Astrocyte Transcriptomics in a Three-Dimensional Tissue-Engineered Rostral Migratory Stream
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
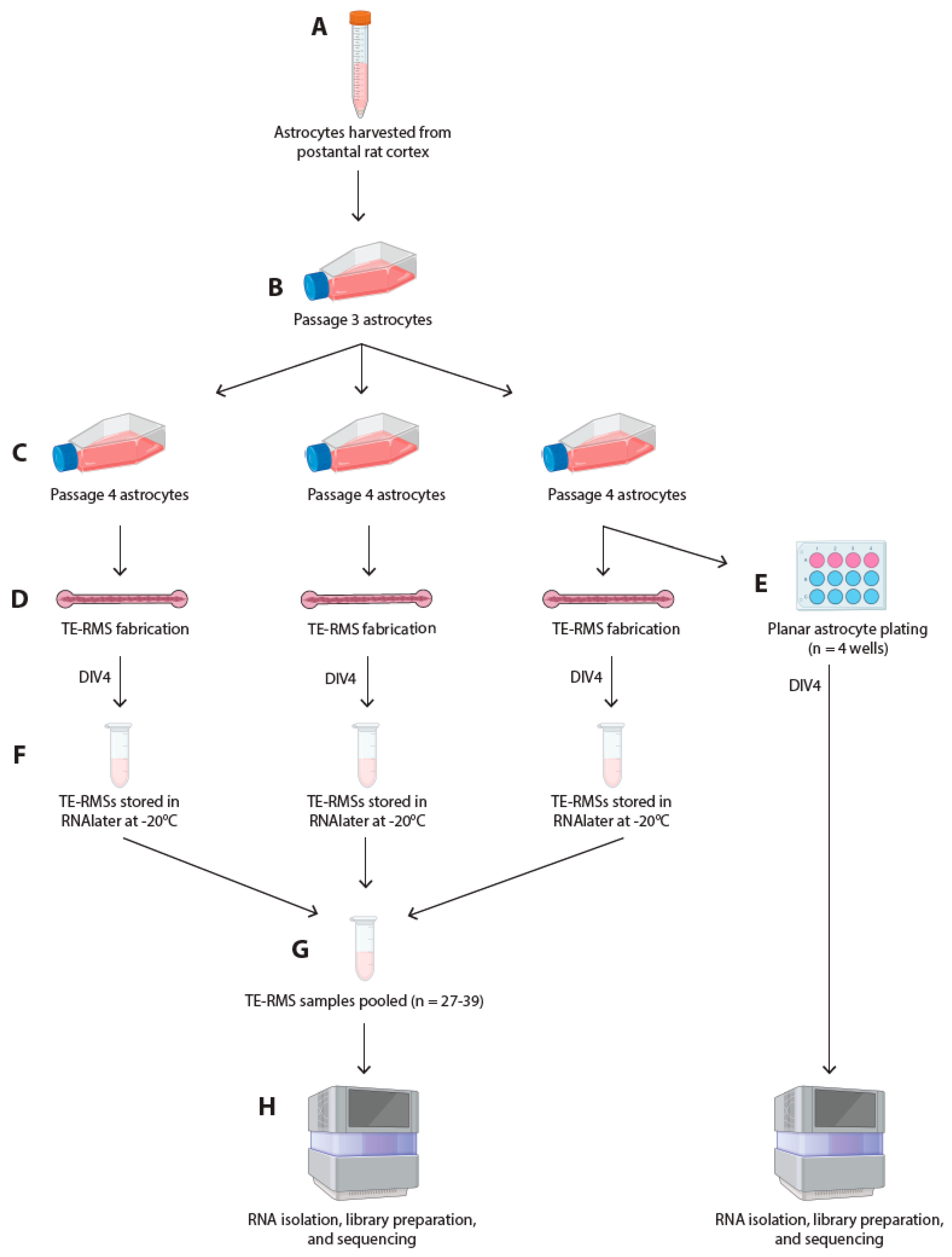
2.1. Isolation and Culture of Astrocytes
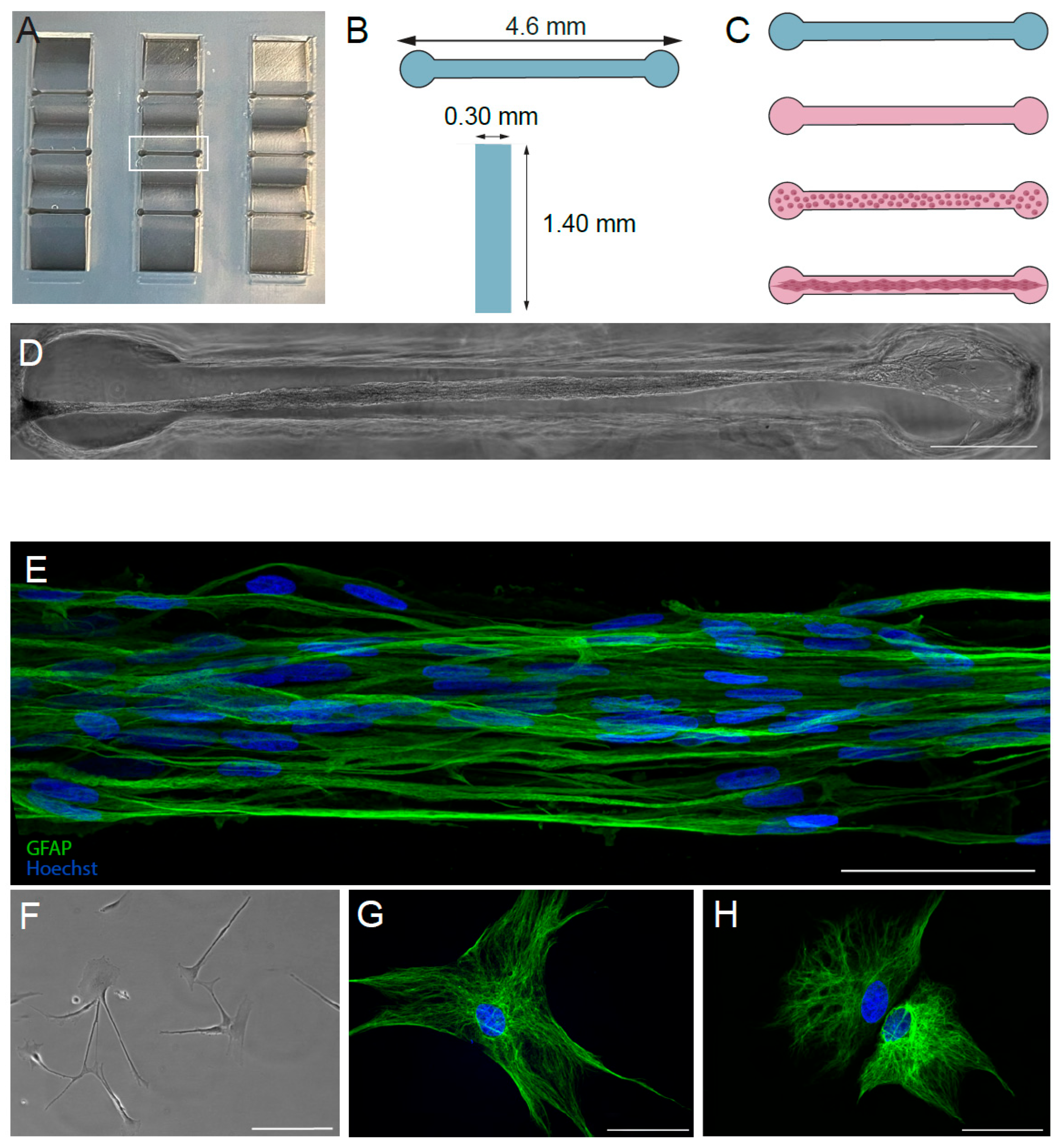
2.2. Fabrication of Molds and Hydrogel Microchannels
2.3. Fabrication of Tissue-Engineered Rostral Migratory Streams and Planar Astrocyte Cultures
2.4. Immunocytochemistry
2.5. Imaging
2.6. RNA Extraction and RNA Sequencing
2.7. Data Analysis
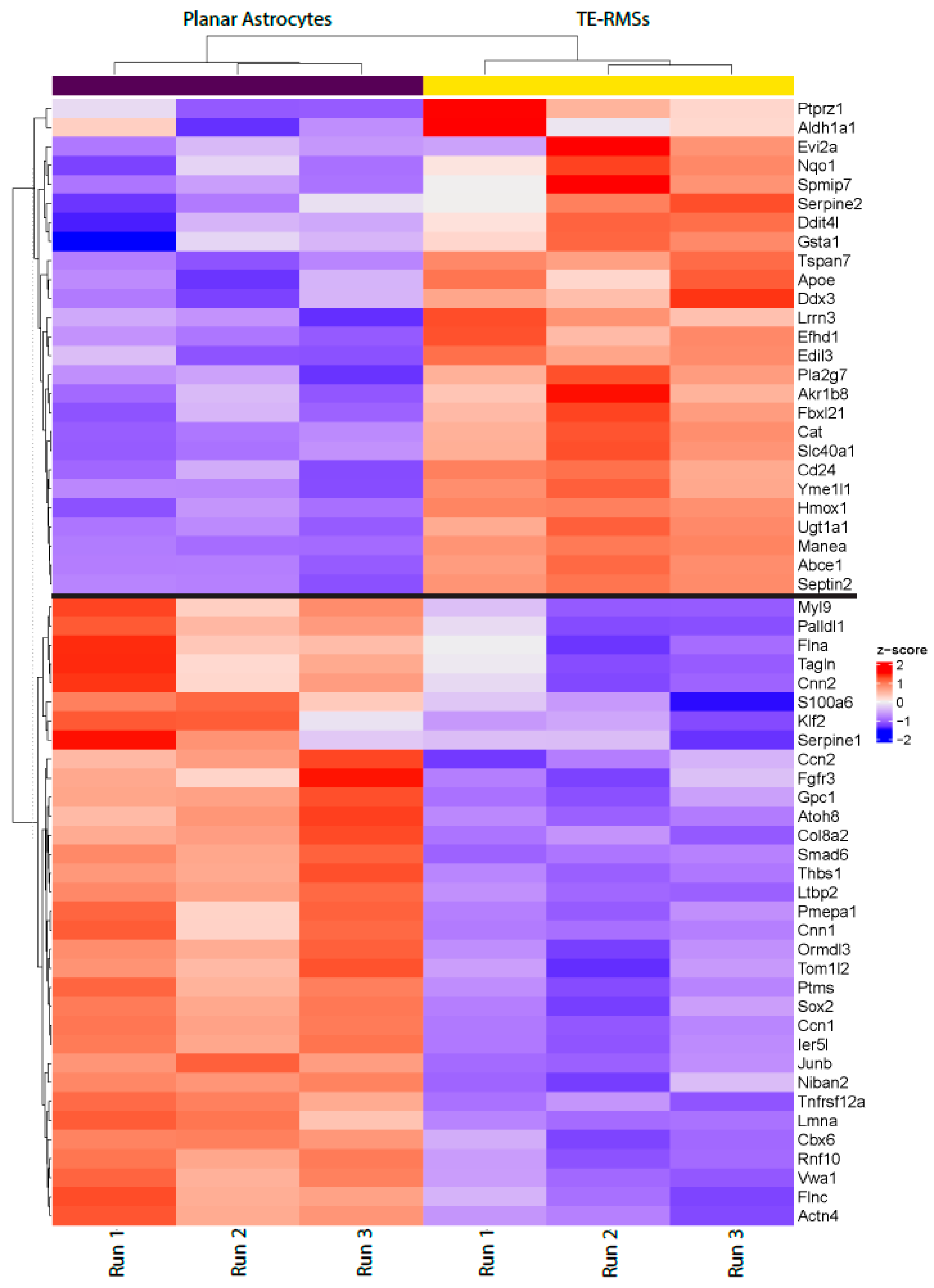
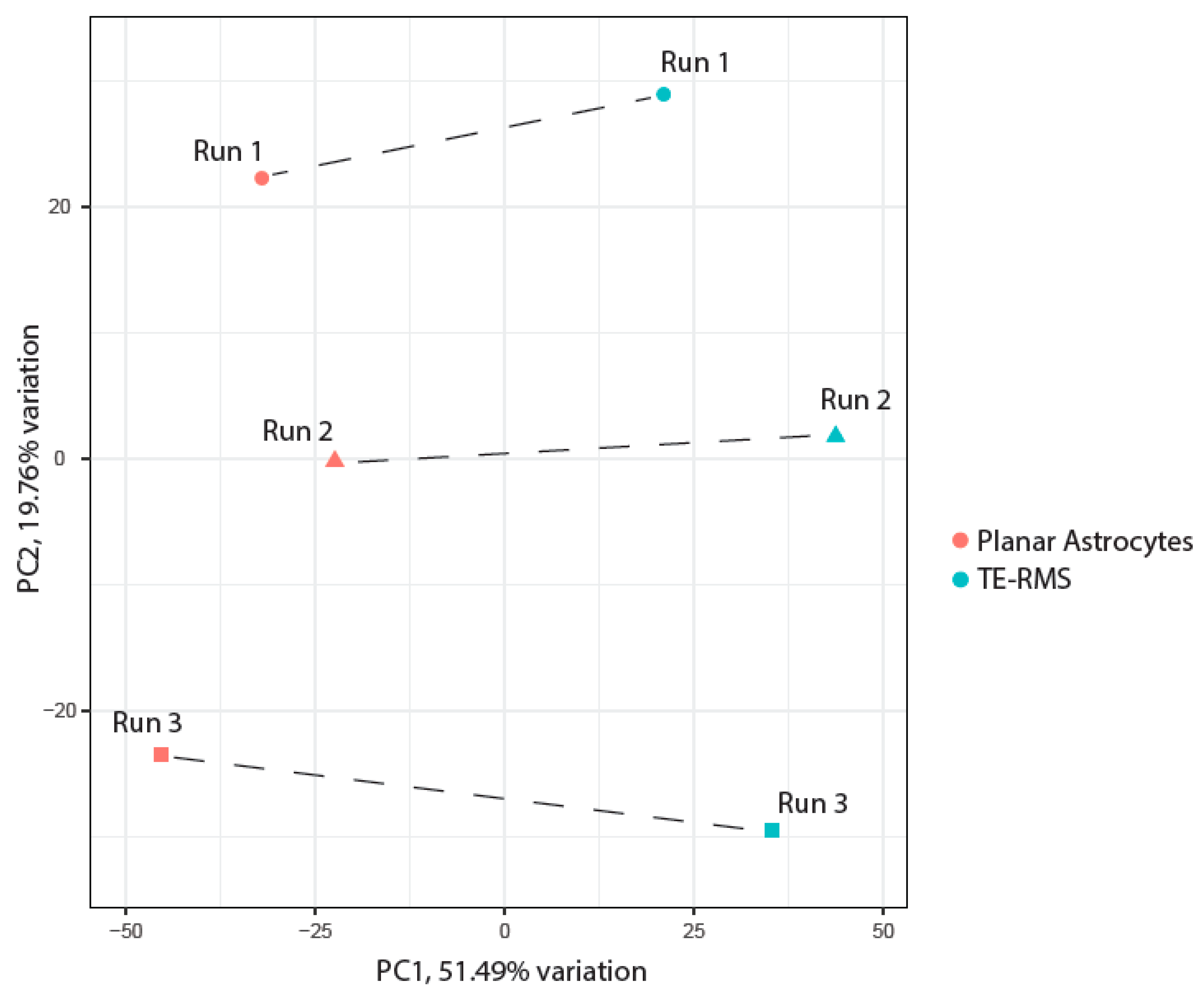
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SVZ | Subventricular Zone |
| NPC | Neural Precursor Cell |
| RMS | Rostral Migratory Stream |
| TE-RMS | Tissue Engineered-Rostral Migratory Stream |
| RNA | Ribonucleic Acid |
| DIV | Days In Vitro |
| GFAP | Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein |
| PCA | Principle Component Analysis |
| DE | Differential Expression |
| NES | Normalized Enrichment Score |
References
- Sofroniew, M.V.; Vinters, H.V. Astrocytes: Biology and pathology. Acta Neuropathol. 2010, 119, 7–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, K.T.; Murai, K.K.; Khakh, B.S. Astrocyte morphology. Trends Cell Biol. 2024, 34, 547–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khakh, B.S.; Deneen, B. The Emerging Nature of Astrocyte Diversity. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2019, 42, 187–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matyash, V.; Kettenmann, H. Heterogeneity in astrocyte morphology and physiology. Brain Res. Rev. 2010, 63, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bushong, E.A.; Martone, M.E.; Jones, Y.Z.; Ellisman, M.H. Protoplasmic Astrocytes in CA1 Stratum Radiatum Occupy Separate Anatomical Domains. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Haim, L.; Rowitch, D.H. Functional diversity of astrocytes in neural circuit regulation. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2017, 18, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peretto, P.; Merighi, A.; Fasolo, A.; Bonfanti, L. Glial tubes in the rostral migratory stream of the adult rat. Brain Res. Bull. 1997, 42, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peretto, P.; Giachino, C.; Aimar, P.; Fasolo, A.; Bonfanti, L. Chain formation and glial tube assembly in the shift from neonatal to adult subventricular zone of the rodent forebrain. J. Comp. Neurol. 2005, 487, 407–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, C.C.; Katiyar, K.S.; Hernandez, N.S.; Song, Y.J.; Struzyna, L.A.; Harris, J.P.; Cullen, D.K. Transplantable living scaffolds comprised of micro-tissue engineered aligned astrocyte networks to facilitate central nervous system regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2016, 38, 44–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katiyar, K.S.; Winter, C.C.; Gordián-Vélez, W.J.; O’DOnnell, J.C.; Song, Y.J.; Hernandez, N.S.; Struzyna, L.A.; Cullen, D.K. Three-dimensional