Extracellular Vesicles Profiling in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cell Lines: A Proteomic Characterization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. AML Cells Culture and Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Purification
2.2. Dynamic Light Scattering Analysis
2.3. Western Blotting Analysis
2.4. Proteomics and Bioinformatic Analyses
3. Results
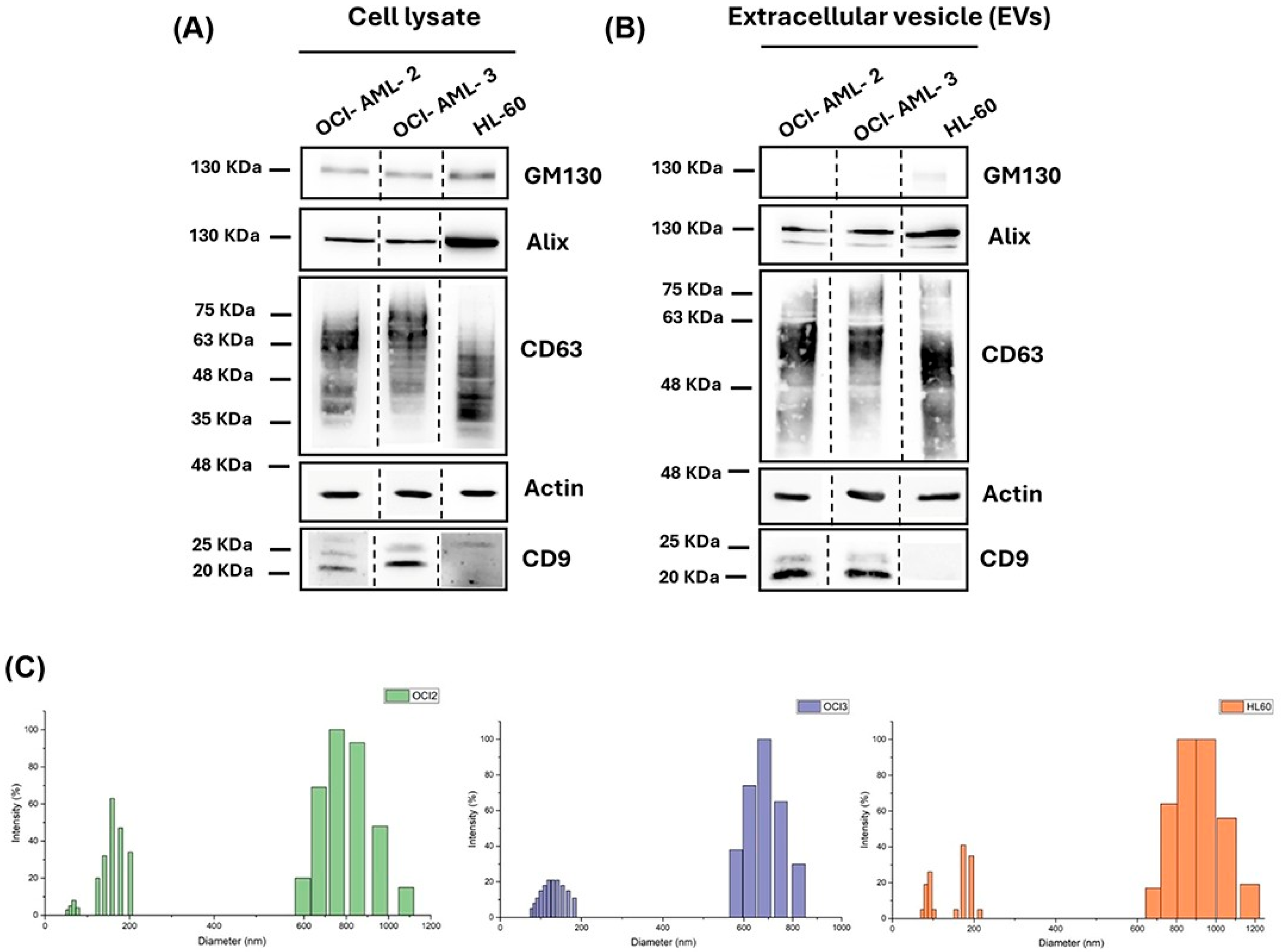
3.1. Extracellular Vesicles Isolation, Validation, and Characterization
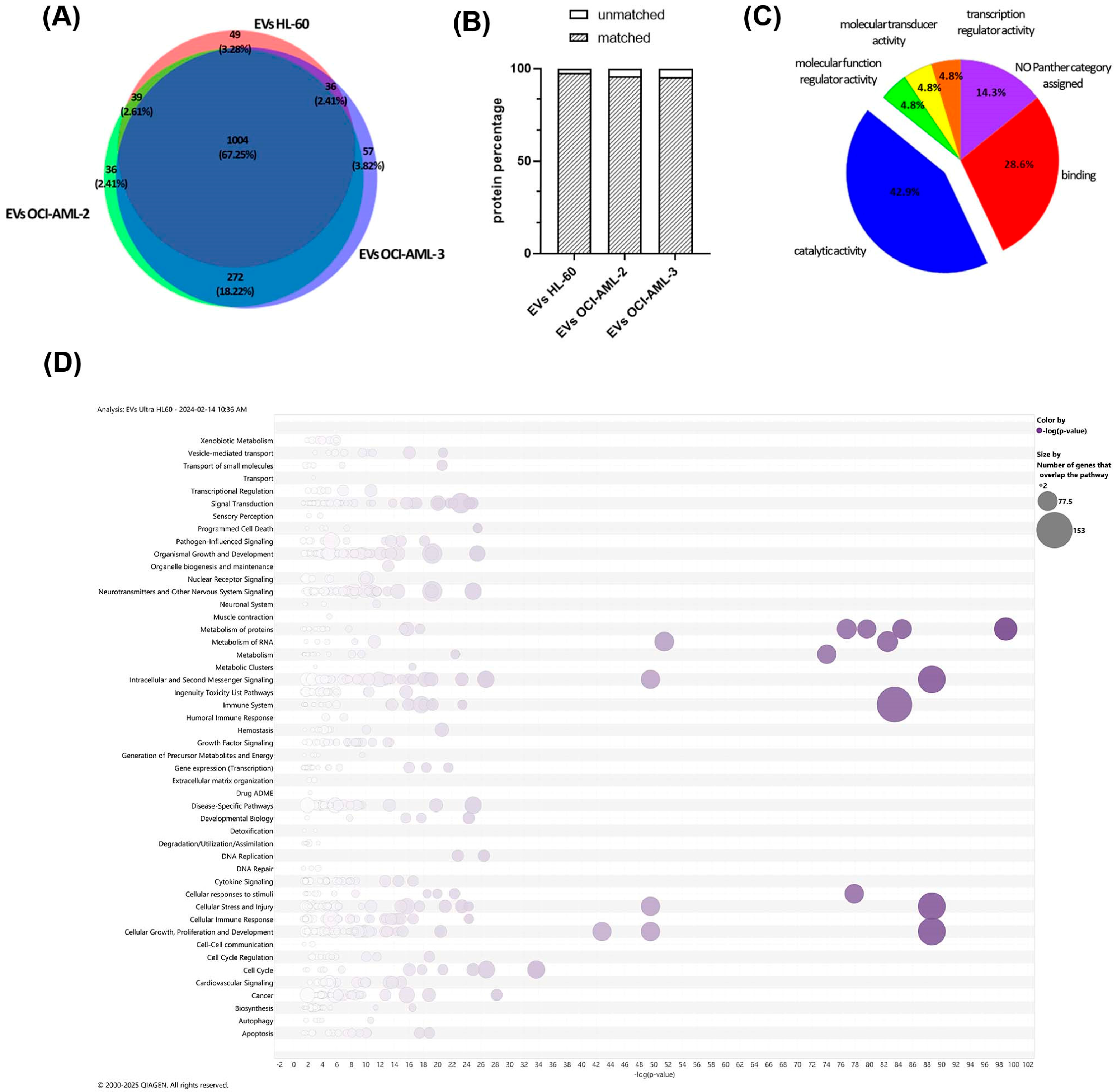
3.2. Proteome Profiling of AML-Derived EVs
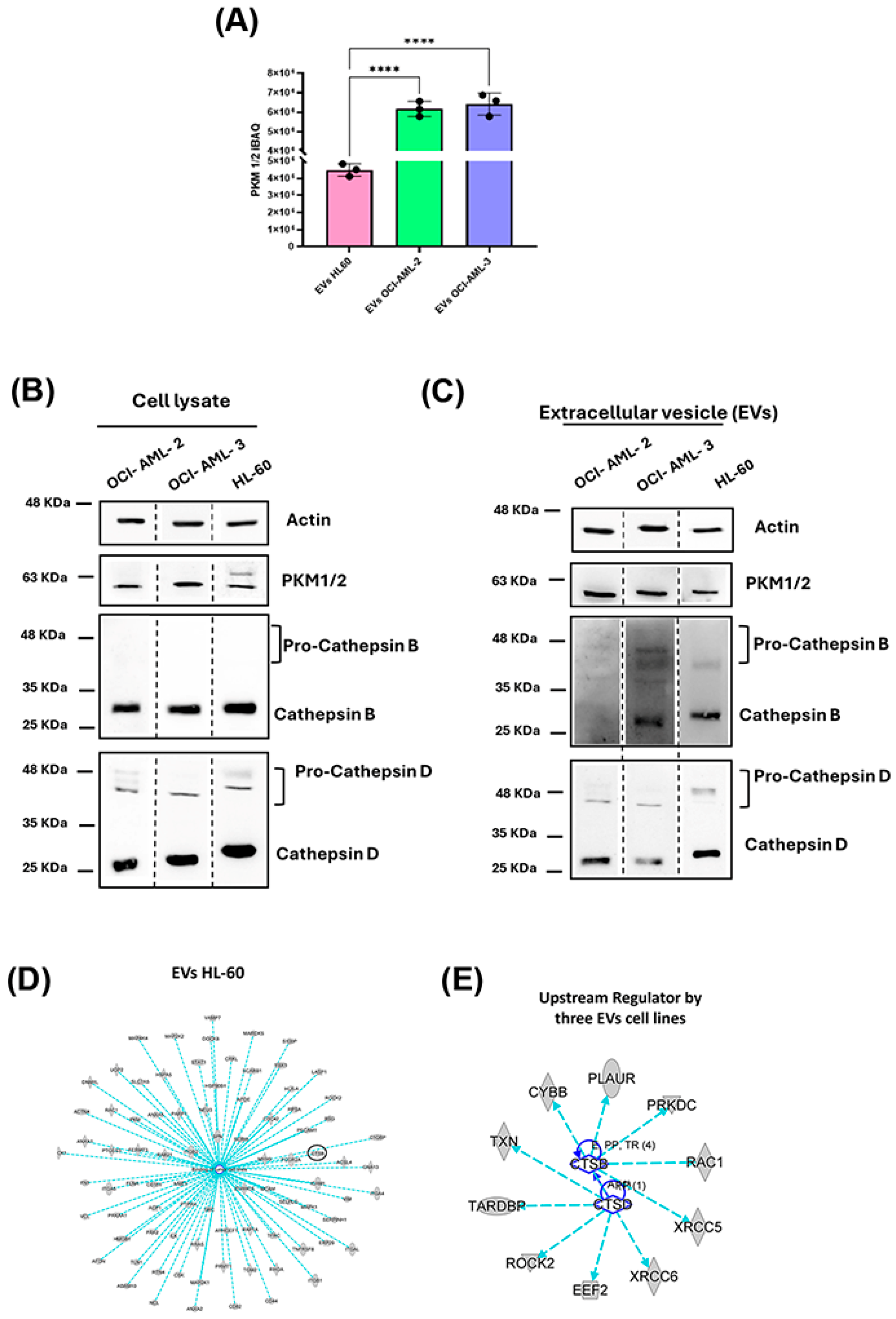
3.3. Evaluation of Selected Protein Biomarkers for AML-Derived EVs
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AML | Acute Myeloid Leukemia |
| BM | Bone Marrow |
| BSA | Bovine Serum Albumin |
| CD | Cluster of Differentiation |
| CTS | Cathepsin |
| DNMT3A | DNA Methyltransferase 3 A |
| ECL | Enhanced Chemiluminescence |
| EIF2 | Eukaryotic Initiation Factor 2 |
| EVs | Extracellular Vesicle |
| HSD | Honestly Significant Difference Test |
| iBAQ | Intensity-Based Absolute Quantification |
| IPA | Ingenuity Pathway Analysis |
| LC-MS/MS | Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry |
| MISEV | Minimal Information for Studies of Extracellular Vesicles |
| NPM1 | Nucleolar Protein Nucleophosmin 1 |
| PKM | Pyruvate Kinase |
| SP3 | Single-Pot Solid-Phase-Enhanced sample preparation |
| TPA | 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-1 3-acetate |
| UPLC | Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography |
References
- Shimony, S.; Stahl, M.; Stone, R.M. Acute Myeloid Leukemia: 2023 Update on Diagnosis, Risk-Stratification, and Management. Am. J. Hematol. 2023, 98, 502–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döhner, H.; Weisdorf, D.J.; Bloomfield, C.D. Acute Myeloid Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1136–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/about-cancer/acute-myeloid-leukaemia-aml/survival (accessed on 5 May 2025).
