Reactivation of Human X-Linked Gene and Stable X-Chromosome Inactivation Observed in Generation and Differentiation of iPSCs from a Female Patient with HNRNPH2 Mutation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Reprogramming of Human Skin Fibroblasts
2.3. Monolayer Differentiation Assay
2.4. Neural Stem Cell (iNSC) Differentiation and Expansion
2.5. Gene Expression Analysis by RT-qPCR
2.6. DNA Sequencing
2.7. Immunocytochemistry
2.8. Flow Cytometry Analysis
3. Results
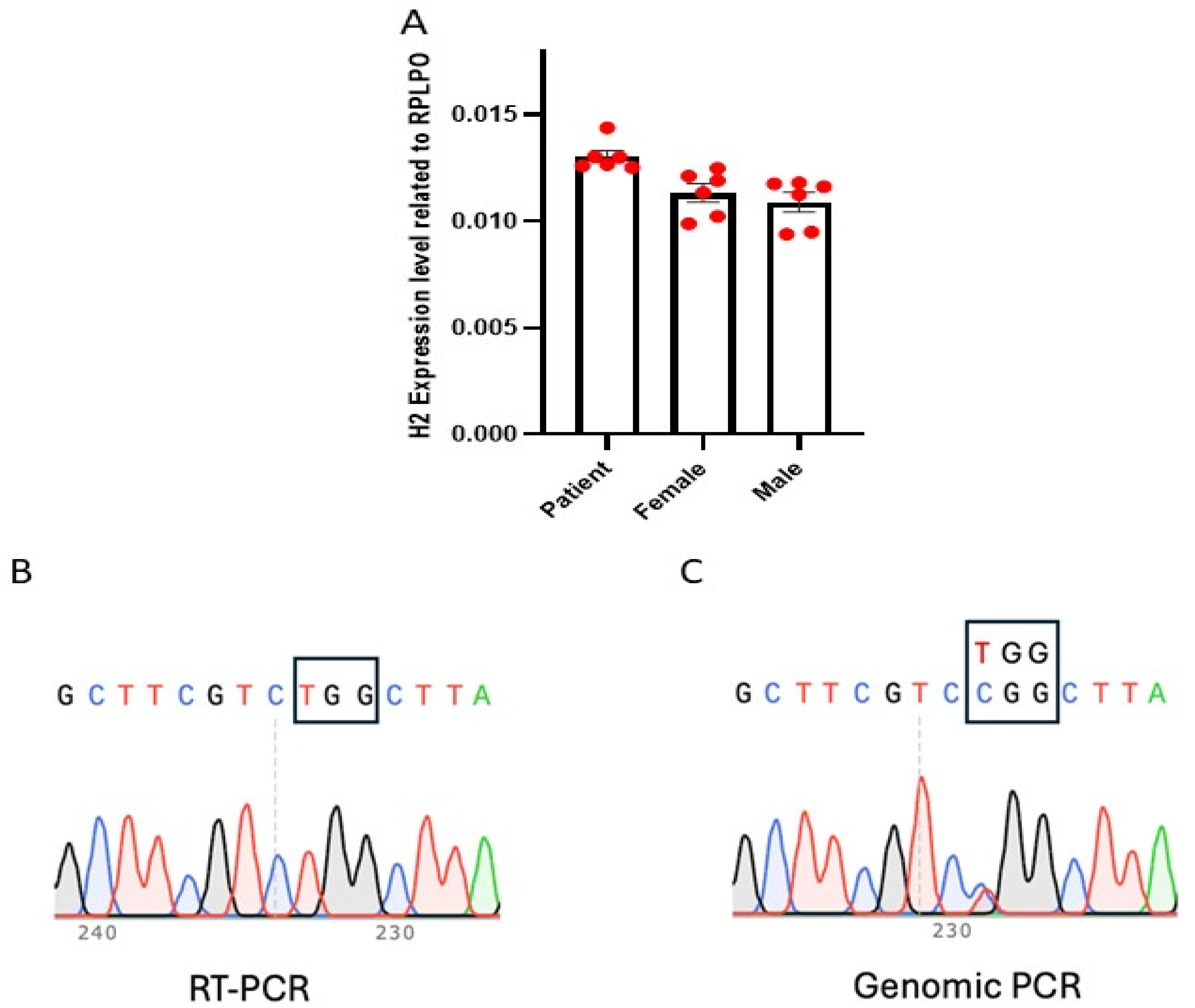
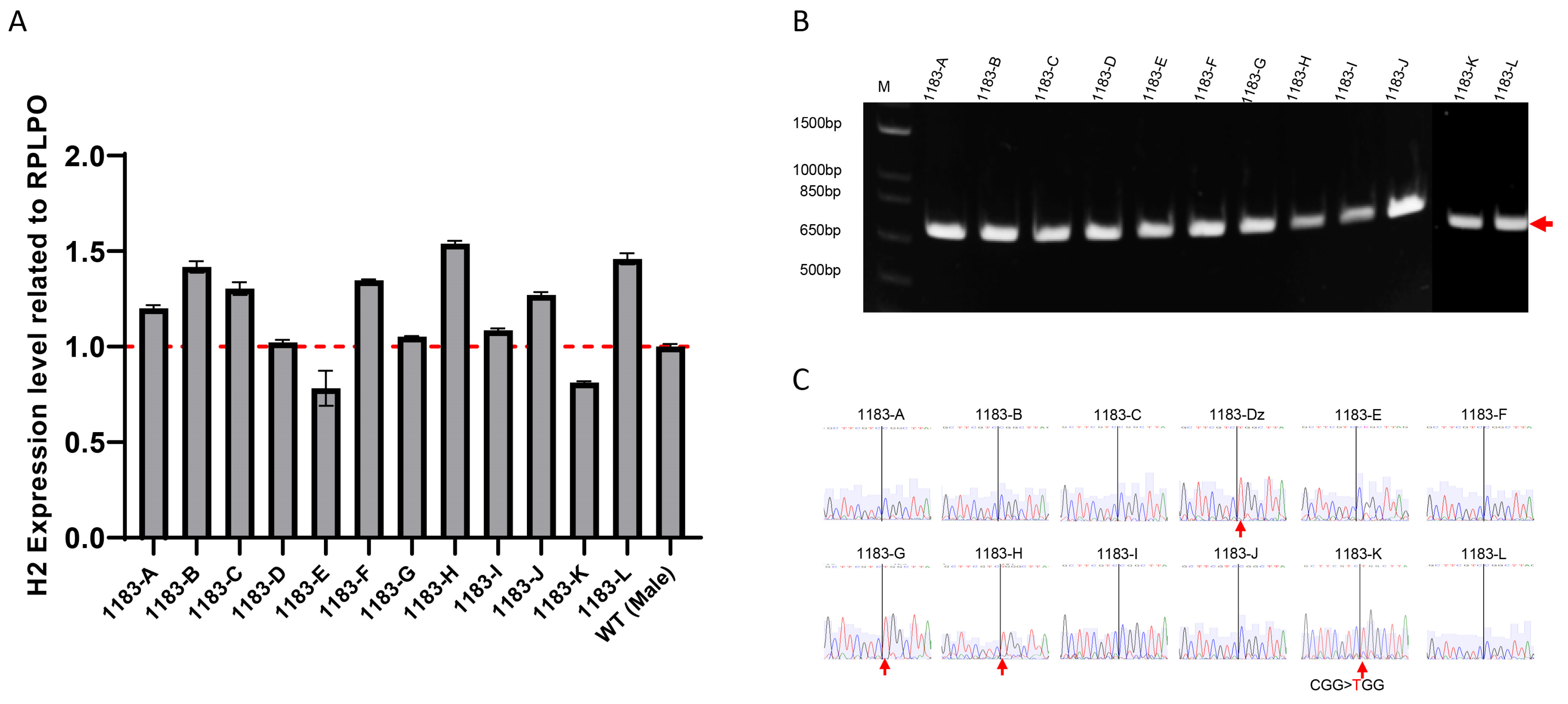
3.1. X Chromosome Reactivation and Inactivation in Human iPSC Clones Generated from Female MRXSB Patient Fibroblasts
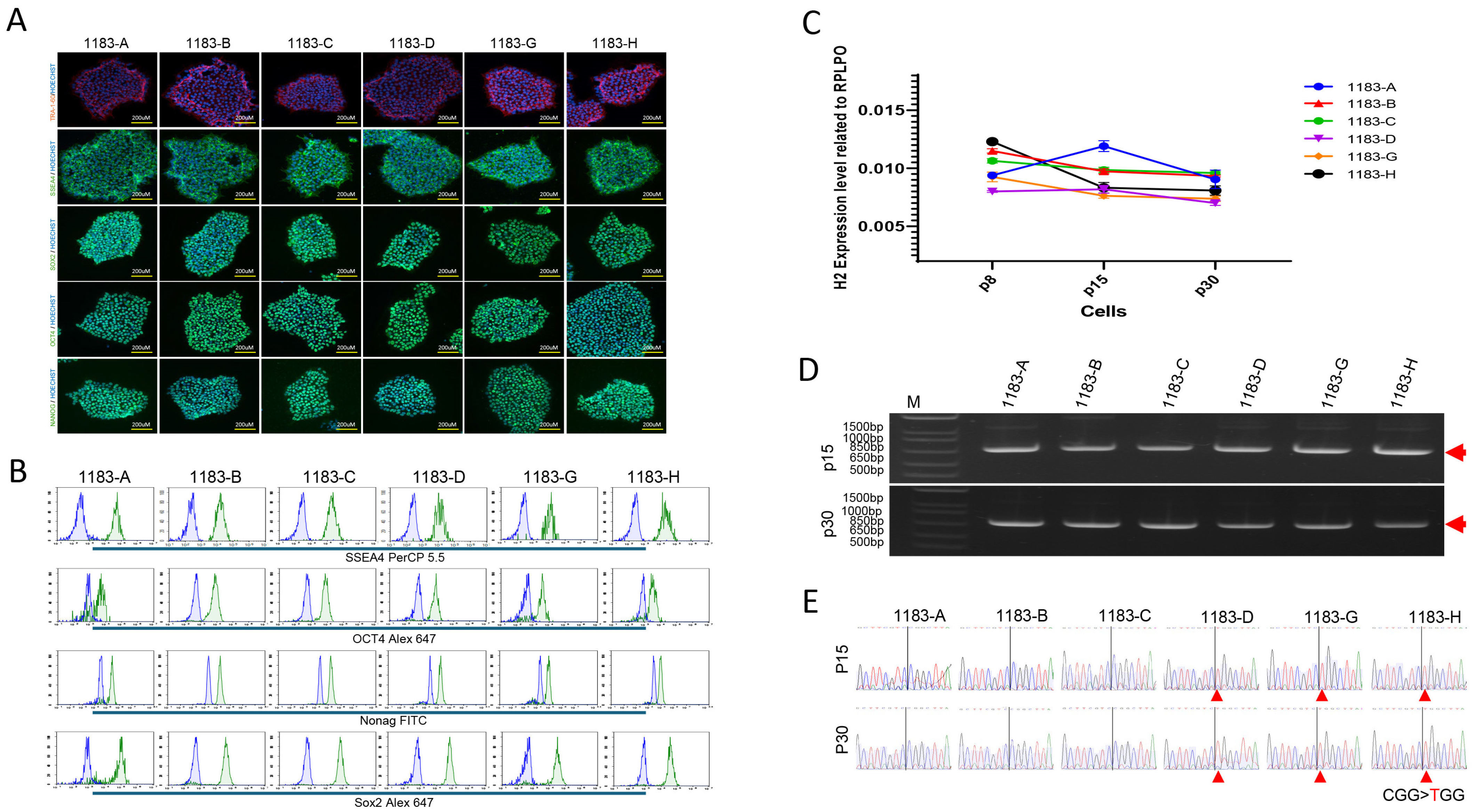
3.2. Allele-Specific Expression Analysis Demonstrates Stable XCI During iPSCs Propagation
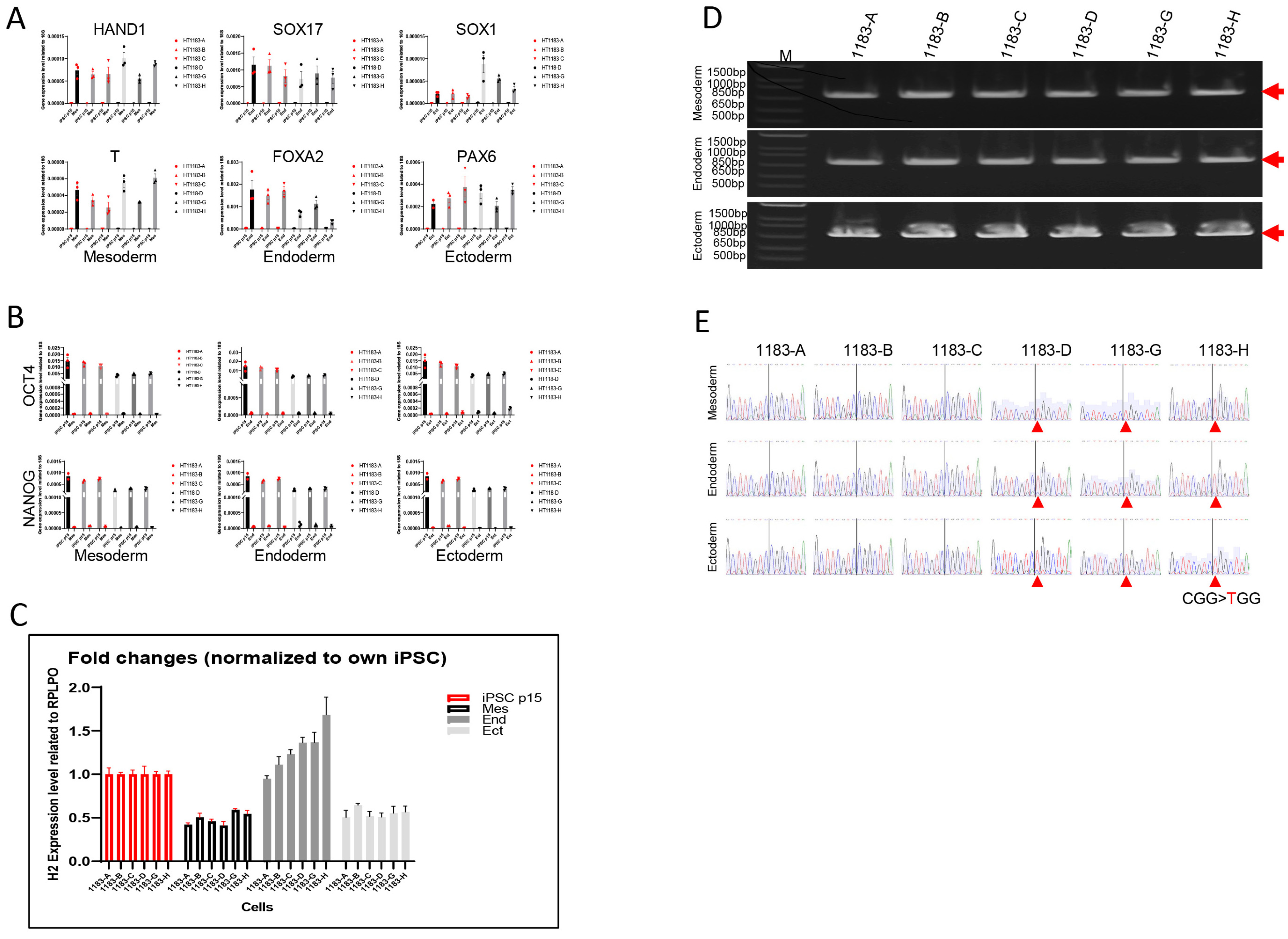
3.3. The Three Germ Layer Cells Derived from iPSCs Exhibited the Same XCI Pattern as Their Parental Cells
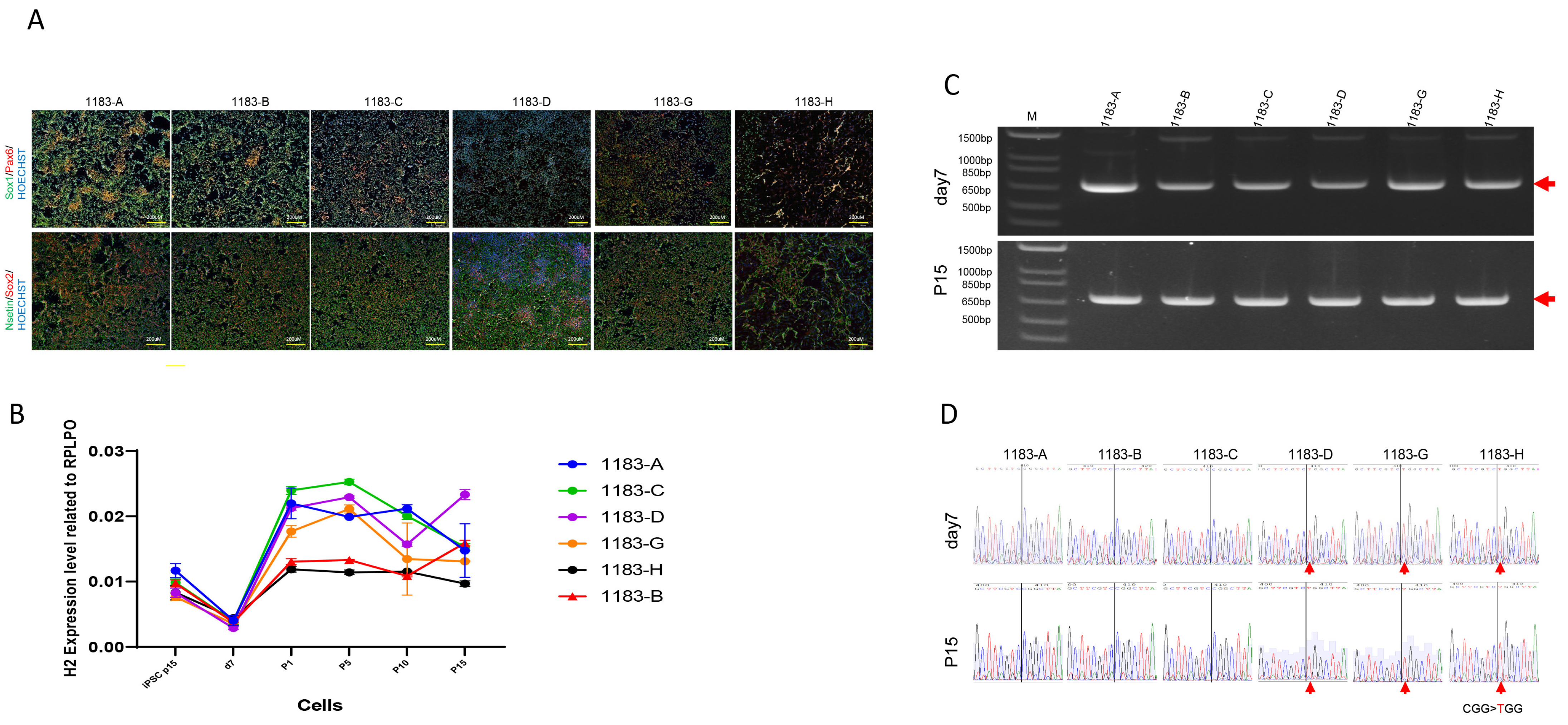
3.4. The Neural Stem Cells Derived from iPSCs Maintain Stable XCI Patterns
