Neuroprotective Effects of Calpain Inhibition in Parkinson’s Disease: Insights from Cellular and Murine Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
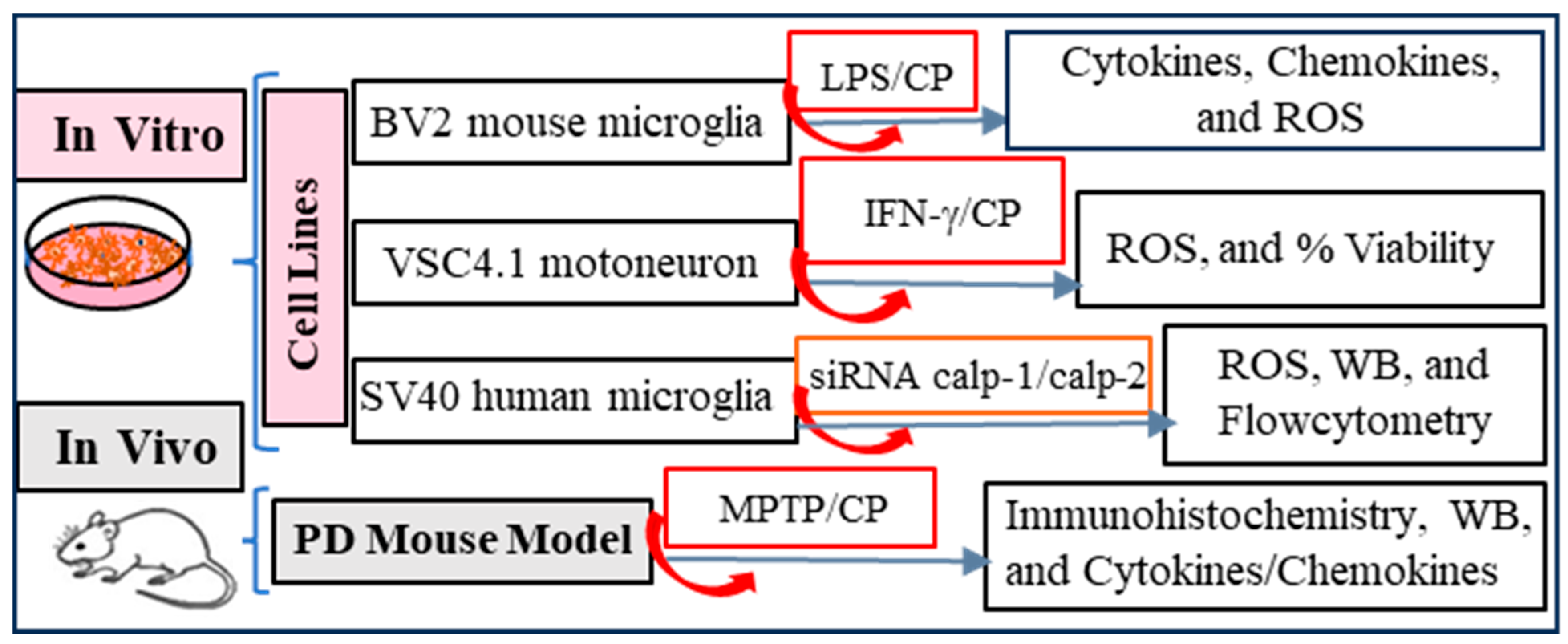
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Cell Lines
2.3. MTS Assay for Measuring Cell Viability
2.4. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Assay
2.5. Knockdown of Calpain-1 and Calpain-2 in SV40 Human Microglia Cells
2.6. Flow Cytometry
2.7. Western Blot Analysis
2.8. Animals
2.9. MPTP Mouse Model
2.10. Animal Tissue Sample Collection
2.11. Cytokine and Chemokine Arrays
2.12. Immunohistochemistry
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
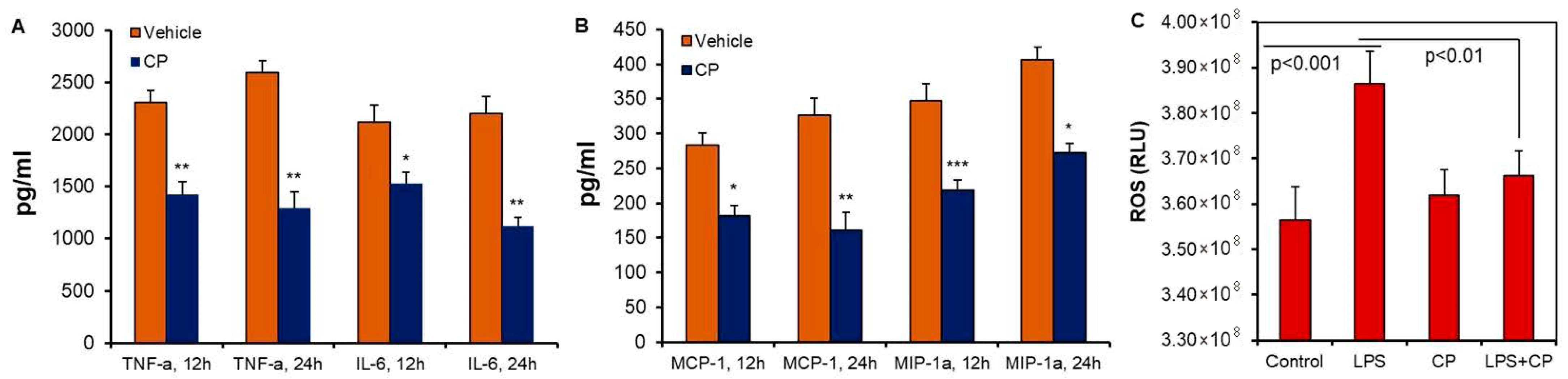
3.1. Calpain Activation and Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Production in Microglia Cells
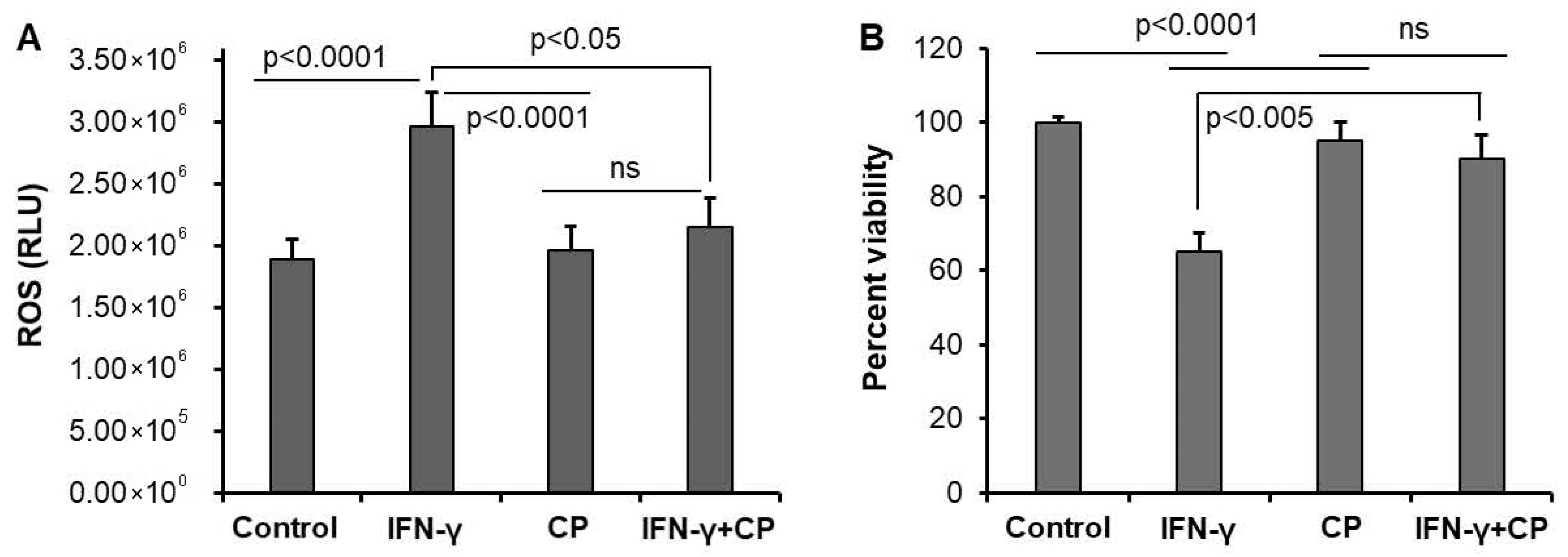
3.2. Calpain Inhibition Reduces ROS Production and Enhances Cell Survival in Motoneuron Cells
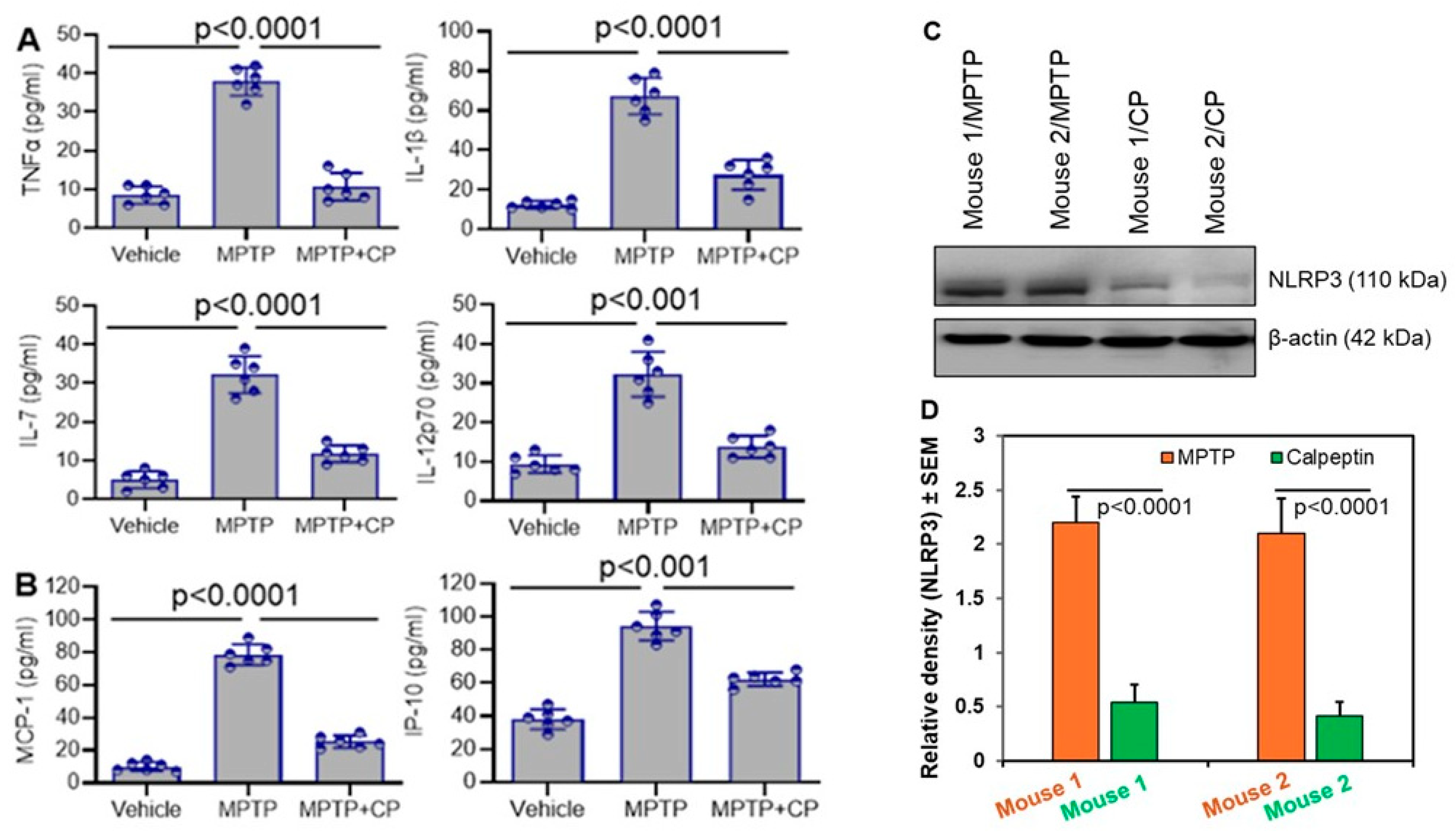
3.3. Calpain Inhibition Reduces Systemic Inflammation in MPTP-Treated Mice
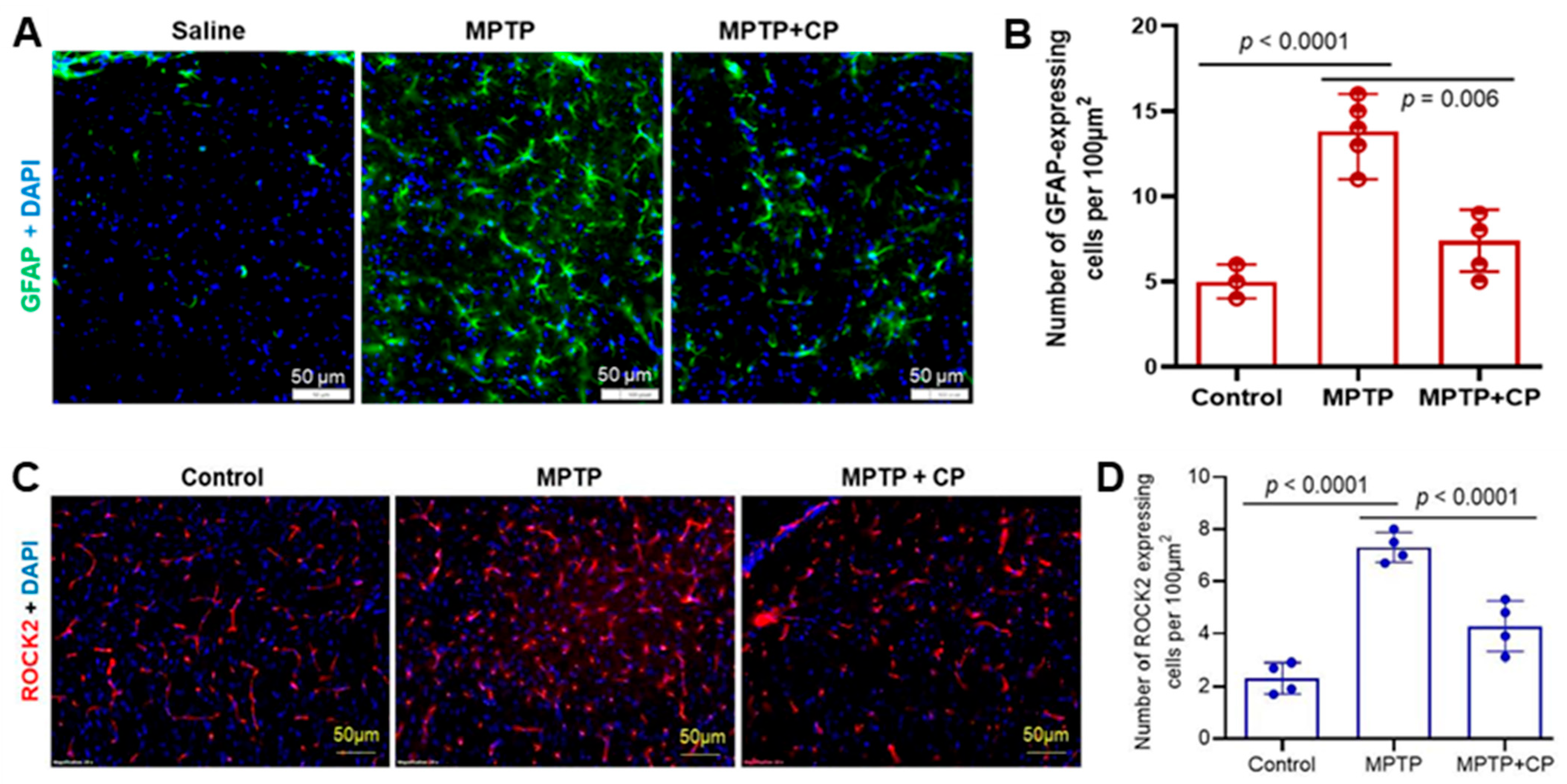
3.4. Calpain Inhibition Attenuates Neuroinflammation and Astrocyte Activation in MPTP-Treated Mice
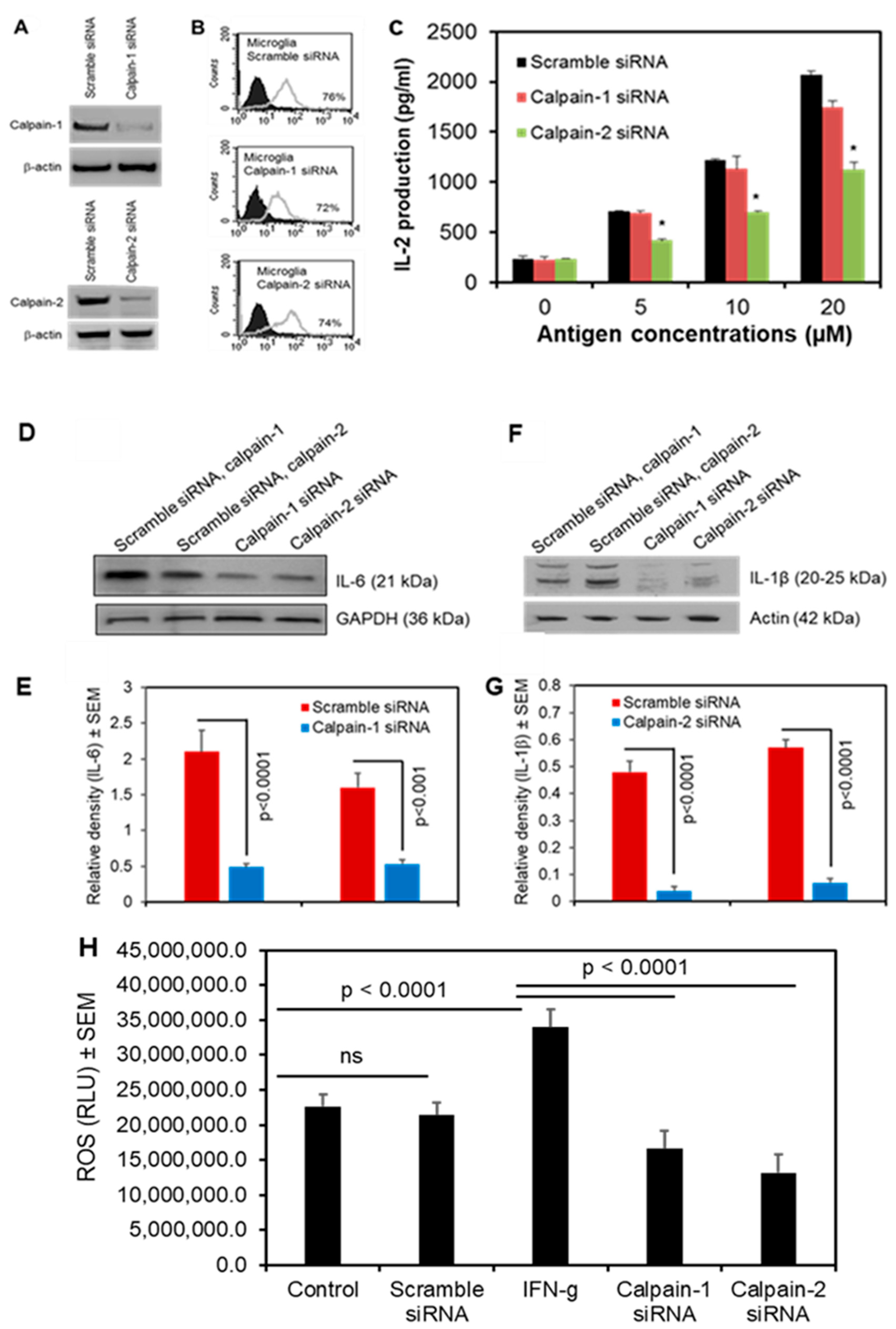
3.5. Calpain-2 Knockdown Reduces Antigen Presentation and Production of Inflammatory Cytokines and ROS in Human Microglia
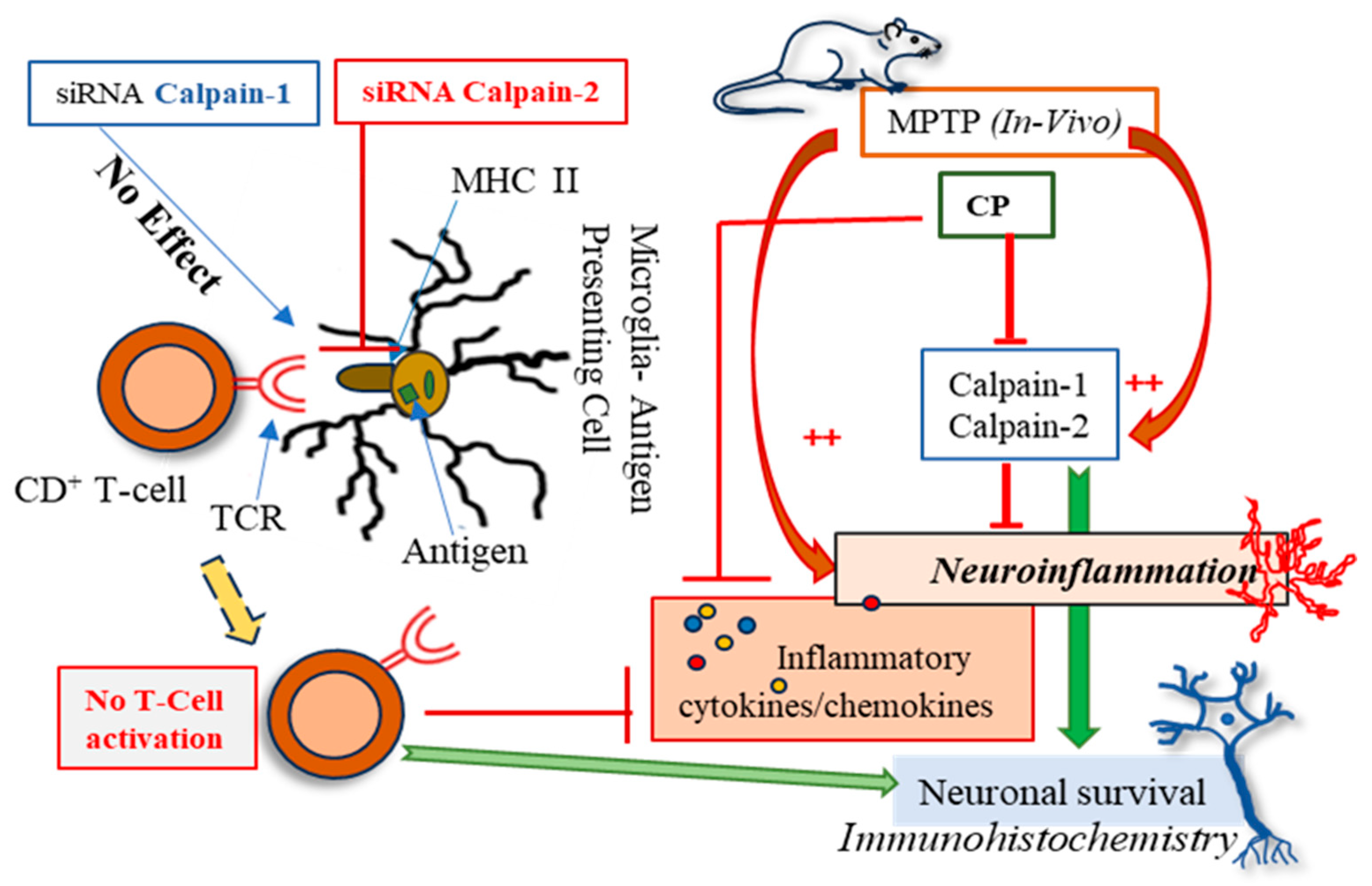
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jankovic, J.; Tan, E.K. Parkinson’s disease: Etiopathogenesis and treatment. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2020, 91, 795–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, L. Recent advances in Alzheimer’s disease: Mechanisms, clinical trials and new drug development strategies. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L. Updates on Disease Mechanisms and Therapeutics for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Cells 2024, 13, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, M.; Choi, I.; Sarrafha, L.; Liang, M.; Ho, L.; Farrell, K.; Beaumont, K.G.; Sebra, R.; De Sanctis, C.; et al. Molecular profiling of human substantia nigra identifies diverse neuron types associated with vulnerability in Parkinson’s disease. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10, eadi8287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blokhuis, A.M.; Groen, E.J.; Koppers, M.; van den Berg, L.H.; Pasterkamp, R.J. Protein aggregation in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Acta Neuropathol. 