MicroRNA miR-193b-3p Regulates Esophageal Cancer Progression Through Targeting RSF1
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bioinformatics Analysis
2.2. Immunohistochemistry Assay
2.3. Cell Culture
2.4. Cell Transfection Assay
2.5. Immunoblots
2.6. Quantitative Real-Time PCR Assay
2.7. MicroRNA Immunoprecipitation (RIP) Assay
2.8. Dual-Luciferase Reporter Assay
2.9. Cell-Counting Assay
2.10. Colony Formation Assay
2.11. EdU Incorporation Assay
2.12. Wound-Healing Assay
2.13. Transwell Assay
2.14. Cell Apoptosis Analysis
2.15. Xenograft Assay
2.16. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
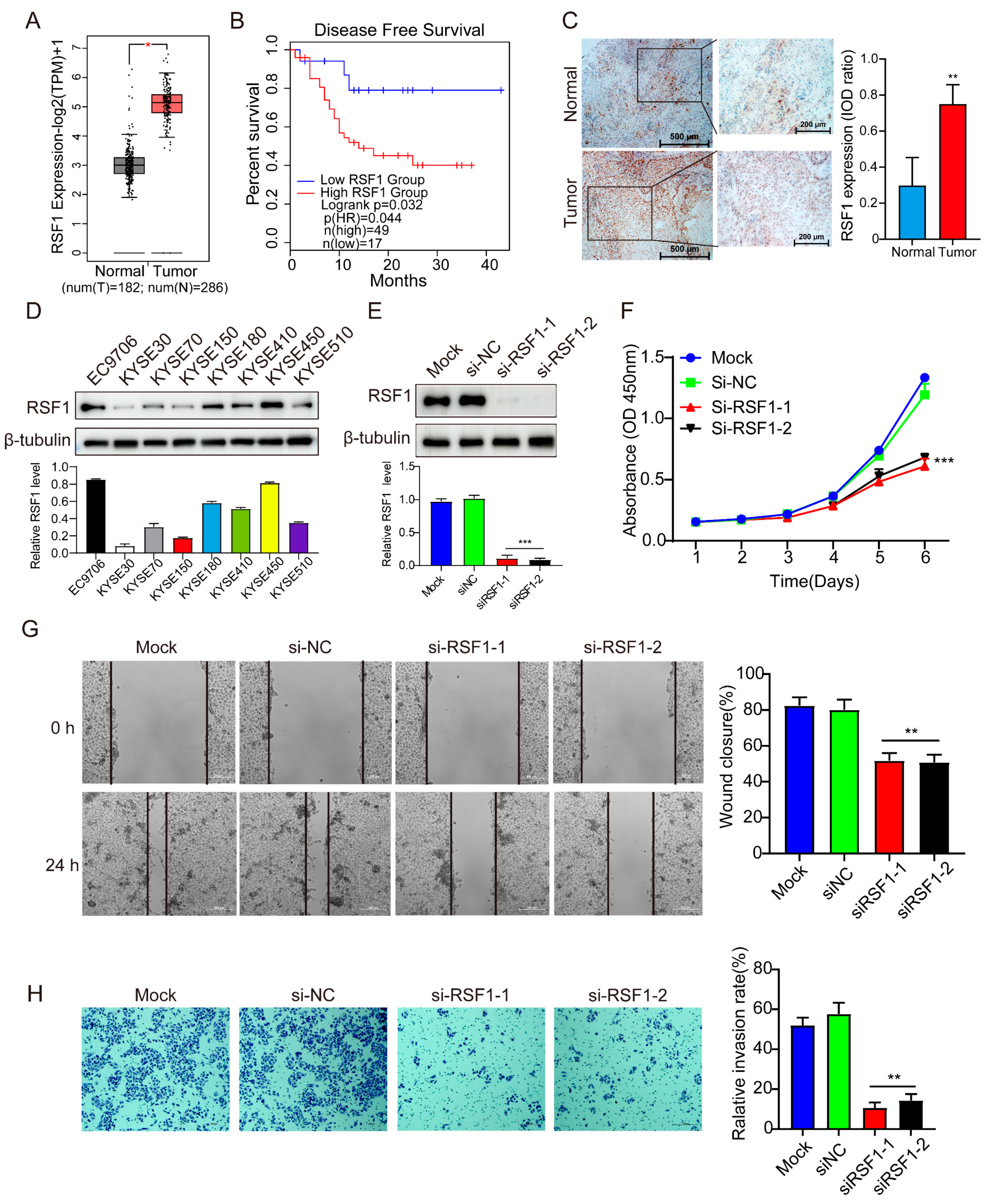
3.1. RSF1 Levels Are Elevated in ESCC and Correlate with Disease Progression
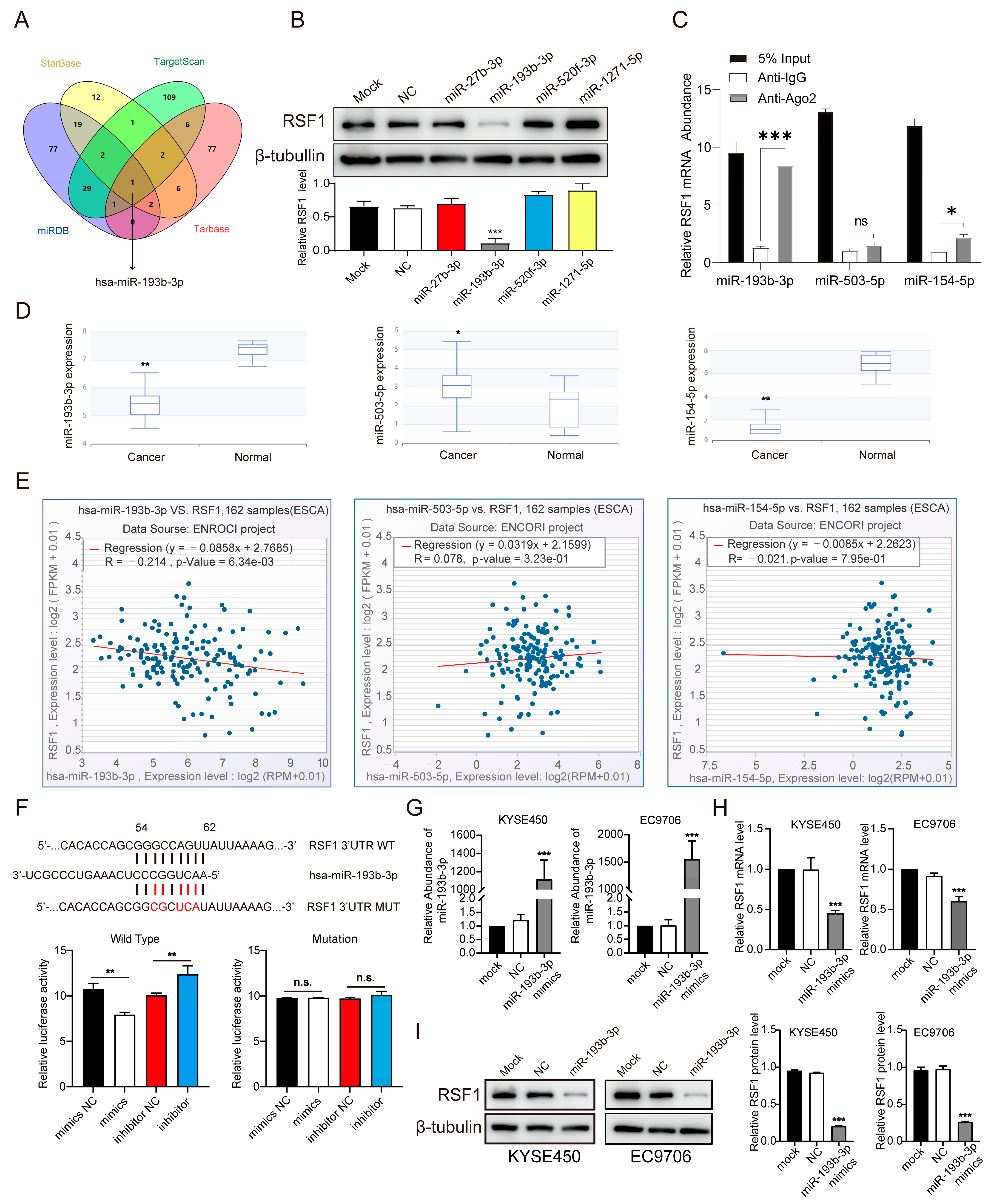
3.2. Identification of miR-193b-3p as a Critical Regulator of RSF1 in ESCC
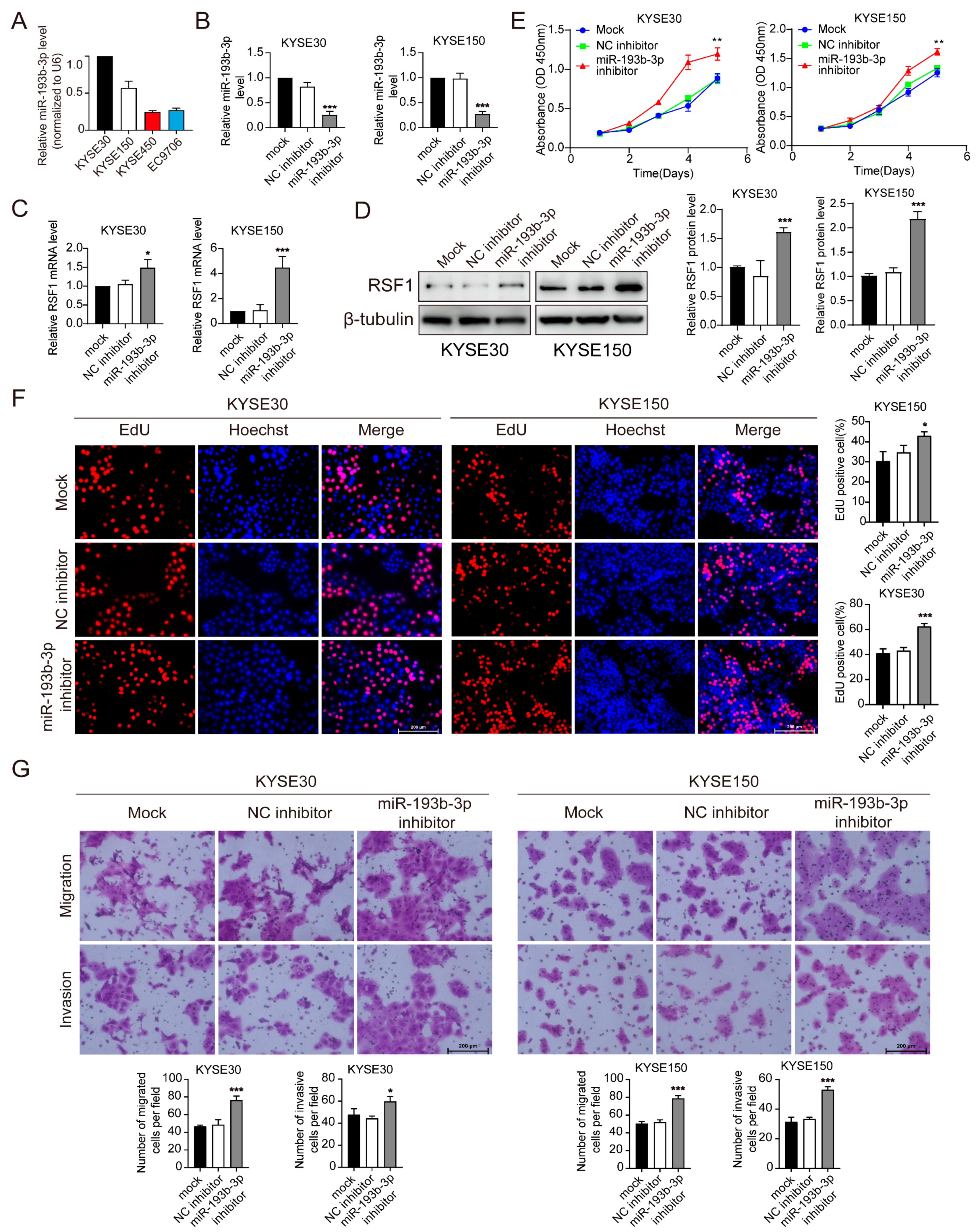
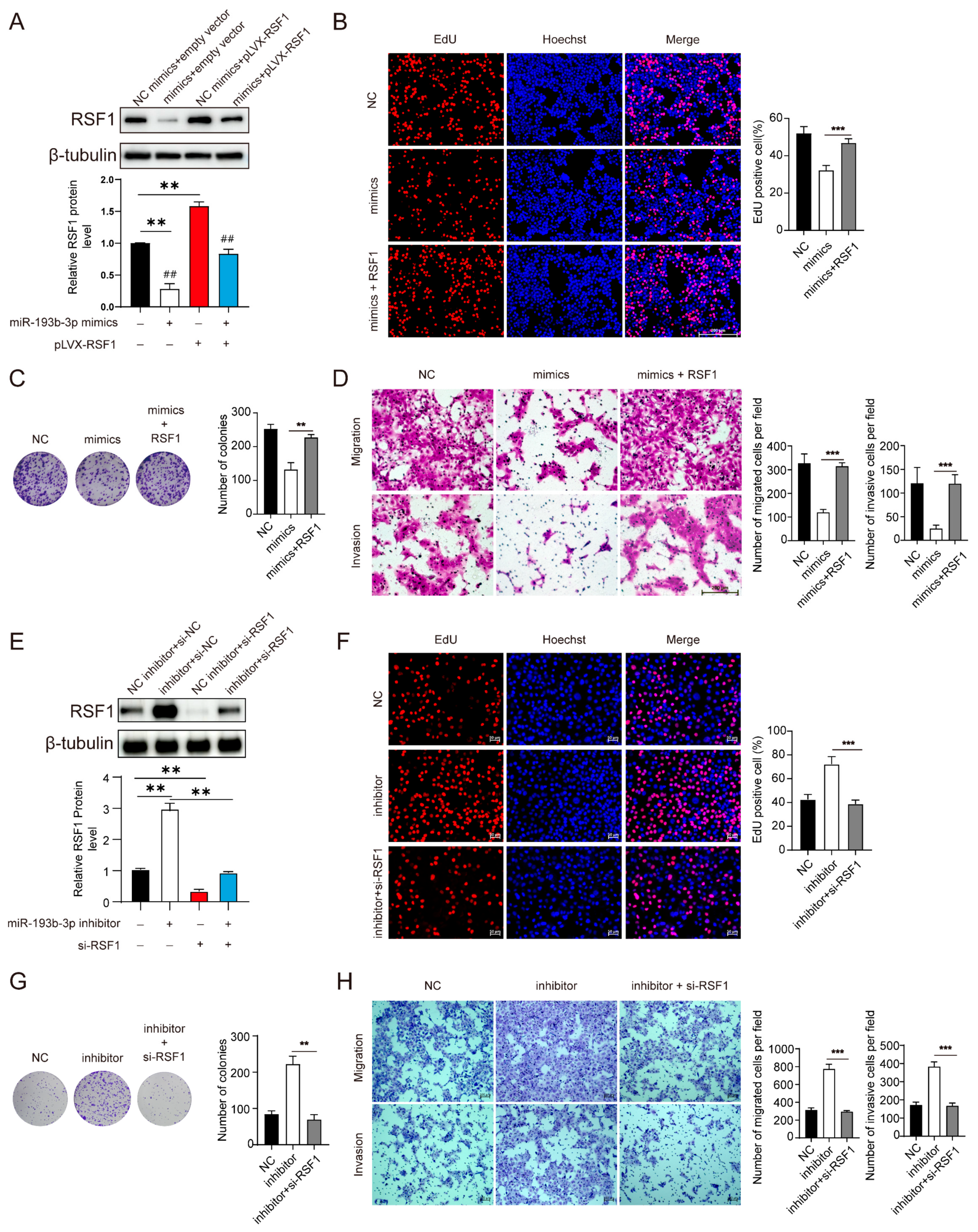
3.3. Suppression of miR-193b-3p Increases RSF1 Protein Levels and Enhances ESCC Progression
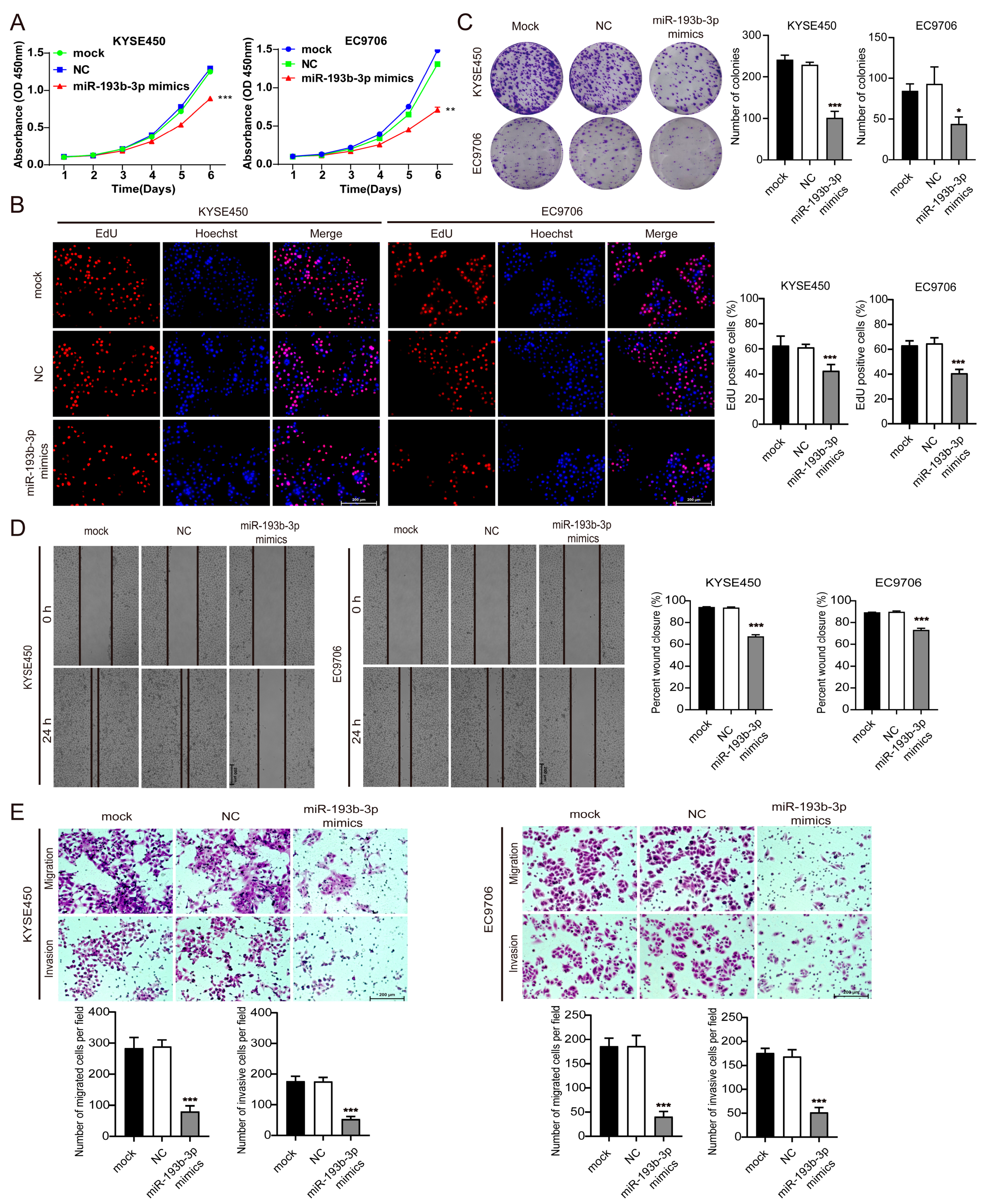
3.4. Elevation of miR-193b-3p Inhibits ESCC Cell Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion
3.5. miR-193b-3p Inhibits ESCC Tumor Growth In Vivo
3.6. RSF1 Is a Key Target of miR-193b-3p During ESCC Progression
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, L.; Li, H.; Chang, W.; Ao, Y.; Wen, Z.; Chen, Y. TP53 Mutations in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Front. Bio-Sci. 2023, 28, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abby, E.; Dentro, S.C.; Hall, M.W.J.; Fowler, J.C.; Ong, S.H.; Sood, R.; Herms, A.; Piedrafita, G.; Abnizova, I.; Siebel, C.W.; et al. Notch1 mutations drive clonal expansion in normal esophageal epithelium but impair tumor growth. Nat. Genet. 2023, 55, 232–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.-Y.; Chen, W.; Chughtai, E.A.; Qiao, Z.; Jiang, J.-T.; Li, S.-M.