- Berumen Sánchez, G.; Bunn, K.E.; Pua, H.H.; Rafat, M. Extracellular Vesicles: Mediators of Intercellular Communication in Tissue Injury and Disease. Cell Commun. Signal. 2021, 19, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Morckhoven, D.; Dubois, N.; Bron, D.; Meuleman, N.; Lagneaux, L.; Stamatopoulos, B. Extracellular Vesicles in Hematological Malignancies: EV-Dence for Reshaping the Tumoral Microenvironment. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1265969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, R.; LeBleu, V.S. The Biology, Function, and Biomedical Applications of Exosomes. Science 2020, 367, eaau6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, N.; Lässer, C.; Dalirfardouei, R.; Dias, T.; Lötvall, J. Tetraspanins Distinguish Separate Extracellular Vesicle Subpopulations in Human Serum and Plasma—Contributions of Platelet Extracellular Vesicles in Plasma Samples. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2022, 11, e12213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Jiang, D.; Li, W.; Xiang, X.; Zhao, J.; Yu, B.; Wang, C.; He, Z.; Zhu, L.; Yang, Y. Evaluation of Serum Extracellular Vesicles as Noninvasive Diagnostic Markers of Glioma. Theranostics 2019, 9, 5347–5358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gargiulo, E.; Viry, E.; Morande, P.E.; Largeot, A.; Gonder, S.; Xian, F.; Ioannou, N.; Benzarti, M.; Borgmann, F.B.K.; Mittelbronn, M.; et al. Extracellular Vesicle Secretion by Leukemia Cells In Vivo Promotes CLL Progression by Hampering Antitumor T-Cell Responses. Blood Cancer Discov. 2023, 4, 54–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgievski, A.; Michel, A.; Thomas, C.; Mlamla, Z.; Barros, J.P. De Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Affect Quiescence of Hematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cells. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, C.S.; Muller, L.; Whiteside, T.L.; Boyiadzis, M. Plasma Exosomes as Markers of Therapeutic Response in Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczepanski, M.J.; Szajnik, M.; Welsh, A.; Whiteside, T.L.; Boyiadzis, M. Blast-Derived Microvesicles in Sera from Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia Suppress Natural Killer Cell Function via Membrane-Associated Transforming Growth Factor-Β1. Haematologica 2011, 96, 1302–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huan, J.; Hornick, N.I.; Shurtleff, M.J.; Skinner, A.M.; Goloviznina, N.A.; Roberts, C.T.; Kurre, P. RNA Trafficking by Acute Myelogenous Leukemia Exosomes. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 918–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Cai, X.; Li, D. Significance of Targeting DNMT3A Mutations in AML. Ann. Hematol. 