Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts in Solid Tumors and Sarcomas: Heterogeneity, Function, and Therapeutic Implications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Data Collection
2.1. Study Selection, Data Extraction, and Appraisal
2.2. Synthesis and Bias Mitigation
2.3. Limitations
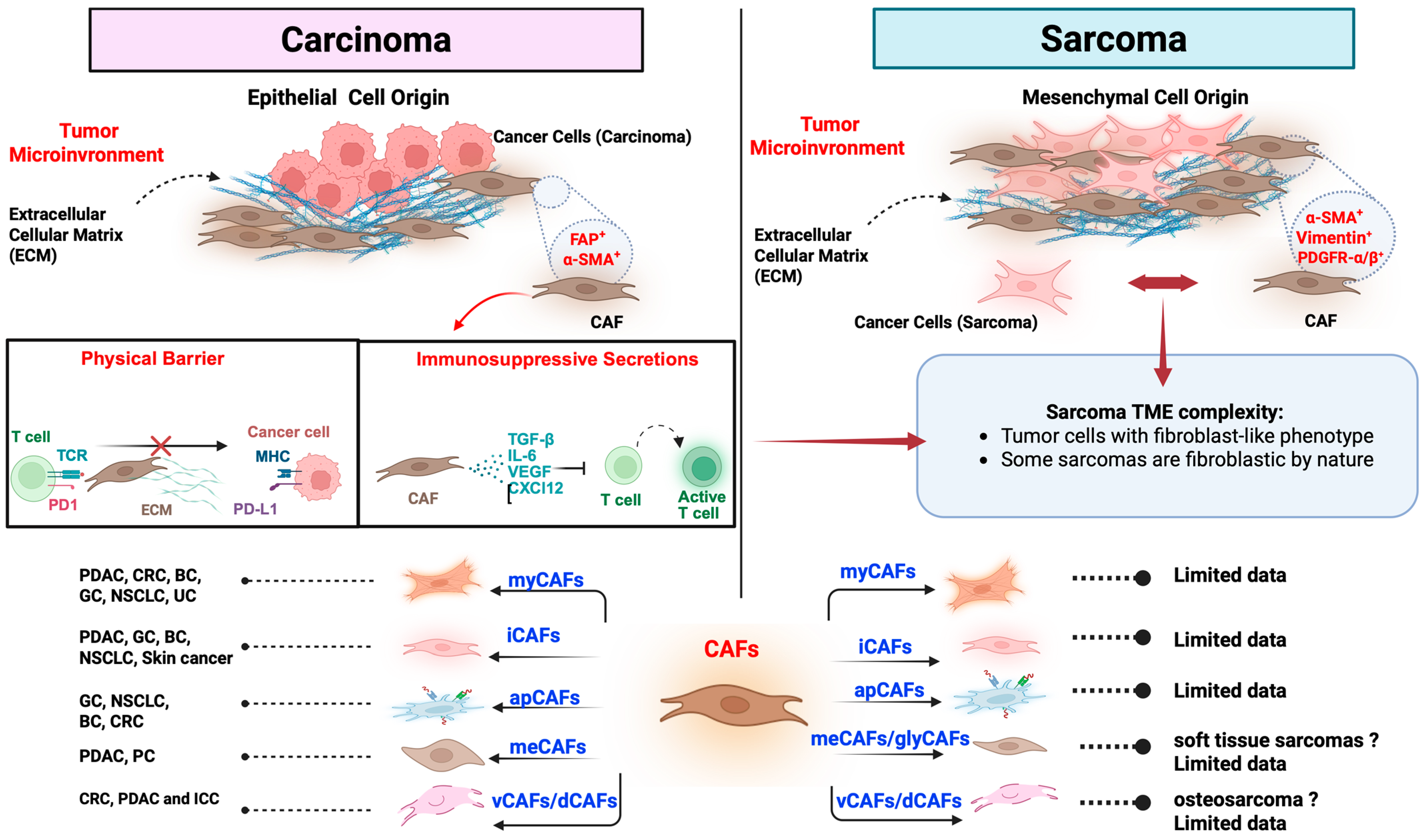
3. Subtypes of Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts (CAFs)
3.1. Myofibroblastic CAFs (myCAFs)
3.2. Inflammatory CAFs (iCAFs)
3.3. Antigen-Presenting CAFs (apCAFs)
3.4. Metabolic CAFs (meCAFs)
3.5. Vascular and Developmental CAFs (vCAFs and dCAFs)
3.6. Tumor-Promoting Versus Tumor-Suppressive Functions of CAFs
4. Crosstalk with Cancer Stem Cells (CSCs)
5. CAFs in Sarcomas
6. Clinical Implications
6.1. CAF Subtypes as Predictive Biomarkers
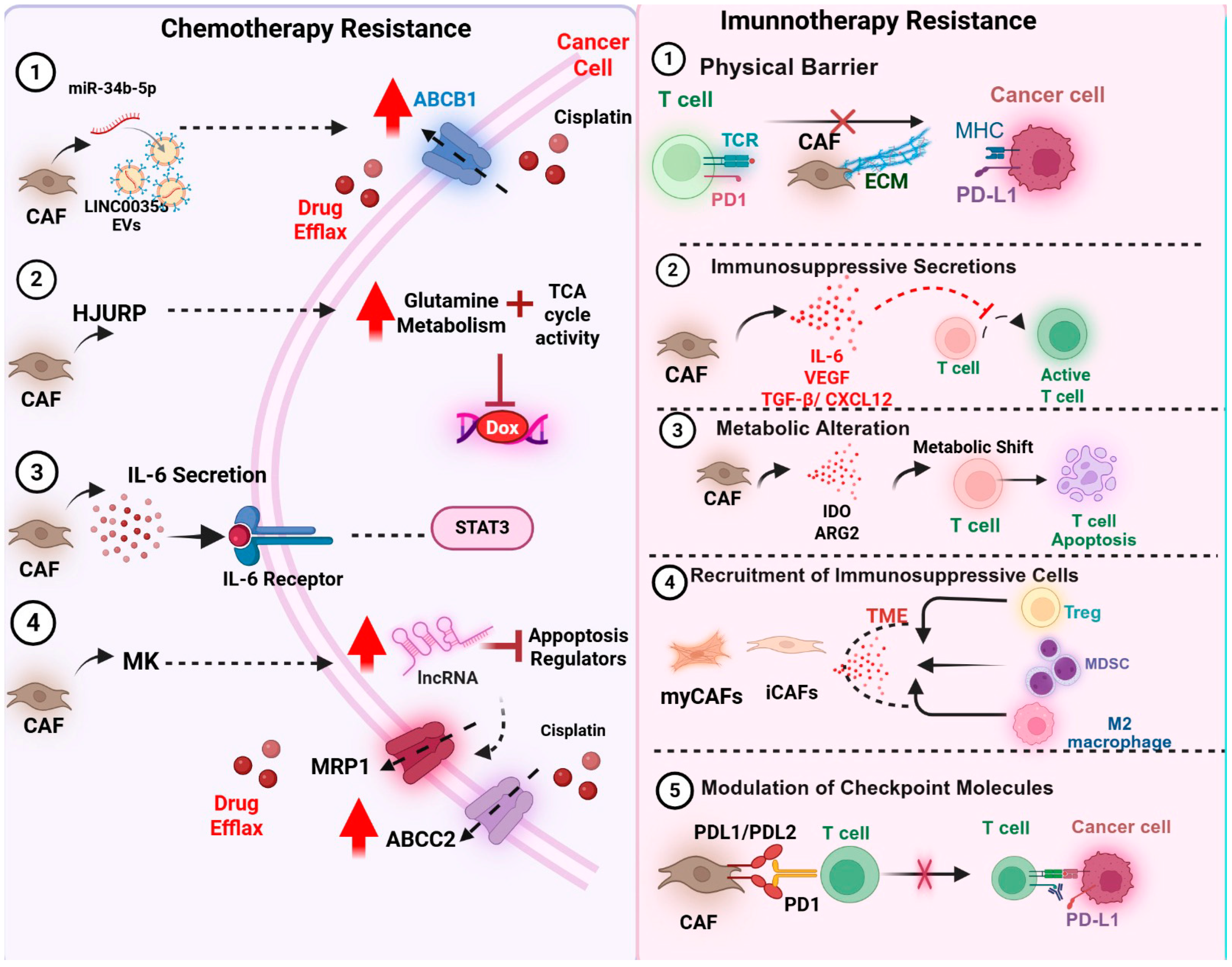
6.2. CAFs and Therapeutic Resistance
6.2.1. Chemotherapy Resistance
6.2.2. CAFs and Resistance to Immunotherapy
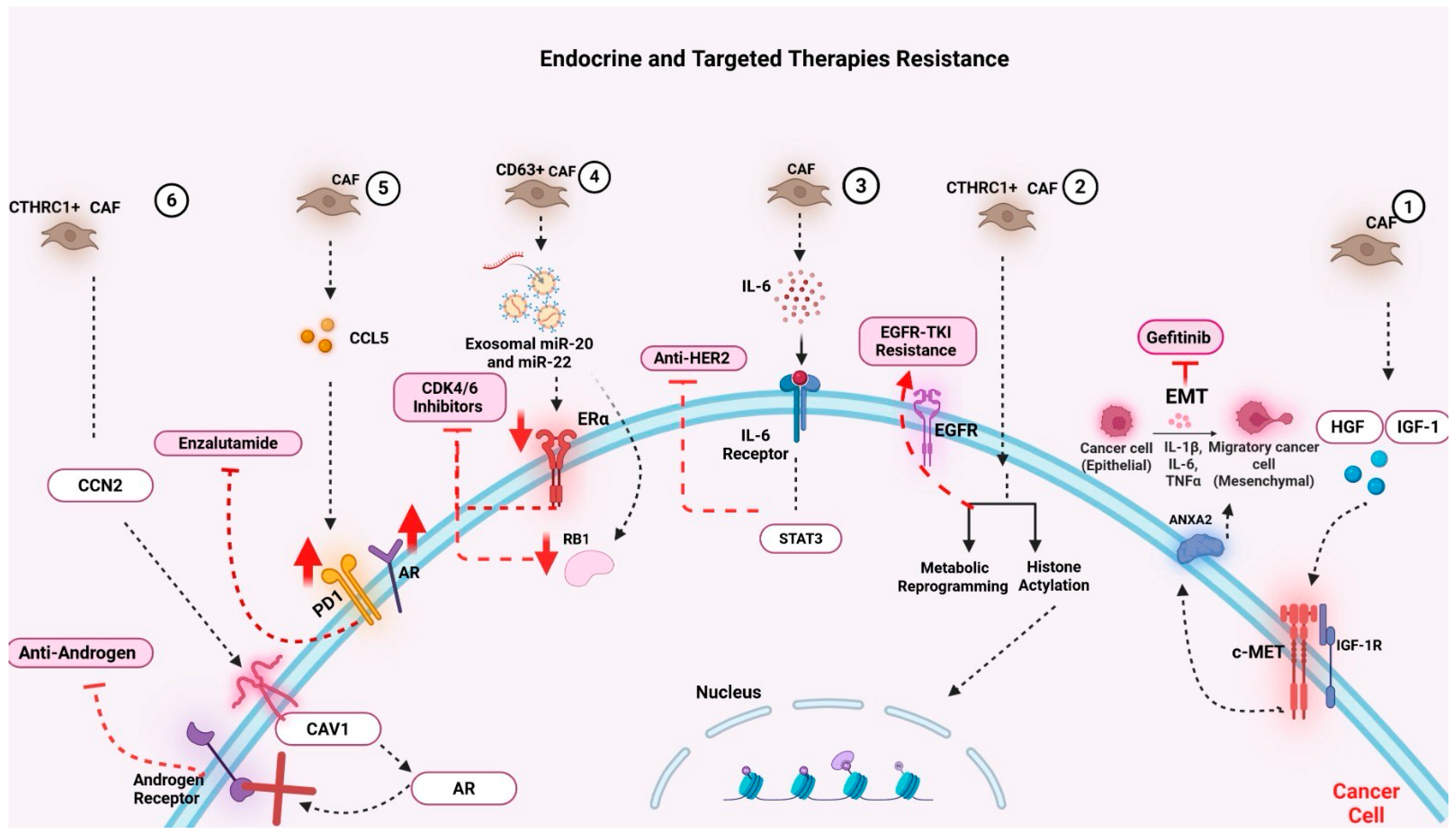
6.2.3. CAFs and Resistance to Endocrine and Targeted Therapies
7. Challenges and Future Directions
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CAF | Cancer-Associated Fibroblast |
| myCAF | Myofibroblastic Cancer-Associated Fibroblast |
| iCAF | Inflammatory Cancer-Associated Fibroblast |
| apCAF | Antigen-Presenting Cancer-Associated Fibroblast |
| meCAF | Metabolic Cancer-Associated Fibroblast |
| vCAF | Vascular Cancer-Associated Fibroblast |
| dCAF | Developmental Cancer-Associated Fibroblast |
| rCAF | Tumor-Restraining Cancer-Associated Fibroblast |
| pCAF | Tumor-Promoting Cancer-Associated Fibroblast |
| CSCs | Cancer Stem Cells |
| ECM | Extracellular Matrix |
| EMT | Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition |
| EndMT | Endothelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition |
| TGF-β | Transforming Growth Factor Beta |
| IL-6 | Interleukin 6 |
| IL-10 | Interleukin 10 |
| CXCL12 | C-X-C Motif Chemokine Ligand 12 |
| CXCL1 | C-X-C Motif Chemokine Ligand 1 |
| CXCL16 | C-X-C Motif Chemokine Ligand 16 |
| JAK/STAT | Janus Kinase/Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription |
| NF-κB | Nuclear Factor Kappa-Light-Chain-Enhancer of Activated B Cells |
| PDGF | Platelet-Derived Growth Factor |
| VEGF | Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor |
| WNT | Wingless/Integrated Signaling Pathway |
| HGF | Hepatocyte Growth Factor |
| IGF-1 | Insulin-Like Growth Factor 1 |
| PD-L1/PD-L2 | Programmed Death Ligand 1/2 |
| TLR4 | Toll-Like Receptor 4 |
| ATM | Ataxia Telangiectasia Mutated (signaling kinase) |
| IDO | Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase |
| ARG2 | Arginase 2 |
| α-SMA | Alpha Smooth Muscle Actin |
| FAP | Fibroblast Activation Protein |
| CD4+ T cells | Cluster of Differentiation 4 Positive T Lymphocytes |
| CD8+ T cells | Cluster of Differentiation 8 Positive T Lymphocytes |
| Tregs | Regulatory T Cells |
| TAMs | Tumor-Associated Macrophages |
| MDSCs | Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells |
| MHC | Major Histocompatibility Complex |
| TLS | Tertiary Lymphoid Structures |
| DCN | Decorin |
| CTHRC1 | Collagen Triple Helix Repeat Containing 1 |
| CD63 | Cluster of Differentiation 63 |
| CD10 | Cluster of Differentiation 10 |
| PDGFR | Platelet-Derived Growth Factor Receptor |
| SDF-1 | Stromal-Derived Factor 1 |
| CXCR4 | C-X-C Chemokine Receptor Type 4 |
| scRNA-seq | Single-Cell RNA Sequencing |
| TME | Tumor Microenvironment |
| TIME | Tumor Immune Microenvironment |
| 3D | Three-Dimensional |
| EVs | Extracellular Vesicles |
| PDAC | Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma |
| NSCLC | Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer |
| HCC | Hepatocellular Carcinoma |
| RMS | Rhabdomyosarcoma |
| UPS | Undifferentiated Pleomorphic Sarcoma |
| STS | Soft Tissue Sarcoma |
| EwS | Ewing Sarcoma |
| HNSCC | Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma |
| NETs | Neuroendocrine Tumors |
| MHC-II | Major Histocompatibility Complex Class II |
| ZEB1 | Zinc Finger E-Box Binding Homeobox 1 |
| TBX2 | T-Box Transcription Factor 2 |
| SOX9 | SRY-Box Transcription Factor 9 |
| COL6A1 | Collagen Type VI Alpha 1 Chain |
| HJURP | Holliday Junction Recognition Protein |
| MCM2 | Minichromosome Maintenance Complex Component 2 |
| ANXA2 | Annexin A2 |
| AR | Androgen Receptor |
| CXCL14 | C-X-C Motif Chemokine Ligand 14 |
| ABCB1 | ATP-Binding Cassette Sub-Family B Member 1 |
| ABCC2 | ATP-Binding Cassette Sub-Family C Member 2 |
| MRP1 | Multidrug Resistance-Associated Protein 1 |
| miRNA/miR | MicroRNA, e.g., miR-105, miR-21, miR-146a, miR-1228, miR-4717-5p |
| lncRNA | Long Non-Coding RNA, e.g., ANRIL, LINC00355 |
| ICB | Immune Checkpoint Blockade |
| CAR-T | Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy |
| TKIs | Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors |
| ADC | Antibody–Drug Conjugate |
| MMAE | Monomethyl Auristatin E |
| OXPHOS | Oxidative Phosphorylation |
| TCA Cycle | Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle (Krebs Cycle) |
References
- Plikus, M.V.; Wang, X.; Sinha, S.; Forte, E.; Thompson, S.M.; Herzog, E.L.; Driskell, R.R.; Rosenthal, N.; Biernaskie, J.; Horsley, V. Fibroblasts: Origins, definitions, and functions in health and disease. Cell 2021, 184, 3852–3872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diller, R.B.; Tabor, A.J. The Role of the Extracellular Matrix (ECM) in Wound Healing: A Review. Biomimetics 2022, 7, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tracy, L.E.; Minasian, R.A.; Caterson, E.J. Extracellular Matrix and Dermal Fibroblast Function in the Healing Wound. Adv. Wound Care 2016, 5, 119–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Wang, J.H.C. Fibroblasts and myofibroblasts in wound healing: Force generation and measurement. J. Tissue Viability 2011, 20, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Ma, Y.; Li, D.; Wei, J.; Chen, K.; Zhang, E.; Liu, G.; Chu, X.; Liu, X.; Liu, W.; et al. Cancer associated fibroblasts and metabolic reprogramming: Unraveling the intricate crosstalk in tumor evolution. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2024, 17, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glabman, R.A.; Choyke, P.L.; Sato, N. Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts: Tumorigenicity and Targeting for Cancer Therapy. Cancers 2022, 14, 3906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.; Choi, S.; Yoo, S.; Lee, M.; Kim, I.S. Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts in the Hypoxic Tumor Microenvironment. Cancers 2022, 14, 3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, X.; Li, W.; Zhao, K.; Wang, J.; Li, S.; Zhao, H. Revisiting the role of cancer-associated fibroblasts in tumor microenvironment. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1582532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, J.; Li, Z.; Liu, F.; Wang, A.; Gao, Z.; Wu, C.; Yin, H. Overcoming cancer treatment resistance: Unraveling the role of cancer-associated fibroblasts. J. Natl. Cancer Cent. 2025, 5, 237–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhabra, Y.; Weeraratna, A.T. Fibroblasts in cancer: Unity in heterogeneity. Cell 2023, 186, 1580–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, M.; Nguyen, T.; Gundre, E.; Ogunlusi, O.; El-Sobky, M.; Giri, B.; Sarkar, T.R. Cancer-associated fibroblasts: The chief architect in the tumor microenvironment. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1089068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeisberg, E.M.; Potenta, S.; Xie, L.; Zeisberg, M.; Kalluri, R. Discovery of Endothelial to Mesenchymal Transition as a Source for Carcinoma-Associated Fibroblasts. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 10123–10128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, C.E.; Kothari, A.N.; Wai, P.Y.; Li, N.Y.; Driver, J.; Zapf, M.A.; Franzen, C.; Gupta, G.N.; Osipo, C.; Zlobin, A.; et al. Osteopontin mediates an MZF1–TGF-β1-dependent transformation of mesenchymal stem cells into cancer-associated fibroblasts in breast cancer. Oncogene 2015, 34, 4821–4833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffaghello, L.; Vacca, A.; Pistoia, V.; Ribatti, D. Cancer-associated fibroblasts in hematological malignancies. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 2589–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotsitzoudis, C.; Koulouridi, A.; Messaritakis, I.; Konstantinidis, T.; Gouvas, N.; Tsiaoussis, J.; Souglakos, J. Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts: The Origin, Biological Characteristics and Role in Cancer—A Glance on Colorectal Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 4394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kay, E.J.; Zanivan, S. The tumor microenvironment is an ecosystem sustained by metabolic interactions. Cell Rep. 2025, 44, 115432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Sinjab, A.; Min, J.; Han, G.; Paradiso, F.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, R.; Pei, G.; Dai, Y.; Liu, Y.; et al. Conserved spatial subtypes and cellular neighborhoods of cancer-associated fibroblasts revealed by single-cell spatial multi-omics. Cancer Cell 2025, 43, 905–924.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Tsang, W.Y.; Li, Z.H.; Guan, X.Y. The Origin, Differentiation, and Functions of Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts in Gastrointestinal Cancer. Cell Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 16, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elyada, E.; Bolisetty, M.; Laise, P.; Flynn, W.F.; Courtois, E.T.; Burkhart, R.A.; Teinor, J.A.; Belleau, P.; Biffi, G.; Lucito, M.S.; et al. Cross-Species Single-Cell Analysis of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Reveals Antigen-Presenting Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 1102–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peiffer, R.; Boumahd, Y.; Gullo, C.; Crake, R.; Letellier, E.; Bellahcène, A.; Peulen, O. Cancer-Associated Fibroblast Diversity Shapes Tumor Metabolism in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancers 2022, 15, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, R.; Younesi, F.; Ezzo, M.; Hinz, B. The Role of Myofibroblasts in Physiological and Pathological Tissue Repair. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2023, 15, a041231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, A.; Gentile, M.T.; Pentimalli, F.; Cortellino, S.; Grieco, M.; Giordano, A. Multiple aspects of matrix stiffness in cancer progression. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1406644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, H.; Hara, T.; Meng, S.; Tsuji, Y.; Arao, Y.; Saito, Y.; Sasaki, K.; Kobayashi, S.; Doki, Y.; Eguchi, H.; et al. Multifaced roles of desmoplastic reaction and fibrosis in pancreatic cancer progression: Current understanding and future directions. Cancer Sci. 2023, 114, 3487–3495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccolo, S.; Panciera, T.; Contessotto, P.; Cordenonsi, M. YAP/TAZ as master regulators in cancer: Modulation, function and therapeutic approaches. Nat. Cancer 2022, 4, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Jin, X.; Hou, Y.; Gu, B.; Li, H.; Yi, L.; Wu, W.; Hu, S. Comprehensive analysis of the critical role of the epithelial mesenchymal transition subtype - TAGLN-positive fibroblasts in colorectal cancer progression and immunosuppression. Cell Biosci. 2025, 15, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Zhang, K.; Ni, C.; Wan, J.; Duan, X.; Lou, X.; Yao, X.; Li, X.; Wang, M.; Gu, Z.; et al. Transgelin promotes lung cancer progression via activation of cancer-associated fibroblasts with enhanced IL-6 release. Oncogenesis 2023, 12, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, K.; Ly, T.; Kriet, M.; Czirok, A.; Thomas, S.M. Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts: Master Tumor Microenvironment Modifiers. Cancers 2023, 15, 1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdemir, B.C.; Pentcheva-Hoang, T.; Carstens, J.L.; Zheng, X.; Wu, C.C.; Simpson, T.R.; Laklai, H.; Sugimoto, H.; Kahlert, C.; Novitskiy, S.V.; et al. Depletion of Carcinoma-Associated Fibroblasts and Fibrosis Induces Immunosuppression and Accelerates Pancreas Cancer with Reduced Survival. Cancer Cell 2014, 25, 719–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saúde-Conde, R.; Öztürk, A.A.; Stosic, K.; Senar, O.A.; Navez, J.; Bouchart, C.; Arsenijevic, T.; Flamen, P.; Van Laethem, J.-L. Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma or a Metaphor for Heterogeneity: From Single-Cell Analysis to Whole-Body Imaging. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghahremanifard, P.; Chanda, A.; Bonni, S.; Bose, P. TGF-β Mediated Immune Evasion in Cancer—Spotlight on Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts. Cancers 2020, 12, 3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, P.; Mielgo, A. Cancer-Associated Fibroblast Mediated Inhibition of CD8+ Cytotoxic T Cell Accumulation in Tumours: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Opportunities. Cancers 2020, 12, 2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, W. Role of TGFβ-activated cancer-associated fibroblasts in the resistance to checkpoint blockade immunotherapy. Front. Oncol. 