Tissue Engineered Aligned Astrocyte Networks to Recapitulate Developmental Mechanisms and Facilitate Nervous System Regeneration. J. Vis. Exp. 2018, 131, e55848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullen, D.K.; O′Donnell, J.; Katiyar, K.S.; Panzer, K.V. A tissue-engineered rostral migratory stream for directed neuronal replacement. Neural Regen. Res. 2018, 13, 1327–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’dOnnell, J.C.; Purvis, E.M.; Helm, K.V.T.; Adewole, D.O.; Zhang, Q.; Le, A.D.; Cullen, D.K. An implantable human stem cell-derived tissue-engineered rostral migratory stream for directed neuronal replacement. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, D.A.; Alvarez-Buylla, A. The adult Ventricular–Subventricular Zone (V-SVZ) and Olfactory Bulb (OB) neurogenesis. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2016, 8, a018820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lledo, P.-M.; Merkle, F.T.; Alvarez-Buylla, A. Origin and function of olfactory bulb interneuron diversity. Trends Neurosci. 2008, 31, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Deng, W.; Gage, F.H. Mechanisms and Functional Implications of Adult Neurogenesis. Cell 2008, 132, 645–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, G.-L.; Song, H. Adult Neurogenesis in the Mammalian Brain: Significant Answers and Significant Questions. Neuron 2011, 70, 687–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brill, M.S.; Ninkovic, J.; Winpenny, E.; Hodge, R.D.; Ozen, I.; Yang, R.; Lepier, A.; Gascón, S.; Erdelyi, F.; Szabo, G.; et al. Adult generation of glutamatergic olfactory bulb interneurons. Nat. Neurosci. 2009, 12, 1524–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarini, F.; Lledo, P.-M. Is adult neurogenesis essential for olfaction? Trends Neurosci. 2011, 34, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Wang, Y.; Xie, L.; Mao, X.; Won, S.J.; Galvan, V.; Jin, K. Effect of neural precursor proliferation level on neurogenesis in rat brain during aging and after focal ischemia. Neurobiol. Aging 2009, 30, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, E.H.; Adorjan, I.; Mundim, M.V.; Sun, B.; Dizon, M.L.V.; Szele, F.G. Traumatic Brain Injury Activation of the Adult Subventricular Zone Neurogenic Niche. Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Manaenko, A.; Hu, Q. Targeting Adult Neurogenesis for Poststroke Therapy. Stem Cells Int. 2017, 2017, 5868632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.-W.; Wang, Y.-Q.; Xu, M.; Shen, D.-H.; Wang, J.-J.; Huang, F.; Yu, Z.; Sun, F.-Y. Functional Integration of newly generated neurons into striatum after cerebral ischemia in the adult rat brain. Stroke 2008, 39, 2837–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneko, N.; Herranz-Pérez, V.; Otsuka, T.; Sano, H.; Ohno, N.; Omata, T.; Nguyen, H.B.; Thai, T.Q.; Nambu, A.; Kawaguchi, Y.; et al. New neurons use Slit-Robo signaling to migrate through the glial meshwork and approach a lesion for functional regeneration. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaav0618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Zheng, M.; Zhong, J.; Ma, F.; Zhou, B.; Zhu, J. Neurogenic Niche Conversion Strategy Induces Migration and Functional Neuronal Differentiation of Neural Precursor Cells Following Brain Injury. Stem Cells Dev. 2020, 29, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohab, J.J.; Fleming, S.; Blesch, A.; Carmichael, S.T. A neurovascular niche for neurogenesis after stroke. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 13007–13016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, B.; Morshead, C.; Gonzalez, C.; Kim, M.; Gregg, C.; Shingo, T.; Weiss, S. Growth factor-stimulated generation of new cortical tissue and functional recovery after stroke damage to the motor cortex of rats. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2007, 27, 983–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SchäbItz, W.-R.; Steigleder, T.; Cooper-Kuhn, C.M.; Schwab, S.; Sommer, C.; Schneider, A.; Kuhn, H.G. Intravenous brain-derived neurotrophic factor enhances poststroke sensorimotor recovery and stimulates neurogenesis. Stroke 2007, 38, 2165–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popa-Wagner, A.; StöcKer, K.; Balseanu, A.T.; Rogalewski, A.; Diederich, K.; Minnerup, J.; Margaritescu, C.; SchäbItz, W.-R. Effects of granulocyte-colony stimulating factor after stroke in aged rats. Stroke 2010, 41, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erlandsson, A.; Lin, C.-H.A.; Yu, F.; Morshead, C.M. Immunosuppression promotes endogenous neural stem and progenitor cell migration and tissue regeneration after ischemic injury. Exp. Neurol. 2011, 230, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.-J.; Tseng, K.-Y.; Shen, H.; Harvey, B.K.; Airavaara, M.; Wang, Y. Local administration of AAV-BDNF to subventricular zone induces functional recovery in stroke rats. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, A.R.; Carter, A.B.; Hager, L.E.; Price, E.M. In Vivo Neural Tissue Engineering: Cylindrical Biocompatible Hydrogels That Create New Neural Tracts in the Adult Mammalian Brain. Stem Cells Dev. 2016, 25, 1109–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundelach, J.; Koch, M. Redirection of neuroblast migration from the rostral migratory stream into a lesion in the prefrontal cortex of adult rats. Exp. Brain Res. 2018, 236, 1181–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinnou, H.; Sawada, M.; Kawase, K.; Kaneko, N.; Herranz-Pérez, V.; Miyamoto, T.; Kawaue, T.; Miyata, T.; Tabata, Y.; Akaike, T.; et al. Radial Glial Fibers Promote Neuronal Migration and Functional Recovery after Neonatal Brain Injury. Cell Stem Cell 2018, 22, 128–137.