2024, 104, 1399–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.J.; Kwon, A.; Cho, B.S.; Kim, H.J.; Hwang, K.A.; Kim, M.; Kim, Y. Characteristics of DNMT3A Mutations in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Blood Res. 2020, 55, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falini, B.; Mecucci, C.; Tiacci, E.; Alcalay, M.; Rosati, R.; Pasqualucci, L.; La Starza, R.; Diverio, D.; Colombo, E.; Santucci, A.; et al. Cytoplasmic Nucleophosmin in Acute Myelogenous Leukemia with a Normal Karyotype. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 254–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falini, B.; Sorcini, D.; Perriello, V.M.; Sportoletti, P. Functions of the Native NPM1 Protein and Its Leukemic Mutant: Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Leukemia 2025, 39, 276–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Cola, A.; Pietrangelo, L.; Forlì, F.; Barcaroli, D.; Budani, M.C.; Graziano, V.; Protasi, F.; Di Ilio, C.; De Laurenzi, V.; Federici, L. AML Cells Carrying NPM1 Mutation Are Resistant to Nucleophosmin Displacement from Nucleoli Caused by the G-Quadruplex Ligand TmPyP4. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, 3–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, S.J. The HL-60 Promyelocytic Leukemia Cell Line: Proliferation, Differentiation, and Cellular Oncogene Expression. Blood 1987, 70, 1233–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birnie, G.D. The HL60 Cell Line: A Model System for Studying Human Myeloid Cell Differentiation. Br. J. Cancer 1988, 58, 41–45. [Google Scholar]
- Théry, C.; Amigorena, S.; Raposo, G.; Clayton, A. Isolation and Characterization of Exosomes from Cell Culture Supernatants and Biological Fluids. Curr. Protoc. Cell Biol. 2006, 30, 3.22.1–3.22.29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ucci, A.; Giacchi, L.; Cufaro, M.C.; Puri, C.; Ciocca, M.; Di Ferdinando, F.; Del Boccio, P.; Cappariello, A.; Rucci, N. Human Osteosarcoma Cell Secretome Impairs Neonatal Mouse Calvarial Osteogenic Cells Functions and Modifies the Nanoparticles-Derived Protein Profile. Life Sci. 2025, 379, 123837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moggridge, S.; Sorensen, B.; Poul, H.; Morin, G.B.; Hughes, C.S. Extending the Compatibility of the SP3 Paramagnetic Bead Processing Approach for