hirano, F.; Lehmann, K.; Heissmeyer, V.; Ansieau, S.; Wulczyn, F.G.; Scheidereit, C.; Leutz, A. The Bcl-3 oncoprotein acts as a bridging factor between NF-kappaB/Rel and nuclear co-regulators. Oncogene 1999, 18, 3316–3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, V.Y.; Huang, W.; Asagiri, M.; Spann, N.; Hoffmann, A.; Glass, C.; Ghosh, G. The transcriptional specificity of NF-kappaB dimers is coded within the kappaB DNA response elements. Cell Rep. 2012, 2, 824–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, C.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Tao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, Y.; Li, C.; Ye, D.; et al. Bcl-3 promotes Wnt signaling by maintaining the acetylation of beta-catenin at lysine 49 in colorectal cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, B.; Cai, L.; Choi, H.J.; Ohgi, K.A.; Tran, C.; Chen, C.; Chung, C.H.; Huber, O.; Rose, D.W.; et al. Transcriptional regulation of a metastasis suppressor gene by Tip60 and beta-catenin complexes. Nature 2005, 434, 921–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwata, H.; Watanabe, Y.; Miyoshi, H.; Yamamoto, M.; Kaisho, T.; Takeda, K.; Akira, S. IL-10-inducible Bcl-3 negatively regulates LPS-induced TNF-alpha production in macrophages. Blood 2003, 102, 4123–4129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagvadorj, J.; Naiki, Y.; Tumurkhuu, G.; Noman, A.S.; Iftekar, E.K.I.; Koide, N.; Komatsu, T.; Yoshida, T.; Yokochi, T. Interleukin (IL)-10 attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced IL-6 production via inhibition of IkappaB-zeta activity by Bcl-3. Innate Immun. 2009, 15, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehrke, N.; Worns, M.A.; Huber, Y.; Hess, M.; Straub, B.K.; Hovelmeyer, N.; Waisman, A.; Kim, Y.O.; Schuppan, D.; Galle, P.R.; et al. Hepatic B cell leukemia-3 promotes hepatic steatosis and inflammation through insulin-sensitive metabolic transcription factors. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 1188–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzoso, G.; Carlson, L.; Scharton-Kersten, T.; Shores, E.W.; Epstein, S.; Grinberg, A.; Tran, T.; Shacter, E.; Leonardi, A.; Anver, M.; et al. Critical roles for the Bcl-3 oncoprotein in T cell-mediated immunity, splenic microarchitecture, and germinal center reactions. Immunity 1997, 6, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoriello, C.; Zon, L.I. Hooked! Modeling human disease in zebrafish. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 2337–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, Y.M.; Toro, S.; Ramachandran, S.; Ruzicka, L.; Howe, D.G.; Eagle, A.; Kalita, P.; Martin, R.; Taylor Moxon, S.A.; Schaper, K.; et al. Zebrafish Models of Human Disease: Gaining Insight into Human Disease at ZFIN. ILAR J. 2017, 58, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howe, K.; Clark, M.D.; Torroja, C.F.; Torrance, J.; Berthelot, C.; Muffato, M.; Collins, J.E.; Humphray, S.; McLaren, K.; Matthews, L.; et al. The zebrafish reference genome sequence and its relationship to the human genome. Nature 2013, 496, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correa, R.G.; Tergaonkar, V.; Ng, J.K.; Dubova, I.; Izpisua-Belmonte, J.C.; Verma, I.M. Characterization of NF-kappa B/I kappa B proteins in zebra fish and their involvement in notochord development. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 5257–5268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, C.A.; Calderon, R.; Pavani, G.; Cheng, X.; Barakat, R.; Snella, E.; Liu, F.; Peng, X.; Essner, J.J.; Dorman, K.S.; et al. p65 signaling dynamics drive the developmental progression of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells through cell cycle regulation. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 7787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, G.; Liao, Q.; Zhang, D.; Rong, F.; Cai, X.; Fan, S.; Zhu, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, X.; et al. Zebrafish NF-kappaB/p65 Is Required for Antiviral Responses. J. Immunol. 