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bain, J.M.; Cho, M.T.; Telegrafi, A.; Wilson, A.; Brooks, S.; Botti, C.; Gowans, G.; Autullo, L.A.; Krishnamurthy, V.; Willing, M.C.; et al. Variants in HNRNPH2 on the X Chromosome Are Associated with a Neurodevelopmental Disorder in Females. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2016, 99, 728–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harmsen, S.; Buchert, R.; Mayatepek, E.; Haack, T.B.; Distelmaier, F. Bain type of X-linked syndromic mental retardation in boys. Clin. Genet. 2019, 95, 734–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White-Brown, A.M.; Lemire, G.; Ito, Y.A.; Thornburg, O.; Bain, J.M.; Dyment, D.A. A disease-causing variant in HNRNPH2 inherited from an unaffected mother with skewed X-inactivation. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2022, 188, 668–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somashekar, P.H.; Narayanan, D.L.; Jagadeesh, S.; Suresh, B.; Vaishnavi, R.D.; Bielas, S.; Girisha, K.M.; Shukla, A. Bain type of X-linked syndromic mental retardation in a male with a pathogenic variant in HNRNPH2. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2020, 182, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peron, A.; Novara, F.; La Briola, F.; Merati, E.; Giannusa, E.; Segalini, E.; Anniballi, G.; Vignoli, A.; Ciccone, R.; Canevini, M.P. Missense variants in the Arg206 residue of HNRNPH2: Further evidence of causality and expansion of the phenotype. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2020, 182, 823–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bain, J.M.; Thornburg, O.; Pan, C.; Rome-Martin, D.; Boyle, L.; Fan, X.; Devinsky, O.; Frye, R.; Hamp, S.; Keator, C.G.; et al. Detailed Clinical and Psychological Phenotype of the X-Linked HNRNPH2-Related Neurodevelopmental Disorder. Neurol. Genet. 2021, 7, e551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreienkamp, H.-J.; Wagner, M.; Weigand, H.; McConkie-Rossell, A.; McDonald, M.; Keren, B.; Mignot, C.; Gauthier, J.; Soucy, J.-F.; Michaud, J.L.; et al. Variant-specific effects define the phenotypic spectrum of HNRNPH2-associated neurodevelopmental disorders in males. Hum. Genet. 2022, 141, 257–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madhok, S.; Bain, J. HNRNPH2-Related Neurodevelopmental Disorder. In GeneReviews®; Adam, M.P., Feldman, J., Mirzaa, G.M., Eds.; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.Y.; Hysolli, E.; Tanaka, Y.; Wang, B.; Jung, Y.-W.; Pan, X.; Weissman, S.M.; Park, I.-H. X Chromosome of female cells shows dynamic changes in status during human somatic cell reprogramming. Stem Cell Rep. 2014, 2, 896–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bar, S.; Seaton, L.R.; Weissbein, U.; Eldar-Geva, T.; Benvenisty, N. Global Characterization of X Chromosome Inactivation in Human Pluripotent Stem Cells. Cell Rep. 2019, 27, 20–29.e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raposo, A.C.; Caldas, P.; Arez, M. Erosion of X-Chromosome Inactivation in female hiPSCs is heterogeneous and persists during differentiation. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beers, J.; Linask, K.L.; Chen, J.A.; Siniscalchi, L.I.; Lin, Y.; Zheng, W.; Rao, M.; Chen, G. A cost-effective and efficient reprogramming platform for large-scale production of integration-free human induced pluripotent stem cells in chemically defined culture. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahabian, A.; Dahlmann, J.; Martin, U.; Olmer, R. Production and cryopreservation of definitive endoderm from human pluripotent stem cells under defined and scalable culture conditions. Nat. Protoc. 2021, 16, 1581–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobner, J.; Diecke, S.; Krutmann, J.; Prigione, A.; Rossi, A. Reassessment of marker genes in human induced pluripotent stem cells for enhanced quality control. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 8547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolagar, T.A.; Farzaneh, M.; Nikkar, N.; Khoshnam, S.E. Human Pluripotent Stem Cells in Neurodegenerative Diseases: Potentials, Advances and Limitations. Curr. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2020, 15, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tchieu, J.; Kuoy, E.; Chin, M.H.; Trinh, H.; Patterson, M.; Sherman, S.P.; Aimiuwu, O.; Lindgren, A.; Hakimian, S.; Zack, J.A.; et al. Female Human iPSCs Retain an Inactive X Chromosome. Cell Stem Cell 2010, 7, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mekhoubad, S.; Bock, C.; de Boer, A.S.; Kiskinis, E.; Meissner, A.; Eggan, K. Erosion of dosage compensation impacts human iPSC disease modeling. Cell Stem Cell 2012, 10, 595–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plath, K.; Mlynarczyk-Evans, S.; Nusinow, D.A.; Panning, B. Xist RNA and the mechanism of X chromosome inactivation. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2002, 36, 233–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, P.; Chambers, I.; Karwacki-Neisius, V.; Chureau, C.; Morey, C.; Rougeulle, C.; Avner, P. Molecular coupling of Xist regulation and pluripotency. Science 2005, 309, 1139–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Adli, M.; Zou, J.Y.; Verstappen, G.; Coyne, M.; Zhang, X.; Durham, T.; Miri, M.; Deshpande, V.; De Jager, P.L.; et al. Genome-wide chromatin state transitions associated with developmental and lineage-specific gene regulation. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 478–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stergachis, A.B.; Neph, S.; Reynolds, A.; Humbert, R.; Miller, B.; Paige, S.L.; Vernot, B.; Cheng, J.B.; Thurman, R.E.; Sandstrom, R.; et al. Developmental fate and cellular maturity encoded in human regulatory DNA landscapes. Cell 2023, 154, 888–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, G.; Rodriguez-Lopez, A.; Wangsa, D.; Lomash, R.M.; Huang, X.; Chen, C.Z.; Bowling, R.A., Jr.; Ghousifam, N.; Banks, C.J.; Hurd, K.A.; et al. Reactivation of Human X-Linked Gene and Stable X-Chromosome Inactivation Observed in Generation and Differentiation of iPSCs from a Female Patient with HNRNPH2 Mutation. Cells 2025, 14, 1486. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14191486
