Combined Preventive and Preconditioning Treatments for the Comorbidity of Alzheimer’s Disease and Ischemic Stroke in a GluN3A Knockout Mouse and a 5xFAD Mouse
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals, Animal Care, and Euthanasia Methods
2.2. Memantine Treatment
2.3. Cerebral Focal Ischemic Stroke Model of the Mouse
2.4. Local Cerebral Blood Flow Measurement (LCBF)
2.5. Animal Scarification Method
2.6. Ischemia-Induced Infarct Volume Assessments
2.7. Immunostaining and TUNEL Assays
2.8. Western Blotting Analysis
2.9. Locomotion and Sensorimotor Functional Tests
2.10. Social Behavior and Psychological Tests
2.11. Cognition Functional Tests
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
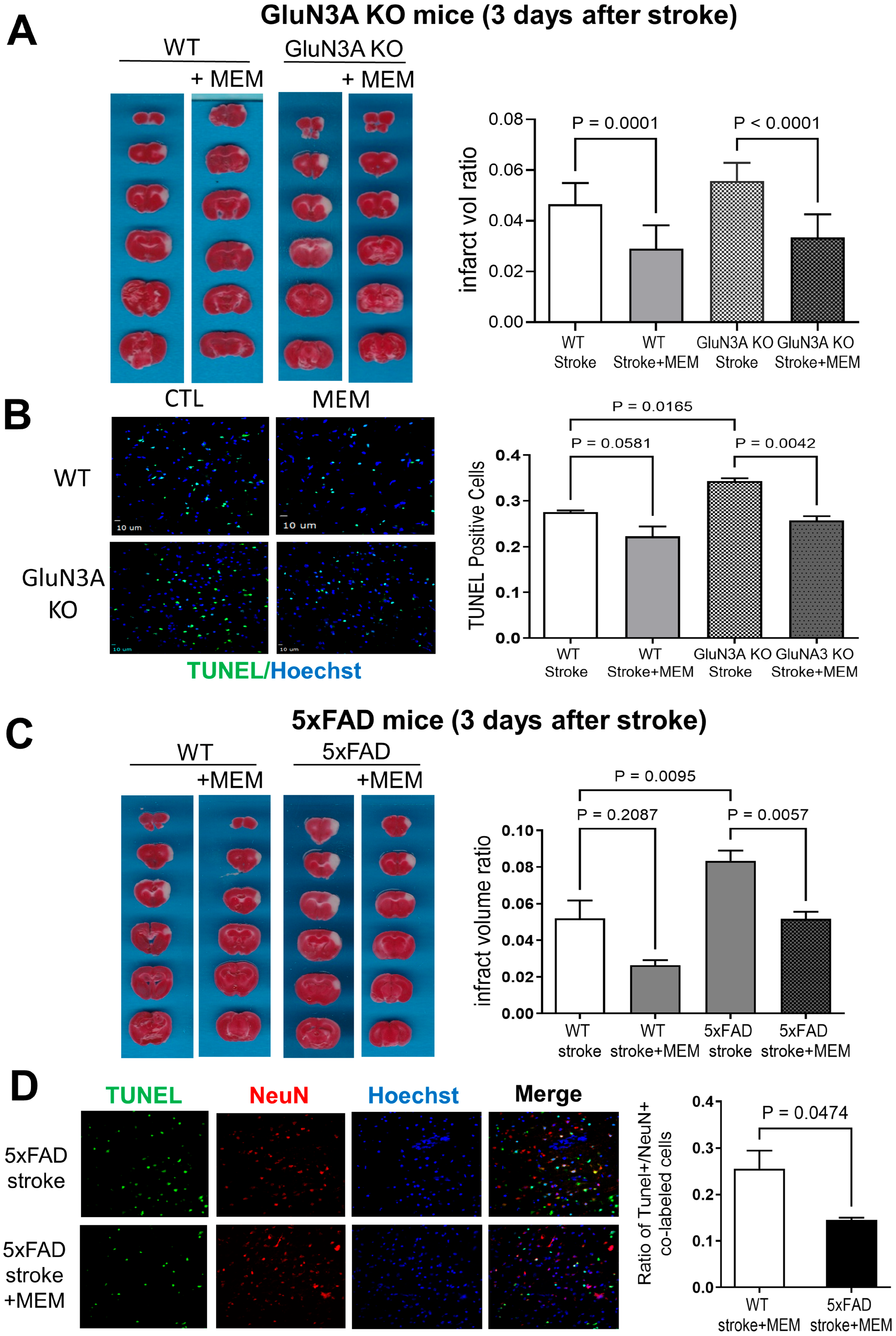
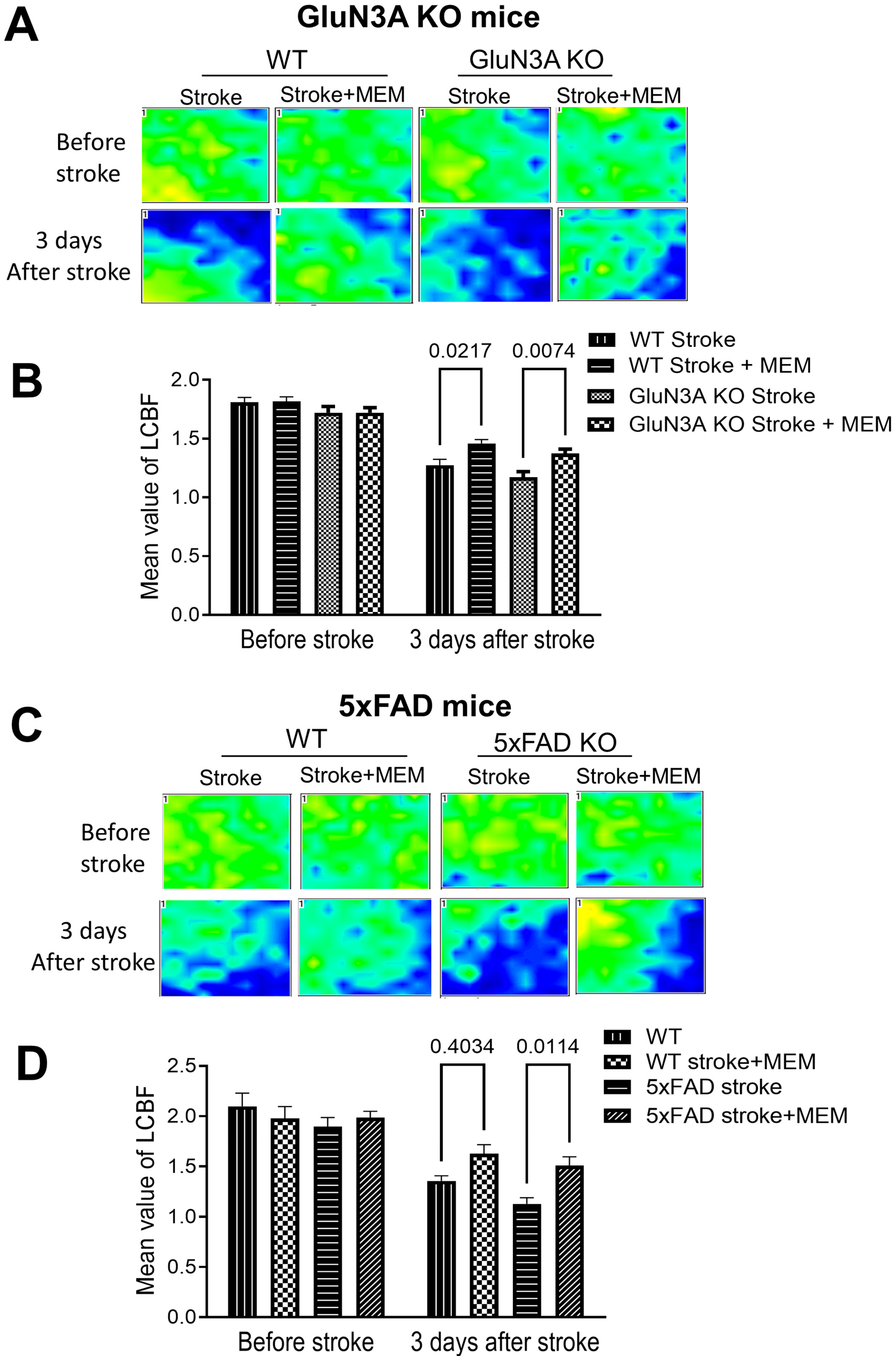
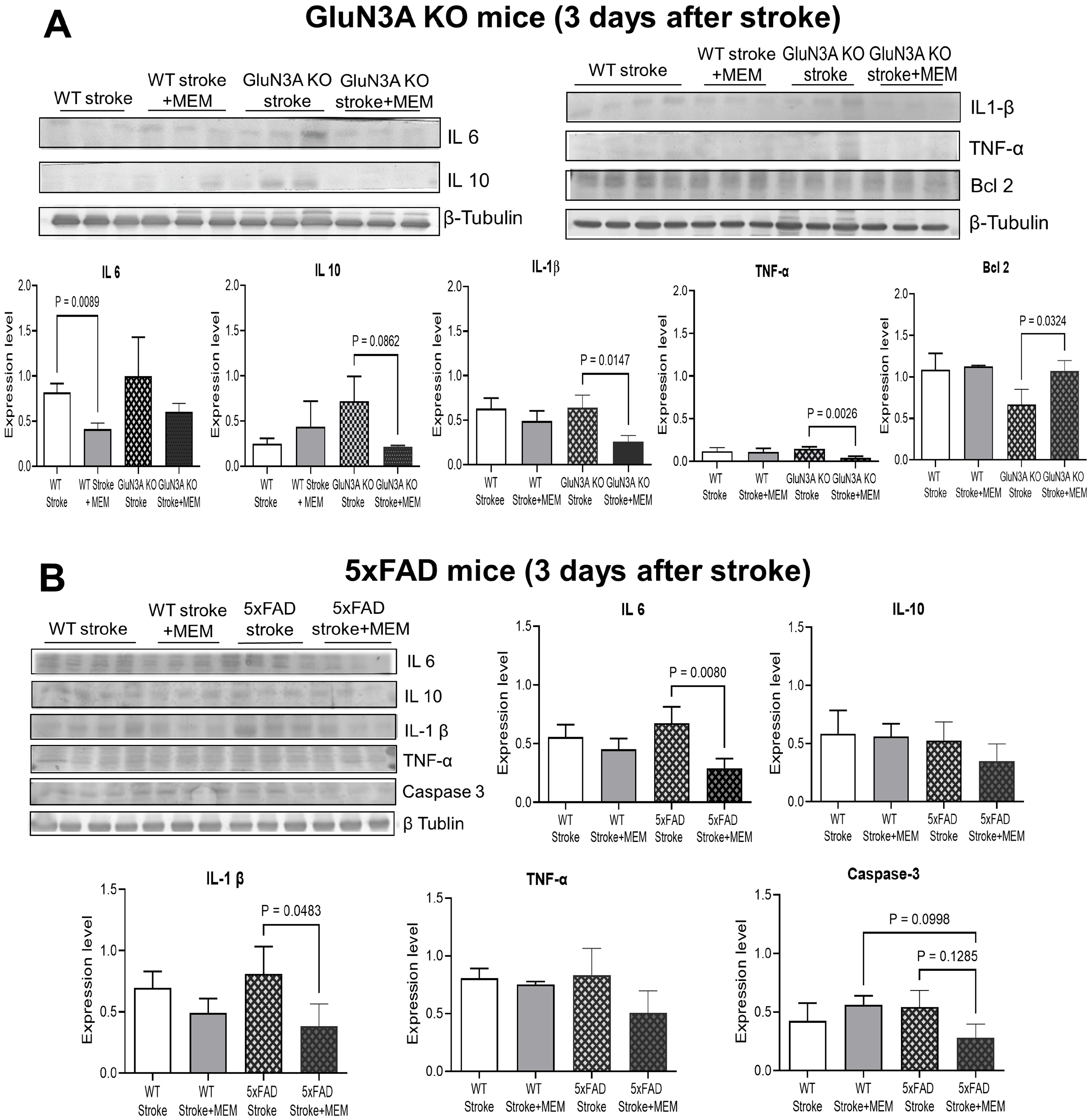
3.1. Preconditioning Effects of Early MEM Treatment Against Ischemic Stroke in Different AD Mouse Models
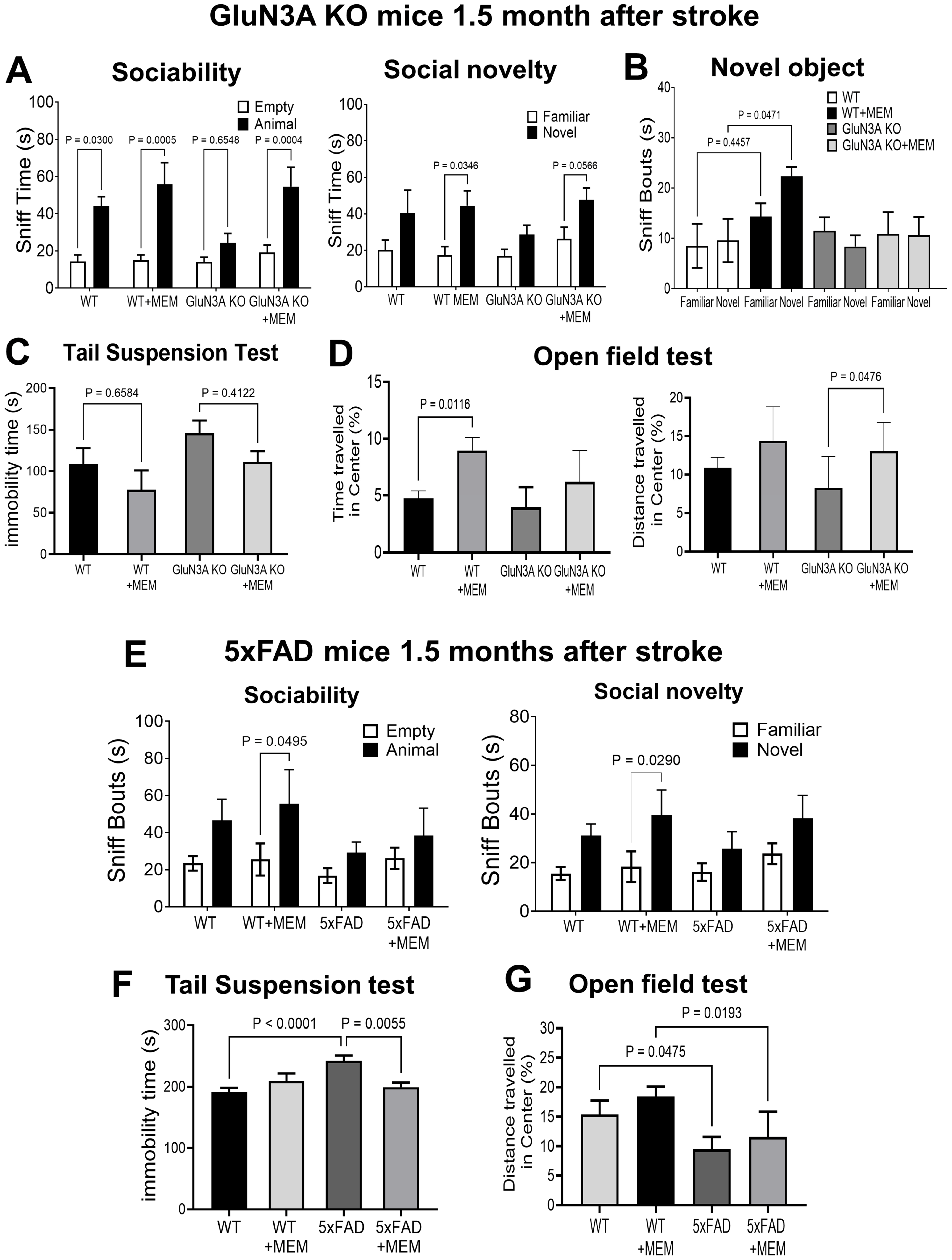
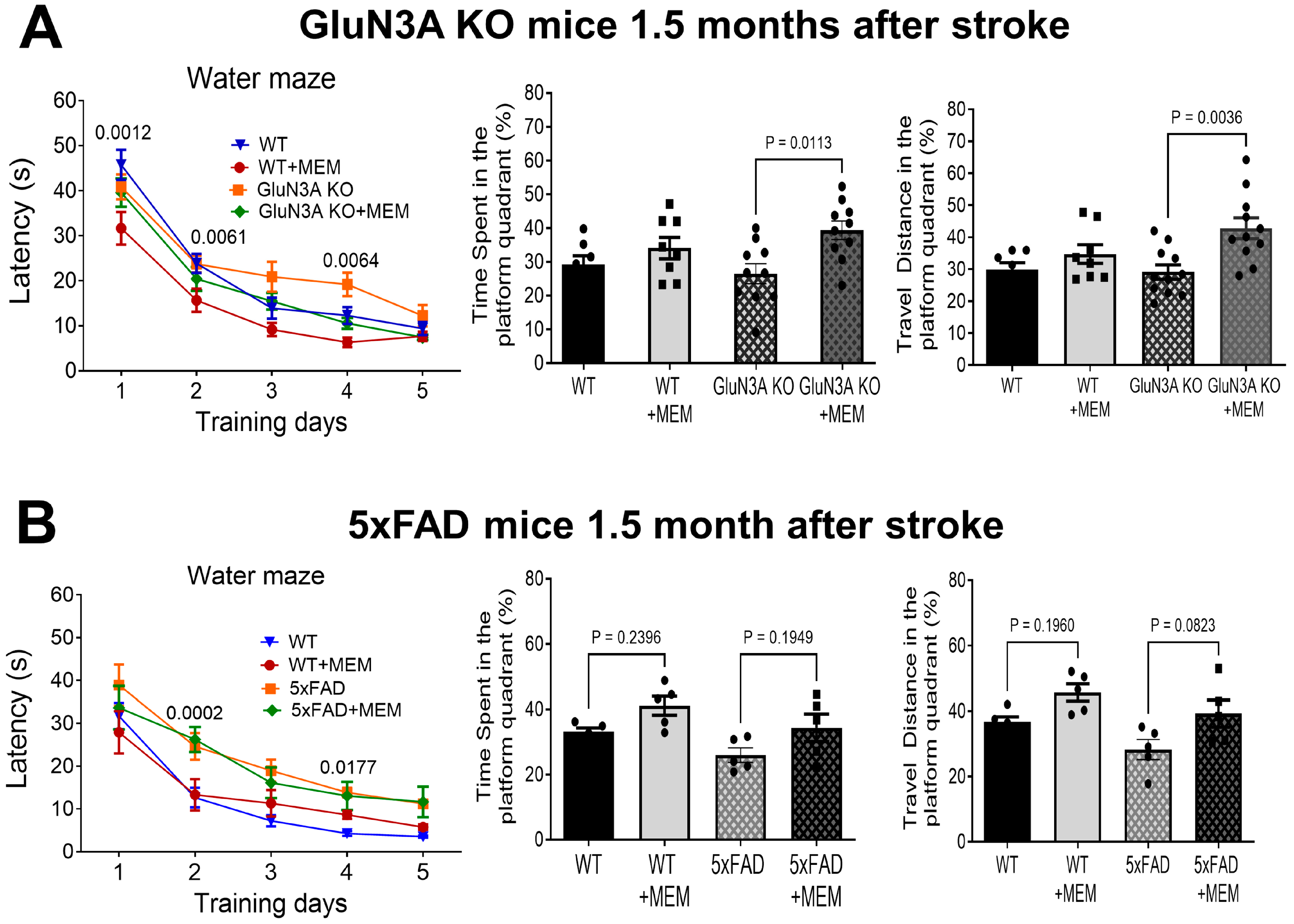
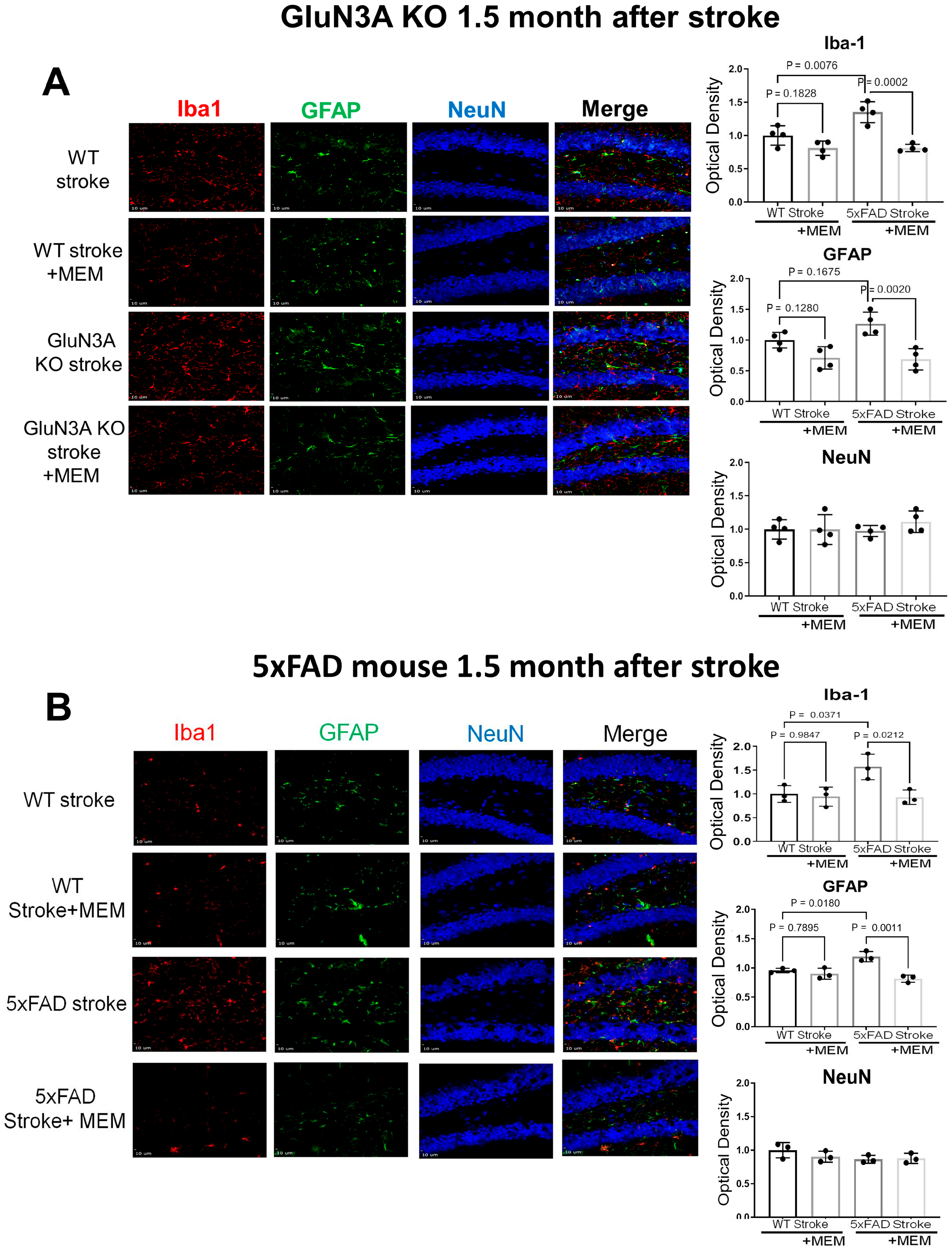
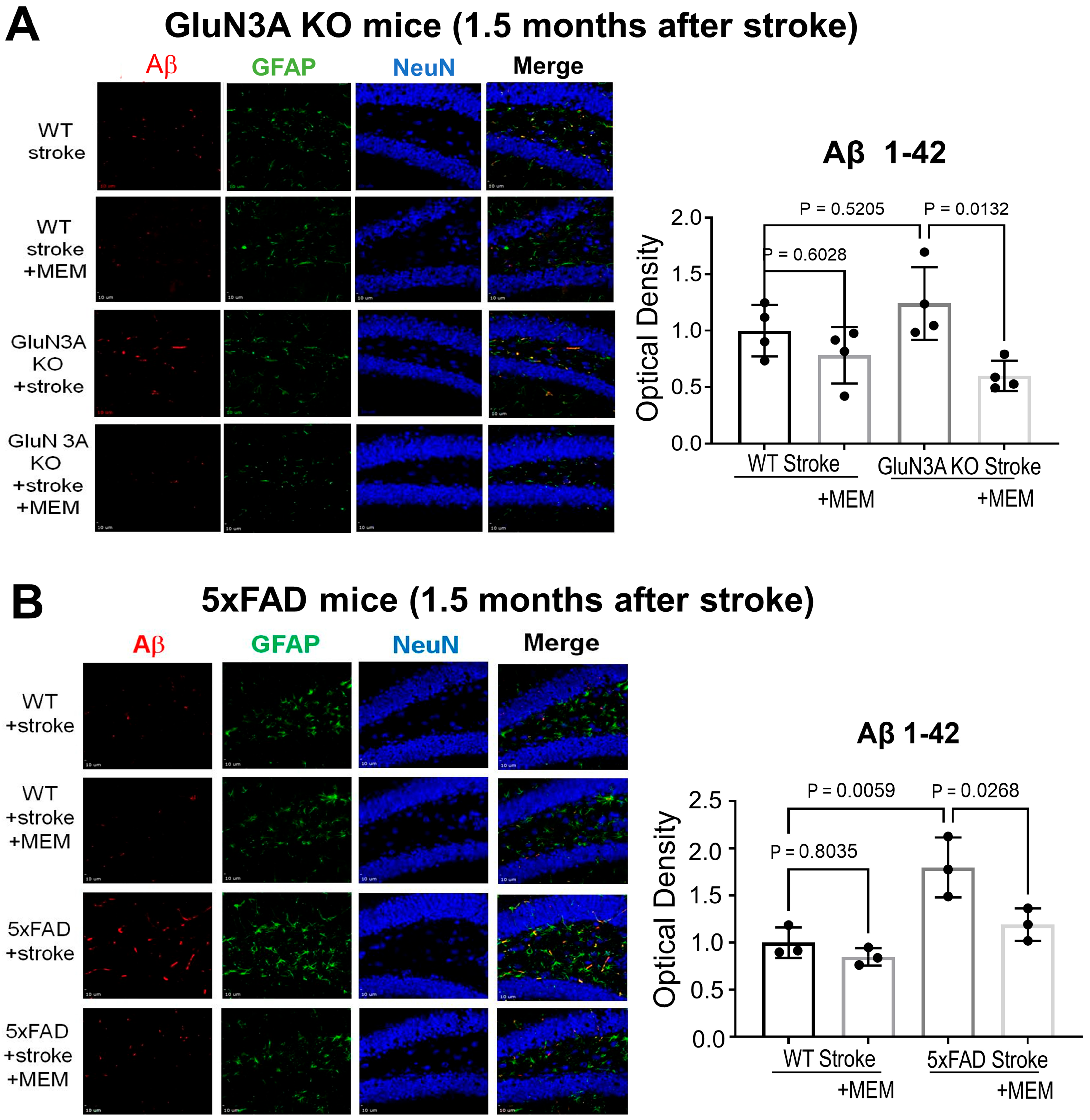
3.2. Sustained Effects of MEM Chronic Treatment in Aging Post-Stroke AD Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Future Direction
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vijayan, M.; Reddy, P.H. Stroke, Vascular Dementia, and Alzheimer’s Disease: Molecular Links. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2016, 54, 427–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalaria, R.N.; Akinyemi, R.; Ihara, M. Stroke injury, cognitive impairment and vascular dementia. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1862, 915–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinho, J.; Quintas-Neves, M.; Dogan, I.; Reetz, K.; Reich, A.; Costa, A.S. Incident stroke in patients with Alzheimer’s disease: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.P.; Jiang, M.Q.; Shim, S.S.; Pourkhodadad, S.; Wei, L. Extrasynaptic NMDA receptors in acute and chronic excitotoxicity: Implications for preventive treatments of ischemic stroke and late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2023, 18, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zupanic, E.; von Euler, M.; Winblad, B.; Xu, H.; Secnik, J.; Kramberger, M.G.; Religa, D.; Norrving, B.; Garcia-Ptacek, S. Mortality After Ischemic Stroke in Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease Dementia and Other Dementia Disorders. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2021, 81, 1253–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, A.W.; Elser, H.; Rosso, M.; Cornblath, E.J.; Fonkeu, Y.; Prasad, S.; Rothstein, A.; Nasrallah, I.M.; Wolk, D.A.; Guo, M.H. Ischemic staroke associated with amyloid-related imaging abnormalities in a patient treated with lecanemab. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2024, 20, 8192–8197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattson, M.P.; Rydel, R.E.; Lieberburg, I.; Smith-Swintosky, V.L. Altered calcium signaling and neuronal injury: Stroke and Alzheimer’s disease as examples. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1993, 679, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoyte, L.; Barber, P.A.; Buchan, A.M.; Hill, M.D. The rise and fall of NMDA antagonists for ischemic stroke. Curr. Mol. Med. 2004, 4, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.K.; Lee, Y.R.; Ong, L.; Gold, M.; Kalali, A.; Sarkar, J. Alzheimer’s Disease: Key Insights from Two Decades of Clinical Trial Failures. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2022, 87, 83–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.W. Excitotoxicity: Still Hammering the Ischemic Brain in 2020. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 579953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothman, S.M.; Olney, J.W. Glutamate and the pathophysiology of hypoxic-ischemic brain damage. Ann. Neurol. 1986, 19, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.W. Glutamate neurotoxicity and diseases of the nervous system. Neuron 1988, 1, 623–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.P.; Yeh, C.; Strasser, U.; Tian, M.; Choi, D.W. NMDA receptor-mediated K+ efflux and neuronal apoptosis. Science 1999, 284, 336–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, M.; Yu, S.P. Ionic regulation of cell volume changes and cell death after ischemic stroke. Transl. Stroke Res. 2014, 5, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khachaturian, Z.S. Calcium hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease and brain aging. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1994, 747, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzheimer’s Association Calcium Hypothesis Workgroup. Calcium Hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease and brain aging: A framework for integrating new evidence into a comprehensive theory of pathogenesis. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2017, 13, 178–182.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.; Wu, A.; Berglund, K.; Gu, X.; Jiang, M.Q.; Talati, J.; Zhao, J.; Wei, L.; Yu, S.P. Pathogenesis of sporadic Alzheimer’s disease by deficiency of NMDA receptor subunit GluN3A. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2022, 12, 222–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhakaran, S.; Ruff, I.; Bernstein, R.A. Acute stroke intervention: A systematic review. JAMA 2015, 313, 1451–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thushara Vijayakumar, N.; Sangwan, A.; Sharma, B.; Majid, A.; Rajanikant, G.K. Cerebral Ischemic Preconditioning: The Road So Far. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 2579–2593. [Google Scholar]