2020, 204, 3019–3029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Giaimo, R.; Durovic, T.; Barquin, P.; Kociaj, A.; Lepko, T.; Aschenbroich, S.; Breunig, C.T.; Irmler, M.; Cernilogar, F.M.; Schotta, G.; et al. The Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Pathway Defines the Time Frame for Restorative Neurogenesis. Cell Rep. 2018, 25, 3241–3251.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.T.; Shi, K.H.; Su, Y.; Liang, L.Y.; Yan, Y.; Postlethwait, J.; Meng, A.M. Two variants of zebrafish p100 are expressed during embryogenesis and regulated by Nodal signaling. FEBS Lett. 2003, 543, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, W.Y.; Fu, Y.; Reyon, D.; Maeder, M.L.; Tsai, S.Q.; Sander, J.D.; Peterson, R.T.; Yeh, J.R.; Joung, J.K. Efficient genome editing in zebrafish using a CRISPR-Cas system. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 227–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jao, L.E.; Wente, S.R.; Chen, W. Efficient multiplex biallelic zebrafish genome editing using a CRISPR nuclease system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 13904–13909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashhadi, Z.; Huff Towle, H.; Schneider, C.; Davies, S.S. A Simple and Rapid Method to Measure Food Intake in Fish Using Brine Shrimp. Zebrafish 2020, 17, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, N.; Wang, Y.H.; Lee, H.K.; Ito, T.; Wang, Y.H.; Cao, W.; Liu, Y.J. Hassall’s corpuscles instruct dendritic cells to induce CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells in human thymus. Nature 2005, 436, 1181–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trede, N.S.; Langenau, D.M.; Traver, D.; Look, A.T.; Zon, L.I. The use of zebrafish to understand immunity. Immunity 2004, 20, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franza, M.; Varricchio, R.; Alloisio, G.; De Simone, G.; Di Bella, S.; Ascenzi, P.; di Masi, A. Zebrafish (Danio rerio) as a Model System to Investigate the Role of the Innate Immune Response in Human Infectious Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornet, V.; Douxfils, J.; Mandiki, S.N.M.; Kestemont, P. Early-life infection with a bacterial pathogen increases expression levels of innate immunity related genes during adulthood in zebrafish. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2020, 108, 103672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Lopez, A.; Tyrkalska, S.D.; Alcaraz-Perez, F.; Cabas, I.; Candel, S.; Martinez Morcillo, F.J.; Sepulcre, M.P.; Garcia-Moreno, D.; Cayuela, M.L.; Mulero, V. Evolution of LPS recognition and signaling: The bony fish perspective. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2023, 145, 104710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Cao, X.; Jin, X.; Jin, T. Pattern recognition receptors in zebrafish provide functional and evolutionary insight into innate immune signaling pathways. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2017, 14, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbomel, P.; Thisse, B.; Thisse, C. Ontogeny and behaviour of early macrophages in the zebrafish embryo. Development 1999, 126, 3735–3745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y. BCL3, GBP1, IFI16, and CCR1 as potential brain-derived biomarkers for parietal grey matter lesions in multiple sclerosis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 28543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Stone, S.; Lin, W. Role of nuclear factor kappaB in multiple sclerosis and experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Neural Regen. Res. 2018, 13, 1507–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meguro, K.; Suzuki, K.; Hosokawa, J.; Sanayama, Y.; Tanaka, S.; Furuta, S.; Ikeda, K.; Takatori, H.; Suto, A.; Sakamoto, A.; et al. Role of Bcl-3 in the development of follicular helper T cells and in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 2651–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beg, A.A.; Sha, W.C.; Bronson, R.T.; Ghosh, S.; Baltimore, D. Embryonic lethality and liver degeneration in mice lacking the RelA component of NF-kappa B. Nature 1995, 376, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klement, J.F.; Rice, N.R.; Car, B.D.; Abbondanzo, S.J.; Powers, G.D.; Bhatt, P.H.; Chen, C.H.; Rosen, C.A.; Stewart, C.L. IkappaBalpha deficiency results in a sustained NF-kappaB response and severe widespread dermatitis in mice. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1996, 16, 2341–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sha, W.C.; Liou, H.C.; Tuomanen, E.I.; Baltimore, D. Targeted disruption of the p50 subunit of NF-kappa B leads to multifocal defects in immune responses. Cell 1995, 80, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kontgen, F.; Grumont, R.J.; Strasser, A.; Metcalf, D.; Li, R.; Tarlinton, D.; Gerondakis, S. Mice lacking the c-rel proto-oncogene exhibit defects in lymphocyte proliferation, humoral immunity, and interleukin-2 expression. Genes Dev. 1995, 9, 1965–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caamano, J.H.; Rizzo, C.A.; Durham, S.K.; Barton, D.S.; Raventos-Suarez, C.; Snapper, C.M.; Bravo, R. Nuclear factor (NF)-kappa B2 (p100/p52) is required for normal splenic microarchitecture and B cell-mediated immune responses. J. Exp. Med. 1998, 187, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weih, F.; Carrasco, D.; Durham, S.K.; Barton, D.S.; Rizzo, C.A.; Ryseck, R.P.; Lira, S.A.; Bravo, R. Multiorgan inflammation and hematopoietic abnormalities in mice with a targeted disruption of RelB, a member of the NF-kappa B/Rel family. Cell 1995, 80, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, A.E.; Chang, A.B.; Purbey, P.K.; Williams, K.J.; Li, S.; Redelings, B.D.; Yeh, G.; Wu, Y.; Pope, S.D.; Venkatesh, B.; et al. Stepwise neofunctionalization of the NF-kappaB family member Rel during vertebrate evolution. Nat. Immunol. 2025, 26, 760–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, G.Y.; Li, W.G.; Suman, T.Y.; Jia, P.P.; Ma, Y.B.; Pei, D.S. Gut bacteria Vibrio sp. and Aeromonas sp. trigger the expression levels of proinflammatory cytokine: First evidence from the germ-free zebrafish. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 106, 518–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotman, J.; van Gils, W.; Butler, D.; Spaink, H.P.; Meijer, A.H. Rapid screening of innate immune gene expression in zebrafish using reverse transcription—Multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification. BMC Res. Notes 2011, 4, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.; Payan, B.; Zambrano, A.; Du, Y.; Bondesson, M.; Mohan, C. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate suppresses neutrophil migration speed in a transgenic zebrafish model accompanied by reduced inflammatory mediators. J. Inflamm. Res. 2019, 12, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madesh, S.; Murugan, R.; Sau, A.; Jubie, S.; Swaroop, A.K.; Rajagopal, R.; Kumaradoss, K.M.; Arockiaraj, J. Nano-Encapsulated Coumarin Derivative, CS-QM2 Inhibits Neoplasm Growth: Experimented in Zebrafish Model. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2025, 39, e70239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wang, W.; Zhao, Q.; Hu, G.; Deng, K.; Liu, Y. BCL3 exerts an oncogenic function by regulating STAT3 in human cervical cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 2016, 9, 6619–6629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Gao, J.; Liu, S.; Yu, L.; Zhang, W.; Liang, Y.; Wang, H. Transcription Coactivator BCL3 Acts as a Potential Regulator of Lipid Metabolism Through the Effects on Inflammation. J. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 14, 4915–4926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, C.; Ai, N.; Ge, W.; Wang, V.Y.-F. Bcl3 Deficiency Leads to Hyperinflammation in Zebrafish. Cells 2025, 14, 1935. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14241935
Fan C, Ai N, Ge W, Wang VY-F. Bcl3 Deficiency Leads to Hyperinflammation in Zebrafish. Cells. 2025; 14(24):1935. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14241935
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Chengjian, Nana Ai, Wei Ge, and Vivien Ya-Fan Wang. 2025. "Bcl3 Deficiency Leads to Hyperinflammation in Zebrafish" Cells 14, no. 24: 1935. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14241935
APA StyleFan, C., Ai, N., Ge, W., & Wang, V. Y.-F. (2025). Bcl3 Deficiency Leads to Hyperinflammation in Zebrafish. Cells, 14(24), 1935. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14241935







