Calpain-1 and Calpain-2 in the Brain: What Have We Learned from 45 Years of Research?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Early Period, 1978–1985: Focus on Synaptic Plasticity
3. Calpain and Neurodegeneration: 1985–1994
4. Calpain and Glutamate Receptors: 1995–2012
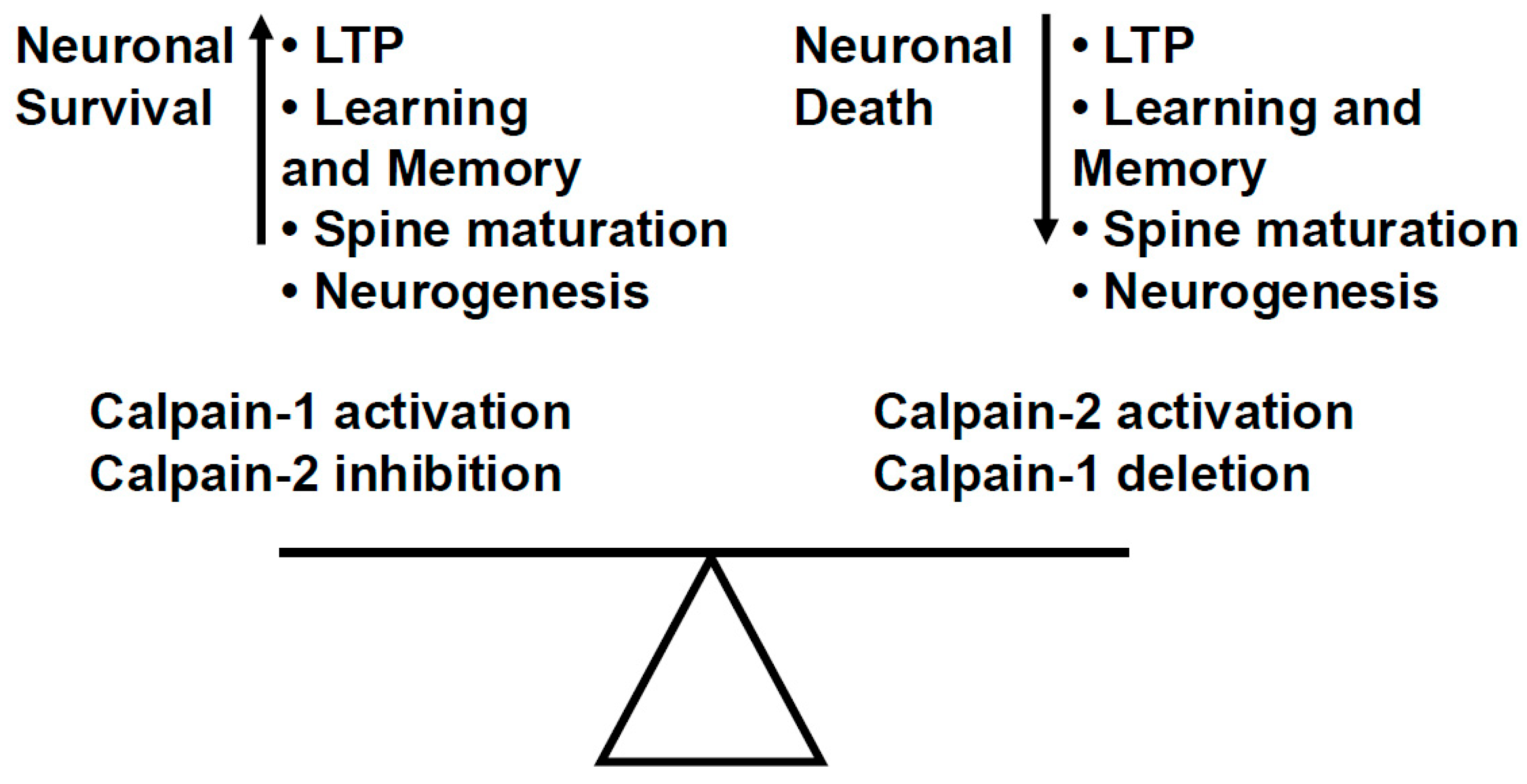
5. Opposite Functions of Calpain-1 and Calpain-2 in the Brain: 2012–2025
6. Development of Selective Calpain-2 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Neurodegenerative Disorders
7. Conclusions and Future Directions
8. Limitations
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TBI | Traumatic brain injury |
| AMPA | α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid |
| NMDA | N-methyl-D-aspartate |
| LTP | Long-term potentiation |
| LTD | Long-term depression |
| GFAP | Glial fibrillary acidic protein |
| PKA | cAMP-dependent protein kinase |
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| APP | ß-amyloid precursor protein |
| MAPs | Microtubule-associated proteins |
| CaM KIV | Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IV |
| GSK-3ß | Glycogen synthase kinase 3 |
| PSD-95 | Postsynaptic density protein 95 |
| GRIP | Glutamate-receptor-interacting protein |
| Cdk5 | Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 |
| PD | Parkinson’s disease |
| BDNF | Brain-derived nerve growth factor |
| MAP Kinase | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| PTEN | Phosphatase and tensin homolog |
| PHLPP1 | PH domain and Leucine-rich repeat Protein Phosphatase 1 |
References
- Guroff, G. A Neutral, Calcium-Activated Proteinase from the Soluble Fraction of Rat Brain. J. Biol. Chem. 1964, 239, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugita, H.; Ishiura, S.; Suzuki, K.; Imahori, K. Ca-activated neutral protease and its inhibitors: In vitro effect on intact myofibrils. Muscle Nerve 1980, 3, 335–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murachi, T.; Tanaka, K.; Hatanaka, M.; Murakami, T. Intracellular Ca2+-dependent protease (calpain) and its high-molecular-weight endogenous inhibitor (calpastatin). Adv. Enzyme Regul. 1980, 19, 407–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, S.; Emori, Y.; Imajoh, S.; Kawasaki, H.; Kisaragi, M.; Suzuki, K. Evolutionary origin of a calcium-dependent protease by fusion of genes for a thiol protease and a calcium-binding protein? Nature 1984, 312, 566–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siman, R.; Baudry, M.; Lynch, G. Brain fodrin: Substrate for calpain I, an endogenous calcium-activated protease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1984, 81, 3572–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glenney, J.R., Jr.; Glenney, P. Fodrin is the general spectrin-like protein found in most cells whereas spectrin and the TW protein have a restricted distribution. Cell 1983, 34, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goll, D.E.; Thompson, V.F.; Li, H.; Wei, W.; Cong, J. The calpain system. Physiol. Rev. 2003, 83, 731–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Hata, S.; Kawabata, Y.; Sorimachi, H. Structure, activation, and biology of calpain. Diabetes 2004, 53 (Suppl. S1), S12–S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croall, D.E.; Ersfeld, K. The calpains: Modular designs and functional diversity. Genome Biol. 2007, 8, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudry, M.; Lynch, G. Regulation of glutamate receptors by cations. Nature 1979, 282, 748–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baudry, M.; Lynch, G. Regulation of hippocampal glutamate receptors: Evidence for the involvement of a calcium-activated protease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1980, 77, 2298–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudry, M.; Bundman, M.C.; Smith, E.K.; Lynch, G.S. Micromolar calcium stimulates proteolysis and glutamate binding in rat brain synaptic membranes. Science 1981, 212, 937–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudry, M.; Smith, E.; Lynch, G. Influences of temperature, detergents, and enzymes on glutamate receptor binding and its regulation by calcium in rat hippocampal membranes. Mol. Pharmacol. 1981, 20, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siman, R.; Baudry, M.; Lynch, G. Purification from synaptosomal plasma membranes of calpain I, a thiol protease activated by micromolar calcium concentrations. J. Neurochem. 1983, 41, 950–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pant, H.C.; Virmani, M.; Gallant, P.E. Calcium-induced proteolysis of spectrin and band 3 protein in rat erythrocyte membranes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1983, 117, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, G.; Larson, J.; Kelso, S.; Barrionuevo, G.; Schottler, F. Intracellular injections of EGTA block induction of hippocampal long-term potentiation. Nature 1983, 305, 719–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, G.; Baudry, M. The biochemistry of memory: A new and specific hypothesis. Science 1984, 224, 1057–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staubli, U.; Baudry, M.; Lynch, G. Olfactory discrimination learning is blocked by leupeptin, a thiol protease inhibitor. Brain Res. 1985, 337, 333–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmerman, U.J.; Schlaepfer, W.W. Characterization of calcium-activated neutral protease (CANP)-associated protein kinase from bovine brain and its phosphorylation of neurofilaments. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1985, 129, 804–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coolican, S.A.; Hathaway, D.R. Effect of L-alpha-phosphatidylinositol on a vascular smooth muscle Ca2+-dependent protease. Reduction of the Ca2+ requirement for autolysis. J. Biol. Chem. 1984, 259, 11627–11630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pontremoli, S.; Melloni, E.; Sparatore, B.; Salamino, F.; Michetti, M.; Sacco, O.; Horecker, B.L. Role of phospholipids in the activation of the Ca2+-dependent neutral proteinase of human erythrocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1985, 129, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, U.J.; Schlaepfer, W.W. Calcium-activated neutral protease (CANP) in brain and other tissues. Prog. Neurobiol. 