2025, 15, 1602452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clifton, G.T.; Rothenberg, M.; Ascierto, P.A.; Begley, G.; Cecchini, M.; Eder, J.P.; Ghiringhelli, F.; Italiano, A.; Kochetkova, M.; Li, R.; et al. Developing a definition of immune exclusion in cancer: Results of a modified Delphi workshop. J. Immunother. Cancer 2023, 11, e006773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Liu, T.; Yin, R. Biomarkers for cancer-associated fibroblasts. Biomark Res. 2020, 8, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohlund, D.; Handly-Santana, A.; Biffi, G.; Elyada, E.; Almeida, A.S.; Ponz-Sarvise, M.; Corbo, V.; Oni, T.E.; Hearn, S.A.; Lee, E.J.; et al. Distinct populations of inflammatory fibroblasts and myofibroblasts in pancreatic cancer. J. Exp. Med. 2017, 214, 579–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biffi, G.; Oni, T.E.; Spielman, B.; Hao, Y.; Elyada, E.; Park, Y.; Preall, J.; Tuveson, D.A. IL1-Induced JAK/STAT Signaling Is Antagonized by TGFβ to Shape CAF Heterogeneity in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 282–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, V.W.; Chung, J.Y.-F.; Córdoba, C.A.G.; Cheung, A.H.-K.; Kang, W.; Lam, E.W.-F.; Leung, K.-T.; To, K.-F.; Lan, H.-Y.; Tang, P.M.-K. Transforming Growth Factor-β: A Multifunctional Regulator of Cancer Immunity. Cancers 2020, 12, 3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.; De Wever, O. The plasticity of cancer-associated fibroblasts. Trends Cancer 2025, 11, 770–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, Y.J.; Koo, J.S. Role of Tumor-Associated Myeloid Cells in Breast Cancer. Cells 2020, 9, 1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakiba, M.; Tuveson, D.A. Macrophages and fibroblasts as regulators of the immune response in pancreatic cancer. Nat. Immunol. 2025, 26, 678–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, T. IL-6 in inflammation, autoimmunity and cancer. Int. Immunol. 2021, 33, 127–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amer, H.; Flanagan, K.L.; Kampan, N.C.; Itsiopoulos, C.; Scott, C.L.; Kartikasari, A.E.R.; Plebanski, M. Interleukin-6 Is a Crucial Factor in Shaping the Inflammatory Tumor Microenvironment in Ovarian Cancer and Determining Its Hot or Cold Nature with Diagnostic and Prognostic Utilities. Cancers 2025, 17, 1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruni, S.; Mercogliano, M.F.; Mauro, F.L.; Cordo Russo, R.I.; Schillaci, R. Cancer immune exclusion: Breaking the barricade for a successful immunotherapy. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1135456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zboralski, D.; Hoehlig, K.; Eulberg, D.; Frömming, A.; Vater, A. Increasing Tumor-Infiltrating T Cells through Inhibition of CXCL12 with NOX-A12 Synergizes with PD-1 Blockade. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2017, 5, 950–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhu, R.; Yu, D.; Wang, J.; Yan, Y.; Xu, K. Single-cell RNA sequencing to explore cancer-associated fibroblasts heterogeneity: “Single” vision for “heterogeneous” environment. Cell Prolif. 2024, 57, e13592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goulet, C.R.; Champagne, A.; Bernard, G.; Vandal, D.; Chabaud, S.; Pouliot, F.; Bolduc, S. Cancer-associated fibroblasts induce epithelial–mesenchymal transition of bladder cancer cells through paracrine IL-6 signalling. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Pradhan, R.N.; Ganguly, D.; Chandra, R.; Murimwa, G.; Wright, S.; Gu, X.; Maddipati, R.; et al. Mesothelial cell-derived antigen-presenting cancer-associated fibroblasts induce expansion of regulatory T cells in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Cell 2022, 40, 656–673.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Ren, Y.; Yang, P.; Wang, J.; Zhou, H. Cancer-associated fibroblasts in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerdidani, D.; Aerakis, E.; Verrou, K.-M.; Angelidis, I.; Douka, K.; Maniou, M.-A.; Stamoulis, P.; Goudevenou, K.; Prados, A.; Tzaferis, C.; et al. Lung tumor MHCII immunity depends on in situ antigen presentation by fibroblasts. J. Exp. Med. 2022, 219, e20210815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caligiuri, G.; Tuveson, D.A. Activated fibroblasts in cancer: Perspectives and challenges. Cancer Cell 2023, 41, 434–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerdidani, D.; Aerakis, E.; Verrou, K.-M.; Stamoulis, P.; Goudevenou, K.; Prados, A.; Tzaferis, C.; Vamvakaris, I.; Kaniaris, E.; Vachlas, K.; et al. Tumor MHCII immunity requires in situ antigen presentation by cancer-associated fibroblasts. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.C.; Sharma, R.; Anang, N.A.S.; Levine, J.H.; Zhao, Y.; Mancuso, J.J.; Setty, M.; Sharma, P.; Wang, J.; Pe’er, D.; et al. Negative Co-stimulation Constrains T Cell Differentiation by Imposing Boundaries on Possible Cell States. Immunity 2019, 50, 1084–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hünig, T.; Beyersdorf, N.; Kerkau, T. CD28 co-stimulation in T-cell homeostasis: A recent perspective. Immunotargets Ther. 2015, 4, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Sun, C.; Qin, Z. Metabolic reprogramming of cancer-associated fibroblasts and its effect on cancer cell reprogramming. Theranostics 2021, 11, 8322–8336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlides, S.; Whitaker-Menezes, D.; Castello-Cros, R.; Flomenberg, N.; Witkiewicz, A.K.; Frank, P.G.; Casimiro, M.C.; Wang, C.; Fortina, P.; Addya, S.; et al. The reverse Warburg effect: Aerobic glycolysis in cancer associated fibroblasts and the tumor stroma. Cell Cycle 2009, 8, 3984–4001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M. Metabolic interplay between glycolysis and mitochondrial oxidation: The reverse Warburg effect and its therapeutic implication. World J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 6, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Outschoorn, U.E.; Lisanti, M.P.; Sotgia, F. Catabolic cancer-associated fibroblasts transfer energy and biomass to anabolic cancer cells, fueling tumor growth. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2014, 25, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faubert, B.; Li, K.Y.; Cai, L.; Hensley, C.T.; Kim, J.; Zacharias, L.G.; Yang, C.; Do, Q.N.; Doucette, S.; Burguete, D.; et al. Lactate Metabolism in Human Lung Tumors. Cell 2017, 171, 358–371.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Hall, G.; Stømstad, M.; Rasmussen, P.; Jans, Ø.; Zaar, M.; Gam, C.; Quistorff, B.; Secher, N.H.; Nielsen, H.B. Blood Lactate is an Important Energy Source for the Human Brain. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2009, 29, 1121–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, J.M.; Tabernero, A. Lactate utilization by brain cells and its role in CNS development. J. Neurosci. Res. 2005, 79, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartelds, B.; Knoester, H.; Beaufort-Krol, G.C.M.; Smid, G.B.; Takens, J.; Zijlstra, W.G.; Heymans, H.S.A.; Kuipers, J.R.G. Myocardial Lactate Metabolism in Fetal and Newborn Lambs. Circulation 1999, 99, 1892–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Zhuo, L.; Wang, X. Metabolic reprogramming of carcinoma-associated fibroblasts and its impact on metabolic heterogeneity of tumors. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 64, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonio, M.J.; Zhang, C.; Le, A. Different Tumor Microenvironments Lead to Different Metabolic Phenotypes. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2021, 1311, 137–147. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Liang, Y.; Xu, H.; Zhang, X.; Mao, T.; Cui, J.; Yao, J.; Wang, Y.; Jiao, F.; Xiao, X.; et al. Single-cell analysis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma identifies a novel fibroblast subtype associated with poor prognosis but better immunotherapy response. Cell Discov. 2021, 7, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruksha, T.; Palkina, N. Role of exosomes in transforming growth factor-β-mediated cancer cell plasticity and drug resistance. Explor. Target. Antitumor Ther. 2025, 6, 1002322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiro, N.; Gonzalez, L.; Fraile, M.; Cid, S.; Schneider, J.; Vizoso, F. Breast Cancer Tumor Stroma: Cellular Components, Phenotypic Heterogeneity, Intercellular Communication, Prognostic Implications and Therapeutic Opportunities. Cancers 2019, 11, 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Xie, Y.; Yang, F.; Hua, Y.; Zeng, T.; Sun, C.; Yang, M.; Huang, X.; Wu, H.; Fu, Z.; et al. Comprehensive description of the current breast cancer microenvironment advancements via single-cell analysis. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 40, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Palma, M.; Biziato, D.; Petrova, T.V. Microenvironmental regulation of tumour angiogenesis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 457–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuazo-Gaztelu, I.; Casanovas, O. Unraveling the Role of Angiogenesis in Cancer Ecosystems. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenc, P.; Sikorska, A.; Molenda, S.; Guzniczak, N.; Dams-Kozlowska, H.; Florczak, A. Physiological and tumor-associated angiogenesis: Key factors and therapy targeting VEGF/VEGFR pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 180, 117585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, Q.; Tan, Y.; Tang, Y.; Ye, J.; Yuan, B.; Yu, W. Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Suppress Cancer Development: The Other Side of the Coin. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 613534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Yue, X.; Chen, Z.; Liu, C.; Wu, W.; Zhang, N.; Liu, Z.; Yang, L.; Jiang, Q.; Cheng, Q.; et al. Define cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) in the tumor microenvironment: New opportunities in cancer immunotherapy and advances in clinical trials. Mol. Cancer 2023, 22, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilmi, M.; Nicolle, R.; Bousquet, C.; Neuzillet, C. Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts: Accomplices in the Tumor Immune Evasion. Cancers 2020, 12, 2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, X.; Xu, J.; Wang, W.; Liang, C.; Hua, J.; Liu, J.; Zhang, B.; Meng, Q.; Yu, X.; Shi, S. Crosstalk between cancer-associated fibroblasts and immune cells in the tumor microenvironment: New findings and future perspectives. Mol. Cancer 2021, 20, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanandi, S.I.; Ningsih, S.S.; Asikin, H.; Hosea, R.; Neolaka, G.M.G. Metabolic Interplay between Tumour Cells and Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts (CAFs) under Hypoxia versus Normoxia. Malays. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 25, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, B.; Wu, J.; Shen, B.; Jiang, F.; Feng, J. Cancer-associated fibroblasts and resistance to anticancer therapies: Status, mechanisms, and countermeasures. Cancer Cell Int. 2022, 22, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Ye, H.; Li, G.; Lu, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Zheng, S.; Lin, Q.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Chen, R. Cancer-associated fibroblasts promote progression and gemcitabine resistance via the SDF-1/SATB-1 pathway in pancreatic cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbazan, J.; Pérez-González, C.; Gómez-González, M.; Dedenon, M.; Richon, S.; Latorre, E.; Serra, M.; Mariani, P.; Descroix, S.; Sens, P.; et al. Cancer-associated fibroblasts actively compress cancer cells and modulate mechanotransduction. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 6966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Li, T.; Sun, L.; Yuan, Y.; Zhu, Y. Potential mechanisms of cancer-associated fibroblasts in therapeutic resistance. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 166, 115425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, N.; Yashiro, M.; Hatano, T.; Fujikawa, H.; Motomura, H. CD9-positive Exosomes Derived from Cancer-associated Fibroblasts Might Inhibit the Proliferation of Malignant Melanoma Cells. Anticancer Res. 2023, 43, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishibashi, M.; Neri, S.; Hashimoto, H.; Miyashita, T.; Yoshida, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Udagawa, H.; Kirita, K.; Matsumoto, S.; Umemura, S.; et al. CD200-positive cancer associated fibroblasts augment the sensitivity of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor mutation-positive lung adenocarcinomas to EGFR Tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papavassiliou, K.A.; Sofianidi, A.A.; Cholidou, K.; Papavassiliou, A.G. The IGF Signalling Axis in Lung Cancer: Clinical Significance and Therapeutic Challenges. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2025, 29, e70540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanley, C.J.; Thomas, G.J. Targeting cancer-associated fibroblasts to enhance immunotherapy: Emerging strategies and future perspectives. Oncotarget 2021, 12, 1427–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Wei, R.; Liu, C.