Chen G, Rodriguez-Lopez A, Wangsa D, Lomash RM, Huang X, Chen CZ, Bowling RA Jr., Ghousifam N, Banks CJ, Hurd KA, et al. Reactivation of Human X-Linked Gene and Stable X-Chromosome Inactivation Observed in Generation and Differentiation of iPSCs from a Female Patient with HNRNPH2 Mutation. Cells. 2025; 14(19):1486. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14191486
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Guibin, Alexander Rodriguez-Lopez, Darawalee Wangsa, Richa Madan Lomash, Xiuli Huang, Catherine Z. Chen, Rodney A. Bowling, Jr., Neda Ghousifam, Courtney J. Banks, Kerstin A. Hurd, and et al. 2025. "Reactivation of Human X-Linked Gene and Stable X-Chromosome Inactivation Observed in Generation and Differentiation of iPSCs from a Female Patient with HNRNPH2 Mutation" Cells 14, no. 19: 1486. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14191486
APA StyleChen, G., Rodriguez-Lopez, A., Wangsa, D., Lomash, R. M., Huang, X., Chen, C. Z., Bowling, R. A., Jr., Ghousifam, N., Banks, C. J., Hurd, K. A., Zou, J., & Zheng, W. (2025). Reactivation of Human X-Linked Gene and Stable X-Chromosome Inactivation Observed in Generation and Differentiation of iPSCs from a Female Patient with HNRNPH2 Mutation. Cells, 14(19), 1486. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14191486