1984, 23, 63–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siman, R.; Gall, C.; Perlmutter, L.S.; Christian, C.; Baudry, M.; Lynch, G. Distribution of calpain I, an enzyme associated with degenerative activity, in rat brain. Brain Res. 1985, 347, 399–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siman, R.; Noszek, J.C. Excitatory amino acids activate calpain I and induce structural protein breakdown in vivo. Neuron 1988, 1, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siman, R.; Noszek, J.C.; Kegerise, C. Calpain I activation is specifically related to excitatory amino acid induction of hippocampal damage. J. Neurosci. 1989, 9, 1579–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seubert, P.; Ivy, G.; Larson, J.; Lee, J.; Shahi, K.; Baudry, M.; Lynch, G. Lesions of entorhinal cortex produce a calpain-mediated degradation of brain spectrin in dentate gyrus. I. Biochemical studies. Brain Res. 1988, 459, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivy, G.; Seubert, P.; Lynch, G.; Baudry, M. Lesions of entorhinal cortex produce a calpain-mediated degradation of brain spectrin in dentate gyrus. II. Anatomical studies. Brain Res. 1988, 459, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inuzuka, T.; Tamura, A.; Sato, S.; Kirino, T.; Toyoshima, I.; Miyatake, T. Suppressive effect of E-64c on ischemic degradation of cerebral proteins following occlusion of the middle cerebral artery in rats. Brain Res. 1990, 526, 177–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, A.; Kessler, M.; Lee, K.; Lynch, G. Calpain inhibitors improve the recovery of synaptic transmission from hypoxia in hippocampal slices. Brain Res. 1990, 532, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arlinghaus, L.; Mehdi, S.; Lee, K.S. Improved posthypoxic recovery with a membrane-permeable calpain inhibitor. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1991, 209, 123–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts-Lewis, J.M.; Savage, M.J.; Marcy, V.R.; Pinsker, L.R.; Siman, R. Immunolocalization of calpain I-mediated spectrin degradation to vulnerable neurons in the ischemic gerbil brain. J. Neurosci. 1994, 14, 3934–3944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.C.; Goto, Y.; Lanzino, G.; Soleau, S.; Kassell, N.F.; Lee, K.S. Neuroprotection with a calpain inhibitor in a model of focal cerebral ischemia. Stroke 1994, 25, 663–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, E.; Alafuzoff, I.; Blennow, K.; Blomgren, K.; Hall, C.M.; Janson, I.; Karlsson, I.; Wallin, A.; Gottfries, C.G.; Karlsson, J.O. Calpain and calpastatin in normal and Alzheimer-degenerated human brain tissue. Neurobiol. Aging 1990, 11, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nixon, R.A.; Saito, K.I.; Grynspan, F.; Griffin, W.R.; Katayama, S.; Honda, T.; Mohan, P.S.; Shea, T.B.; Beermann, M. Calcium-activated neutral proteinase (calpain) system in aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Ann. N. York Acad. Sci. 1994, 747, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siman, R.; Card, J.P.; Davis, L.G. Proteolytic processing of beta-amyloid precursor by calpain I. J. Neurosci. 1990, 10, 2400–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, K.; Elce, J.S.; Hamos, J.E.; Nixon, R.A. Widespread activation of calcium-activated neutral proteinase (calpain) in the brain in Alzheimer disease: A potential molecular basis for neuronal degeneration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 2628–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Patil, G.S.; Golubski, Z.E.; Hori, H.; Tehrani, K.; Foreman, J.E.; Eveleth, D.D.; Bartus, R.T.; Powers, J.C. Peptide alpha-keto ester, alpha-keto amide, and alpha-keto acid inhibitors of calpains and other cysteine proteases. J. Med. Chem. 1993, 36, 3472–3480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartus, R.T.; Hayward, N.J.; Elliott, P.J.; Sawyer, S.D.; Baker, K.L.; Dean, R.L.; Akiyama, A.; Straub, J.A.; Harbeson, S.L.; Li, Z.; et al. Calpain inhibitor AK295 protects neurons from focal brain ischemia. Effects of postocclusion intra-arterial administration. Stroke 1994, 25, 2265–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saatman, K.E.; Murai, H.; Bartus, R.T.; Smith, D.H.; Hayward, N.J.; Perri, B.R.; McIntosh, T.K. Calpain inhibitor AK295 attenuates motor and cognitive deficits following experimental brain injury in the rat. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 3428–3433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartus, R.T.; Elliott, P.J.; Hayward, N.J.; Dean, R.L.; Harbeson, S.; Straub, J.A.; Li, Z.; Powers, J.C. Calpain as a novel target for treating acute neurodegenerative disorders. Neurol. Res. 1995, 17, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, M.W.; Baudry, M.; Lynch, G. The protease inhibitor leupeptin interferes with the development of LTP in hippocampal slices. Brain Res. 1989, 505, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- del Cerro, S.; Larson, J.; Oliver, M.W.; Lynch, G. Development of hippocampal long-term potentiation is reduced by recently introduced calpain inhibitors. Brain Res. 1990, 530, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staubli, U.; Larson, J.; Thibault, O.; Baudry, M.; Lynch, G. Chronic administration of a thiol-proteinase inhibitor blocks long-term potentiation of synaptic responses. Brain Res. 1988, 444, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denny, J.B.; Polan-Curtain, J.; Ghuman, A.; Wayner, M.J.; Armstrong, D.L. Calpain inhibitors block long-term potentiation. Brain Res. 1990, 534, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahr, B.A.; Vanderklish, P.W.; Ha, L.T.; Tin, M.T.; Lynch, G. Spectrin breakdown products increase with age in telencephalon of mouse brain. Neurosci. Lett. 1991, 131, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudry, M.; DuBrin, R.; Beasley, L.; Leon, M.; Lynch, G. Low levels of calpain activity in Chiroptera brain: Implications for mechanisms of aging. Neurobiol. Aging 1986, 7, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudry, M.; Simonson, L.; Dubrin, R.; Lynch, G. A comparative study of soluble calcium-dependent proteolytic activity in brain. J. Neurobiol. 1986, 17, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billger, M.; Wallin, M.; Karlsson, J.O. Proteolysis of tubulin and microtubule-associated proteins 1 and 2 by calpain I and II. Difference in sensitivity of assembled and disassembled microtubules. Cell Calcium 1988, 9, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, W.J.; Traub, P. Proteolysis of vimentin and desmin by the Ca2+-activated proteinase specific for these intermediate filament proteins. Mol. Cell Biol. 1983, 3, 1146–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGinnis, K.M.; Whitton, M.M.; Gnegy, M.E.; Wang, K.K. Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IV is cleaved by caspase-3 and calpain in SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells undergoing apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 19993–20000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Freitas, M.S.; de Mattos-Dutra, A.; Wannmacher, C.M.; Pessoa-Pureur, R. Ca(2+)-mediated phosphorylation and proteolysis activity associated with the cytoskeletal fraction from cerebral cortex of rats. Neurochem. Res. 1996, 21, 1489–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shea, T.B.; Spencer, M.J.; Beermann, M.L.; Cressman, C.M.; Nixon, R.A. Calcium influx into human neuroblastoma cells induces ALZ-50 immunoreactivity: Involvement of calpain-mediated hydrolysis of protein kinase C. J. Neurochem. 1996, 66, 1539–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goni-Oliver, P.; Lucas, J.J.; Avila, J.; Hernandez, F. N-terminal cleavage of GSK-3 by calpain: A new form of GSK-3 regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 22406–22413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pain, S.; Monstero-Lastres, A.; Falet, H.; Brohard-Bohn, B.; Fraiz, N.; Bachelot-Loza, C.; Cano, E.; Rendu, F. Calpain controls the balance between protein tyrosine kinase and tyrosine phosphatase activities during platelet activation. FEBS Lett. 1999, 453, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil-Henn, H.; Volohonsky, G.; Elson, A. Regulation of protein-tyrosine phosphatases alpha and epsilon by calpain-mediated proteolytic cleavage. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 31772–31779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, X.; Tocco, G.; Baudry, M. Calpain-mediated regulation of AMPA receptors in adult rat brain. Neuroreport 1994, 6, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, X.; Chang, V.; Molnar, E.; McIlhinney, R.A.; Baudry, M. The C-terminal domain of glutamate receptor subunit 1 is a target for calpain-mediated proteolysis. Neuroscience 1996, 73, 903–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, X.; Chen, J.; Dang, S.; Wenthold, R.J.; Tocco, G.; Baudry, M. Characterization of calpain-mediated proteolysis of GluR1 subunits of alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionate receptors in rat brain. J. Neurochem. 1997, 68, 1484–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, X.; Rong, Y.; Chen, J.; Dang, S.; Wang, Z.; Baudry, M. Calpain-mediated regulation of NMDA receptor structure and function. Brain Res. 1998, 790, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, R.; Rong, Y.; Bernard, A.; Khrestchatisky, M.; Baudry, M. Src-mediated tyrosine phosphorylation of NR2 subunits of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors protects from calpain-mediated truncation of their C-terminal domains. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 26477–26483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guttmann, R.P.; Baker, D.L.; Seifert, K.M.; Cohen, A.S.; Coulter, D.A.; Lynch, D.R. Specific proteolysis of the NR2 subunit at multiple sites by calpain. J. Neurochem. 2001, 78, 1083–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guttmann, R.P.; Sokol, S.; Baker, D.L.; Simpkins, K.L.; Dong, Y.; Lynch, D.R. Proteolysis of the N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor by calpain in situ. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2002, 302, 1023–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpkins, K.L.; Guttmann, R.P.; Dong, Y.; Chen, Z.; Sokol, S.; Neumar, R.W.; Lynch, D.R. Selective activation induced cleavage of the NR2B subunit by calpain. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 11322–11331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.Y.; Lynch, D.R. Calpain and synaptic function. Mol. Neurobiol. 2006, 33, 215–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Rong, Y.; Baudry, M. Calpain-mediated degradation of PSD-95 in developing and adult rat brain. Neurosci. Lett. 2000, 286, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Wyszynski, M.; Sheng, M.; Baudry, M. Proteolysis of glutamate receptor-interacting protein by calpain in rat brain: Implications for synaptic plasticity. J. Neurochem. 2001, 77, 1553–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Rostamiani, K.; Hsu, Y.T.; Wang, Y.; Bi, X.; Baudry, M. Calpain-mediated regulation of stargazin in adult rat brain. Neuroscience 2011, 178, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuen, E.Y.; Liu, W.; Yan, Z. The phosphorylation state of GluR1 subunits determines the susceptibility of AMPA receptors to calpain cleavage. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 16434–16440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rong, Y.; Lu, X.; Bernard, A.; Khrestchatisky, M.; Baudry, M. Tyrosine phosphorylation of ionotropic glutamate receptors by Fyn or Src differentially modulates their susceptibility to calpain and enhances their binding to spectrin and PSD-95. J. Neurochem. 2001, 79, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litersky, J.M.; Scott, C.W.; Johnson, G.V. Phosphorylation, calpain proteolysis and tubulin binding of recombinant human tau isoforms. Brain Res. 1993, 604, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamei, H.; Saito, T.; Ozawa, M.; Fujita, Y.; Asada, A.; Bibb, J.A.; Saido, T.C.; Sorimachi, H.; Hisanaga, S. Suppression of calpain-dependent cleavage of the CDK5 activator p35 to p25 by site-specific phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 1687–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedrelow, J.H.; Cianci, C.D.; Morrow, J.S. c-Src binds alpha II spectrin’s Src homology 3 (SH3) domain and blocks calpain susceptibility by phosphorylating Tyr1176. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 7735–7741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Li, S.F.; Qian, S.W.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Liu, Y.; Tang, Q.Q.; Li, X. Phosphorylation prevents C/EBPbeta from the calpain-dependent degradation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 419, 550–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Liu, S.; Huang, Q.; Xie, B.; Lai, B.; Wang, C.; Song, B.; Li, M. Site-specific phosphorylation protects glycogen synthase kinase-3beta from calpain-mediated truncation of its N and C termini. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 22521–22532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Wong, T.P.; Chery, N.; Gaertner, T.; Wang, Y.T.; Baudry, M. Calpain-mediated mGluR1alpha truncation: A key step in excitotoxicity. Neuron 2007, 53, 399–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Zhou, M.; Baudry, M. Neuroprotection by cell permeable TA-mGluR1 peptide in ischemia: Synergy between carrier and cargo sequences. Neuroscientist 2008, 14, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, X.; Standley, S.; Baudry, M. Posttranslational regulation of ionotropic glutamate receptors and synaptic plasticity. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 1998, 42, 227–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, S.J.; Huttenlocher, A. Regulating cell migration: Calpains make the cut. J. Cell Sci. 2005, 118, 3829–3838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebart, M.C.; Benyamin, Y. Calpain involvement in the remodeling of cytoskeletal anchorage complexes. FEBS J. 2006, 273, 3415–3426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camins, A.; Verdaguer, E.; Folch, J.; Pallas, M. Involvement of calpain activation in neurodegenerative processes. CNS Drug Rev. 2006, 12, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, K.; Johnson, G.V. The role of tau phosphorylation in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2006, 3, 449–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tani, E. Molecular mechanisms involved in development of cerebral vasospasm. Neurosurg. Focus 2002, 12, ECP1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dargelos, E.; Poussard, S.; Brule, C.; Daury, L.; Cottin, P. Calcium-dependent proteolytic system and muscle dysfunctions: A possible role of calpains in sarcopenia. Biochimie 2008, 90, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorimachi, H.; Imajoh-Ohmi, S.; Emori, Y.; Kawasaki, H.; Ohno, S.; Minami, Y.; Suzuki, K. Molecular cloning of a novel mammalian calcium-dependent protease distinct from both m- and mu-types. Specific expression of the mRNA in skeletal muscle. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 20106–20111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorimachi, H.; Toyama-Sorimachi, N.; Saido, T.C.; Kawasaki, H.; Sugita, H.; Miyasaka, M.; Arahata, K.; Ishiura, S.; Suzuki, K. Muscle-specific calpain, p94, is degraded by autolysis immediately after translation, resulting in disappearance from muscle. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 10593–10605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorimachi, H.; Hata, S.; Ono, Y. Calpain chronicle—An enzyme family under multidisciplinary characterization. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B Phys. Biol. Sci. 2011, 87, 287–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, Y.; Sorimachi, H. Calpains: An elaborate proteolytic system. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1824, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudry, M.; Su, W.; Bi, X. The calpain proteolytic system. Encycl. Cell Biol. 2023, 1, 852–864. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, R.L.; Davies, P.L. Structure-function relationships in calpains. Biochem. J. 2012, 447, 335–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richard, I.; Broux, O.; Allamand, V.; Fougerousse, F.; Chiannilkulchai, N.; Bourg, N.; Brenguier, L.; Devaud, C.; Pasturaud, P.; Roudaut, C.; et al. Mutations in the proteolytic enzyme calpain 3 cause limb-girdle muscular dystrophy type 2A. Cell 1995, 81, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herasse, M.; Ono, Y.; Fougerousse, F.; Kimura, E.; Stockholm, D.; Beley, C.; Montarras, D.; Pinset, C.; Sorimachi, H.; Suzuki, K.; et al. Expression and functional characteristics of calpain 3 isoforms generated through tissue-specific transcriptional and posttranscriptional events. Mol. Cell Biol. 1999, 19, 4047–4055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, Y.; Mukai, H.; Hino, F.; Asada, K.; Kato, I. Isolation of two novel genes, down-regulated in gastric cancer. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 2000, 91, 459–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kampfl, A.; Posmantur, R.M.; Zhao, X.; Schmutzhard, E.; Clifton, G.L.; Hayes, R.L. Mechanisms of calpain proteolysis following traumatic brain injury: Implications for pathology and therapy: Implications for pathology and therapy: A review and update. J. Neurotrauma 1997, 14, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grynspan, F.; Griffin, W.R.; Cataldo, A.; Katayama, S.; Nixon, R.A. Active site-directed antibodies identify calpain II as an early-appearing and pervasive component of neurofibrillary pathology in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res. 1997, 763, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markgraf, C.G.; Velayo, N.L.; Johnson, M.P.; McCarty, D.R.; Medhi, S.; Koehl, J.R.; Chmielewski, P.A.; Linnik, M.D. Six-hour window of opportunity for calpain inhibition in focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Stroke 1998, 29, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.K. Calpain and caspase: Can you tell the difference?, by kevin K.W. Wang. Trends Neurosci. 2000, 23, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nixon, R.A. A “protease activation cascade” in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2000, 924, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, S.K.; Matzelle, D.D.; Sribnick, E.A.; Guyton, M.K.; Wingrave, J.M.; Banik, N.L. Calpain inhibitor prevented apoptosis and maintained transcription of proteolipid protein and myelin basic protein genes in rat spinal cord injury. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2003, 26, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samantaray, S.; Ray, S.K.; Banik, N.L. Calpain as a potential therapeutic target in Parkinson’s disease. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2008, 7, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, S.K.; Banik, N.L. Calpain and its involvement in the pathophysiology of CNS injuries and diseases: Therapeutic potential of calpain inhibitors for prevention of neurodegeneration. Curr. Drug Targets CNS Neurol. Disord. 2003, 2, 173–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glading, A.; Bodnar, R.J.; Reynolds, I.J.; Shiraha, H.; Satish, L.; Potter, D.A.; Blair, H.C.; Wells, A. Epidermal growth factor activates m-calpain (calpain II), at least in part, by extracellular signal-regulated kinase-mediated phosphorylation. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004, 24, 2499–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zadran, S.; Jourdi, H.; Rostamiani, K.; Qin, Q.; Bi, X.; Baudry, M. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and epidermal growth factor activate neuronal m-calpain via mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent phosphorylation. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 1086–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiraha, H.; Glading, A.; Chou, J.; Jia, Z.; Wells, A. Activation of m-calpain (calpain II) by epidermal growth factor is limited by protein kinase A phosphorylation of m-calpain. Mol. Cell Biol. 2002, 22, 2716–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.D.; Jia, Z.; Huynh, K.K.; Wells, A.; Elce, J.S. Glutamate substitutions at a PKA consensus site are consistent with inactivation of calpain by phosphorylation. FEBS Lett. 2003, 542, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, J.; Horiike, Y.; Matsuzaki, M.; Miyazaki, T.; Ellis-Davies, G.C.; Kasai, H. Protein synthesis and neurotrophin-dependent structural plasticity of single dendritic spines. Science 2008, 319, 1683–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
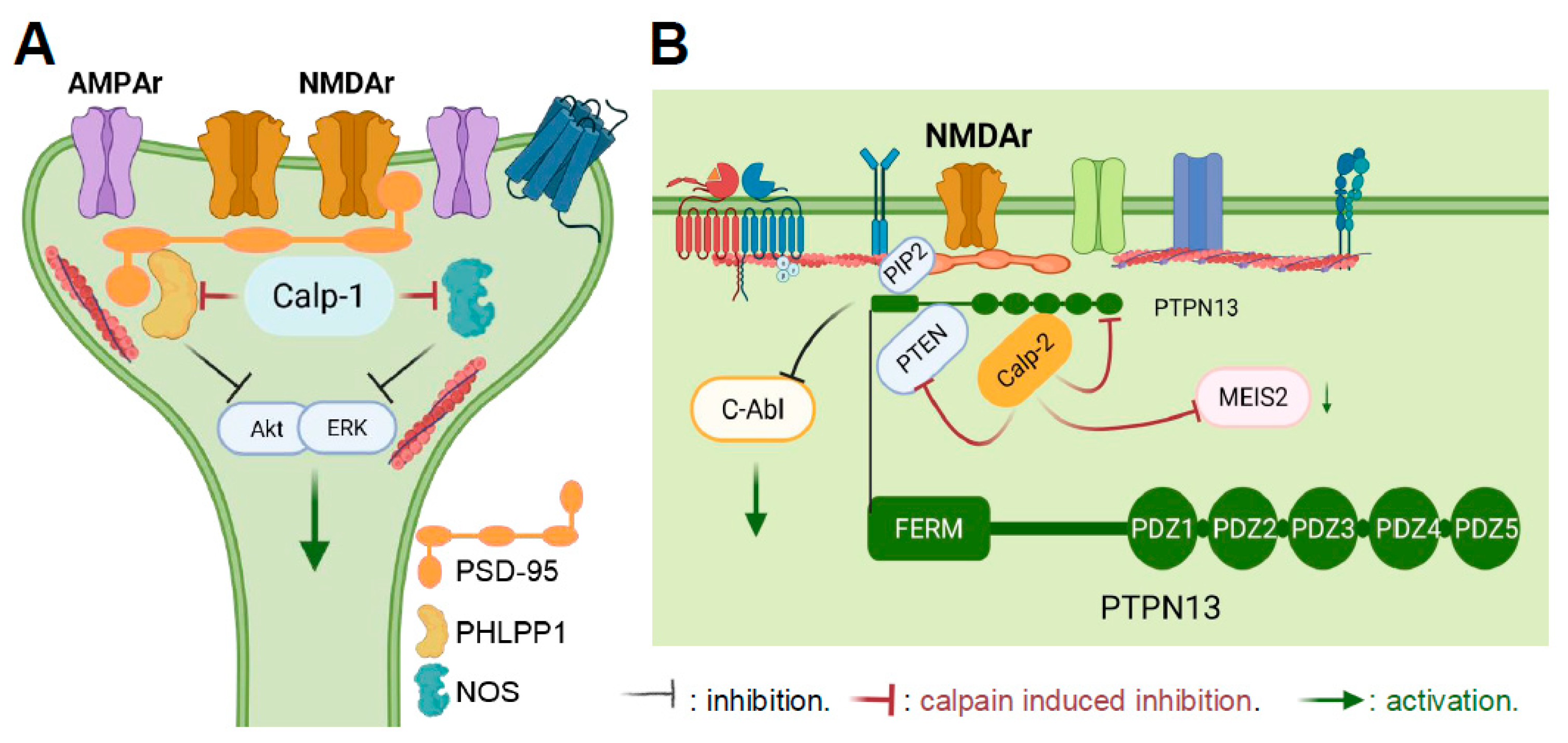
- Briz, V.; Hsu, Y.T.; Li, Y.; Lee, E.; Bi, X.; Baudry, M. Calpain-2-mediated PTEN degradation contributes to BDNF-induced stimulation of dendritic protein synthesis. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 4317–4328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, M.; Ma, C.L.; Farazifard, R.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Vanderluit, J.; Zoltewicz, J.S.; Hage, F.; Savitt, J.M.; Lagace, D.C.; et al. Conditional disruption of calpain in the CNS alters dendrite morphology, impairs LTP, and promotes neuronal survival following injury. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 5773–5784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardingham, G.E.; Arnold, F.J.; Bading, H. A calcium microdomain near NMDA receptors: On switch for ERK-dependent synapse-to-nucleus communication. Nat. Neurosci. 2001, 4, 565–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardingham, G.E.; Bading, H. Synaptic versus extrasynaptic NMDA receptor signalling: Implications for neurodegenerative disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2010, 11, 682–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Briz, V.; Chishti, A.; Bi, X.; Baudry, M. Distinct roles for mu-calpain and m-calpain in synaptic NMDAR-mediated neuroprotection and extrasynaptic NMDAR-mediated neurodegeneration. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 18880–18892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, K.; Phan, T.; Mansuy, I.M.; Storm, D.R. Proteolytic degradation of SCOP in the hippocampus contributes to activation of MAP kinase and memory. Cell 2007, 128, 1219–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, G.; Briz, V.; Hsu, Y.T.; Bi, X.; Baudry, M. A molecular brake controls the magnitude of long-term potentiation. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Bi, X.; Baudry, M. Different patterns of electrical activity lead to long-term potentiation by activating different intracellular pathways. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 621–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forman, O.P.; De Risio, L.; Mellersh, C.S. Missense mutation in CAPN1 is associated with spinocerebellar ataxia in the Parson Russell Terrier dog breed. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Hersheson, J.; Lopez, D.; Hammer, M.; Liu, Y.; Lee, K.H.; Pinto, V.; Seinfeld, J.; Wiethoff, S.; Sun, J.; et al. Defects in the CAPN1 Gene Result in Alterations in Cerebellar Development and Cerebellar Ataxia in Mice and Humans. Cell Rep. 2016, 16, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, Y.; Chishti, A.; Li, Q.Q.; Dayal, S.; Shiehzadegan, S.; Cheng, A.; Moore, C.; Bi, X.; et al. Deletion of the Capn1 Gene Results in Alterations in Signaling Pathways Related to Alzheimer’s Disease, Protein Quality Control and Synaptic Plasticity in Mouse Brain. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lopez, D.; Davey, P.G.; Cameron, D.J.; Nguyen, K.; Tran, J.; Marquez, E.; Liu, Y.; Bi, X.; Baudry, M. Calpain-1 and calpain-2 play opposite roles in retinal ganglion cell degeneration induced by retinal ischemia/reperfusion injury. Neurobiol. Dis. 2016, 93, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Lopez, D.; Lee, M.; Dayal, S.; Hurtado, A.; Bi, X.; Baudry, M. Protection against TBI-Induced Neuronal Death with Post-Treatment with a Selective Calpain-2 Inhibitor in Mice. J. Neurotrauma 2018, 35, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Nham, A.; Sherbaf, A.; Quach, D.; Yahya, E.; Ranburger, D.; Bi, X.; Baudry, M. Calpain-2 as a therapeutic target in repeated concussion-induced neuropathy and behavioral impairment. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaba5547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yahya, E.; Quach, D.; Bi, X.; Baudry, M. Calpain-2 activation in mouse hippocampus plays a critical role in seizure-induced neuropathology. Neurobiol. Dis. 2021, 147, 105149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudry, M.; Bi, X. Calpain-1 and Calpain-2: The Yin and Yang of Synaptic Plasticity and Neurodegeneration. Trends Neurosci. 2016, 39, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Bi, X.; Baudry, M. Calpain-1 and Calpain-2 in the Brain: New Evidence for a Critical Role of Calpain-2 in Neuronal Death. Cells 2020, 9, 2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunet, A.; Park, J.; Tran, H.; Hu, L.S.; Hemmings, B.A.; Greenberg, M.E. Protein kinase SGK mediates survival signals by phosphorylating the forkhead transcription factor FKHRL1 (FOXO3a). Mol. Cell Biol. 2001, 21, 952–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deacon, K.; Mistry, P.; Chernoff, J.; Blank, J.L.; Patel, R. p38 Mitogen-activated protein kinase mediates cell death and p21-activated kinase mediates cell survival during chemotherapeutic drug-induced mitotic arrest. Mol. Biol. Cell 2003, 14, 2071–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Kurup, P.; Zhang, Y.; Goebel-Goody, S.M.; Wu, P.H.; Hawasli, A.H.; Baum, M.L.; Bibb, J.A.; Lombroso, P.J. Extrasynaptic NMDA receptors couple preferentially to excitotoxicity via calpain-mediated cleavage of STEP. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 9330–9343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Bi, X.; Baudry, M. Calpain-2 as a therapeutic target for acute neuronal injury. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2018, 22, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christopherson, K.S.; Hillier, B.J.; Lim, W.A.; Bredt, D.S. PSD-95 assembles a ternary complex with the N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor and a bivalent neuronal NO synthase PDZ domain. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 27467–27473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Hall, R.A.; Lee, M.; Kamgar-Parsi, A.; Bi, X.; Baudry, M. The tyrosine phosphatase PTPN13/FAP-1 links calpain-2, TBI and tau tyrosine phosphorylation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Brazdzionis, J.; Dong, F.; Patchana, T.; Ghanchi, H.; Podkovik, S.; Wiginton, J.G.T.; Marino, M.; Duong, J.; Wacker, M.; et al. P13BP, a Calpain-2-Mediated Breakdown Product of PTPN13, Is a Novel Blood Biomarker for Traumatic Brain Injury. J. Neurotrauma 2021, 38, 3077–3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freiss, G.; Chalbos, D. PTPN13/PTPL1: An important regulator of tumor aggressiveness. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2011, 11, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sotelo, N.S.; Schepens, J.T.; Valiente, M.; Hendriks, W.J.; Pulido, R. PTEN-PDZ domain interactions: Binding of PTEN to PDZ domains of PTPN13. Methods 2015, 77–78, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kock, G.; Dicks, M.; Yip, K.T.; Kohl, B.; Putz, S.; Heumann, R.; Erdmann, K.S.; Stoll, R. Molecular Basis of Class III Ligand Recognition by PDZ3 in Murine Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase PTPN13. J. Mol. Biol. 2018, 430, 4275–4292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, D.M.; Xavier, J.M.; Morgado, A.L.; Sola, S.; Rodrigues, C.M. Distinct regulatory functions of calpain 1 and 2 during neural stem cell self-renewal and differentiation. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persson, A.; Lindberg, O.R.; Kuhn, H.G. Radixin inhibition decreases adult neural progenitor cell migration and proliferation in vitro and in vivo. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2013, 7, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, K.M.; Park, H.; Jung, S.; Ha, S.; Yoo, S.J.; Woo, H.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, E.K.; Moon, C.; et al. Calpain Determines the Propensity of Adult Hippocampal Neural Stem Cells to Autophagic Cell Death Following Insulin Withdrawal. Stem Cells 2015, 33, 3052–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, V.M.; Morte, M.I.; Carreira, B.P.; Azevedo, M.M.; Takano, J.; Iwata, N.; Saido, T.C.; Asmussen, H.; Horwitz, A.R.; Carvalho, C.M.; et al. Involvement of calpains in adult neurogenesis: Implications for stroke. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2015, 9, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Regulation of TET protein stability by calpains. Cell Rep. 2014, 6, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huttenlocher, A.; Palecek, S.P.; Lu, Q.; Zhang, W.; Mellgren, R.L.; Lauffenburger, D.A.; Ginsberg, M.H.; Horwitz, A.F. Regulation of cell migration by the calcium-dependent protease calpain. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 32719–32722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yajima, Y.; Kawashima, S. Calpain function in the differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Biol. Chem. 2002, 383, 757–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moyen, C.; Goudenege, S.; Poussard, S.; Sassi, A.H.; Brustis, J.J.; Cottin, P. Involvement of micro-calpain (CAPN 1) in muscle cell differentiation. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2004, 36, 728–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raynaud, F.; Marcilhac, A.; Chebli, K.; Benyamin, Y.; Rossel, M. Calpain 2 expression pattern and sub-cellular localization during mouse embryogenesis. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2008, 52, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jessberger, S.; Gage, F.H.; Eisch, A.J.; Lagace, D.C. Making a neuron: Cdk5 in embryonic and adult neurogenesis. Trends Neurosci. 2009, 32, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moudilou, E.N.; Mouterfi, N.; Exbrayat, J.M.; Brun, C. Calpains expression during Xenopus laevis development. Tissue Cell 2010, 42, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storr, S.J.; Carragher, N.O.; Frame, M.C.; Parr, T.; Martin, S.G. The calpain system and cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lade, A.; Ranganathan, S.; Luo, J.; Monga, S.P. Calpain induces N-terminal truncation of beta-catenin in normal murine liver development: Diagnostic implications in hepatoblastomas. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 22789–22798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Brown, R.C.; Fletcher, J.C.; Opsahl-Sorteberg, H.G. Calpain-Mediated Positional Information Directs Cell Wall Orientation to Sustain Plant Stem Cell Activity, Growth and Development. Plant Cell Physiol. 2015, 56, 1855–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joy, J.; Nalabothula, N.; Ghosh, M.; Popp, O.; Jochum, M.; Machleidt, W.; Gil-Parrado, S.; Holak, T.A. Identification of calpain cleavage sites in the G1 cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p19(INK4d). Biol. Chem. 2006, 387, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawauchi, T. Cdk5 regulates multiple cellular events in neural development, function and disease. Dev. Growth Differ. 2014, 56, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.Q.; Habegger, L.; Noisa, P.; Szekely, A.; Qiu, C.; Hutchison, S.; Raha, D.; Egholm, M.; Lin, H.; Weissman, S.; et al. Dynamic transcriptomes during neural differentiation of human embryonic stem cells revealed by short, long, and paired-end sequencing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 5254–5259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudry, M.; Su, W.; Seinfeld, J.; Sun, J.; Bi, X. Role of Calpain-1 in Neurogenesis. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 685938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baudry, M.; Reece, T.; Shahi, R.; Ta, K.; Bi, X. Calpain-2 inhibition or deletion enhances levels of the transcription factor, MEIS2, and stimulates neurogenesis. BMS-CN-2025-281 2025.