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettikiriarachchi, J.T.S.; Parish, C.L.; Shoichet, M.S.; Forsythe, J.S.; Nisbet, D.R. Biomaterials for brain tissue engineering. Aust. J. Chem. 2010, 63, 1143–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, E.P.; Silva-Correia, J.; Reis, R.L.; Oliveira, J.M. Biomaterials Developments for Brain Tissue Engineering. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018, 1078, 323–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purvis, E.M.; O’DOnnell, J.C.; Chen, H.I.; Cullen, D.K. Tissue Engineering and Biomaterial Strategies to Elicit Endogenous Neuronal Replacement in the Brain. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purvis, E.M.; O’donnell, J.C.; Cullen, D.K. Unique Astrocyte Cytoskeletal and Nuclear Morphology in a Three-Dimensional Tissue-Engineered Rostral Migratory Stream. Neuroglia 2022, 3, 41–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purvis, E.M.; Garcia-Epelboim, A.D.; Krizman, E.N.; O’dOnnell, J.C.; Cullen, D.K. A three-dimensional tissue-engineered rostral migratory stream as an in vitro platform for subventricular zone-derived cell migration. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2024, 12, 1410717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belaadi, N.; Aureille, J.; Guilluy, C. Under pressure: Mechanical stress management in the nucleus. Cells 2016, 5, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spichal, M.; Fabre, E. The emerging role of the cytoskeleton in chromosome dynamics. Front. Genet. 2017, 8, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Luo, Q.; Sun, J.; Song, G. Nucleus and nucleus-cytoskeleton connections in 3D cell migration. Exp. Cell Res. 2016, 348, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patro, R.; Duggal, G.; Love, M.I.; Irizarry, R.A.; Kingsford, C. Salmon provides fast and bias-aware quantification of transcript expression. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 417–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Core Team; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Love, M.I.; Soneson, C.; Hickey, P.F.; Johnson, L.K.; Pierce, N.T.; Shepherd, L.; Morgan, M.; Patro, R. Tximeta: Reference sequence checksums for provenance identification in RNA-seq. PLOS Comput. Biol. 2020, 16, e1007664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durinck, S.; Moreau, Y.; Kasprzyk, A.; Davis, S.; De Moor, B.; Brazma, A.; Huber, W. BioMart and Bioconductor: A powerful link between biological databases and microarray data analysis. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 3439–3440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blighe, K.; Lun, A. PCAtools: Everything Principal Components Analysis; R Package Version 2.20.0. 2024. Available online: https://github.com/kevinblighe/PCAtools (accessed on 7 August 2025). [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Eils, R.; Schlesner, M. Complex heatmaps reveal patterns and correlations in multidimensional genomic data. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 2847–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberzon, A.; Subramanian, A.; Pinchback, R.; Thorvaldsdóttir, H.; Tamayo, P.; Mesirov, J.P. Molecular signatures database (MSigDB) 3.0. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 1739–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, A.; Tamayo, P.; Mootha, V.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Ebert, B.L.; Gillette, M.A.; Paulovich, A.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Golub, T.R.; Lander, E.S.; et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: A knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15545–15550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacco, D.A.; Ouyang, J.; Lee, H.-Y.; Catic, A.; Ploegh, H.; Gill, G. The SUMO-Specific Protease SENP5 Is Required for Cell Division. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2006, 26, 4489–4498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, E.T.; Gong, L.; Kamitani, T. Ubiquitin-like proteins: New wines in new bottles. Gene 2000, 248, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Cui, Z.; Yan, T.; Wu, J.; Liu, Z. CCN5 inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. Cell Biol. Int. 2020, 44, 998–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, J.; Mah, W.; Kim, E. The SALM/Lrfn family of leucine-rich repeat-containing cell adhesion molecules. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2011, 22, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Huang, N.; Bao, Y.; Zhou, H.; Teng, J.; Chen, J. LRRC45 is a centrosome linker component required for centrosome cohesion. Cell Rep. 2013, 4, 1100–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, H.; Schiebel, E. Emerging roles of centrosome cohesion. Open Biol. 2022, 12, 220229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckerich, C.; Zapf, S.; Ulbricht, U.; Müller, S.; Fillbrandt, R.; Westphal, M.; Lamszus, K. Contactin is expressed in human astrocytic gliomas and mediates repulsive effects. Glia 2006, 53, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.-J.; Ma, M.-H.; Li, J.-M.; Lu, X.-Y.; Lu, C.-B.; Zhou, S.-F.; Zhang, L.-X.; Li, M.-Q.; Shao, T.-Z.; Bai, S.-P.; et al. CNTN1 Aggravates Neuroinflammation and Triggers Cognitive Deficits in Male Mice by Boosting Crosstalk between Microglia and Astrocytes. Aging Dis. 2023, 14, 1853–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Pizarro, A.; Picó, S.; López-Márquez, A.; Rodriguez-López, C.; Montalvo, E.; Alvarez, M.; Castro, M.; Ramón-Maiques, S.; Pérez, B.; Lucas, J.J.; et al. PAH deficient pathology in humanized c.1066-11G>A phenylketonuria mice. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2024, 33, 1074–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleary, M.; Uboha, N.; Picciotto, M.; Beech, R. Expression of ezrin in glial tubes in the adult subventricular zone and rostral migratory stream. Neuroscience 2006, 143, 851–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, N.; Sawada, M.; Sawamoto, K. Mechanisms of neuronal migration in the adult brain. J. Neurochem. 