2013, 125, 777–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicardi, M.E.; Marrone, L.; Azzouz, M.; Trotti, D. Proteostatic imbalance and protein spreading in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. EMBO J. 2021, 40, e106389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimaldi, A.; Brighi, C.; Peruzzi, G.; Ragozzino, D.; Bonanni, V.; Limatola, C.; Ruocco, G.; Di Angelantonio, S. Inflammation, neurodegeneration and protein aggregation in the retina as ocular biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease in the 3xTg-AD mouse model. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, V.; Drasites, K.P.; Myatich, A.; Shams, R.; Shields, D.C.; Matzelle, D.; Haque, A.; Banik, N.L. Inhibition of Calpain Attenuates Degeneration of Substantia Nigra Neurons in the Rotenone Rat Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samantaray, S.; Knaryan, V.H.; Le Gal, C.; Ray, S.K.; Banik, N.L. Calpain inhibition protected spinal cord motoneurons against 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium ion and rotenone. Neuroscience 2011, 192, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomgren, K.; Zhu, C.; Wang, X.; Karlsson, J.O.; Leverin, A.L.; Bahr, B.A.; Mallard, C.; Hagberg, H. Synergistic activation of caspase-3 by m-calpain after neonatal hypoxia-ischemia: A mechanism of “pathological apoptosis”? J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 10191–10198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, M.; Ma, C.L.; Farazifard, R.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Vanderluit, J.; Zoltewicz, J.S.; Hage, F.; Savitt, J.M.; Lagace, D.C.; et al. Conditional disruption of calpain in the CNS alters dendrite morphology, impairs LTP, and promotes neuronal survival following injury. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 5773–5784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.Y.; Lynch, D.R. Calpain and synaptic function. Mol. Neurobiol. 2006, 33, 215–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadran, S.; Bi, X.; Baudry, M. Regulation of calpain-2 in neurons: Implications for synaptic plasticity. Mol. Neurobiol. 2010, 42, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, M.C.; Wang, K.K. Calpain in the CNS: From synaptic function to neurotoxicity. Sci. Signal 2008, 1, re1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, W.S.; Lee, E.H.; Chung, C.W.; Jung, Y.K.; Jin, B.K.; Kim, S.U.; Oh, T.H.; Saido, T.C.; Oh, Y.J. Cleavage of Bax is mediated by caspase-dependent or -independent calpain activation in dopaminergic neuronal cells: Protective role of Bcl-2. J. Neurochem. 2001, 77, 1531–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goll, D.E.; Thompson, V.F.; Li, H.; Wei, W.; Cong, J. The calpain system. Physiol. Rev. 2003, 83, 731–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Bi, X.; Baudry, M. Calpain-1 and Calpain-2 in the Brain: New Evidence for a Critical Role of Calpain-2 in Neuronal Death. Cells 2020, 9, 2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, W.C.; Pikor, L.; Gao, Y.; Elliott, B.E.; Greer, P.A. Calpain 2 regulates Akt-FoxO-p27(Kip1) protein signaling pathway in mammary carcinoma. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 15458–15465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutt, P.; Croall, D.E.; Arthur, J.S.; Veyra, T.D.; Williams, K.; Elce, J.S.; Greer, P.A. m-Calpain is required for preimplantation embryonic development in mice. BMC Dev. Biol. 2006, 6, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, A.H.; Huang, Z.; Mafnas, C.; Hara, J.H.; Hoffmann, F.W.; Hashimoto, A.S.; Bertino, P.; Hoffmann, P.R. Calpain-2 Inhibitor Therapy Reduces Murine Colitis and Colitis-associated Cancer. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2015, 21, 2005–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marciel, M.P.; Rose, A.H.; Martinez, V.; Horio, D.T.; Hashimoto, A.S.; Hoffmann, F.W.; Bertino, P.; Hoffmann, P.R. Calpain-2 inhibitor treatment preferentially reduces tumor progression for human colon cancer cells expressing highest levels of this enzyme. Cancer Med. 2018, 7, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podbielska, M.; Das, A.; Smith, A.W.; Chauhan, A.; Ray, S.K.; Inoue, J.; Azuma, M.; Nozaki, K.; Hogan, E.L.; Banik, N.L. Neuron-microglia interaction induced bi-directional cytotoxicity associated with calpain activation. J. Neurochem. 2016, 139, 440–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, A.; McCoy, H.M.; Zaman, V.; Shields, D.C.; Banik, N.L.; Haque, A. Calpain activation and progression of inflammatory cycles in Parkinson’s disease. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed.) 2022, 27, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, A.; Drasites, K.P.; Cox, A.; Capone, M.; Myatich, A.I.; Shams, R.; Matzelle, D.; Garner, D.P.; Bredikhin, M.; Shields, D.C.; et al. Protective Effects of Estrogen via Nanoparticle Delivery to Attenuate Myelin Loss and Neuronal Death after Spinal Cord Injury. Neurochem. Res. 2021, 46, 2979–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, J.D.; Kan, M. Media for Culture of Mammalian Cells. Curr. Protoc. Cell Biol. 1998, 1, 1.2.1–1.2.15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hathaway-Schrader, J.D.; Norton, D.; Hastings, K.; Doonan, B.P.; Fritz, S.T.; Bethard, J.R.; Blum, J.S.; Haque, A. GILT Expression in Human Melanoma Cells Enhances Generation of Antigenic Peptides for HLA Class II-Mediated Immune Recognition. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraiwa, A.; Yamanaka, K.; Kwok, W.W.; Mickelson, E.M.; Masewicz, S.; Hansen, J.A.; Radka, S.F.; Nepom, G.T. Structural requirements for recognition of the HLA-Dw14 class II epitope: A key HLA determinant associated with rheumatoid arthritis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 8051–8055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, A.; Radwan, F.F.; Doonan, B.P.; God, J.M.; Zhang, L.; Bell, P.D.; Haque, A. A possible cross-talk between autophagy and apoptosis in generating an immune response in melanoma. Apoptosis 2012, 17, 1066–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- God, J.M.; Cameron, C.; Figueroa, J.; Amria, S.; Hossain, A.; Kempkes, B.; Bornkamm, G.W.; Stuart, R.K.; Blum, J.S.; Haque, A. Elevation of c-MYC disrupts HLA class II-mediated immune recognition of human B cell tumors. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 1434–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haque, M.A.; Hawes, J.W.; Blum, J.S. Cysteinylation of MHC class II ligands: Peptide endocytosis and reduction within APC influences T cell recognition. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 4543–4551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, J.R. TNF-mediated inflammatory disease. J. Pathol. 2008, 214, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Narazaki, M.; Kishimoto, T. IL-6 in inflammation, immunity, and disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a016295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmane, S.L.; Kremlev, S.; Amini, S.; Sawaya, B.E. Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 (MCP-1): An Overview. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2009, 29, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhavsar, I.; Miller, C.S.; Al-Sabbagh, M. Macrophage Inflammatory Protein-1 Alpha (MIP-1 alpha)/CCL3: As a Biomarker. In General Methods in Biomarker Research and Their Applications; Preedy, V.R., Patel, V.B., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 223–249. [Google Scholar]
- Menten, P.; Wuyts, A.; Van Damme, J. Macrophage inflammatory protein-1. Cytokine Growth Factor. Rev. 2002, 13, 455–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, D.N. The role of MIP-1 alpha in inflammation and hematopoiesis. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1996, 59, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamoto, Y.; Kim, S.U. Cytokine-induced production of macrophage inflammatory protein-1alpha (MIP-1alpha) in cultured human astrocytes. J. Neurosci. Res. 1999, 55, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McManus, C.M.; Brosnan, C.F.; Berman, J.W. Cytokine induction of MIP-1 alpha and MIP-1 beta in human fetal microglia. J. Immunol. 