- Saez, M.E.; Ramirez-Lorca, R.; Moron, F.J.; Ruiz, A. The therapeutic potential of the calpain family: New aspects. Drug Discov. Today 2006, 11, 917–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potz, B.A.; Abid, M.R.; Selke, F.W. Role of calpain in pathogenesis of human disease processes. J. Nat.Sci. 2016, 2, e218. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Miyazaki, T. Calpain and Cardiometabolic Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderklish, P.W.; Bahr, B.A. The pathogenic activation of calpain: A marker and mediator of cellular toxicity and disease states. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2000, 81, 323–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ono, Y.; Saido, T.C.; Sorimachi, H. Calpain research for drug discovery: Challenges and potential. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2016, 15, 854–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinozzi, S.; Albini, S.; Best, H.; Richard, I. Calpains for dummies: What you need to know about the calpain family. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Proteins Proteom. 2021, 1869, 140616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vosler, P.S.; Brennan, C.S.; Chen, J. Calpain-mediated signaling mechanisms in neuronal injury and neurodegeneration. Mol. Neurobiol. 2008, 38, 78–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yildiz-Unal, A.; Korulu, S.; Karabay, A. Neuroprotective strategies against calpain-mediated neurodegeneration. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2015, 11, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koumura, A.; Nonaka, Y.; Hyakkoku, K.; Oka, T.; Shimazawa, M.; Hozumi, I.; Inuzuka, T.; Hara, H. A novel calpain inhibitor, ((1S)-1((((1S)-1-benzyl-3-cyclopropylamino-2,3-di-oxopropyl)amino)carbonyl)-3-methylbutyl) carbamic acid 5-methoxy-3-oxapentyl ester, protects neuronal cells from cerebral ischemia-induced damage in mice. Neuroscience 2008, 157, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anagli, J.; Han, Y.; Stewart, L.; Yang, D.; Movsisyan, A.; Abounit, K.; Seyfried, D. A novel calpastatin-based inhibitor improves postischemic neurological recovery. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 385, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yin, F.; Zhang, J.; Qian, Y. The role of calpains in traumatic brain injury. Brain Inj. 2014, 28, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cagmat, E.B.; Guingab-Cagmat, J.D.; Vakulenko, A.V.; Hayes, R.L.; Anagli, J. Potential Use of Calpain Inhibitors as Brain Injury Therapy. In Brain Neurotrauma: Molecular, Neuropsychological, and Rehabilitation Aspects; Kobeissy, F.H., Ed.; Frontiers in Neuroengineering: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Siklos, M.; BenAissa, M.; Thatcher, G.R. Cysteine proteases as therapeutic targets: Does selectivity matter? A systematic review of calpain and cathepsin inhibitors. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2015, 5, 506–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, S.N.; Carrico, K.M.; Mustafa, A.G.; Bains, M.; Hall, E.D. A pharmacological analysis of the neuroprotective efficacy of the brain- and cell-permeable calpain inhibitor MDL-28170 in the mouse controlled cortical impact traumatic brain injury model. J. Neurotrauma 2010, 27, 2233–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bains, M.; Cebak, J.E.; Gilmer, L.K.; Barnes, C.C.; Thompson, S.N.; Geddes, J.W.; Hall, E.D. Pharmacological analysis of the cortical neuronal cytoskeletal protective efficacy of the calpain inhibitor SNJ-1945 in a mouse traumatic brain injury model. J. Neurochem. 2013, 125, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoch, K.M.; von Reyn, C.R.; Bian, J.; Telling, G.C.; Meaney, D.F.; Saatman, K.E. Brain injury-induced proteolysis is reduced in a novel calpastatin-overexpressing transgenic mouse. J. Neurochem. 2013, 125, 909–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saatman, K.E.; Zhang, C.; Bartus, R.T.; McIntosh, T.K. Behavioral efficacy of posttraumatic calpain inhibition is not accompanied by reduced spectrin proteolysis, cortical lesion, or apoptosis. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2000, 20, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buki, A.; Farkas, O.; Doczi, T.; Povlishock, J.T. Preinjury administration of the calpain inhibitor MDL-28170 attenuates traumatically induced axonal injury. J. Neurotrauma 2003, 20, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ai, J.; Liu, E.