2017, 141, 835–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Walsh, C.A. The many faces of filamin: A versatile molecular scaffold for cell motility and signalling. Nat. Cell Biol. 2004, 6, 1034–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, N.-X.; Yin, J.-C.; Chen, G. Transcriptome Analysis of Small Molecule–Mediated Astrocyte-to-Neuron Reprogramming. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 7, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boukhelifa, M.; Hwang, S.J.; Valtschanoff, J.G.; Meeker, R.B.; Rustioni, A.; Otey, C.A. A critical role for palladin in astrocyte morphology and response to injury. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asensio-Juárez, G.; Llorente-González, C.; Vicente-Manzanares, M. Linking the Landscape of MYH9-Related Diseases to the Molecular Mechanisms that Control Non-Muscle Myosin II-A Function in Cells. Cells 2020, 9, 1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okubo-Suzuki, R.; Okada, D.; Sekiguchi, M.; Inokuchi, K. Synaptopodin maintains the neural activity-dependent enlargement of dendritic spines in hippocampal neurons. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2008, 38, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Jin, J.-P. Calponin isoforms CNN 1, CNN 2 and CNN 3: Regulators for actin cytoskeleton functions in smooth muscle and non-muscle cells. Gene 2016, 585, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankar, R.; John, S.; Devi, P.; Gupta, S.; Gupta, S. Exploring the prognosis of calponin h1 in carcinogenesis: A novel target in biomedical research. Oral Oncol. Rep. 2024, 10, 100325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, A.C.; Young, P.W. The actinin family of actin cross-linking proteins—A genetic perspective. Cell Biosci. 2015, 5, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauen, D.W.; Haffner, M.C.; Kim, J.; Zheng, Q.; Yin, H.; DeMarzo, A.M.; Mahairaki, V.; Colantuoni, C.; Pickering, J.G.; Johnson, T.P. Putative Autoantigen Leiomodin-1 Is Expressed in the Human Brain and in the Membrane Fraction of Newly Formed Neurons. Pathogens 2020, 9, 1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignataro, L.; Varodayan, F.P.; Tannenholz, L.E.; Protiva, P.; Harrison, N.L. Brief alcohol exposure alters transcription in astrocytes via the heat shock pathway. Brain Behav. 2013, 3, 114–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villablanca, C.; Vidal, R.; Gonzalez-Billault, C. Are cytoskeleton changes observed in astrocytes functionally linked to aging? Brain Res. Bull. 2023, 196, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murk, K.; Suarez, E.M.B.; Cockbill, L.M.R.; Banks, P.; Hanley, J.G. The antagonistic modulation of Arp2/3 activity by N-WASP/WAVE2 and PICK1 defines dynamic changes in astrocyte morphology. J. Cell Sci. 2013, 126, 3873–3883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmor-Kollet, N.; Berkun, V.; Cummings, G.; Keren-Shaul, H.; David, E.; Addadi, Y.; Schuldiner, O. Actin-dependent astrocytic infiltration is a key step for axon defasciculation during remodeling. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 112117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

