Spinal Dorsal Horn Neurons Receiving Descending Input from the Primary Somatosensory Cortex Contribute to Aβ Fiber-Induced Neuropathic Allodynia in Male Rats
Highlights
- Descending neuronal signaling from the primary somatosensory (S1) cortex to the spinal dorsal horn (SDH) directly contributes to Aβ fiber-derived neuropathic allodynia in male rats.
- Superficial SDH neurons receiving direct projections from S1 cortical neurons integrate excitatory inputs from Aβ fibers and inhibitory inputs from SDH interneurons; loss of this inhibition unmasks their excitatory influence on spinal circuits, leading to allodynia.
- This study demonstrates that an aberrant brain–spinal cord circuit involving the S1→SDH pathway underlies the pathological conversion of innocuous touch into pain.
- Targeting this corticospinal pathway may represent a promising therapeutic strategy for neuropathic allodynia.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Recombinant Adeno-Associated Virus (rAAV) Vector Production
2.3. Intra-SDH Injection of rAAV Vectors
2.4. Intra-S1 Injection of rAAV Vectors
2.5. Immunohistochemistry
2.6. Neuropathic Pain Model and Behavioral Assays
2.7. Chemogenetic Manipulation of S1→SDH Neurons
2.8. Whole-Cell Patch-Clamp Recordings
2.9. Administration of Diphtheria Toxin (DTX)
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
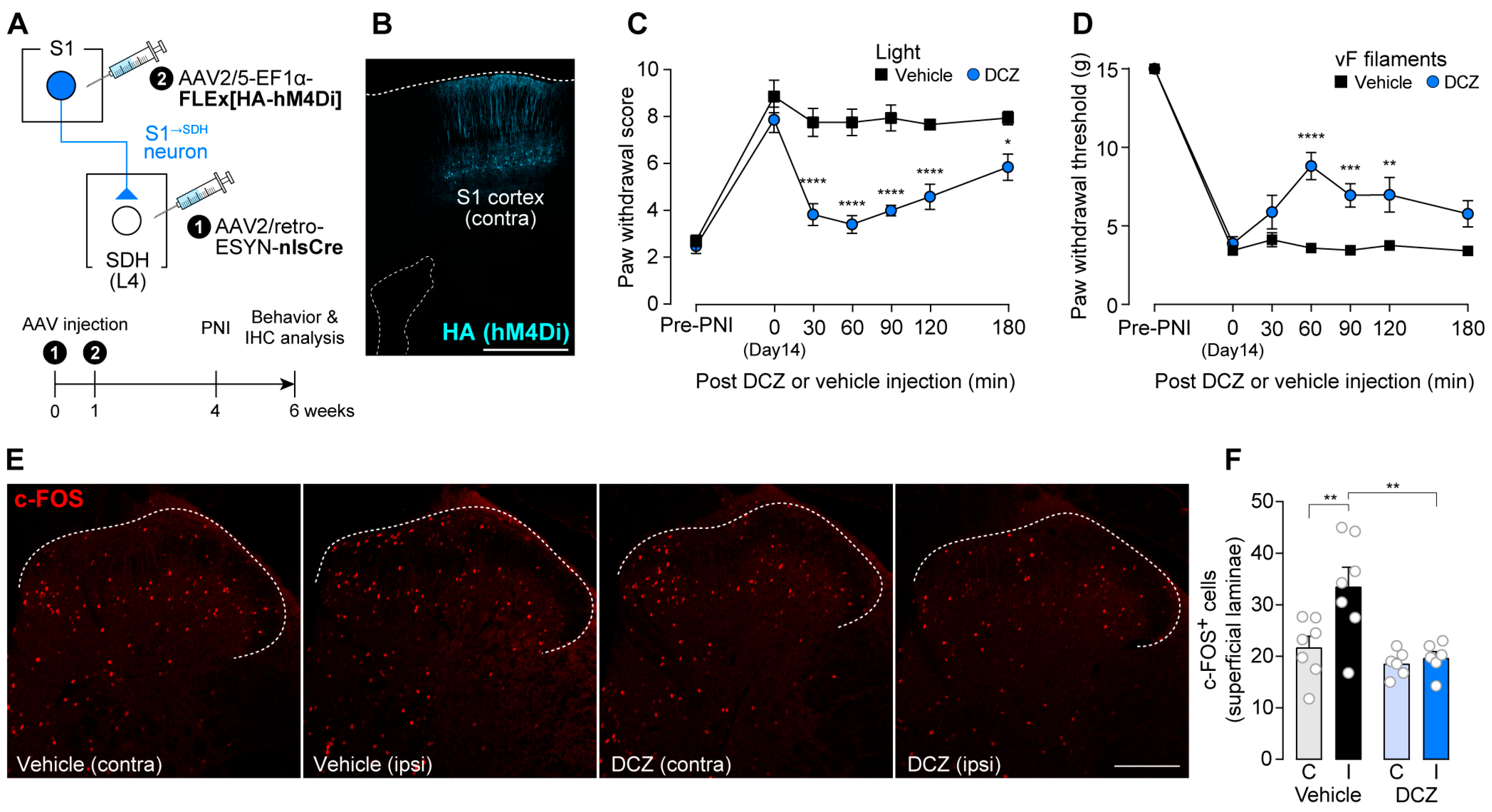
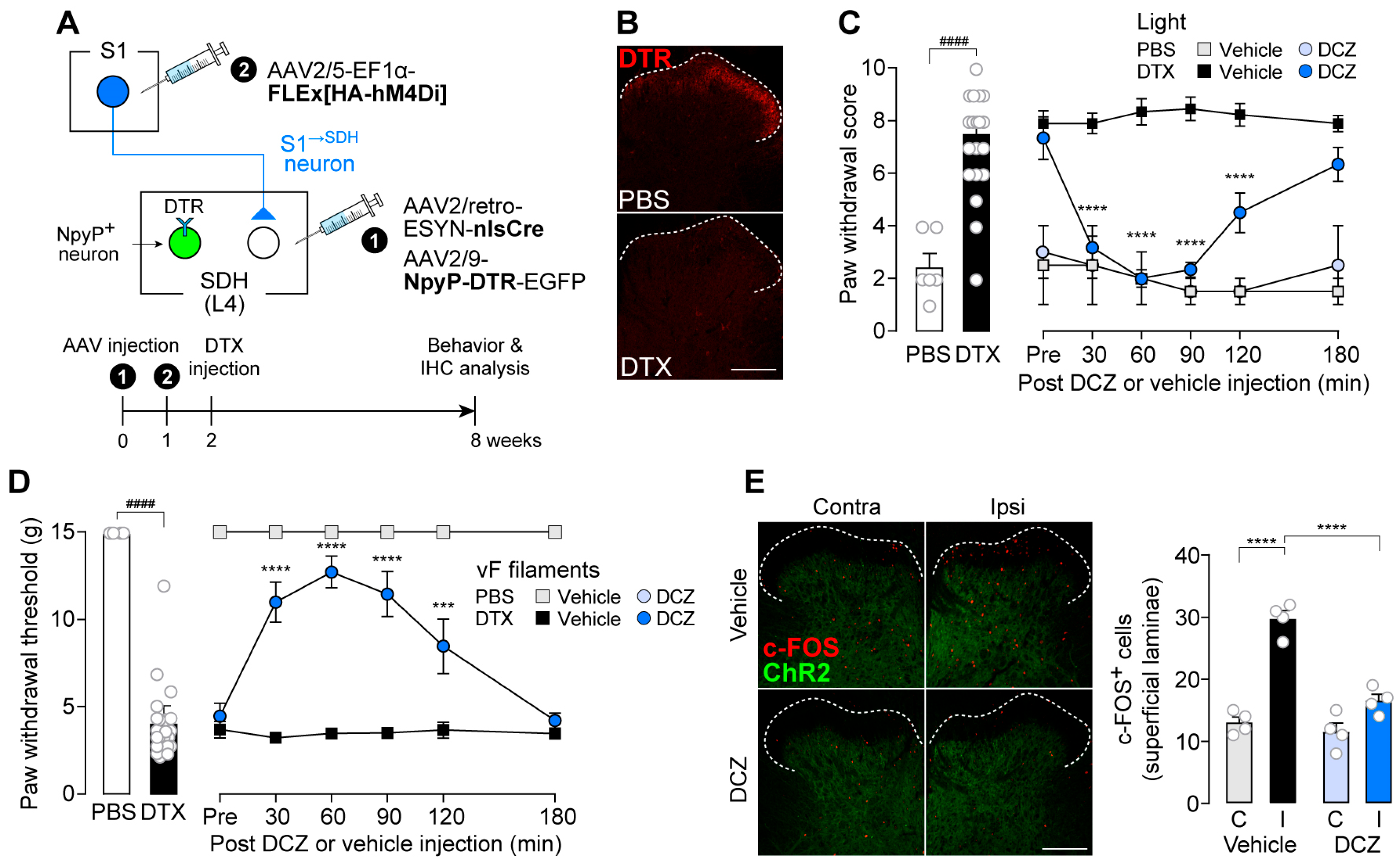
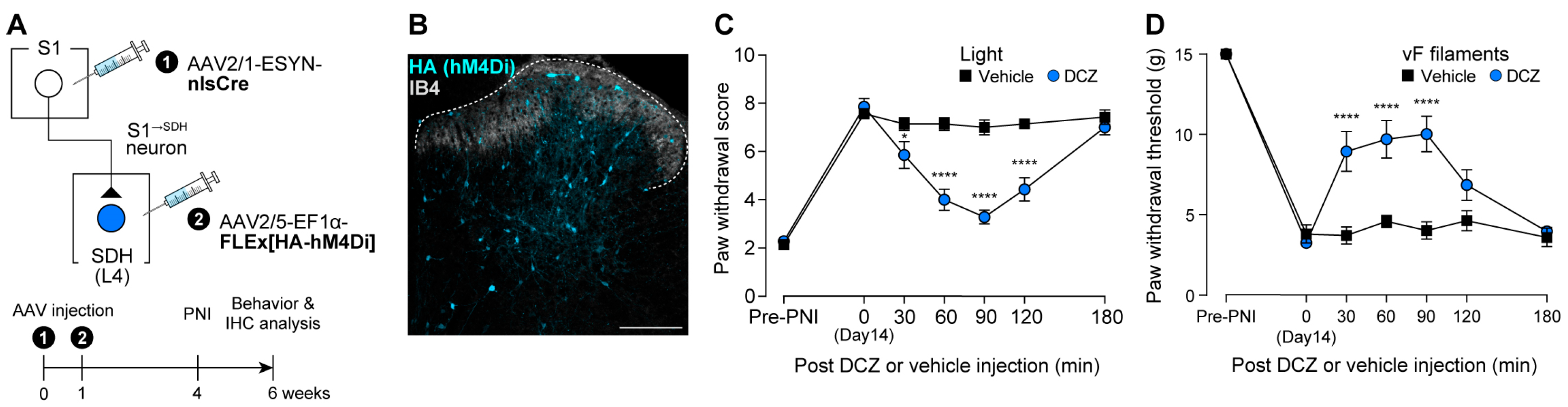
3.1. S1→SDH Neurons Contribute to Aβ Fiber-Derived Neuropathic Allodynia in Rats
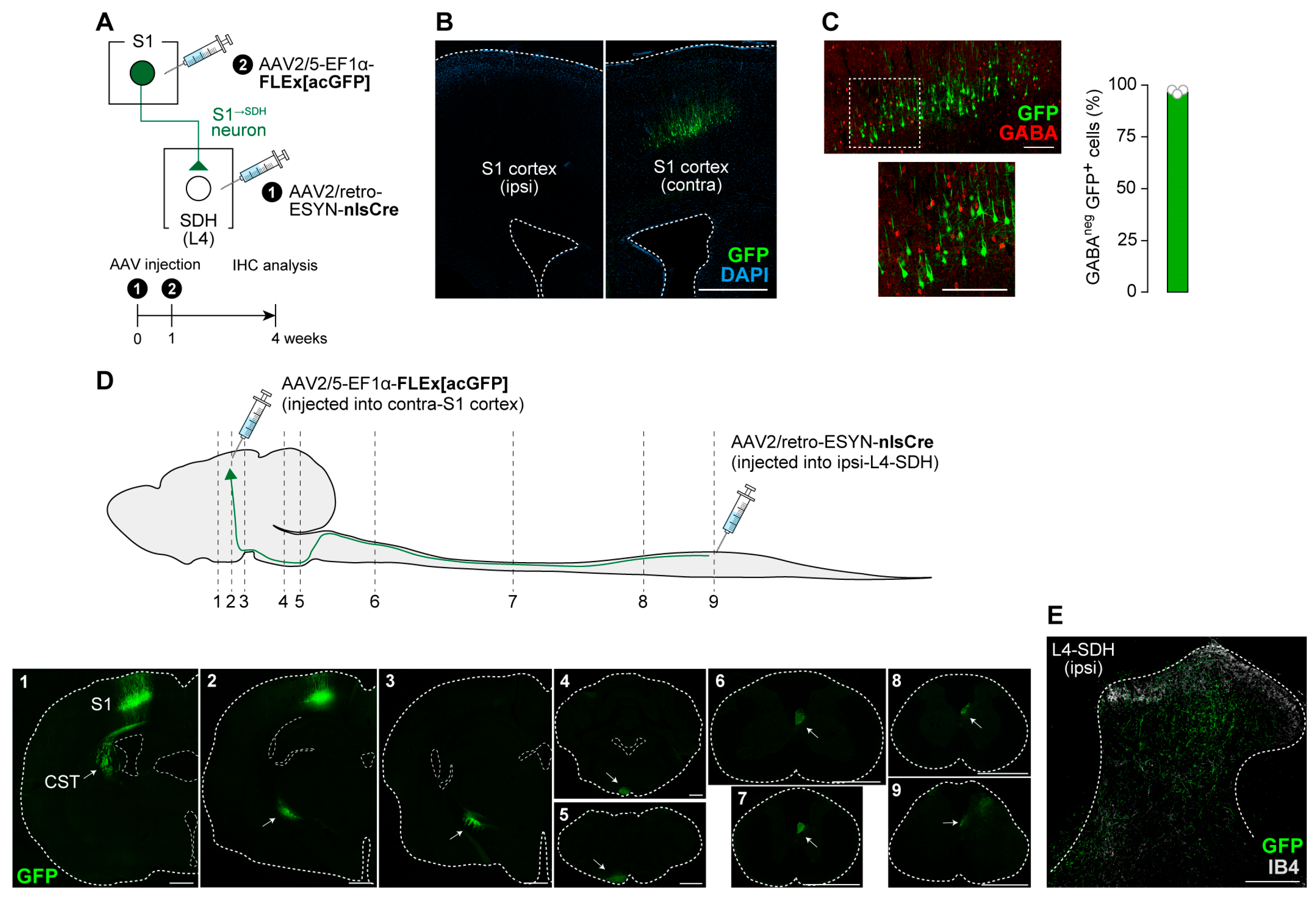
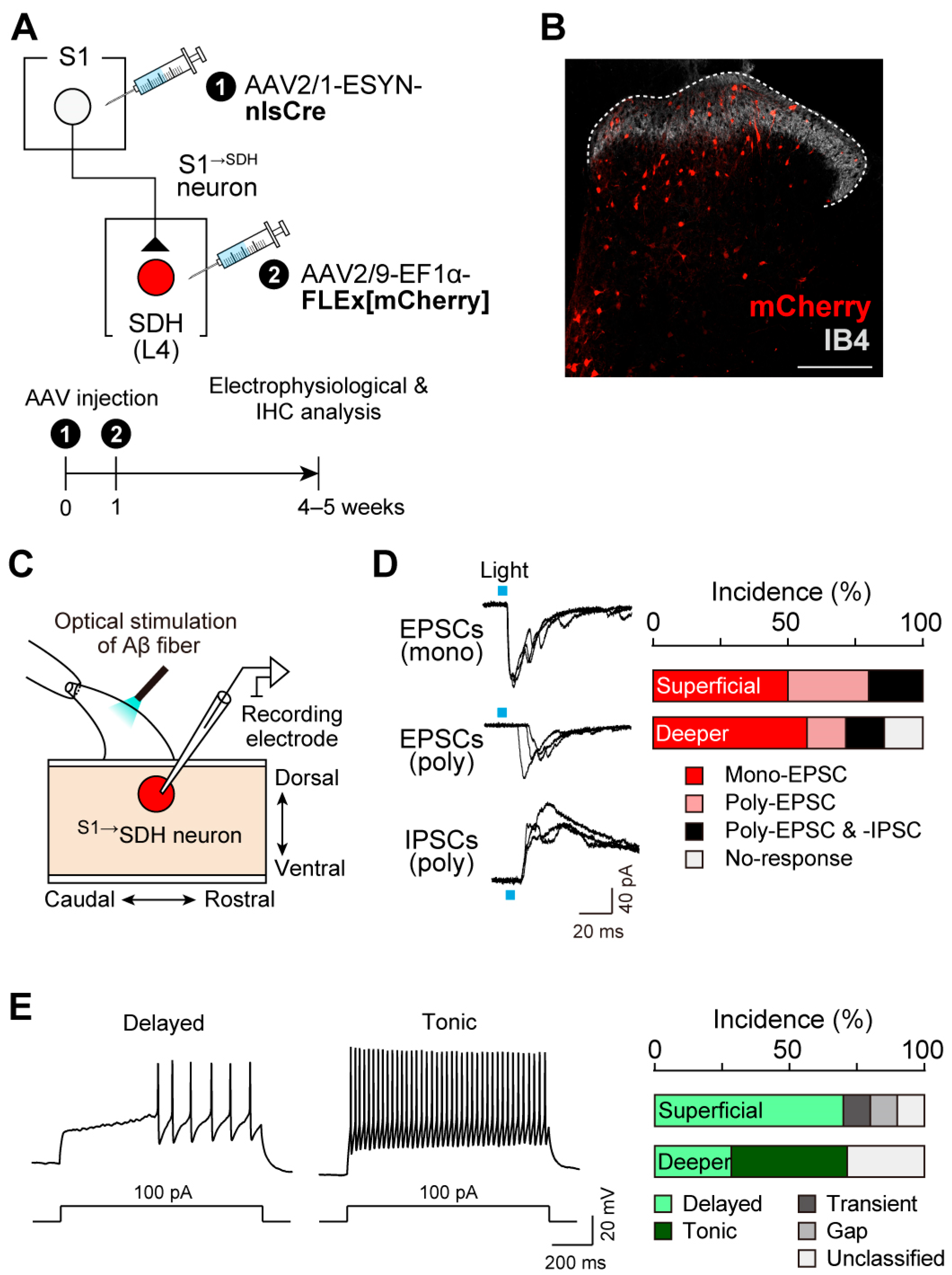
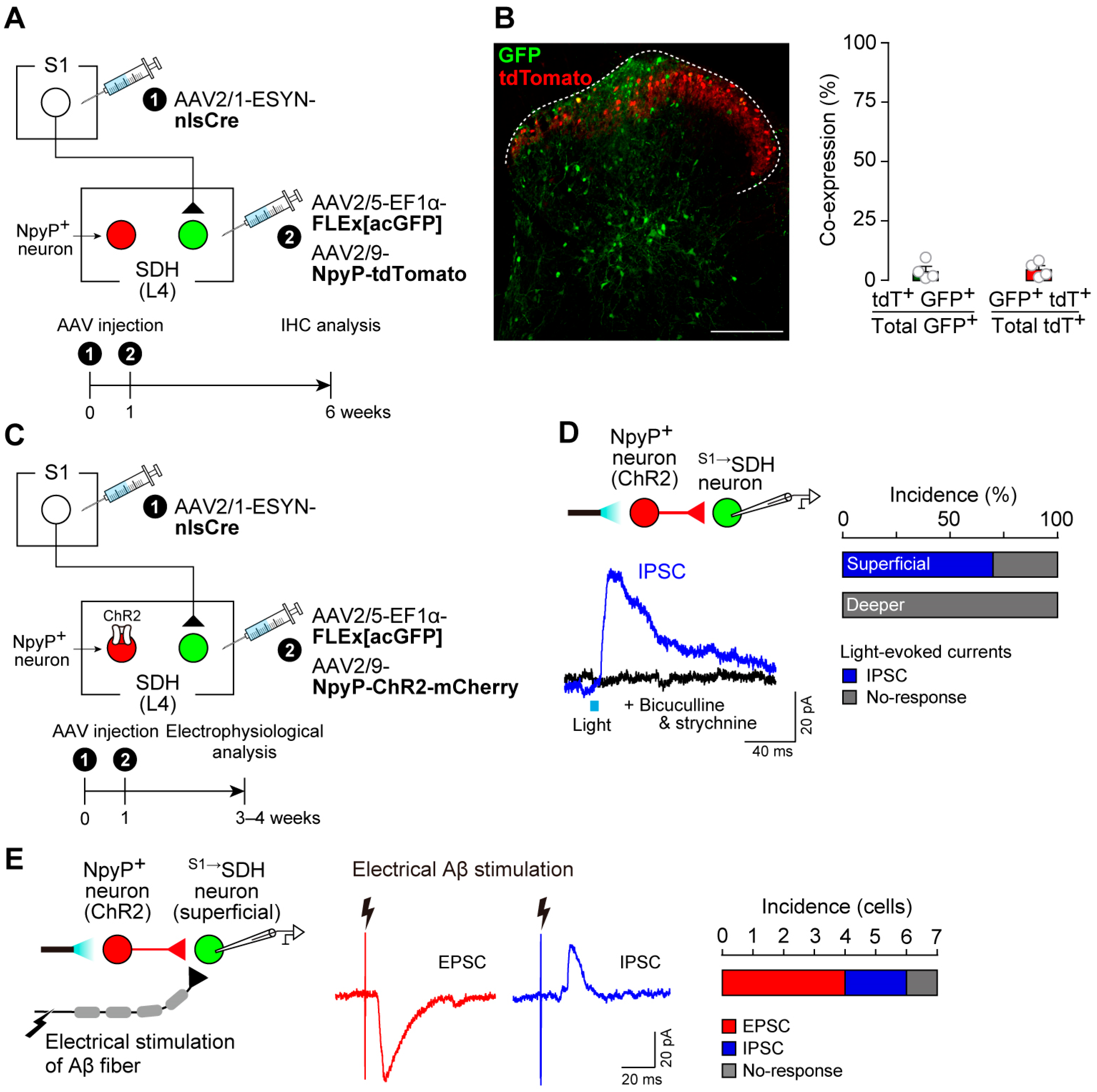
3.2. S1→SDH Neurons Form Synaptic Connections with SDH Neurons That Receive Aβ Fiber Input
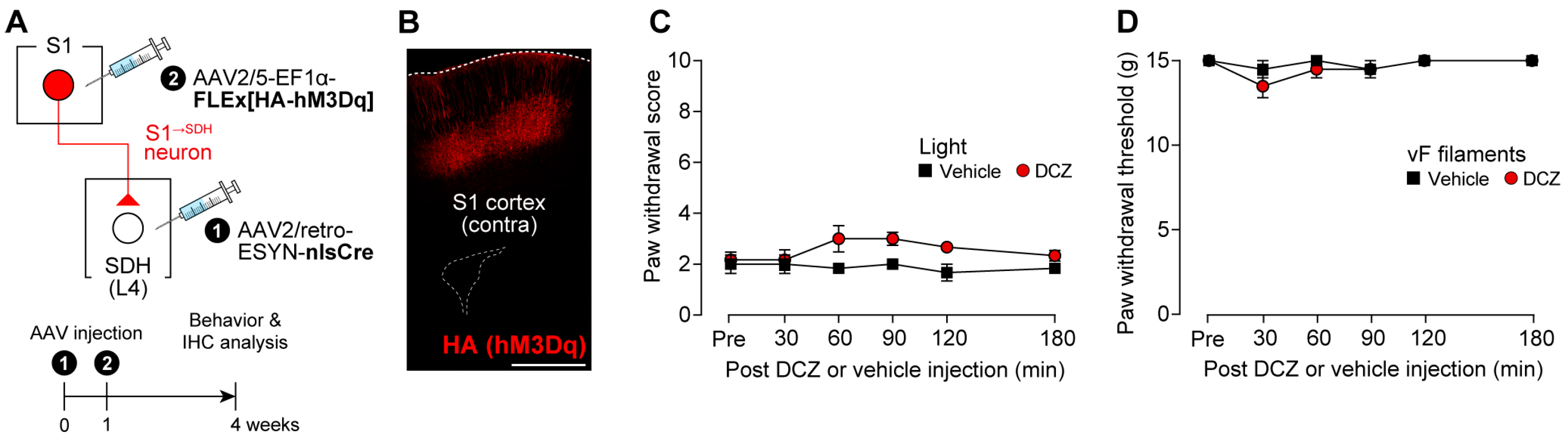
3.3. Impact of S1→SDH Neuron Signaling on Allodynia Is Unmasked Under Pathological Conditions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PNI | Peripheral nerve injury |
| SDH | Spinal dorsal horn |
| S1 | Primary somatosensory |
| S1→SDH neurons | Descending neurons projecting directly from the S1 cortex to the SDH |
| S1→SDH neurons | SDH neurons directly receiving projections from S1 |