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Yu, J.; Baker, A.J. Calpain inhibitor MDL-28170 reduces the functional and structural deterioration of corpus callosum following fluid percussion injury. J. Neurotrauma 2007, 24, 960–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Li, L.; Wang, X.; Bull, D.L.; Shofer, F.S.; Meaney, D.F.; Neumar, R.W. Short-duration treatment with the calpain inhibitor MDL-28170 does not protect axonal transport in an in vivo model of traumatic axonal injury. J. Neurotrauma 2012, 29, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donkor, I.O. Calpain inhibitors: A survey of compounds reported in the patent and scientific literature. Expert. Opin. Ther. Pat. 2011, 21, 601–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnsten, A.F.T.; Baudry, M. Targeting calpain-2 for Alzheimer’s disease treatment. Med. Res. Arch. 2023, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudry, M.; Luo, Y.L.; Bi, X. Calpain-2 Inhibitors as Therapy for Traumatic Brain Injury. Neurotherapeutics 2023, 20, 1592–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, P.; Botello-Smith, W.M.; Zhang, H.; Qian, L.; Alsamarah, A.; Kent, D.; Lacroix, J.J.; Baudry, M.; Luo, Y. Can Relative Binding Free Energy Predict Selectivity of Reversible Covalent Inhibitors? J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 17945–17952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lon, H.K.; Mendonca, N.; Goss, S.; Othman, A.A.; Locke, C.; Jin, Z.; Rendenbach-Mueller, B. Pharmacokinetics, Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacodynamics of Alicapistat, a Selective Inhibitor of Human Calpains 1 and 2 for the Treatment of Alzheimer Disease: An Overview of Phase 1 Studies. Clin. Pharmacol. Drug Dev. 2019, 8, 290–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Ortega-Vilain, A.C.; Patil, G.S.; Chu, D.L.; Foreman, J.E.; Eveleth, D.D.; Powers, J.C. Novel peptidyl alpha-keto amide inhibitors of calpains and other cysteine proteases. J. Med. Chem. 1996, 39, 4089–4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovat, A.; Li, Z.Z.; Hampton, C.Y.; Asress, S.A.; Fernandez, F.M.; Glass, J.D.; Powers, J.C. Peptidyl alpha-ketoamides with nucleobases, methylpiperazine, and dimethylaminoalkyl substituents as calpain inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 6326–6336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustach, V.D.; Lakkaraju, S.K.; Jo, S.; Yu, W.; Jiang, W.; MacKerell, A.D., Jr. Optimization and Evaluation of Site-Identification by Ligand Competitive Saturation (SILCS) as a Tool for Target-Based Ligand Optimization. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2019, 59, 3018–3035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
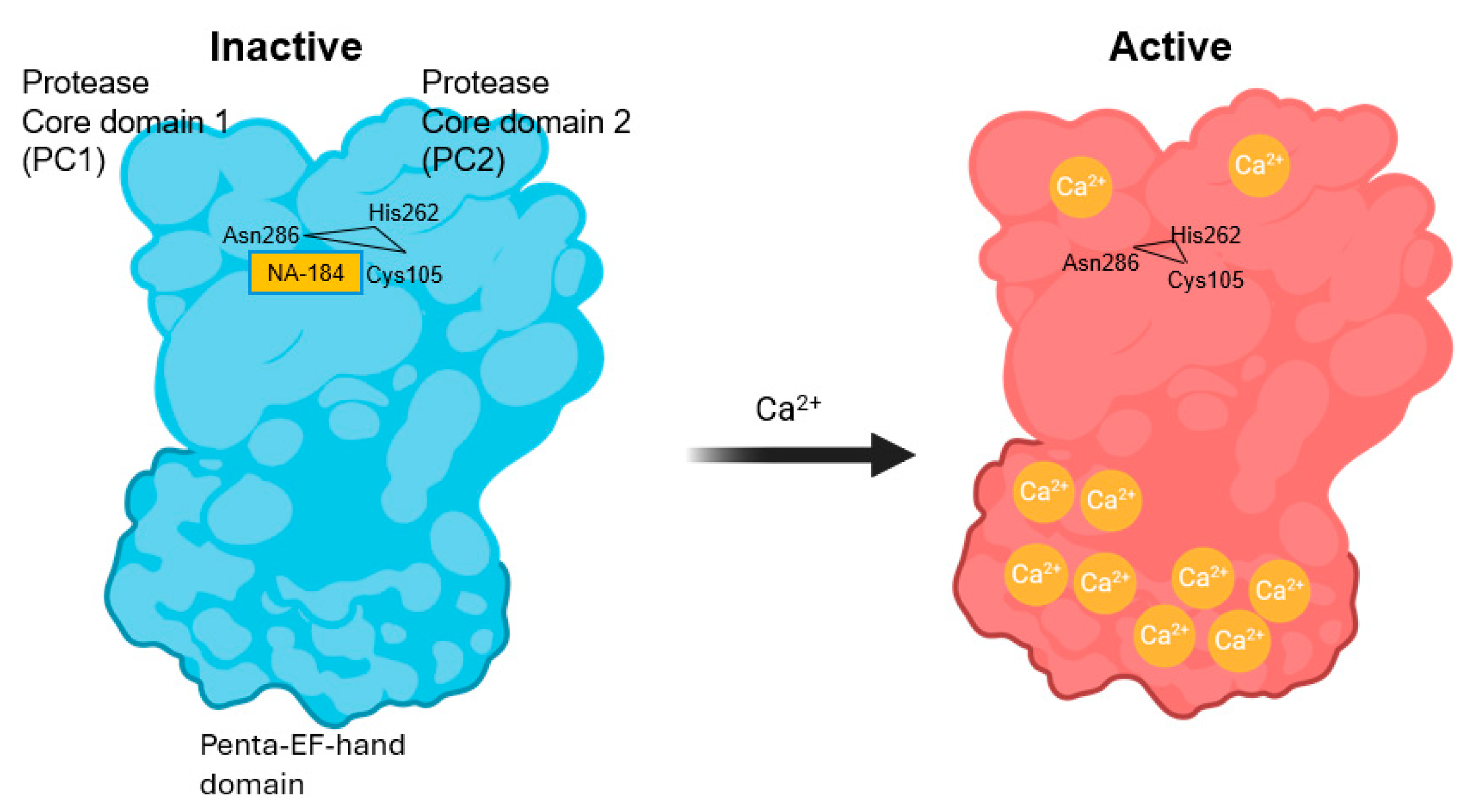
- Baudry, M.; Wang, Y.; Bi, X.; Luo, Y.L.; Wang, Z.; Kamal, Z.; Shirokov, A.; Sullivan, E.; Lagasca, D.; Khalil, H.; et al. Identification and neuroprotective properties of NA-184, a calpain-2 inhibitor. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2024, 12, e1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahay, A.; Scobie, K.N.; Hill, A.S.; O’Carroll, C.M.; Kheirbek, M.A.; Burghardt, N.S.; Fenton, A.A.; Dranovsky, A.; Hen, R. Increasing adult hippocampal neurogenesis is sufficient to improve pattern separation. Nature 2011, 472, 466–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babcock, K.R.; Page, J.S.; Fallon, J.R.; Webb, A.E. Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis in Aging and Alzheimer’s Disease. Stem Cell Rep. 2021, 16, 681–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, W.; Aimone, J.B.; Gage, F.H. New neurons and new memories: How does adult hippocampal neurogenesis affect learning and memory? Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2010, 11, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, M.H. The BDNF-Interactive Model for Sustainable Hippocampal Neurogenesis in Humans: Synergistic Effects of Environmentally-Mediated Physical Activity, Cognitive Stimulation, and Mindfulness. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisch, A.J.; Petrik, D. Depression and hippocampal neurogenesis: A road to remission? Science 2012, 338, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekdahl, C.T. Microglial activation—Tuning and pruning adult neurogenesis. Front. Pharmacol. 2012, 3, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumitru, I.; Paterlini, M.; Zamboni, M.; Ziegenhain, C.; Giatrellis, S.; Saghaleyni, R.; Bjorklund, A.; Alkass, K.; Tata, M.; Druid, H.; et al. Identification of proliferating neural progenitors in the adult human hippocampus. Science 2025, 389, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baudry, M.; Bi, X. Calpain-1 and Calpain-2 in the Brain: What Have We Learned from 45 Years of Research? Cells 2025, 14, 1301. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14171301
Baudry M, Bi X. Calpain-1 and Calpain-2 in the Brain: What Have We Learned from 45 Years of Research? Cells. 2025; 14(17):1301. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14171301
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaudry, Michel, and Xiaoning Bi. 2025. "Calpain-1 and Calpain-2 in the Brain: What Have We Learned from 45 Years of Research?" Cells 14, no. 17: 1301. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14171301
APA StyleBaudry, M., & Bi, X. (2025). Calpain-1 and Calpain-2 in the Brain: What Have We Learned from 45 Years of Research? Cells, 14(17), 1301. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14171301