1998, 160, 1449–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, S.K.; Fidan, M.; Nowak, M.W.; Wilford, G.G.; Hogan, E.L.; Banik, N.L. Oxidative stress and Ca2+ influx upregulate calpain and induce apoptosis in PC12 cells. Brain Res. 2000, 852, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conos, S.A.; Lawlor, K.E.; Vaux, D.L.; Vince, J.E.; Lindqvist, L.M. Cell death is not essential for caspase-1-mediated interleukin-1beta activation and secretion. Cell Death Differ. 2016, 23, 1827–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajtko, A.; Bakk, E.; Hegedus, K.; Ducza, L.; Hollo, K. IL-1beta Induced Cytokine Expression by Spinal Astrocytes Can Play a Role in the Maintenance of Chronic Inflammatory Pain. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 543331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Jones, L.L.; Geiger, T.L. IL-6 Promotes T Cell Proliferation and Expansion under Inflammatory Conditions in Association with Low-Level RORgammat Expression. J. Immunol. 2018, 201, 2934–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Tang, T.X.; Deng, H.; Yang, X.P.; Tang, Z.H. Interleukin-7 Biology and Its Effects on Immune Cells: Mediator of Generation, Differentiation, Survival, and Homeostasis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 747324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gee, K.; Guzzo, C.; Che Mat, N.F.; Ma, W.; Kumar, A. The IL-12 family of cytokines in infection, inflammation and autoimmune disorders. Inflamm. Allergy Drug Targets 2009, 8, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perera, P.Y.; Lichy, J.H.; Waldmann, T.A.; Perera, L.P. The role of interleukin-15 in inflammation and immune responses to infection: Implications for its therapeutic use. Microbes Infect. 2012, 14, 247–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sofroniew, M.V.; Vinters, H.V. Astrocytes: Biology and pathology. Acta Neuropathol. 2010, 119, 7–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.G.; Wheeler, M.A.; Quintana, F.J. Function and therapeutic value of astrocytes in neurological diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2022, 21, 339–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gathings, A.; Zaman, V.; Banik, N.L.; Haque, A. Insights into Calpain Activation and Rho-ROCK Signaling in Parkinson’s Disease and Aging. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, C.; Han, T.; Liu, H.; Sun, L.; Hong, J.; Hashimoto, M.; Wei, J. The reciprocal interactions between microglia and T cells in Parkinson’s disease: A double-edged sword. J. Neuroinflamm. 2023, 20, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samantaray, S.; Knaryan, V.H.; Shields, D.C.; Cox, A.A.; Haque, A.; Banik, N.L. Inhibition of Calpain Activation Protects MPTP-Induced Nigral and Spinal Cord Neurodegeneration, Reduces Inflammation, and Improves Gait Dynamics in Mice. Mol. Neurobiol. 