| NpyP | Neuropeptide Y promoter |
| LTMRs | Low-threshold mechanoreceptors |
| ChR2 | Channelrhodopsin-2 |
| AAV | Adeno-associated virus |
| ACC | Anterior cingulate cortex |
| IC | Insular cortex |
| TRECK | Toxin receptor-mediated cell knockout |
| rAAV | Recombinant adeno-associated virus |
| DTR | Diphtheria toxin receptor |
| HA | Hemagglutinin |
| hM4Di | Human muscarinic Gi-coupled receptor |
| hM3Dq | Human muscarinic Gq-coupled receptor |
| GFP | Green fluorescent protein |
| acGFP | Aequorea coerulescens GFP |
| ESYN | Enhanced synapsin |
| EF1α | Elongation factor 1α |
| WPRE | Woodchuck hepatitis virus post-transcriptional response element |
| HEK293T | Human embryonic kidney 293T |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| i.p. | Intraperitoneal |
| Th12 | The twelfth thoracic |
| L4 | The fourth lumbar |
| GC | Genome copy |
| AP | Anteroposterior |
| ML | Mediolateral |
| DV | Dorsoventral |
| PFA | Paraformaldehyde |
| IB4 | Isolectin B4 |
| GABA | γ-aminobutyric acid |
| PAX2 | Paired box 2 |
| DAPI | 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole |
| DCZ | Deschloroclozapine |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| NMDG | N-Methyl-D-glucamine |
| aCSF | Artificial cerebrospinal fluid |
| EPSCs | Excitatory postsynaptic currents |
| IPSCs | Inhibitory postsynaptic currents |
| DTX | Diphtheria toxin |
| SEM | Standard error of the mean |
| CST | Corticospinal tract |
| DREADD | Designer receptors exclusively activated by designer drugs |
| E/I | Excitatory/Inhibitory |
References
- Colloca, L.; Ludman, T.; Bouhassira, D.; Baron, R.; Dickenson, A.H.; Yarnitsky, D.; Freeman, R.; Truini, A.; Attal, N.; Finnerup, N.B.; et al. Neuropathic pain. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, N.; Moisset, X.; Ferraro, M.C.; de Andrade, D.C.; Baron, R.; Belton, J.; Bennett, D.L.H.; Calvo, M.; Dougherty, P.; Gilron, I.; et al. Pharmacotherapy and non-invasive neuromodulation for neuropathic pain: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2025, 24, 413–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todd, A.J. Neuronal circuitry for pain processing in the dorsal horn. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2010, 11, 823–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peirs, C.; Seal, R.P. Neural circuits for pain: Recent advances and current views. Science 2016, 354, 578–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuda, M. New approach for investigating neuropathic allodynia by optogenetics. Pain 2019, 160 (Suppl. 1), S53–S58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, S.C.; Acton, D.; Goulding, M. Spinal circuits for touch, pain, and itch. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2018, 80, 189–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moehring, F.; Halder, P.; Seal, R.P.; Stucky, C.L. Uncovering the cells and circuits of touch in normal and pathological settings. Neuron 2018, 100, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peirs, C.; Dallel, R.; Todd, A.J. Recent advances in our understanding of the organization of dorsal horn neuron populations and their contribution to cutaneous mechanical allodynia. J. Neural Transm. 2020, 127, 505–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuner, R.; Flor, H. Structural plasticity and reorganisation in chronic pain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2016, 18, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, D.I.; Todd, A.J. Central nervous system targets: Inhibitory interneurons in the spinal cord. Neurotherapeutics 2020, 17, 874–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashima, R.; Koga, K.; Sekine, M.; Kanehisa, K.; Kohro, Y.; Tominaga, K.; Matsushita, K.; Tozaki-Saitoh, H.; Fukazawa, Y.; Inoue, K.; et al. Optogenetic activation of non-nociceptive aβ fibers induces neuropathic pain-like sensory and emotional behaviors after nerve injury in rats. eNeuro 2018, 5, e0450-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashima, R.; Koga, K.; Yoshikawa, Y.; Sekine, M.; Watanabe, M.; Tozaki-Saitoh, H.; Furue, H.; Yasaka, T.; Tsuda, M. A subset of spinal dorsal horn interneurons crucial for gating touch-evoked pain-like behavior. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2021220118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Z.G.; Ito, S.; Honjoh, T.; Ohta, H.; Ishizuka, T.; Fukazawa, Y.; Yawo, H. Light-evoked somatosensory perception of transgenic rats that express channelrhodopsin-2 in dorsal root ganglion cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koga, K.; Descalzi, G.; Chen, T.; Ko, H.G.; Lu, J.; Li, S.; Son, J.; Kim, T.; Kwak, C.; Huganir, R.L.; et al. Coexistence of two forms of ltp in acc provides a synaptic mechanism for the interactions between anxiety and chronic pain. Neuron 2015, 85, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Taniguchi, W.; Chen, Q.Y.; Tozaki-Saitoh, H.; Song, Q.; Liu, R.H.; Koga, K.; Matsuda, T.; Kaito-Sugimura, Y.; Wang, J.; et al. Top-down descending facilitation of spinal sensory excitatory transmission from the anterior cingulate cortex. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Wei, A.; Xu, H.; Gu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Dong, N.; Zheng, C.; Wang, Q.; Gao, M.; Sun, S.; et al. An acc-vta-acc positive-feedback loop mediates the persistence of neuropathic pain and emotional consequences. Nat. Neurosci. 2024, 27, 272–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Gao, Y.; Bao, S.T.; Wang, Y.D.; Jia, T.; Yin, C.; Xiao, C.; Zhou, C. Insula→amygdala and insula→thalamus pathways are involved in comorbid chronic pain and depression-like behavior in mice. J. Neurosci. 2024, 44, e2062232024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Latremoliere, A.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, M.; Wang, X.; Fang, C.; Zhu, J.; Alexandre, C.; Gao, Z.; et al. Touch and tactile neuropathic pain sensitivity are set by corticospinal projections. Nature 2018, 561, 547–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danjo, Y.; Shigetomi, E.; Hirayama, Y.J.; Kobayashi, K.; Ishikawa, T.; Fukazawa, Y.; Shibata, K.; Takanashi, K.; Parajuli, B.; Shinozaki, Y.; et al. Transient astrocytic mglur5 expression drives synaptic plasticity and subsequent chronic pain in mice. J. Exp. Med. 2022, 219, e20210989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.K.; Hayashi, H.; Ishikawa, T.; Shibata, K.; Shigetomi, E.; Shinozaki, Y.; Inada, H.; Roh, S.E.