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, F.; Liu, X. Antigen-presenting cancer-associated fibroblasts enhance antitumor immunity and predict immunotherapy response. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayob, A.Z.; Ramasamy, T.S. Cancer stem cells as key drivers of tumour progression. J. Biomed. Sci. 2018, 25, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razi, S.; Haghparast, A.; Khameneh, S.C.; Sadrabadi, A.E.; Aziziyan, F.; Bakhtiyari, M.; Nabi-Afjadi, M.; Tarhriz, V.; Jalili, A.; Zalpoor, H. The role of tumor microenvironment on cancer stem cell fate in solid tumors. Cell Commun. Signal. 2023, 21, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Xu, J. Cancer-associated fibroblasts: A versatile mediator in tumor progression, metastasis, and targeted therapy. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2024, 43, 1095–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharti, R.; Dey, G.; Mandal, M. Cancer development, chemoresistance, epithelial to mesenchymal transition and stem cells: A snapshot of IL-6 mediated involvement. Cancer Lett. 2016, 375, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Tao, P.; Zhou, Q.; Li, J.; Yu, Z.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Li, C.; Yan, M.; Zhu, Z.; et al. IL-6 secreted by cancer-associated fibroblasts promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of gastric cancer via JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 20741–20750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Young, C.D.; Zhou, H.; Wang, X.J. Transforming Growth Factor-β Signaling in Fibrotic Diseases and Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.X.; Guan, X.Y.; Fu, L. Therapeutic targeting of the crosstalk between cancer-associated fibroblasts and cancer stem cells. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2019, 9, 1889–1904. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Teng, Y. Harnessing cancer stem cell-derived exosomes to improve cancer therapy. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 42, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; He, G.; Yu, Y.; Li, X.; Peng, X.; Yang, L. Exosome crosstalk between cancer stem cells and tumor microenvironment: Cancer progression and therapeutic strategies. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2024, 15, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Nedaeinia, R.; Najafgholian, S.; Salehi, R.; Goli, M.; Ranjbar, M.; Nickho, H.; Javanmard, S.H.; Ferns, G.A.; Manian, M. The role of cancer-associated fibroblasts and exosomal miRNAs-mediated intercellular communication in the tumor microenvironment and the biology of carcinogenesis: A systematic review. Cell Death Discov. 2024, 10, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Liu, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, H. Exosome-Mediated Chemoresistance in Cancers: Mechanisms, Therapeutic Implications, and Future Directions. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prager, B.C.; Xie, Q.; Bao, S.; Rich, J.N. Cancer Stem Cells: The Architects of the Tumor Ecosystem. Cell Stem Cell 2019, 24, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Chen, X.; Zhang, L.; Chen, M. Cancer-associated fibroblasts in cancer development and therapy. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2025, 18, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popovich, J.R.; Kashyap, S.; Gasalberti, D.P.; Cassaro, S. Sarcoma. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 14 August 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Muse, M.E.; Shumway, K.R.; Crane, J.S. Physiology, Epithelialization. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 4 September 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.; Liu, J.; Qian, H.; Zhuang, Q. Cancer-associated fibroblasts: From basic science to anticancer therapy. Exp. Mol. Med. 2023, 55, 1322–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkler, J.; Abisoye-Ogunniyan, A.; Metcalf, K.J.; Werb, Z. Concepts of extracellular matrix remodelling in tumour progression and metastasis. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muchlińska, A.; Nagel, A.; Popęda, M.; Szade, J.; Niemira, M.; Zieliński, J.; Skokowski, J.; Bednarz-Knoll, N.; Żaczek, A.J. Alpha-smooth muscle actin-positive cancer-associated fibroblasts secreting osteopontin promote growth of luminal breast cancer. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2022, 27, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, Y.; Novruzov, E.; Schmitt, D.; Cardinale, J.; Watabe, T.; Choyke, P.L.; Alavi, A.; Haberkorn, U.; Giesel, F.L. Clinical applications of fibroblast activation protein inhibitor positron emission tomography (FAPI-PET). npj Imaging 2024, 2, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukamoto, H.; Mishima, Y.; Hayashibe, K.; Sasase, A. α-Smooth Muscle Actin Expression in Tumor and Stromal Cells of Benign and Malignant Human Pigment Cell Tumors. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1992, 98, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wrenn, E.D.; Apfelbaum, A.A.; Rudzinski, E.R.; Deng, X.; Jiang, W.; Sud, S.; Van Noord, R.A.; Newman, E.A.; Garcia, N.M.; Miyaki, A.; et al. Cancer-Associated Fibroblast-Like Tumor Cells Remodel the Ewing Sarcoma Tumor Microenvironment. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 29, 5140–5154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Wang, L.; Guo, H.; Zhang, W.; Shao, Z. Single-cell transcriptomics reveals the regulative roles of cancer-associated fibroblasts in tumor immune microenvironment of recurrent osteosarcoma. Theranostics 2022, 12, 5877–5887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yang, X.; Lu, W.; Chen, Y.; Lin, Y.; Wang, J.; Lin, S.; Yun, J.-P. H3K27 acetylation activated-COL6A1 promotes osteosarcoma lung metastasis by repressing STAT1 and activating pulmonary cancer-associated fibroblasts. Theranostics 2021, 11, 1473–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broz, M.T.; Ko, E.Y.; Ishaya, K.; Xiao, J.; De Simone, M.; Hoi, X.P.; Piras, R.; Gala, B.; Tessaro, F.H.G.; Karlstaedt, A.; et al. Metabolic targeting of cancer associated fibroblasts overcomes T-cell exclusion and chemoresistance in soft-tissue sarcomas. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Wei, R.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, J.; Wang, W.; Wang, Z.; Wupur, Z.; Li, Y.; Meng, H. Synergistic Chemoimmunotherapy Augmentation via Sequential Nanocomposite Hydrogel-Mediated Reprogramming of Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts in Osteosarcoma. Adv. Mater. 