Targeting the FABP Axis: Interplay Between Lipid Metabolism, Neuroinflammation, and Neurodegeneration
Abstract
1. Introduction
Search Strategy and Selection Criteria
2. FABP-Mediated Metabolic Dysregulation: A Core Driver of Neurodegeneration
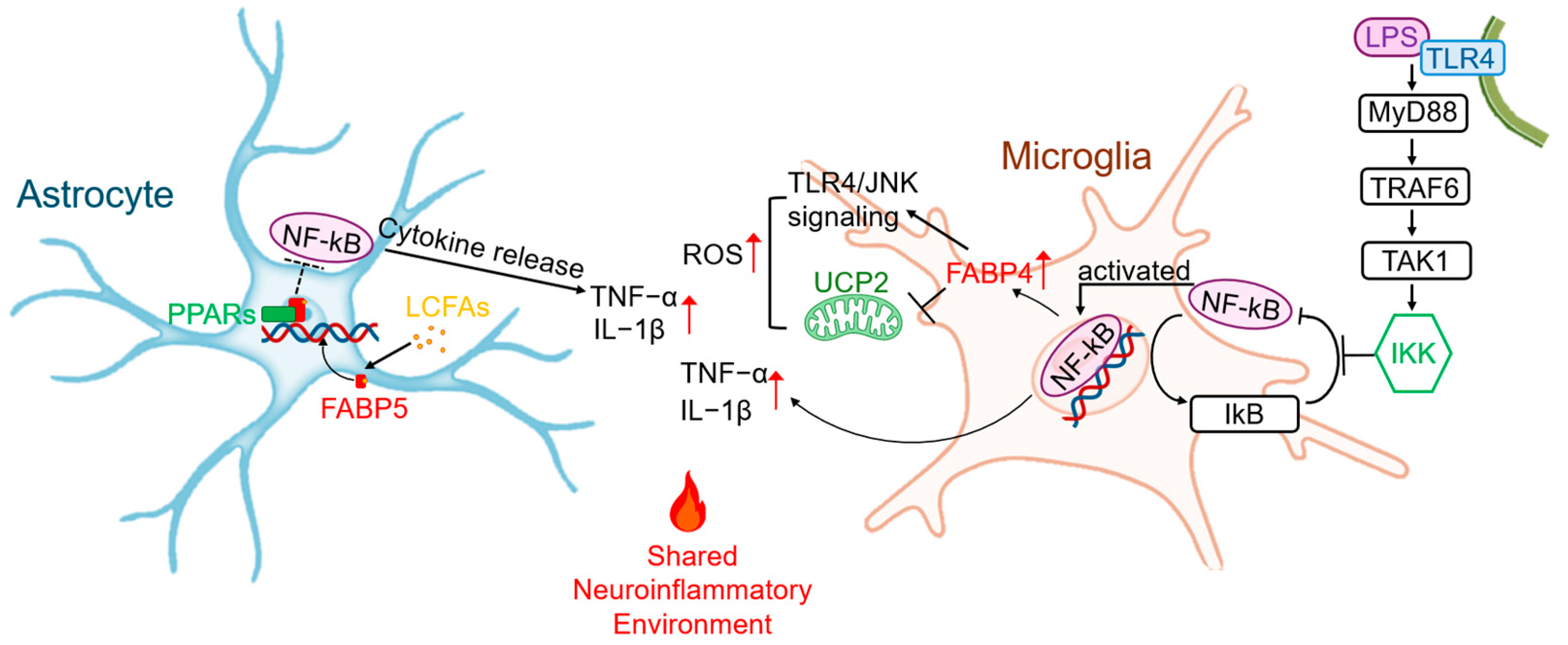
2.1. The FABP-Driven “Meta-Inflammatory” Axis in Glial Cells
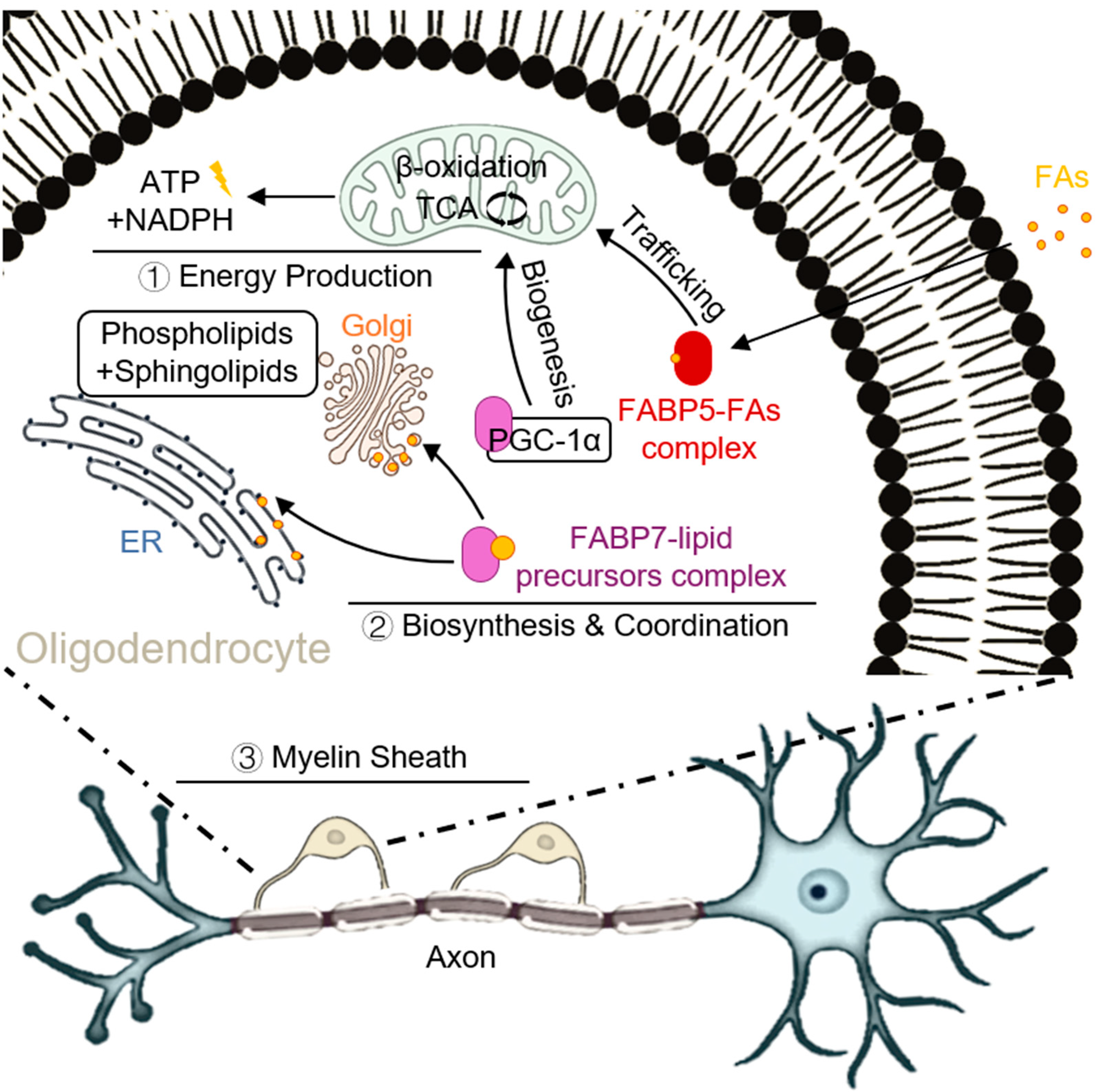
2.2. The FABP-Driven “Metabolic-Survival” Balance in Oligodendrocytes
2.3. The Metabolic Link Between FABPs and Proteotoxicity: A Liquid–Liquid Phase Separation Perspective
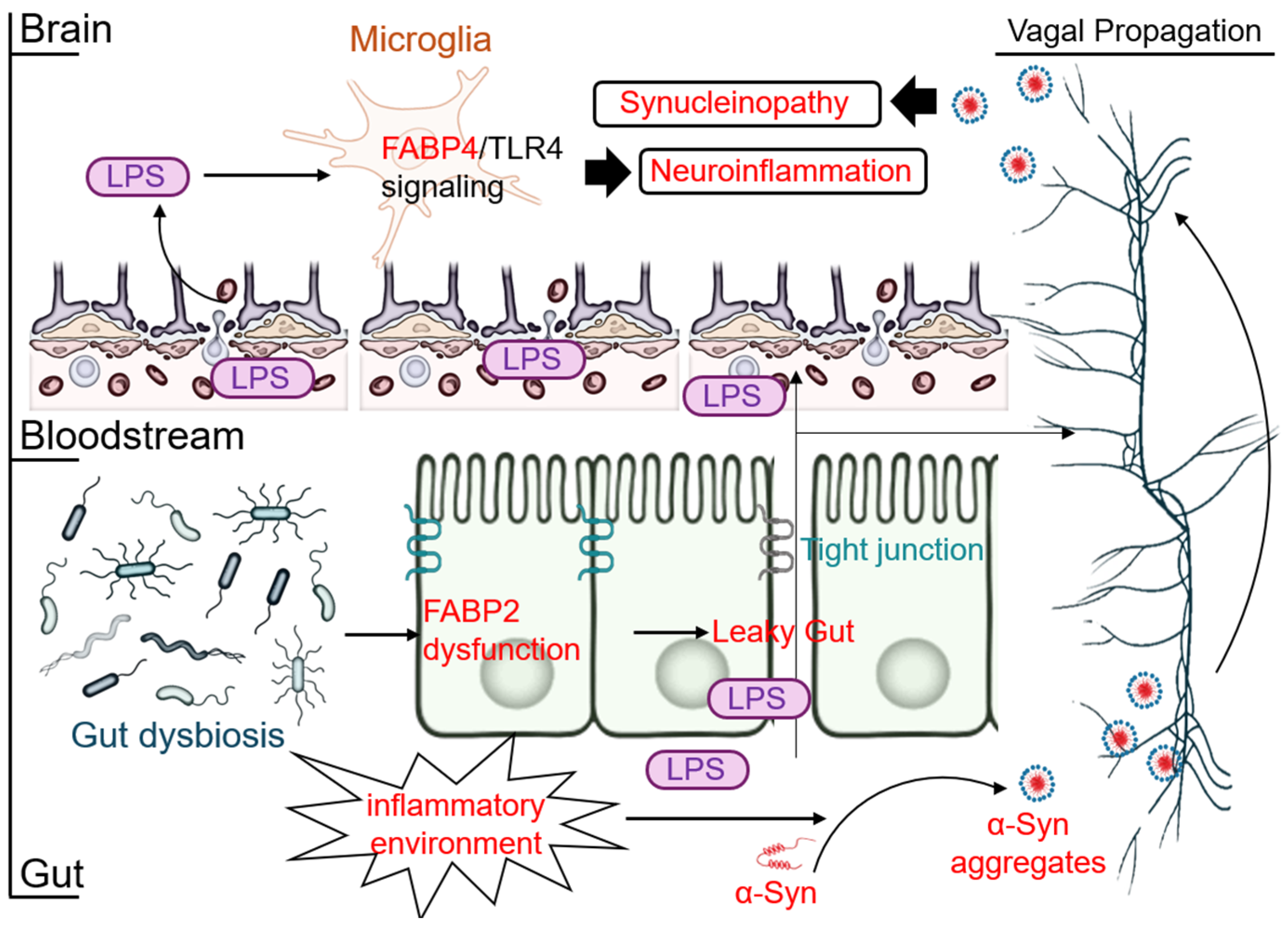
2.4. The New Frontier: The Gut–Brain-FABP Axis and Systemic Inflammation
2.5. The FABP-Ferroptosis Link: A New Frontier in Neurotoxic Cell Death
3. Pharmacological Modulation of FABPs:
3.1. CNS-Penetrant Inhibitors: Resetting Central Metabolism
3.1.1. MF6: A CNS-Penetrant Candidate Targeting the Meta-Inflammatory Axis
3.1.2. Targeting FABP3 in Neurotherapeutics: From MF1 to the High-Potency Ligand HY-11-9
3.1.3. HY08: A FABP3/5 Ligand Targeting Mitochondrial Damage
3.2. Peripherally Restricted Inhibitors: Modulating Neuro-Immune Crosstalk
4. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
4.1. Summary
4.2. Outlook: From “What to Inhibit” to “Where and How to Modulate” with Precision
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 4-HNE | 4-Hydroxynonenal |
| AA | Arachidonic Acid |
| Acetyl-CoA | Acetyl-Coenzyme A |
| AD | Alzheimer’s Disease |
| ALS | Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis |
| BBB | Blood–Brain Barrier |
| CNS | Central Nervous System |
| EAE | Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis |
| ENS | Enteric nervous system |
| FABPs | Fatty acid-binding proteins |
| HK | Hexokinase |
| LCFAs | Long-chain fatty acids |
| LD | Lipid droplets |
| LDH | Lactate dehydrogenase |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| MBP | Myelin basic protein |
| MF6 | FABP Ligand 6 |
| mPTP | mitochondrial permeability transition pore |
| MPTP | 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine |
| MS | Multiple sclerosis |
| MSA | Multiple system atrophy |
| NDDs | Neurodegenerative diseases |
| NOAEL | No observed adverse effect level |
| OIPN | Oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy |
| OXPHOS | Oxidative phosphorylation |
| PD | Parkinson’s disease |
| PFK | Phosphofructokinase |
| PIPN | Paclitaxel-induced neuropathy |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| TCA | Tricarboxylic acid cycle |
| TLR4 | Toll-like receptor 4 |
| tMCAO/R | transient middle cerebral artery occlusion/reperfusion |
| α-syn | α-synuclein |
References
- Scheltens, P.; De Strooper, B.; Kivipelto, M.; Holstege, H.; Chételat, G.; Teunissen, C.E.; Cummings, J.; van der Flier, W.M. Alzheimer’s Disease. Lancet 2021, 397, 10284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agnello, L.; Gambino, C.M.; Ciaccio, A.M.; Cacciabaudo, F.; Massa, D.; Masucci, A.; Tamburello, M.; Vassallo, R.; Midiri, M.; Scazzone, C.; et al. From Amyloid to Synaptic Dysfunction: Biomarker-Driven Insights into Alzheimer’s Disease. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, M.Y.; Kwon, H.S.; Kwon, M.S.; Nahm, M.; Jin, H.K.; Bae, J.S.; Kim, S.H. Biomarkers and Therapeutic Strategies Targeting Microglia in Neurodegenerative Diseases: Current Status and Future Directions. Mol. Neurodegener. 2025, 20, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuhashi, M.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Fatty Acid-Binding Proteins: Role in Metabolic Diseases and Potential as Drug Targets. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 489–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storch, J.; Corsico, B. The Emerging Functions and Mechanisms of Mammalian Fatty Acid-Binding Proteins. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2008, 28, 73–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, K.; Uysal, K.T.; Makowski, L.; Görgün, C.Z.; Atsumi, G.; Parker, R.A.; Brüning, J.; Hertzel, A.V.; Bernlohr, D.A.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Role of the Fatty Acid Binding Protein Mal1 in Obesity and Insulin Resistance. Diabetes 2003, 52, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Hao, J.; Zeng, J.; Sauter, E.R. SnapShot: FABP Functions. Cell 2020, 182, 1066–1066.