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, J. PIK3CA gene mutations in Northwest Chinese esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 2585–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Yang, W.; Chen, L.; Qian, L. The DNA methylation-regulated MCTP1 activates the drug-resistance of esophageal cancer cells. Aging 2021, 13, 3342–3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Jiang, Q.; Gong, T.; Fan, D.; Zhang, J.; Chen, F.; Zhu, X.; Wang, X.; Qiao, Y.; Chen, H.; et al. Loss of grand histone H3 lysine 27 trimethylation domains mediated transcriptional activation in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. npj Genom. Med. 2021, 6, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, W.; Chen, H.-D.; Yu, Y.-W.; Li, N.; Chen, W.-Q. Changing profiles of cancer burden worldwide and in China: A secondary analysis of the global cancer statistics 2020. Chin. Med. J. 2021, 134, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsop, B.R.; Sharma, P. Esophageal Cancer. Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 45, 399–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.L.; Yu, S.J. Esophageal cancer: Risk factors, genetic association, and treatment. Asian J. Surg. 2018, 41, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheu, J.J.; Guan, B.; Choi, J.H.; Lin, A.; Lee, C.H.; Hsiao, Y.T.; Wang, T.L.; Tsai, F.J.; Shih, I.M. Rsf-1, a chromatin remodeling protein, induces DNA damage and promotes genomic instability. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 38260–38269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, G.; Yang, Q.; Sun, W. RSF1 in cancer: Interactions and functions. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perpelescu, M.; Nozaki, N.; Obuse, C.; Yang, H.; Yoda, K. Active establishment of centromeric CENP-A chromatin by RSF com-plex. J. Cell Biol. 2009, 185, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeitlin, S.G.; Baker, N.M.; Chapados, B.R.; Soutoglou, E.; Wang, J.Y.; Berns, M.W.; Cleveland, D.W. Double-strand DNA breaks recruit the centro-meric histone CENP-A. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 15762–15767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Jones, A.E.; Wu, W.; Kim, J.; Kang, Y.; Bi, X.; Gu, Y.; Popov, I.K.; Renfrow, M.B.; Vassylyeva, M.N.; et al. Role of remodeling and spacing factor 1 in histone H2A ubiquitina-tion-mediated gene silencing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E7949–E7958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.H.; Sheu, J.J.; Guan, B.; Jinawath, N.; Markowski, P.; Wang, T.L.; Shih, I.M. Functional analysis of 11q13.5 amplicon identifies Rsf-1 (HBXAP) as a gene involved in paclitaxel resistance in ovarian cancer. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 1407–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chae, S.; Ji, J.H.; Kwon, S.H.; Lee, H.S.; Lim, J.M.; Kang, D.; Lee, C.W.; Cho, H. HBxAPα/Rsf-1-mediated HBx-hBubR1 interactions regulate the mi-totic spindle checkpoint and chromosome instability. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 1680–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Sheu, J.J.; Lai, M.T.; Yin-Yi Chang, C.; Sheng, X.; Wei, L.; Gao, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, N.; Xie, W.; et al. RSF-1 overexpression determines cancer progression and drug resistance in cervical cancer. BioMedicine 2018, 8, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheu, J.J.; Choi, J.H.; Yildiz, I.; Tsai, F.J.; Shaul, Y.; Wang, T.L.; Shih, I.M. The roles of human sucrose nonfermenting protein 2 homologue in the tumor-promoting functions of Rsf-1. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 4050–4057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, K.; Fang, X.; Ouyang, G. MicroRNAs: Novel regulators in the hallmarks of human cancer. Cancer Lett. 2009, 285, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennecke, J.; Hipfner, D.R.; Stark, A.; Russell, R.B.; Cohen, S.M. bantam Encodes a Developmentally Regulated microRNA that Controls Cell Proliferation and Regulates the Proapoptotic Gene hid in Drosophila. Cell 2003, 113, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, S.; Pataillot-Meakin, T.; Shibakawa, A.; Ren, R.; Bevan, C.L.; Ladame, S.; Ivanov, A.P.; Edel, J.B. Single-molecule amplification-free multiplexed detection of circulating microRNA cancer biomarkers from serum. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.-P.; Lai, H.-M.; Guo, Z. Prostate cancer early diagnosis: Circulating microRNA pairs potentially beyond single microRNAs upon 1231 serum samples. Brief. Bioinform. 2021, 22, bbaa111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.; Wen, Y.; Tian, Z.; Hart, N.; Han, S.; Hughes, S.J.; Zeng, Y. A one-pot isothermal Cas12-based assay for the sensitive detection of microRNAs. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2023, 7, 1583–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Sun, W.; Gong, T.; Chai, Y.; Wang, J.; Hui, B.; Li, Y.; Song, L.; Gao, Y. miR-30a radiosensitizes non-small cell lung cancer by targeting ATF1 that is involved in the phosphorylation of ATM. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 1980–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Shao, J.; Zhao, Q.; Ren, X.; Cai, W.; Li, L.; Bai, Q.; Chen, X.; Xu, B.; Wang, J.; et al. MiR-30b Attenuates Neuropathic Pain by Regulating Voltage-Gated Sodium Channel Nav1.3 in Rats. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Zheng, F.; Li, Z.; Wang, H.; Yuan, H.; Zhang, X.; Ma, Z.; Li, X.; Gao, X.; Wang, B. miR-148a-3p regulates adipocyte and osteoblast differentiation by targeting lysine-specific demethylase 6b. Gene 2017, 627, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Liu, C.-Y.; Zhou, L.-Y.; Wang, J.-X.; Wang, M.; Zhao, B.; Zhao, W.-K.; Xu, S.-J.; Fan, L.-H.; Zhang, X.-J.; et al. APF lncRNA regulates autophagy and myocardial infarction by targeting miR-188-3p. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Z.; Wang, P.; Xue, Y.; Shang, C.; Liu, X.; Ma, J.; Li, Z.; Li, Z.; Bao, M.; Liu, Y. Overexpression of miR-29a reduces the oncogenic properties of glioblastoma stem cells by downregulating Quaking gene isoform 6. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 24949–24963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, E.; Li, X.; Zhang, M.; Tang, Z.; He, L.; Lv, K. miR-155 contributes to Df1-induced asthma by increasing the proliferative response of Th cells via CTLA-4 downregulation. Cell. Immunol. 2017, 314, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Xu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, W.; Zhao, H.; Guo, Y.; Cui, J. Exosome-delivered circRNA circSYT15 contributes to cisplatin resistance in cervical cancer cells through the miR-503-5p/RSF1 axis. Cell Cycle 2023, 22, 2211–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, J.; Cheng, L.; Kong, E.; Gu, W.; Jiang, Y.; Hao, Q.; Kong, B.; Sun, L. linc00958/miR-185-5p/RSF-1 modulates cisplatin resistance and angio-genesis through AKT1/GSK3β/VEGFA pathway in cervical cancer. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. RBE 2022, 20, 132. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Ji, Z.; Xie, Y.; Liu, G.; Li, H. MicroRNA-154 as a prognostic factor in bladder cancer inhibits cellular malignancy by targeting RSF1 and RUNX2. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 2727–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhao, G. Long Noncoding RNA SNHG6 Promotes Proliferation and Inhibits Apoptosis in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Cells by Regulating miR-490-3p/RSF1 Axis. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2020, 35, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, J.; Wei, H.; Qi, Y.; Liu, H. miR-129-5p Plays an Anticancer Role in Colon Cancer by Targeting RSF1. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2022, 67, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Hong, L. lncRNA-PRLB Confers Paclitaxel Resistance of Ovarian Cancer Cells by Regulating RSF1/NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2021, 36, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wang, M.; He, P. LncRNA NEAT1 Promotes the Progression of Gastric Cancer Through Modifying the miR-1224-5p/RSF1 Signaling Axis. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 11845–11855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Ye, Z.; Liu, F. GEPIA2021: Integrating multiple deconvolution-based analysis into GEPIA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W242–W246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGeary, S.E.; Lin, K.S.; Shi, C.Y.; Pham, T.M.; Bisaria, N.; Kelley, G.M.; Bartel, D.P. The biochemical basis of microRNA targeting efficacy. Science 2019, 366, eaav1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.H.; Liu, S.; Zhou, H.; Qu, L.H.; Yang, J.H. starBase v2.0: Decoding miRNA-ceRNA, miRNA-ncRNA and protein-RNA interaction networks from large-scale CLIP-Seq data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D92–D97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoufos, G.; Kakoulidis, P.; Tastsoglou, S.; Zacharopoulou, E.; Kotsira, V.; Miliotis, M.; Mavromati, G.; Grigoriadis, D.; Zioga, M.; Velli, A.; et al. TarBase-v9.0 extends experimentally supported miRNA–gene interactions to cell-types and virally encoded miRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, D304–D310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, X. miRDB: An online database for prediction of functional microRNA targets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D127–D131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Wang, X. Prediction of functional microRNA targets by integrative modeling of microRNA binding and target expression data. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Wang, Y.; Ling, Y.; Zhou, C.; Wang, H.; Teschendorff, A.E.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, H.; He, Y.; Zhang, G.; et al. dbDEMC 3.0: Functional Exploration of Differentially Ex-pressed miRNAs in Cancers of Human and Model Organisms. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2022, 20, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, H.; Zou, B.; Li, H.; Dong, S.; Guan, J.; Wang, C.; Li, W.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; et al. Cryo-EM structure and functional analysis of the chromatin remodeler RSF. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. F Struct. Biol. Commun. 