2015, 52, 1054–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sojka, D.K.; Bruniquel, D.; Schwartz, R.H.; Singh, N.J. IL-2 secretion by CD4+ T cells in vivo is rapid, transient, and influenced by TCR-specific competition. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 6136–6143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, G.; Sun, J.; Bi, X.; Baudry, M. A calpain-2 selective inhibitor enhances learning & memory by prolonging ERK activation. Neuropharmacology 2016, 105, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siman, R.; Gall, C.; Perlmutter, L.S.; Christian, C.; Baudry, M.; Lynch, G. Distribution of calpain I, an enzyme associated with degenerative activity, in rat brain. Brain Res. 1985, 347, 399–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Briz, V.; Chishti, A.; Bi, X.; Baudry, M. Distinct roles for mu-calpain and m-calpain in synaptic NMDAR-mediated neuroprotection and extrasynaptic NMDAR-mediated neurodegeneration. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 18880–18892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouatt-Prigent, A.; Karlsson, J.O.; Agid, Y.; Hirsch, E.C. Increased M-calpain expression in the mesencephalon of patients with Parkinson’s disease but not in other neurodegenerative disorders involving the mesencephalon: A role in nerve cell death? Neuroscience 1996, 73, 979–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nixon, R.A. The calpains in aging and aging-related diseases. Ageing Res. Rev. 2003, 2, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Nixon, R.; Messer, A.; Berman, S.; Bursztajn, S. Altered gene expression for calpain/calpastatin system in motor neuron degeneration (Mnd) mutant mouse brain and spinal cord. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 1998, 53, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, M.Q.; Hyman, B.T. Chemokines/chemokine receptors in the central nervous system and Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurovirol 1999, 5, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, K.L.; Moodley, D.; Rajkumar-Bhugeloo, K.; Baiyegunhi, O.O.; Karim, F.; Ndlovu, H.; Ndung’u, T.; Marakalala, M.J. Elevated IP-10 at the Protein and Gene Level Associates With Pulmonary TB. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 908144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Cacalano, G.; Camerato, T.; Toy, K.; Moore, M.W.; Wood, W.I. Chemokine binding and activities mediated by the mouse IL-8 receptor. J. Immunol. 