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, K.; Cao, H.; Kono, K.; Gorgun, C.Z.; Furuhashi, M.; Uysal, K.T.; Cao, Q.; Atsumi, G.; Malone, H.; Krishnan, B.; et al. Adipocyte/Macrophage Fatty Acid Binding Proteins Control Integrated Metabolic Responses in Obesity and Diabetes. Cell Metab. 2005, 1, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, R.; Hao, J.; Yi, Y.; Sauter, E.; Li, B. Regulation of Macrophage Functions by FABP-Mediated Inflammatory and Metabolic Pathways. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2021, 1866, 158964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuhashi, M.; Tuncman, G.; Görgün, C.Z.; Makowski, L.; Atsumi, G.; Vaillancourt, E.; Kono, K.; Babaev, V.R.; Fazio, S.; Linton, M.F.; et al. Treatment of Diabetes and Atherosclerosis by Inhibiting Fatty-acid-Binding Protein aP2. Nature 2007, 447, 959–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Başarır Sivri, F.N.; Çiftçi, S. A New Insight into Fatty Acid Binding Protein 4 Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications in Obesity-Associated Diseases: A Mini Review. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2024, 68, e2300840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, A.; Yamaguchi, N.; Lu, H.; Pareek, O.; Elman, I.; Gold, M.S.; Pinhasov, A.; Blum, K.; Thanos, P.K. The Role of Fatty Acid Binding Proteins in Neuropsychiatric Diseases: A Narrative Review. Front. Biosic. 2025, 30, 26812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowers, M.; Liang, T.; Gonzalez-Bohorquez, D.; Zocher, S.; Jaeger, B.N.; Kovacs, W.J.; Röhrl, C.; Cramb, K.M.L.; Winterer, J.; Kruse, M.; et al. FASN-Dependent Lipid Metabolism Links Neurogenic Stem/Progenitor Cell Activity to Learning and Memory Deficits. Cell Stem Cell 2020, 27, 98–109.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiasserini, D.; Biscetti, L.; Eusebi, P.; Salvadori, N.; Frattini, G.; Simoni, S.; De Roeck, N.; Tambasco, N.; Stoops, E.; Vanderstichele, H.; et al. Differential Role of CSF Fatty Acid Binding Protein 3, α-Synuclein, and Alzheimer’s Disease Core biomarkers in Lewy Body Disorders and Alzheimer’s Dementia. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2017, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, E.; Singh, P.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chi, Y.I.; Suttles, J.; Li, B. Targeting Epidermal Fatty Acid Binding Protein for Treatment of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. BMC Immunol. 2015, 16, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, C.E.; Veerhuis, R.; De Vente, J.; Verhey, F.R.; Vreeling, F.; van Boxtel, M.P.; Glatz, J.F.; Pelsers, M.A. Brain-Specific Fatty Acid-Binding Protein is Elevated in Serum of Patients with Dementia-Related Diseases. Eur. J. Neurol. 2011, 18, 865–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Killoy, K.M.; Harlan, B.A.; Pehar, M.; Vargas, M.R. Fabp7 Upregulation Induces a Neurotoxic Phenotype in Astrocytes. Glia 2020, 68, 2693–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yuan, Z.; Yang, S.; Zhu, Y.; Xue, M.; Zhang, J.; Leng, L. Brain Energy Metabolism: Astrocytes in Neurodegenerative Diseases. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2023, 29, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Chen, S.; Liang, F. Glycometabolic Reprogramming of Microglia in Neurodegenerative Diseases: Insights from Neuroinflammation. Aging Dis. 2024, 15, 1155–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gimeno-Bayón, J.; López-López, A.; Rodríguez, M.J.; Mahy, N. Glucose Pathways Adaptation Supports Acquisition of Activated Microglia Phenotype. J. Neurosci. Res. 2014, 92, 723–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Eichinger, K.M.; Zhang, A.; Li, S. Targeting Cancer Metabolic Pathways for Improving Chemotherapy and Immunotherapy. Cancer Lett. 2023, 575, 216396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Xing, C.; Yu, B.; Guo, L.; Dou, X.; Gao, L.; Yang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, X.; Li, S.; et al. Metabolic Reprogramming of Neural Stem Cells by Chiral Nanofiber for Spinal Cord Injury. ACS Nano 2025, 19, 4785–4801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Zhou, S.; Tao, J.; Gao, Y.; Meng, G.; Cao, D.; Gao, L. HIV-1 Tat Drives the Fabp4/NF-κB Feedback Loop in Microglia to Mediate Inflammatory Response and Neuronal Apoptosis. J. Neurovirol. 