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, G.; et al. Cortical astrocytes rewire somatosensory cortical circuits for peripheral neuropathic pain. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 1983–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Li, M.; Zhao, R.; Sun, L.; Yang, G. A sleep-active basalocortical pathway crucial for generation and maintenance of chronic pain. Nat. Neurosci. 2023, 26, 458–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basbaum, A.I.; Clanton, C.H.; Fields, H.L. Opiate and stimulus-produced analgesia: Functional anatomy of a medullospinal pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1976, 73, 4685–4688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basbaum, A.I.; Fields, H.L. The origin of descending pathways in the dorsolateral funiculus of the spinal cord of the cat and rat: Further studies on the anatomy of pain modulation. J. Comp. Neurol. 1979, 187, 513–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leong, S.K.; Shieh, J.Y.; Wong, W.C. Localizing spinal-cord-projecting neurons in adult albino rats. J. Comp. Neurol. 1984, 228, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nudo, R.J.; Masterton, R.B. Descending pathways to the spinal cord: A comparative study of 22 mammals. J. Comp. Neurol. 1988, 277, 53–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Paxinos, G.; Watson, C. Projections from the brain to the spinal cord in the mouse. Brain Struct. Funct. 2011, 215, 159–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Maunze, B.; Wang, Y.; Tsoulfas, P.; Blackmore, M.G. Global connectivity and function of descending spinal input revealed by 3d microscopy and retrograde transduction. J. Neurosci. 2018, 38, 10566–10581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, C.C.; Jacobi, A.; Su, J.; Chung, L.; van Velthoven, C.T.J.; Yao, Z.; Lee, C.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, S.; Gao, K.; et al. A transcriptomic taxonomy of mouse brain-wide spinal projecting neurons. Nature 2023, 624, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Feng, R.; Chen, Y.; Gao, L. Morphological analysis of descending tracts in mouse spinal cord using tissue clearing, tissue expansion and tiling light sheet microscopy techniques. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 16445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimori, K.; Sekine, M.; Watanabe, M.; Tashima, R.; Tozaki-Saitoh, H.; Tsuda, M. Chemogenetic silencing of spinal cord-projecting cortical neurons attenuates aβ fiber-derived neuropathic allodynia in mice. Neurosci. Res. 2022, 181, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, M.; Iwawaki, T.; Taya, C.; Yonekawa, H.; Noda, M.; Inui, Y.; Mekada, E.; Kimata, Y.; Tsuru, A.; Kohno, K. Diphtheria toxin receptor-mediated conditional and targeted cell ablation in transgenic mice. Nat. Biotechnol. 2001, 19, 746–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, H.; Sugano, E.; Fukazawa, Y.; Isago, H.; Sugiyama, Y.; Hiroi, T.; Ishizuka, T.; Mushiake, H.; Kato, M.; Hirabayashi, M.; et al. Visual properties of transgenic rats harboring the channelrhodopsin-2 gene regulated by the thy-1.2 promoter. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho Kim, S.; Mo Chung, J. An experimental model for peripheral neuropathy produced by segmental spinal nerve ligation in the rat. Pain 1992, 50, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuda, M.; Shigemoto-Mogami, Y.; Koizumi, S.; Mizokoshi, A.; Kohsaka, S.; Salter, M.W.; Inoue, K. P2x4 receptors induced in spinal microglia gate tactile allodynia after nerve injury. Nature 2003, 424, 778–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuda, M.; Kohro, Y.; Yano, T.; Tsujikawa, T.; Kitano, J.; Tozaki-Saitoh, H.; Koyanagi, S.; Ohdo, S.; Ji, R.R.; Salter, M.W.; et al. Jak-stat3 pathway regulates spinal astrocyte proliferation and neuropathic pain maintenance in rats. Brain 2011, 134, 1127–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sueto, D.; I, E.; Onishi, A.; Tsuda, M. Spinal dorsal horn neurons involved in the alleviating effects of cannabinoid receptor agonists on neuropathic allodynia-like behaviors in rats. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2025, 157, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petreanu, L.; Huber, D.; Sobczyk, A.; Svoboda, K. Channelrhodopsin-2-assisted circuit mapping of long-range callosal projections. Nat. Neurosci. 