2023, 36, e2309591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umakoshi, M.; Kudo-Asabe, Y.; Tsuchie, H.; Li, Z.; Koyama, K.; Miyabe, K.; Yoshida, M.; Nagasawa, H.; Nanjo, H.; Okada, K.; et al. Prognostic value of CAF marker expression in the intratumoral and marginal areas of soft tissue sarcoma. Pathobiology 2024, 92, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’aGostino, S.; Tombolan, L.; Saggioro, M.; Frasson, C.; Rampazzo, E.; Pellegrini, S.; Favaretto, F.; Biz, C.; Ruggieri, P.; Gamba, P.; et al. Rhabdomyosarcoma Cells Produce Their Own Extracellular Matrix With Minimal Involvement of Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts: A Preliminary Study. Front. Oncol. 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Ami, E.; Perret, R.; Huang, Y.; Courgeon, F.; Gokhale, P.C.; Laroche-Clary, A.; Eschle, B.K.; Velasco, V.; Le Loarer, F.; Algeo, M.-P.; et al. LRRC15 Targeting in Soft-Tissue Sarcomas: Biological and Clinical Implications. Cancers 2020, 12, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demetri, G.D.; Luke, J.J.; Hollebecque, A.; Powderly, J.D.; Spira, A.I.; Subbiah, V.; Naumovski, L.; Chen, C.; Fang, H.; Lai, D.W.; et al. First-in-Human Phase I Study of ABBV-085, an Antibody–Drug Conjugate Targeting LRRC15, in Sarcomas and Other Advanced Solid Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 3556–3566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunami, Y.; Böker, V.; Kleeff, J. Targeting and Reprogramming Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts and the Tumor Microenvironment in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavudi, K.; Nuguri, S.M.; Olverson, Z.; Dhanabalan, A.K.; Patnaik, S.; Kokkanti, R.R. Targeting the retinoic acid signaling pathway as a modern precision therapy against cancers. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1254612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilsed, C.M.; Casey, T.H.; de Jong, E.; Bosco, A.; Zemek, R.M.; Salmons, J.; Wan, G.; Millward, M.J.; Nowak, A.K.; Lake, R.A.; et al. Retinoic Acid Induces an IFN-Driven Inflammatory Tumour Microenvironment, Sensitizing to Immune Checkpoint Therapy. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 849793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobin, R.P.; Cogswell, D.T.; Cates, V.M.; Davis, D.M.; Borgers, J.S.; Van Gulick, R.J.; Katsnelson, E.; Couts, K.L.; Jordan, K.R.; Gao, D.; et al. Targeting MDSC Differentiation Using ATRA: A Phase I/II Clinical Trial Combining Pembrolizumab and All-Trans Retinoic Acid for Metastatic Melanoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 29, 1209–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łabędź, N.; Anisiewicz, A.; Stachowicz-Suhs, M.; Banach, J.; Kłopotowska, D.; Maciejczyk, A.; Gazińska, P.; Piotrowska, A.; Dzięgiel, P.; Matkowski, R.; et al. Dual effect of vitamin D3 on breast cancer-associated fibroblasts. BMC Cancer 2024, 24, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorchs, L.; Ahmed, S.; Mayer, C.; Knauf, A.; Moro, C.F.; Svensson, M.; Heuchel, R.; Rangelova, E.; Bergman, P.; Kaipe, H. The vitamin D analogue calcipotriol promotes an anti-tumorigenic phenotype of human pancreatic CAFs but reduces T cell mediated immunity. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chronopoulos, A.; Robinson, B.; Sarper, M.; Cortes, E.; Auernheimer, V.; Lachowski, D.; Attwood, S.; García, R.; Ghassemi, S.; Fabry, B.; et al. ATRA mechanically reprograms pancreatic stellate cells to suppress matrix remodelling and inhibit cancer cell invasion. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-I.; Chaurasiya, S.; Sivanandam, V.; Kang, S.; Park, A.K.; Lu, J.; Yang, A.; Zhang, Z.; Bagdasarian, I.A.; Woo, Y.; et al. Priming stroma with a vitamin D analog to optimize viroimmunotherapy for pancreatic cancer. Mol. Ther.-Oncolytics 2022, 24, 864–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, C.; Li, S.; Tan, Z.; Fan, Z. Targeting MCM2 activates cancer-associated fibroblasts-like phenotype and affects chemo-resistance of liposarcoma cells against doxorubicin. Anticancer Drugs 2024, 35, 883–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.W.; Wu, X.F.; Gu, X.J.; Jiang, X.H. Exosomal miR-1228 From Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Promotes Cell Migration and Invasion of Osteosarcoma by Directly Targeting SCAI. Oncol. Res. Featur. Preclin. Clin. Cancer Ther. 2019, 27, 979–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moutafi, M.; Martinez-Morilla, S.; Divakar, P.; Vathiotis, I.; Gavrielatou, N.; Aung, T.N.; Yaghoobi, V.; Fernandez, A.I.; Zugazagoitia, J.; Herbst, R.S.; et al. Discovery of Biomarkers of Resistance to Immune Checkpoint Blockade in NSCLC Using High-Plex Digital Spatial Profiling. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, 991–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grout, J.A.; Sirven, P.; Leader, A.M.; Maskey, S.; Hector, E.; Puisieux, I.; Steffan, F.; Cheng, E.; Tung, N.; Maurin, M.; et al. Spatial Positioning and Matrix Programs of Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Promote T-cell Exclusion in Human Lung Tumors. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 2606–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minini, M.; Fouassier, L. Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts and Extracellular Matrix: Therapeutical Strategies for Modulating the Cholangiocarcinoma Microenvironment. Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 4185–4196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Ma, W.; Wu, J.; Wu, Q.; Sun, C. Paracrine signaling in cancer-associated fibroblasts: Central regulators of the tumor immune microenvironment. J. Transl. Med. 2025, 23, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Yang, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Mu, J.; Zeng, Q.; Deng, S.; Zhou, H. Signaling pathways in cancer-associated fibroblasts and targeted therapy for cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raaijmakers, K.T.P.M.; Adema, G.J.; Bussink, J.; Ansems, M. Cancer-associated fibroblasts, tumor and radiotherapy: Interactions in the tumor micro-environment. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 43, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Fei, Y.; Wang, H.; Hu, S.; Liu, C.; Hu, R.; Du, Q. CAFs orchestrates tumor immune microenvironment—A new target in cancer therapy? Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1113378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppensteiner, L.; Mathieson, L.; O’Connor, R.A.; Akram, A.R. Cancer Cancer-associated fibroblasts—An Impediment to Effective Anti-Cancer T Cell Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 887380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, T.; Chen, X.; Qiu, F.; Zhang, X.; Wu, F.