2022, 28, 483–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagawa, Y.; Low, Y.L.; Pyun, J.; Doglione, U.; Short, J.L.; Pan, Y.; Nicolazzo, J.A. Fatty Acid-Binding Protein 4 is Essential for the Inflammatory and Metabolic Response of Microglia to Lipopolysaccharide. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2023, 18, 448–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciesielska, A.; Matyjek, M.; Kwiatkowska, K. TLR4 and CD14 Trafficking and Its Influence on LPS-Induced Pro-Inflammatory Signaling. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 1233–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.J.; Xu, B.; Huang, S.W.; Luo, X.; Deng, X.L.; Luo, S.; Liu, C.; Wang, Q.; Chen, J.Y.; Zhou, L. Baicalin Prevents LPS-Induced Activation of TLR4/NF-κB p65 Pathway and Inflammation in Mice via Inhibiting the Expression of CD14. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2021, 42, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Meng, T.; Liu, S.; Liu, J.; Liu, D.; Laxman, B.; Chen, S.; Dong, Z. β-Caryophyllene Reduces Inflammation to Protect Against Ischemic Stroke by Suppressing HMGB1 Signaling. Mol. Med. 2025, 31, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Luo, H.Y.; Liu, Q.; Xiao, Y.; Tang, L.; Zhong, F.; Huang, G.; Xu, J.M.; Xu, A.M.; Zhou, Z.G.; et al. Intermittent High Glucose Exacerbates A-FABP Activation and Inflammatory Response through TLR4-JNK Signaling in THP-1 Cells. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 1319272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, S.W.; Fleming, K.M.; Duffy, C.M.; Nixon, J.P.; Bernlohr, D.A.; Butterick, T.A. Microglial FABP4-UCP2 Axis Modulates Neuroinflammation and Cognitive Decline in Obese Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.Y.; Feng, M.; Chen, Y.; Jia, H.L.; Zhang, Q.; Tong, M.; Li, Y.X.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, X.X.; Cao, S.F.; et al. Asprosin-FABP5 Interaction Modulates Mitochondrial Fatty Acid Oxidation through PPARα Contributing to MASLD Development. Adv. Sci. 2025, 12, e2415846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Zhang, H.; Yu, X.; Pan, K.; Yao, X.; Shen, X.; Lei, H. Fc-Binding Cyclopeptide Induces Allostery from Fc to Fab: Revealed Through in Silico Structural Analysis to Anti-Phenobarbital Antibody. Foods 2025, 14, 1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namiecinska, M.; Piatek, P.; Lewkowicz, P. Nervonic Acid Synthesis Substrates as Essential Components in Profiled Lipid Supplementation for More Effective Central Nervous System Regeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nsiah-Sefaa, A.; McKenzie, M. Combined Defects in Oxidative Phosphorylation and Fatty Acid β-Oxidation in Mitochondrial Disease. Biosci. Rep. 2016, 36, e00313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, J.; He, Y.; Lü, Y.; Yu, W. The Role of Fatty Acid Binding Protein 7 in Neurological Diseases. Mol. Neurobiol. 2025; ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.X.; Wei, P.; Zhao, K.; Sheng, Z.C.; Song, B.L.; Yin, L.; Luo, J. Fatty Acid-Binding Proteins 3, 7, and 8 Bind Cholesterol and Facilitate Its Egress from Lysosomes. J. Cell Biol. 2024, 223, e202211062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamizato, K.; Sato, S.; Shil, S.K.; Umaru, B.A.; Kagawa, Y.; Yamamoto, Y.; Ogata, M.; Yasumoto, Y.; Okuyama, Y.; Ishii, N.; et al. The Role of Fatty Acid Binding Protein 7 in Spinal Cord Astrocytes in a Mouse Model of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. Neuroscience 2019, 409, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burré, J.; Sharma, M.; Südhof, T.C. Cell Biology and Pathophysiology of α-Synuclein. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2018, 8, a024091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pingale, T.D.; Gupta, G.L. Novel Therapeutic Approaches for Parkinson’s Disease by Targeting Brain Cholesterol Homeostasis. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2021, 73, 862–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyko, S.; Surewicz, W.K. Tau Liquid-Liquid Phase Separation in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Trends Cell Biol. 2022, 32, 611–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, S.; Singh, N.; Kumar, R.; Patel, K.; Pandey, S.; Datta, D.; Mahato, J.; Panigrahi, R.; Navalkar, A.; Mehra, S.; et al. α-Synuclein Aggregation Nucleates Through Liquid-Liquid Phase Separation. Nat. Chem. 2020, 12, 705–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoni, V.; Khaddaj, R.; Campomanes, P.; Thiam, A.R.; Schneiter, R.; Vanni, S. Pre-Existing Bilayer Stresses Modulate Triglyceride Accumulation in the ER Versus Lipid Droplets. Elife 2021, 10, e62886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegmann, S.; Eftekharzadeh, B.; Tepper, K.; Zoltowska, K.M.; Bennett, R.E.; Dujardin, S.; Laskowski, P.R.; MacKenzie, D.; Kamath, T.; Commins, C.; et al. Tau Protein Liquid-Liquid Phase Separation Can Initiate Tau Aggregation. EMBO J. 2018, 37, e98049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, A.; Wang, Y.F.; Shinoda, Y.; Kawahata, I.; Yamamoto, T.; Jia, W.B.; Yamamoto, H.; Mizobata, T.; Kawata, Y.; Fukunaga, K. Fatty Acid-Binding Protein 7 Triggers α-Synuclein Oligomerization in Glial Cells and Oligodendrocytes Associated with Oxidative Stress. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2022, 43, 552–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, A.; Kawahata, I.; Wang, Y.; Jia, W.; Wang, H.; Sekimori, T.; Chen, Y.; Suzuki, H.; Takeda, A.; Stefanova, N.; et al. Epsin2, a Novel Target for Multiple System Atrophy Therapy via α-Synuclein/FABP7 Propagation. Brain 2023, 146, 3172–3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shinoda, Y.; Cheng, A.; Kawahata, I.; Fukunaga, K. Epidermal Fatty Acid-Binding Protein 5 (FABP5) Involvement in Alpha-Synuclein-Induced Mitochondrial Injury under Oxidative Stress. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Yang, Q.; Liu, X. The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis and Neurodevelopmental Disorders. Protein Cell 2023, 14, 762–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cryan, J.F.; O’Riordan, K.J.; Sandhu, K.; Peterson, V.; Dinan, T.G. The Gut Microbiome in Neurological Disorders. Lancet Neurol. 2020, 19, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, J.; Tang, J.; Kang, F.; Ye, J.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Wu, S.; Ye, K. Gut-induced alpha-Synuclein and Tau propagation initiate Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s disease co-pathology and behavior impairments. Neuron 2024, 112, 3585–3601.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, B.R.; Goel, R.; Seungbum, K.; Richards, E.M.; Holbert, R.C.; Pepine, C.J.; Raizada, M.K. Increased Human Intestinal Barrier Permeability Plasma Biomarkers Zonulin and FABP2 Correlated with Plasma LPS and Altered Gut Microbiome in Anxiety or Depression. Gut 2018, 67, 1555–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, G.B.; Keating, D.J.; Young, R.L.; Wong, M.L.; Licinio, J.; Wesselingh, S. From Gut Dysbiosis to Altered Brain Function and Mental Illness: Mechanisms and Pathways. Mol. Psychiatry 2016, 21, 738–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keyhanian, K.; Davoudi, V.; Saxena, S.; Kivisakk, P.; Baharnoori, M.; Chitnis, T. Fatty Acid-Binding Protein 4 (FABP4) Enhances TLR2, TNFa and IL23 Expression in CD14+ Monocytes In Vitro. Neurol. J. 2017, 88 (Suppl. S16), P1.395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, L.E.; Dixon, S.J. Regulation of Ferroptosis by Lipid Metabolism. Trends Cell Biol. 2023, 33, 1077–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, H.; Xin, S.; Pfeiffer, S.; Müller, C.; Merl-Pham, J.; Hauck, S.M.; Harter, P.N.; Spitzer, D.; Devraj, K.; Varynskyi, B.; et al. Fatty Acid-Binding Protein 5 is a Functional Biomarker and Indicator of Ferroptosis in Cerebral Hypoxia. Cell Death Dis. 2024, 15, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Esplugues, E.; Bort, A.; Cardelo, M.P.; Ruz-Maldonado, I.; Fernández-Tussy, P.; Wong, C.; Wang, H.; Ojima, I.; Kaczocha, M.; et al. Fatty Acid Binding Protein 5 Suppression Attenuates Obesity-Induced Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Promoting Ferroptosis and Intratumoral Immune Rewiring. Nat. Metab. 2024, 6, 741–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas-Cortez, M.A.; Masrorpour, F.; Jiang, H.; Mahmud, I.; Lu, Y.; Huang, A.; Duong, L.K.; Wang, Q.; Voss, T.A.; Kettlun Leyton, C.S.; et al. Cancer Cells Avoid Ferroptosis Induced by Immune Cells via Fatty Acid Binding Proteins. Mol. Cancer 2025, 24, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocsis, D.; Papp, M.; Tornai, T.; Tulassay, Z.; Herszényi, L.; Tóth, M.; Juhász, M. Intestinal Fatty Acid Binding Protein: Marker of Enterocyte Damage in Acute and Chronic Gastroenterological Diseases. Orvosi Hetil. 