2024, 80, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gai, J.; Fu, L.; Zhang, X.; Wang, E.; Li, Q. Effects of RSF-1 on proliferation and apoptosis of breast cancer cells. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 4279–4284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.-I.; Ahn, J.-H.; Lee, K.-T.; Shih, I.-M.; Choi, J.-H. RSF1 Is a Positive Regulator of NF-κB–Induced Gene Expression Required for Ovarian Cancer Chemoresistance. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 2258–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussen, B.M.; Hidayat, H.J.; Salihi, A.; Sabir, D.K.; Taheri, M.; Ghafouri-Fard, S. MicroRNA: A signature for cancer progression. Biomed. Pharmacother. = Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 138, 111528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozaki, K.; Imoto, I.; Mogi, S.; Omura, K.; Inazawa, J. Exploration of tumor-suppressive microRNAs silenced by DNA hyper-methylation in oral cancer. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 2094–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kober, P.; Mossakowska, B.J.; Rusetska, N.; Baluszek, S.; Grecka, E.; Konopiński, R.; Matyja, E.; Oziębło, A.; Mandat, T.; Bujko, M. Epigenetic Downregulation of Hsa-miR-193b-3p Increases Cyclin D1 Expression Level and Cell Proliferation in Human Meningiomas. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupaimoole, R.; Slack, F.J. MicroRNA therapeutics: Towards a new era for the management of cancer and other diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 203–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Sequence Name | Sequence (5′→3′) |
|---|---|
| miR-193b-3p mimic-S | AACUGGCCCUCAAAGUCCCGCU |
| miR-193b-3p mimic-AS | CGGGACUUUGAGGGCCAGUUUU |
| miR-193b-3p mimic negative control-S | UUCUCCGAACGUGUCACGUTT |
| miR-193b-3p mimic negative control-AS | ACGUGACACGUUCGGAGAATT |
| miR-193b-3p inhibitor | AGCGGGACUUUGAGGGCCAGUU |
| miR-193b-3p inhibitor negative control | CAGUACUUUUGUGUAGUACAA |
| miR-27b-3p mimic-S | UUCACAGUGGCUAAGUUCUGC |