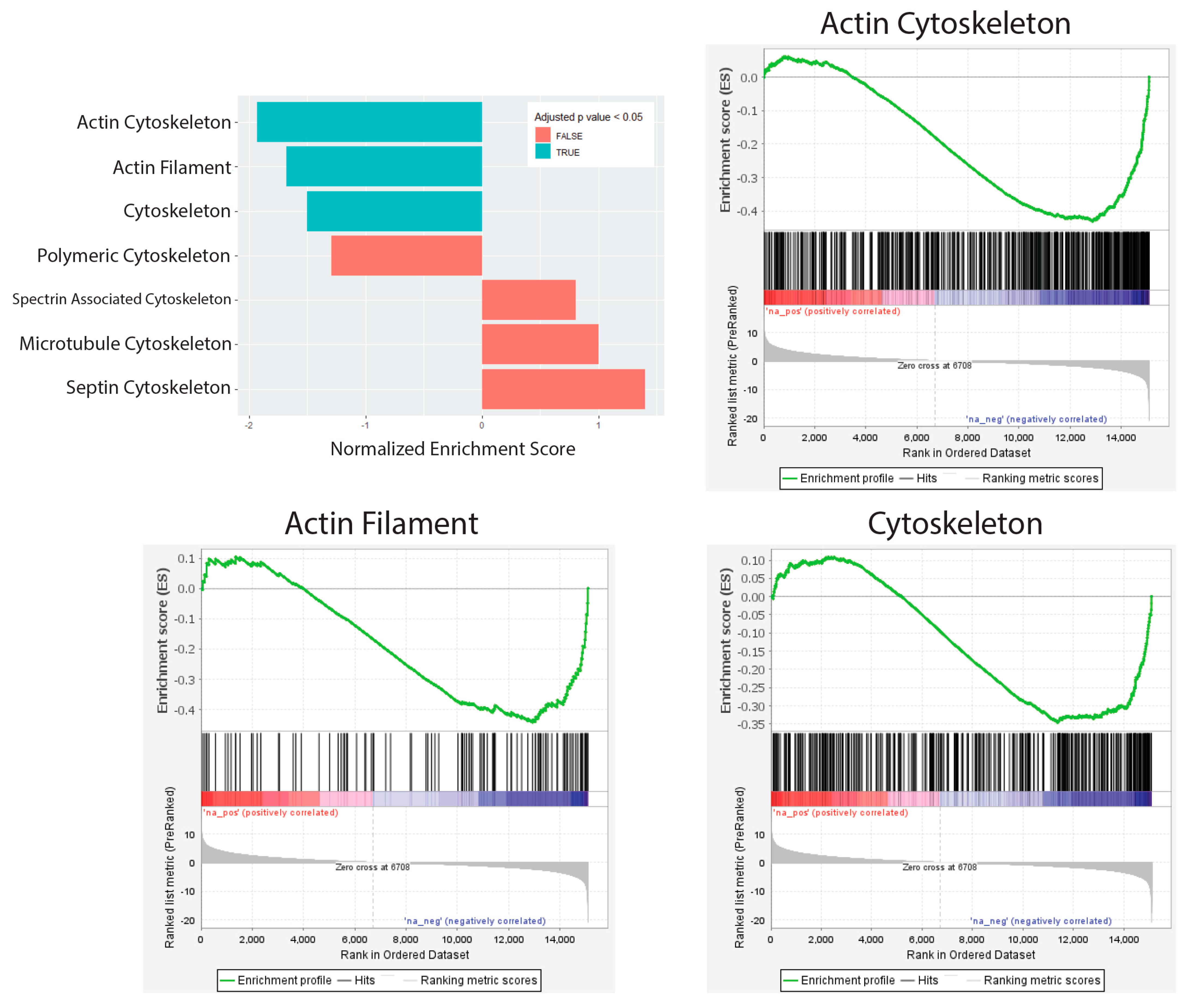

| Gene Name | Description | Fold Change (log2) | Adjusted p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| LOC690251 | similar to SUMO/sentrin specific protease 5 [Accession Number:1582860] | −10.06 | 0.0358 |
| wbp4-ps1 | WW domain binding protein 4, pseudogene 1 [Accession Number:2320129] | −9.73 | 0.0088 |
| ENSRNOG00000067245 | Unknown | −9.17 | 1.135 × 10−7 |
| ccn5 | cellular communication network factor 5 [Accession Number 621867] | −9.05 | 0.0021 |
| LOC685989 | hypothetical protein LOC685989 [Accession Number:1587786] | −8.57 | 0.0074 |
| lrfn1 | leucine rich repeat and fibronectin type III domain containing 1 [Accession Number:1304707] | −8.02 | 7.813 × 10−5 |
| hs3st3b1 | heparan sulfate-glucosamine 3-sulfotransferase 3B1 [Accession Number:1307326] | −7.55 | 0.0011 |
| xkr4 | XK related 4 [Accession Number:1549780] | −7.49 | 0.0022 |
| lypd8 | Ly6/Plaur domain containing 8 [Accession Number:1586251] | −7.46 | 0.0011 |
| LOC102549173 | histone H3.2-like [Accession Number:7709329] | −7.40 | 0.0016 |
| Gene Name | Description | Fold Change (log2) | Adjusted p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| lrrc45 | leucine rich repeat containing 45 [Accession Number:1590053] | 8.27 | 0.0343 |
| cym | chymosin [Accession Number:708486] | 8.26 | 1.1964 × 10−11 |
| cntn1 | contactin 1 [Accession Number:621300] | 7.18 | 0.0010 |
| abca17 | ATP-binding cassette, subfamily A (ABC1), member 17 [Accession Number:1560494] | 6.93 | 0.0189 |
| pah | phenylalanine hydroxylase [Accession Number:3248] | 6.62 | 0.0137 |
| arhgef37 | Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor 37 [Accession Number:1560471] | 6.56 | 0.0137 |
| lrrc25 | leucine rich repeat containing 25 [Accession Number:1564818] | 6.18 | 9.820 × 10−15 |
| itga2 | integrin subunit alpha 2 [Accession Number:621632] | 6.07 | 0.0164 |
| ppfia2 | PTPRF interacting protein alpha 2 [Accession Number:1305021] | 5.99 | 0.0251 |
| col10a1 | collagen type X alpha 1 chain [Accession Number:2371] | 5.86 | 0.0154 |
| Gene Name | Description | Rank in Gene List | Rank Metric Score | Running Enrichment Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| flna | Filamin A [Accession Number: HGNC:3754] | 15,098 | −13.501 | 0.0006 |
| myl9 | Myosin light chain 9 [Accession Number: HGNC:15754] | 15,097 | −13.221 | −0.0183 |
| palld | Paladin, cytoskeletal associated protein [Accession Number: HGNC:3754] | 15,084 | −10.851 | −0.0360 |
| myh9 | Myosin heavy chain 9 [Accession Number: HGNC:7579] | 15,033 | −8.190 | −0.0479 |