2016, 157, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Weiss, E.P.; Brown, M.D.; Shuldiner, A.R.; Hagberg, J.M. Fatty Acid Binding Protein-2 Gene Variants and Insulin Resistance: Gene and Gene-Environment Interaction Effects. Physiol. Genom. 2002, 10, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albala, B.C.; Jiménez, R.B.; Pérez, B.F.; Liberman, G.C. Fatty Acid Binding Protein 2 (FABP-2) Polymorphism, Obesity and Insulin Resistance. Rev. Med. Chile 2006, 134, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sekimori, T.; Fukunaga, K.; Oizumi, H.; Baba, T.; Totsune, T.; Takeda, A.; Sasaki, T.; Kawahata, I. FABP2 is Involved in Intestinal α-Synuclein Pathologies. J. Integr. Neurosci. 2024, 23, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Hu, D.L.; Liu, Y.Q.; Zhang, Q.J.; Chen, F.K.; Kong, X.Q.; Cao, K.J.; Zhang, J.S.; Qian, L.M. Fabp3 Inhibits Proliferation and Promotes Apoptosis of Embryonic Myocardial Cells. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2011, 60, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.M.; Lee, S.H.; Jung, Y.; Lee, Y.; Yoon, J.H.; Choi, J.Y.; Hwang, C.Y.; Son, Y.H.; Park, S.S.; Hwang, G.S.; et al. FABP3-Mediated Membrane Lipid Saturation Alters Fluidity and Induces ER Stress in Skeletal Muscle with Aging. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Shioda, N.; Owada, Y.; Fukunaga, K. Regulation of Dopaminergic Neuronal Activity by Heart-Type Fatty Acid Binding Protein in the Brain. Yakugaku Zasshi 2011, 131, 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nakamura, Y.; Sato, T.; Shiimura, Y.; Miura, Y.; Kojima, M. FABP3 and Brown Adipocyte-Characteristic Mitochondrial Fatty Acid Oxidation Enzymes Are Induced in Beige Cells in a Different Pathway from UCP1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 441, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corales, L.G.; Inada, H.; Owada, Y.; Osumi, N. Fatty Acid Preference for Beta-Oxidation in Mitochondria of Murine Cultured Astrocytes. Genes Cells 2024, 29, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shioda, N.; Yabuki, Y.; Kobayashi, Y.; Onozato, M.; Owada, Y.; Fukunaga, K. FABP3 Protein Promotes α-Synuclein Oligomerization Associated with 1-methyl-1,2,3,6-Tetrahydropiridine-Induced Neurotoxicity. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 18957–18965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, A.; Shinoda, Y.; Yamamoto, T.; Miyachi, H.; Fukunaga, K. Development of FABP3 Ligands That Inhibit Arachidonic Acid-Induced α-Synuclein Oligomerization. Brain Res. 2019, 1707, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulewicz, M.; Kulczyńska-Przybik, A.; Słowik, A.; Borawska, R.; Mroczko, B. Fatty Acid Binding Protein 3 (FABP3) and Apolipoprotein E4 (ApoE4) as Lipid Metabolism-Related Biomarkers of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhiman, K.; Villemagne, V.L.; Fowler, C.; Bourgeat, P.; Li, Q.X.; Collins, S.; Rowe, C.C.; Masters, C.L.; Ames, D.; Blennow, K.; et al. Cerebrospinal Fluid Levels of Fatty Acid-Binding Protein 3 Are Associated with Likelihood of Amyloidopathy in Cognitively Healthy Individuals. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2022, 14, e12377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargari, P.; Mukhopadhyay, P.; Saboo, B.; Misra, A.; Ghosh, S. Fabkin and Glucose Homeostasis. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2022, 16, 102565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wu, D.; Fan, Z.; Yang, J.; Li, Y.; Meng, Y.; Gao, C.; Zhan, H. FABP4 in Obesity-Associated Carcinogenesis: Novel Insights into Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 973955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuhashi, M.; Saitoh, S.; Shimamoto, K.; Miura, T. Fatty Acid-Binding Protein 4 (FABP4): Pathophysiological Insights and Potent Clinical Biomarker of Metabolic and Cardiovascular Diseases. Clin. Med. Insights Cardiol. 2014, 8, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, C.M.; Xu, H.; Nixon, J.P.; Bernlohr, D.A.; Butterick, T.A. Identification of a Fatty Acid Binding Protein4-UCP2 Axis Regulating Microglial Mediated Neuroinflammation. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2017, 80, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Xu, J.; Ren, Q.; Cheng, L.; Guo, F.; Liang, Y.; Yang, L.; Tan, Z.; Fu, P.; Ma, L. Fatty Acid-Binding Protein 4 is a Therapeutic Target for Septic Acute Kidney Injury by Regulating Inflammatory Response and Cell Apoptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerkamp, J.H.; Zimmerman, A.W. Fatty Acid-Binding Proteins of Nervous Tissue. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2001, 16, 133–142; discussion 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawahata, I.; Fukunaga, K. Pathogenic Impact of Fatty Acid-Binding Proteins in Parkinson’s Disease-Potential Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 17037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oubraim, S.; Fauzan, M.; Studholme, K.; Gordon, C.; Glaser, S.T.; Shen, R.Y.; Ojima, I.; Kaczocha, M.; Haj-Dahmane, S. Astrocytic FABP5 Mediates Retrograde Endocannabinoid Transport at Central Synapses. iScience 2025, 28, 112342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haj-Dahmane, S.; Shen, R.Y.; Elmes, M.W.; Studholme, K.; Kanjiya, M.P.; Bogdan, D.; Thanos, P.K.; Miyauchi, J.T.; Tsirka, S.E.; Deutsch, D.G.; et al. Fatty-Acid-Binding Protein 5 Controls Retrograde Endocannabinoid Signaling at Central Glutamate Synapses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 3482–3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharifi, K.; Ebrahimi, M.; Kagawa, Y.; Islam, A.; Tuerxun, T.; Yasumoto, Y.; Hara, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Miyazaki, H.; Tokuda, N.; et al. Differential Expression and Regulatory Roles of FABP5 and FABP7 in Oligodendrocyte Lineage Cells. Cell Tissue Res. 2013, 354, 683–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, W.A.; Tangeman, A.; El-Hodiri, H.M.; Hawthorn, E.C.; Hathoot, M.; Blum, S.; Hoang, T.; Blackshaw, S.; Fischer, A.J. Fatty Acid-Binding Proteins and Fatty Acid Synthase Influence Glial Reactivity and Promote the Formation of Müller Glia-Derived Progenitor Cells in the Chick Retina. Development 2022, 149, dev200127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, A.; Kawahata, I.; Fukunaga, K. Fatty Acid Binding Protein 5 Mediates Cell Death by Psychosine Exposure through Mitochondrial Macropores Formation in Oligodendrocytes. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kou, F.; Li, X.Y.; Feng, Z.; Hua, J.; Wu, X.; Gao, H.; Lin, J.; Kang, D.; Li, A.; Li, J.; et al. GPR171 Restrains Intestinal Inflammation by Suppressing FABP5-Mediated Th17 Cell Differentiation and Lipid Metabolism. Gut 2025, 74, 1279–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, S.; Xu, W.; Li, Y.; Zhao, P.; Wang, D.; Cheng, H.; Ke, Y.; Zhang, X. Oxidative Stress-Induced FABP5 S-Glutathionylation Protects Against acute Lung Injury by Suppressing Inflammation in Macrophages. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 7094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabre, T.; Barron, A.M.S.; Christensen, S.M.; Asano, S.; Bound, K.; Lech, M.P.; Wadsworth, M.H., 2nd; Chen, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, J.; et al. Identification of a Broadly Fibrogenic Macrophage Subset Induced by Type 3 Inflammation. Sci. Immunol. 2023, 8, eadd8945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, A.; Jia, W.; Kawahata, I.; Fukunaga, K. A Novel Fatty Acid-Binding Protein 5 and 7 Inhibitor Ameliorates Oligodendrocyte Injury in Multiple Sclerosis Mouse Models. EBioMedicine 2021, 72, 103582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Q.; Kawahata, I.; Cheng, A.; Wang, H.; Jia, W.; Yoshino, H.; Fukunaga, K. Fatty Acid-Binding Proteins 3 and 5 Are Involved in the Initiation of Mitochondrial Damage in Ischemic Neurons. Redox Biol. 2023, 59, 102547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, R.M.; Eriksson, P.; Hoffstedt, J.; Hotamisligil, G.S.; Thörne, A.; Rydén, M.; Hamsten, A.; Arner, P. Fatty acid Binding Protein Expression in Different Adipose Tissue Depots from Lean and Obese Individuals. Diabetologia 2001, 44, 1268–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hamilton, H.L.; Kinscherf, N.A.; Balmer, G.; Bresque, M.; Salamat, S.M.; Vargas, M.R.; Pehar, M. FABP7 Drives an Inflammatory Response in Human Astrocytes and Is Upregulated in Alzheimer’s Disease. Geroscience 2024, 46, 1607–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, M.; Yamamoto, Y.; Sharifi, K.; Kida, H.; Kagawa, Y.; Yasumoto, Y.; Islam, A.; Miyazaki, H.; Shimamoto, C.; Maekawa, M.; et al. Astrocyte-Expressed FABP7 Regulates Dendritic Morphology and Excitatory Synaptic Function of Cortical Neurons. Glia 2016, 64, 48–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mita, R.; Coles, J.E.; Glubrecht, D.D.; Sung, R.; Sun, X.; Godbout, R. B-FABP-Expressing Radial Glial Cells: The Malignant Glioma Cell of Origin? Neoplasia 2007, 9, 734–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Luo, B.L.; Yang, Q.G.; Ni, M.Z.; Wu, Q.T.; Li, Y.; Li, X.W.; Chen, G.H. Prenatal Exposure to Inflammation Increases Anxiety-like Behaviors in F1 and F2 Generations: Possible Links to Decreased FABP7 in Hippocampus. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 973069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, R.; King, D.; LaBarre, B.; Lokhande, H.; Caefer, D.; Varghese, J.F.; Warner, K.; Bouffard, M.A.; Saxena, S.; Zhirova, A.; et al. FABP7 Is Increased in Progressive Multiple Sclerosis and Induces a Pro-Inflammatory Phenotype in Monocytes Through a Glycolytic Switch. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 6049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; He, Y.; Wang, Y.; Hu, W.; Chu, C.; Huang, L.; Hong, Y.; Han, L.; Zhang, X.; Gao, Y.; et al. Deficiency of FABP7 Triggers Premature Neural Differentiation in Idiopathic Normocephalic Autism Organoids. Adv. Sci. 2025, 12, e2406849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, K.; Morihiro, Y.; Maekawa, M.; Yasumoto, Y.; Hoshi, H.; Adachi, Y.; Sawada, T.; Tokuda, N.; Kondo, H.; Yoshikawa, T.; et al. FABP7 Expression in Normal and Stab-Injured Brain Cortex and Its Role in Astrocyte Proliferation. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2011, 136, 501–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, S.W.; Leong, C.; Zhai, D.; Tan, Y.L.; Lim, L.; Bi, X.; Lee, J.J.; Kim, H.J.; Kang, N.Y.; Ng, S.H.; et al. Neural Stem Cell Specific Fluorescent Chemical Probe Binding to FABP7. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 10214–10217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kipp, M.; Clarner, T.; Gingele, S.; Pott, F.; Amor, S.; van der Valk, P.; Beyer, C. Brain Lipid Binding Protein (FABP7) as Modulator of Astrocyte Function. Physiol. Res. 2011, 60, S49–S60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Needham, H.; Torpey, G.; Flores, C.C.; Davis, C.J.; Vanderheyden, W.M.; Gerstner, J.R. A Dichotomous Role for FABP7 in Sleep and Alzheimer’s Disease Pathogenesis: A Hypothesis. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 798994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardridge, W.M. The Blood-Brain Barrier: Bottleneck in Brain Drug Development. NeuroRx 2005, 2, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinoda, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yamamoto, T.; Miyachi, H.; Fukunaga, K. Analysis of Binding Affinity and Docking of Novel Fatty Acid-Binding Protein (FABP) Ligands. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 143, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, A.; Jia, W.; Finkelstein, D.I.; Stefanova, N.; Wang, H.; Sasaki, T.; Kawahata, I.; Fukunaga, K. Pharmacological Inhibition of FABP7 by MF 6 Counteracts Cerebellum Dysfunction in an Experimental Multiple System Atrophy Mouse Model. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2024, 45, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Kawahata, I.; Degawa, T.; Ikeda-Matsuo, Y.; Sun, M.; Han, F.; Fukunaga, K. Fatty Acid-Binding Proteins Aggravate Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Mice. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, K.; Cheng, A.; Yabuki, Y.; Takahata, I.; Miyachi, H.; Fukunaga, K. Inhibition of MPTP-Induced α-Synuclein Oligomerization by Fatty Acid-Binding Protein 3 Ligand in MPTP-Treated Mice. Neuropharmacology 2019, 150, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yabuki, Y.; Liu, J.; Kawahata, I.; Izumi, H.; Shinoda, Y.; Koga, K.; Ueno, S.; Shioda, N.; Fukunaga, K. Anti-Epileptic Effects of FABP3 Ligand MF1 through the Benzodiazepine Recognition Site of the GABA(A) Receptor. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Fukunaga, K.; Cheng, A.; Wang, Y.; Arimura, N.; Yoshino, H.; Sasaki, T.; Kawahata, I. Novel FABP3 Ligand, HY-11-9, Ameliorates Neuropathological Deficits in MPTP-Induced Parkinsonism in Mice. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2023, 152, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, G.; Osborn, M.; Tsantoulas, C.; David-Pereira, A.; Cohn, D.; Duffy, P.; Ruston, L.; Johnson, C.; Bradshaw, H.; Kaczocha, M.; et al. Discovery and Preclinical Evaluation of a Novel Inhibitor of FABP5, ART26.12, Effective in Oxaliplatin-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy. J. Pain 2024, 25, 104470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, W.G.; Osborn, M.; David-Pereira, A.; Tsantoulas, C.; Xue, W.; Yates, A.; SE, O.S. ART26.12, a Novel Fatty Acid-Binding Protein 5 Inhibitor, Shows Efficacy in Multiple Preclinical Neuropathy Models. Eur. J. Pain 2025, 29, e4718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warren, W.G.; Osborn, M.; Yates, A.; O’Sullivan, S.E. ART26.12, an FABP5 Inhibitor, Shows Efficacy in Preclinical Psoriasis Models. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2025, 145, 2510–2523.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

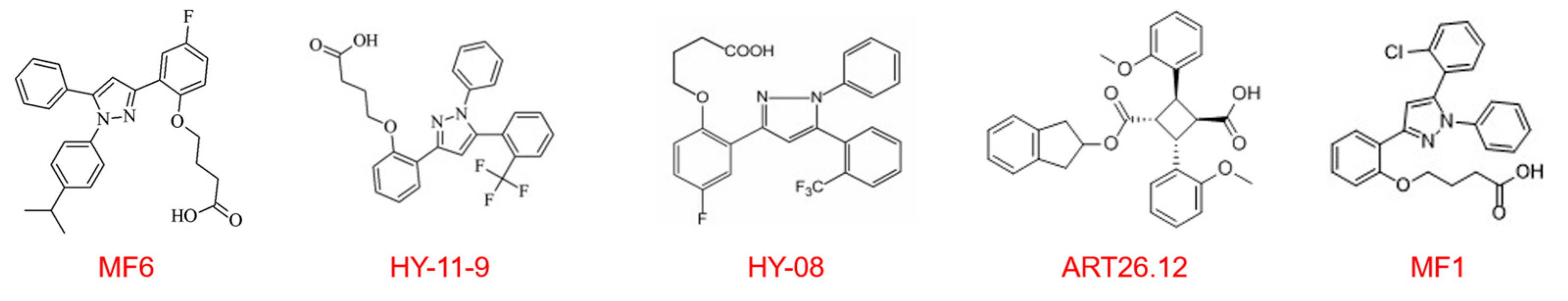
| Isoform | Major Peripheral Tissue/Cell Type | Major CNS Tissue/Cell Type | Core Function | Associated Neurodegenerative Disease |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FABP2 | Small intestine epithelial cells [56] | Not expressed | Fatty acid absorption [57,58], maintaining intestinal barrier integrity [49] | PD (via gut–brain axis) [59] |
| FABP3 | Myocardial cells [60], skeletal muscle cells [61] | Neurons (especially dopaminergic neurons) [62] | Mitochondrial β-oxidation [63,64], promoting α-syn oligomerization [65,66] | PD [65,66], AD [67,68] |
| FABP4 | Adipocytes [69], macrophages [70] | Microglia [24] | Systemic insulin resistance [71], mediating microglial inflammation [72] | Obesity-associated cognitive decline [29], Microglia-mediated neuroinflammation [73] |
| FABP5 | Epidermal cells [74], macrophages [74] | Neurons [75], astrocytes [76,77], oligodendrocytes [78,79,80] | Driving inflammation [81,82,83], regulating myelination [84] | MS [15,84], Stroke [85] |
| FABP7 | Adipocytes [86] | Astrocytes [87,88], radial glial cells [89] | Driving glial meta-inflammation [90,91], neural stem cell development [92,93,94] | MS [84,91,95], MSA [44], AD [87,96], ALS [17] |
| Ligand | Target Isoform and Selectivity | Affinity (Kd/Ki, nM) | CNS Penetrance | Key Preclinical Model | Primary Efficacy Endpoint |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MF6 [43,66,84,98] | FABP7 > FABP5 >> FABP3 | FABP7: 20; FABP5: 874 | Good, Plasma Cmax ~522 nM (4 h) | EAE (MS), MSA | Reduced demyelination, inhibited glial activation, improved motor function |
| MF1 [66,98,101] | FABP3 | 302.8 | Good (confirmed by in vivo efficacy) | MPTP (PD), Epilepsy | Reduced α-syn aggregation, improved motor and cognitive function, anticonvulsant |
| HY-11-9 | FABP3 | 11.7 | Good (confirmed by in vivo efficacy) | MPTP (PD) | Improved motor function, reduced pS129-α-syn aggregation (superior to MF1) |
| HY08 [85] | FABP3 > FABP5 | FABP3: 24; FABP5: 410 | Good (confirmed by in vivo efficacy) | tMCAO/R (Stroke) | Reduced infarct volume, improved neurological function, inhibited mitochondrial damage |
| ART26.12 [104,106] | FABP5 >> FABP7, FABP3, FABP4 | FABP5: 770 (Ki) | Limited (Brain/Plasma Ratio ≈ 2.3%) | Neuropathic Pain | Reversed mechanical allodynia and cold hyperalgesia |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, C.; Lin, J.; Chen, Q.; Zhao, W.; Kawahata, I.; Cheng, A. Targeting the FABP Axis: Interplay Between Lipid Metabolism, Neuroinflammation, and Neurodegeneration. Cells 2025, 14, 1502. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14191502
Wu C, Lin J, Chen Q, Zhao W, Kawahata I, Cheng A. Targeting the FABP Axis: Interplay Between Lipid Metabolism, Neuroinflammation, and Neurodegeneration. Cells. 2025; 14(19):1502. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14191502
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Chuantao, Jiejing Lin, Qikai Chen, Wenxue Zhao, Ichiro Kawahata, and An Cheng. 2025. "Targeting the FABP Axis: Interplay Between Lipid Metabolism, Neuroinflammation, and Neurodegeneration" Cells 14, no. 19: 1502. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14191502
APA StyleWu, C., Lin, J., Chen, Q., Zhao, W., Kawahata, I., & Cheng, A. (2025). Targeting the FABP Axis: Interplay Between Lipid Metabolism, Neuroinflammation, and Neurodegeneration. Cells, 14(19), 1502. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14191502