2007, 10, 663–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honsek, S.D.; Seal, R.P.; Sandkühler, J. Presynaptic inhibition of optogenetically identified vglut3+ sensory fibres by opioids and baclofen. Pain 2015, 156, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, B.L. Dreadds for neuroscientists. Neuron 2016, 89, 683–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishibashi, T.; Yoshikawa, Y.; Sueto, D.; Tashima, R.; Tozaki-Saitoh, H.; Koga, K.; Yamaura, K.; Tsuda, M. Selective involvement of a subset of spinal dorsal horn neurons operated by a prodynorphin promoter in aβ fiber-mediated neuropathic allodynia-like behavioral responses in rats. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 911122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, Y.; Miyakawa, N.; Takuwa, H.; Hori, Y.; Oyama, K.; Ji, B.; Takahashi, M.; Huang, X.P.; Slocum, S.T.; DiBerto, J.F.; et al. Deschloroclozapine, a potent and selective chemogenetic actuator enables rapid neuronal and behavioral modulations in mice and monkeys. Nat. Neurosci. 2020, 23, 1157–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Arata, A.; Mizuguchi, R.; Qian, Y.; Karunaratne, A.; Gray, P.A.; Arata, S.; Shirasawa, S.; Bouchard, M.; Luo, P.; et al. Tlx3 and tlx1 are post-mitotic selector genes determining glutamatergic over gabaergic cell fates. Nat. Neurosci. 2004, 7, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koga, K.; Kanehisa, K.; Kohro, Y.; Shiratori-Hayashi, M.; Tozaki-Saitoh, H.; Inoue, K.; Furue, H.; Tsuda, M. Chemogenetic silencing of gabaergic dorsal horn interneurons induces morphine-resistant spontaneous nocifensive behaviours. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasaka, T.; Tiong, S.Y.X.; Hughes, D.I.; Riddell, J.S.; Todd, A.J. Populations of inhibitory and excitatory interneurons in lamina ii of the adult rat spinal dorsal horn revealed by a combined electrophysiological and anatomical approach. Pain 2010, 151, 475–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercer Lindsay, N.; Chen, C.; Gilam, G.; Mackey, S.; Scherrer, G. Brain circuits for pain and its treatment. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eabj7360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.K.; Nabekura, J. Rapid synaptic remodeling in the adult somatosensory cortex following peripheral nerve injury and its association with neuropathic pain. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 5477–5482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, I.; Yoshihara, K.; Cheung, D.L.; Kobayashi, T.; Agetsuma, M.; Tsuda, M.; Eto, K.; Koizumi, S.; Wake, H.; Moorhouse, A.J.; et al. Controlled activation of cortical astrocytes modulates neuropathic pain-like behaviour. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.M.; Hu, R.; Mao, Y.; Tai, Y.; Qun, S.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, D.; Jin, Y. Up-regulation of hcn2 channels in a thalamocortical circuit mediates allodynia in mice. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2023, 10, nwac275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shinotsuka, S.; I, E.; Sueto, D.; Fujimori, K.; Yamaura, K.; Tsuda, M. Spinal Dorsal Horn Neurons Receiving Descending Input from the Primary Somatosensory Cortex Contribute to Aβ Fiber-Induced Neuropathic Allodynia in Male Rats. Cells 2025, 14, 1870. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14231870
Shinotsuka S, I E, Sueto D, Fujimori K, Yamaura K, Tsuda M. Spinal Dorsal Horn Neurons Receiving Descending Input from the Primary Somatosensory Cortex Contribute to Aβ Fiber-Induced Neuropathic Allodynia in Male Rats. Cells. 2025; 14(23):1870. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14231870
Chicago/Turabian StyleShinotsuka, Sho, Eriko I, Daichi Sueto, Kazuki Fujimori, Ken Yamaura, and Makoto Tsuda. 2025. "Spinal Dorsal Horn Neurons Receiving Descending Input from the Primary Somatosensory Cortex Contribute to Aβ Fiber-Induced Neuropathic Allodynia in Male Rats" Cells 14, no. 23: 1870. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14231870
APA StyleShinotsuka, S., I, E., Sueto, D., Fujimori, K., Yamaura, K., & Tsuda, M. (2025). Spinal Dorsal Horn Neurons Receiving Descending Input from the Primary Somatosensory Cortex Contribute to Aβ Fiber-Induced Neuropathic Allodynia in Male Rats. Cells, 14(23), 1870. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14231870