| synpo | Synaptopodin [Accession Number: HGNC:30672] | 15,023 | −8.037 | −0.0587 |
| Gene Name | Description | Rank in Gene List | Rank Metric Score | Running Enrichment Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| cnn1 | Calponin 1 [Accession Number: HGNC:2155] | 15,101 | −13.986 | 0.0004 |
| flna | Filamin A [Accession Number: HGNC:3754] | 15,098 | −13.501 | −0.0132 |
| myl9 | Myosin light chain 9 [Accession Number: HGNC:15754] | 15,097 | −13.221 | −0.0265 |
| actn4 | Actinin Alpha 4 [Accession Number: HGNC:166] | 15,085 | −10.932 | −0.0388 |
| palld | Paladin, cytoskeletal associated protein [Accession Number: HGNC:3754] | 15,084 | −10.851 | −0.0495 |
| Gene Name | Description | Rank in Gene List | Rank Metric Score | Running Enrichment Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| flna | Filamin A [Accession Number: HGNC:3754] | 15,098 | −13.501 | 0.0006 |
| palld | Paladin, cytoskeletal associated protein [Accession Number: HGNC:3754] | 15,084 | −10.851 | −0.0480 |
| actn1 | Actinin Alpha 1 [Accession Number: HGNC:163] | 15,042 | −8.538 | −0.0851 |
| lmod1 | Leiomodin 1 [Accession Number: HGNC:6647] | 15,019 | −7.929 | −0.1149 |
| tpm2 | Tropomyosin 2 [Accession Number: HGNC:12011] | 15,000 | −7.515 | −0.1428 |
| Gene Name | Biological Function and Role | References |
|---|---|---|
| flna |
| [63] Feng & Walsh, 2004 |
| myl9 |
| [64] Ma et al., 2019 |
| palld |
| [65] Boukhelifa et al., 2003 |
| myh9 |
| [66] Asensio-Juárez et al., 2020 |
| synpo |
| [67] Okubo-Suzuki et al., 2008 |
| cnn1 |
| [68] Liu & Jin., 2016 [69] Sankar et al., 2024 |
| actn1 |
| [70] Murphy & Young, 2015 |
| actn4 |
| [70] Murphy & Young, 2015 |
| imod1 |
| [71] Nauen et al., 2020 |
| tpm2 |
| [72] Pignataro et al., 2013 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grovola, M.R.; Purvis, E.M.; Garcia-Epelboim, A.D.; Krizman, E.N.; O’Donnell, J.C.; Cullen, D.K. Astrocyte Transcriptomics in a Three-Dimensional Tissue-Engineered Rostral Migratory Stream. Cells 2025, 14, 1646. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14211646
Grovola MR, Purvis EM, Garcia-Epelboim AD, Krizman EN, O’Donnell JC, Cullen DK. Astrocyte Transcriptomics in a Three-Dimensional Tissue-Engineered Rostral Migratory Stream. Cells. 2025; 14(21):1646. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14211646
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrovola, Michael R., Erin M. Purvis, Andrés D. Garcia-Epelboim, Elizabeth N. Krizman, John C. O’Donnell, and D. Kacy Cullen. 2025. "Astrocyte Transcriptomics in a Three-Dimensional Tissue-Engineered Rostral Migratory Stream" Cells 14, no. 21: 1646. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14211646
APA StyleGrovola, M. R., Purvis, E. M., Garcia-Epelboim, A. D., Krizman, E. N., O’Donnell, J. C., & Cullen, D. K. (2025). Astrocyte Transcriptomics in a Three-Dimensional Tissue-Engineered Rostral Migratory Stream. Cells, 14(21), 1646. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14211646