- Rogawski, M.A.; Wenk, G.L. The neuropharmacological basis for the use of memantine in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. CNS Drug Rev. 2003, 9, 275–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermunt, L.; Sikkes, S.A.M.; van den Hout, A.; Handels, R.; Bos, I.; van der Flier, W.M.; Kern, S.; Ousset, P.J.; Maruff, P.; Skoog, I.; et al. Duration of preclinical, prodromal, and dementia stages of Alzheimer’s disease in relation to age, sex, and APOE genotype. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2019, 15, 888–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aisen, P.S.; Cummings, J.; Jack, C.R., Jr.; Morris, J.C.; Sperling, R.; Frolich, L.; Jones, R.W.; Dowsett, S.A.; Matthews, B.R.; Raskin, J.; et al. On the path to 2025: Understanding the Alzheimer’s disease continuum. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2017, 9, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, Y.; Yang, X.; Fu, Y.; Li, Z.; Gong, R.; Lu, W. NMDAR-dependent somatic potentiation of synaptic inputs is correlated with beta amyloid-mediated neuronal hyperactivity. Transl. Neurodegener. 2021, 10, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, P.; Feng, J.; Wu, M. Dysfunction of NMDA receptors in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurol. Sci. 2016, 37, 1039–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busche, M.A.; Chen, X.; Henning, H.A.; Reichwald, J.; Staufenbiel, M.; Sakmann, B.; Konnerth, A. Critical role of soluble amyloid-beta for early hippocampal hyperactivity in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 8740–8745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciarelli, R.; Fedele, E. The Amyloid Cascade Hypothesis in Alzheimer’s Disease: It’s Time to Change Our Mind. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2017, 15, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrup, K. The case for rejecting the amyloid cascade hypothesis. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 794–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kametani, F.; Hasegawa, M. Reconsideration of Amyloid Hypothesis and Tau Hypothesis in Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.P.; Clark, I.A.; Vissel, B. Inconsistencies and controversies surrounding the amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2014, 2, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golde, T.E. Alzheimer’s disease—The journey of a healthy brain into organ failure. Mol. Neurodegener. 2022, 17, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaren, A.M.R.; Kawaja, M.D. Olfactory Dysfunction and Alzheimer’s Disease: A Review. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2024, 99, 811–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barresi, M.; Ciurleo, R.; Giacoppo, S.; Foti Cuzzola, V.; Celi, D.; Bramanti, P.; Marino, S. Evaluation of olfactory dysfunction in neurodegenerative diseases. J. Neurol. Sci. 2012, 323, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehjar, F.; Almarghalani, D.A.; Mahajan, R.; Hasan, S.A.; Shah, Z.A. The Multifaceted Role of Cofilin in Neurodegeneration and Stroke: Insights into Pathogenesis and Targeting as a Therapy. Cells 2024, 13, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hachinski, V.; Avan, A. A new definition of brain reserve. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2022, 18, 535–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.P.; Jiang, M.; Berglund, K.; Wei, L. Strain hypothesis and additional evidence of the GluN3A deficiency-mediated pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2023, 19, 4267–4269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.P.; Choi, E.; Jiang, M.Q.; Wei, L. Acute and chronic excitotoxicity in ischemic stroke and late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Neural Regen. Res. 2025, 20, 1981–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, W.Y.; Tanaka, K.; Dawe, G.S.; Ittner, L.M.; Farooqui, A.A. Slow excitotoxicity in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2013, 35, 643–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soria Lopez, J.A.; Gonzalez, H.M.; Leger, G.C. Alzheimer’s disease. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2019, 167, 231–255. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tahami Monfared, A.A.; Byrnes, M.J.; White, L.A.; Zhang, Q. Alzheimer’s Disease: Epidemiology and Clinical Progression. Neurol. Ther. 2022, 11, 553–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardingham, G.E.; Fukunaga, Y.; Bading, H. Extrasynaptic NMDARs oppose synaptic NMDARs by triggering CREB shut-off and cell death pathways. Nat. Neurosci. 2002, 5, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, M.P.; Raymond, L.A. Extrasynaptic NMDA receptor involvement in central nervous system disorders. Neuron 2014, 82, 279–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, X.; Yu, S.P.; Jiang, M.Q.; Zhong, W.; Sastry, A.; Wei, L. Preventive Memantine Treatment at the Preclinical Stage in the Alzheimer’s Disease Model of the 5xFAD Mouse. Neurosci. Bull. 2025; online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Sasaki, Y.F.; Rothe, T.; Premkumar, L.S.; Takasu, M.; Crandall, J.E.; Dikkes, P.; Conner, D.A.; Rayudu, P.V.; Cheung, W.; et al. Increased NMDA current and spine density in mice lacking the NMDA receptor subunit NR3A. Nature 1998, 393, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzman, E.A.; Bouter, Y.; Richard, B.C.; Lannfelt, L.; Ingelsson, M.; Paetau, A.; Verkkoniemi-Ahola, A.; Wirths, O.; Bayer, T.A. Abundance