1995, 155, 2158–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, N.; Sanz-Rodriguez, F. Induction of the CXCL1 (KC) chemokine in mouse astrocytes by infection with the murine encephalomyelitis virus of Theiler. Virology 2007, 358, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerche, S.; Zimmermann, M.; Roeben, B.; Wurster, I.; Fries, F.L.; Deuschle, C.; Waniek, K.; Lachmann, I.; Jakobi, M.; Joos, T.O.; et al. Inflammatory CSF profiles and longitudinal development of cognitive decline in sporadic and GBA-associated PD. NPJ Park. Dis. 2023, 9, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Zhou, G.; Yu, T.; Chen, L.; Yu, L.; Guo, Y.; Cong, Y.; Liu, Z. Critical role of ROCK2 activity in facilitating mucosal CD4(+) T cell activation in inflammatory bowel disease. J. Autoimmun. 2018, 89, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crocker, S.J.; Smith, P.D.; Jackson-Lewis, V.; Lamba, W.R.; Hayley, S.P.; Grimm, E.; Callaghan, S.M.; Slack, R.S.; Melloni, E.; Przedborski, S.; et al. Inhibition of calpains prevents neuronal and behavioral deficits in an MPTP mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 4081–4091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samantaray, S.; Knaryan, V.H.; Guyton, M.K.; Matzelle, D.D.; Ray, S.K.; Banik, N.L. The parkinsonian neurotoxin rotenone activates calpain and caspase-3 leading to motoneuron degeneration in spinal cord of Lewis rats. Neuroscience 2007, 146, 741–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilcek, J.; Lee, T.H. Tumor necrosis factor. New insights into the molecular mechanisms of its multiple actions. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 7313–7316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idriss, H.T.; Naismith, J.H. TNF alpha and the TNF receptor superfamily: Structure-function relationship(s). Microsc. Res. Tech. 2000, 50, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendiola, A.S.; Cardona, A.E. The IL-1beta phenomena in neuroinflammatory diseases. J. Neural. Transm. 2018, 125, 781–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, A.; Samantaray, S.; Knaryan, V.H.; Capone, M.; Hossain, A.; Matzelle, D.; Chandran, R.; Shields, D.C.; Farrand, A.Q.; Boger, H.A.; et al. Calpain mediated expansion of CD4+ cytotoxic T cells in rodent models of Parkinson’s disease. Exp. Neurol. 2020, 330, 113315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brochard, V.; Combadiere, B.; Prigent, A.; Laouar, Y.; Perrin, A.; Beray-Berthat, V.; Bonduelle, O.; Alvarez-Fischer, D.; Callebert, J.; Launay, J.M.; et al. Infiltration of CD4+ lymphocytes into the brain contributes to neurodegeneration in a mouse model of Parkinson disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kustrimovic, N.; Comi, C.; Magistrelli, L.; Rasini, E.; Legnaro, M.; Bombelli, R.; Aleksic, I.; Blandini, F.; Minafra, B.; Riboldazzi, G.; et al. Parkinson’s disease patients have a complex phenotypic and functional Th1 bias: Cross-sectional studies of CD4+ Th1/Th2/T17 and Treg in drug-naive and drug-treated patients. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, G.P.; Schonhoff, A.M.; Jurkuvenaite, A.; Gallups, N.J.; Standaert, D.G.; Harms, A.S. CD4 T cells mediate brain inflammation and neurodegeneration in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Brain 2021, 144, 2047–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGeer, P.L.; Itagaki, S.; Boyes, B.E.; McGeer, E.G. Reactive microglia are positive for HLA-DR in the substantia nigra of Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s disease brains. Neurology 1988, 38, 1285–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yildiz-Unal, A.; Korulu, S.; Karabay, A. Neuroprotective strategies against calpain-mediated neurodegeneration. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2015, 11, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metwally, E.; Al-Abbadi, H.A.; Hussain, T.; Murtaza, G.; Abdellatif, A.M.; Ahmed, M.F. Calpain signaling: From biology to therapeutic opportunities in neurodegenerative disorders. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1235163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yahya, E.; Quach, D.; Bi, X.; Baudry, M. Calpain-2 activation in mouse hippocampus plays a critical role in seizure-induced neuropathology. Neurobiol. Dis. 2021, 147, 105149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, S.K.; Wilford, G.G.; Ali, S.F.; Banik, N.L. Calpain upregulation in spinal cords of mice with 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP)-induced Parkinson’s disease. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2000, 914, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zaman, V.; Gathings, A.; Drasites, K.P.; Shields, D.C.; Banik, N.L.; Haque, A. Neuroprotective Effects of Calpain Inhibition in Parkinson’s Disease: Insights from Cellular and Murine Models. Cells 2025, 14, 1310. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14171310
Zaman V, Gathings A, Drasites KP, Shields DC, Banik NL, Haque A. Neuroprotective Effects of Calpain Inhibition in Parkinson’s Disease: Insights from Cellular and Murine Models. Cells. 2025; 14(17):1310. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14171310
Chicago/Turabian StyleZaman, Vandana, Amy Gathings, Kelsey P. Drasites, Donald C. Shields, Narendra L. Banik, and Azizul Haque. 2025. "Neuroprotective Effects of Calpain Inhibition in Parkinson’s Disease: Insights from Cellular and Murine Models" Cells 14, no. 17: 1310. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14171310
APA StyleZaman, V., Gathings, A., Drasites, K. P., Shields, D. C., Banik, N. L., & Haque, A. (2025). Neuroprotective Effects of Calpain Inhibition in Parkinson’s Disease: Insights from Cellular and Murine Models. Cells, 14(17), 1310. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14171310