Proteomics. J. Proteome Res. 2018, 17, 1730–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adenocarcinoma, F.D.; Crosstalk, C.; Damiani, V.; Cufaro, M.C.; Fucito, M.; Dufrusine, B.; Rossi, C.; Del Boccio, P.; Federici, L.; Turco, M.C.; et al. Proteomics Approach Highlights Early Changes in Human. Cells 2022, 11, 1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potenza, F.; Cufaro, M.C.; Di Biase, L.; Panella, V.; Di Campli, A.; Ruggieri, A.G.; Dufrusine, B.; Restelli, E.; Pietrangelo, L.; Protasi, F.; et al. Proteomic Analysis of Marinesco–Sjogren Syndrome Fibroblasts Indicates pro-Survival Metabolic Adaptation to SIL1 Loss. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dufrusine, B.; Valentinuzzi, S.; Bibbò, S.; Damiani, V.; Lanuti, P.; Pieragostino, D.; Del Boccio, P.; D’Alessandro, E.; Rabottini, A.; Berghella, A.; et al. Iron Dyshomeostasis in COVID-19: Biomarkers Reveal a Functional Link to 5-Lipoxygenase Activation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chitti, S.V.; Gummadi, S.; Shahi, S.; Marzan, A.L.; Sanwlani, R.; Br, K.; Petro, M.; Sen, B.; Ozkan, A.; Akinfen, M.; et al. Vesiclepedia 2024: An Extracellular Vesicles and Extr Acellular Par Ticles Reposit Ory. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, D1694–D1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Théry, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Aikawa, E.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Anderson, J.D.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Antoniou, A.; Arab, T.; Archer, F.; Atkin-Smith, G.K.; et al. Minimal Information for Studies of Extracellular Vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A Position Statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and Update of the MISEV2014 Guidelines. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1535750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsh, J.A.; Goberdhan, D.C.I.; O’Driscoll, L.; Buzas, E.I.; Blenkiron, C.; Bussolati, B.; Cai, H.; Di Vizio, D.; Driedonks, T.A.P.; Erdbrügger, U.; et al. Minimal Information for Studies of Extracellular Vesicles (MISEV2023): From Basic to Advanced Approaches. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2024, 13, e12404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Chen, L.; Christman, K.J. Regulation of CD9 Expression during 1 2-O-Tetradecanoyl- Phorbol-1 3-Acetate-Induced Differentiation of Human Myeloid Leukemia (HL-60) Cells. Cell Growth Differ. 1994, 5, 1225–1234. [Google Scholar]