of Abeta(5)-x like immunoreactivity in transgenic 5XFAD, APP/PS1KI and 3xTG mice, sporadic and familial Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2014, 9, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamad, O.; Song, M.; Wei, L.; Yu, S.P. Regulatory roles of the NMDA receptor GluN3A subunit in locomotion, pain perception and cognitive functions in adult mice. J. Physiol. 2013, 591, 149–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Wei, L.; Deveau, T.C.; Gu, X.; Yu, S.P. Expression of the NMDA receptor subunit GluN3A (NR3A) in the olfactory system and its regulatory role on olfaction in the adult mouse. Brain Struct. Funct. 2016, 221, 3259–3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavirajan, H. Memantine: A comprehensive review of safety and efficacy. Expert. Opin. Drug Saf. 2009, 8, 89–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.; Yuan, Y.; Gu, X.; Kim, S.I.; Chin, R.; Loye, M.; Dix, T.A.; Wei, L.; Yu, S.P. Neuropsychological Deficits Chronically Developed after Focal Ischemic Stroke and Beneficial Effects of Pharmacological Hypothermia in the Mouse. Aging Dis. 2020, 11, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.Q.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Cao, W.; Wei, Z.Z.; Gu, X.; Wei, L.; Yu, S.P. Long-term survival and regeneration of neuronal and vasculature cells inside the core region after ischemic stroke in adult mice. Brain Pathol. 2017, 27, 480–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swanson, R.A.; Morton, M.T.; Tsao-Wu, G.; Savalos, R.A.; Davidson, C.; Sharp, F.R. A semiautomated method for measuring brain infarct volume. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 1990, 10, 290–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilic, U.; Yilmaz, B.; Reiter, R.J.; Yuksel, A.; Kilic, E. Effects of memantine and melatonin on signal transduction pathways vascular leakage and brain injury after focal cerebral ischemia in mice. Neuroscience 2013, 237, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, S.; Taka, E.; Darling-Reed, S.; Soliman, K.F.A. Neuroprotective Effects of Metformin Through the Modulation of Neuroinflammation and Oxidative Stress. Cells 2025, 14, 1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amidfar, M.; de Oliveira, J.; Kucharska, E.; Budni, J.; Kim, Y.K. The role of CREB and BDNF in neurobiology and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Life Sci. 2020, 257, 118020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volloch, V.; Rits-Volloch, S. On the Inadequacy of the Current Transgenic Animal Models of Alzheimer’s Disease: The Path Forward. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaguri, H.; Hashimoto, S.; Watamura, N.; Sato, K.; Takamura, R.; Nagata, K.; Tsubuki, S.; Ohshima, T.; Yoshiki, A.; Sato, K.; et al. Recent Advances in the Modeling of Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 807473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molinuevo, J.L.; Llado, A.; Rami, L. Memantine: Targeting glutamate excitotoxicity in Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias. Am. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. Other Demen 2005, 20, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danysz, W.; Parsons, C.G. Alzheimer’s disease, beta-amyloid, glutamate, NMDA receptors and memantine--searching for the connections. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 167, 324–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, V.; Chandel, A.; Minhas, Y.; Kushawaha, S.K. “Advances in biomarker discovery and diagnostics for alzheimer’s disease”. Neurol. Sci. 2025, 46, 2419–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janeiro, M.H.; Ardanaz, C.G.; Sola-Sevilla, N.; Dong, J.; Cortes-Erice, M.; Solas, M.; Puerta, E.; Ramirez, M.J. Biomarkers in Alzheimer’s disease. Adv. Lab. Med. 2021, 2, 27–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Baek, S.H.; Lai, M.K.P.; Arumugam, T.V.; Jo, D.G. Aging-associated sensory decline and Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2024, 19, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardingham, G.E.; Bading, H. Coupling of extrasynaptic NMDA receptors to a CREB shut-off pathway is developmentally regulated. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2002, 1600, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blurton-Jones, M.; Kitazawa, M.; Martinez-Coria, H.; Castello, N.A.; Muller, F.J.; Loring, J.F.; Yamasaki, T.R.; Poon, W.W.; Green, K.N.; LaFerla, F.M. Neural stem cells improve cognition via BDNF in a transgenic model of Alzheimer disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 13594–13599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Garcia, S.; Sancho-Balsells, A.; Longueville, S.; Herve, D.; Gruart, A.; Delgado-Garcia, J.M.; Alberch, J.; Giralt, A. Astrocytic BDNF and TrkB regulate severity and neuronal activity in mouse models of temporal lobe epilepsy. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caccamo, A.; Maldonado, M.A.; Bokov, A.F.; Majumder, S.; Oddo, S. CBP gene transfer increases BDNF levels and ameliorates learning and memory deficits in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 22687–22692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.; Liu, S.; Rubin, L.; Lazarovici, P.; Zheng, W. Research Progress on Neuroprotection of Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 towards Glutamate-Induced Neurotoxicity. Cells 2022, 11, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi Tari, P.; Parsons, C.G.; Collingridge, G.L.; Rammes, G. Memantine: Updating a rare success story in pro-cognitive therapeutics. Neuropharmacology 2024, 244, 109737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipton, S.A. Paradigm shift in neuroprotection by NMDA receptor blockade: Memantine and beyond. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tricco, A.C.; Ashoor, H.M.; Soobiah, C.; Rios, P.; Veroniki, A.A.; Hamid, J.S.; Ivory, J.D.; Khan, P.A.; Yazdi, F.; Ghassemi, M.; et al. Comparative Effectiveness and Safety of Cognitive Enhancers for Treating Alzheimer’s Disease: Systematic Review and Network Metaanalysis. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2018, 66, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farlow, M.R.; Graham, S.M.; Alva, G. Memantine for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease: Tolerability and safety data from clinical trials. Drug Saf. 2008, 31, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.J.; Tymianski, M. Targeting NMDA receptors in stroke: New hope in neuroprotection. Mol. Brain 2018, 11, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, S.L.; Vartanian, K.B.; Stenzel-Poore, M.P. Reprogramming the response to stroke by preconditioning. Stroke 2014, 45, 2527–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Pinzon, M.A. Mechanisms of neuroprotection during ischemic preconditioning: Lessons from anoxic tolerance. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2007, 147, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijajlovic, M.D.; Pavlovic, A.; Brainin, M.; Heiss, W.D.; Quinn, T.J.; Ihle-Hansen, H.B.; Hermann, D.M.; Assayag, E.B.; Richard, E.; Thiel, A.; et al. Post-stroke dementia—A comprehensive review. BMC Med. 2017, 15, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fride, Y.; Adamit, T.; Maeir, A.; Ben Assayag, E.; Bornstein, N.M.; Korczyn, A.D.; Katz, N. What are the correlates of cognition and participation to return to work after first ever mild stroke? Top. Stroke Rehabil. 2015, 22, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouet, V.; Freret, T.; Toutain, J.; Divoux, D.; Boulouard, M.; Schumann-Bard, P. Sensorimotor and cognitive deficits after transient middle cerebral artery occlusion in the mouse. Exp. Neurol. 2007, 203, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuartero, M.I.; de la Parra, J.; Perez-Ruiz, A.; Bravo-Ferrer, I.; Duran-Laforet, V.; Garcia-Culebras, A.; Garcia-Segura, J.M.; Dhaliwal, J.; Frankland, P.W.; Lizasoain, I.; et al. Abolition of aberrant neurogenesis ameliorates cognitive impairment after stroke in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 1536–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Wei, Z.Z.; Chen, D.; Gu, X.; Wei, L.; Yu, S.P. A neuroprotective role of the NMDA receptor subunit GluN3A (NR3A) in ischemic stroke of the adult mouse. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2015, 308, C570–C577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mira, R.G.; Cerpa, W. Building a Bridge Between NMDAR-Mediated Excitotoxicity and Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Chronic and Acute Diseases. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 41, 1413–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoque, A.; Hossain, M.I.; Ameen, S.S.; Ang, C.S.; Williamson, N.; Ng, D.C.; Chueh, A.C.; Roulston, C.; Cheng, H.C. A beacon of hope in stroke therapy-Blockade of pathologically activated cellular events in excitotoxic neuronal death as potential neuroprotective strategies. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 160, 159–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, R.G. NMDA receptors and memory encoding. Neuropharmacology 2013, 74, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kniffin, A.R.; Briand, L.A. Sex differences in glutamate transmission and plasticity in reward related regions. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2024, 18, 1455478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torrisi, S.A.; Rizzo, S.; Laudani, S.; Ieraci, A.; Drago, F.; Leggio, G.M. Acute stress alters recognition memory and AMPA/NMDA receptor subunits in a sex-dependent manner. Neurobiol. Stress 2023, 25, 100545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, S.P.; Gu, X.; Jiang, M.Q.; Sastry, A.; Wu, L.; Li, Y.; Wei, L. Combined Preventive and Preconditioning Treatments for the Comorbidity of Alzheimer’s Disease and Ischemic Stroke in a GluN3A Knockout Mouse and a 5xFAD Mouse. Cells 2025, 14, 1871. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14231871
Yu SP, Gu X, Jiang MQ, Sastry A, Wu L, Li Y, Wei L. Combined Preventive and Preconditioning Treatments for the Comorbidity of Alzheimer’s Disease and Ischemic Stroke in a GluN3A Knockout Mouse and a 5xFAD Mouse. Cells. 2025; 14(23):1871. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14231871
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Shan Ping, Xiaohuan Gu, Michael Q. Jiang, Ananth Sastry, Lingyue Wu, Yiying Li, and Ling Wei. 2025. "Combined Preventive and Preconditioning Treatments for the Comorbidity of Alzheimer’s Disease and Ischemic Stroke in a GluN3A Knockout Mouse and a 5xFAD Mouse" Cells 14, no. 23: 1871. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14231871
APA StyleYu, S. P., Gu, X., Jiang, M. Q., Sastry, A., Wu, L., Li, Y., & Wei, L. (2025). Combined Preventive and Preconditioning Treatments for the Comorbidity of Alzheimer’s Disease and Ischemic Stroke in a GluN3A Knockout Mouse and a 5xFAD Mouse. Cells, 14(23), 1871. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14231871