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, M.; Chen, M.; Shen, J.-W.; Shen, Q.; et al. Regulation of cancer-associated fibroblasts for enhanced cancer immunotherapy using advanced functional nanomedicines: An updated review. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2025, 23, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Tong, Z.; Ren, Z.; Ye, M.; Hu, K. Cancer-associated fibroblasts and its derived exosomes: A new perspective for reshaping the tumor microenvironment. Mol. Med. 2023, 29, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoucair, I.; Weber Mello, F.; Jabalee, J.; Maleki, S.; Garnis, C. The Role of Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts and Extracellular Vesicles in Tumorigenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheteh, E.H.; Sarne, V.; Ceder, S.; Bianchi, J.; Augsten, M.; Rundqvist, H.; Egevad, L.; Östman, A.; Wiman, K.G. Interleukin-6 derived from cancer-associated fibroblasts attenuates the p53 response to doxorubicin in prostate cancer cells. Cell Death Discov. 2020, 6, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Ren, D.; Xu, X.; Wang, Y. Molecular cross-talk of IL-6 in tumors and new progress in combined therapy. Thorac. Cancer 2018, 9, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Huang, L.; Qin, G.; Qiao, Y.; Ren, F.; Shen, C.; Wang, S.; Liu, S.; Lian, J.; Wang, D.; et al. Cancer-associated fibroblasts induce monocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cell generation via IL-6/exosomal miR-21-activated STAT3 signaling to promote cisplatin resistance in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2021, 518, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, D.E.; O’Keefe, R.A.; Grandis, J.R. Targeting the IL-6/JAK/STAT3 signalling axis in cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Mao, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, P.; Zhou, Y.; Tong, J.; Peng, H.; Yang, B.; Fu, Q. CAF-derived exosomal lncRNA FAL1 promotes chemoresistance to oxaliplatin by regulating autophagy in colorectal cancer. Dig. Liver Dis. 2023, 56, 330–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Liang, C.; Chen, X. Exosomal LINC00355 derived from cancer-associated fibroblasts promotes bladder cancer cell resistance to cisplatin by regulating miR-34b-5p/ABCB1 axis. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2021, 53, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Ding, L.; Li, Y.; Ren, J.; Shi, G.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, S.; Ni, Y.; Hou, Y. Midkine derived from cancer-associated fibroblasts promotes cisplatin-resistance via up-regulation of the expression of lncRNA ANRIL in tumour cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Y.; Xu, H.; Jin, L. HJURP Derived from Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Promotes Glutamine Metabolism to Induce Resistance to Doxorubicin in Ovarian Cancer. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2024, 264, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhaidly, R.; Mechta-Grigoriou, F. Role of cancer-associated fibroblast subpopulations in immune infiltration, as a new means of treatment in cancer. Immunol. Rev. 2021, 302, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Lei, W.; Wang, H.; Ni, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yan, H.; Tian, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Z.; et al. CXCL12-CXCR4/CXCR7 Axis in Cancer: From Mechanisms to Clinical Applications. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2023, 19, 3341–3359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batlle, E.; Massagué, J. Transforming Growth Factor-β Signaling in Immunity and Cancer. Immunity 2019, 50, 924–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavie, D.; Ben-Shmuel, A.; Erez, N.; Scherz-Shouval, R. Cancer-associated fibroblasts in the single-cell era. Nat. Cancer 2022, 3, 793–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, A.; Griffin, M.; Kameni, L.; Wan, D.C.; Longaker, M.T.; Norton, J.A. Medical Biology of Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts in Pancreatic Cancer. Biology 2023, 12, 1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.; Song, J.; Liu, X.; Huo, S.; Liu, C.; Liu, X. Immunosuppressive MFAP2+ cancer-associated fibroblasts conferred unfavorable prognosis and therapeutic resistance in gastric cancer. Cell. Oncol. 2024, 47, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.T.; Lee, M.H.; Shin, S.-J.; Cho, I.; Kuk, J.C.; Yun, J.; Choi, Y.Y. Decorin as a key marker of desmoplastic cancer-associated fibroblasts mediating first-line immune checkpoint blockade resistance in metastatic gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer 2024, 28, 12–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, L.; Jungwirth, U.; Avgustinova, A.; Iravani, M.; Mills, A.; Haider, S.; Harper, J.; Isacke, C.M. Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Suppress CD8+ T-cell Infiltration and Confer Resistance to Immune-Checkpoint Blockade. Cancer Res. 2022, 82, 2904–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuhashi, S.; Morita, Y.; Matsumoto, A.; Ida, S.; Muraki, R.; Kitajima, R.; Takeda, M.; Kikuchi, H.; Hiramatsu, Y.; Takeuchi, H. Abstract 1585: Tenascin C in pancreatic cancer-associated fibroblasts enhances epithelial mesenchymal transition and is associated with resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitor. Cancer Res. 2024, 84, 1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakemura, R.; Hefazi, M.; Siegler, E.L.; Cox, M.J.; Larson, D.P.; Hansen, M.J.; Roman, C.M.; Schick, K.J.; Can, I.; Tapper, E.E.; et al. Targeting cancer-associated fibroblasts in the bone marrow prevents resistance to CART-cell therapy in multiple myeloma. Blood 2022, 139, 3708–3721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraman, M.; Bambrough, P.J.; Arnold, J.N.; Roberts, E.W.; Magiera, L.; Jones, J.O.; Gopinathan, A.; Tuveson, D.A.; Fearon, D.T. Suppression of Antitumor Immunity by Stromal Cells Expressing Fibroblast Activation Protein–α. Science 2010, 330, 827–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feig, C.; Jones, J.O.; Kraman, M.; Wells, R.J.; Deonarine, A.; Chan, D.S.; Connell, C.M.; Roberts, E.W.; Zhao, Q.; Caballero, O.L.; et al. Targeting CXCL12 from FAP-expressing carcinoma-associated fibroblasts synergizes with anti-PD-L1 immunotherapy in pancreatic cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 20212–20217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Cao, F.; Yin, H.; Huang, Z.; Lin, Z.; Mao, N.; Sun, B.; Wang, G. Ferroptosis: Past, present and future. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, X.; Yu, Y. Autophagy, ferroptosis, pyroptosis, and necroptosis in tumor immunotherapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Jia, K.; Chen, Y.; Ji, C.; Chong, X.; Li, Z.; Zhao, F.; Bai, Y.; Ge, S.; Gao, J.; et al. ANO1-Mediated Inhibition of Cancer Ferroptosis Confers Immunotherapeutic Resistance through Recruiting Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, e2300881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, P.; Wang, L.; Li, M.; Ge, Z.; Noordam, L.; Lieshout, R.; Verstegen, M.M.; Ma, B.; Su, J.; et al. Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Provide a Stromal Niche for Liver Cancer Organoids That Confers Trophic Effects and Therapy Resistance. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 11, 407–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zi, R.; Hao, J.; Ding, Q.; Jiang, H.; Wang, X.; Lu, F.; et al. Cancer-associated fibroblasts derived fibronectin extra domain A promotes sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma cells by activating SHMT1. Genes Dis. 2024, 11, 101330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, Y.; Zeng, S.; Wang, Z.; Wu, M.; Ma, Y.; Ye, X.; Zhang, B.; Liu, H. Cancer-associated fibroblasts promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition and EGFR-TKI resistance of non-small cell lung cancers via HGF/IGF-1/ANXA2 signaling. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Mol. Basis Dis. 2018, 1864, 793–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Zhou, W.; Xu, H.; Xu, J.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Lu, X.; Dai, J.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, W.; et al. Cancer-associated fibroblasts promote EGFR-TKI resistance via the CTHRC1/glycolysis/H3K18la positive feedback loop. Oncogene 2025, 44, 1400–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, F.M.; Helal, D.S.; Ali, D.A.; Abd-Ellatif, R.N.; Elkady, A.M.; Sharshar, R.; Gharib, F.; Elnasr, M.A.; El-Guindy, D.M. Prognostic role of annexin A2 and cancer-associated fibroblasts in advanced non-small cell lung cancer: Implication in epithelial-mesenchymal transition and gefitinib resistance. Pathol.-Res. Pract. 2022, 241, 154293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Yang, H.; Xu, K.; Zhu, A.; Hall, S.R.R.; Jia, Y.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, E.; Liu, G.; Xu, J.; et al. Transitional CXCL14+ cancer-associated fibroblasts enhance tumour metastasis and confer resistance to EGFR-TKIs, revealing therapeutic vulnerability to filgotinib in lung adenocarcinoma. Clin. Transl. Med. 2025, 15, e70281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Du, R.; Li, X.; Liu, C.; Wang, D.; He, X.; Li, G.; Zhang, K.; Wang, S.; Hao, Q.; et al. CD63+ cancer-associated fibroblasts confer CDK4/6 inhibitor resistance to breast cancer cells by exosomal miR-20. Cancer Lett. 2024, 588, 216747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Li, X.; Zeng, C.; Liu, C.; Hao, Q.; Li, W.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, W.; Wang, S.; Zhao, H.; et al. CD63+ Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Confer Tamoxifen Resistance to Breast Cancer Cells through Exosomal miR-22. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 2002518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Qu, Q.; Zhao, M.; Lou, Y.; Liu, J.; Huang, O.; Chen, X.; Wu, J.; Shen, K. Cancer-associated fibroblasts induce trastuzumab resistance in HER2 positive breast cancer cells. Mol. Biosyst. 2015, 11, 1029–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busch, S.; Rydén, L.; Stål, O.; Jirström, K.; Landberg, G. Low ERK Phosphorylation in Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Is Associated with Tamoxifen Resistance in Pre-Menopausal Breast Cancer. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Z.; Yu, S.-L.; Xie, Z.-X.; Zhuang, R.-L.; Peng, S.-R.; Wang, Q.; Gao, Z.; Li, B.-H.; Xie, J.-J.; Huang, H.; et al. Cancer-associated fibroblasts promote enzalutamide resistance and PD-L1 expression in prostate cancer through CCL5-CCR5 paracrine axis. iScience 2024, 27, 109674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.-Q.; He, Q.-H.; Wei, Q.-J.; Mo, Q.-Z.; Yang, G.-L.; Wei, F.-Y.; Wei, L.-W.; Li, Y.-J.; Qin, M.; Cheng, J.-W. CTHRC1 expresses in cancer-associated fibroblasts and is associated with resistance to anti-androgen therapy in prostate cancer. Genes Genom. 2025, 47, 541–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, R.; De, P.; Aske, J.C.; Lin, X.; Dale, A.; Koirala, N.; Gaster, K.; Espaillat, L.R.; Starks, D.; Dey, N. Patient-Derived Primary Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Mediate Resistance to Anti-Angiogenic Drug in Ovarian Cancers. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, J.B.; Cohen, E.E.W. Mechanisms of resistance to EGFR inhibitors in head and neck cancer. Head Neck 2009, 31, 1086–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, T.; Viol, F.; Krause, J.; Fahl, M.; Eggers, C.; Awwad, F.; Schmidt, B.; Benten, D.; Ungefroren, H.; Fraune, C.; et al. Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Induce Proliferation and Therapeutic Resistance to Everolimus in Neuroendocrine Tumors through STAT3 Activation. Neuroendocrinology 2022, 113, 501–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Visser, K.E.; Joyce, J.A. The evolving tumor microenvironment: From cancer initiation to metastatic outgrowth. Cancer Cell 2023, 41, 374–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Badran, O.; Cohen, I.; Bar-Sela, G. Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts in Solid Tumors and Sarcomas: Heterogeneity, Function, and Therapeutic Implications. Cells 2025, 14, 1398. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14171398
Badran O, Cohen I, Bar-Sela G. Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts in Solid Tumors and Sarcomas: Heterogeneity, Function, and Therapeutic Implications. Cells. 2025; 14(17):1398. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14171398
Chicago/Turabian StyleBadran, Omar, Idan Cohen, and Gil Bar-Sela. 2025. "Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts in Solid Tumors and Sarcomas: Heterogeneity, Function, and Therapeutic Implications" Cells 14, no. 17: 1398. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14171398
APA StyleBadran, O., Cohen, I., & Bar-Sela, G. (2025). Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts in Solid Tumors and Sarcomas: Heterogeneity, Function, and Therapeutic Implications. Cells, 14(17), 1398. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14171398