- Pilato, S.; Mrakic-Sposta, S.; Verratti, V.; Santangelo, C.; di Giacomo, S.; Moffa, S.; Fontana, A.; Pietrangelo, T.; Ciampini, F.; Bonan, S.; et al. Urineprint of High-Altitude: Insights from Analyses of Urinary Biomarkers and Bio-Physical-Chemical Features of Extracellular Vesicles. Biophys. Chem. 2025, 316, 107351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadati, T.; Houben, T.; Bitorina, A.; Shiri-Sverdlov, R. The Ins and Outs of Cathepsins: Physiological Function and Role in Disease Management. Cells 2020, 9, 1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zeng, Q.; Deng, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Yao, W.; Liao, Y. Glycosylated Cathepsin V Serves as a Prognostic Marker in Lung Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 876245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Wang, D.; Jin, F.; Bian, Z.; Li, L.; Liang, H.; Li, M.; Shi, L.; Pan, C.; Zhu, D.; et al. Pyruvate Kinase Type M2 Promotes Tumour Cell Exosome Release via Phosphorylating Synaptosome-Associated Protein 23. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Zhao, M.; Yan, C.; Kong, W.; Lan, F.; Narengaowa; Zhao, S.; Yang, Q.; Bai, Z.; Qing, H.; et al. Cathepsin B in Programmed Cell Death Machinery: Mechanisms of Execution and Regulatory Pathways. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacobuzio-Donahue, C.A.; Shuja, S.; Cai, J.; Peng, P.; Murnane, M.J. Elevations in Cathepsin B Protein Content and Enzyme Activity Occur Independently of Glycosylation during Colorectal Tumor Progression. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 29190–29199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.A.; Baba, S.K.; Sadida, H.Q.; Marzooqi, S.A.; Jerobin, J.; Altemani, F.H.; Algehainy, N.; Alanazi, M.A.; Abou-Samra, A.B.; Kumar, R.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles as Tools and Targets in Therapy for Diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, I.K.; Wood, M.J.A.; Fuhrmann, G. Extracellular Vesicles as a Next-Generation Drug Delivery Platform. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2021, 16, 748–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, K.W.; Kim, H.; Hur, W.; Jung, J.H.; Jeong, S.J.; Shin, H.; Seo, D.; Jeong, H.; Choi, B.H.; Hong, S.; et al. A Proteomic Approach to Understand the Clinical Significance of Acute Myeloid Leukemia–Derived Extracellular Vesicles Reflecting Essential Characteristics of Leukemia. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2021, 20, 100017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tominaga, N.; Hagiwara, K.; Kosaka, N.; Honma, K.; Nakagama, H.; Ochiya, T. RPN2-Mediated Glycosylation of Tetraspanin CD63 Regulates Breast Cancer Cell Malignancy. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, S.; Basu, S.; Ranjan, A. Revisiting the Role of CD63 as Pro-Tumorigenic or Anti-Tumorigenic Tetraspanin in Cancers and Its Theragnostic Implications. Adv. Biol. 2023, 7, 2300078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufrusine, B.; Capone, E.; Ponziani, S.; Lattanzio, R.; Lanuti, P.; Giansanti, F.; De Laurenzi, V.; Iacobelli, S.; Ippoliti, R.; Mangiola, A.; et al. Extracellular LGALS3BP: A Potential Disease Marker and Actionable Target for Antibody–Drug Conjugate Therapy in Glioblastoma. Mol. Oncol. 2023, 17, 1460–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Pionneau, C.; Cocozza, F.; Boëlle, P.Y.; Chardonnet, S.; Charrin, S.; Théry, C.; Zimmermann, P.; Rubinstein, E. Differential Proteomics Argues against a General Role for CD9, CD81 or CD63 in the Sorting of Proteins into Extracellular Vesicles. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2023, 12, 12352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.; Mao, Q.; Xia, W.; Xu, Y.; Wang, J.; Xu, L.; Jiang, F. PKM2 and Cancer: The Function of PKM2 beyond Glycolysis (Review). Oncol. Lett. 2016, 11, 1980–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Yang, H.; Bai, M.; Ning, T.; Deng, T.; Liu, R.; Fan, Q.; Zhu, K.; Li, J.; et al. Exosome-Delivered CircRNA Promotes Glycolysis to Induce Chemoresistance through the MiR-122-PKM2 Axis in Colorectal Cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2020, 14, 539–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, M.C.; Hung, W.C. Pyruvate Kinase M2 Fuels Multiple Aspects of Cancer Cells: From Cellular Metabolism, Transcriptional Regulation to Extracellular Signaling. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, J.S.; Gondi, C.S. Cathepsin B as a Cancer Target. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2013, 17, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, G.; Bakhshi, S.; Kumar, M.; Thakur, B.; Jain, P.; Kaur, P.; Shyam, S. Prognostic and Therapeutic Relevance of Cathepsin B in Pediatric Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2019, 9, 2634–2649. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Skopek, R.; Palusińska, M.; Kaczor-Keller, K.; Pingwara, R.; Papierniak-Wyglądała, A.; Schenk, T.; Lewicki, S.; Zelent, A.; Szymański, Ł. Choosing the Right Cell Line for Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) Research. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuppone, S.; Zarovni, N.; Vago, R. The Cell Type Dependent Sorting of CD9- and CD81 to Extracellular Vesicles Can Be Exploited to Convey Tumor Sensitive Cargo to Target Cells. Drug Deliv. 2023, 30, 2162161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dufrusine, B.; Cufaro, M.C.; Di Sebastiano, A.; Pizzinato, E.; Nardinocchi, P.; Cicalini, I.; Pilato, S.; Fontana, A.; Pieragostino, D.; Dainese, E.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles Profiling in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cell Lines: A Proteomic Characterization. Cells 2025, 14, 1651. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14211651
Dufrusine B, Cufaro MC, Di Sebastiano A, Pizzinato E, Nardinocchi P, Cicalini I, Pilato S, Fontana A, Pieragostino D, Dainese E, et al. Extracellular Vesicles Profiling in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cell Lines: A Proteomic Characterization. Cells. 2025; 14(21):1651. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14211651
Chicago/Turabian StyleDufrusine, Beatrice, Maria Concetta Cufaro, Alice Di Sebastiano, Erika Pizzinato, Pina Nardinocchi, Ilaria Cicalini, Serena Pilato, Antonella Fontana, Damiana Pieragostino, Enrico Dainese, and et al. 2025. "Extracellular Vesicles Profiling in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cell Lines: A Proteomic Characterization" Cells 14, no. 21: 1651. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14211651
APA StyleDufrusine, B., Cufaro, M. C., Di Sebastiano, A., Pizzinato, E., Nardinocchi, P., Cicalini, I., Pilato, S., Fontana, A., Pieragostino, D., Dainese, E., & Federici, L. (2025). Extracellular Vesicles Profiling in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cell Lines: A Proteomic Characterization. Cells, 14(21), 1651. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14211651