| miR-27b-3p mimic-AS | AGAACUUAGCCACUGUGAAUU |
| miR-520f-3p mimic-S | AAGUGCUUCCUUUUAGAGGGUU |
| miR-520f-3p mimic-AS | CCCUCUAAAAGGAAGCACUUUU |
| miR-1271-5p mimic-S | CUUGGCACCUAGCAAGCACUCA |
| miR-1271-5p mimic-AS | AGUGCUUGCUAGGUGCCAAGUU |
| miR-503-5p mimic-S | UAGCAGCGGGAACAGUUCUGCAG |
| miR-503-5p mimic-AS | GCAGAACUGUUCCCGCUGCUAUU |
| miR-154-5p mimic-S | UAGGUUAUCCGUGUUGCCUUCG |
| miR-154-5p mimic-AS | AAGGCAACACGGAUAACCUAUU |
| si-RSF1-1-S | CCAAGAAGCCCUACCGGAU |
| si-RSF1-1-AS | AUCCGGUAGGGCUUCUUGG |
| si-RSF1-2-S | GGUAGAAUGCCAGAGUACA |
| si-RSF1-2-AS | UGUACUCUGGCAUUCUACC |
| Sequence Name | Sequence (5′→3′) |
|---|---|
| miR-193b-3p-F | GCGAACTGGCCCTCAAAGT |
| miR-193b-3p-R | AGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATT |
| U6-F | CTCGCTTCGGCAGCACA |
| U6-R | AACGCTTCACGAATTTGCGT |
| RSF1-F | GCAGATGAGGAGGAGGAGGAAGAG |
| RSF1-R | CTGTCACGGGCAGGCTGATTTG |
| GAPDH-F | TGACATCAAGAAGGTGGTGAAGCAG |
| GAPDH-R | GTGTCGCTGTTGAAGTCAGAGGAG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, Y.; Zhao, X.; Du, Z.; Jia, Z.; Zhou, S.; Cao, G.; Wang, H. MicroRNA miR-193b-3p Regulates Esophageal Cancer Progression Through Targeting RSF1. Cells 2025, 14, 928. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14120928
Lin Y, Zhao X, Du Z, Jia Z, Zhou S, Cao G, Wang H. MicroRNA miR-193b-3p Regulates Esophageal Cancer Progression Through Targeting RSF1. Cells. 2025; 14(12):928. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14120928
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Yao, Xudong Zhao, Zhenhua Du, Zhili Jia, Siyu Zhou, Gengsheng Cao, and Hengbin Wang. 2025. "MicroRNA miR-193b-3p Regulates Esophageal Cancer Progression Through Targeting RSF1" Cells 14, no. 12: 928. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14120928
APA StyleLin, Y., Zhao, X., Du, Z., Jia, Z., Zhou, S., Cao, G., & Wang, H. (2025). MicroRNA miR-193b-3p Regulates Esophageal Cancer Progression Through Targeting RSF1. Cells, 14(12), 928. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14120928







